fabf24d10282c0a45d18409ab8ea1464.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

High Intensity SRF Proton Accelerator at Fermilab: Project-X Shekhar Mishra ILC, Project-X & SRF Program Fermilab
Fermilab and the World Program
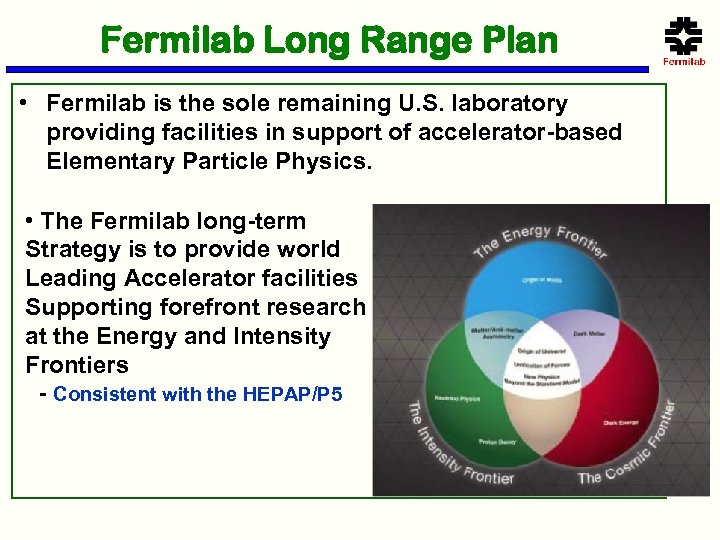
Fermilab Long Range Plan • Fermilab is the sole remaining U. S. laboratory providing facilities in support of accelerator-based Elementary Particle Physics. • The Fermilab long-term Strategy is to provide world Leading Accelerator facilities Supporting forefront research at the Energy and Intensity Frontiers - Consistent with the HEPAP/P 5
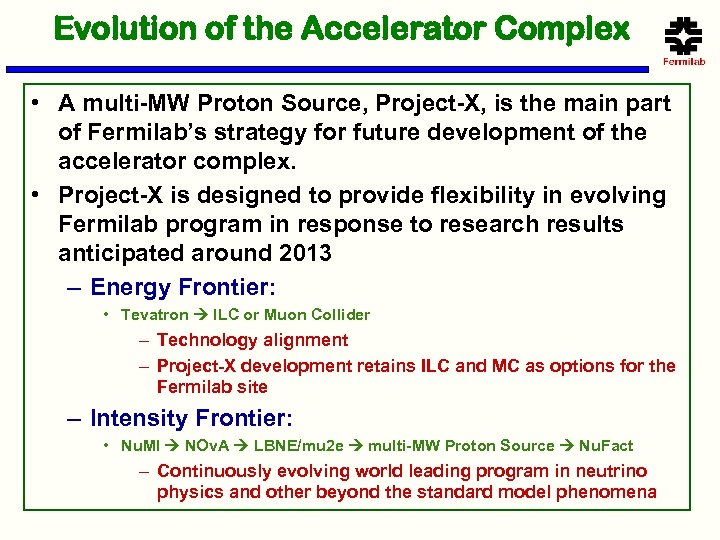
Evolution of the Accelerator Complex • A multi-MW Proton Source, Project-X, is the main part of Fermilab’s strategy for future development of the accelerator complex. • Project-X is designed to provide flexibility in evolving Fermilab program in response to research results anticipated around 2013 – Energy Frontier: • Tevatron ILC or Muon Collider – Technology alignment – Project-X development retains ILC and MC as options for the Fermilab site – Intensity Frontier: • Nu. MI NOv. A LBNE/mu 2 e multi-MW Proton Source Nu. Fact – Continuously evolving world leading program in neutrino physics and other beyond the standard model phenomena
Evolution of the Accelerator Complex: LBNE

Near Term Strategy • Project X is moving through the DOE system in coordination with the Long Baseline Neutrino Experiment (LBNE) and the muon to electron conversion experiment (Mu 2 e) – LBNE and Mu 2 e will both establish mission need (CD-0) on the basis of modest upgrades to the existing complex. • Both have been told to expect CD-0 “shortly”, and to be prepared for CD-1 at the end of FY 2010. – The Project-X mission will be to provide significant extension of the reach of these two initiatives, while simultaneously creating a broader range of intensity frontier opportunities. • Several briefings for the Office of Science on strategy, including to Brinkman by Pier on Aug 13 th. – CD-0 for LBNE and Mu 2 e are pre-requisites to CD-0 for Project-X
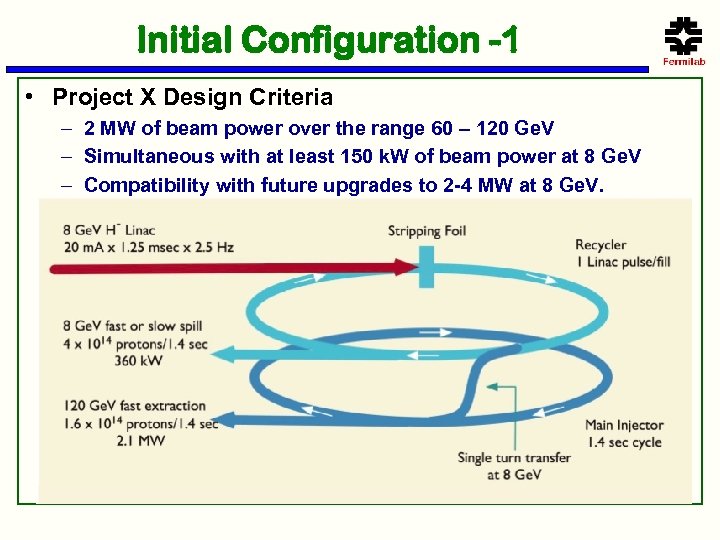
Initial Configuration -1 • Project X Design Criteria – 2 MW of beam power over the range 60 – 120 Ge. V – Simultaneous with at least 150 k. W of beam power at 8 Ge. V – Compatibility with future upgrades to 2 -4 MW at 8 Ge. V.
