65723723bad583536d3d14a602ec4104.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

High Performance Buildings Research & Implementation Center (Hi. Per. BRIC) National Lab-Industry-University Partnership February 5, 2008 1

Outline • Current Situation of Building Energy Performance and Gaps • Hi. Per. BRIC Vision and Mission • Hi. Per. BRIC Role, Value and Differentiation • Hi. Per. BRIC Structure and Operations • Action Plan and Next Steps 2
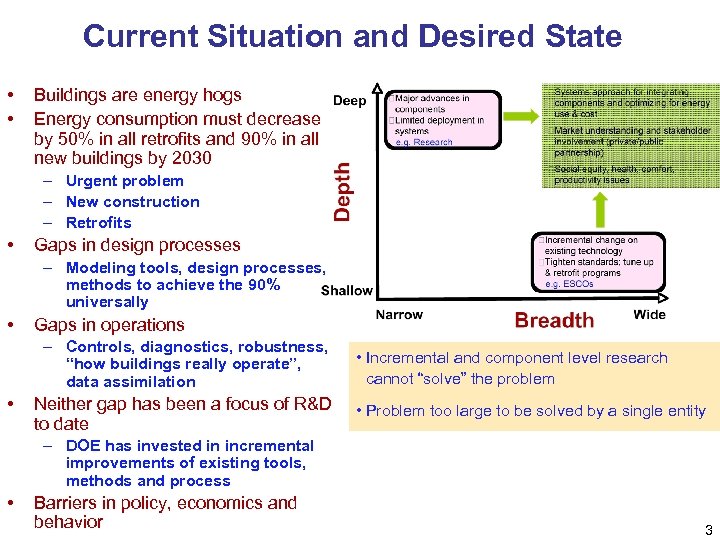
Current Situation and Desired State • • Buildings are energy hogs Energy consumption must decrease by 50% in all retrofits and 90% in all new buildings by 2030 – Urgent problem – New construction – Retrofits • Gaps in design processes – Modeling tools, design processes, methods to achieve the 90% universally • Gaps in operations – Controls, diagnostics, robustness, “how buildings really operate”, data assimilation • Neither gap has been a focus of R&D to date • Incremental and component level research cannot “solve” the problem • Problem too large to be solved by a single entity – DOE has invested in incremental improvements of existing tools, methods and process • Barriers in policy, economics and behavior 3

Hi. Per. BRIC Vision and Mission § Vision Enable transformation of U. S. Commercial buildings sector in 20 years, starting NOW – Save >4 Quads of energy and reduce >400 million tons of CO 2 annually • Reduction in energy consumption: 90% in new buildings; >50% in retrofits – Enhance health, comfort, safety/security and water usage while gaining energy efficiency § Mission – Team: Create a consortium to bring unique team of scientists, engineers and economists from national lab, academia and industries to conduct comprehensive R&D, implementation, and market transformation programs – Technology: Use a systems approach to create scalable, fault tolerant, and robust technologies for retrofit and new commercial buildings – Training: Create facility for component and systems validation/testing; education; and training – Transition: Engage and leverage all stake holders for implementation & policies • Commercial Buildings Initiative (CBI); Federal & State Agencies; Utilities; Industry Organizations (e. g. ASHRAE); A&E Firms; Building Materials and Equipment Suppliers; Building Owners & Operators; ESCOs; Service Contractors; Advocacy Groups; Financial 4

Value Derived From Hi. Per. BRIC Creation of infrastructure and an experimental facility to reduce risk in the commercial adoption of building technologies Create a collaborative research facility for partnering among diverse stakeholders and building technology providers Train a new generation of scientists and engineers with direct access to grand challenge problems and multi-disciplinary research issues pertaining to high performance buildings 5

