ff1157da304c2cee947d06f89c73d2d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Hidden Advertising in Latvian media
Hidden Advertising in Latvian media
 Lesson overview n n n n Advertisers’ interests Public’s interests Media’s interests Ethics and Law Is hidden advertising corruption? Indications of hidden advertising Latvian cases Discussion
Lesson overview n n n n Advertisers’ interests Public’s interests Media’s interests Ethics and Law Is hidden advertising corruption? Indications of hidden advertising Latvian cases Discussion
 Advertiser’s interests Advertising - major source of financing for media companies (other main sources: sales of newspapers, subscription fee, state support) n n Advertisers use media to present goods and services in a positive light Advertisers pay media that deliver the right kind of audience for their advertisement. n Advertisers like media that focus on information that could increase their sales (bad drinking water – mineral water, problems in state hospitals – private hospitals, pollution – cars? ) n
Advertiser’s interests Advertising - major source of financing for media companies (other main sources: sales of newspapers, subscription fee, state support) n n Advertisers use media to present goods and services in a positive light Advertisers pay media that deliver the right kind of audience for their advertisement. n Advertisers like media that focus on information that could increase their sales (bad drinking water – mineral water, problems in state hospitals – private hospitals, pollution – cars? ) n
 Advertiser’s interests Advertisers want to get the best effect - difference in putting the ad as an island, in the beginning, middle or end of a block of ads be exclusive, be frequent and be regular n Advertisers dream of being invited to TV and radio programs as competent guests, to be able to address a wider audience without having the “ad tag” n Advertisers can never pay for hidden advertising to media that does not want to have money for hidden advertising n
Advertiser’s interests Advertisers want to get the best effect - difference in putting the ad as an island, in the beginning, middle or end of a block of ads be exclusive, be frequent and be regular n Advertisers dream of being invited to TV and radio programs as competent guests, to be able to address a wider audience without having the “ad tag” n Advertisers can never pay for hidden advertising to media that does not want to have money for hidden advertising n
 Public’s interests The public want to trust the information from the media companies n If the public can trust, they must believe that editorial-journalistic material is made in an independent and unbiased manner n The public must thus know when they read/watch/listen to editorial/journalistic information and when they read/watch/listen to ads n
Public’s interests The public want to trust the information from the media companies n If the public can trust, they must believe that editorial-journalistic material is made in an independent and unbiased manner n The public must thus know when they read/watch/listen to editorial/journalistic information and when they read/watch/listen to ads n
 Public’s interests If the public don’t feel the division or firewall between journalism and advertising they will loose trust in information from media companies, possibly stop to buy it n A public that doesn’t know what is ads and what is journalistic material does not have the preconditions for making up their minds and making decision in an independent manner n If the public can not make independent decision, a democracy can not function n
Public’s interests If the public don’t feel the division or firewall between journalism and advertising they will loose trust in information from media companies, possibly stop to buy it n A public that doesn’t know what is ads and what is journalistic material does not have the preconditions for making up their minds and making decision in an independent manner n If the public can not make independent decision, a democracy can not function n
 Media interests n n Media can serve the advertisers or serve the public Media’s role is primarily to serve the public Media is supposed to divide advertising and news material and not masquerade advertising as news n In serving the public and making honest and impartial news media makes all decisions on the program or story themselves, including whom to interview, topic selection, research, script writing and final editing without influence from anybody from outside n
Media interests n n Media can serve the advertisers or serve the public Media’s role is primarily to serve the public Media is supposed to divide advertising and news material and not masquerade advertising as news n In serving the public and making honest and impartial news media makes all decisions on the program or story themselves, including whom to interview, topic selection, research, script writing and final editing without influence from anybody from outside n
 Key question n Whose pressure is the strongest? n n n the pressure from the advertisers? the pressure from the public? the pressure from the media?
Key question n Whose pressure is the strongest? n n n the pressure from the advertisers? the pressure from the public? the pressure from the media?
