8674994a6fe0d211f6e062c0a0951524.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 High-throughput genotyping Finnish Genome Center 18 March 2018 1
High-throughput genotyping Finnish Genome Center 18 March 2018 1
 What is genotyping? • the analysis of DNA-sequence variation • genotype = the genetic constitution of an individual Finnish Genome Center
What is genotyping? • the analysis of DNA-sequence variation • genotype = the genetic constitution of an individual Finnish Genome Center
 Alleles • alternative form of a gene or DNA sequence at a specific chromosomal location (locus) • at each locus an individual possesses two alleles, one inherited from the father one from the mother → genotype: a sum of these two alleles Finnish Genome Center
Alleles • alternative form of a gene or DNA sequence at a specific chromosomal location (locus) • at each locus an individual possesses two alleles, one inherited from the father one from the mother → genotype: a sum of these two alleles Finnish Genome Center
 Genetic differences: • may cause or predispose to diseases • determines e. g. individual drug response • used as markers to identify predisposing genes for diseases → high-throughput genotyping technologies needed Finnish Genome Center
Genetic differences: • may cause or predispose to diseases • determines e. g. individual drug response • used as markers to identify predisposing genes for diseases → high-throughput genotyping technologies needed Finnish Genome Center
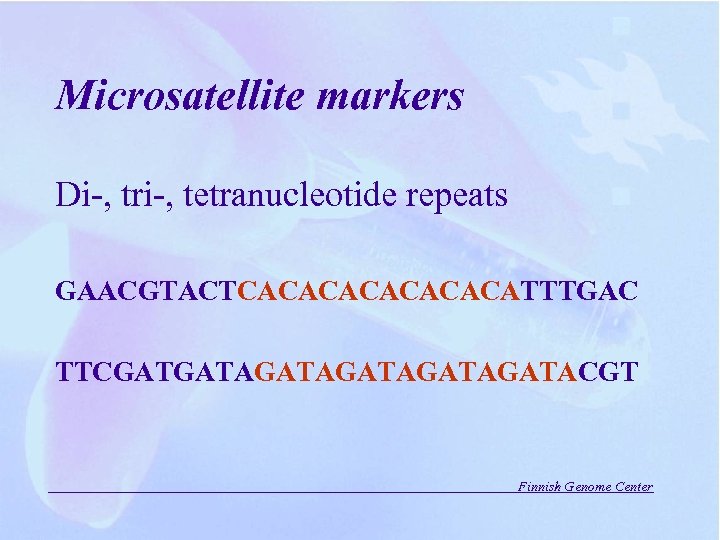 Microsatellite markers Di-, tri-, tetranucleotide repeats GAACGTACTCACACACATTTGAC TTCGATGATAGATAGATACGT Finnish Genome Center
Microsatellite markers Di-, tri-, tetranucleotide repeats GAACGTACTCACACACATTTGAC TTCGATGATAGATAGATACGT Finnish Genome Center
 . . . Microsatellite markers • also called: • STR= Single Tandem Repeat • SSR= Simple Sequence Repeat • SSLP= Simple Sequence Length Polymorphism • • the number of repeats varies (→ 30) highly polymorphic distributed evenly throughout the genome easy to detect by PCR Finnish Genome Center
. . . Microsatellite markers • also called: • STR= Single Tandem Repeat • SSR= Simple Sequence Repeat • SSLP= Simple Sequence Length Polymorphism • • the number of repeats varies (→ 30) highly polymorphic distributed evenly throughout the genome easy to detect by PCR Finnish Genome Center
![SNP markers • single nucleotide variation GTGGACGTGCTT[G/C]TCGATTTACCTAG Finnish Genome Center SNP markers • single nucleotide variation GTGGACGTGCTT[G/C]TCGATTTACCTAG Finnish Genome Center](https://present5.com/presentation/8674994a6fe0d211f6e062c0a0951524/image-7.jpg) SNP markers • single nucleotide variation GTGGACGTGCTT[G/C]TCGATTTACCTAG Finnish Genome Center
SNP markers • single nucleotide variation GTGGACGTGCTT[G/C]TCGATTTACCTAG Finnish Genome Center
