01e0b5c71b5027875a41886fd844eb80.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 HIGH VOLUME SLIDE SCANNING ARCHITECTURE AND APPLICATIONS Dr. André Huisman Department of pathology UMC Utrecht, The Netherlands a. huisman-4@umcutrecht. nl
HIGH VOLUME SLIDE SCANNING ARCHITECTURE AND APPLICATIONS Dr. André Huisman Department of pathology UMC Utrecht, The Netherlands a. huisman-4@umcutrecht. nl
 Department of pathology UMCU • UMC Utrecht • >1, 000 beds • >10, 000 employees • Department of pathology: • 20. 000 surgical pathology cases • 156. 000 glass slides (histology, cytology, IHC) • 15 pathologists, 10 residents
Department of pathology UMCU • UMC Utrecht • >1, 000 beds • >10, 000 employees • Department of pathology: • 20. 000 surgical pathology cases • 156. 000 glass slides (histology, cytology, IHC) • 15 pathologists, 10 residents
 Digital pathology - advantages • Digital Archiving • Instant access from multiple locations by multiple people • No searching for slides • Constant quality • Telepathology • Consultations, revisions and panels • Education • Research • Automated image processing
Digital pathology - advantages • Digital Archiving • Instant access from multiple locations by multiple people • No searching for slides • Constant quality • Telepathology • Consultations, revisions and panels • Education • Research • Automated image processing
 Project background Clinico pathological conferences: • 900 meetings every year • No (multi headed) microscope needed • Quicker preparation of meetings • No retrieval of glass slides from archive
Project background Clinico pathological conferences: • 900 meetings every year • No (multi headed) microscope needed • Quicker preparation of meetings • No retrieval of glass slides from archive
 Aim (2007) Digitize all diagnostic slides we have (prospectively)
Aim (2007) Digitize all diagnostic slides we have (prospectively)
 Challenges • Scanners • Image size: up to 1 GB x 500 slides per day • No existing infrastructure present for storage of this size at our facility • Image presentation and software integration • Logistics
Challenges • Scanners • Image size: up to 1 GB x 500 slides per day • No existing infrastructure present for storage of this size at our facility • Image presentation and software integration • Logistics
 Scanners • Different manufacturers: • Speed • Focusing method • Acquisition technique • z-stack acquisition • File format policy • Application integration • 2007: 3 D Histech (Zeiss), Aperio, Hamamatsu, Olympus (US: Dmetrix, Bio. Imagene) • 2010: Leica, Menarini, Philips, Omnyx, Bio. Imagene
Scanners • Different manufacturers: • Speed • Focusing method • Acquisition technique • z-stack acquisition • File format policy • Application integration • 2007: 3 D Histech (Zeiss), Aperio, Hamamatsu, Olympus (US: Dmetrix, Bio. Imagene) • 2010: Leica, Menarini, Philips, Omnyx, Bio. Imagene
 Scanning logistics • 3 Aperio XT scanners (120 slides per scanner) • Morgue assistants • Mark slides after scanning • 6 Hours per run at 20 x magnification (~3 minutes/scan)
Scanning logistics • 3 Aperio XT scanners (120 slides per scanner) • Morgue assistants • Mark slides after scanning • 6 Hours per run at 20 x magnification (~3 minutes/scan)
 Storage – HSM • • • HSM = Hierarchical Storage Management Sun Microsystems (Oracle) 6 TB available on very fast fibre channel disks 120 TB available on tape (750 GB each) 2 Tape drives • Completely transparent archiving and retrieval (robot) • Access time from tape: 1 - 3 minutes
Storage – HSM • • • HSM = Hierarchical Storage Management Sun Microsystems (Oracle) 6 TB available on very fast fibre channel disks 120 TB available on tape (750 GB each) 2 Tape drives • Completely transparent archiving and retrieval (robot) • Access time from tape: 1 - 3 minutes
 Linking systems • • • 1 D Barcodes U-DPS: reporting system LMS: Laboratory Management System Spectrum: Aperio’s image management solution Storage system • Own development: integration layer
Linking systems • • • 1 D Barcodes U-DPS: reporting system LMS: Laboratory Management System Spectrum: Aperio’s image management solution Storage system • Own development: integration layer
 Scanner workflow Other images (e. g. macro) Scanning Database Order form scanner LIS Image / Data server U-DPS HSM Storage 120 TB on tape 6 TB fast disks pathology users Speech recognition
Scanner workflow Other images (e. g. macro) Scanning Database Order form scanner LIS Image / Data server U-DPS HSM Storage 120 TB on tape 6 TB fast disks pathology users Speech recognition
 Validation • Aim: validate diagnostic use of digital slides • Method: reevaluate diagnosis with same pathologist on scanned slide after washout period (1 year) for several organs • Gold standard: original diagnosis using ‘traditional’ microscopy
