08e9b3f1437c5d527733eb53493ca8b8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 Higher Computing Science Procedures, Functions and Parameters
Higher Computing Science Procedures, Functions and Parameters
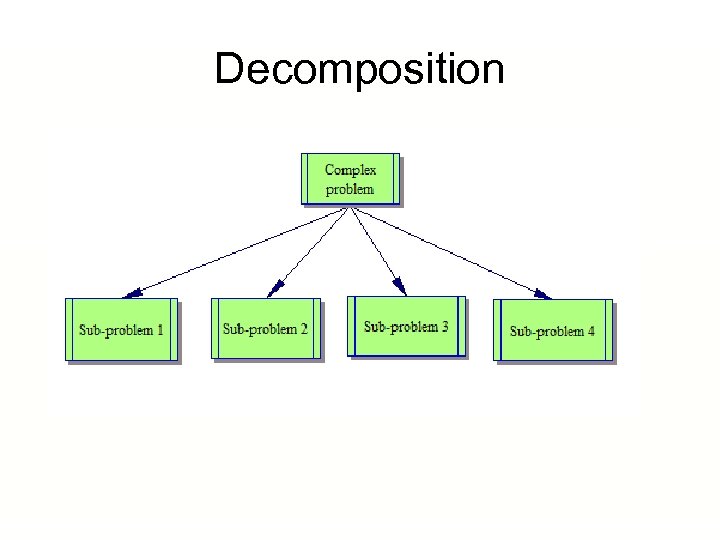 Decomposition
Decomposition
 Local Variables A Local variable only has scope within the subprogram where it has been defined. PROCEDURE looper() FOR counter FROM 1 TO 10 # Local variable SEND counter TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE
Local Variables A Local variable only has scope within the subprogram where it has been defined. PROCEDURE looper() FOR counter FROM 1 TO 10 # Local variable SEND counter TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE
 Why use local variables? • Local variables mean that they only have a value inside the sub-program they are declared in. • Using local variables means that subprograms are “self contained” and can be reused without affecting the value of variables elsewhere in the program
Why use local variables? • Local variables mean that they only have a value inside the sub-program they are declared in. • Using local variables means that subprograms are “self contained” and can be reused without affecting the value of variables elsewhere in the program
 Why use local variables? • You can use the same variable name again in a different sub-program • The memory used by a local variable is freed up when its sub-program has finished running
Why use local variables? • You can use the same variable name again in a different sub-program • The memory used by a local variable is freed up when its sub-program has finished running
 Global Variables • Global variables are variables which have scope throughout a program. • Any change to the value of a global variable within a sub-program will change its value anywhere else it occurs in the code.
Global Variables • Global variables are variables which have scope throughout a program. • Any change to the value of a global variable within a sub-program will change its value anywhere else it occurs in the code.
 Global Variables • Global variables should be avoided as they make your procedures and functions less portable and your code less maintainable • The memory required by a global variable is locked up for the entire time your program is running • Using Global variables can cause unexpected changes if variables with the same name are used elsewhere in the program
Global Variables • Global variables should be avoided as they make your procedures and functions less portable and your code less maintainable • The memory required by a global variable is locked up for the entire time your program is running • Using Global variables can cause unexpected changes if variables with the same name are used elsewhere in the program
 A simple procedure This procedure can only perform one task PROCEDURE eight. Stars() FOR counter FROM 1 TO 8 # Local variable SEND " * " TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE
A simple procedure This procedure can only perform one task PROCEDURE eight. Stars() FOR counter FROM 1 TO 8 # Local variable SEND " * " TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE
 Parameters • A parameter is a variable which is used to modify how a sub program behaves • A parameter is declared in the definition of a sub program (called a formal parameter) • Parameters make sub programs more flexible and more portable
Parameters • A parameter is a variable which is used to modify how a sub program behaves • A parameter is declared in the definition of a sub program (called a formal parameter) • Parameters make sub programs more flexible and more portable
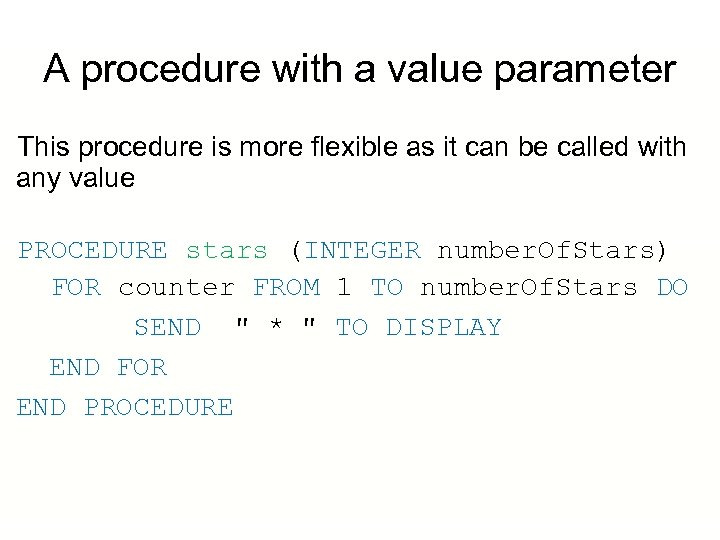 A procedure with a value parameter This procedure is more flexible as it can be called with any value PROCEDURE stars (INTEGER number. Of. Stars) FOR counter FROM 1 TO number. Of. Stars DO SEND " * " TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE
A procedure with a value parameter This procedure is more flexible as it can be called with any value PROCEDURE stars (INTEGER number. Of. Stars) FOR counter FROM 1 TO number. Of. Stars DO SEND " * " TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE
 Calling the stars procedure with an actual parameter PROCEDURE stars (INTEGER number. Of. Stars) FOR counter FROM 1 TO number. Of. Stars DO SEND " * " TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE DECLARE total. Stars AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SEND " How many stars? " TO DISPLAY RECEIVE total. Stars FROM KEYBOARD stars (total. Stars) If the input to the question “How many stars” was 10 then the result would be: * * * * *