Hi. Per. BRIC Value and Differentiation • Strategic – Form a National Labs-Industry-Academia partnership that engages relevant stakeholders to provide the broad and deep R&D base needed to enable market transformation • Technology – Focus on a systems approach to identify, develop and mature new enabling hardware and software technology to facilitate commercialization and market adoption • User Facility – Create a unique facility (physical infrastructure and virtual presence) to evaluate, validate and mature new technologies in real buildings – Enable commercialization, education, and training • People – Recruit and train a new generation of scientists and engineers and building industry professionals educated in systems approach to energy efficiency • Jobs – Create job growth through revitalizing the US commercial buildings industry, including suppliers, building operators, architects 6
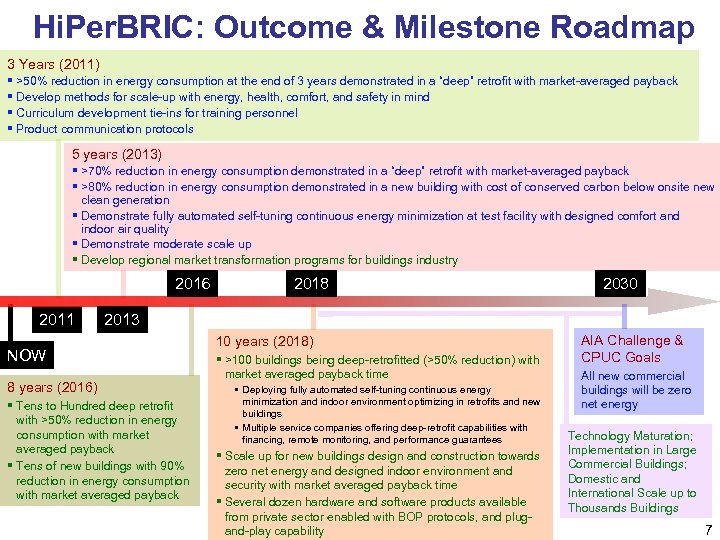
Hi. Per. BRIC: Outcome & Milestone Roadmap 3 Years (2011) § >50% reduction in energy consumption at the end of 3 years demonstrated in a “deep” retrofit with market-averaged payback § Develop methods for scale-up with energy, health, comfort, and safety in mind § Curriculum development tie-ins for training personnel § Product communication protocols 5 years (2013) § >70% reduction in energy consumption demonstrated in a “deep” retrofit with market-averaged payback § >80% reduction in energy consumption demonstrated in a new building with cost of conserved carbon below onsite new clean generation § Demonstrate fully automated self-tuning continuous energy minimization at test facility with designed comfort and indoor air quality § Demonstrate moderate scale up § Develop regional market transformation programs for buildings industry 2016 2011 2018 2030 2013 NOW 8 years (2016) § Tens to Hundred deep retrofit with >50% reduction in energy consumption with market averaged payback § Tens of new buildings with 90% reduction in energy consumption with market averaged payback 10 years (2018) § >100 buildings being deep-retrofitted (>50% reduction) with market averaged payback time § Deploying fully automated self-tuning continuous energy minimization and indoor environment optimizing in retrofits and new buildings § Multiple service companies offering deep-retrofit capabilities with financing, remote monitoring, and performance guarantees § Scale up for new buildings design and construction towards zero net energy and designed indoor environment and security with market averaged payback time § Several dozen hardware and software products available from private sector enabled with BOP protocols, and plugand-play capability AIA Challenge & CPUC Goals All new commercial buildings will be zero net energy Technology Maturation; Implementation in Large Commercial Buildings; Domestic and International Scale up to Thousands Buildings 7
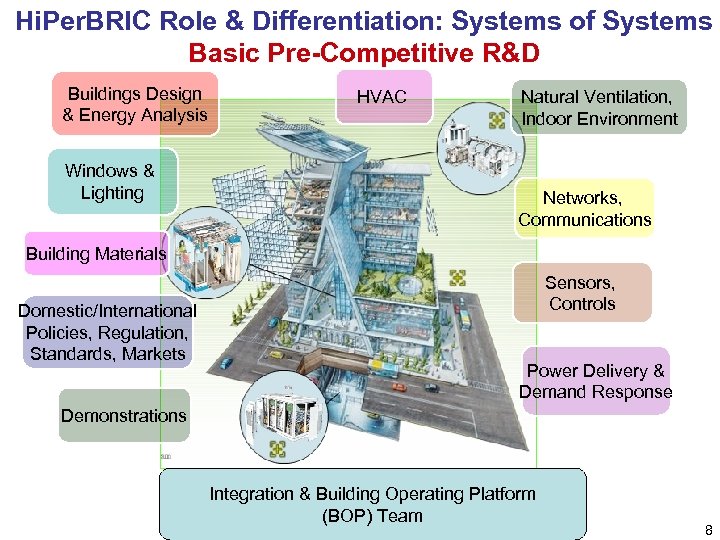
Hi. Per. BRIC Role & Differentiation: Systems of Systems Basic Pre-Competitive R&D Buildings Design & Energy Analysis Windows & Lighting HVAC Natural Ventilation, Indoor Environment Networks, Communications Building Materials Domestic/International Policies, Regulation, Standards, Markets Sensors, Controls Power Delivery & Demand Response Demonstrations Integration & Building Operating Platform (BOP) Team 8