 . . . SNP markers • The most simple and common type of polymorphism • Highly abundant; every 1000 bp along human genome • Most SNPs do not affect on cell function • some SNPs could predispose people to disease • influence the individual’s response to a drug • Widely used as genetic markers Finnish Genome Center
. . . SNP markers • The most simple and common type of polymorphism • Highly abundant; every 1000 bp along human genome • Most SNPs do not affect on cell function • some SNPs could predispose people to disease • influence the individual’s response to a drug • Widely used as genetic markers Finnish Genome Center
 SNP genotyping methods • over 100 different approaches • Ideal SNP genotyping platform: • • • high-throughput capacity simple assay design robust affordable price automated genotype calling accurate and reliable results Finnish Genome Center
SNP genotyping methods • over 100 different approaches • Ideal SNP genotyping platform: • • • high-throughput capacity simple assay design robust affordable price automated genotype calling accurate and reliable results Finnish Genome Center
 . . . SNP genotyping methods • PCR • discrimination between alleles: • • allele-specific hybridization allele-specific primer extension allele-specific oligonucleotide ligation allele-specific enzymatic cleavage • detection of the allelic discrimination: • light emitted by the products • mass • change in the electrical property Finnish Genome Center
. . . SNP genotyping methods • PCR • discrimination between alleles: • • allele-specific hybridization allele-specific primer extension allele-specific oligonucleotide ligation allele-specific enzymatic cleavage • detection of the allelic discrimination: • light emitted by the products • mass • change in the electrical property Finnish Genome Center
 The Finnish Genome Center • Independent department of University of Helsinki • Since 1998 • National core facility for the genetic research of multifactorial diseases • Provides collaboration and genotyping service to scientist and research groups in Finland, also abroad Finnish Genome Center
The Finnish Genome Center • Independent department of University of Helsinki • Since 1998 • National core facility for the genetic research of multifactorial diseases • Provides collaboration and genotyping service to scientist and research groups in Finland, also abroad Finnish Genome Center
 The Finnish Genome Center; Goals • • • help designing genetic studies perform high-throughput genotyping perform data analysis training of scientists adopt and develop new strategies & technologies Finnish Genome Center
The Finnish Genome Center; Goals • • • help designing genetic studies perform high-throughput genotyping perform data analysis training of scientists adopt and develop new strategies & technologies Finnish Genome Center
 Research strategies • Genome wide scans with microsatellite markers • ~400 dinucleotidemarkers, ~10 c. M spacing • Fine mapping • Project specific (microsatellite) markers • SNP genotyping • Primer extension –methods (SNu. Pe and Mass. Array; MALDI-TOF), restriction enzyme –methods, project specific markers Finnish Genome Center