Calling the stars procedure with an actual parameter PROCEDURE stars (INTEGER number. Of. Stars) FOR counter FROM 1 TO number. Of. Stars DO SEND " * " TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE DECLARE total. Stars AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SEND " How many stars? " TO DISPLAY RECEIVE total. Stars FROM KEYBOARD stars (total. Stars) If the input to the question “How many stars” was 10 then the result would be: * * * * *
 Formal and Actual Parameters • Formal Parameters are variables which are declared when a sub-procedure or function is defined • Actual parameters are used when a subprocedure or function is called
Formal and Actual Parameters • Formal Parameters are variables which are declared when a sub-procedure or function is defined • Actual parameters are used when a subprocedure or function is called
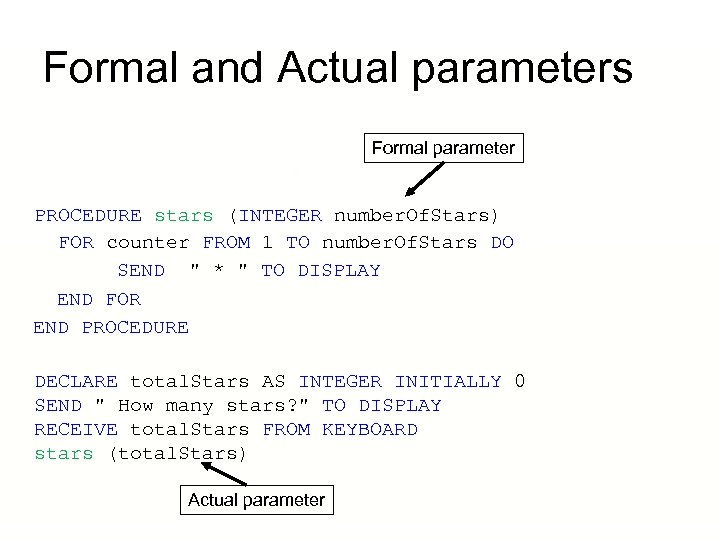 Formal and Actual parameters Formal parameter PROCEDURE stars (INTEGER number. Of. Stars) FOR counter FROM 1 TO number. Of. Stars DO SEND " * " TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE DECLARE total. Stars AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SEND " How many stars? " TO DISPLAY RECEIVE total. Stars FROM KEYBOARD stars (total. Stars) Actual parameter
Formal and Actual parameters Formal parameter PROCEDURE stars (INTEGER number. Of. Stars) FOR counter FROM 1 TO number. Of. Stars DO SEND " * " TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE DECLARE total. Stars AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SEND " How many stars? " TO DISPLAY RECEIVE total. Stars FROM KEYBOARD stars (total. Stars) Actual parameter
 Functions
Functions
 How a function differs from a procedure • A function returns a value • A procedure performs a sequence of actions • Function names are usually nouns • Functions return a value so need to be declared as returning a particular data type • Procedure names are usually verbs
How a function differs from a procedure • A function returns a value • A procedure performs a sequence of actions • Function names are usually nouns • Functions return a value so need to be declared as returning a particular data type • Procedure names are usually verbs
 Built in mathematical functions • int() • sqr() • abs()
Built in mathematical functions • int() • sqr() • abs()
 Using mathematical functions SET value TO -56 SET new. Value TO abs(value) SEND new. Value TO DISPLAY Result would be 56
Using mathematical functions SET value TO -56 SET new. Value TO abs(value) SEND new. Value TO DISPLAY Result would be 56
 Using mathematical functions SET value TO 4 SET new. Value TO sqr(value) SEND new. Value TO DISPLAY Result would be 2
Using mathematical functions SET value TO 4 SET new. Value TO sqr(value) SEND new. Value TO DISPLAY Result would be 2
 Using mathematical functions SET value TO 3. 4 SET new. Value TO int(value) SEND new. Value TO DISPLAY Result would be 3
Using mathematical functions SET value TO 3. 4 SET new. Value TO int(value) SEND new. Value TO DISPLAY Result would be 3
 String functions • • Left$() Right$() Len() Mid$()
String functions • • Left$() Right$() Len() Mid$()
 Using String Functions SET my. String TO "banana" SET new. String TO left$(my. String, 2) SEND new. String TO DISPLAY new. String would have the value "ba"
Using String Functions SET my. String TO "banana" SET new. String TO left$(my. String, 2) SEND new. String TO DISPLAY new. String would have the value "ba"
 Using String Functions SET my. String TO "banana" SET new. String TO right$(my. String, 2) SEND new. String TO DISPLAY new. String would have the value "na"
Using String Functions SET my. String TO "banana" SET new. String TO right$(my. String, 2) SEND new. String TO DISPLAY new. String would have the value "na"
 Using String Functions SET my. String TO "banana" SET new. String TO mid$(my. String, 2, 3) SEND new. String TO DISPLAY new. String would have the value "nan"
Using String Functions SET my. String TO "banana" SET new. String TO mid$(my. String, 2, 3) SEND new. String TO DISPLAY new. String would have the value "nan"
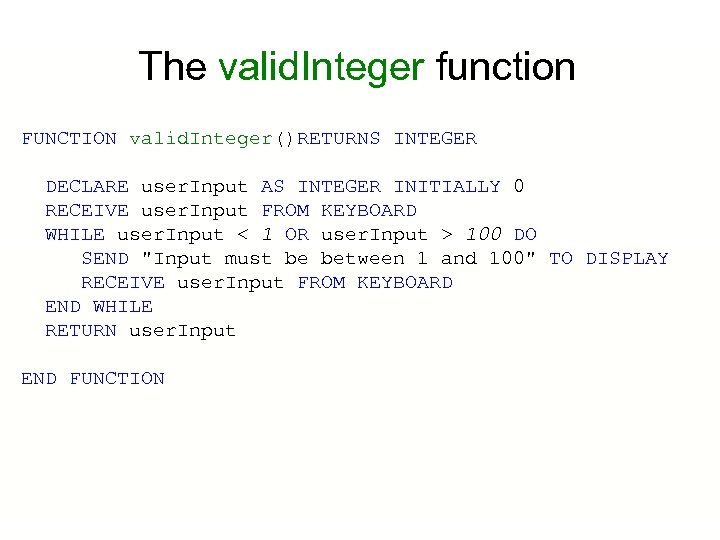 The valid. Integer function FUNCTION valid. Integer()RETURNS INTEGER DECLARE user. Input AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 RECEIVE user. Input FROM KEYBOARD WHILE user. Input < 1 OR user. Input > 100 DO SEND "Input must be between 1 and 100" TO DISPLAY RECEIVE user. Input FROM KEYBOARD END WHILE RETURN user. Input END FUNCTION
