40c312bff43cad123e707d12e155644c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78

High Availability Mia Malaise Systeem Analist Mainframe Mia. Malaise@kbc. be Paul Hauwaerts Diensthoofd Mainframe Infrastructuur

Agenda Introduction KBC Group ICT High Availability Mia Malaise Vision on HR Paul Hauwaerts Questions & Answers Guided Tour Kurt Mees

Agenda Introduction KBC Group ICT High Availability Vision on HR Questions & Answers Guided Tour

KBC Bank & Insurance Group n Ranking l One of the top 2 banks in Belgium l One of the top 3 insurers in Belgium l One of the top 20 banks in Europe l Leading financial group in Central Europe n Market share in Belgium l Banking : 20 -25% l Insurance : 9% (non-life) 22% (life) n Head office in Brussels n 50. 000 employees n 13. 000 clients
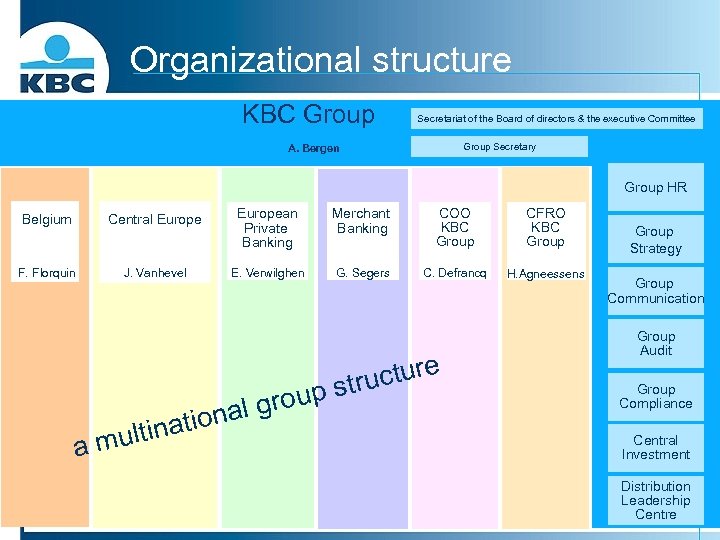
Organizational structure KBC Group Secretariat of the Board of directors & the executive Committee Group Secretary A. Bergen Group HR Belgium Central European Private Banking Merchant Banking COO KBC Group CFRO KBC Group F. Florquin J. Vanhevel E. Verwilghen G. Segers C. Defrancq H. Agneessens o ltinati a mu cture p stru l grou na Group Strategy Group Communication Group Audit Group Compliance Central Investment Distribution Leadership Centre
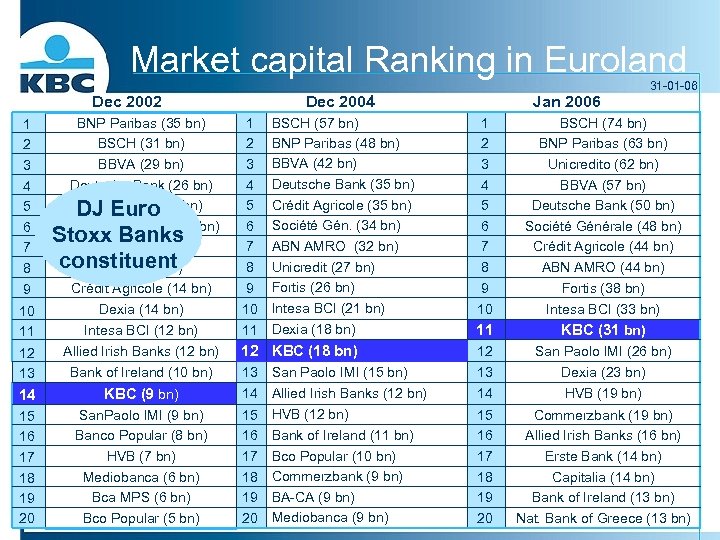
Market capital Ranking in Euroland 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BNP Paribas (35 bn) BSCH (31 bn) BBVA (29 bn) Deutsche Bank (26 bn) ABN AMRO DJ Euro(25 bn) Société Générale (24 bn) Stoxx Banks Unicredito (22 bn) constituent Fortis (22 bn) Crédit Agricole (14 bn) 10 11 Dexia (14 bn) Intesa BCI (12 bn) Allied Irish Banks (12 bn) 12 13 Bank of Ireland (10 bn) 14 KBC (9 bn) 15 16 17 18 19 20 San. Paolo IMI (9 bn) Banco Popular (8 bn) HVB (7 bn) Mediobanca (6 bn) Bca MPS (6 bn) Bco Popular (5 bn) Jan 2006 Dec 2004 Dec 2002 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BSCH (57 bn) BNP Paribas (48 bn) BBVA (42 bn) Deutsche Bank (35 bn) Crédit Agricole (35 bn) Société Gén. (34 bn) ABN AMRO (32 bn) Unicredit (27 bn) Fortis (26 bn) 31 -01 -06 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BSCH (74 bn) BNP Paribas (63 bn) Unicredito (62 bn) BBVA (57 bn) Deutsche Bank (50 bn) Société Générale (48 bn) Crédit Agricole (44 bn) ABN AMRO (44 bn) Fortis (38 bn) 10 Intesa BCI (21 bn) 11 Dexia (18 bn) 10 Intesa BCI (33 bn) 11 KBC (31 bn) 12 KBC (18 bn) 12 San Paolo IMI (26 bn) 13 San Paolo IMI (15 bn) 14 Allied Irish Banks (12 bn) 13 Dexia (23 bn) 14 HVB (19 bn) 15 16 17 18 19 20 Commerzbank (19 bn) Allied Irish Banks (16 bn) Erste Bank (14 bn) Capitalia (14 bn) Bank of Ireland (13 bn) Nat. Bank of Greece (13 bn) 15 16 17 18 19 20 HVB (12 bn) Bank of Ireland (11 bn) Bco Popular (10 bn) Commerzbank (9 bn) BA-CA (9 bn) Mediobanca (9 bn)
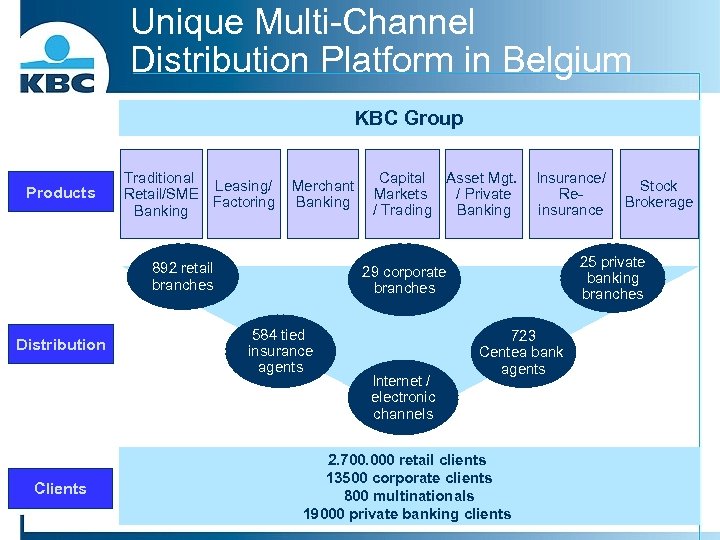
Unique Multi-Channel Distribution Platform in Belgium KBC Group Products Traditional Leasing/ Retail/SME Factoring Banking Merchant Banking 892 retail branches Distribution Clients Capital Asset Mgt. Markets / Private / Trading Banking Insurance/ Reinsurance 25 private banking branches 29 corporate branches 584 tied insurance agents Internet / electronic channels Stock Brokerage 723 Centea bank agents 2. 700. 000 retail clients 13500 corporate clients 800 multinationals 19000 private banking clients dd. 31 -12 -2005
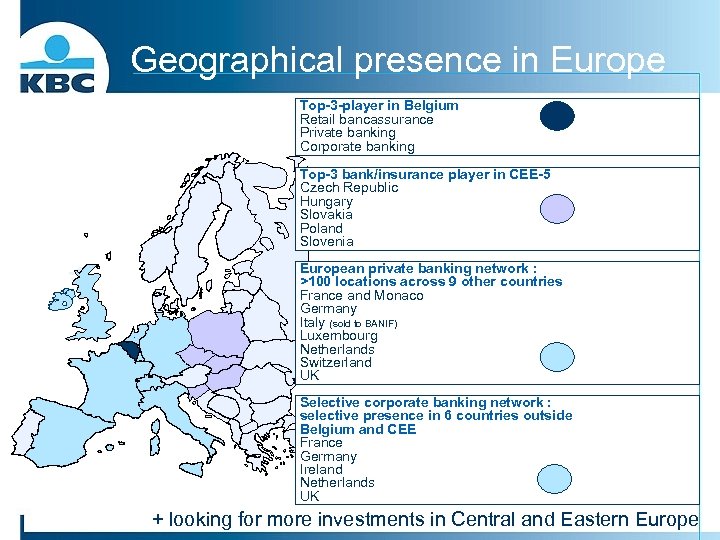
Geographical presence in Europe Top-3 -player in Belgium Retail bancassurance Private banking Corporate banking Top-3 bank/insurance player in CEE-5 Czech Republic Hungary Slovakia Poland Slovenia European private banking network : >100 locations across 9 other countries France and Monaco Germany Italy (sold to BANIF) Luxembourg Netherlands Switzerland UK Selective corporate banking network : selective presence in 6 countries outside Belgium and CEE France Germany Ireland Netherlands UK + looking for more investments in Central and Eastern Europe
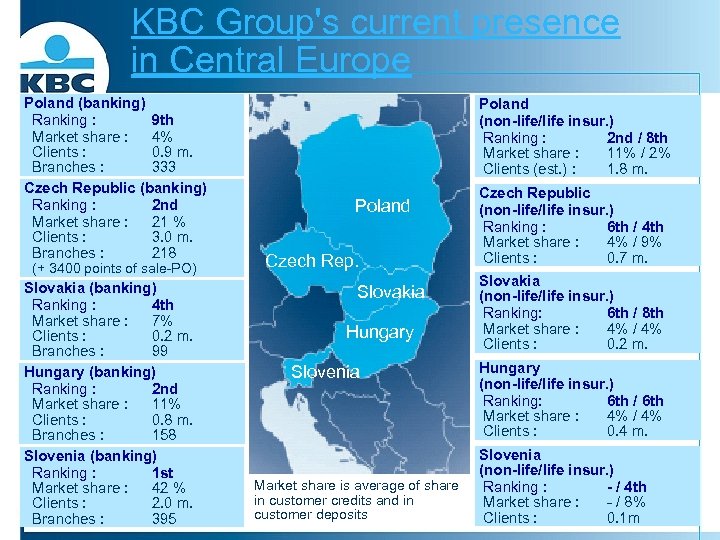
KBC Group's current presence in Central Europe Poland (banking) Ranking : 9 th Market share : 4% Clients : 0. 9 m. Branches : 333 Czech Republic (banking) Ranking : 2 nd Market share : 21 % Clients : 3. 0 m. Branches : 218 (+ 3400 points of sale-PO) Slovakia (banking) Ranking : 4 th Market share : 7% Clients : 0. 2 m. Branches : 99 Hungary (banking) Ranking : 2 nd Market share : 11% Clients : 0. 8 m. Branches : 158 Slovenia (banking) Ranking : 1 st Market share : 42 % Clients : 2. 0 m. Branches : 395 Poland (non-life/life insur. ) Ranking : 2 nd / 8 th Market share : 11% / 2% Clients (est. ) : 1. 8 m. Poland Czech Rep. Slovakia Hungary Slovenia Market share is average of share in customer credits and in customer deposits Czech Republic (non-life/life insur. ) Ranking : 6 th / 4 th Market share : 4% / 9% Clients : 0. 7 m. Slovakia (non-life/life insur. ) Ranking: 6 th / 8 th Market share : 4% / 4% Clients : 0. 2 m. Hungary (non-life/life insur. ) Ranking: 6 th / 6 th Market share : 4% / 4% Clients : 0. 4 m. Slovenia (non-life/life insur. ) Ranking : - / 4 th Market share : - / 8% Clients : 0. 1 m
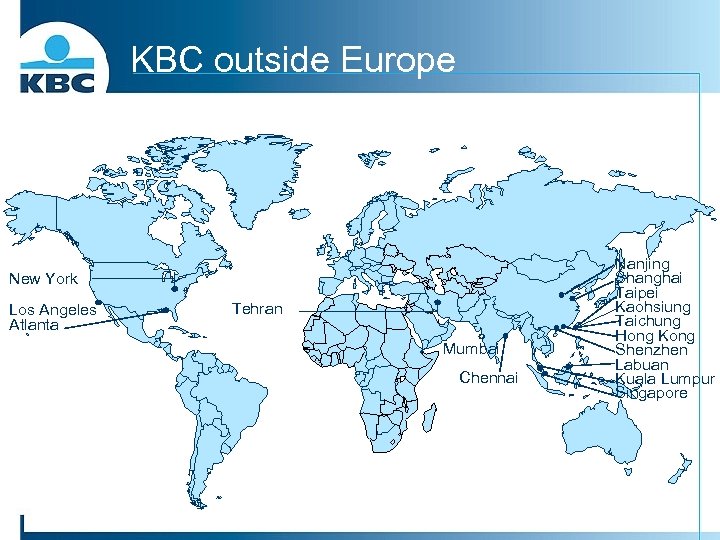
KBC outside Europe New York Los Angeles Atlanta Tehran Mumbai Chennai Nanjing Shanghai Taipei Kaohsiung Taichung Hong Kong Shenzhen Labuan Kuala Lumpur Singapore
KBC Group ICT