 Open and Hidden Advertising Open advertising is information about commercial goods and services, people, politicians and others that is placed in a newspaper, internet portal, radio or TV program and is clearly divided from journalistic information visually and or by sound and that is paid for officially. n Hidden advertising is to positively or negatively report about commercial goods and services, people, politicians and others against pay or other agreement and not as a result of a journalistic evaluation n
Open and Hidden Advertising Open advertising is information about commercial goods and services, people, politicians and others that is placed in a newspaper, internet portal, radio or TV program and is clearly divided from journalistic information visually and or by sound and that is paid for officially. n Hidden advertising is to positively or negatively report about commercial goods and services, people, politicians and others against pay or other agreement and not as a result of a journalistic evaluation n
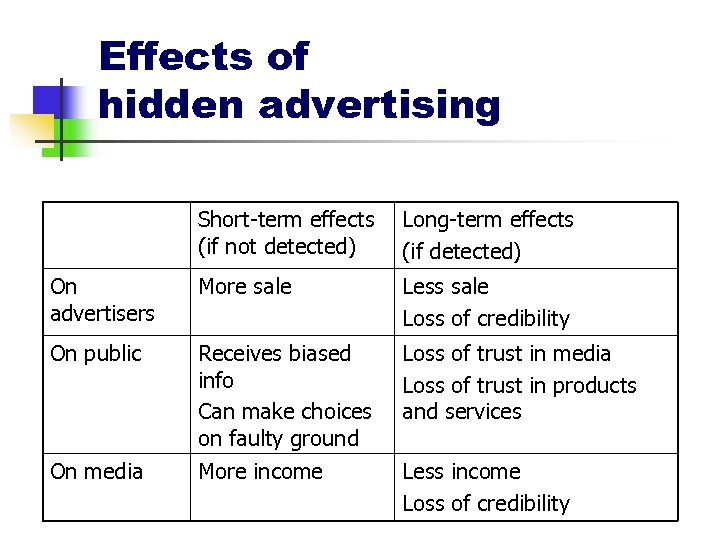 Effects of hidden advertising Short-term effects (if not detected) Long-term effects (if detected) On advertisers More sale Less sale Loss of credibility On public Receives biased info Can make choices on faulty ground Loss of trust in media Loss of trust in products and services On media More income Less income Loss of credibility
Effects of hidden advertising Short-term effects (if not detected) Long-term effects (if detected) On advertisers More sale Less sale Loss of credibility On public Receives biased info Can make choices on faulty ground Loss of trust in media Loss of trust in products and services On media More income Less income Loss of credibility
 Key questions Will the public be wise and educated enough to detect hidden advertising? n Will media be ethical and strong enough to resist temptations of possible short-term financial profits? n
Key questions Will the public be wise and educated enough to detect hidden advertising? n Will media be ethical and strong enough to resist temptations of possible short-term financial profits? n
 Media Ethics and Latvian Laws n n n Code of ethics Law on Advertising Law on Radio and TV
Media Ethics and Latvian Laws n n n Code of ethics Law on Advertising Law on Radio and TV
 Code of Ethics n Not make advertising as story Not give signals to advertisers and sponsors that they can get a favorable story about themselves if they provide a big ad or sponsor a program n n Not take orders from people outside the editorial staff n Not mention events that carry sponsor’s name n Not wear sponsored clothes or cars n Not accept any other advantages from possible advertisers or sponsors
Code of Ethics n Not make advertising as story Not give signals to advertisers and sponsors that they can get a favorable story about themselves if they provide a big ad or sponsor a program n n Not take orders from people outside the editorial staff n Not mention events that carry sponsor’s name n Not wear sponsored clothes or cars n Not accept any other advantages from possible advertisers or sponsors
 Code of Ethics n Not accept pay or any other benefits for interviewing people n Not use directly and uncritically PR material n Freelancers must inform about incomes for programs that they make n Not use false news and photos to make negative stories about competitors Not keep quiet about matters subject to critical comments because of pressure from advertisers and sponsors n n Not show only one side of a story due to pressure from advertisers or sponsors
