2b5145a8de08f02e6a7d53ab4127e538.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 High Resolution and Advanced Systems Lecture 3 Prof. Dr. Scott Madry Research Associate Professor, University of North Carolina, USA
High Resolution and Advanced Systems Lecture 3 Prof. Dr. Scott Madry Research Associate Professor, University of North Carolina, USA
 High Resolution and Advanced Systems
High Resolution and Advanced Systems
 High Resolution History l 1994 Clinton decision to license 1 m data l Commerce Dept. granted 9 companies licenses for 11 satellite systems l Origins-US Corona in 1960’s-film-30 cm (1 foot) l 1972 -US Landsat 1 -80 m l 1982 -US Landsat 4 -30 m l 1986 FR SPOT 1 20 and 10 m l 1987 RU Russian film data 5 m (limited geog. and dates)
High Resolution History l 1994 Clinton decision to license 1 m data l Commerce Dept. granted 9 companies licenses for 11 satellite systems l Origins-US Corona in 1960’s-film-30 cm (1 foot) l 1972 -US Landsat 1 -80 m l 1982 -US Landsat 4 -30 m l 1986 FR SPOT 1 20 and 10 m l 1987 RU Russian film data 5 m (limited geog. and dates)
 High Resolution History l 1992 RU Russian film data 2 m l 1993 -US Bush admin. eases barriers to allow 3 m l 1994 -US Clinton admin. eases barriers to allow. 8 m with “shutter control” in war and to certain countries l 1996 -India launches 5 m satellite l 2000 -Commerce Dept. licenses three. 5 meter systems
High Resolution History l 1992 RU Russian film data 2 m l 1993 -US Bush admin. eases barriers to allow 3 m l 1994 -US Clinton admin. eases barriers to allow. 8 m with “shutter control” in war and to certain countries l 1996 -India launches 5 m satellite l 2000 -Commerce Dept. licenses three. 5 meter systems
 U. S. Private Remote Sensing Satellites U. S. policy supports a competitive U. S. commercial remote sensing industry for several reasons l U. S. companies are authorized to develop and launch commercial remote sensing satellites under: l – Land Remote Sensing Policy Act of 1992 – PDD 23: US Policy on Foreign Access to Remote Sensing Space Capabilities (President Clinton, 1994) – U. S. Commercial Remote Sensing Policy (President Bush, 2003) Replaces PDD 23 but similar l Military and civil agencies to rely on U. S. commercial systems for imaging needs
U. S. Private Remote Sensing Satellites U. S. policy supports a competitive U. S. commercial remote sensing industry for several reasons l U. S. companies are authorized to develop and launch commercial remote sensing satellites under: l – Land Remote Sensing Policy Act of 1992 – PDD 23: US Policy on Foreign Access to Remote Sensing Space Capabilities (President Clinton, 1994) – U. S. Commercial Remote Sensing Policy (President Bush, 2003) Replaces PDD 23 but similar l Military and civil agencies to rely on U. S. commercial systems for imaging needs
 Shutter Control: 1992 Land Remote Sensing Act gives the U. S. Department of Commerce the legal authority to limit the collection and distribution of commercial satellite imagery, i. e. “shutter control”, “when national security, international obligations, or foreign policy interests may be compromised”. l The government may place operational conditions or limitations on SAR or hyperspectral systems seeking licensure. l The US government also limits remote sensing of Israel. l
Shutter Control: 1992 Land Remote Sensing Act gives the U. S. Department of Commerce the legal authority to limit the collection and distribution of commercial satellite imagery, i. e. “shutter control”, “when national security, international obligations, or foreign policy interests may be compromised”. l The government may place operational conditions or limitations on SAR or hyperspectral systems seeking licensure. l The US government also limits remote sensing of Israel. l