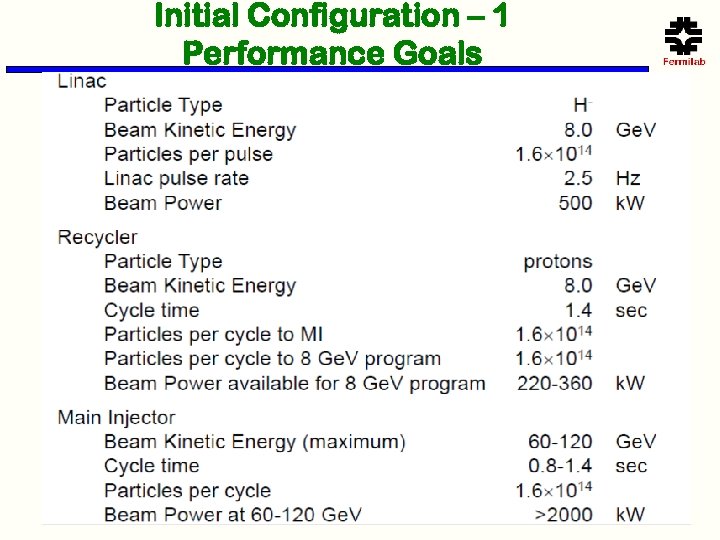
Initial Configuration – 1 Performance Goals
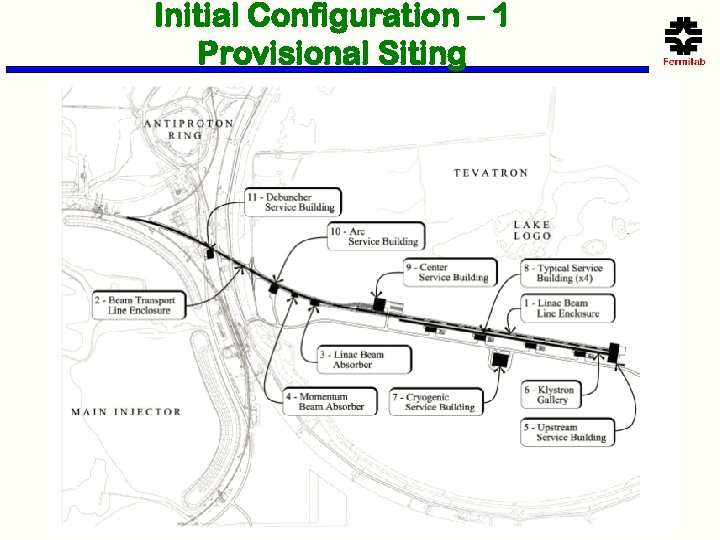
Initial Configuration – 1 Provisional Siting
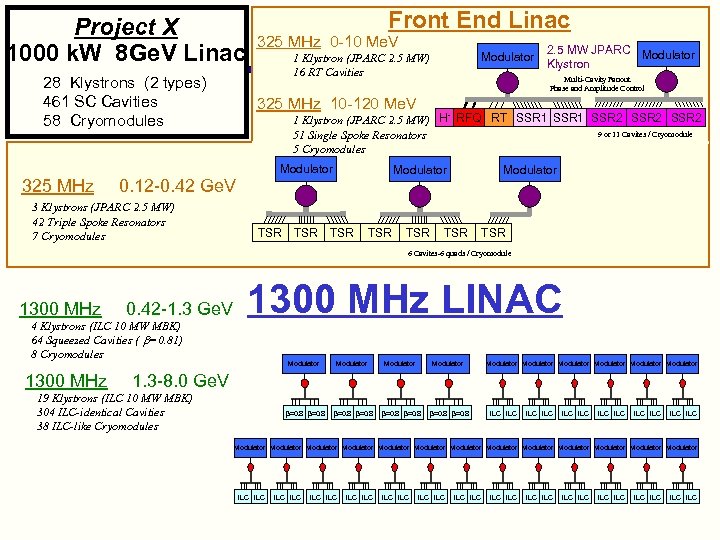
Project X 1000 k. W 8 Ge. V Linac 28 Klystrons (2 types) 461 SC Cavities 58 Cryomodules 325 MHz Front End Linac 325 MHz 0 -10 Me. V 2. 5 MW JPARC Modulator Klystron Multi-Cavity Fanout Phase and Amplitude Control 325 MHz 10 -120 Me. V 1 Klystron (JPARC 2. 5 MW) H RFQ RT SSR 1 SSR 2 9 or 11 Cavites / Cryomodule 51 Single Spoke Resonators 5 Cryomodules Modulator 0. 12 -0. 42 Ge. V 3 Klystrons (JPARC 2. 5 MW) 42 Triple Spoke Resonators 7 Cryomodules Modulator 1 Klystron (JPARC 2. 5 MW) 16 RT Cavities TSR TSR Modulator TSR TSR 6 Cavites-6 quads / Cryomodule 1300 MHz 0. 42 -1. 3 Ge. V 4 Klystrons (ILC 10 MW MBK) 64 Squeezed Cavities ( b=0. 81) 8 Cryomodules 1300 MHz LINAC Modulator =0. 8 =0. 8 Modulator Modulator 1. 3 -8. 0 Ge. V 19 Klystrons (ILC 10 MW MBK) 304 ILC-identical Cavities 38 ILC-like Cryomodules ILC ILC ILC Modulator Modulator Modulator Modulator ILC ILC ILC ILC ILC ILC ILC
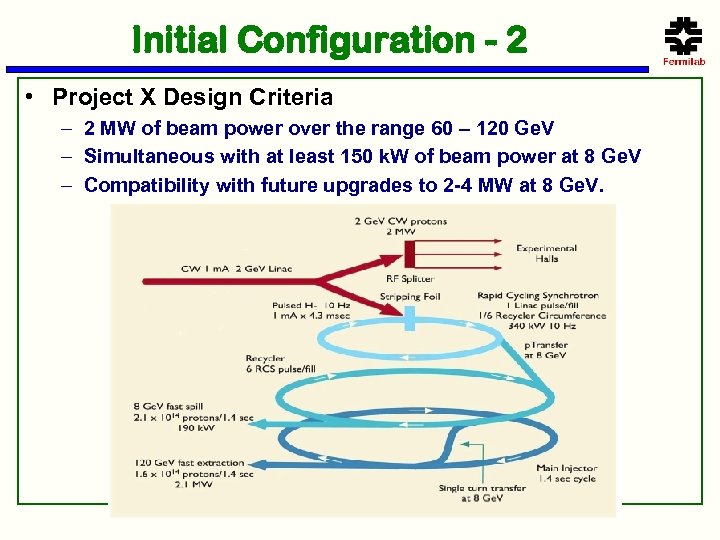
Initial Configuration - 2 • Project X Design Criteria – 2 MW of beam power over the range 60 – 120 Ge. V – Simultaneous with at least 150 k. W of beam power at 8 Ge. V – Compatibility with future upgrades to 2 -4 MW at 8 Ge. V.