Code of Ethics n Not accept pay or any other benefits for interviewing people n Not use directly and uncritically PR material n Freelancers must inform about incomes for programs that they make n Not use false news and photos to make negative stories about competitors Not keep quiet about matters subject to critical comments because of pressure from advertisers and sponsors n n Not show only one side of a story due to pressure from advertisers or sponsors
 Latvian Law on Advertising The distributer of the advertisement must divide the advertisement from other forms of information n
Latvian Law on Advertising The distributer of the advertisement must divide the advertisement from other forms of information n
 Latvian Law on Radio and TV Advertising and TV shop can not exceed 20 % of the total broadcasting time per day. The advertising time can not exceed 15 % of the total broadcasting time per day n The broadcasting time for advertising and TV shop can not exceed 20 % (12 minutes) per hour. In programs defined as National Order program the percentage can not exceed 10 (6 minutes) n n Hidden advertising and hidden TV shop is illegal Except for self-advertising it is not legal in advertising and TV shop to use the image and voice material of persons that on a regular basis head the news report or other programs focusing on current problems in the society n
Latvian Law on Radio and TV Advertising and TV shop can not exceed 20 % of the total broadcasting time per day. The advertising time can not exceed 15 % of the total broadcasting time per day n The broadcasting time for advertising and TV shop can not exceed 20 % (12 minutes) per hour. In programs defined as National Order program the percentage can not exceed 10 (6 minutes) n n Hidden advertising and hidden TV shop is illegal Except for self-advertising it is not legal in advertising and TV shop to use the image and voice material of persons that on a regular basis head the news report or other programs focusing on current problems in the society n
 Latvian Law on Radio and TV n. If a program is sponsored, this has to clearly shown at the start or in the end of the program by giving the name of the sponsor and the company’s logo The sponsor can not influence the content and the choice of time of distribution of the sponsored program and thus limiting the broadcasting organization’s editorial independence n In the sponsored program it is not allowed to advertise products or services of the sponsorer including direct or invitational signs regarding the purchase or rent of the product or service n It is prohibited to sponsor news (except for narrow tematic news) (!) or programs focusing on current problems in the society n
Latvian Law on Radio and TV n. If a program is sponsored, this has to clearly shown at the start or in the end of the program by giving the name of the sponsor and the company’s logo The sponsor can not influence the content and the choice of time of distribution of the sponsored program and thus limiting the broadcasting organization’s editorial independence n In the sponsored program it is not allowed to advertise products or services of the sponsorer including direct or invitational signs regarding the purchase or rent of the product or service n It is prohibited to sponsor news (except for narrow tematic news) (!) or programs focusing on current problems in the society n