ICT in a bank: boring or not?

Group ICT n Employees l l l n Services l l n Your ICT, our business Delivering end-to-end ICT solutions (software, hardware, service) Maintenance of ICT solutions Hosting services Network & infrastructure management Clients l l l n Belgium: 1. 820 KBC & 500 external consultants Central Europe: 1. 300 KBC India: 250 Valuesource (100% daughter of KBC) KBC Group Belgium KBC Group international Other corporate clients in the Benelux (Orbay, IFB, …) Turnover: € 650 mn

Our ICT organisation n Client focused l l n Organisation l l l n Process driven Matrix organisation & project approach Fast growing international project portfolio Technology & architecture l l n Strong governance & business-ICT alignment Best-in-class ICT services Fast follower in new technologies High availability Architecture driven Integrator of components Multi-sourcing l l Core business by our own people Fixed price outsourcing & package solutions for non-core (e. g. SAP) External consultants for temporary needs India for technical implementations & conversions
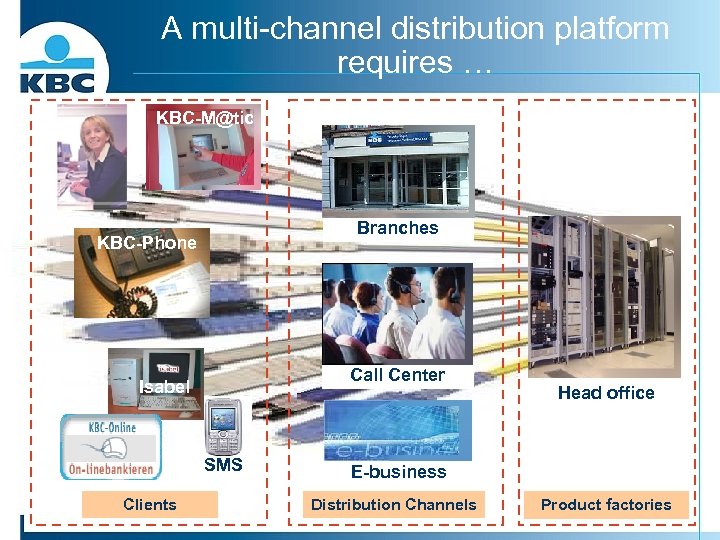
A multi-channel distribution platform requires … KBC-M@tic Branches KBC-Phone Call Center Isabel SMS Clients Head office E-business Distribution Channels Product factories
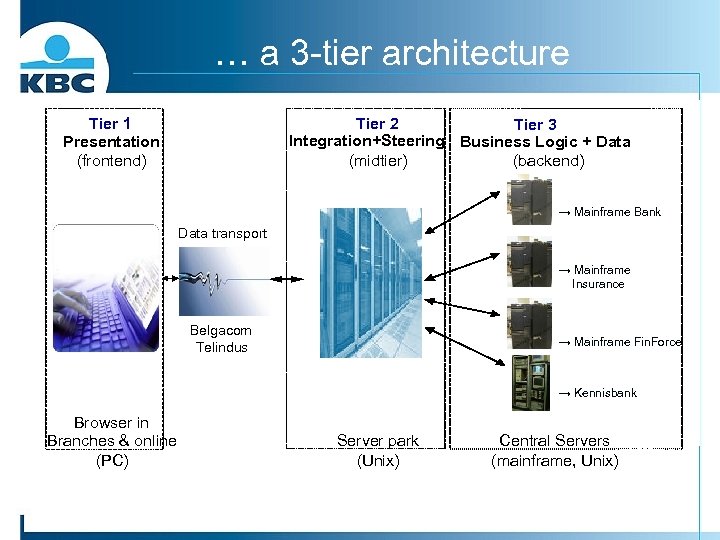
… a 3 -tier architecture Tier 1 Presentation (frontend) Tier 2 Tier 3 Integration+Steering Business Logic + Data (midtier) (backend) → Mainframe Bank Data transport → Mainframe Insurance Belgacom Telindus → Mainframe Fin. Force → Kennisbank Browser in Branches & online (PC) Server park (Unix) Central Servers (mainframe, Unix)
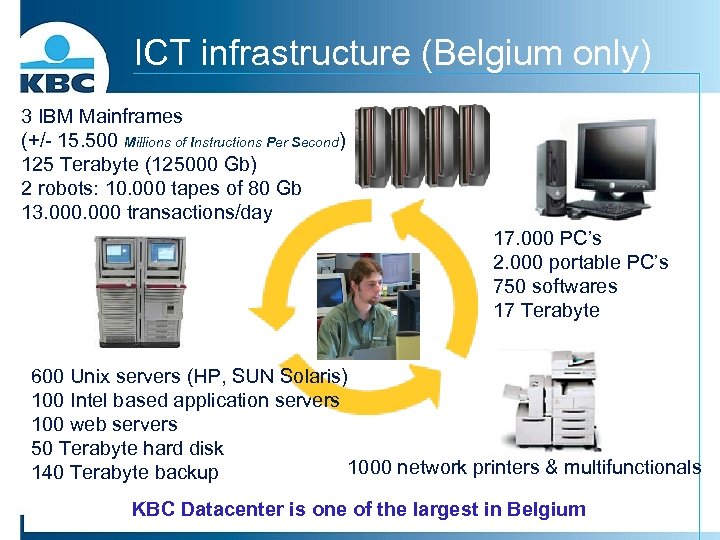
ICT infrastructure (Belgium only) 3 IBM Mainframes (+/- 15. 500 Millions of Instructions Per Second) 125 Terabyte (125000 Gb) 2 robots: 10. 000 tapes of 80 Gb 13. 000 transactions/day 17. 000 PC’s 2. 000 portable PC’s 750 softwares 17 Terabyte 600 Unix servers (HP, SUN Solaris) 100 Intel based application servers 100 web servers 50 Terabyte hard disk 1000 network printers & multifunctionals 140 Terabyte backup KBC Datacenter is one of the largest in Belgium
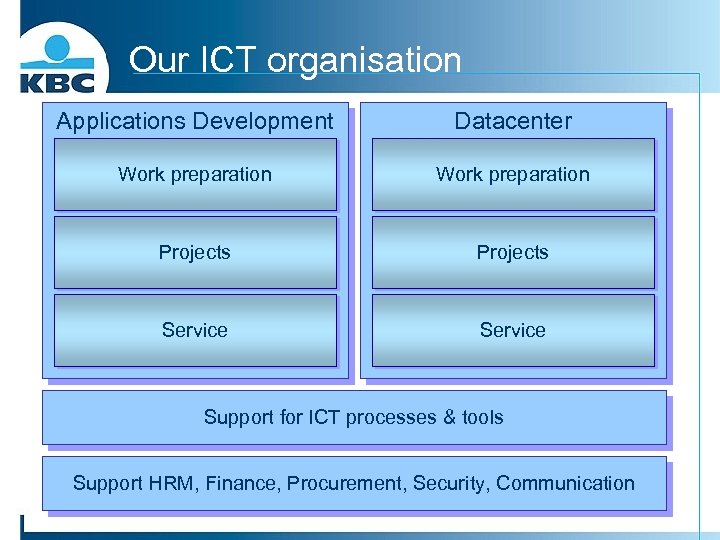
Our ICT organisation Applications Development Datacenter Work preparation Projects Service Support for ICT processes & tools Support HRM, Finance, Procurement, Security, Communication