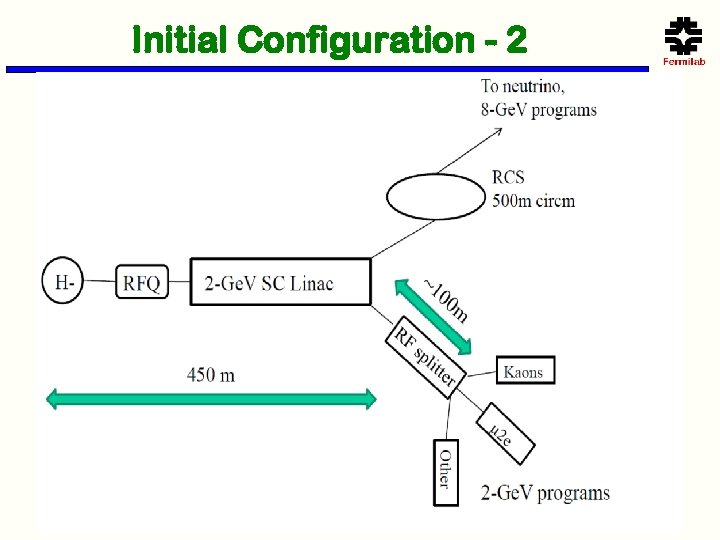
Initial Configuration - 2
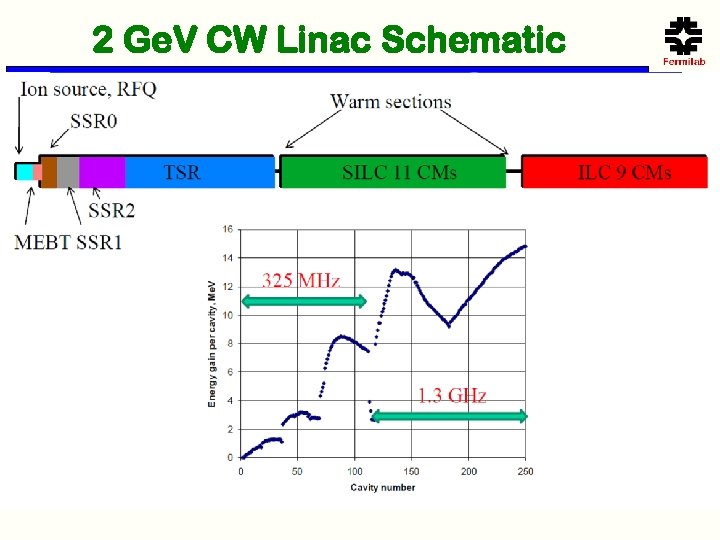
2 Ge. V CW Linac Schematic
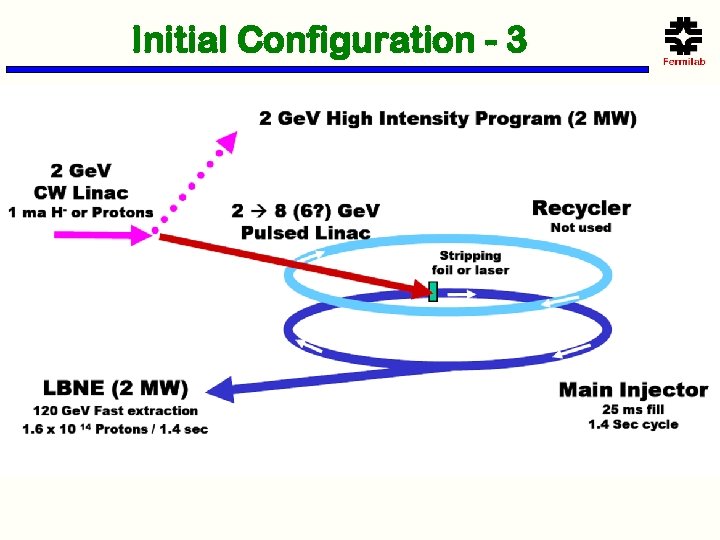
Initial Configuration - 3

SRF Development • Regardless of which configuration is selected a considerable amount of SRF development is needed to support Project-X. • Fermilab with collaborating US and International laboratories is doing a considerable SRF R&D and infrastructure development – We are expecting that the construction will take about 3 -4 years. DOE Site Visit 15
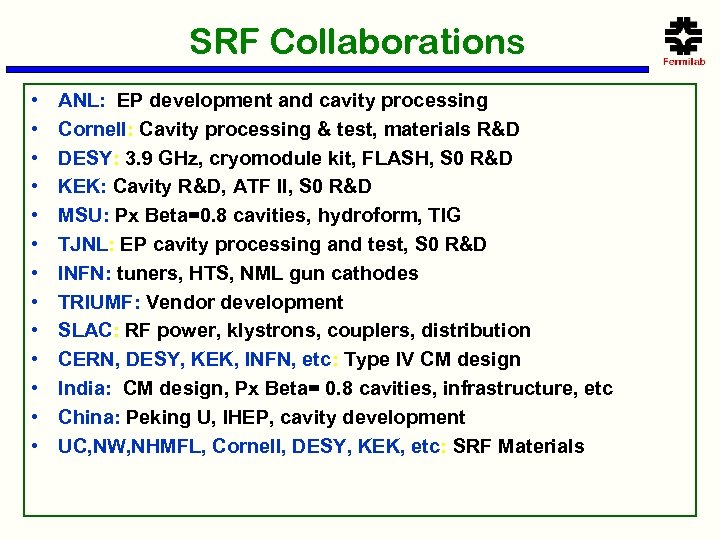
SRF Collaborations • • • • ANL: EP development and cavity processing Cornell: Cavity processing & test, materials R&D DESY: 3. 9 GHz, cryomodule kit, FLASH, S 0 R&D KEK: Cavity R&D, ATF II, S 0 R&D MSU: Px Beta=0. 8 cavities, hydroform, TIG TJNL: EP cavity processing and test, S 0 R&D INFN: tuners, HTS, NML gun cathodes TRIUMF: Vendor development SLAC: RF power, klystrons, couplers, distribution CERN, DESY, KEK, INFN, etc: Type IV CM design India: CM design, Px Beta= 0. 8 cavities, infrastructure, etc China: Peking U, IHEP, cavity development UC, NW, NHMFL, Cornell, DESY, KEK, etc: SRF Materials
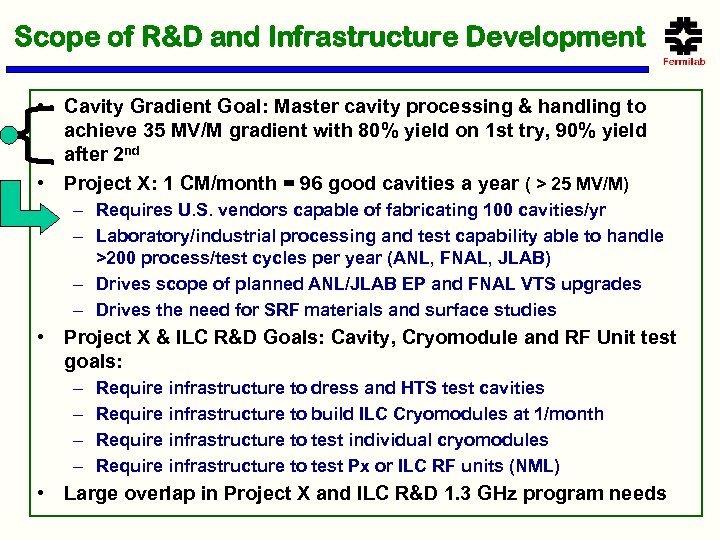
Scope of R&D and Infrastructure Development • Cavity Gradient Goal: Master cavity processing & handling to achieve 35 MV/M gradient with 80% yield on 1 st try, 90% yield after 2 nd • Project X: 1 CM/month = 96 good cavities a year ( > 25 MV/M) – Requires U. S. vendors capable of fabricating 100 cavities/yr – Laboratory/industrial processing and test capability able to handle >200 process/test cycles per year (ANL, FNAL, JLAB) – Drives scope of planned ANL/JLAB EP and FNAL VTS upgrades – Drives the need for SRF materials and surface studies • Project X & ILC R&D Goals: Cavity, Cryomodule and RF Unit test goals: – – Require infrastructure to dress and HTS test cavities Require infrastructure to build ILC Cryomodules at 1/month Require infrastructure to test individual cryomodules Require infrastructure to test Px or ILC RF units (NML) • Large overlap in Project X and ILC R&D 1. 3 GHz program needs
Combined SRF + CM Plan
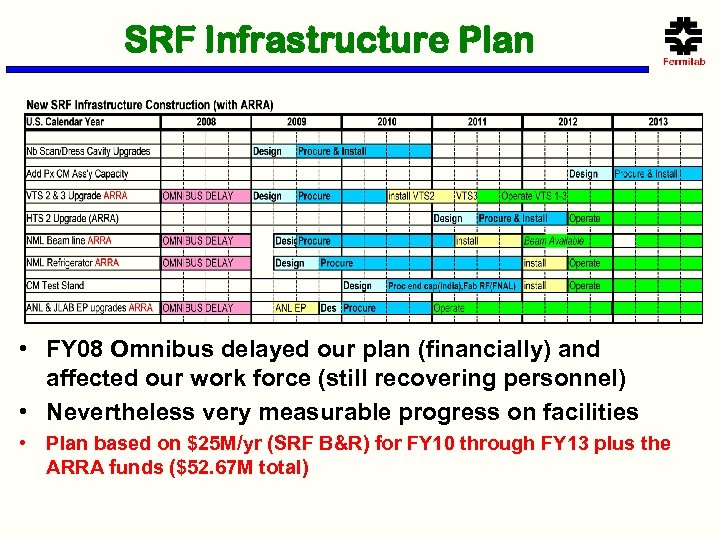
SRF Infrastructure Plan • FY 08 Omnibus delayed our plan (financially) and affected our work force (still recovering personnel) • Nevertheless very measurable progress on facilities • Plan based on $25 M/yr (SRF B&R) for FY 10 through FY 13 plus the ARRA funds ($52. 67 M total)

Nb Cryomodule • • • Niobium purchased from Industry Nb QA/QC at Fermilab Cavity Fabricated by Industry Cavity QA/QC at Fermilab Cavity Processed and tested at Jlab, Cornell, ANL/FNAL – We are working to transfer the processing to industry • Cavity Dressed (He vessel, Tuner, Coupler) at FNAL – This will be transferred to industy • High Power Test at FNAL • Cavity String and Cryomodule Fabrication at FNAL • Cryomodule Testing at FNAL