The valid. Integer function FUNCTION valid. Integer()RETURNS INTEGER DECLARE user. Input AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 RECEIVE user. Input FROM KEYBOARD WHILE user. Input < 1 OR user. Input > 100 DO SEND "Input must be between 1 and 100" TO DISPLAY RECEIVE user. Input FROM KEYBOARD END WHILE RETURN user. Input END FUNCTION
 valid. Integer function We would call this function within a program: DECLARE number AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SET number TO valid. Integer To give the variable number a value between 1 and 100
valid. Integer function We would call this function within a program: DECLARE number AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SET number TO valid. Integer To give the variable number a value between 1 and 100
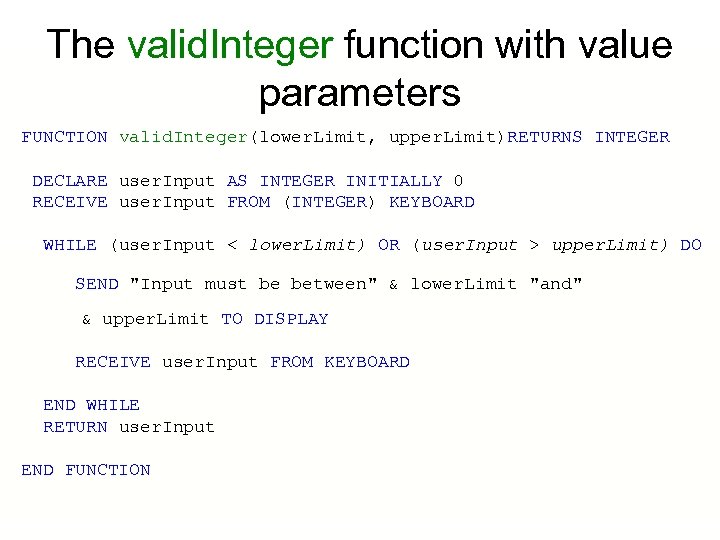 The valid. Integer function with value parameters FUNCTION valid. Integer(lower. Limit, upper. Limit)RETURNS INTEGER DECLARE user. Input AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 RECEIVE user. Input FROM (INTEGER) KEYBOARD WHILE (user. Input < lower. Limit) OR (user. Input > upper. Limit) DO SEND "Input must be between" & lower. Limit "and" & upper. Limit TO DISPLAY RECEIVE user. Input FROM KEYBOARD END WHILE RETURN user. Input END FUNCTION
The valid. Integer function with value parameters FUNCTION valid. Integer(lower. Limit, upper. Limit)RETURNS INTEGER DECLARE user. Input AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 RECEIVE user. Input FROM (INTEGER) KEYBOARD WHILE (user. Input < lower. Limit) OR (user. Input > upper. Limit) DO SEND "Input must be between" & lower. Limit "and" & upper. Limit TO DISPLAY RECEIVE user. Input FROM KEYBOARD END WHILE RETURN user. Input END FUNCTION
 Calling the valid. Integer function We could call this function with actual parameters, 1 and 50 to return a number between 1 and 50: SET number. To. Use TO valid. Integer(1, 50) or we could call it with the actual parameters 1 and input. Range which is a variable which has a value assigned elsewhere in the program: SEND "What is the maximum input value" TO SCREEN RECEIVE max. Input FROM (INTEGER) KEYBOARD SET number. To. Use TO valid. Integer(1, max. Input) This function call would return a value between 1 and max. Input.
Calling the valid. Integer function We could call this function with actual parameters, 1 and 50 to return a number between 1 and 50: SET number. To. Use TO valid. Integer(1, 50) or we could call it with the actual parameters 1 and input. Range which is a variable which has a value assigned elsewhere in the program: SEND "What is the maximum input value" TO SCREEN RECEIVE max. Input FROM (INTEGER) KEYBOARD SET number. To. Use TO valid. Integer(1, max. Input) This function call would return a value between 1 and max. Input.
 Why user defined functions? • Functions return a value • Functions make code more readable • Functions, like procedures can be reused so make programming more efficient
Why user defined functions? • Functions return a value • Functions make code more readable • Functions, like procedures can be reused so make programming more efficient
 Parameters passed by Value • A parameter passed by value is one which is passed into a procedure or function and whose value is used by that procedure • When a sub procedure is called with a variable passed by value, a copy of that variable is made using its formal parameter while the procedure is running. • The copy of the variable is destroyed when the procedure has completed, so the memory can be reused
Parameters passed by Value • A parameter passed by value is one which is passed into a procedure or function and whose value is used by that procedure • When a sub procedure is called with a variable passed by value, a copy of that variable is made using its formal parameter while the procedure is running. • The copy of the variable is destroyed when the procedure has completed, so the memory can be reused
 Parameters passed by Reference • When a sub procedure is declared with a formal parameter passed by reference then when it is called with an actual parameter its value is changed by that sub procedure. • When a variable is passed by reference the reference is to the memory location of the variable itself. No copy is being made.
Parameters passed by Reference • When a sub procedure is declared with a formal parameter passed by reference then when it is called with an actual parameter its value is changed by that sub procedure. • When a variable is passed by reference the reference is to the memory location of the variable itself. No copy is being made.
