fbd568f75d1cfd1891947eff2b0181a2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Higher Business Management Unit 2 Learning Outcome 5 Operations BM Unit 2 - L 05 1
Operations/Production Three distinct phases Inputs Process Outputs BM Unit 2 - L 05 2
Inputs n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Raw materials Labour 3
Process n n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Converting raw materials into something useful Use of machinery and other processes Assembly 4
Output n n Packaging n Storage n Distribution n BM Unit 2 - L 05 The finished product! Transport 5
Factors Affecting Production Systems n n Quantity to be produced n Resources available n Labour n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Nature of the product Capital 6
Methods of Production n Job Production n Batch Production n Flow Production MASS PRODUCTION IN LARGE FACTORY BM Unit 2 - L 05 7

Job Production n n A custom-built boat n A piece of artwork n BM Unit 2 - L 05 A house built to your own design A hand-turned wooden bowl 8
Batch Production n BM Unit 2 - L 05 A number of similar products (repeated jobs) The same house repeated on a building site Bakery produce - each batch may differ slightly 9
Flow Production n Mass production of almost identical products n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Cars Washing machines 10

Quality Control n ‘Bolting the door after the horse has gone’ n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Leads to waste and scrap Can be very “costly” 11

Quality Assurance n n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Making sure the horse cannot bolt Getting it right first time All aspects of the business including the commitment of the workforce 12

Quality - A Definition n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Those features of a product or service that allow it to satisfy customers’ requirements 13
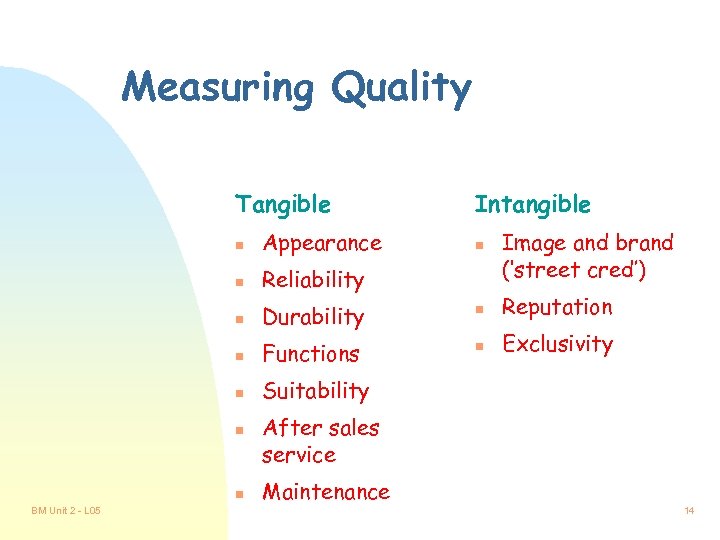
Measuring Quality Tangible Intangible Image and brand (‘street cred’) n Appearance n Reliability n Durability n Reputation n Functions n Exclusivity n Suitability n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 n After sales service Maintenance 14
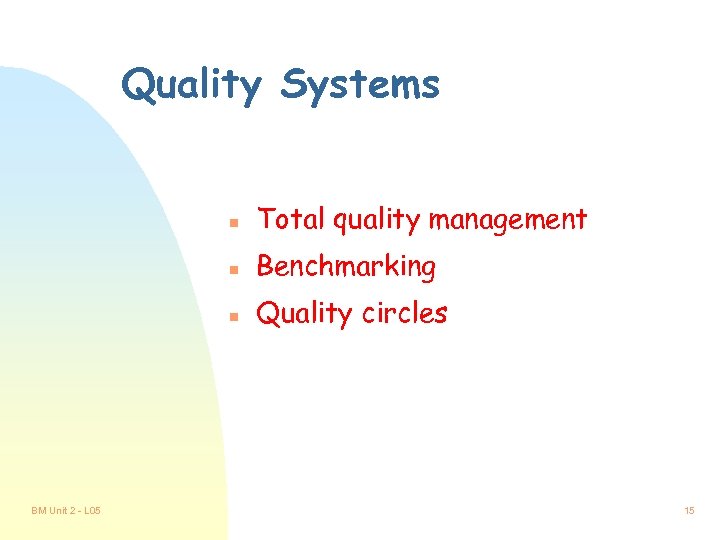
Quality Systems n n Benchmarking n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Total quality management Quality circles 15