Agenda Introduction KBC Group ICT High Availability Vision on HR Questions & Answers Guided Tour

INTRO High Availability (HA)
INTRO: welcome at KBC online
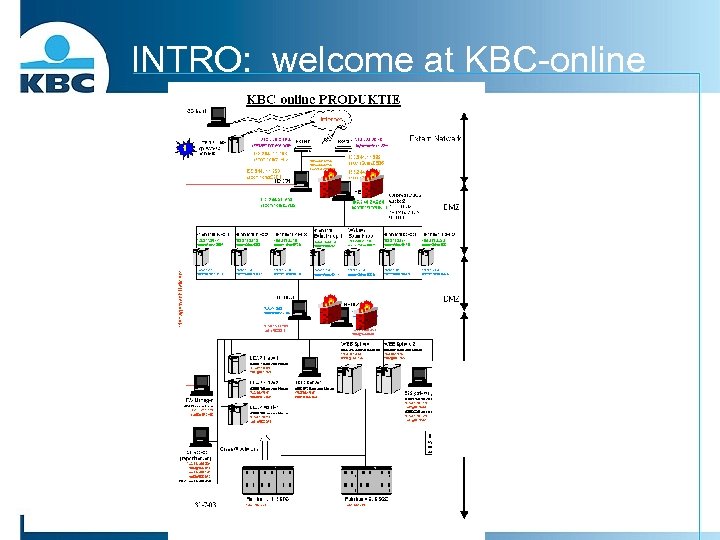
INTRO: welcome at KBC-online

WHAT does HA mean to KBC ? n Theory …. 1. 2. 3. 4. n What is (high) availability and why do we care ? What does availability depend on ? How and why do we measure availability ? What does it cost <> what profit do we get? … and reality l l High Availability@KBC DRP@KBC

1. What is availability …. n The degree to which a service (fi KBC-online) is able to perform its function when you want it to n The ratio of the total time a service is capable of being used during a given interval, to the length of the interval. n What does it mean l l l n Operation system running ? Network available ? Hardware available ? There are gray areas too…. l Is the system available if it is severely degraded?
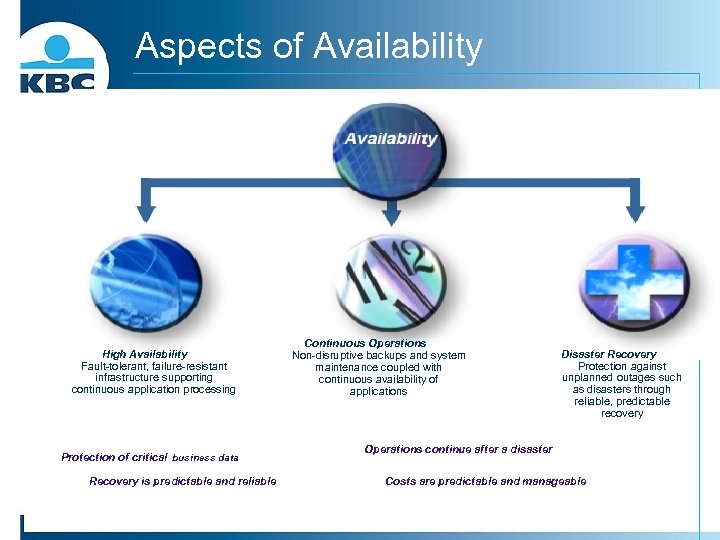
Aspects of Availability High Availability Fault-tolerant, failure-resistant infrastructure supporting continuous application processing Protection of critical business data Recovery is predictable and reliable Continuous Operations Non-disruptive backups and system maintenance coupled with continuous availability of applications Disaster Recovery Protection against unplanned outages such as disasters through reliable, predictable recovery Operations continue after a disaster Costs are predictable and manageable

…. and why do we care ? …. Because availability of IT services is at the core of our business l The Availability and reliability of IT can directly influence Customer satisfaction and the reputation of the business l Downtime of IT services can have direct financial impact. l Growing demand for the availability of the business that are time and place independent

WHAT does HA mean to KBC ? n Theory …. 1. 2. 3. 4. n What is (high) availability and why do we care ? What does availability depend on ? How and why do we measure availability ? What does it cost <> what profit do we get? … and reality l l High availability@KBC DRP@KBC
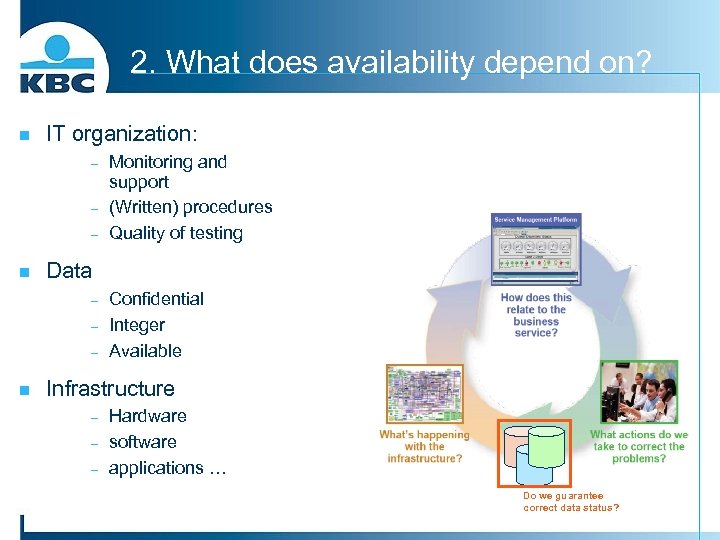
2. What does availability depend on? n IT organization: - n Data - n Monitoring and support (Written) procedures Quality of testing Confidential Integer Available Infrastructure - Hardware software applications … Do we guarantee correct data status?
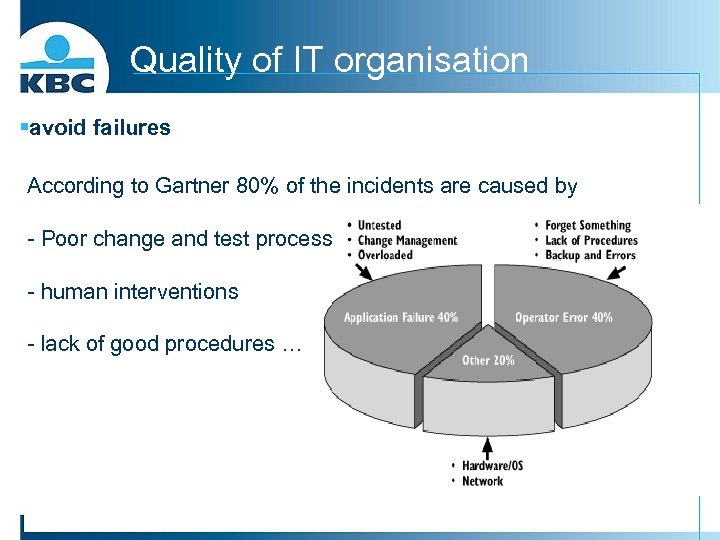
Quality of IT organisation §avoid failures According to Gartner 80% of the incidents are caused by - Poor change and test process - human interventions - lack of good procedures …
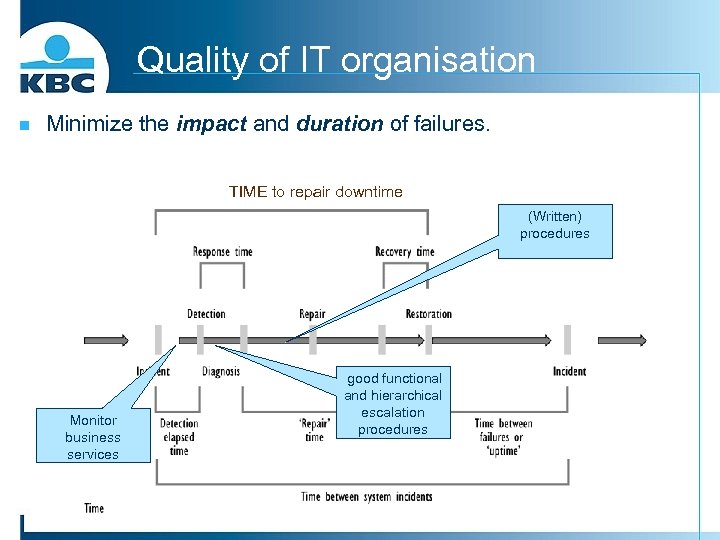
Quality of IT organisation n Minimize the impact and duration of failures. TIME to repair downtime (Written) procedures Monitor business services good functional and hierarchical escalation procedures
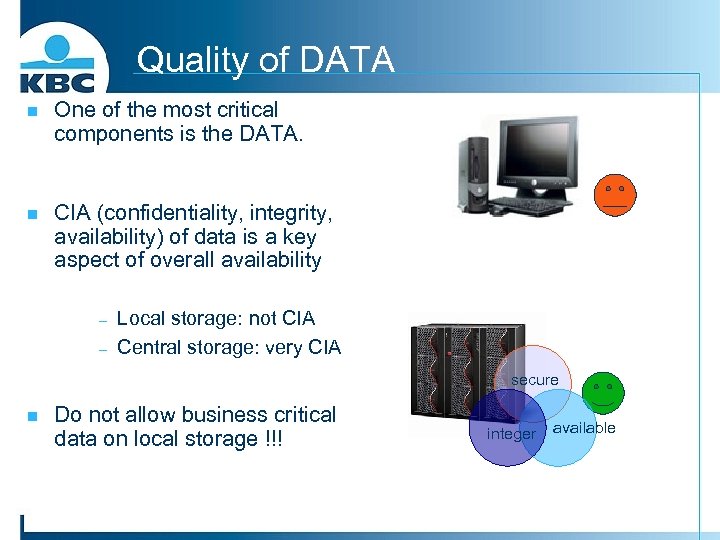
Quality of DATA n One of the most critical components is the DATA. n CIA (confidentiality, integrity, availability) of data is a key aspect of overall availability - Local storage: not CIA Central storage: very CIA secure n Do not allow business critical data on local storage !!! integer available
Quality of infrastructure n Reliability : l n Resilience to failure: l n How frequently infrastructure fails ? Can the failure be masked ? Serviceability: l How quick can the infrastructure recover from failures ?
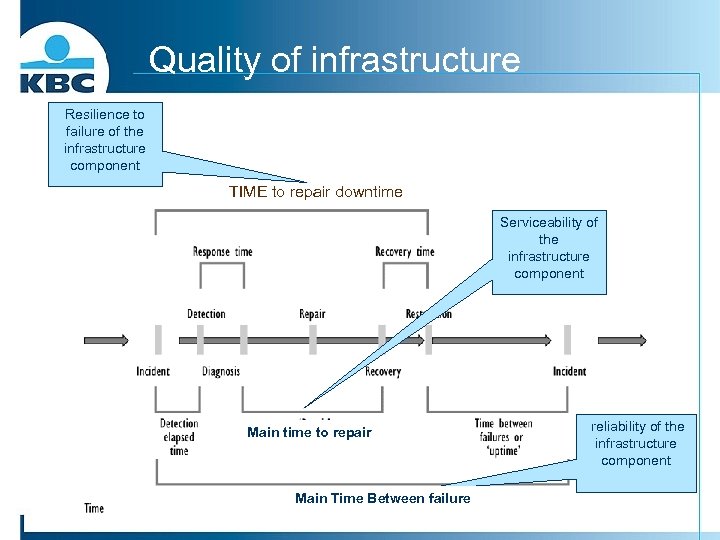
Quality of infrastructure Resilience to failure of the infrastructure component TIME to repair downtime Serviceability of the infrastructure component Main time to repair Main Time Between failure reliability of the infrastructure component