 Is hidden advertising corruption? Medical corruption – we pay one official sum to get treatment, pay another sum unofficially to avoid lines and get a better treatment n Construction corruption – companies pay one official sum to take part in a construction competition, pay another sum unofficially to win the competition n Media corruption – advertisers pay one sum officially for ads, another sum unofficially for hidden advertising to get better sales n
Is hidden advertising corruption? Medical corruption – we pay one official sum to get treatment, pay another sum unofficially to avoid lines and get a better treatment n Construction corruption – companies pay one official sum to take part in a construction competition, pay another sum unofficially to win the competition n Media corruption – advertisers pay one sum officially for ads, another sum unofficially for hidden advertising to get better sales n
 Indicators of hidden advertising It does not have to be hidden advertising, could also be poor journalism, the more systematic the more suspicious n
Indicators of hidden advertising It does not have to be hidden advertising, could also be poor journalism, the more systematic the more suspicious n
 Indicators of hidden advertising n A) the material is one-sided or uncritical In the interview there are only pleasant questions or only unpleasant questions, the attitude of the journalist is seen, shaking his head, moving his head etc. n In the material there is very often refered to unofficial information, to unanimous sources n Very often emotional words are used in the program/story, positive or negative, praising or slaughtering n
Indicators of hidden advertising n A) the material is one-sided or uncritical In the interview there are only pleasant questions or only unpleasant questions, the attitude of the journalist is seen, shaking his head, moving his head etc. n In the material there is very often refered to unofficial information, to unanimous sources n Very often emotional words are used in the program/story, positive or negative, praising or slaughtering n
 Indicators of hidden advertising n A) the material is one-sided or uncritical There is information only about what one part of the story or program thinks n There is an invitation to support or not to support somebody or something, or to buy or not to buy something n
Indicators of hidden advertising n A) the material is one-sided or uncritical There is information only about what one part of the story or program thinks n There is an invitation to support or not to support somebody or something, or to buy or not to buy something n
 Indicators of hidden advertising B) The material shows up without a clear, obvious reason other than to popularize or slander a person or a product, here the word obvious refers to the context, what does the media usually make stories about for the informed reader, spectator, listener, based on what people generally would understand is current and important n A person, party or company is very often reflected or portrayed in a very positive or negative way, huge coverage for events of giving n There is much information about a person’s life that is not connected to his professional job n
Indicators of hidden advertising B) The material shows up without a clear, obvious reason other than to popularize or slander a person or a product, here the word obvious refers to the context, what does the media usually make stories about for the informed reader, spectator, listener, based on what people generally would understand is current and important n A person, party or company is very often reflected or portrayed in a very positive or negative way, huge coverage for events of giving n There is much information about a person’s life that is not connected to his professional job n