Total Quality Management (TQM) n n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Right first time Consistent, clear message on quality Staff commitment to ongoing improvement Partnership with suppliers Educate and train staff Supervisors encourage and help n n n Eliminate fear of failure Departments integrate and share problems Set clear, achievable goals Help employees to take pride in their work Train and educate Establish a structure and culture to support these aims 16
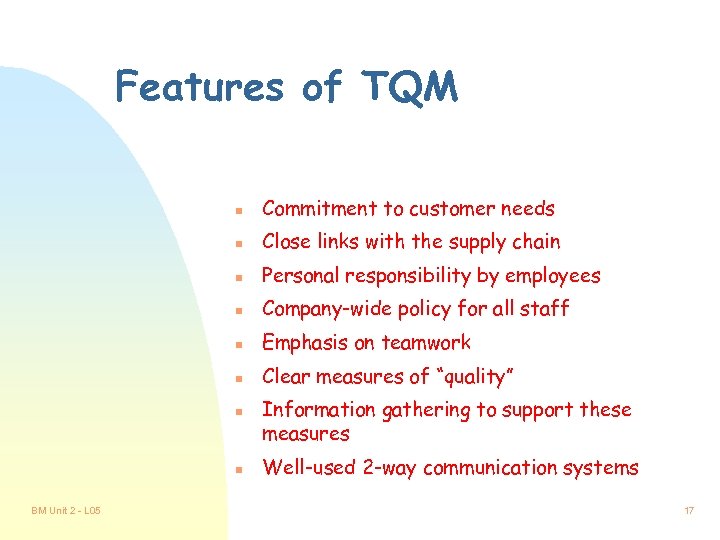
Features of TQM n Commitment to customer needs n Close links with the supply chain n Personal responsibility by employees n Company-wide policy for all staff n Emphasis on teamwork n Clear measures of “quality” n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Information gathering to support these measures Well-used 2 -way communication systems 17
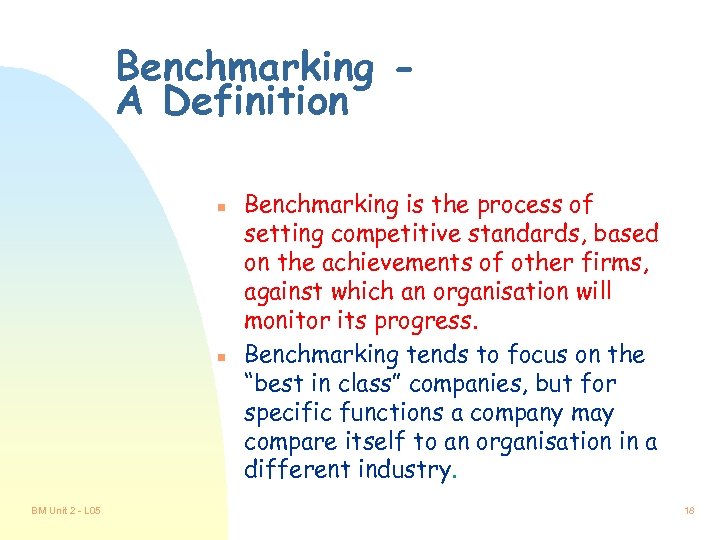
Benchmarking A Definition n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Benchmarking is the process of setting competitive standards, based on the achievements of other firms, against which an organisation will monitor its progress. Benchmarking tends to focus on the “best in class” companies, but for specific functions a company may compare itself to an organisation in a different industry. 18
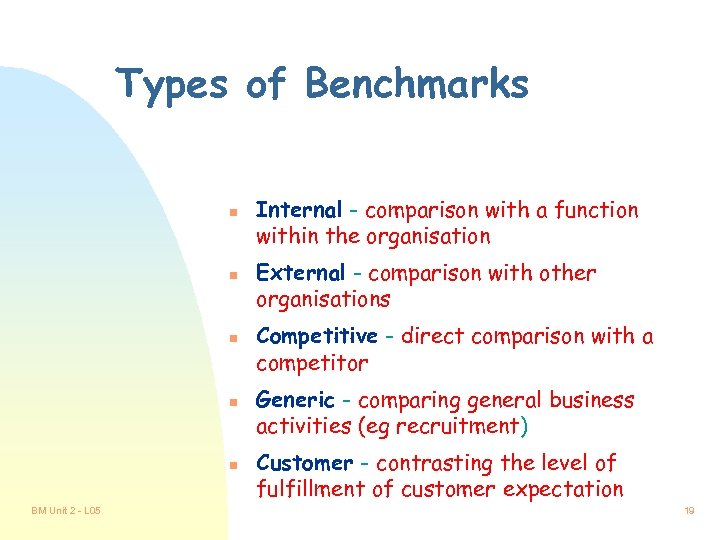
Types of Benchmarks n n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Internal - comparison with a function within the organisation External - comparison with other organisations Competitive - direct comparison with a competitor Generic - comparing general business activities (eg recruitment) Customer - contrasting the level of fulfillment of customer expectation 19

