e4cf8b651004327e0d658c98886a0e7b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

High Value Care in Ob/Gyn

Goals and Objectives • Define Value • Understand value from the perspective of the stakeholders – The Population, the Patient and the Physician • Understand teaching value in medical education • Utilize existing resources to understand practice high value care
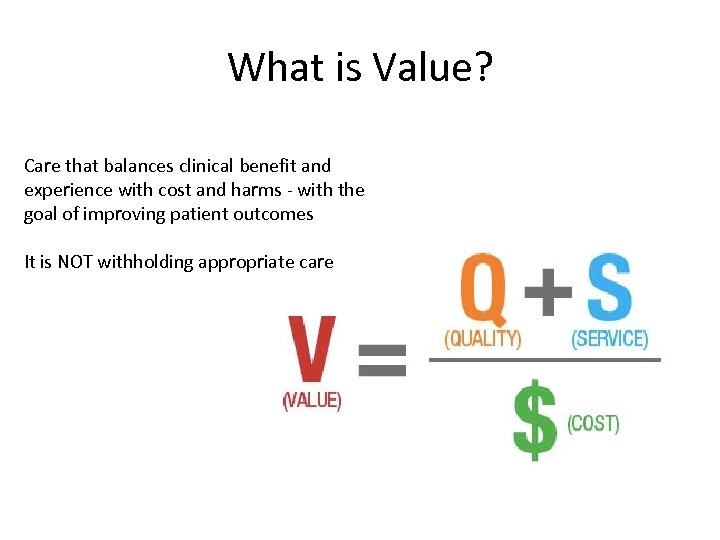
What is Value? Care that balances clinical benefit and experience with cost and harms - with the goal of improving patient outcomes It is NOT withholding appropriate care
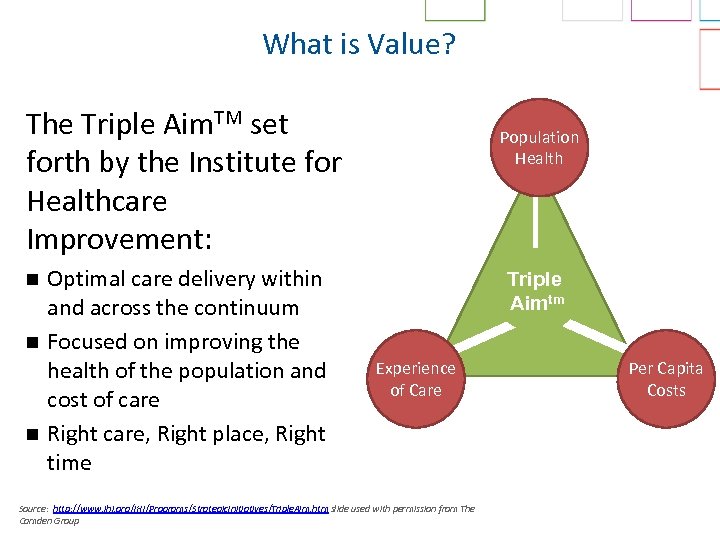
What is Value? The Triple Aim. TM set forth by the Institute for Healthcare Improvement: n n n Optimal care delivery within and across the continuum Focused on improving the health of the population and cost of care Right care, Right place, Right time Population Health Triple Aimtm Experience of Care Source: http: //www. ihi. org/IHI/Programs/Strategic. Initiatives/Triple. Aim. htm slide used with permission from The Camden Group Per Capita Costs
What is Cost – It Depends • To providers: The expense incurred to deliver healthcare services to patients • To payers: the amount they pay to the providers for services rendered • To patients: the amount they pay out-ofpocket for healthcare services
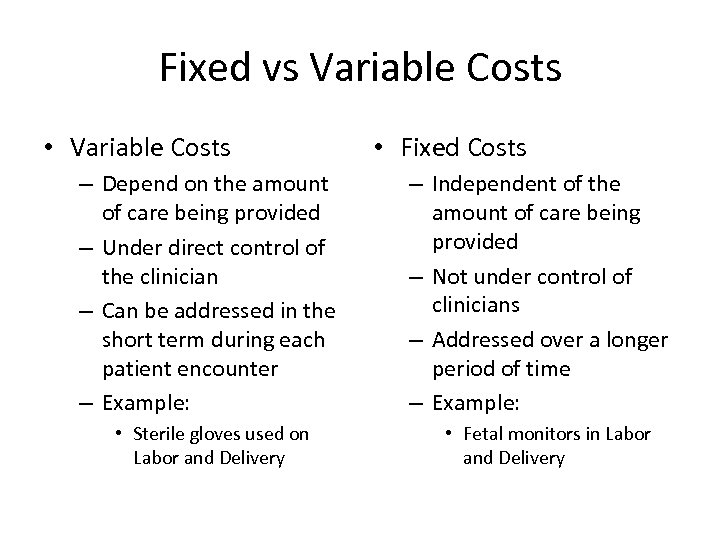
Fixed vs Variable Costs • Variable Costs – Depend on the amount of care being provided – Under direct control of the clinician – Can be addressed in the short term during each patient encounter – Example: • Sterile gloves used on Labor and Delivery • Fixed Costs – Independent of the amount of care being provided – Not under control of clinicians – Addressed over a longer period of time – Example: • Fetal monitors in Labor and Delivery
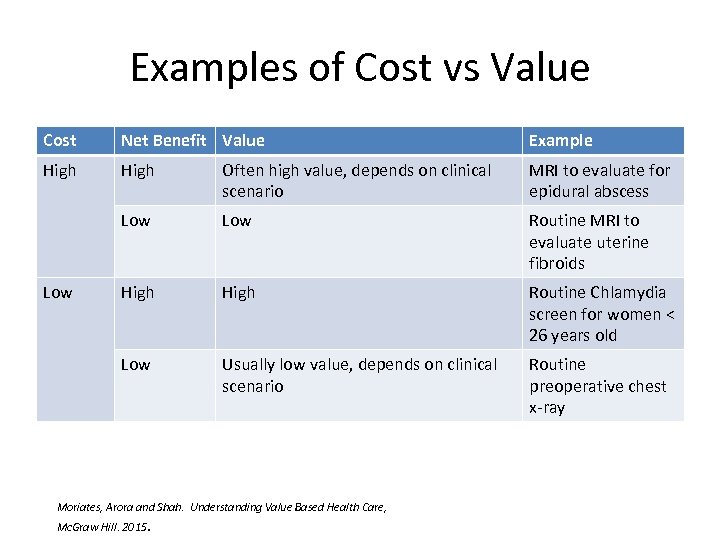
Examples of Cost vs Value Cost Net Benefit Value Example High Often high value, depends on clinical scenario MRI to evaluate for epidural abscess Low Routine MRI to evaluate uterine fibroids High Routine Chlamydia screen for women < 26 years old Low Usually low value, depends on clinical scenario Routine preoperative chest x-ray Low Moriates, Arora and Shah. Understanding Value Based Health Care, Mc. Graw Hill. 2015.