 Parameters passed by Reference The value of the variable changes as a result of calling the sub procedure with it as a parameter PROCEDURE swap (a, b) DECLARE temp AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SET temp TO a SET a TO b SET b TO temp END PROCEDURE
Parameters passed by Reference The value of the variable changes as a result of calling the sub procedure with it as a parameter PROCEDURE swap (a, b) DECLARE temp AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SET temp TO a SET a TO b SET b TO temp END PROCEDURE
 Parameters passed by Reference Write a program which asks for two values (stored in the variables a and b) prints their values, then swaps the contents of the variables around and prints the new values
Parameters passed by Reference Write a program which asks for two values (stored in the variables a and b) prints their values, then swaps the contents of the variables around and prints the new values
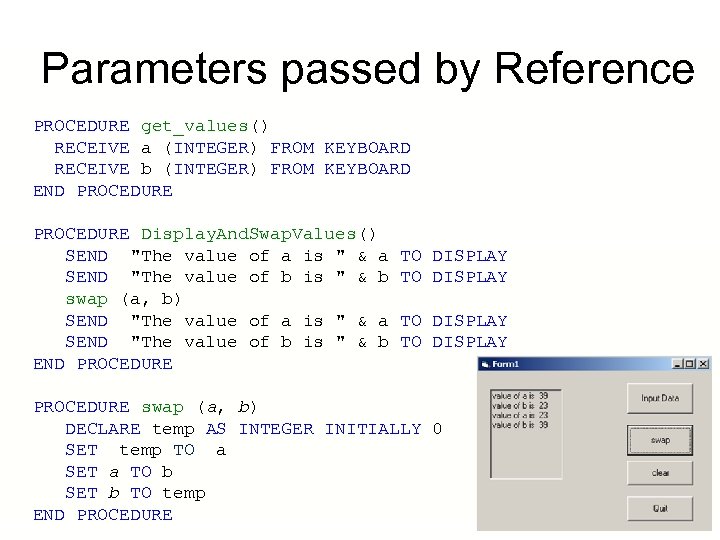 Parameters passed by Reference PROCEDURE get_values() RECEIVE a (INTEGER) FROM KEYBOARD RECEIVE b (INTEGER) FROM KEYBOARD END PROCEDURE Display. And. Swap. Values() SEND "The value of a is " & a TO DISPLAY SEND "The value of b is " & b TO DISPLAY swap (a, b) SEND "The value of a is " & a TO DISPLAY SEND "The value of b is " & b TO DISPLAY END PROCEDURE swap (a, b) DECLARE temp AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SET temp TO a SET a TO b SET b TO temp END PROCEDURE
Parameters passed by Reference PROCEDURE get_values() RECEIVE a (INTEGER) FROM KEYBOARD RECEIVE b (INTEGER) FROM KEYBOARD END PROCEDURE Display. And. Swap. Values() SEND "The value of a is " & a TO DISPLAY SEND "The value of b is " & b TO DISPLAY swap (a, b) SEND "The value of a is " & a TO DISPLAY SEND "The value of b is " & b TO DISPLAY END PROCEDURE swap (a, b) DECLARE temp AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SET temp TO a SET a TO b SET b TO temp END PROCEDURE
 Parameters passed by Reference Example: Write a program allows the user to swap the positions of any two values in an array
Parameters passed by Reference Example: Write a program allows the user to swap the positions of any two values in an array
 The print. Array procedure PROCEDURE print. Array (numbers) FOR counter = 0 TO 5 DO SEND numbers[counter] TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE
The print. Array procedure PROCEDURE print. Array (numbers) FOR counter = 0 TO 5 DO SEND numbers[counter] TO DISPLAY END FOR END PROCEDURE
 The swap procedure PROCEDURE swap (a, b) DECLARE temp AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SET temp TO a SET a TO b SET b TO temp END PROCEDURE
The swap procedure PROCEDURE swap (a, b) DECLARE temp AS INTEGER INITIALLY 0 SET temp TO a SET a TO b SET b TO temp END PROCEDURE
 Parameters passed by Reference DECLARE numbers AS ARRAY OF INTEGER INITIALLY [1, 3, 5, 7, 9 11] PROCEDURE main. Program (numbers) print. Array (numbers) SEND "Please enter index position 1 to swap" TO DISPLAY RECEIVE index 1 (INTEGER) FROM KEYBOARD SEND "Please enter index position 2 to swap" TO DISPLAY RECEIVE index 2 (INTEGER) FROM KEYBOARD swap (numbers[index 1], numbers[index 2] ) print. Array (numbers) END PROCEDURE
Parameters passed by Reference DECLARE numbers AS ARRAY OF INTEGER INITIALLY [1, 3, 5, 7, 9 11] PROCEDURE main. Program (numbers) print. Array (numbers) SEND "Please enter index position 1 to swap" TO DISPLAY RECEIVE index 1 (INTEGER) FROM KEYBOARD SEND "Please enter index position 2 to swap" TO DISPLAY RECEIVE index 2 (INTEGER) FROM KEYBOARD swap (numbers[index 1], numbers[index 2] ) print. Array (numbers) END PROCEDURE
 Parameter Passing Parameter passing by value creates a copy of the variable when the sub procedure is called - this is inefficient if the variable is an array. Arrays are normally passed as reference parameters because of the memory space they occupy.
Parameter Passing Parameter passing by value creates a copy of the variable when the sub procedure is called - this is inefficient if the variable is an array. Arrays are normally passed as reference parameters because of the memory space they occupy.