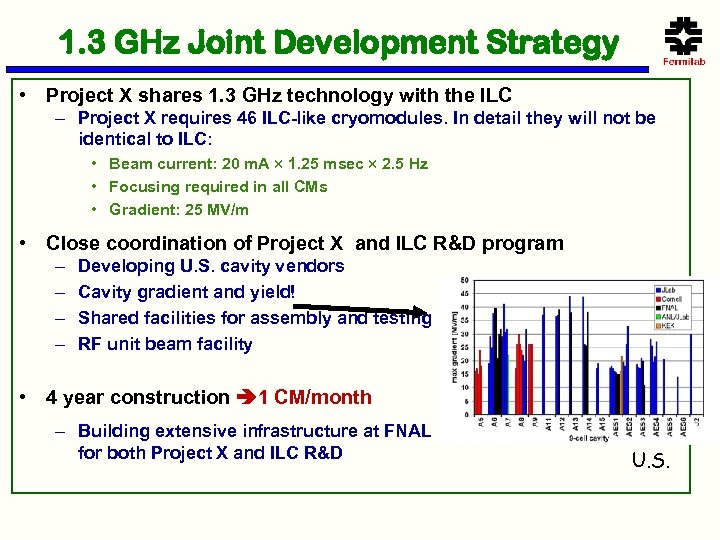
1. 3 GHz Joint Development Strategy • Project X shares 1. 3 GHz technology with the ILC – Project X requires 46 ILC-like cryomodules. In detail they will not be identical to ILC: • Beam current: 20 m. A 1. 25 msec 2. 5 Hz • Focusing required in all CMs • Gradient: 25 MV/m • Close coordination of Project X and ILC R&D program – – Developing U. S. cavity vendors Cavity gradient and yield! Shared facilities for assembly and testing RF unit beam facility • 4 year construction 1 CM/month – Building extensive infrastructure at FNAL for both Project X and ILC R&D U. S.
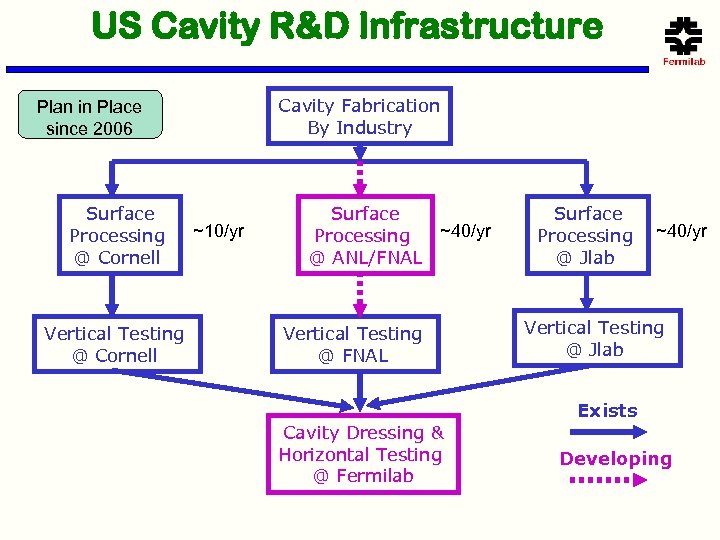
US Cavity R&D Infrastructure Cavity Fabrication By Industry Plan in Place since 2006 Surface Processing @ Cornell Vertical Testing @ Cornell ~10/yr Surface ~40/yr Processing @ ANL/FNAL Vertical Testing @ FNAL Cavity Dressing & Horizontal Testing @ Fermilab Surface Processing @ Jlab ~40/yr Vertical Testing @ Jlab Exists Developing

SRF: FNAL-ANL Cavity Processing Facility • ANL and Fermilab has jointly built and commissioned a processing facility at ANL. • It provides a complete processing of 1. 3 GHz cavities: – electro-polishing, ultrasonic cleaning, high-pressure rinse, assembly, etc. • Three single-cell cavities and one 9 -cell cavity electro-polished so far – Optimization of processing procedure is in progress • Electro-polishing Room New Ultrasonic cleaning system New High-pressure rinse system
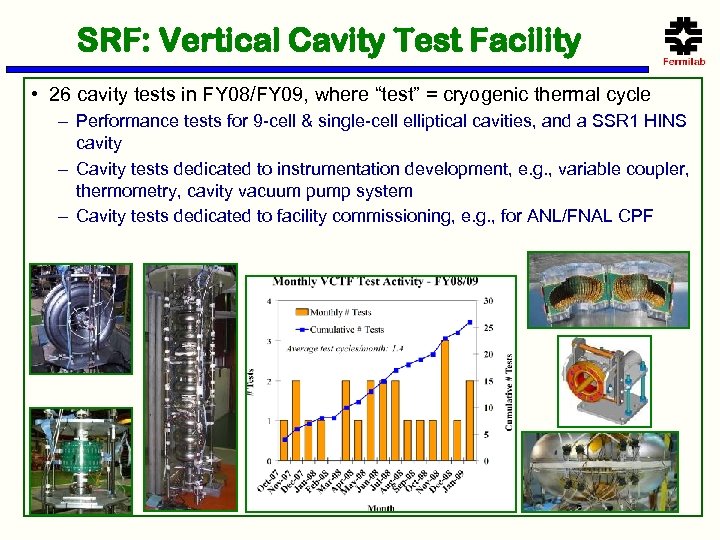