Quality of infrastructure: Reliability n Bulletproof (bowling ball, hammer …) l MTBF > 10 000 years l This does not mean a hammer lasts a thousand years l Of several thousand hammers, one a year might fail n Highly reliable (computer hardware, consumer goods) l MTBF = 10 to 1000 years l Mainframe 1000 years! l one failure per 1000 units per year n Unreliable (young child’s birthday gift) l MTBF < 5 minutes n Software reliability generally falls between the last two
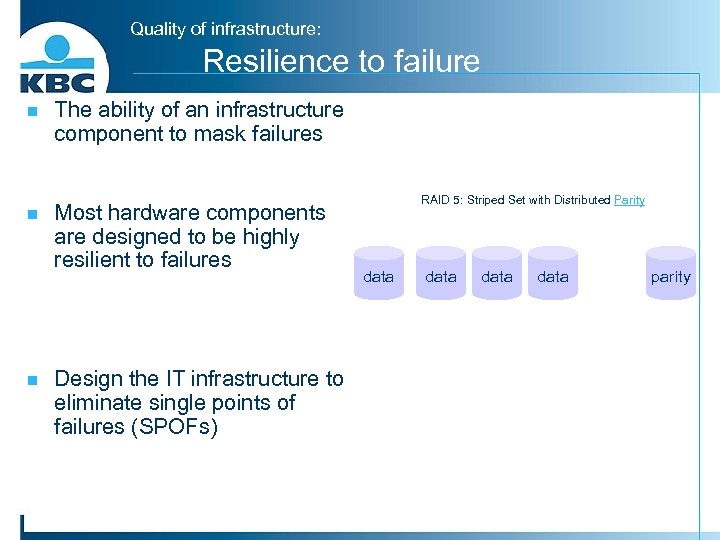
Quality of infrastructure: Resilience to failure n The ability of an infrastructure component to mask failures n Most hardware components are designed to be highly resilient to failures n Design the IT infrastructure to eliminate single points of failures (SPOFs) RAID 5: Striped Set with Distributed Parity data parity
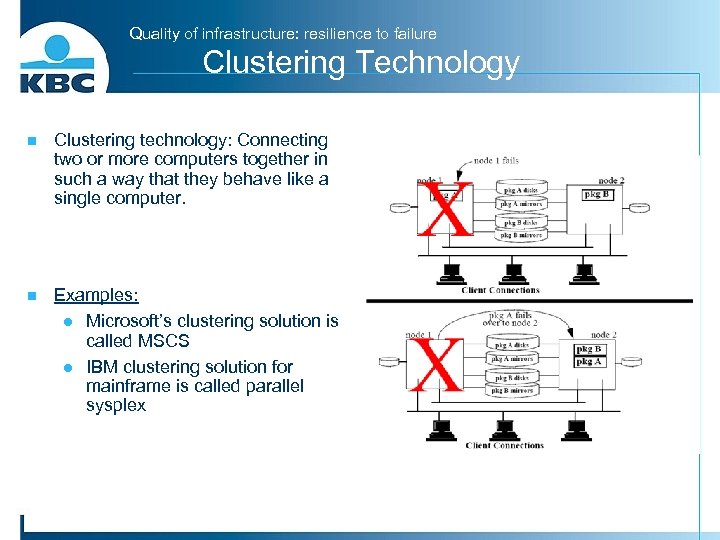
Quality of infrastructure: resilience to failure Clustering Technology n Clustering technology: Connecting two or more computers together in such a way that they behave like a single computer. n Examples: l Microsoft’s clustering solution is called MSCS l IBM clustering solution for mainframe is called parallel sysplex
Quality of infrastructure: Serviceability n Highly serviceable (hot standby, redundancy) l l n Somewhat serviceable (parts in stock) l l n MTTR is typically seconds or less Mathematically guarantees decent availability MTTR may be minutes to hours Probably ok if the MTBF is high enough Unserviceable (parts not available) l l MTTR is anyone’s guess Might still be ok if MTBF is very high

WHAT does HA mean to KBC ? n Theory …. 1. 2. 3. 4. n What is (high) availability and why do we care ? What does availability depend on ? How and why do we measure availability ? What does it cost <> what profit do we get? … and reality l l High availability@KBC DRP@KBC