 US License The Licensee is obligated to “operate the system in a manner that preserves the national security and observes the international obligations and foreign policies of the United States. ” l Maintain and make available to the US government a record of all satellite tasking operations for the previous year l Data collection and/or distribution may be limited by the US government during periods when “national security or international obligations and/or foreign policies may be compromised. ”. This restriction is commonly known as “shutter control” l The government of any country has the right to unenhanced data and images of territory under their jurisdiction. l
US License The Licensee is obligated to “operate the system in a manner that preserves the national security and observes the international obligations and foreign policies of the United States. ” l Maintain and make available to the US government a record of all satellite tasking operations for the previous year l Data collection and/or distribution may be limited by the US government during periods when “national security or international obligations and/or foreign policies may be compromised. ”. This restriction is commonly known as “shutter control” l The government of any country has the right to unenhanced data and images of territory under their jurisdiction. l
 US License The US government has the right to unenhanced data for archival purposes. These data would be available to public after a reasonable period of time l Data to be purged by a licensee must be offered to the US government for archival purposes and would be immediately available to the public l The US government must be notified of any substantial agreements that the licensee intends to enter with any foreign nation, entity or consortium. The foreign party must comply with license regulations l
US License The US government has the right to unenhanced data for archival purposes. These data would be available to public after a reasonable period of time l Data to be purged by a licensee must be offered to the US government for archival purposes and would be immediately available to the public l The US government must be notified of any substantial agreements that the licensee intends to enter with any foreign nation, entity or consortium. The foreign party must comply with license regulations l
 U. S. Commercial Hi Res Remote Sensing Satellites
U. S. Commercial Hi Res Remote Sensing Satellites
 Space Imaging Eosat Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Raytheon Systems Company, Mitsubishi and Hyundai. l Purchased Eosat (Landsat /Indian data distributor) l First launch from Vandenburg in Sept. 1999 l Offering l . 5 m digital airborne Imaging system 1 and 4 m IKONOS 5 m Indian IRS 15 m Landsat 7 Radarsat
Space Imaging Eosat Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Raytheon Systems Company, Mitsubishi and Hyundai. l Purchased Eosat (Landsat /Indian data distributor) l First launch from Vandenburg in Sept. 1999 l Offering l . 5 m digital airborne Imaging system 1 and 4 m IKONOS 5 m Indian IRS 15 m Landsat 7 Radarsat
 Space Imaging
Space Imaging
 Ikonos Images
Ikonos Images
 Digital. Globe (Earth. Watch) Earlybird l l l l l Pixel size 3 m (at nadir) Image size 3 km x 3 km per 30 degree inline and 28 crosstrack pointing Starting array sensor-stereo capable Sensor characteristics: Panchromatic sensor Multispectral sensor Exposure 15 km x 15 km per exposure 15 m (at nadir) 470 km orbit First launch failed in 1999 Decision not to re-launch and develop 1 meter system Ball Aerospace and Hitachi
Digital. Globe (Earth. Watch) Earlybird l l l l l Pixel size 3 m (at nadir) Image size 3 km x 3 km per 30 degree inline and 28 crosstrack pointing Starting array sensor-stereo capable Sensor characteristics: Panchromatic sensor Multispectral sensor Exposure 15 km x 15 km per exposure 15 m (at nadir) 470 km orbit First launch failed in 1999 Decision not to re-launch and develop 1 meter system Ball Aerospace and Hitachi
 Digitalglobe, Quickbird-2001 l l l Launch date October, 2001 Earlier launch in 2000 failed Sensor characteristics Panchromatic sensor Multispectral sensor Image size 17 or 32 km 11 bit data (up to 2048 levels of gray scale) Pixel size 0. 61 m (at nadir) 2. 5 m (at nadir)