SRF: Vertical Cavity Test Facility • 26 cavity tests in FY 08/FY 09, where “test” = cryogenic thermal cycle – Performance tests for 9 -cell & single-cell elliptical cavities, and a SSR 1 HINS cavity – Cavity tests dedicated to instrumentation development, e. g. , variable coupler, thermometry, cavity vacuum pump system – Cavity tests dedicated to facility commissioning, e. g. , for ANL/FNAL CPF
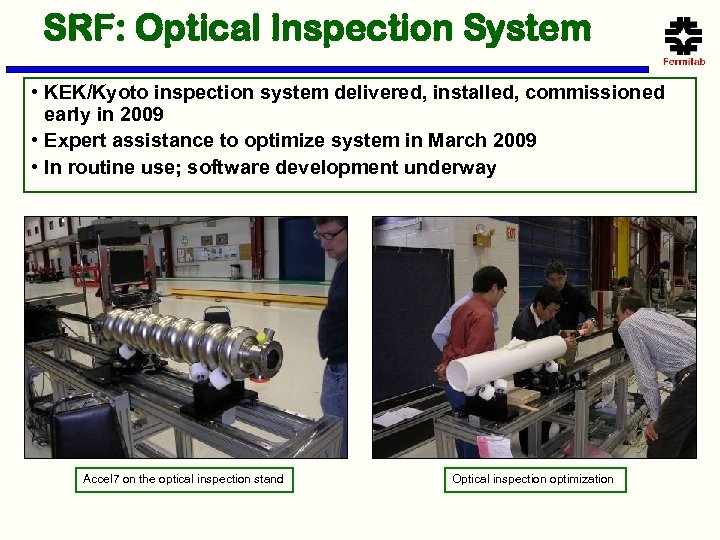
SRF: Optical Inspection System • KEK/Kyoto inspection system delivered, installed, commissioned early in 2009 • Expert assistance to optimize system in March 2009 • In routine use; software development underway Accel 7 on the optical inspection stand Optical inspection optimization

SRF: New Temperature Mapping New single-cell temperature mapping system uses multiplexed diodes as sensing elements New diode based system with 960 sensors and 62 wires can be installed in about 15 minutes Traditional carbon resistor based system
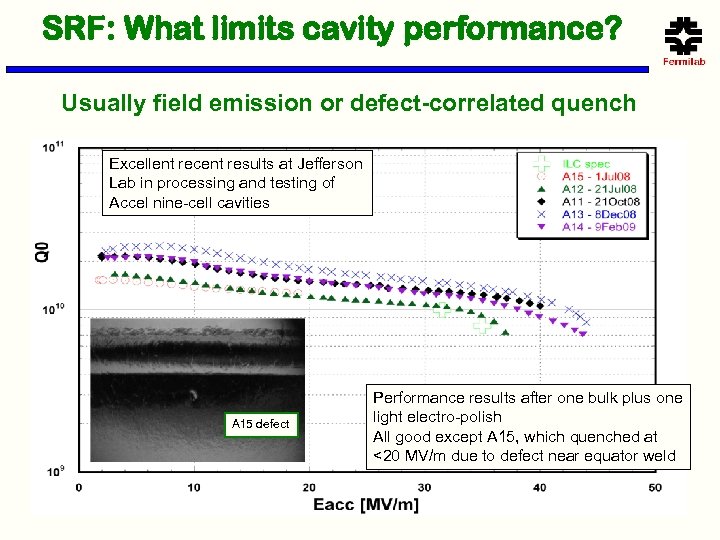
SRF: What limits cavity performance? Usually field emission or defect-correlated quench Excellent recent results at Jefferson Lab in processing and testing of Accel nine-cell cavities A 15 defect Performance results after one bulk plus one light electro-polish All good except A 15, which quenched at <20 MV/m due to defect near equator weld
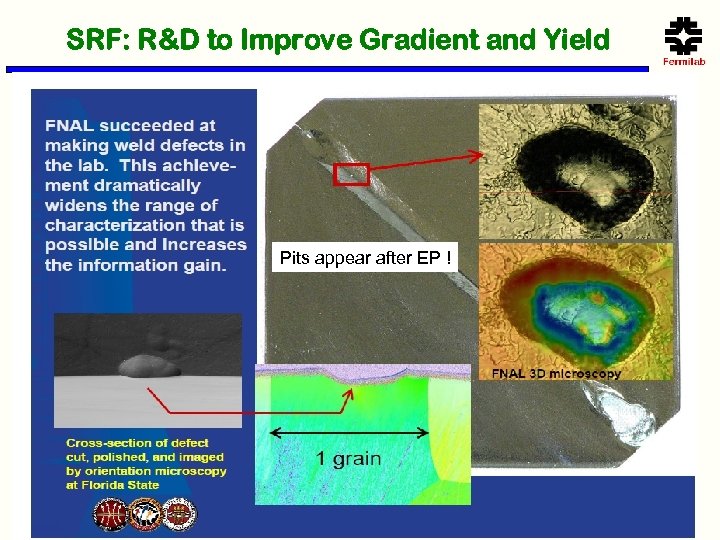
SRF: R&D to Improve Gradient and Yield Pits appear after EP !