3. How and why do we measure availabity? n To avoid individual perception n To MEASURE=To KNOW l l n if you don’t measure it you can’t improve it. If you can’t influence it, then don’t measure it. Two ways to measure: l l the impact of the failure component availability
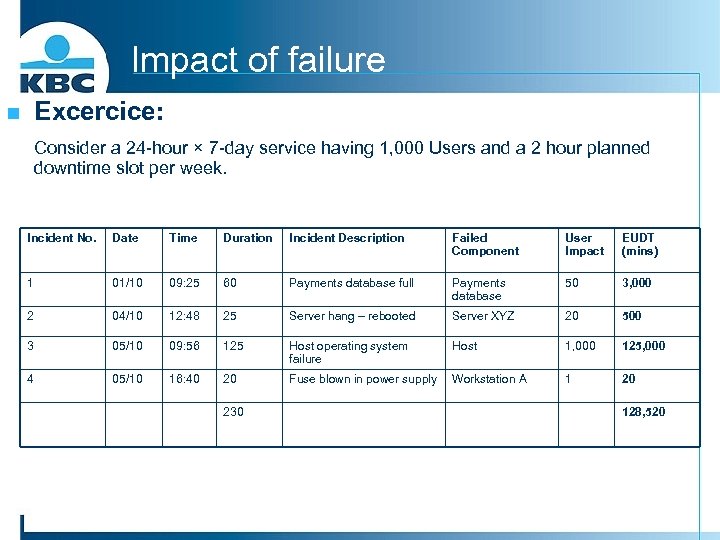
Impact of failure Excercice: n Consider a 24 -hour × 7 -day service having 1, 000 Users and a 2 hour planned downtime slot per week. Incident No. Date Time Duration Incident Description Failed Component User Impact EUDT (mins) 1 01/10 09: 25 60 Payments database full Payments database 50 3, 000 2 04/10 12: 48 25 Server hang – rebooted Server XYZ 20 500 3 05/10 09: 56 125 Host operating system failure Host 1, 000 125, 000 4 05/10 16: 40 20 Fuse blown in power supply Workstation A 1 20 230 128, 520
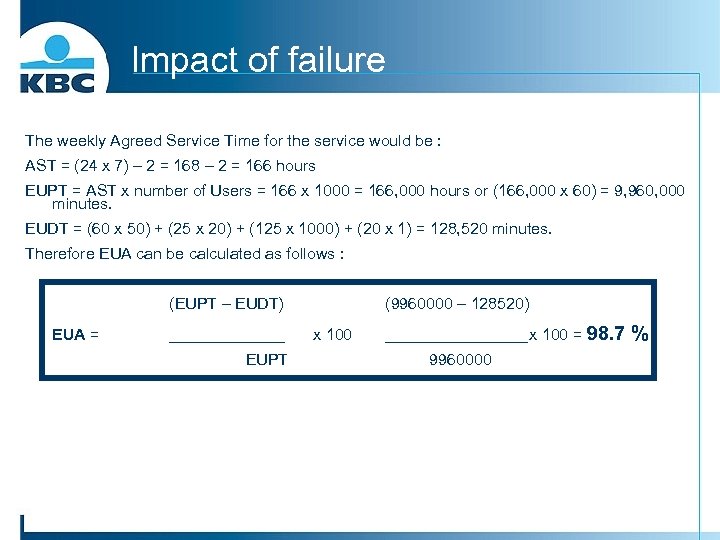
Impact of failure The weekly Agreed Service Time for the service would be : AST = (24 x 7) – 2 = 168 – 2 = 166 hours EUPT = AST x number of Users = 166 x 1000 = 166, 000 hours or (166, 000 x 60) = 9, 960, 000 minutes. EUDT = (60 x 50) + (25 x 20) + (125 x 1000) + (20 x 1) = 128, 520 minutes. Therefore EUA can be calculated as follows : (EUPT – EUDT) EUA = _______ EUPT (9960000 – 128520) x 100 ________ x 100 = 98. 7 9960000 %
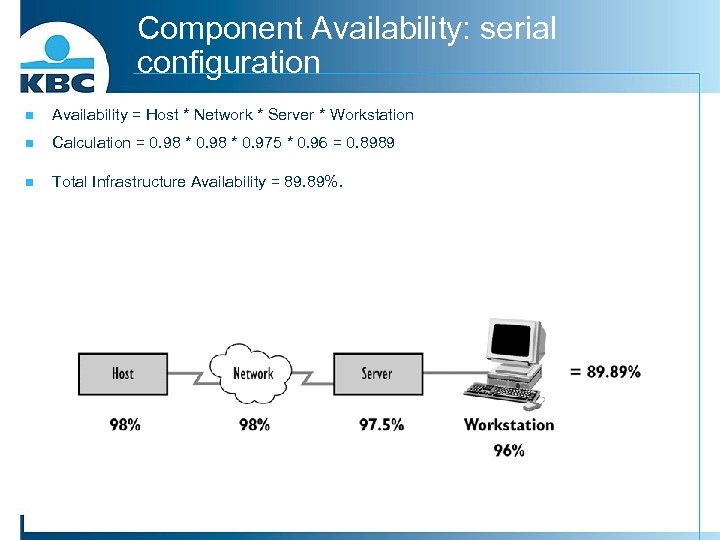
Component Availability: serial configuration n Availability = Host * Network * Server * Workstation n Calculation = 0. 98 * 0. 975 * 0. 96 = 0. 8989 n Total Infrastructure Availability = 89. 89%.
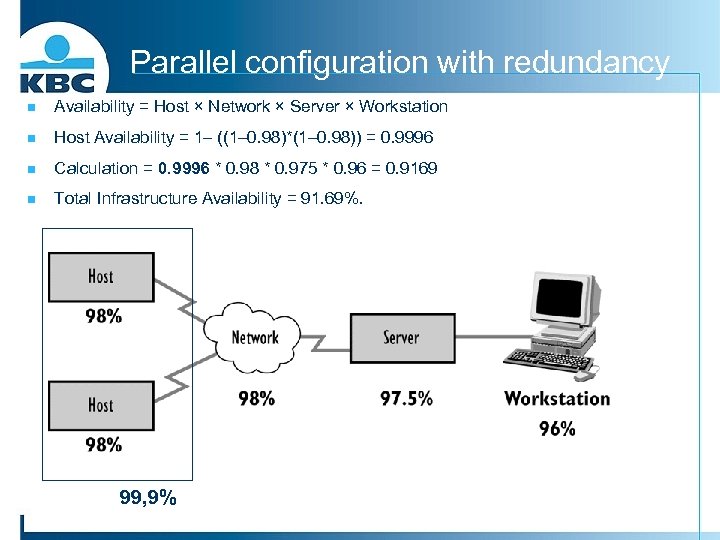
Parallel configuration with redundancy n Availability = Host × Network × Server × Workstation n Host Availability = 1– ((1– 0. 98)*(1– 0. 98)) = 0. 9996 n Calculation = 0. 9996 * 0. 98 * 0. 975 * 0. 96 = 0. 9169 n Total Infrastructure Availability = 91. 69%. 99, 9%
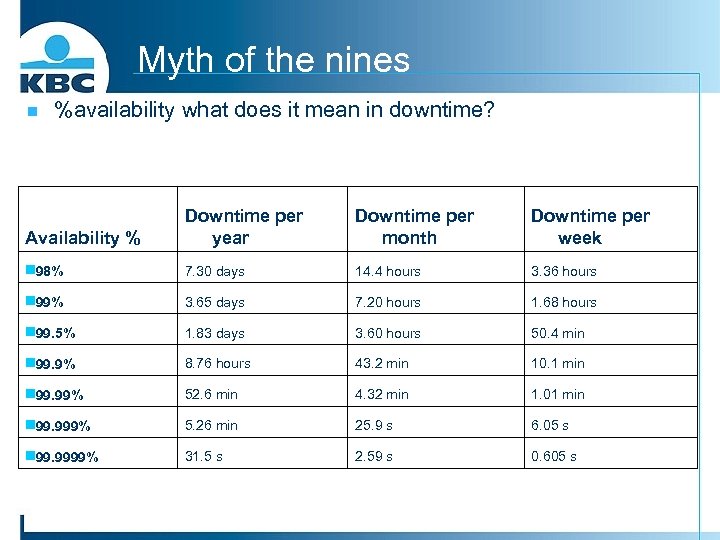
Myth of the nines n %availability what does it mean in downtime? Availability % Downtime per year Downtime per month Downtime per week n 98% 7. 30 days 14. 4 hours 3. 36 hours n 99% 3. 65 days 7. 20 hours 1. 68 hours n 99. 5% 1. 83 days 3. 60 hours 50. 4 min n 99. 9% 8. 76 hours 43. 2 min 10. 1 min n 99. 99% 52. 6 min 4. 32 min 1. 01 min n 99. 999% 5. 26 min 25. 9 s 6. 05 s n 99. 9999% 31. 5 s 2. 59 s 0. 605 s

WHAT does HA mean to KBC ? n Theory …. 1. 2. 3. 4. n What is (high) availability and why do we care ? What does availability depend on ? How and why do we measure availability ? What does it cost <> what profit do we get? … and reality l l High availability@KBC DRP@KBC
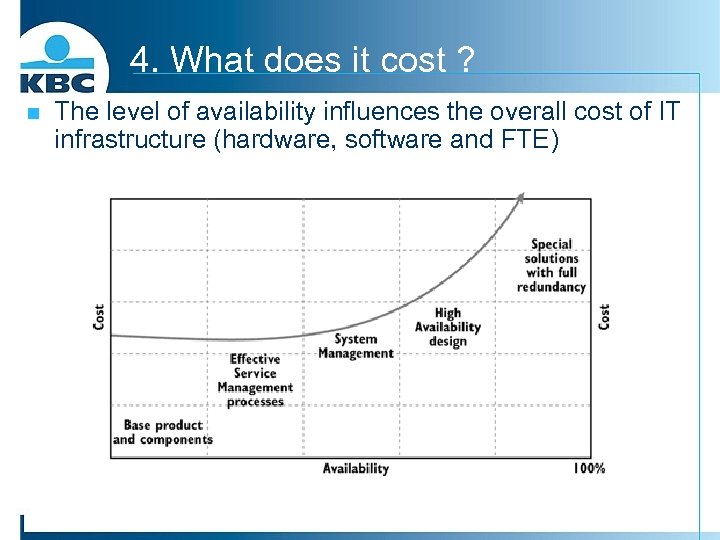
4. What does it cost ? n The level of availability influences the overall cost of IT infrastructure (hardware, software and FTE)
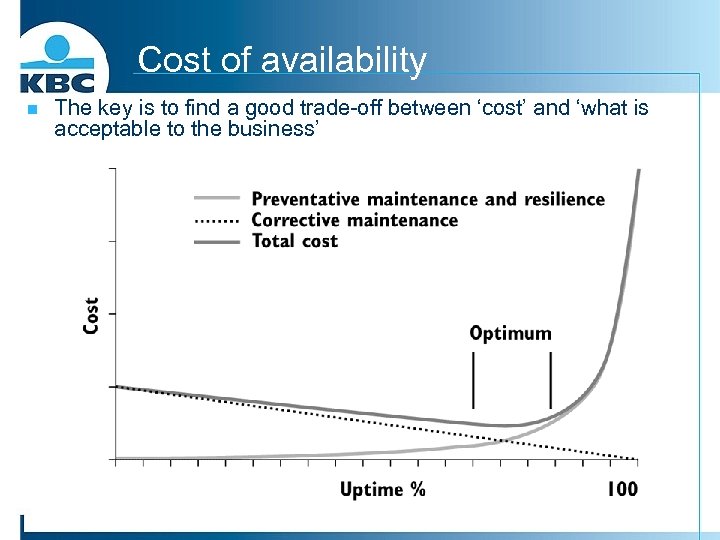
Cost of availability n The key is to find a good trade-off between ‘cost’ and ‘what is acceptable to the business’
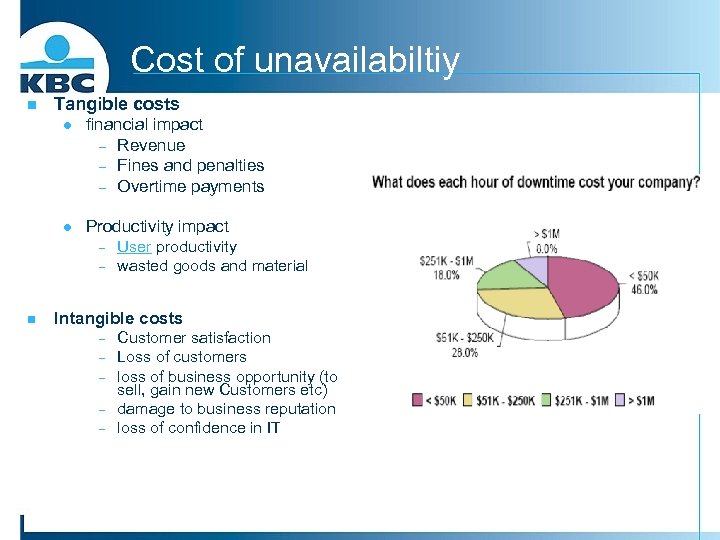
Cost of unavailabiltiy n Tangible costs l financial impact - Revenue - Fines and penalties - Overtime payments l Productivity impact - n User productivity wasted goods and material Intangible costs - Customer satisfaction Loss of customers loss of business opportunity (to sell, gain new Customers etc) damage to business reputation loss of confidence in IT