 Summary • A local variable only has scope within the-sub procedure where it has been defined. A global variable has scope throughout a program. Using global variables makes code less readable, less modular and thus less maintainable • The advantages of using parameter passing rather than global variables is to increase the modularity, portability readability and maintainability of the code. • A formal parameter is one declared in the definition of a procedure or function • An actual parameter is one used when calling a procedure or function • A value parameter is one which is passed into a sub-procedure and whose value is copied, used by that procedure then discarded. • A reference parameter is a variable which is passed into a sub-procedure and then out again and whose value is changed by that sub- procedure
Summary • A local variable only has scope within the-sub procedure where it has been defined. A global variable has scope throughout a program. Using global variables makes code less readable, less modular and thus less maintainable • The advantages of using parameter passing rather than global variables is to increase the modularity, portability readability and maintainability of the code. • A formal parameter is one declared in the definition of a procedure or function • An actual parameter is one used when calling a procedure or function • A value parameter is one which is passed into a sub-procedure and whose value is copied, used by that procedure then discarded. • A reference parameter is a variable which is passed into a sub-procedure and then out again and whose value is changed by that sub- procedure
 Summary • A function returns a value, a procedure performs a sequence of actions • A built in function is supplied as part of the development environment, a user defined function is one created by the programmer. • Using procedures and functions improves the readability and maintainability of code • Procedures and functions which use local variables make code more portable • Procedures and functions can be tested independently making code easier to debug
Summary • A function returns a value, a procedure performs a sequence of actions • A built in function is supplied as part of the development environment, a user defined function is one created by the programmer. • Using procedures and functions improves the readability and maintainability of code • Procedures and functions which use local variables make code more portable • Procedures and functions can be tested independently making code easier to debug
 Question Examples 2016 Q 10 b, c, d 2015 Q 14 c Specimen Paper Q 9 c Example Paper Q 9 b(ii) Example Paper Q 11 a, b Old Higher 2012 Q 22 Old Higher 2011 Q 10 c
Question Examples 2016 Q 10 b, c, d 2015 Q 14 c Specimen Paper Q 9 c Example Paper Q 9 b(ii) Example Paper Q 11 a, b Old Higher 2012 Q 22 Old Higher 2011 Q 10 c
 2016 Q 10 b (b) Mrs Mc. Coll implements the program using global variables. Another teacher suggests that she makes use of parameter passing instead. State two benefits of using parameter passing rather than global variables.
2016 Q 10 b (b) Mrs Mc. Coll implements the program using global variables. Another teacher suggests that she makes use of parameter passing instead. State two benefits of using parameter passing rather than global variables.
 2016 Q 10 b Using Global variables can cause unexpected changes if variables with the same name are used in the program The code is less readable because it is not obvious how data is flowing between procedures Memory used by local variables is reused once the procedure has completed its task but global variables will always be using memory resources Procedures declared with parameters can be re-used making the code more modular and the code more portable
2016 Q 10 b Using Global variables can cause unexpected changes if variables with the same name are used in the program The code is less readable because it is not obvious how data is flowing between procedures Memory used by local variables is reused once the procedure has completed its task but global variables will always be using memory resources Procedures declared with parameters can be re-used making the code more modular and the code more portable
 2016 Q 10 c (c) Parameters are used to pass data between subprograms. Parameters can be passed by reference or passed by value. Explain why passing by value is more demanding on system resources when the data being passed is held in an array.
2016 Q 10 c (c) Parameters are used to pass data between subprograms. Parameters can be passed by reference or passed by value. Explain why passing by value is more demanding on system resources when the data being passed is held in an array.
 2016 Q 10 c • Passing a parameter by value means that a copy of that parameter is made while the procedure is running. This means that more memory resources are being used and more processor instructions are needed to manage it.
2016 Q 10 c • Passing a parameter by value means that a copy of that parameter is made while the procedure is running. This means that more memory resources are being used and more processor instructions are needed to manage it.
 2016 Q 10 d d) Mrs Mc. Coll’s program is modular and makes use of functions. Explain what is meant by a function.
2016 Q 10 d d) Mrs Mc. Coll’s program is modular and makes use of functions. Explain what is meant by a function.
 2016 Q 10 d A function returns a single value The value of a function can be assigned to a variable eg. Uservalue = valid. Integer (1, 10)
2016 Q 10 d A function returns a single value The value of a function can be assigned to a variable eg. Uservalue = valid. Integer (1, 10)
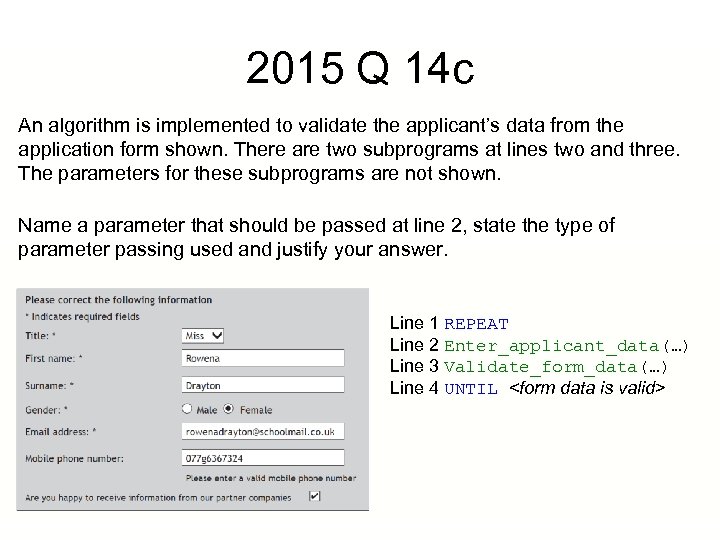 2015 Q 14 c An algorithm is implemented to validate the applicant’s data from the application form shown. There are two subprograms at lines two and three. The parameters for these subprograms are not shown. Name a parameter that should be passed at line 2, state the type of parameter passing used and justify your answer. Line 1 REPEAT Line 2 Enter_applicant_data(…) Line 3 Validate_form_data(…) Line 4 UNTIL
2015 Q 14 c An algorithm is implemented to validate the applicant’s data from the application form shown. There are two subprograms at lines two and three. The parameters for these subprograms are not shown. Name a parameter that should be passed at line 2, state the type of parameter passing used and justify your answer. Line 1 REPEAT Line 2 Enter_applicant_data(…) Line 3 Validate_form_data(…) Line 4 UNTIL
 2015 Q 14 c The parameter could be any item from the form such as title, first name, surname etc. It will be passed by reference because the value will be updated and then passed back out of the sub-program PROCEDURE validate_form_data(gender) RECEIVE gender FROM (CHARACTER) KEYBOARD WHILE gender ≠ "M" AND gender ≠ "F" < error message> RECEIVE gender FROM (CHARACTER) KEYBOARD END WHILE END PROCEDURE
2015 Q 14 c The parameter could be any item from the form such as title, first name, surname etc. It will be passed by reference because the value will be updated and then passed back out of the sub-program PROCEDURE validate_form_data(gender) RECEIVE gender FROM (CHARACTER) KEYBOARD WHILE gender ≠ "M" AND gender ≠ "F" < error message> RECEIVE gender FROM (CHARACTER) KEYBOARD END WHILE END PROCEDURE
 Specimen Paper Q 9 c Jeanette works for a bank and has downloaded a tax. Code function, from their online library. Bank employees receive an annual salary and bonus pay and Jeanette’s program stores these values in variables salary and bonus. It also stores the employee’s tax code in a variable called code. Using pseudocode or a language with which you are familiar, write an algorithm for a subroutine that will: • Ask the user for the values for variables salary and bonus • Use the function to assign the variable code • Display code on screen
Specimen Paper Q 9 c Jeanette works for a bank and has downloaded a tax. Code function, from their online library. Bank employees receive an annual salary and bonus pay and Jeanette’s program stores these values in variables salary and bonus. It also stores the employee’s tax code in a variable called code. Using pseudocode or a language with which you are familiar, write an algorithm for a subroutine that will: • Ask the user for the values for variables salary and bonus • Use the function to assign the variable code • Display code on screen
 Specimen Paper Q 9 c PROCEDURE calculate. Code RECEIVE salary FROM KEYBOARD RECEIVE bonus FROM KEYBOARD SET code TO tax. Code (salary, bonus) SEND code TO DISPLAY END PROCEDURE
Specimen Paper Q 9 c PROCEDURE calculate. Code RECEIVE salary FROM KEYBOARD RECEIVE bonus FROM KEYBOARD SET code TO tax. Code (salary, bonus) SEND code TO DISPLAY END PROCEDURE
 Example Paper Q 9 b(ii) When implementing code, a programmer can limit the scope of a variable. Explain what is meant by scope and how it can be limited. Scope is the section of code in which a variable can be used and has a value You can create a local variable by declaring it inside sub-program or by defining a formal parameter which is used inside that sub-program.