The Stakeholders • The Population • The Patient • The Provider

Value from the Population perspective
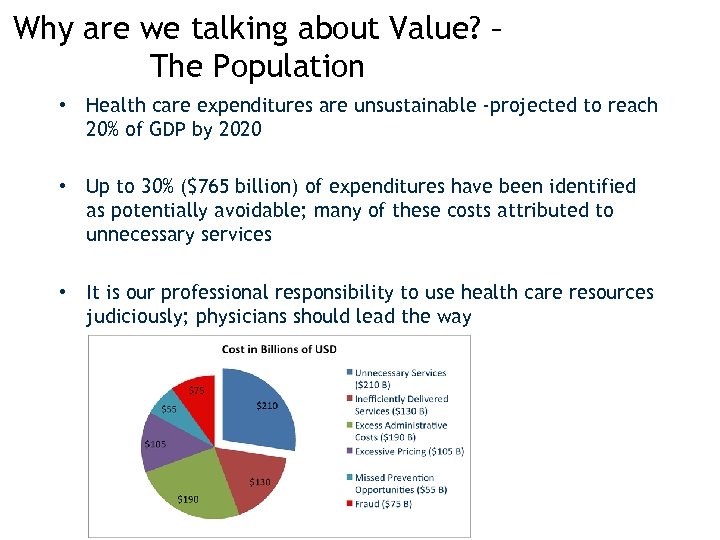
Why are we talking about Value? – The Population • Health care expenditures are unsustainable -projected to reach 20% of GDP by 2020 • Up to 30% ($765 billion) of expenditures have been identified as potentially avoidable; many of these costs attributed to unnecessary services • It is our professional responsibility to use health care resources judiciously; physicians should lead the way
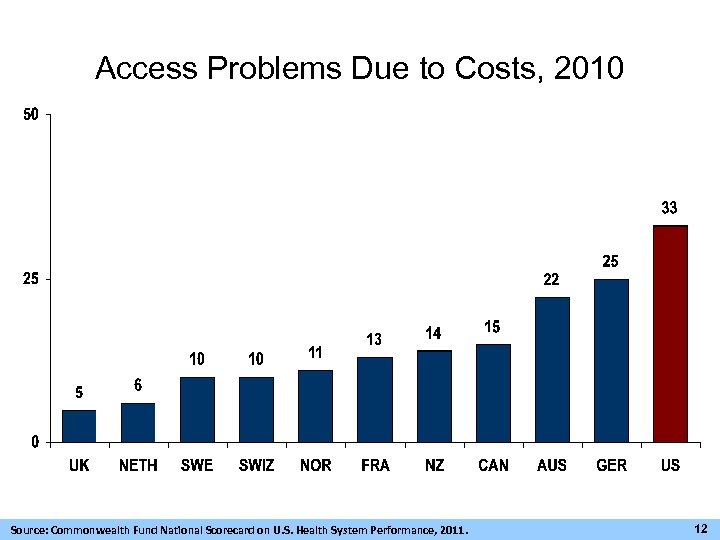
Access Problems Due to Costs, 2010 Source: Commonwealth Fund National Scorecard on U. S. Health System Performance, 2011. 12

What about Ob. Gyn?
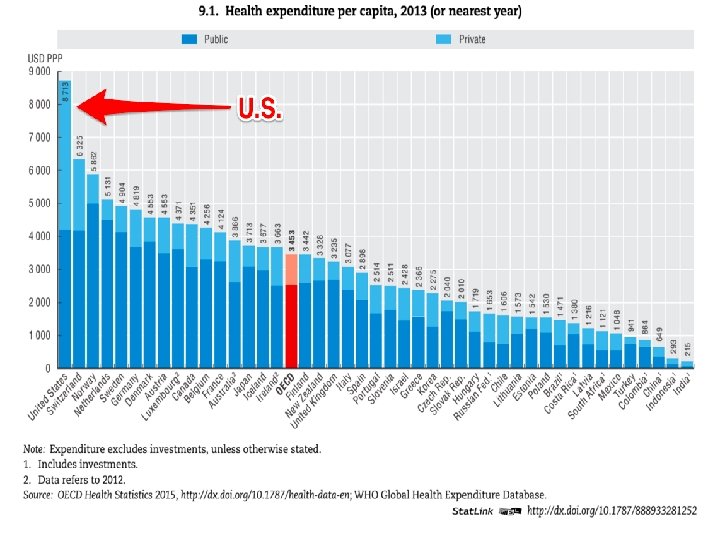
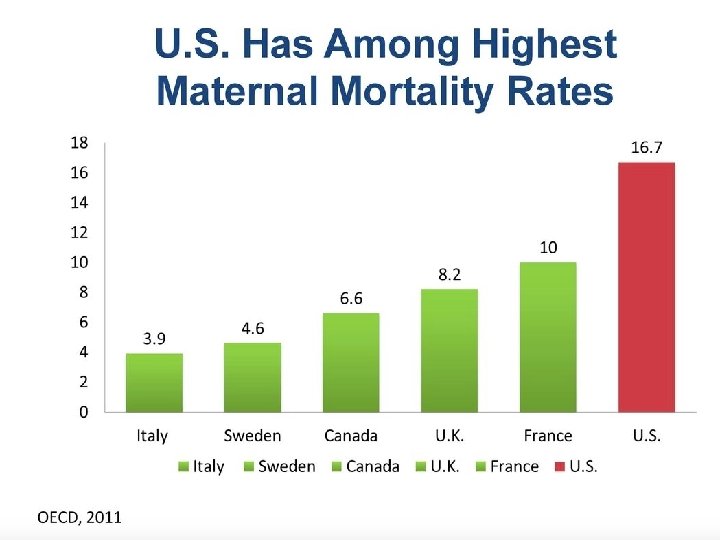
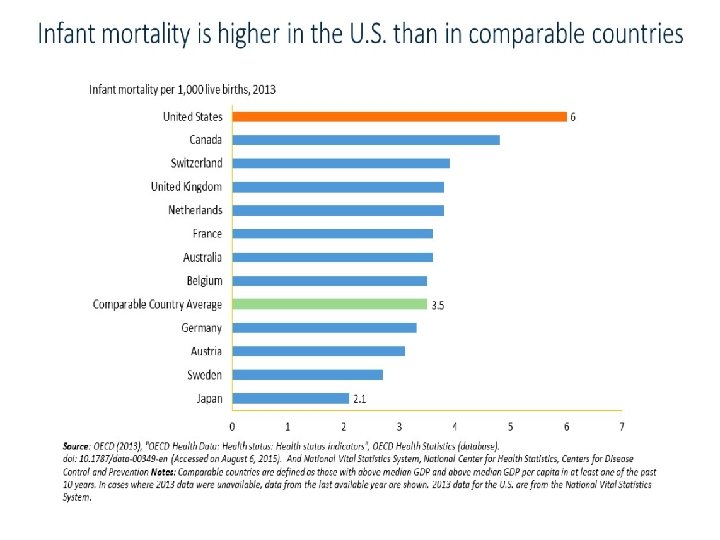