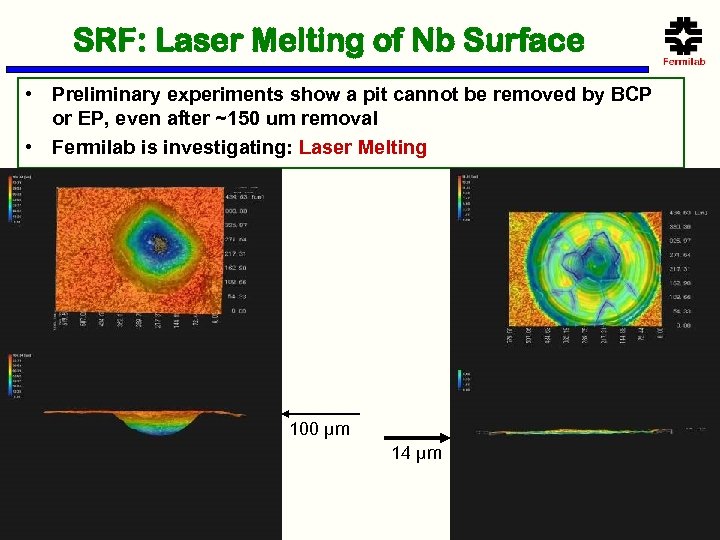
SRF: Laser Melting of Nb Surface • Preliminary experiments show a pit cannot be removed by BCP or EP, even after ~150 um removal • Fermilab is investigating: Laser Melting 100 µm 14 µm
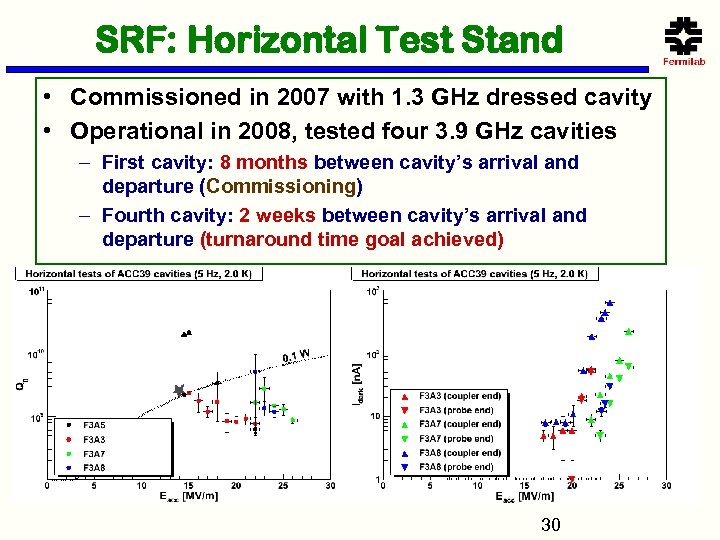
SRF: Horizontal Test Stand • Commissioned in 2007 with 1. 3 GHz dressed cavity • Operational in 2008, tested four 3. 9 GHz cavities – First cavity: 8 months between cavity’s arrival and departure (Commissioning) – Fourth cavity: 2 weeks between cavity’s arrival and departure (turnaround time goal achieved) 30

SRF: Industrial Collaboration • Processing – Cabot • Small effort in progress to assess their process on flat samples • ARRA funds will enable us to apply this process to single cell and 9 -cell cavities – Able Electropolish, Inc. • CRADA for development of their ability to process cavities • Exploring alternative method of full immersion EP 1. 3 GHz Single Cell Full Immersion EP at Able 3. 9 GHz Single Cell EP Tool at Able
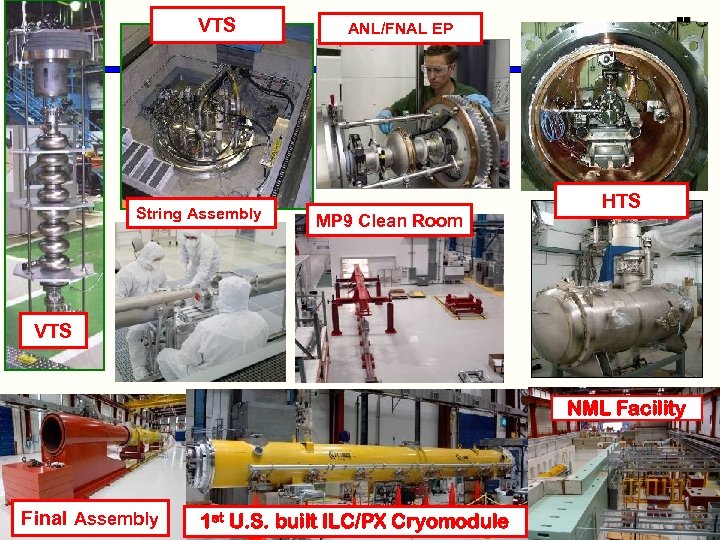
VTS String Assembly ANL/FNAL EP MP 9 Clean Room HTS VTS NML Facility Final Assembly 1 st U. S. built ILC/PX Cryomodule
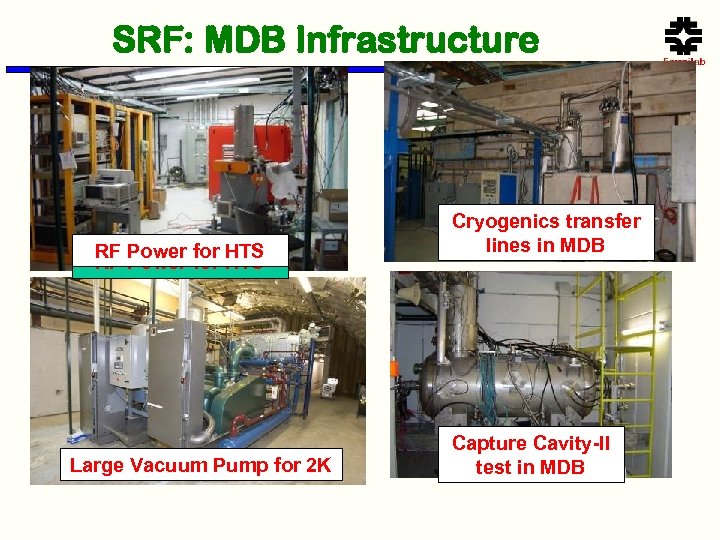
SRF: MDB Infrastructure RF Power for HTS Large Vacuum Pump for 2 K Cryogenics transfer lines in MDB Capture Cavity-II test in MDB

SRF: Cryomodule Assembly Facility • • Goal: Dress cavities; Assemble Cryomodules Where: MP 9 and ICB buildings – MP 9: 2500 ft 2 clean room, Class 10/100 – Cavity dressing and string assembly – ICB: final cryomodule assembly • Infrastructure: – Clean Rooms, Assembly Fixtures – Clean Vacuum, gas, water & Leak Check • DESY Cryomodule “kit” and 3. 9 CM assembled MP 9 Clean Room String Assembly ICB: Final Assembly fixtures Cavity string for 1 st CM

1 st FNAL built Cryomodules Cryomodule 1 From DESY kit 3. 9 GHz Cryomodule Designed/built at FNAL for DESY Cryomodule 2: cold mass parts in hand, from Europe, Need 8 dressed cavities