Example Paper Q 9 b(ii) When implementing code, a programmer can limit the scope of a variable. Explain what is meant by scope and how it can be limited. Scope is the section of code in which a variable can be used and has a value You can create a local variable by declaring it inside sub-program or by defining a formal parameter which is used inside that sub-program.
 Example Paper Q 11 a A function used to perform an arithmetical operation is shown below: FUNCTION combinations (INTEGER number) RETURNS INTEGER SET factor TO 1 FOR counter FROM 1 TO number DO SET factor TO counter * factor END FOR RETURN factor END FUNCTION State the formal parameter in the function.
Example Paper Q 11 a A function used to perform an arithmetical operation is shown below: FUNCTION combinations (INTEGER number) RETURNS INTEGER SET factor TO 1 FOR counter FROM 1 TO number DO SET factor TO counter * factor END FOR RETURN factor END FUNCTION State the formal parameter in the function.
 Example Paper Q 11 b A program has two variables called items and permutations which contain the values 3 and 0 respectively, as shown below: Explain what is meant by an actual parameter, by referring to the following line of code used to call the function above: SET permutations TO combinations(items) State the values contained in items and permutations after execution of the line of code. Explain your answer
Example Paper Q 11 b A program has two variables called items and permutations which contain the values 3 and 0 respectively, as shown below: Explain what is meant by an actual parameter, by referring to the following line of code used to call the function above: SET permutations TO combinations(items) State the values contained in items and permutations after execution of the line of code. Explain your answer
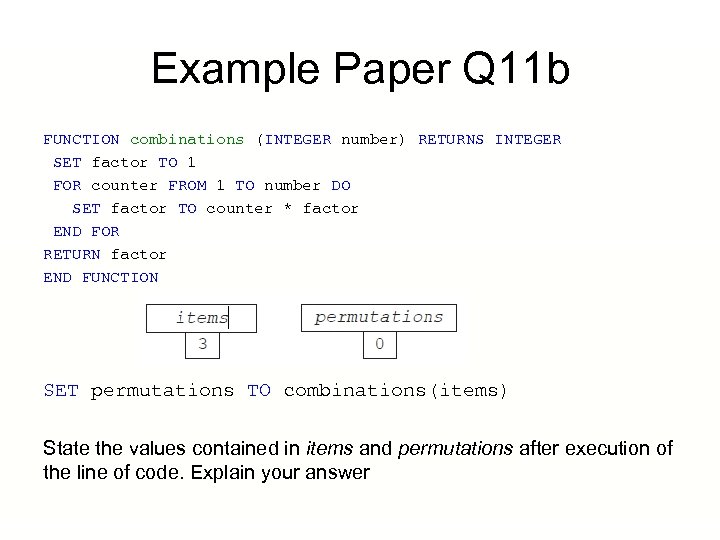 Example Paper Q 11 b FUNCTION combinations (INTEGER number) RETURNS INTEGER SET factor TO 1 FOR counter FROM 1 TO number DO SET factor TO counter * factor END FOR RETURN factor END FUNCTION SET permutations TO combinations(items) State the values contained in items and permutations after execution of the line of code. Explain your answer
Example Paper Q 11 b FUNCTION combinations (INTEGER number) RETURNS INTEGER SET factor TO 1 FOR counter FROM 1 TO number DO SET factor TO counter * factor END FOR RETURN factor END FUNCTION SET permutations TO combinations(items) State the values contained in items and permutations after execution of the line of code. Explain your answer
 Example Paper Q 11 b items = 3 permutations = 6 items is unchanged by the function (it is still 3) We call the function with the actual parameter items (value 3) The loop executes three times factor is set initially to 1 For counter from 1 to 3 we set factor to counter * 3 factor = 1 X 1 =1 then 2 X 1 =2 then 3 X 2 = 6
Example Paper Q 11 b items = 3 permutations = 6 items is unchanged by the function (it is still 3) We call the function with the actual parameter items (value 3) The loop executes three times factor is set initially to 1 For counter from 1 to 3 we set factor to counter * 3 factor = 1 X 1 =1 then 2 X 1 =2 then 3 X 2 = 6
 Old Higher 2012 Q 22 A travel agent uses a suite of software to help advertise holidays and make bookings. Part of the pseudocode that was written for the software is: IF cost_person < 500 THEN SET band TO "cheap" END IF IF cost_person >= 500 AND cost_person < 2000 THEN SET band TO "medium" END IF IF cost_person >= 2000 THEN SET band TO "expensive" END IF
Old Higher 2012 Q 22 A travel agent uses a suite of software to help advertise holidays and make bookings. Part of the pseudocode that was written for the software is: IF cost_person < 500 THEN SET band TO "cheap" END IF IF cost_person >= 500 AND cost_person < 2000 THEN SET band TO "medium" END IF IF cost_person >= 2000 THEN SET band TO "expensive" END IF
 Old Higher 2012 Q 22 (c) When the above is implemented as a subroutine, state whether the variable “cost_person” would be passed by reference or value. Justify your answer. Each holiday booking is assigned a unique reference code. The software which creates this code uses concatenation within a user-defined function. (d) Explain the term concatenation. (e) Explain the term function.