 Indicators of hidden advertising n PR material is used in the program Advertising visually and in other respect copies or looks like a normal journalistic story/program and is not clearly presented as advertising n Advertising for a company or party appear visually or in other ways in the background when a report is made n A person is reguarly invited to give expert comments in his field of operations when there are other well-qualified experts on the market, as well – bank directors, politicians n
Indicators of hidden advertising n PR material is used in the program Advertising visually and in other respect copies or looks like a normal journalistic story/program and is not clearly presented as advertising n Advertising for a company or party appear visually or in other ways in the background when a report is made n A person is reguarly invited to give expert comments in his field of operations when there are other well-qualified experts on the market, as well – bank directors, politicians n
 Indicators of hidden advertising C) Sponsoring of thematic news or current programs where a representative from the company or linked to the company sponsoring the program takes part or a person speaking positively about the company or something that could be in the interest of the company sponsoring the program takes part, examples beer company reps, bank reps, restaurant reps, local governments n
Indicators of hidden advertising C) Sponsoring of thematic news or current programs where a representative from the company or linked to the company sponsoring the program takes part or a person speaking positively about the company or something that could be in the interest of the company sponsoring the program takes part, examples beer company reps, bank reps, restaurant reps, local governments n
 Latvian cases n n Election cases Other cases
Latvian cases n n Election cases Other cases
 Pre-election monitoring 2001 Monitoring of the Latvian 12 national and regional newspapers as well as 4 national TV stations prior to the local elections n Monitoring organized by the Soros Foundation and Delna (Transparency International Latvia) n Press monitored from February 10 – March 10, 2001 n TV stations monitored from February 28 – March 12 n Final day of local elections: March 11 n
Pre-election monitoring 2001 Monitoring of the Latvian 12 national and regional newspapers as well as 4 national TV stations prior to the local elections n Monitoring organized by the Soros Foundation and Delna (Transparency International Latvia) n Press monitored from February 10 – March 10, 2001 n TV stations monitored from February 28 – March 12 n Final day of local elections: March 11 n
 Pre-election monitoring 2001 Objective: To monitor the press or TV stations in the preelection period in order to find out whethere is journalistic material that can be classified as hidden political advertising n Journalists’ comments and editorials were not analyzed n Found cases do not immediate imply that they are hidden political advertising, but they show that professional and ethical principals in journalism have been broken that again can be both a result of ‘buying the media’ and/or lack of professionalism. n