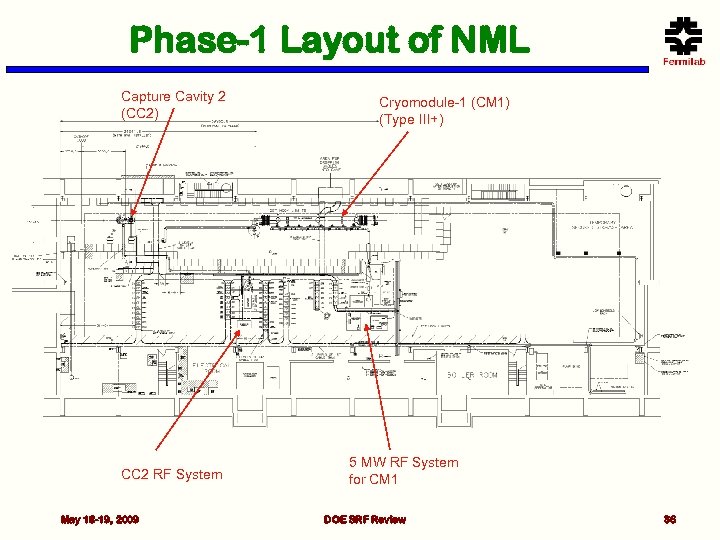
Phase-1 Layout of NML Capture Cavity 2 (CC 2) CC 2 RF System May 18 -19, 2009 Cryomodule-1 (CM 1) (Type III+) 5 MW RF System for CM 1 DOE SRF Review 36
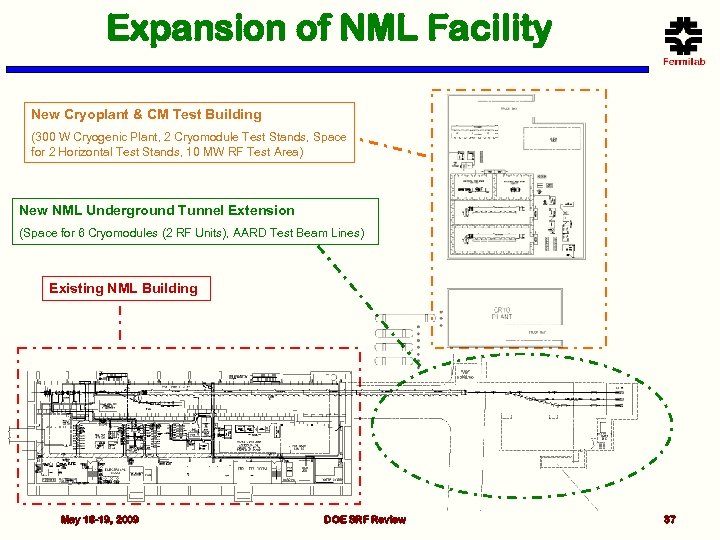
Expansion of NML Facility New Cryoplant & CM Test Building (300 W Cryogenic Plant, 2 Cryomodule Test Stands, Space for 2 Horizontal Test Stands, 10 MW RF Test Area) New NML Underground Tunnel Extension (Space for 6 Cryomodules (2 RF Units), AARD Test Beam Lines) Existing NML Building May 18 -19, 2009 DOE SRF Review 37

RF Unit Test Facility at NML

Progress at NML 1 st Cryomodule Test fit Control Room CM Feed Can Capture Cavity II @ NML Large Vacuum Pump He Refrigerator

NML Facility Milestones • Phase-1 Cryogenic System Operational • Delivery of First Cryomodule to NML (Aug. 2007) (Aug. 2008) • • • (Summer 2009) (Fall 2009) (Winter 2009) (2010) (2011) (2012 -13) Begin Civil Construction of NML Expansion First Cryomodule Ready for Cooldown* Cold RF Testing of First Cryomodule* Delivery of 2 nd Cryomodule to NML (S 1) Install Gun and Injector First Beam Cryoplant Operational Full RF Unit Testing (3 Cryomodules) (S 2) Cryomodule Test Stand (CTS) Operational *Significant project delays occurred due to funding cuts in 2008
Summary • In FY 06 -09 Fermilab has made significant progress towards design, development, construction, commissioning and operation of SRF Infrastructure. – Minimum infrastructure is in place (or will be in place shortly • Nb QC, Materail R&D, Cavity Processing, VTS, HTS, CM Assembly and Testing • Plan is in place and developments are in progress to build SRF infrastructure to support the construction of Project-X. – Addition of 325 MHz infrastructure is needed. • The SRF Program while developing Fermilab infrastructure effectively uses available US laboratory capacity and is working to develop US industrial capabilities.
fabf24d10282c0a45d18409ab8ea1464.ppt