Old Higher 2012 Q 22 (c) When the above is implemented as a subroutine, state whether the variable “cost_person” would be passed by reference or value. Justify your answer. Each holiday booking is assigned a unique reference code. The software which creates this code uses concatenation within a user-defined function. (d) Explain the term concatenation. (e) Explain the term function.
 Old Higher 2012 Q 22 • The variable cost_person would be passed by value because it is not going to be changed by the program • The term concatenation means to join two or more strings together to make one string • A function is a section of code which returns a single value
Old Higher 2012 Q 22 • The variable cost_person would be passed by value because it is not going to be changed by the program • The term concatenation means to join two or more strings together to make one string • A function is a section of code which returns a single value
 Old Higher 2009 A cinema ticket system allows customers to select and pay for their own tickets. The top level algorithm is: 1. Get ticket details 2. Calculate cost 3. Display cost and accept payment The module calculate. Cost uses the number of tickets and the category of ticket to calculate the total payment due. It uses the parameters described below. Parameter Description amount Number of tickets category adult, child, student, OAP cost Total cost of required tickets (a) State the most suitable data type for the parameter called cost.
Old Higher 2009 A cinema ticket system allows customers to select and pay for their own tickets. The top level algorithm is: 1. Get ticket details 2. Calculate cost 3. Display cost and accept payment The module calculate. Cost uses the number of tickets and the category of ticket to calculate the total payment due. It uses the parameters described below. Parameter Description amount Number of tickets category adult, child, student, OAP cost Total cost of required tickets (a) State the most suitable data type for the parameter called cost.
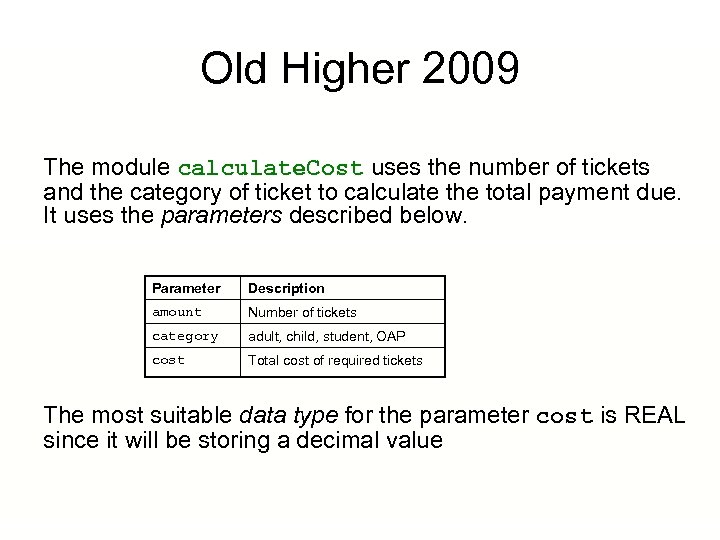 Old Higher 2009 The module calculate. Cost uses the number of tickets and the category of ticket to calculate the total payment due. It uses the parameters described below. Parameter Description amount Number of tickets category adult, child, student, OAP cost Total cost of required tickets The most suitable data type for the parameter cost is REAL since it will be storing a decimal value
Old Higher 2009 The module calculate. Cost uses the number of tickets and the category of ticket to calculate the total payment due. It uses the parameters described below. Parameter Description amount Number of tickets category adult, child, student, OAP cost Total cost of required tickets The most suitable data type for the parameter cost is REAL since it will be storing a decimal value
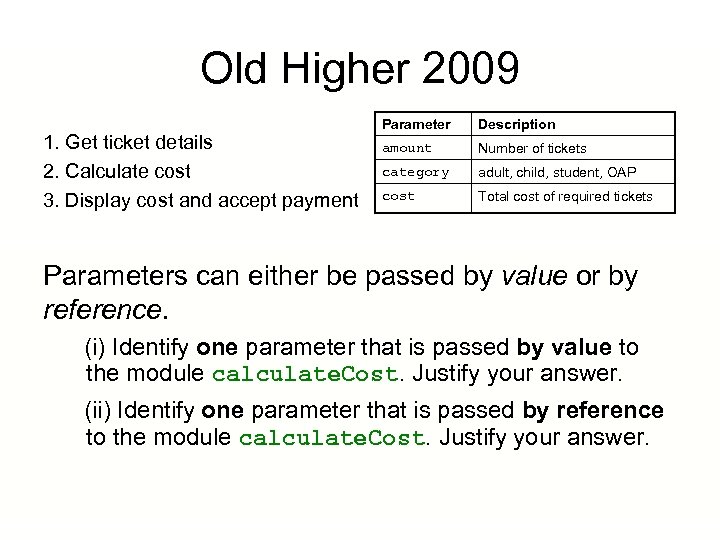 Old Higher 2009 1. Get ticket details 2. Calculate cost 3. Display cost and accept payment Parameter Description amount Number of tickets category adult, child, student, OAP cost Total cost of required tickets Parameters can either be passed by value or by reference. (i) Identify one parameter that is passed by value to the module calculate. Cost. Justify your answer. (ii) Identify one parameter that is passed by reference to the module calculate. Cost. Justify your answer.
Old Higher 2009 1. Get ticket details 2. Calculate cost 3. Display cost and accept payment Parameter Description amount Number of tickets category adult, child, student, OAP cost Total cost of required tickets Parameters can either be passed by value or by reference. (i) Identify one parameter that is passed by value to the module calculate. Cost. Justify your answer. (ii) Identify one parameter that is passed by reference to the module calculate. Cost. Justify your answer.