Research strategies • Genome wide scans with microsatellite markers • ~400 dinucleotidemarkers, ~10 c. M spacing • Fine mapping • Project specific (microsatellite) markers • SNP genotyping • Primer extension –methods (SNu. Pe and Mass. Array; MALDI-TOF), restriction enzyme –methods, project specific markers Finnish Genome Center
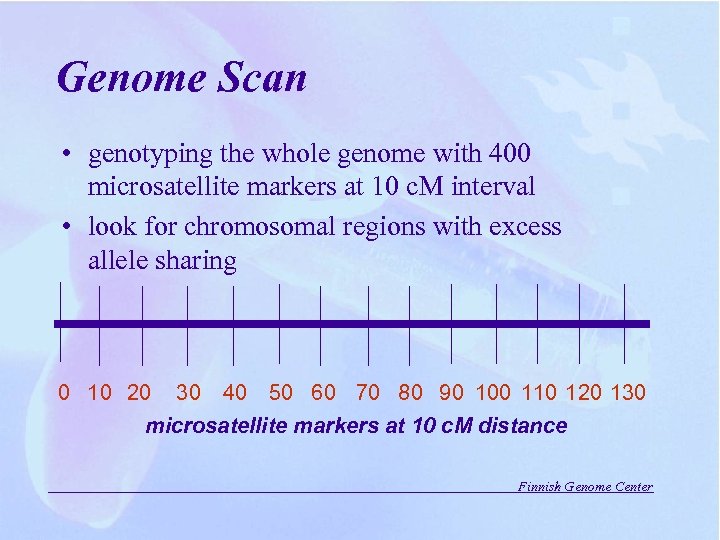 Genome Scan • genotyping the whole genome with 400 microsatellite markers at 10 c. M interval • look for chromosomal regions with excess allele sharing 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 microsatellite markers at 10 c. M distance Finnish Genome Center
Genome Scan • genotyping the whole genome with 400 microsatellite markers at 10 c. M interval • look for chromosomal regions with excess allele sharing 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 microsatellite markers at 10 c. M distance Finnish Genome Center
 Fine mapping • • candidate regions identified by a genome scan candidate genes microsatellite or SNP markers verification of linkage results Finnish Genome Center
Fine mapping • • candidate regions identified by a genome scan candidate genes microsatellite or SNP markers verification of linkage results Finnish Genome Center
 Setting up PCR-reactions Finnish Genome Center
Setting up PCR-reactions Finnish Genome Center
 Electrophoresis run Finnish Genome Center
Electrophoresis run Finnish Genome Center
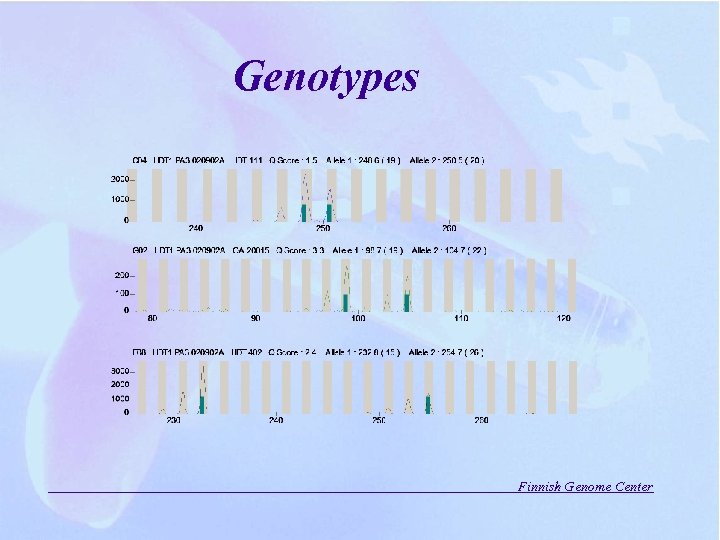 Genotypes Finnish Genome Center
Genotypes Finnish Genome Center
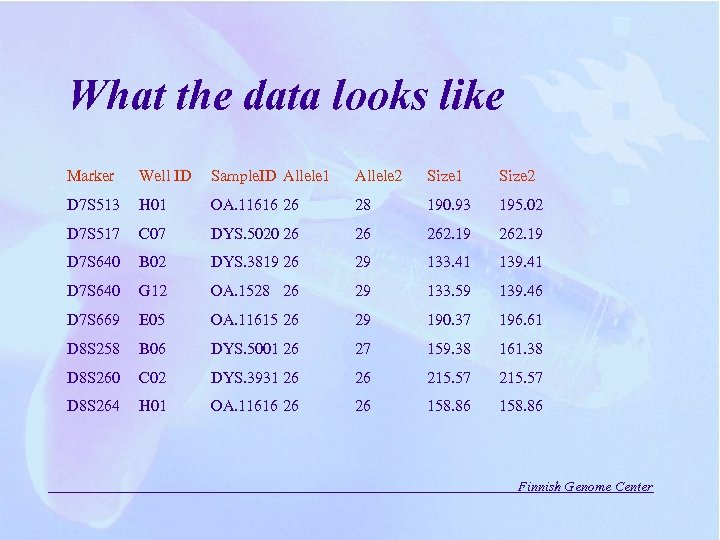 What the data looks like Marker Well ID Sample. ID Allele 1 Allele 2 Size 1 Size 2 D 7 S 513 H 01 OA. 11616 26 28 190. 93 195. 02 D 7 S 517 C 07 DYS. 5020 26 26 262. 19 D 7 S 640 B 02 DYS. 3819 26 29 133. 41 139. 41 D 7 S 640 G 12 OA. 1528 26 29 133. 59 139. 46 D 7 S 669 E 05 OA. 11615 26 29 190. 37 196. 61 D 8 S 258 B 06 DYS. 5001 26 27 159. 38 161. 38 D 8 S 260 C 02 DYS. 3931 26 26 215. 57 D 8 S 264 H 01 OA. 11616 26 26 158. 86 Finnish Genome Center
What the data looks like Marker Well ID Sample. ID Allele 1 Allele 2 Size 1 Size 2 D 7 S 513 H 01 OA. 11616 26 28 190. 93 195. 02 D 7 S 517 C 07 DYS. 5020 26 26 262. 19 D 7 S 640 B 02 DYS. 3819 26 29 133. 41 139. 41 D 7 S 640 G 12 OA. 1528 26 29 133. 59 139. 46 D 7 S 669 E 05 OA. 11615 26 29 190. 37 196. 61 D 8 S 258 B 06 DYS. 5001 26 27 159. 38 161. 38 D 8 S 260 C 02 DYS. 3931 26 26 215. 57 D 8 S 264 H 01 OA. 11616 26 26 158. 86 Finnish Genome Center
 SNP genotyping at FGC • PCR-RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) • SNu. Pe (Single nucleotide primer extension) • Mass. ARRAY; MALDI-TOF (Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-flight mass spectrometry) Finnish Genome Center