Hi. Per. BRIC Technical Scope: Systems of Systems Sunlight External Ventilation Outside Air Temperature/ Humidity Info Thermal Storage Waste Heat Capacity/ Temperature Info Local Thermal/ Humidity Control Sensor Modules • Occupancy • Temperature • Humidity • Air Quality • Light • Appliances Central Air Conditioning/ Heat Pump Local Thermal/ Humidity Control Sensor Modules • Occupancy • Temperature • Humidity • Air Quality • Light • Appliances Coupled Interactions Electricity Storage Coupled Interactions Appliance Power Control Lighting/ Window Control Network Communication Layer Building Operating Platform (BOp. P) Real-time optimization - consumption, cost, carbon footprint Onsite Power Generation External Power Electricity Tariffs & Carbon Emission Rates Current & Future Weather Building Simulation, Modeling & Analysis (DOE-2; Energy. Plus) Output • Energy Consumption • Integrated system performance • Component sub-metered performance Goal • Zero energy building • Zero carbon building 9

From R&D to Commercialization Barriers Enablers Lack of a Long Reach and Broad Scope in Technology and Business Model Exploration Develop Collaboration Among Companies, National Labs and Universities in a pre-competitive basis Lack of a Demonstration Capability for Technology Maturation (TRL 2 to TRL 6) Create a Facility for Full Scale Demonstrations and Concentration of Talent Lack of a System of Systems Engineering Methodology Develop Methodology, Tools and Training for System Level Design Lack of Nontrivial System Architectures and Controls Develop Energy Efficient Technologies and Renewables 10

Connect R&D to Markets Bridge The Gap With Building Integration & Scale R&D • UTRC • UC Berkeley • LBL • UC Santa Barbara • Tsinghua • CMU ABSIC • UIUC ACRC. . . Hi. Per. BRIC Mission • Identification & Maturation of Enabling Technology • System Engineering • Scalable Methodology & Tools • Building scale demonstrations • Systems of systems integration • User demonstrations of tools & processes • Early TRL maturation • Risk reduction • Identification, exploitation and teaching of technology synergies Commercialization • UTC • Carrier • UTC Power • Consortia Partners Hi. Per. BRIC Vision • Completely transform the U. S. Commercial buildings sector in 20 years • Save >4 Quads of energy and reduce more than 400 million tons of CO 2 annually • Reduction in energy consumption: 90% in new buildings; >50% in retrofits • Simultaneously improve health, comfort, safety, and energy 11

