4a21acb2952b5000c5600d9eef1acac9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 HF Digital Communications The Sound Card Radio and FLdigi John Clements Joe Miller Brian Johnston KC 9 ON KJ 8 O W 8 TFI Stephen H. Smith John Mathieson WA 8 LMF AC 8 JW August 1, 2015
HF Digital Communications The Sound Card Radio and FLdigi John Clements Joe Miller Brian Johnston KC 9 ON KJ 8 O W 8 TFI Stephen H. Smith John Mathieson WA 8 LMF AC 8 JW August 1, 2015
 Contents Introductions Why Digital? Olivia Fldigi software
Contents Introductions Why Digital? Olivia Fldigi software
 Contents Flmsg message program Sound Card Station Hints and tips for digital operating Local traffic nets
Contents Flmsg message program Sound Card Station Hints and tips for digital operating Local traffic nets
 Introductions Joe Miller KJ 8 O SWL since 1967, first licensed in 2006 and collects QSL cards President of OCARS (W 8 TNO) MI Affiliated Club Coordinator kj 8 o@arrl. net
Introductions Joe Miller KJ 8 O SWL since 1967, first licensed in 2006 and collects QSL cards President of OCARS (W 8 TNO) MI Affiliated Club Coordinator kj 8 o@arrl. net
 Introductions John Mathieson AC 8 JW Licensed since 2004 Active in CW and digital modes jspokes@arrl. net
Introductions John Mathieson AC 8 JW Licensed since 2004 Active in CW and digital modes jspokes@arrl. net
 Introductions Brian Johnston W 8 TFI Licensed in 1976 Computer operator for a major newspaper Avid experimenter and home brewer w 8 tfi@arrl. net
Introductions Brian Johnston W 8 TFI Licensed in 1976 Computer operator for a major newspaper Avid experimenter and home brewer w 8 tfi@arrl. net
 Why Digital? Send and receive text, images, data, and audio Some modes work very well in noisy and weak signal environments If you can’t hear them you can’t work them is no longer true!
Why Digital? Send and receive text, images, data, and audio Some modes work very well in noisy and weak signal environments If you can’t hear them you can’t work them is no longer true!
 Why Digital? Some modes can provide error free or reduced error transmissions. A few provide ARQ (Automatic repeat request functions)
Why Digital? Some modes can provide error free or reduced error transmissions. A few provide ARQ (Automatic repeat request functions)
 Why Digital? Many modes use smaller bandwidths than voice 97. 1(b) contribute to the advancement of the radio art. 97. 313(a) use the minimum transmitter power necessary to carry out the desired communications.
Why Digital? Many modes use smaller bandwidths than voice 97. 1(b) contribute to the advancement of the radio art. 97. 313(a) use the minimum transmitter power necessary to carry out the desired communications.
 Digital Modes of Operation There are more digital modes than you can shake a stick at! RTTY, PSK, MFSK, Olivia, MT 63, JT 65, Contestia, Hellschreiber, Throb, Packet, WSPR, SSTV, Free. DV and many more! All these are AFSK modes
Digital Modes of Operation There are more digital modes than you can shake a stick at! RTTY, PSK, MFSK, Olivia, MT 63, JT 65, Contestia, Hellschreiber, Throb, Packet, WSPR, SSTV, Free. DV and many more! All these are AFSK modes
 MFSK 16 Like RTTY but uses 16 different frequency shifts Old technology mode - required complicated hardware before sound card software was available Speed of 78 WPM / 62. 5 baud with a 316 Hz bandwidth ARRL Bulletins are transmitted in MFSK 16
MFSK 16 Like RTTY but uses 16 different frequency shifts Old technology mode - required complicated hardware before sound card software was available Speed of 78 WPM / 62. 5 baud with a 316 Hz bandwidth ARRL Bulletins are transmitted in MFSK 16
 MFSK 16 Uses forward error correction (FEC) Typically this is done by sending redundant data The cost penalty is extra time to send the data multiple times Result is greatly reduced errors from QSB, QRN and Multipath propagation
MFSK 16 Uses forward error correction (FEC) Typically this is done by sending redundant data The cost penalty is extra time to send the data multiple times Result is greatly reduced errors from QSB, QRN and Multipath propagation
 Olivia MFSK Variant used for traffic handling Has forward error correction like MT 63 Good with QSB, QRM Will decode 10 -14 d. B below the noise floor
Olivia MFSK Variant used for traffic handling Has forward error correction like MT 63 Good with QSB, QRM Will decode 10 -14 d. B below the noise floor
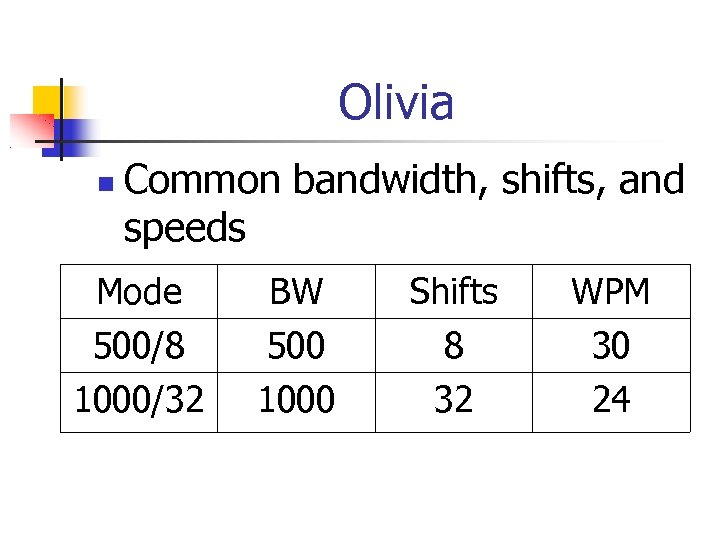 Olivia Common bandwidth, shifts, and speeds Mode 500/8 1000/32 BW 500 1000 Shifts 8 32 WPM 30 24
Olivia Common bandwidth, shifts, and speeds Mode 500/8 1000/32 BW 500 1000 Shifts 8 32 WPM 30 24
 Software Many different programs Most run on windows and Mac A few run on Linux Most are free We will look at FLdigi
Software Many different programs Most run on windows and Mac A few run on Linux Most are free We will look at FLdigi
 Software FLDigi The program of choice for EMCOMM Handles radiogram and ICS forms Note: additional software needed for these on the FLDigi site.