SNP genotyping at FGC • PCR-RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) • SNu. Pe (Single nucleotide primer extension) • Mass. ARRAY; MALDI-TOF (Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-flight mass spectrometry) Finnish Genome Center
 PCR-RFLP • Reactions designed to produce products of different sizes after enzymatic cleavage Undigested PCR product C analyte T analyte size in bp 243 228 94 Finnish Genome Center
PCR-RFLP • Reactions designed to produce products of different sizes after enzymatic cleavage Undigested PCR product C analyte T analyte size in bp 243 228 94 Finnish Genome Center
 SNu. Pe • primer extension reactions designed to produce differentially labelled products • analysis by capillary electrophoresis (Mega. BACE) labelled nucleotide Extendable primer GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACCC C (blue) C analyte GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACCT T (red) T analyte Finnish Genome Center
SNu. Pe • primer extension reactions designed to produce differentially labelled products • analysis by capillary electrophoresis (Mega. BACE) labelled nucleotide Extendable primer GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACCC C (blue) C analyte GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACCT T (red) T analyte Finnish Genome Center
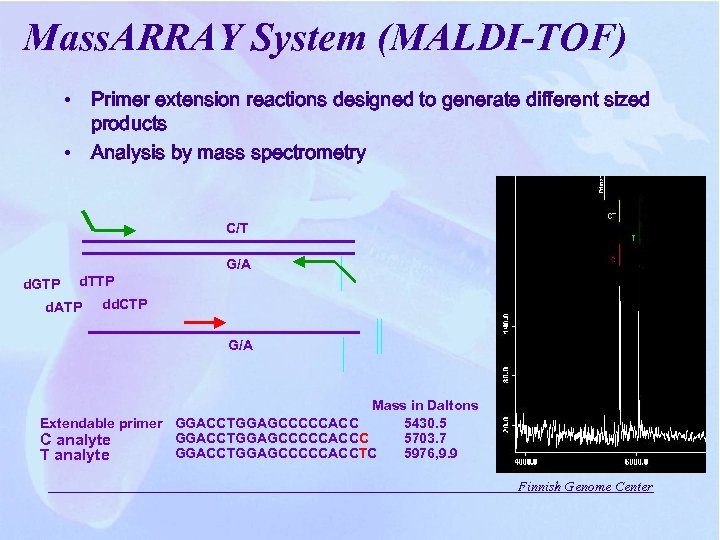 Mass. ARRAY System (MALDI-TOF) • Primer extension reactions designed to generate different sized products • Analysis by mass spectrometry C/T G/A d. GTP d. TTP d. ATP dd. CTP G/A Mass in Daltons Extendable primer GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACC 5430. 5 GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACCC 5703. 7 C analyte GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACCTC 5976, 9. 9 T analyte Finnish Genome Center
Mass. ARRAY System (MALDI-TOF) • Primer extension reactions designed to generate different sized products • Analysis by mass spectrometry C/T G/A d. GTP d. TTP d. ATP dd. CTP G/A Mass in Daltons Extendable primer GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACC 5430. 5 GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACCC 5703. 7 C analyte GGACCTGGAGCCCCCACCTC 5976, 9. 9 T analyte Finnish Genome Center
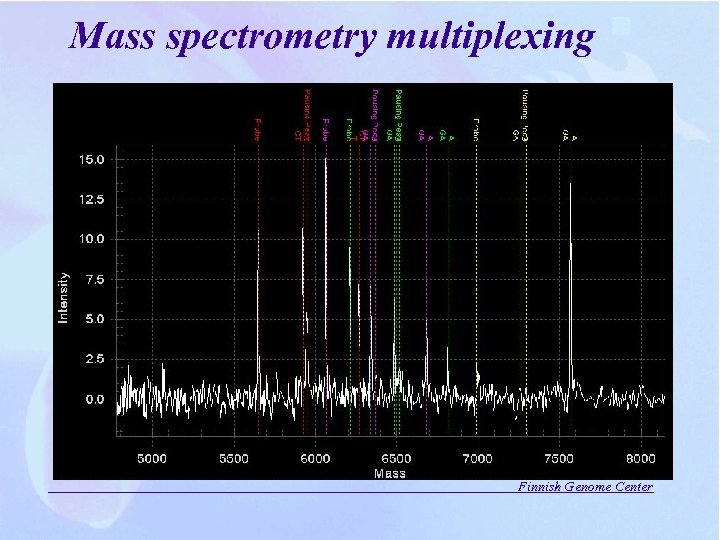 Mass spectrometry multiplexing Finnish Genome Center
Mass spectrometry multiplexing Finnish Genome Center
 Primer extension mass spectrometry Advantages: • • accurate automated assay design fast automated data collection multiplexing capacity Disadvantages: • expensive instruments, consumables • extensive post-PCR processing Finnish Genome Center
Primer extension mass spectrometry Advantages: • • accurate automated assay design fast automated data collection multiplexing capacity Disadvantages: • expensive instruments, consumables • extensive post-PCR processing Finnish Genome Center
 SNP genotyping workflow at FGC Finnish Genome Center
SNP genotyping workflow at FGC Finnish Genome Center