Hi. Per. BRIC Role Relative to Other Initiatives Complements and leverages other evolving commercial buildings programs working towards 2030 net zero energy consumption – Commercial Buildings Initiative (CBI) – loose confederation of activities to bring together the full spectrum of activities and players needed to transform the sector in order to reach 2030 targets; serves as broker, coordinator, convenor, collaborator, advocate for commercial buildings RDD&D; demonstration and deployment focus; business model focuses on building owners and users. New legislation (HR 6) authorizes $20 M in FY 2008 growing to $200 M in FY 2011. CBI can provide key interface for Hi. Per. BRIC to implementation performers and stakeholders. – California PUC Strategic Plan for New Commercial Buildings– focused on new buildings demonstration and deployment activities through California investor owned utilities; includes promotion of integrated R&D and design as necessary to reach 2030 goals. Hi. Per. BRIC clearly meets criteria for an ‘enabling initiative’ in current draft CPUC vision. – Architecture 2030 – poses challenge to global architecture and building community to adopt a series of fossil fuel reduction targets for new and existing buildings by 2030. Hi. Per. BRIC output will provide systems, tools and technologies to support these targets. – Getting to 50 – resource to building community to achieve 50% improvement in energy efficiency of new building construction based on learning from success of 100 new commercial buildings with features that meet the 50% goal. Hi. Per. BRIC will tap into these successes for feedback to research needs. Getting to Fifty™ 12
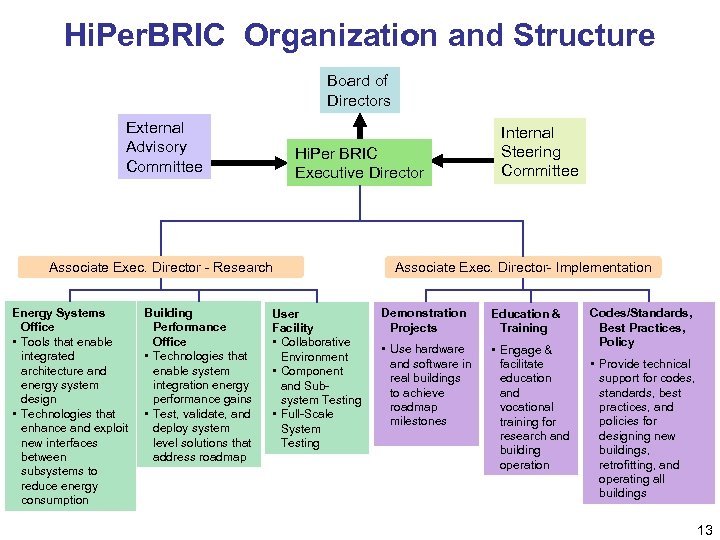
Hi. Per. BRIC Organization and Structure Board of Directors External Advisory Committee Hi. Per BRIC Executive Director Associate Exec. Director - Research Energy Systems Office • Tools that enable integrated architecture and energy system design • Technologies that enhance and exploit new interfaces between subsystems to reduce energy consumption Building Performance Office • Technologies that enable system integration energy performance gains • Test, validate, and deploy system level solutions that address roadmap User Facility • Collaborative Environment • Component and Subsystem Testing • Full-Scale System Testing Internal Steering Committee Associate Exec. Director- Implementation Demonstration Projects Education & Training • Use hardware and software in real buildings to achieve roadmap milestones • Engage & facilitate education and vocational training for research and building operation Codes/Standards, Best Practices, Policy • Provide technical support for codes, standards, best practices, and policies for designing new buildings, retrofitting, and operating all buildings 13
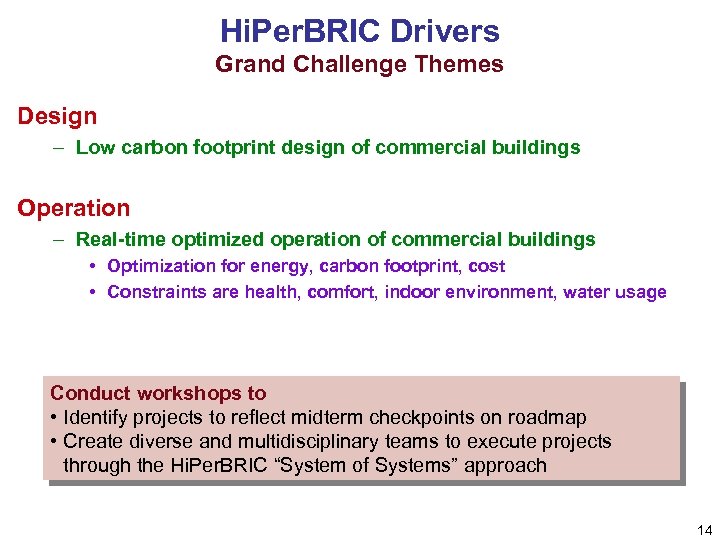
Hi. Per. BRIC Drivers Grand Challenge Themes Design – Low carbon footprint design of commercial buildings Operation – Real-time optimized operation of commercial buildings • Optimization for energy, carbon footprint, cost • Constraints are health, comfort, indoor environment, water usage Conduct workshops to • Identify projects to reflect midterm checkpoints on roadmap • Create diverse and multidisciplinary teams to execute projects through the Hi. Per. BRIC “System of Systems” approach 14

Challenge Problems and Technology Maturation Do. D/NASA Example Projects Seedling Technology Identification & Proposals Consortiu m Steering Committee Unsolicited Proposals Challenge Problems Workshops Enabling Technology and Teaming Increasing scale (teams, resources, demonstrations) 15

Hi. Per. BRIC Output 1. Identification of gaps in technology and policies based on demonstrations, field trials and market assessments 2. Intellectual property and hardware/software technologies for retrofitting, designing new buildings, and operating all buildings 3. Demonstrations, best practices, and know-how for broad scale deployment 4. Facility for users to validate, test hardware/software performance in realistic building environment to reduce risk and enable commercialization 5. Technological support for codes and standards 6. Education and training for scientists, engineers, architects and other building professionals 7. Formation of new joint ventures and business models to revitalize the buildings industry 16