Digitalglobe, Quickbird-2001 l l l Launch date October, 2001 Earlier launch in 2000 failed Sensor characteristics Panchromatic sensor Multispectral sensor Image size 17 or 32 km 11 bit data (up to 2048 levels of gray scale) Pixel size 0. 61 m (at nadir) 2. 5 m (at nadir)


 NGA Next. View Contract September 2003, NGA awarded the first Next. View agreement to Digital. Globe, Inc. l US$ 500 Million over 4 years l The Next. View agreement assures access, priority tasking rights, volume (area coverage), and broad licensing terms for sharing imagery with all U. S. Government potential mission partners. l Funds for development of new. 5 meter PAN, 2 m color ‘Worldview’ Satellite l
NGA Next. View Contract September 2003, NGA awarded the first Next. View agreement to Digital. Globe, Inc. l US$ 500 Million over 4 years l The Next. View agreement assures access, priority tasking rights, volume (area coverage), and broad licensing terms for sharing imagery with all U. S. Government potential mission partners. l Funds for development of new. 5 meter PAN, 2 m color ‘Worldview’ Satellite l
 Orbital Sciences Corp. Orbimage l Orbview 1 (10 km weather) – 1995 l Orbview 2 (1 km global veg) – 1997 l Orbview 3 (1 and 4 m by 8 km) – June 26 ‘ 03 launch (Pegasus) l Orbview 4 (hyperspectral 200 channels plus 1 and 4 meter) l Taurus launch failure 09/21’ 01
Orbital Sciences Corp. Orbimage l Orbview 1 (10 km weather) – 1995 l Orbview 2 (1 km global veg) – 1997 l Orbview 3 (1 and 4 m by 8 km) – June 26 ‘ 03 launch (Pegasus) l Orbview 4 (hyperspectral 200 channels plus 1 and 4 meter) l Taurus launch failure 09/21’ 01
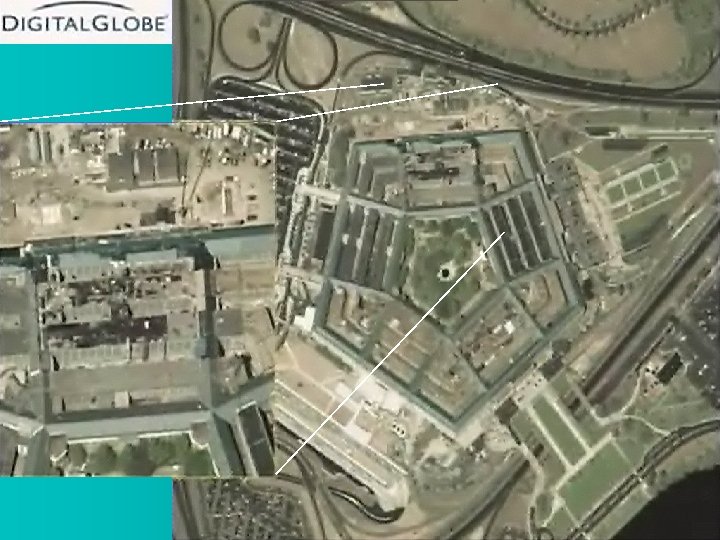
 Orbview 3 One Meter Pan
Orbview 3 One Meter Pan
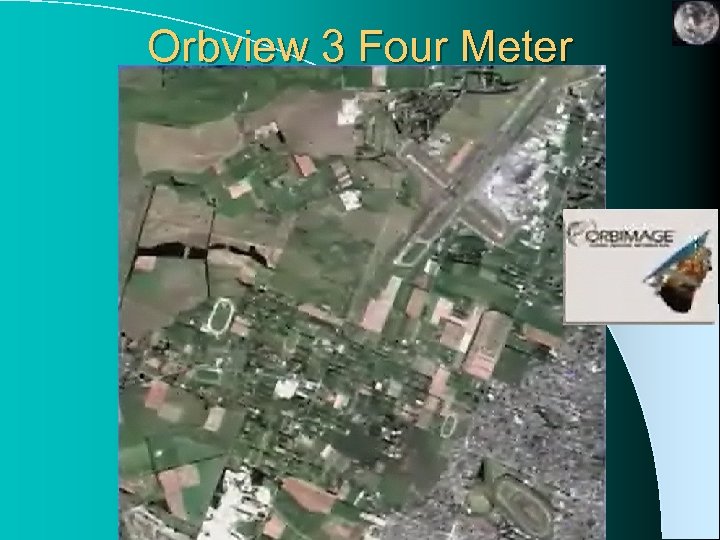 Orbview 3 Four Meter
Orbview 3 Four Meter
 NGA Next. View Contract Orb. Image awarded a 4 year, US$500 million contract by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA, formerly the National Imagery and Mapping Agency, NIMA), valued at approximately $500 million. l The contract will provide ORBIMAGE with both long-term revenue commitments as well as capital for the development of Orb. View-5, ORBIMAGE’s next-generation highresolution Imaging Satellite. l Space Imaging lost the competition l
NGA Next. View Contract Orb. Image awarded a 4 year, US$500 million contract by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA, formerly the National Imagery and Mapping Agency, NIMA), valued at approximately $500 million. l The contract will provide ORBIMAGE with both long-term revenue commitments as well as capital for the development of Orb. View-5, ORBIMAGE’s next-generation highresolution Imaging Satellite. l Space Imaging lost the competition l
 Image. Sat International N. V Image. Sat Int. N. V. – Netherlands Antilles company with offices in Lamassol, Cyprus and Tel Aviv, Israel. l Commercial ‘Ofeq’ Israeli spy satellites. l EROS A 1 8 sats w/ 1. 8 m resolution 14 km alt. 270 Kg- Dec 2000 launch l EROS B 1 -B 6 have. 82 meters resolution in 2006 l
Image. Sat International N. V Image. Sat Int. N. V. – Netherlands Antilles company with offices in Lamassol, Cyprus and Tel Aviv, Israel. l Commercial ‘Ofeq’ Israeli spy satellites. l EROS A 1 8 sats w/ 1. 8 m resolution 14 km alt. 270 Kg- Dec 2000 launch l EROS B 1 -B 6 have. 82 meters resolution in 2006 l
 Surrey Satellite Technology, Ltd. l l l Founded 1985 by Surrey University, UK Earth Observation Microsatellites range from 35 -70 kg. 50 m 3 -spectrum band remote sensing and NIR meteorological imagery 30 m 4 -spectrum band remote sensing 15 m panchromatic remote sensing 100 m resolution 4 -spectrum band, 800 km swath waves, providing images/2 days
Surrey Satellite Technology, Ltd. l l l Founded 1985 by Surrey University, UK Earth Observation Microsatellites range from 35 -70 kg. 50 m 3 -spectrum band remote sensing and NIR meteorological imagery 30 m 4 -spectrum band remote sensing 15 m panchromatic remote sensing 100 m resolution 4 -spectrum band, 800 km swath waves, providing images/2 days
 “Surrey Knowhow Transfer” l 18 month program l Your team helps build your satellite l Algeria, Nigeria, China, Turkey, Thailand, ROC, Argentina, South Africa etc.