Maternity Care Value • Our costs are high and our quality could be better. • What is our value?

Patients as Stakeholders

Patients Care about Costs • Rising number of high deductible plans (avg. of 15% per year since 2011) • Medical bills responsible for bankruptcy

Patients Care about Cost – If Faced with a Financial Emergency: • 62% of households have less than $1000. 00 in savings • 26% have no savings • Healthcare is the cause of 67% of all personal bankruptcies World. Congress. com, “Episodes of Care in Oncology. Nikolas Bueschler, Executive Director of Oncology - Penn Mediicine Lancaster. Sameer Mahesh, Principal Investigator OCM Summa Health Medical Group

What Patients are Saying
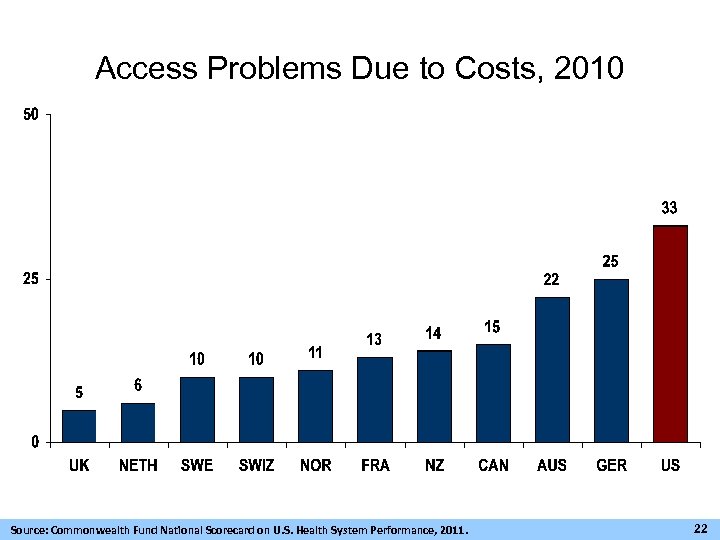
Access Problems Due to Costs, 2010 Source: Commonwealth Fund National Scorecard on U. S. Health System Performance, 2011. 22