Quality Circles n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Production workers know more about the production process than “managers” Workers are motivated by being involved and consulted about production problems (empowerment) 20
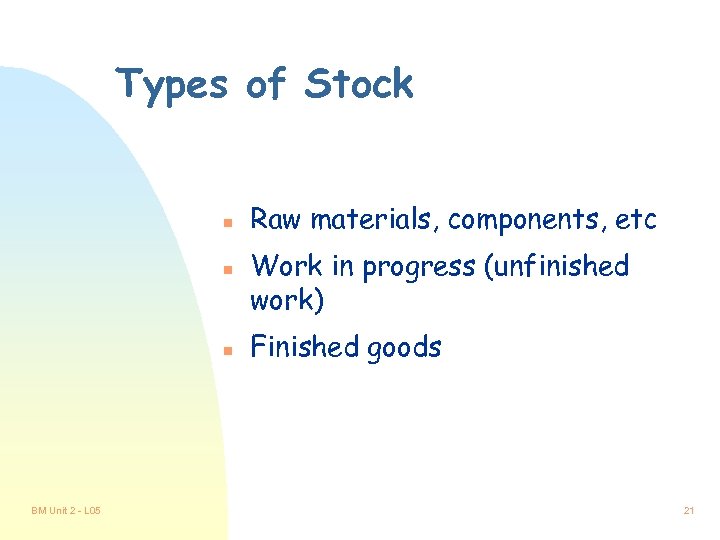
Types of Stock n n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Raw materials, components, etc Work in progress (unfinished work) Finished goods 21

The Importance of Stock Control n n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 “Stock out” = lost sales and poor reputation Excess stock = high storage costs Excess stock runs risk of damage, obsolescence, “opportunity costs” (alternative use for the money tied up in stock) 22
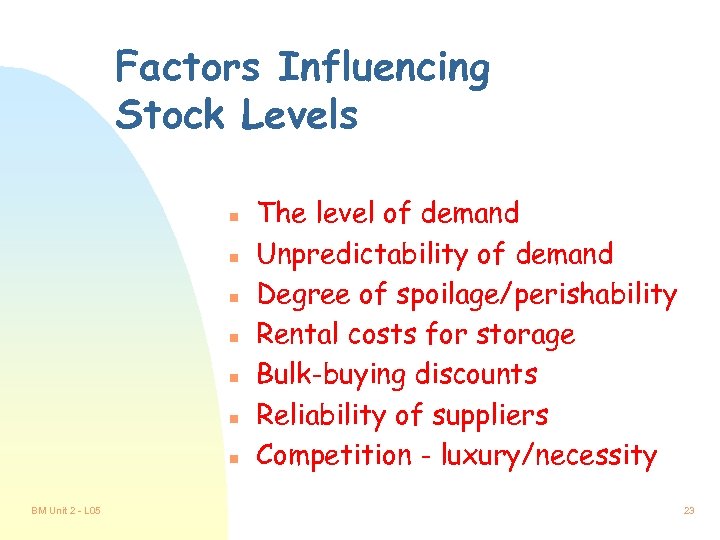
Factors Influencing Stock Levels n n n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 The level of demand Unpredictability of demand Degree of spoilage/perishability Rental costs for storage Bulk-buying discounts Reliability of suppliers Competition - luxury/necessity 23
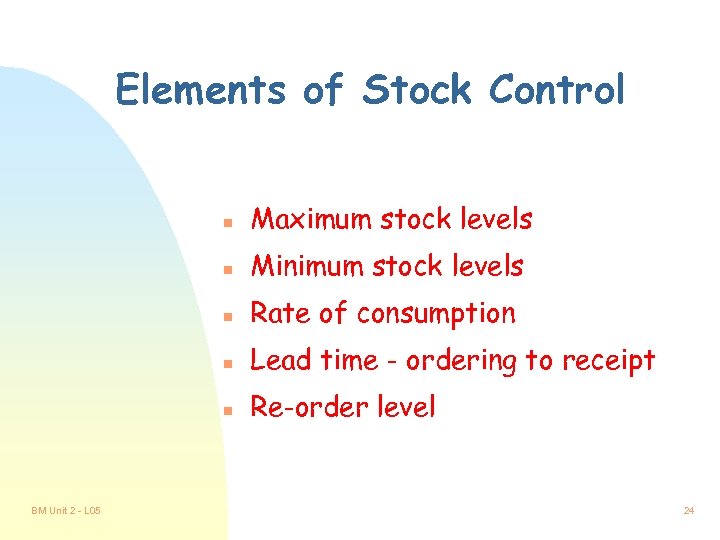
Elements of Stock Control n n Minimum stock levels n Rate of consumption n Lead time - ordering to receipt n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Maximum stock levels Re-order level 24
Just-in-time (Kanban System) Advantages n n Improves cash flow (less tied up) n Savings on purchase and storage costs n Less stock wastage n Production delays prevented n Can respond to changes in demand n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Stock exactly matches production Close ties with suppliers established 25
Just-in-time (Kanban System) Disadvantages n n n BM Unit 2 - L 05 High dependency on suppliers to meet delivery and quality standards Suppliers must be willing to participate (can be high-risk - ‘all the eggs in one basket’ - M&S suppliers) Increase in order processing costs 26

The Purchasing Function n Having sufficient stock available n Avoiding wastage of stock n Having the correct quality n In the factory when needed n Competitive prices paid n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Building good relationship with suppliers 27

The Purchasing Mix n n Lowest price n Delivered in correct quantities n BM Unit 2 - L 05 Best quality Delivered at the correct time 28
fbd568f75d1cfd1891947eff2b0181a2.ppt