Pre-election monitoring 2001 Objective: To monitor the press or TV stations in the preelection period in order to find out whethere is journalistic material that can be classified as hidden political advertising n Journalists’ comments and editorials were not analyzed n Found cases do not immediate imply that they are hidden political advertising, but they show that professional and ethical principals in journalism have been broken that again can be both a result of ‘buying the media’ and/or lack of professionalism. n
 TV monitoring 2001 n TV monitoring of: n n Latvian State TV – Program 1 (LTV-1) Latvian State TV – Program 2 (LTV-2) Latvian Independent TV – (LNT) TV 3 111 videotapes with all programs except for series and entertainment programs where politicians did not take part – totally approximately 20 000 minutes – monitored by Vidzeme students n
TV monitoring 2001 n TV monitoring of: n n Latvian State TV – Program 1 (LTV-1) Latvian State TV – Program 2 (LTV-2) Latvian Independent TV – (LNT) TV 3 111 videotapes with all programs except for series and entertainment programs where politicians did not take part – totally approximately 20 000 minutes – monitored by Vidzeme students n
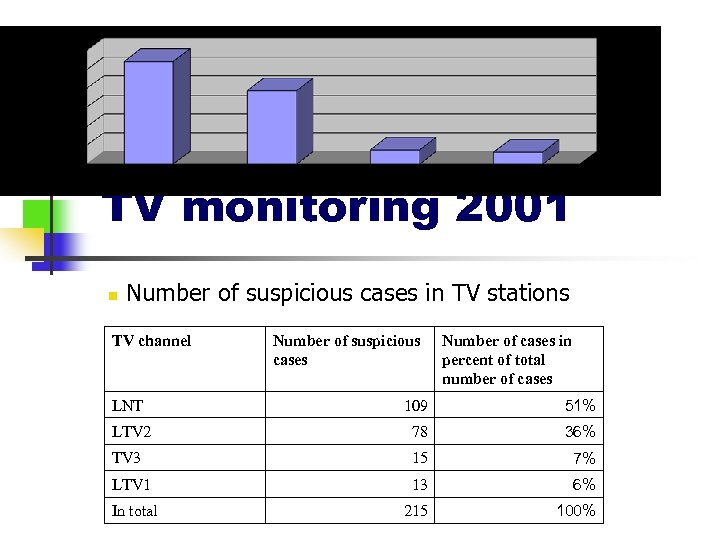 TV monitoring 2001 n Number of suspicious cases in TV stations TV channel Number of suspicious cases Number of cases in percent of total number of cases LNT 109 51% LTV 2 78 36% TV 3 15 7% LTV 1 13 6% In total 215 100%
TV monitoring 2001 n Number of suspicious cases in TV stations TV channel Number of suspicious cases Number of cases in percent of total number of cases LNT 109 51% LTV 2 78 36% TV 3 15 7% LTV 1 13 6% In total 215 100%
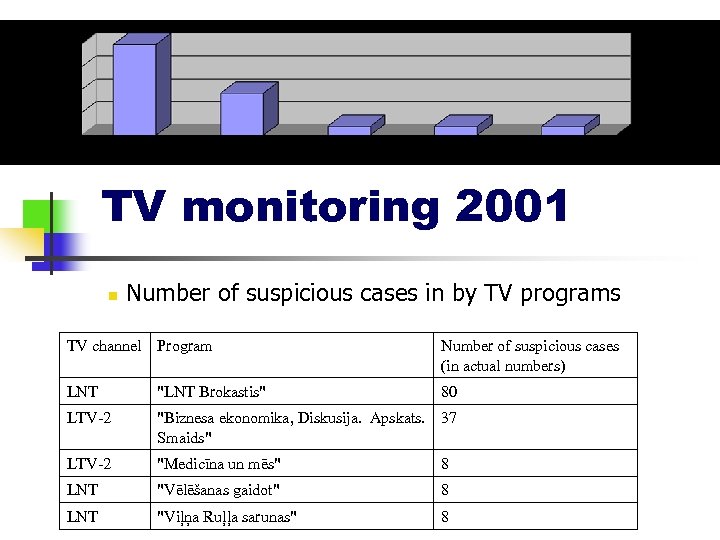 TV monitoring 2001 n Number of suspicious cases in by TV programs TV channel Program Number of suspicious cases (in actual numbers) LNT "LNT Brokastis" 80 LTV-2 "Biznesa ekonomika, Diskusija. Apskats. 37 Smaids" LTV-2 "Medicīna un mēs" 8 LNT "Vēlēšanas gaidot" 8 LNT "Viļņa Ruļļa sarunas" 8
TV monitoring 2001 n Number of suspicious cases in by TV programs TV channel Program Number of suspicious cases (in actual numbers) LNT "LNT Brokastis" 80 LTV-2 "Biznesa ekonomika, Diskusija. Apskats. 37 Smaids" LTV-2 "Medicīna un mēs" 8 LNT "Vēlēšanas gaidot" 8 LNT "Viļņa Ruļļa sarunas" 8
 TV monitoring 2001 example LTV-2 “Biznesa ekonomika. Diskusija. Apskats. Smaids. ” n several interviews with candidates from LC and TB/LNNK, candidates from PCTVL and TP not invited at all n simple and pleasant questions n portrayal interviews n superlatives used by leading journalist in describing the guests became more and more positive n advertising in the program very much look like the material in the program n
TV monitoring 2001 example LTV-2 “Biznesa ekonomika. Diskusija. Apskats. Smaids. ” n several interviews with candidates from LC and TB/LNNK, candidates from PCTVL and TP not invited at all n simple and pleasant questions n portrayal interviews n superlatives used by leading journalist in describing the guests became more and more positive n advertising in the program very much look like the material in the program n
 TV monitoring 2001 example n LNT Brokastis, Vēlēšanas gaidot, Viļņa Ruļļa sarunas, Egila Zariņa rīta mikslis, Balzams dvēselei, Egila Zariņa gardēžu klubs, Baibas Auzānes Mājas akadēmija n often the politicians were not presented as persons that are candidates for the local elections n overall easy and pleasant questions n n LNT Sunday news – Nedēļa refering to inofficial information, rumors, unanimous sources n