Consortium Membership • Tier 1 – $X/per year (Minimum 75% in cash) – Membership in board and steering committee – Participation in R&D teams • Tier 2 – $Y/per year (Minimum 75% in cash) – Participation in R&D teams • Tier 3 – $Z/per year (All cash) – Observer in Annual Meetings – First right of refusal on IP • Intellectual Property – Team being put together to work on framework 17
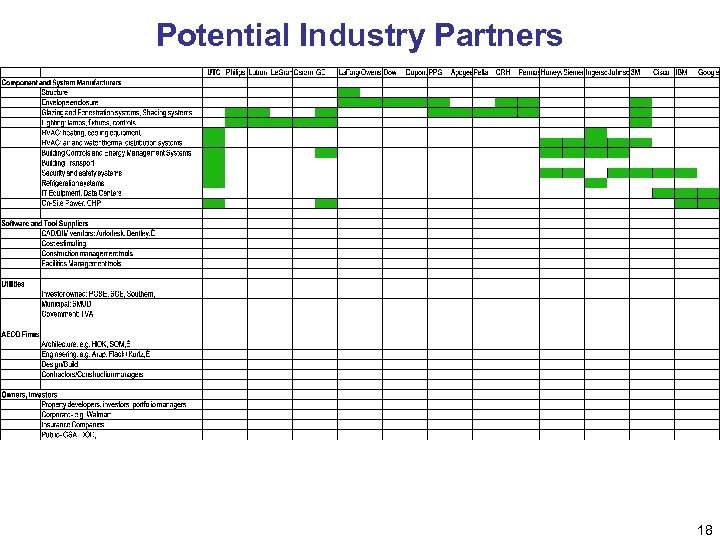
Potential Industry Partners 18

Seed Projects Energy Systems Office • Development of a Building Operating Platform (LBL) and (UCB), Funding : LBNL-LDRD ($150 K); Status - Funded • Building Informatics Environment Enabling Rapid Prototyping and Model Extraction for Building Automation Systems LBNL), Funding: LBNL-LDRD ($150 K); Status - Funded • Development and Demonstration of Integrated Lighting Systems (LBNL), Funding: LBNL-LDRD ($150 K); Status - Funded Building Performance Office • Data Fusion for Building Diagnostics and Operations (LBNL), Funding: LBNL-LDRD ($150 K); Status - Funded • Anomaly Detection and Decision Support Tools for Building Diagnostics (UTRC), Funding: UTRCCSR ($400 K); Status – Funded • Demand Response/Energy Optimizing Controls Demonstration NYSERDA + UTRC cost share; Status – Proposed (LBNL/UTRC), Funding: • Model-based Estimation of Dynamic Phenomena for Energy Efficient Building HVAC (UTRC) Funding: UTRC-CSR ($380 K); Status – Proposed • Data Assimilation for Model-Based Building Diagnostics and Control (UTRC) Funding: TBD proposal ($200 K); Status – Being proposed • Multi-scale Estimation for Indoor Environment Monitoring in Energy Efficient Buildings (UTRC) Funding: UTRC-CSR ($170 K); Status – Proposed 19

Action Plan Challenge Areas Real Time Optimized Building Performance Building Design for Carbon Footprint Reduction Recruitment of partners Secure support from funding agencies Vision Definition Vision Grand Challenges External Advocacy Oversight Partner recruitment Shape Overall Plan Define Grand Challenges Plan Report Out Workshop Defining Teams & Technology Gaps Influence having proposals be part of funding agencies’ budgets for 2009 Consortium Scope, Organization, Grand Challenges, Initial Results Steering committee meeting to Review proposal and seed projects Secure seed project funding Q 1 Gap Assessment External Engagement Consortium feasibility Proposal Preparation Seed project definition and execution Visit to Funding Agencies to present vision, enlist support Influence 2009 funding cycle Q 2 Project Reviews Seed project planning Q 3 Review Proposals Seed projects Q 4 End of year review Preparation of Proposal for Funding Agencies Seed project execution 20