WHAT does HA mean to KBC ? n Theory …. 1. 2. 3. 4. n What is (high) availability and why do we care ? What does availability depend on ? How and why do we measure availability ? What does it cost <> what profit do we get? … and reality l l High availability@KBC DRP@KBC

High availability@KBC
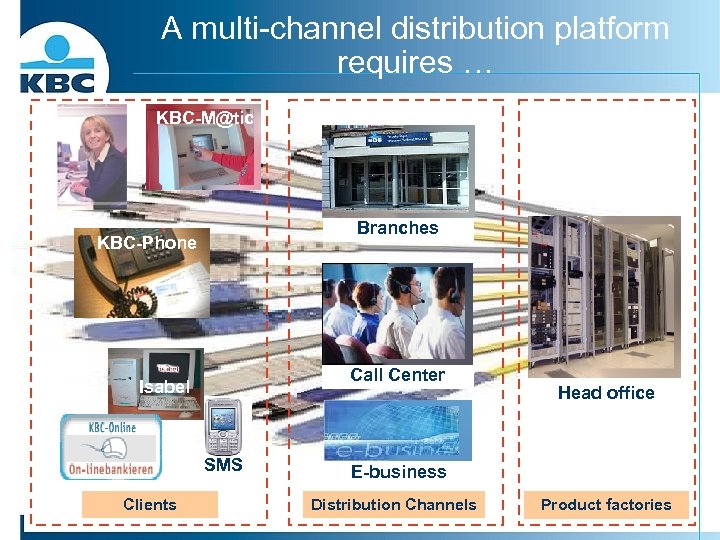
A multi-channel distribution platform requires … KBC-M@tic Branches KBC-Phone Call Center Isabel SMS Clients Head office E-business Distribution Channels Product factories
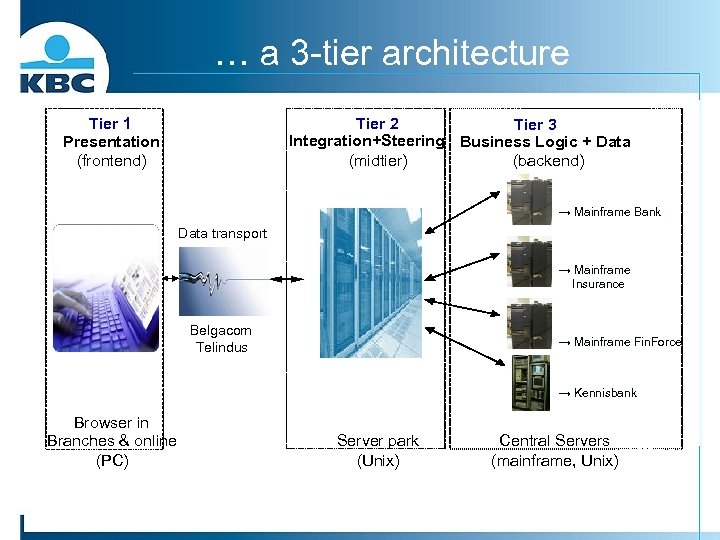
… a 3 -tier architecture Tier 1 Presentation (frontend) Tier 2 Tier 3 Integration+Steering Business Logic + Data (midtier) (backend) → Mainframe Bank Data transport → Mainframe Insurance Belgacom Telindus → Mainframe Fin. Force → Kennisbank Browser in Branches & online (PC) Server park (Unix) Central Servers (mainframe, Unix)
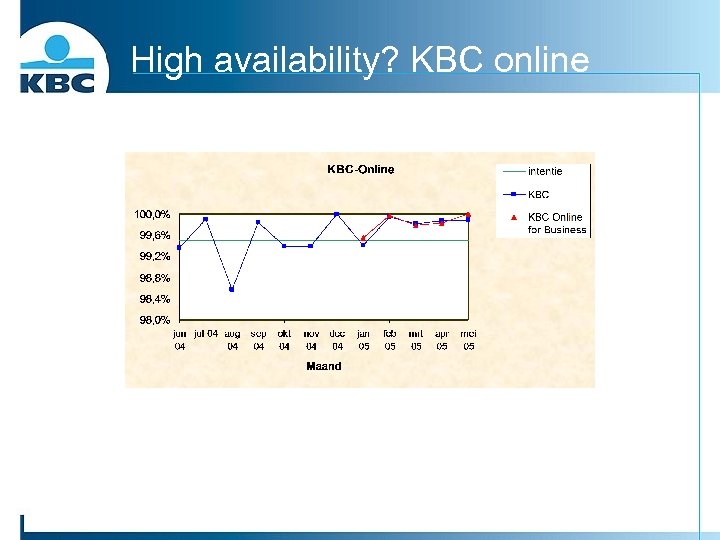
High availability? KBC online
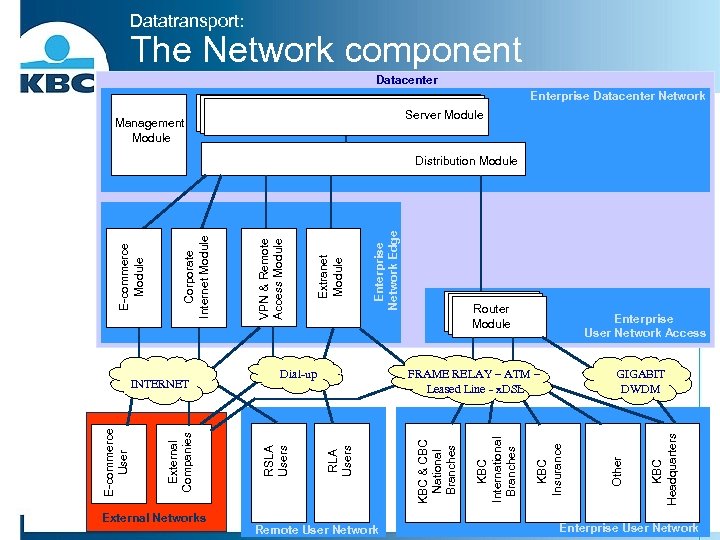
Datatransport: The Network component Datacenter Enterprise Datacenter Network Server Module Management Module External Networks Router Module Enterprise User Network Access Remote User Network KBC Insurance KBC International Branches KBC & CBC National Branches KBC Headquarters GIGABIT DWDM FRAME RELAY – ATM – Leased Line - x. DSL Other Enterprise Network Edge Extranet Module VPN & Remote Access Module Dial-up RLA Users External Companies E-commerce User INTERNET RSLA Users Corporate Internet Module E-commerce Module Distribution Module Enterprise User Network
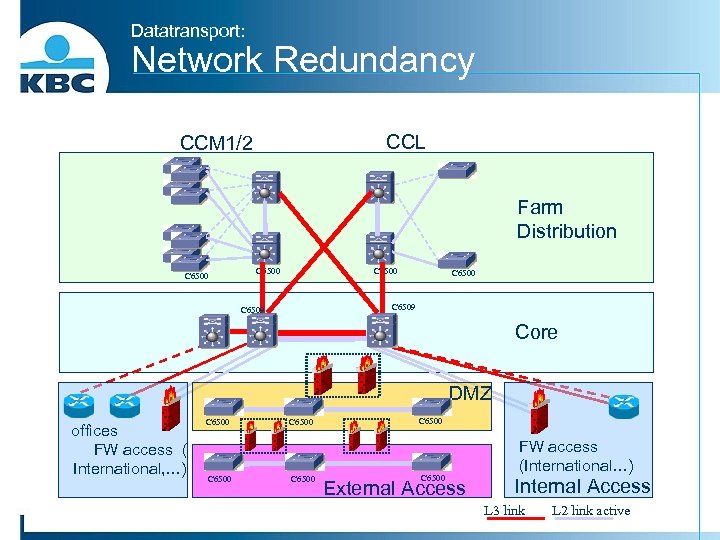
Datatransport: Network Redundancy CCL CCM 1/2 Farm Distribution C 6500 C 6509 Core DMZ offices FW access ( International, …) C 6500 C 6500 External Access FW access (International…) Internal Access L 3 link L 2 link active
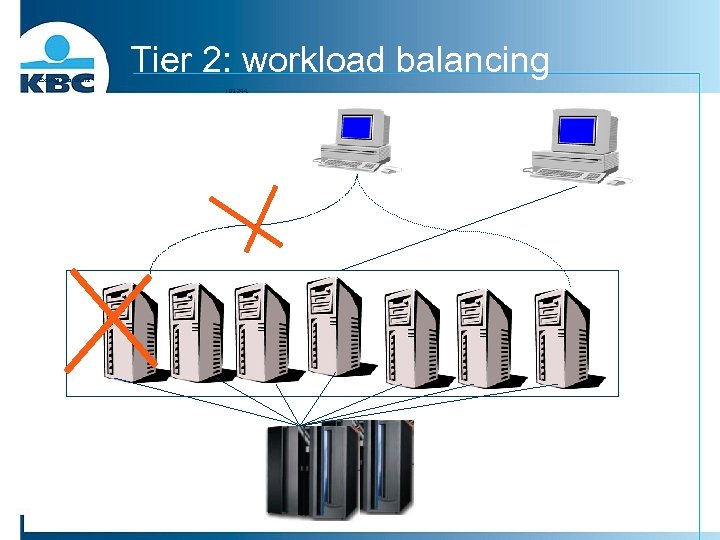
Externe gebruikers Tier 2: workload balancing 193. 244.
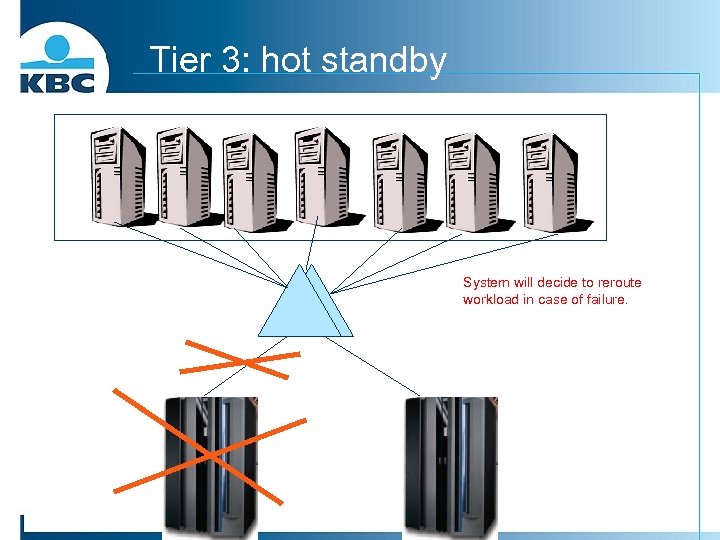
Tier 3: hot standby System will decide to reroute workload in case of failure.
Data center: facilities n Physical admittance control n Redundant power supply n Diesel power generator, nobreak installation (batteries)