TV monitoring 2001 example n LNT Brokastis, Vēlēšanas gaidot, Viļņa Ruļļa sarunas, Egila Zariņa rīta mikslis, Balzams dvēselei, Egila Zariņa gardēžu klubs, Baibas Auzānes Mājas akadēmija n often the politicians were not presented as persons that are candidates for the local elections n overall easy and pleasant questions n n LNT Sunday news – Nedēļa refering to inofficial information, rumors, unanimous sources n
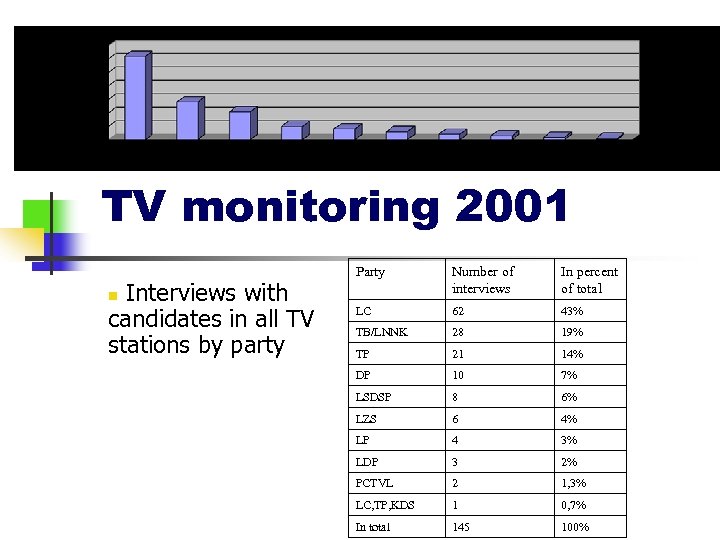 TV monitoring 2001 Interviews with candidates in all TV stations by party Party Number of interviews In percent of total LC 62 43% TB/LNNK 28 19% TP 21 14% DP 10 7% LSDSP 8 6% LZS 6 4% LP 4 3% LDP 3 2% PCTVL 2 1, 3% LC, TP, KDS 1 0, 7% In total 145 100% n
TV monitoring 2001 Interviews with candidates in all TV stations by party Party Number of interviews In percent of total LC 62 43% TB/LNNK 28 19% TP 21 14% DP 10 7% LSDSP 8 6% LZS 6 4% LP 4 3% LDP 3 2% PCTVL 2 1, 3% LC, TP, KDS 1 0, 7% In total 145 100% n
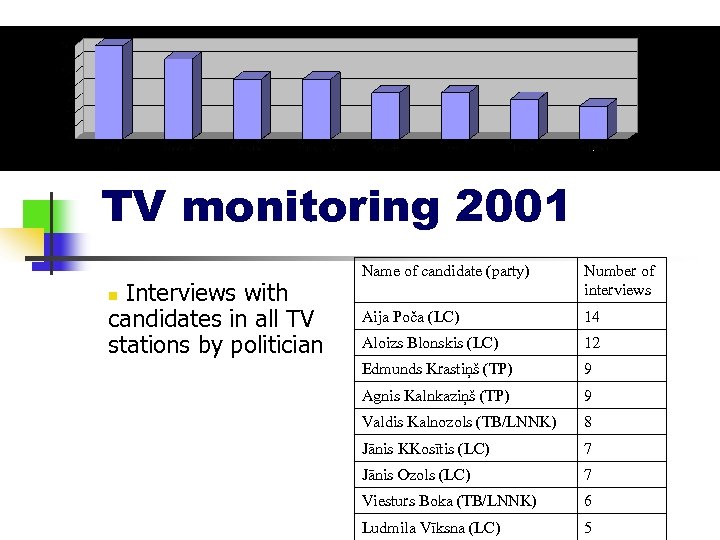 TV monitoring 2001 Interviews with candidates in all TV stations by politician Name of candidate (party) Number of interviews Aija Poča (LC) 14 Aloizs Blonskis (LC) 12 Edmunds Krastiņš (TP) 9 Agnis Kalnkaziņš (TP) 9 Valdis Kalnozols (TB/LNNK) 8 Jānis KKosītis (LC) 7 Jānis Ozols (LC) 7 Viesturs Boka (TB/LNNK) 6 Ludmila Vīksna (LC) 5 n
TV monitoring 2001 Interviews with candidates in all TV stations by politician Name of candidate (party) Number of interviews Aija Poča (LC) 14 Aloizs Blonskis (LC) 12 Edmunds Krastiņš (TP) 9 Agnis Kalnkaziņš (TP) 9 Valdis Kalnozols (TB/LNNK) 8 Jānis KKosītis (LC) 7 Jānis Ozols (LC) 7 Viesturs Boka (TB/LNNK) 6 Ludmila Vīksna (LC) 5 n
 Press monitoring 2001 n 6 national newspapers: Lauku Avīze, Diena, NRA, Rīgas Balss, Час, Панорама Латвии n n 6 regional newspapers: Liesma, Rēzeknes Vēstis, Zemgales Ziņas, Kurzemes Vārds, Ventas Balss, Миллион n
Press monitoring 2001 n 6 national newspapers: Lauku Avīze, Diena, NRA, Rīgas Balss, Час, Панорама Латвии n n 6 regional newspapers: Liesma, Rēzeknes Vēstis, Zemgales Ziņas, Kurzemes Vārds, Ventas Balss, Миллион n
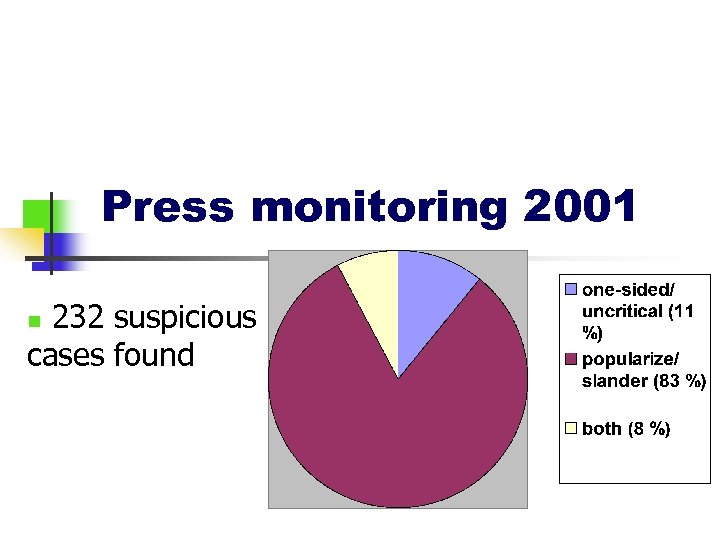 Press monitoring 2001 232 suspicious cases found n
Press monitoring 2001 232 suspicious cases found n
 Press monitoring 2001 62 % of cases in 3 Russian-language newspapers n 24 % of cases in local newspapers n
Press monitoring 2001 62 % of cases in 3 Russian-language newspapers n 24 % of cases in local newspapers n
 Press monitoring 2001 Suspicious cases in national newspapers n
Press monitoring 2001 Suspicious cases in national newspapers n
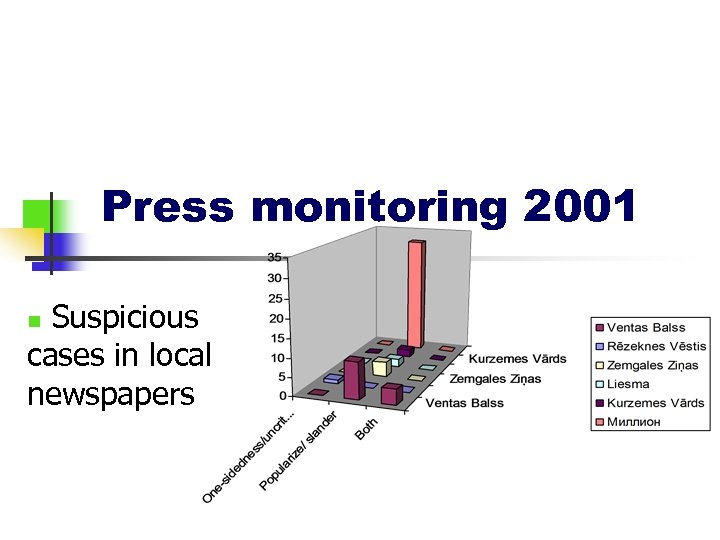 Press monitoring 2001 Suspicious cases in local newspapers n
Press monitoring 2001 Suspicious cases in local newspapers n
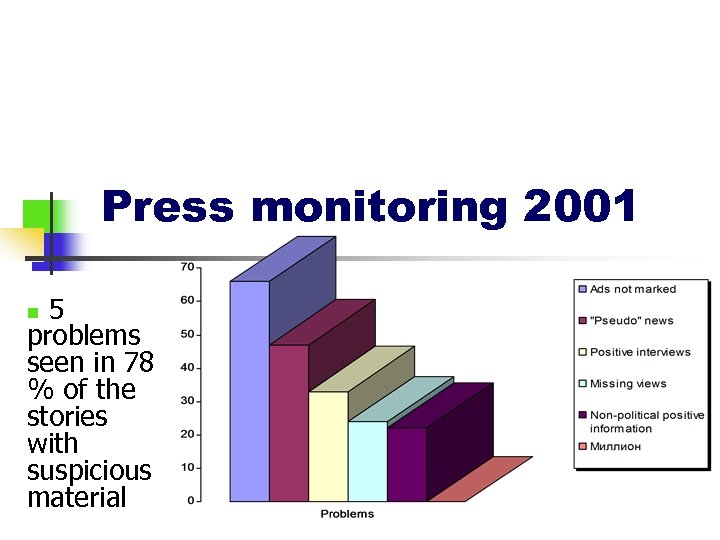 Press monitoring 2001 5 problems seen in 78 % of the stories with suspicious material n
Press monitoring 2001 5 problems seen in 78 % of the stories with suspicious material n
 Press and TV monitoring 2001 n Reactions n n n Negative articles Positive articles Threats of court case
Press and TV monitoring 2001 n Reactions n n n Negative articles Positive articles Threats of court case
 Media monitoring 2002 n Project continued Press – monitoring of 56 newspapers for 60 days (August 5 – October 5, 2002) n n n 17 national newspapers (dailies and weeklies) 39 regional/local newspapers
Media monitoring 2002 n Project continued Press – monitoring of 56 newspapers for 60 days (August 5 – October 5, 2002) n n n 17 national newspapers (dailies and weeklies) 39 regional/local newspapers