“Surrey Knowhow Transfer” l 18 month program l Your team helps build your satellite l Algeria, Nigeria, China, Turkey, Thailand, ROC, Argentina, South Africa etc.
 SPIN-2/Terra. Server l SPIN-2 2 meter Russian film data l Terra. Server-Microsoft massive RS database online (3. 7 Tb of data or 2, 000 books of 500 pp. ) l Sell digital data direct from the website
SPIN-2/Terra. Server l SPIN-2 2 meter Russian film data l Terra. Server-Microsoft massive RS database online (3. 7 Tb of data or 2, 000 books of 500 pp. ) l Sell digital data direct from the website
 Google Earth l l l l Real-time imagery viewer Fly from space to your neighborhood Type in an address and zoom right in. Search for schools, parks, restaurants, and hotels. Get driving directions. Tilt and rotate the view to see 3 D terrain and buildings (some areas). Save and share your searches and favorites. Even add your own annotations.
Google Earth l l l l Real-time imagery viewer Fly from space to your neighborhood Type in an address and zoom right in. Search for schools, parks, restaurants, and hotels. Get driving directions. Tilt and rotate the view to see 3 D terrain and buildings (some areas). Save and share your searches and favorites. Even add your own annotations.
 The Future of the Future MEMS-Microelectromechanical systems and nano technology will begin to impact remote sensing l “Smart Dust” – Sensors so small they float in the air (Kris Pister-U. Cal Berkeley) selfpowered smart sensors with a 5 sq mm computer (asprin tablet), costing 10 cents now (down to dust size for a penny) l Intelligent multitasking, sensors that communicate and make “group decisions” with on-board processing and linked with insitu systems to trigger when, where and what to acquire, process, and distribute l
The Future of the Future MEMS-Microelectromechanical systems and nano technology will begin to impact remote sensing l “Smart Dust” – Sensors so small they float in the air (Kris Pister-U. Cal Berkeley) selfpowered smart sensors with a 5 sq mm computer (asprin tablet), costing 10 cents now (down to dust size for a penny) l Intelligent multitasking, sensors that communicate and make “group decisions” with on-board processing and linked with insitu systems to trigger when, where and what to acquire, process, and distribute l
 In Conclusion l Ultra high resolution systems are opening new areas of space remote sensing applications l “Dual Use” issues are important l New technologies like hyperspectral systems will become the norm and improve data extraction and analysis l Micro technologies are on the horizon
In Conclusion l Ultra high resolution systems are opening new areas of space remote sensing applications l “Dual Use” issues are important l New technologies like hyperspectral systems will become the norm and improve data extraction and analysis l Micro technologies are on the horizon
 Major questions l l l How many of these do we need? What are the drivers? Archiving/storage/protection/retrieval of data Open skies vs. national interests and national security “Global good” vs. national interests/private profit Is more really better? Global. 1 meter/256 channels/12 bit daily data? How can we handle this? Who will use it? It’s just a tool, the use of the tool is in human hands, we will decide how they are used.
Major questions l l l How many of these do we need? What are the drivers? Archiving/storage/protection/retrieval of data Open skies vs. national interests and national security “Global good” vs. national interests/private profit Is more really better? Global. 1 meter/256 channels/12 bit daily data? How can we handle this? Who will use it? It’s just a tool, the use of the tool is in human hands, we will decide how they are used.
 Assignment l Q 1. Define the RED colored terms highlighted in this presentation
Assignment l Q 1. Define the RED colored terms highlighted in this presentation