WHAT does HA mean to KBC ? n Theory …. 1. 2. 3. 4. n What is (high) availability and why do we care ? What does availability depend on ? How and why do we measure availability ? What does it cost <> what profit do we get? … and reality l l High availability@KBC DRP@KBC
DRP@KBC The handling of incidents that might result in the unavailability of a complete computer center or some of its vital parts.

Our disaster recovery plan?
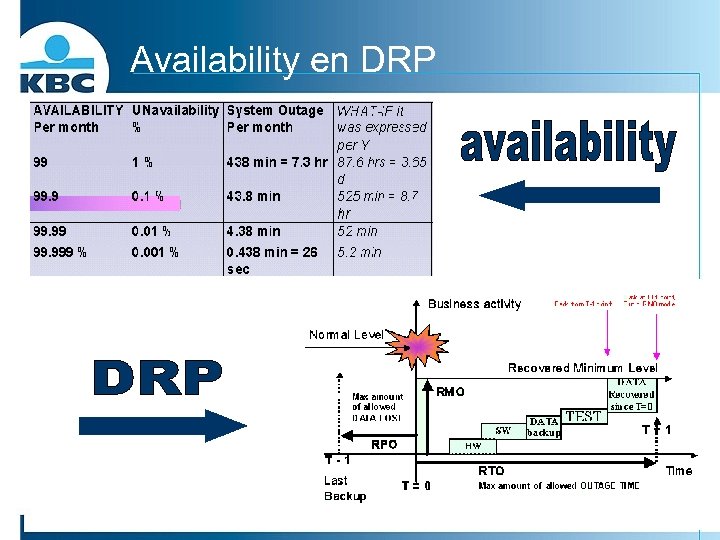
Availability en DRP
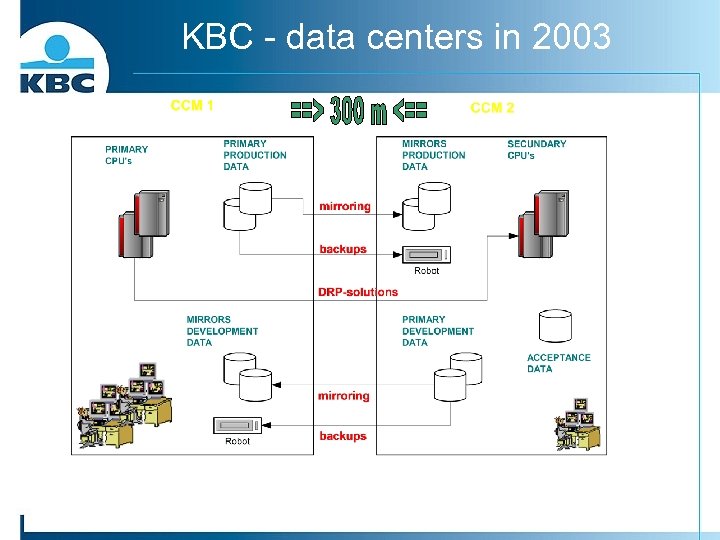
KBC - data centers in 2003
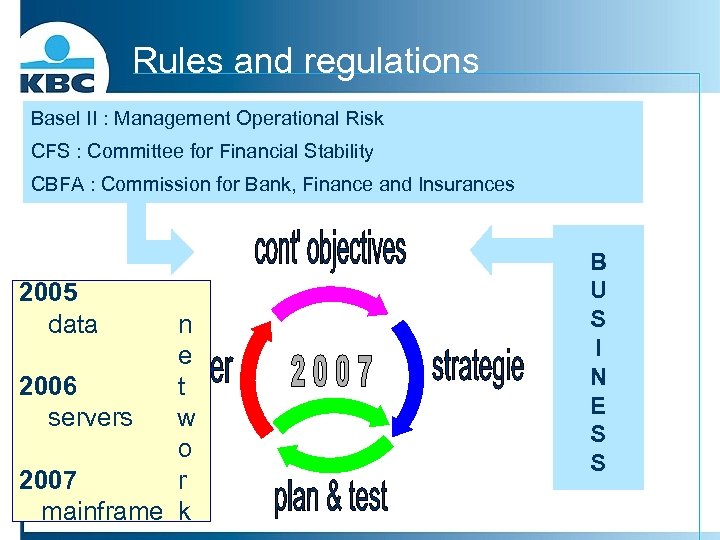
Rules and regulations Basel II : Management Operational Risk CFS : Committee for Financial Stability CBFA : Commission for Bank, Finance and Insurances 2005 data n e 2006 t servers w o 2007 r mainframe k B U S I N E S S
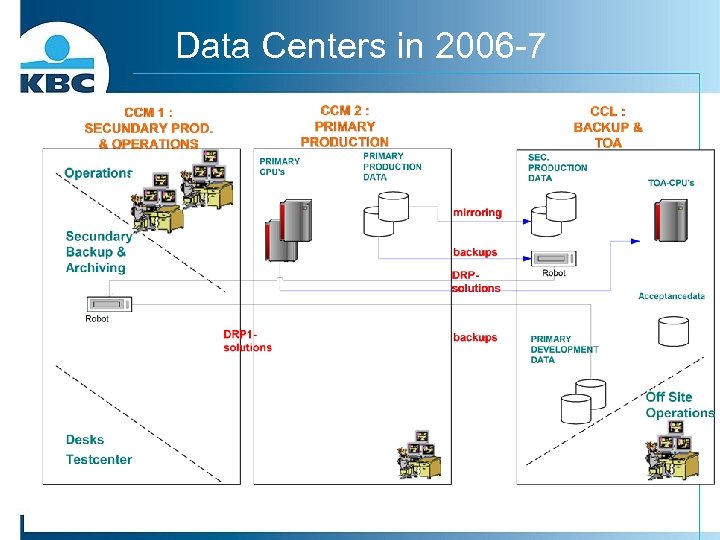
Data Centers in 2006 -7