Providers as Stakeholders
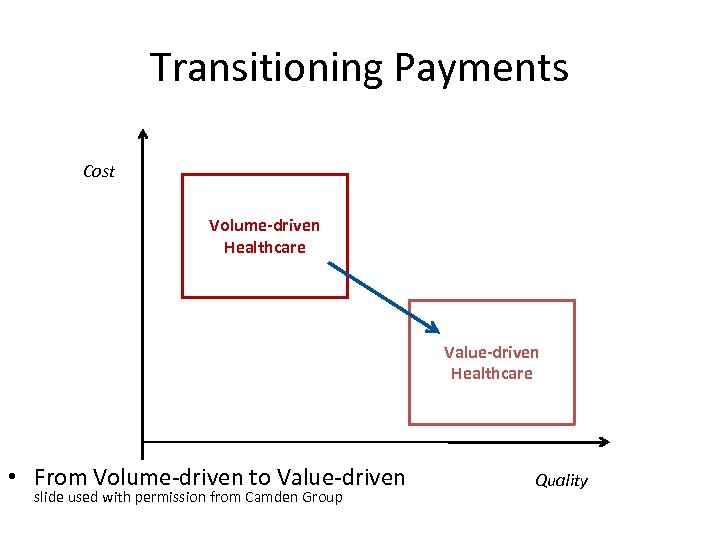
Transitioning Payments Cost Volume-driven Healthcare Value-driven Healthcare • From Volume-driven to Value-driven slide used with permission from Camden Group Quality
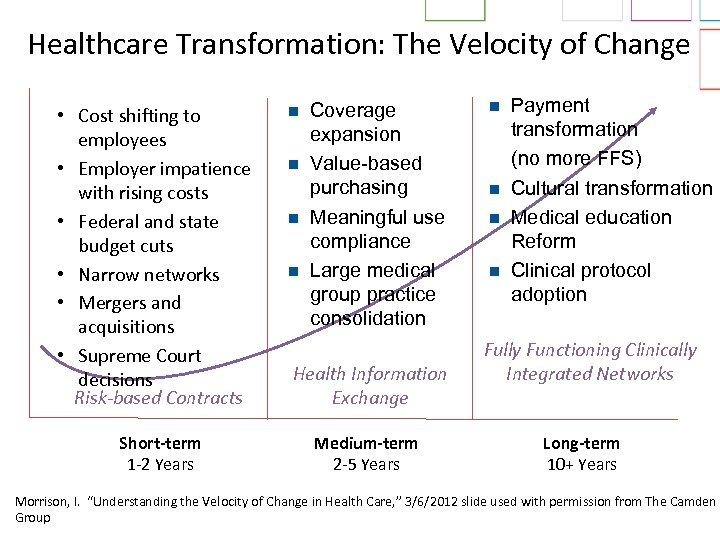
Healthcare Transformation: The Velocity of Change • Cost shifting to employees • Employer impatience with rising costs • Federal and state budget cuts • Narrow networks • Mergers and acquisitions • Supreme Court decisions Risk-based Contracts Short-term 1 -2 Years n n Coverage expansion Value-based purchasing Meaningful use compliance Large medical group practice consolidation Health Information Exchange Medium-term 2 -5 Years n n Payment transformation (no more FFS) Cultural transformation Medical education Reform Clinical protocol adoption Fully Functioning Clinically Integrated Networks Long-term 10+ Years Morrison, I. “Understanding the Velocity of Change in Health Care, ” 3/6/2012 slide used with permission from The Camden Group
Value is not going away – it’s the new quality

ACOG is responding to payment reform



What about Medical Education?


Previously widely ignored in medical training: “The reasons for this silence are historical, philosophical, structural, and cultural. . Combating such forces is a tall order, but I believe that medical educators have an obligation to address cost. ” - Dr Molly Cooke (2010) Reference: Cooke M. Cost consciousness in patient care--what is medical education's responsibility? N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 1253 -5 :


ACGME

Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Oct. 2013

Green Journal Initiative • Editorial retreat June 2017 – decision made to encourage submissions about cost conscious care • Will be highlighted by Dr. Nancy Chescheir, editor-in-chief, in January 2018 editorial

Resources for Identifying Costs • Healthcarebluebook. com • Clearheathcosts. com • Your own hospital can provide this information

Resources for Information on Value Based Care • Choosingwisely. org • https: //vbhc. dellmed. utexas. edu • http: //app 1. medu. org/author/app/player 2/player_selection 2. html? docid=1 500269423293&pmwid=7 E 283 E 7 BE 955 F 5 FDB 6 B 425 D 7 DA 5 041 D 2 • https: //www. acponline. org/clinical-information/high-valuecare/medical-educators-resources/curriculum-foreducators-and-residents • https: //www. acog. org/About-ACOG/ACOGDepartments/CREOG-Search/Cases-for-Cost. Conscious-Care
e4cf8b651004327e0d658c98886a0e7b.ppt