Validation • Aim: validate diagnostic use of digital slides • Method: reevaluate diagnosis with same pathologist on scanned slide after washout period (1 year) for several organs • Gold standard: original diagnosis using ‘traditional’ microscopy
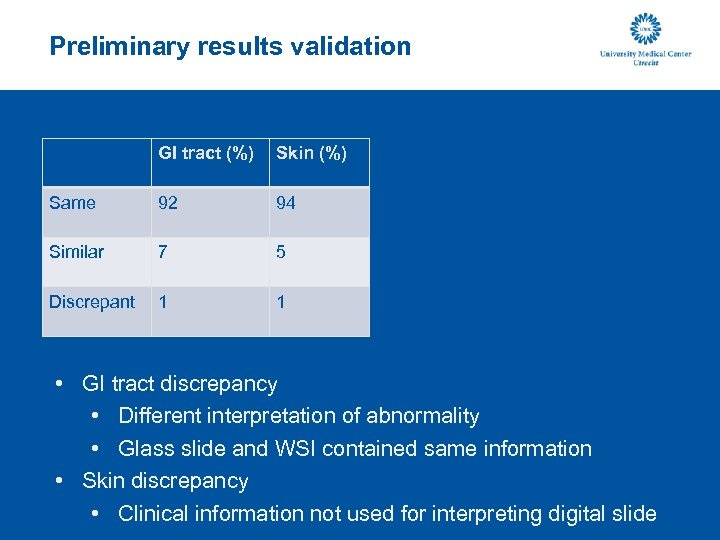 Preliminary results validation GI tract (%) Skin (%) Same 92 94 Similar 7 5 Discrepant 1 1 • GI tract discrepancy • Different interpretation of abnormality • Glass slide and WSI contained same information • Skin discrepancy • Clinical information not used for interpreting digital slide
Preliminary results validation GI tract (%) Skin (%) Same 92 94 Similar 7 5 Discrepant 1 1 • GI tract discrepancy • Different interpretation of abnormality • Glass slide and WSI contained same information • Skin discrepancy • Clinical information not used for interpreting digital slide
 Pitfalls of digital archive • Costs • Huge storage needs – 40 Tera. Byte per year (over 57, 000 CDs) • Largest storage in the UMCU • Logistics of scanning up to 500 slides per day • Currently scanning almost 24 / 7 • Place of scanning in process • Speed of image retrieval • Image compression (JPEG 2000? ) • Backup
Pitfalls of digital archive • Costs • Huge storage needs – 40 Tera. Byte per year (over 57, 000 CDs) • Largest storage in the UMCU • Logistics of scanning up to 500 slides per day • Currently scanning almost 24 / 7 • Place of scanning in process • Speed of image retrieval • Image compression (JPEG 2000? ) • Backup
 Education • All students view the same “best slide” • Slide images can be integrated with • Annotations • Questions • Macroscopic images • Other multimedia • Most UMCU microscopy practical sessions are digital • Student satisfaction is high
Education • All students view the same “best slide” • Slide images can be integrated with • Annotations • Questions • Macroscopic images • Other multimedia • Most UMCU microscopy practical sessions are digital • Student satisfaction is high
 Teleconsultation • Place (small) slide scanners at different labs • Upload digital slides to UMC Utrecht • Aurora m. Scope Clinical Upload new media • www. pathoconsult. com
Teleconsultation • Place (small) slide scanners at different labs • Upload digital slides to UMC Utrecht • Aurora m. Scope Clinical Upload new media • www. pathoconsult. com
 Digital slide panel discussions
Digital slide panel discussions
 Image processing research Image processing applications on virtual slides: • Detecting mitotic figures in breast cancer slides • Use texture features • Establishing histological grade in breast cancer • Segmentation of individual nuclei (on H&E stained slides) • Detect points of interest • Use marker-controlled watershed segmentation • Post processing
Image processing research Image processing applications on virtual slides: • Detecting mitotic figures in breast cancer slides • Use texture features • Establishing histological grade in breast cancer • Segmentation of individual nuclei (on H&E stained slides) • Detect points of interest • Use marker-controlled watershed segmentation • Post processing
 Conclusions • Routine scanning is possible and makes sense • Future of pathology is digital • Digital pathology is expensive • Digital pathology is just starting. . Together we are shaping Pathology 2. 0
Conclusions • Routine scanning is possible and makes sense • Future of pathology is digital • Digital pathology is expensive • Digital pathology is just starting. . Together we are shaping Pathology 2. 0
 Discussion • Limitations current system • Cytology • Speed • Magnification (20 x / 40 x incidental) • Backup • Quality Control
Discussion • Limitations current system • Cytology • Speed • Magnification (20 x / 40 x incidental) • Backup • Quality Control
 Discussion • Archive heavily used • Educational use still growing • Teleconsultation network growing (www. slideconsult. com) • Need for standards • DICOM / JPEG 2000 • Images, annotations and reports • Mixing scanners and integration with other software platforms (middleware? ) • Image management central in workflow for pathologist?
Discussion • Archive heavily used • Educational use still growing • Teleconsultation network growing (www. slideconsult. com) • Need for standards • DICOM / JPEG 2000 • Images, annotations and reports • Mixing scanners and integration with other software platforms (middleware? ) • Image management central in workflow for pathologist?
 Questions? ! Huisman et al. , Creation of a fully digital pathology slide archive by high-volume tissue slide scanning, Human Pathology, 2010 May; 41(5): 751 -7 a. huisman-4@umcutrecht. nl
Questions? ! Huisman et al. , Creation of a fully digital pathology slide archive by high-volume tissue slide scanning, Human Pathology, 2010 May; 41(5): 751 -7 a. huisman-4@umcutrecht. nl