Questions & Answer

Agenda Introduction KBC Group ICT High Availability Vision on HR Questions & Answers Guided Tour
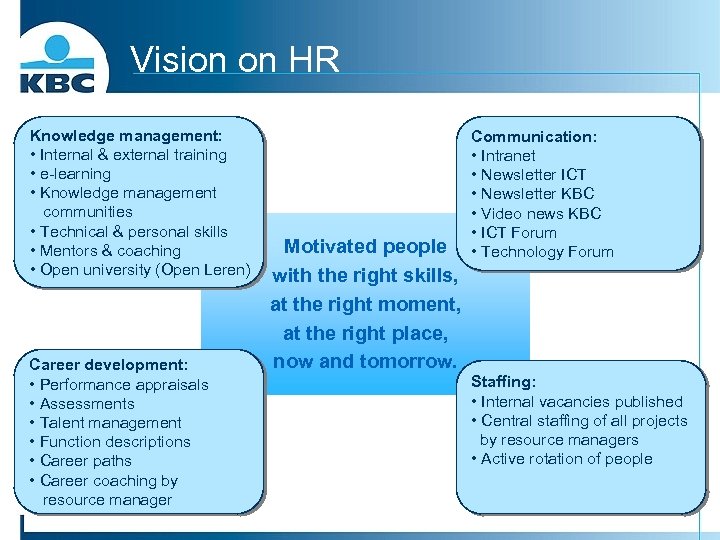
Vision on HR Knowledge management: • Internal & external training • e-learning • Knowledge management communities • Technical & personal skills • Mentors & coaching • Open university (Open Leren) Career development: • Performance appraisals • Assessments • Talent management • Function descriptions • Career paths • Career coaching by resource manager Motivated people with the right skills, at the right moment, at the right place, now and tomorrow. Communication: • Intranet • Newsletter ICT • Newsletter KBC • Video news KBC • ICT Forum • Technology Forum Staffing: • Internal vacancies published • Central staffing of all projects by resource managers • Active rotation of people

Waarom werken in KBC ICT? n KBC ICT is één van de grootste ICT-organisaties in België n Groot bedrijf met veel mogelijkheden in ICT en business n KBC investeert in opleiding en loopbaanbegeleiding n Nieuwste evoluties in technologieën en methoden n Ruimte voor specialisten en generalisten n Internationale mogelijkheden n Imago KBC
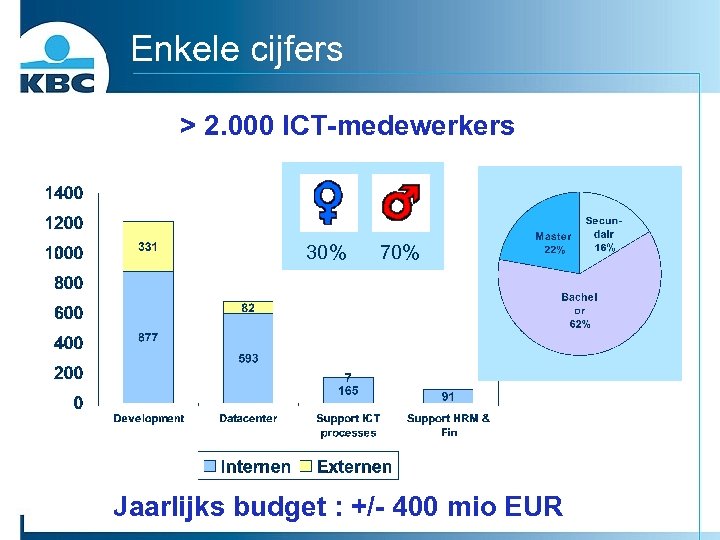
Enkele cijfers > 2. 000 ICT-medewerkers 30% 70% Jaarlijks budget : +/- 400 mio EUR
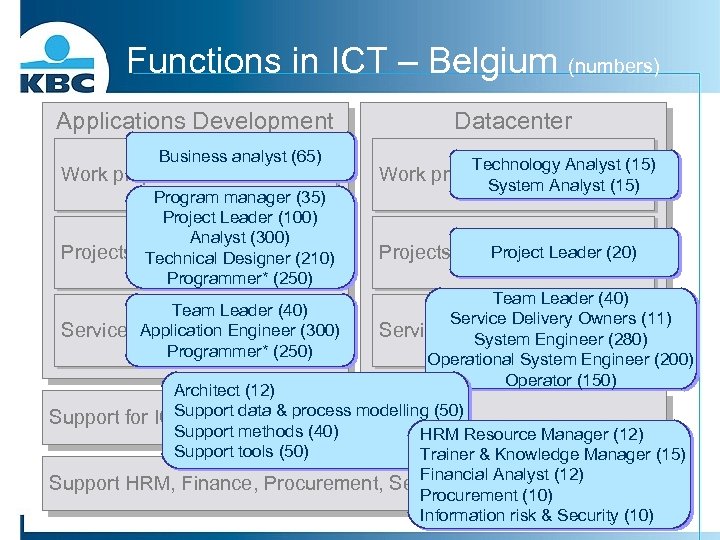
Functions in ICT – Belgium (numbers) Applications Development Business analyst (65) Work preparation Program manager (35) Project Leader (100) Analyst (300) Projects Technical Designer (210) Programmer* (250) Team Leader (40) Service Application Engineer (300) Programmer* (250) Datacenter Technology Analyst (15) Work preparation Analyst (15) System Projects Project Leader (20) Team Leader (40) Service Delivery Owners (11) Service System Engineer (280) Operational System Engineer (200) Operator (150) Architect (12) Support data & process Support for ICT processes & tools modelling (50) Support methods (40) HRM Resource Manager (12) Support tools (50) Trainer & Knowledge Manager (15) Financial Analyst (12) Support HRM, Finance, Procurement, Security, Communication Procurement (10) Information risk & Security (10)
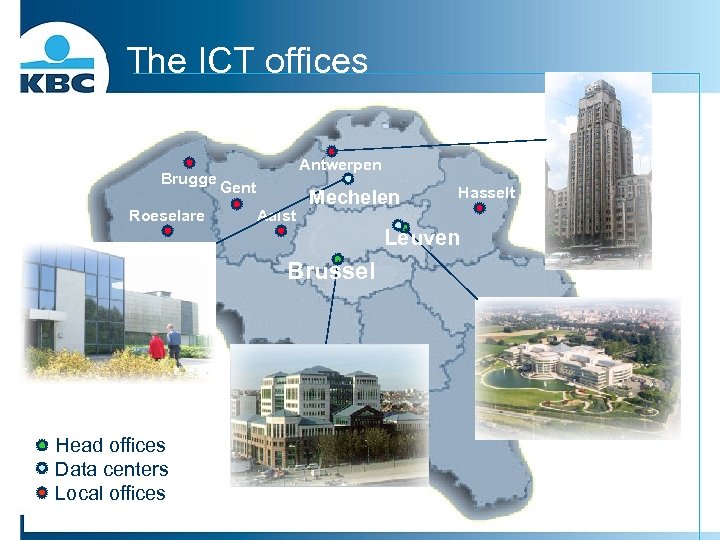
The ICT offices Brugge Roeselare Antwerpen Gent Aalst Mechelen Hasselt Leuven Brussel Head offices Data centers Local offices
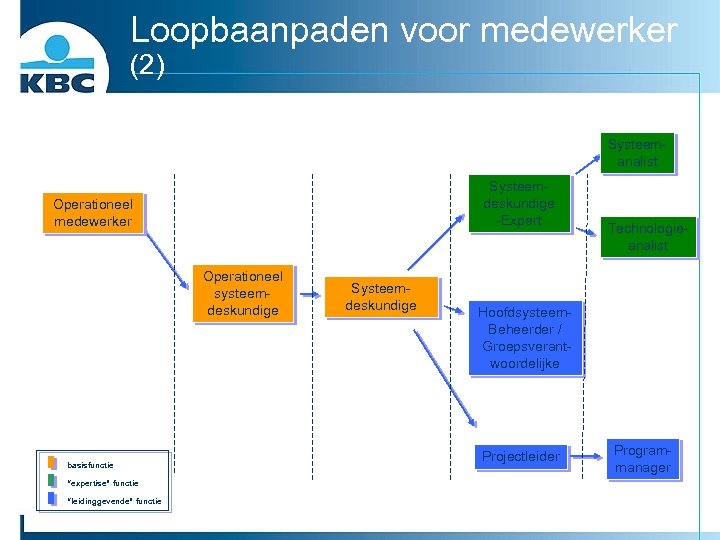
Loopbaanpaden voor medewerker (2) Systeemanalist Systeemdeskundige -Expert Operationeel medewerker Operationeel systeemdeskundige basisfunctie “expertise” functie “leidinggevende” functie Systeemdeskundige Technologieanalist Hoofdsysteem. Beheerder / Groepsverantwoordelijke Projectleider Programmanager

Agenda Introduction KBC Group ICT High Availability Vision on HR Questions & Answers Guided Tour

Questions & Answer

Agenda Introduction KBC Group ICT High Availability Vision on HR Questions & Answers Guided Tour

Guided Tour n Datacenter Mechelen l l l n CCM 1 (1977) - 936 m² computerzaal - Technische ruimtes (diesel, batterijen, cooling, …) - Bureau ruimtes - Controle toren CCM 2 (1994) - 648 m², 162 m² and 486 m² computerzaal (MF, Telecom, Servers Unix & Intel) - Technische ruimtes (diesel, …. ) - Call desk (28. 000 calls/maand) - Bureau ruimte Logistiek Centrum 2003/2004 - Print & Copy - Verzending - Archief Restaurant l Een natje en een droogje

KBC werft 150 ICT-ers aan in 2007 Zin om te groeien ? Solliciteren kan via mail met CV naar ictjobs@kbc. be of via www. kbc. be/jobs Wat bieden we? n n n Een ruim opleidingsaanbod en doorgroeimogelijkheden in ICT en business Ruimte voor specialisten en generalisten Een professionele ICT-omgeving met een ruime waaier aan technologieën, processen en business projecten Lokale en internationale mogelijkheden Een competitieve verloning met extralegale voordelen
40c312bff43cad123e707d12e155644c.ppt