 Media monitoring 2002 n Project continued n TV – monitoring of 5 TV stations n n LTV-1, LTV-2, LNT, TV 3, TV 5 Radio – monitoring of 8 radio stations n LR 1, LR 2, LR 4, SWH+, Radio Skonto, Mix FM, PIK Random analysis from August 5 – September 3 n Analysis of all programs from September 6 – October 6 n
Media monitoring 2002 n Project continued n TV – monitoring of 5 TV stations n n LTV-1, LTV-2, LNT, TV 3, TV 5 Radio – monitoring of 8 radio stations n LR 1, LR 2, LR 4, SWH+, Radio Skonto, Mix FM, PIK Random analysis from August 5 – September 3 n Analysis of all programs from September 6 – October 6 n
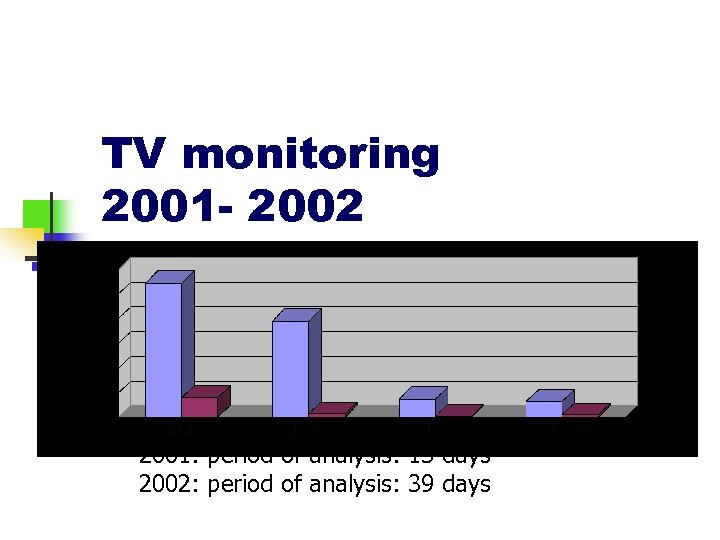 TV monitoring 2001 - 2002 2001: period of analysis: 13 days 2002: period of analysis: 39 days
TV monitoring 2001 - 2002 2001: period of analysis: 13 days 2002: period of analysis: 39 days
 Press monitoring 2001 - 2002 2001: 2002: period of analysis: 30 days 12 papers analyzed period of analysis: 60 days 56 papers analyzed
Press monitoring 2001 - 2002 2001: 2002: period of analysis: 30 days 12 papers analyzed period of analysis: 60 days 56 papers analyzed
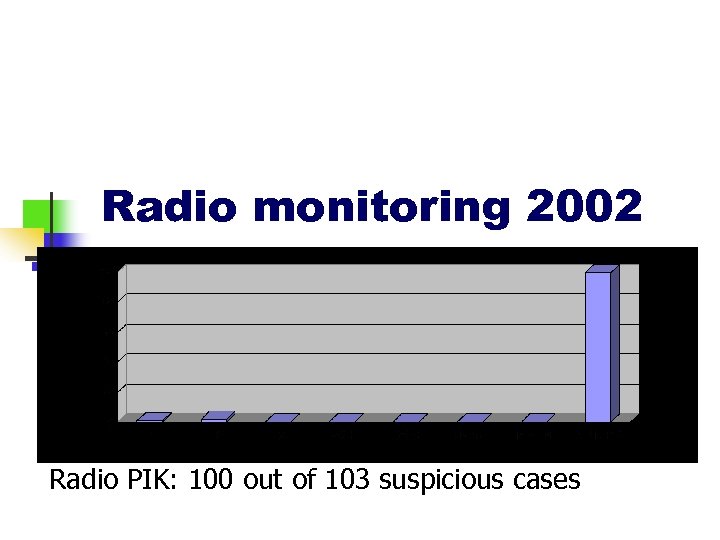 Radio monitoring 2002 Radio PIK: 100 out of 103 suspicious cases
Radio monitoring 2002 Radio PIK: 100 out of 103 suspicious cases
 Press monitoring 2002 Suspicious cases in national newspapers in Latvian
Press monitoring 2002 Suspicious cases in national newspapers in Latvian
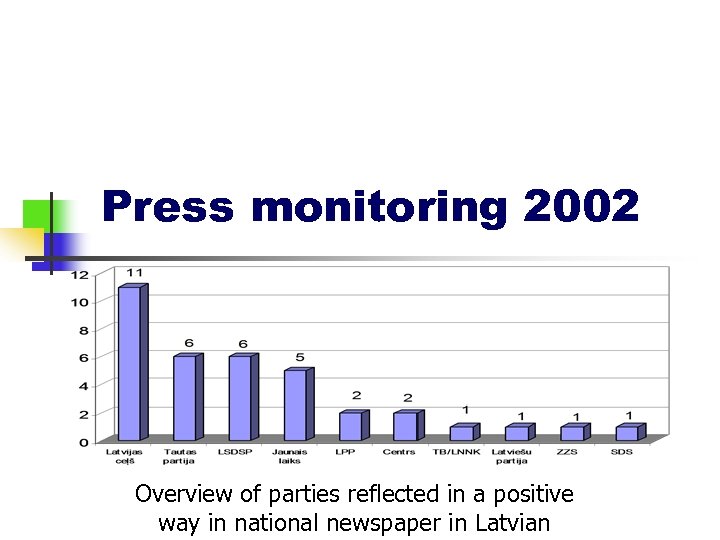 Press monitoring 2002 Overview of parties reflected in a positive way in national newspaper in Latvian
Press monitoring 2002 Overview of parties reflected in a positive way in national newspaper in Latvian
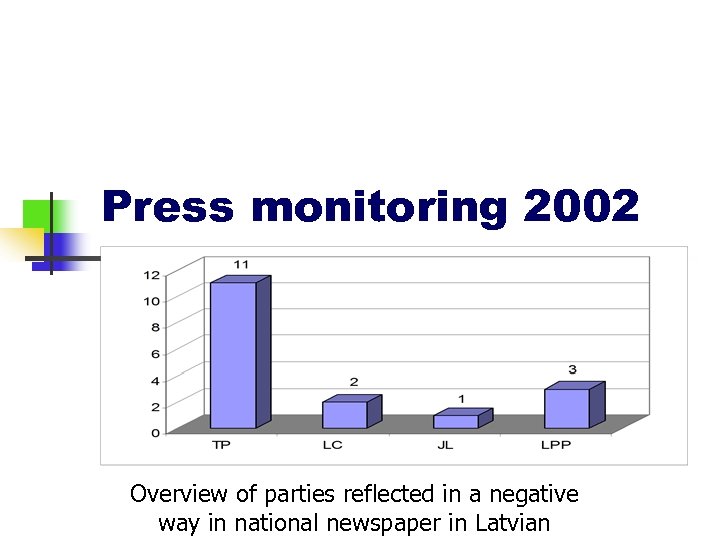 Press monitoring 2002 Overview of parties reflected in a negative way in national newspaper in Latvian
Press monitoring 2002 Overview of parties reflected in a negative way in national newspaper in Latvian
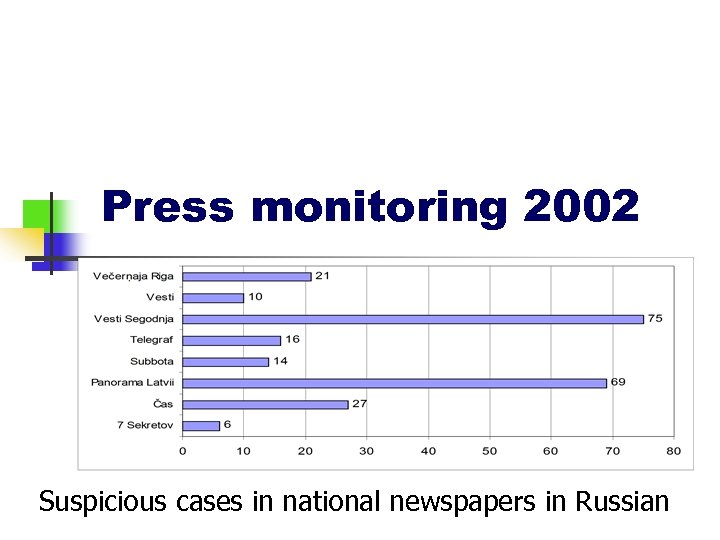 Press monitoring 2002 Suspicious cases in national newspapers in Russian
Press monitoring 2002 Suspicious cases in national newspapers in Russian
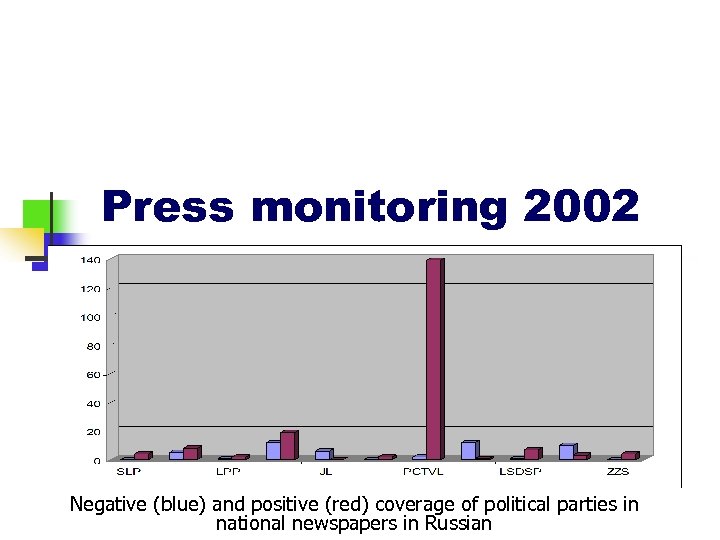 Press monitoring 2002 Negative (blue) and positive (red) coverage of political parties in national newspapers in Russian
Press monitoring 2002 Negative (blue) and positive (red) coverage of political parties in national newspapers in Russian
 Local Suspicious cases in local newspapers in Latvian n
Local Suspicious cases in local newspapers in Latvian n
 Local press monitoring 2002 Overview of parties reflected in a positive way in local newspaper in Latvian n
Local press monitoring 2002 Overview of parties reflected in a positive way in local newspaper in Latvian n
 Local press 2002 n Suspicious cases in local newspapers in Russian
Local press 2002 n Suspicious cases in local newspapers in Russian
 Local press 2002 Overview of parties reflected in a positive way in local newspaper in Russian n
Local press 2002 Overview of parties reflected in a positive way in local newspaper in Russian n
 Other cases n n n Sponsored news Interviews with ministers and mayors “Commercial news” Business people portrayals Higher educaction cases
Other cases n n n Sponsored news Interviews with ministers and mayors “Commercial news” Business people portrayals Higher educaction cases
 Discussion Relationship between media ownership and hidden advertising in Latvia and Lithuania n
Discussion Relationship between media ownership and hidden advertising in Latvia and Lithuania n
 Thank you!
Thank you!