Next Steps • WBCSD & Consortium Members – Define initial target list, create briefing material and approach partners (Feb. xx) • DOE – Create briefing material, schedule visit, and coordinate with DOE High Performance Buildings program and Commercial Buildings Initiative(Feb. xx) • CPUC – Get feedback and coordinate with CPUC strategy (Feb. xx) • CEC & PIER Program – Create briefing material and schedule communication (Feb. xx) • Hi. Per. BRIC Structure – Clarify membership tiering, funding model and develop framework for IP (Feb. xx) • Workshop – Schedule, organize workshop to define teams and technology gaps to prosecute (Mar. xx) • Seed Projects – Convene “steering committee”, review seed projects, decide funding (Mar. xx) 21

Back up 22
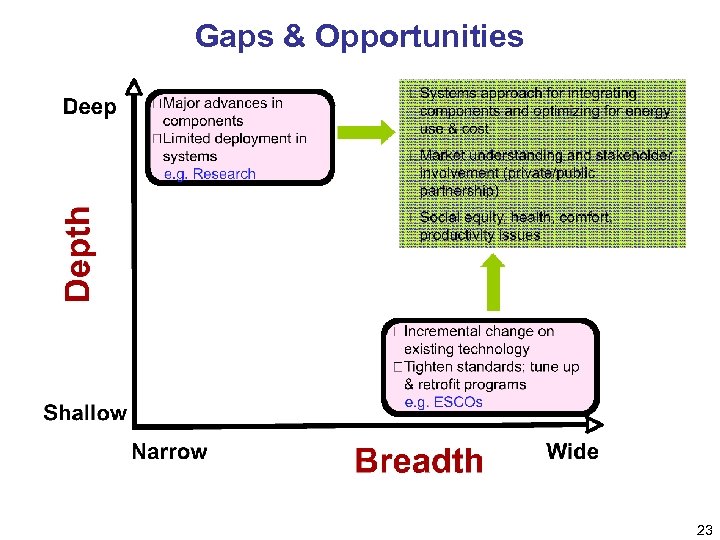
Gaps & Opportunities 23
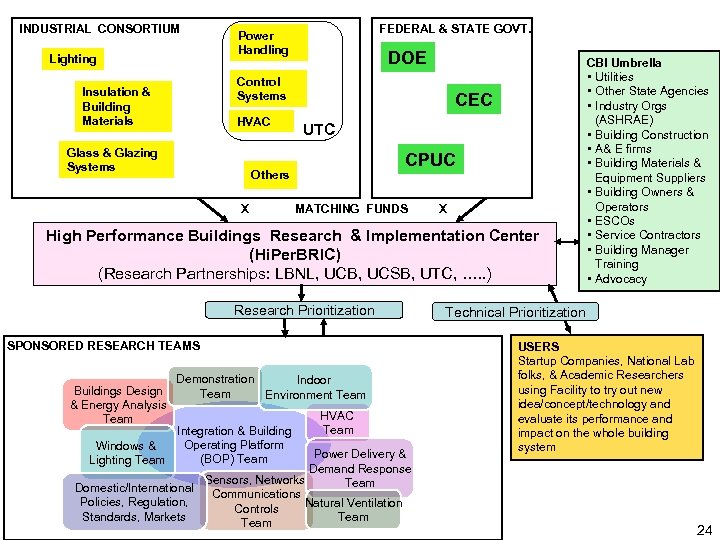
INDUSTRIAL CONSORTIUM Lighting FEDERAL & STATE GOVT. Power Handling DOE Control Systems Insulation & Building Materials HVAC Glass & Glazing Systems CEC UTC CPUC Others X MATCHING FUNDS X High Performance Buildings Research & Implementation Center (Hi. Per. BRIC) (Research Partnerships: LBNL, UCB, UCSB, UTC, …. . ) Research Prioritization SPONSORED RESEARCH TEAMS Buildings Design & Energy Analysis Team Demonstration Indoor Team Environment Team Integration & Building Operating Platform Windows & (BOP) Team Lighting Team HVAC Team Power Delivery & Demand Response Sensors, Networks, Team Domestic/International Communications Policies, Regulation, Natural Ventilation Controls Standards, Markets Team CBI Umbrella • Utilities • Other State Agencies • Industry Orgs (ASHRAE) • Building Construction • A& E firms • Building Materials & Equipment Suppliers • Building Owners & Operators • ESCOs • Service Contractors • Building Manager Training • Advocacy Technical Prioritization USERS Startup Companies, National Lab folks, & Academic Researchers using Facility to try out new idea/concept/technology and evaluate its performance and impact on the whole building system 24
65723723bad583536d3d14a602ec4104.ppt