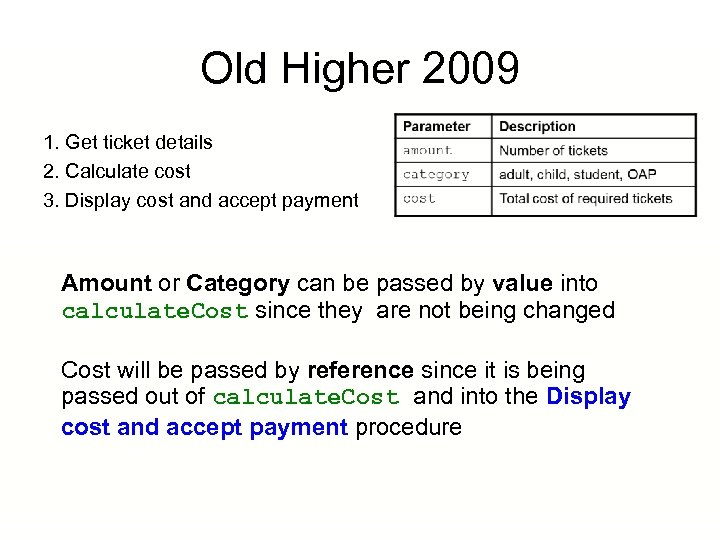 Old Higher 2009 1. Get ticket details 2. Calculate cost 3. Display cost and accept payment Amount or Category can be passed by value into calculate. Cost since they are not being changed Cost will be passed by reference since it is being passed out of calculate. Cost and into the Display cost and accept payment procedure
Old Higher 2009 1. Get ticket details 2. Calculate cost 3. Display cost and accept payment Amount or Category can be passed by value into calculate. Cost since they are not being changed Cost will be passed by reference since it is being passed out of calculate. Cost and into the Display cost and accept payment procedure
 Old Higher 2009 The program will make use of a 1 -D array. (i) When creating, or declaring, a 1 -D array for use in a program, a name must be given to the array. State two other items that should be specified when the array is created. (ii) Explain why it is a more efficient use of system resources to pass an array by reference rather than by value.
Old Higher 2009 The program will make use of a 1 -D array. (i) When creating, or declaring, a 1 -D array for use in a program, a name must be given to the array. State two other items that should be specified when the array is created. (ii) Explain why it is a more efficient use of system resources to pass an array by reference rather than by value.
 Old Higher 2009 (i) When creating, or declaring, a 1 -D array you need to state the number of items in the array (its index) and the data type (integer, string boolean etc) (ii) Passing an array by reference is more efficient than passing by value because arrays consume large amounts of memory and since when a parameter is passed by value, a copy is made, memory is consumed unnecessarily.
Old Higher 2009 (i) When creating, or declaring, a 1 -D array you need to state the number of items in the array (its index) and the data type (integer, string boolean etc) (ii) Passing an array by reference is more efficient than passing by value because arrays consume large amounts of memory and since when a parameter is passed by value, a copy is made, memory is consumed unnecessarily.
 Another example The design for a program is shown below. 1. Initialise variables 2. Enter pupil marks 3. Count the number of pupils with less than 45 marks 4. Display results. (b) Step 3 of the program uses the parameters pupil. Mark and no. Needing. Support. (i) State the variable types for these parameters. (ii) For each parameter, state if it should passed by value or by reference in step 3?
Another example The design for a program is shown below. 1. Initialise variables 2. Enter pupil marks 3. Count the number of pupils with less than 45 marks 4. Display results. (b) Step 3 of the program uses the parameters pupil. Mark and no. Needing. Support. (i) State the variable types for these parameters. (ii) For each parameter, state if it should passed by value or by reference in step 3?
 Another example The design for a program is shown below. 1. Initialise variables 2. Enter pupil marks 3. Count the number of pupils with less than 45 marks 4. Display results. (i) and no. Needing. Support would be INTEGER (ii) In step 3, pupil. Mark would be passed by value and no. Needing. Support would be passed by reference (because it is passed out and then into step 4)
Another example The design for a program is shown below. 1. Initialise variables 2. Enter pupil marks 3. Count the number of pupils with less than 45 marks 4. Display results. (i) and no. Needing. Support would be INTEGER (ii) In step 3, pupil. Mark would be passed by value and no. Needing. Support would be passed by reference (because it is passed out and then into step 4)
 Summary • A local variable only has scope within the-sub procedure where it has been defined. A global variable has scope throughout a program. Using global variables makes code less readable, less modular and thus less maintainable • The advantages of using parameter passing rather than global variables is to increase the modularity, portability readability and maintainability of the code. • A formal parameter is one declared in the definition of a procedure or function • An actual parameter is one used when calling a procedure or function • A value parameter is one which is passed into a sub-procedure and whose value is copied, used by that procedure then discarded. • A reference parameter is a variable which is passed into a sub-procedure and then out again and whose value is changed by that sub- procedure
Summary • A local variable only has scope within the-sub procedure where it has been defined. A global variable has scope throughout a program. Using global variables makes code less readable, less modular and thus less maintainable • The advantages of using parameter passing rather than global variables is to increase the modularity, portability readability and maintainability of the code. • A formal parameter is one declared in the definition of a procedure or function • An actual parameter is one used when calling a procedure or function • A value parameter is one which is passed into a sub-procedure and whose value is copied, used by that procedure then discarded. • A reference parameter is a variable which is passed into a sub-procedure and then out again and whose value is changed by that sub- procedure
 Summary • A function returns a value, a procedure performs a sequence of actions • A built in function is supplied as part of the development environment, a user defined function is one created by the programmer. • Using procedures and functions improves the readability and maintainability of code • Procedures and functions which use local variables make code more portable • Procedures and functions can be tested independently making code easier to debug
Summary • A function returns a value, a procedure performs a sequence of actions • A built in function is supplied as part of the development environment, a user defined function is one created by the programmer. • Using procedures and functions improves the readability and maintainability of code • Procedures and functions which use local variables make code more portable • Procedures and functions can be tested independently making code easier to debug