Software FLDigi The program of choice for EMCOMM Handles radiogram and ICS forms Note: additional software needed for these on the FLDigi site.
 Software FLDigi is FREE! Handles most modes including SSTV and We. Fax Also contains a log book and radio control
Software FLDigi is FREE! Handles most modes including SSTV and We. Fax Also contains a log book and radio control
 Getting started on FLDigi Home: HTTP: //www. w 1 hkj. com/ Downloads: HTTP: //www. w 1 hkj. com/download. html Beginners’ guide HTTP: //www. w 1 hkj. com/beginner
Getting started on FLDigi Home: HTTP: //www. w 1 hkj. com/ Downloads: HTTP: //www. w 1 hkj. com/download. html Beginners’ guide HTTP: //www. w 1 hkj. com/beginner
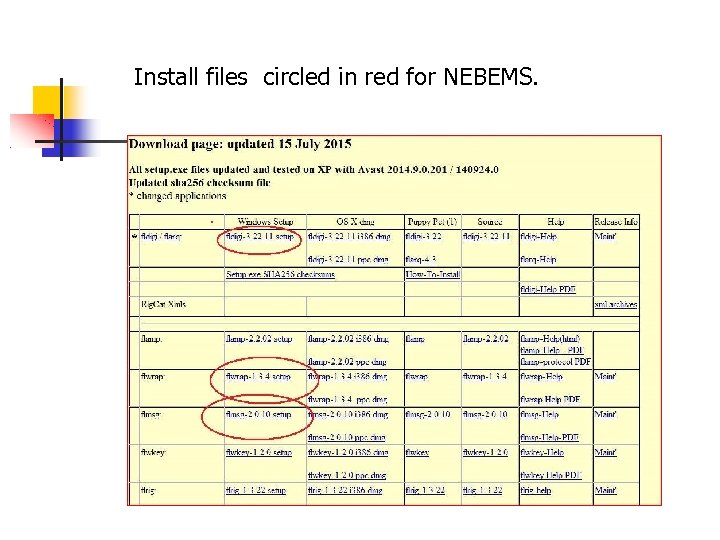 Install files circled in red for NEBEMS.
Install files circled in red for NEBEMS.
 FLdigi, FLmsg and FLwrap All are part of the NBEMS emergency management package. (Narrow Band Emergency Messaging Software)
FLdigi, FLmsg and FLwrap All are part of the NBEMS emergency management package. (Narrow Band Emergency Messaging Software)
 FLdigi Fldigi is main program and communication interface Works with multiple sound card modes Did we mention that it is free!
FLdigi Fldigi is main program and communication interface Works with multiple sound card modes Did we mention that it is free!
 Software FLdigi
Software FLdigi
 Olivia 8/500
Olivia 8/500
 Olivia 8/500
Olivia 8/500
 FLmsg Fldigi manages ICS and ARRL forms via FLmsg an attached program to FLdigi Will send CSV and files
FLmsg Fldigi manages ICS and ARRL forms via FLmsg an attached program to FLdigi Will send CSV and files
 Flmsg FLmsg allows the user to write ARRL radiograms or ICS forms and send them via one of the sound card modes.
Flmsg FLmsg allows the user to write ARRL radiograms or ICS forms and send them via one of the sound card modes.
 FLmsg It allows an almost automatic process for sending text messages and even files.
FLmsg It allows an almost automatic process for sending text messages and even files.
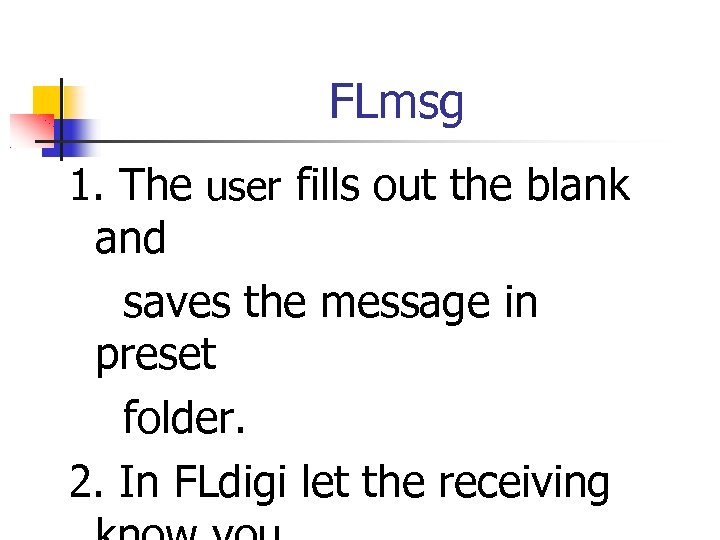 FLmsg 1. The user fills out the blank and saves the message in preset folder. 2. In FLdigi let the receiving
FLmsg 1. The user fills out the blank and saves the message in preset folder. 2. In FLdigi let the receiving
 FLmsg The message when complete will open FLmsg in the recipients computer and port the formatted message to a web browser for printing
FLmsg The message when complete will open FLmsg in the recipients computer and port the formatted message to a web browser for printing
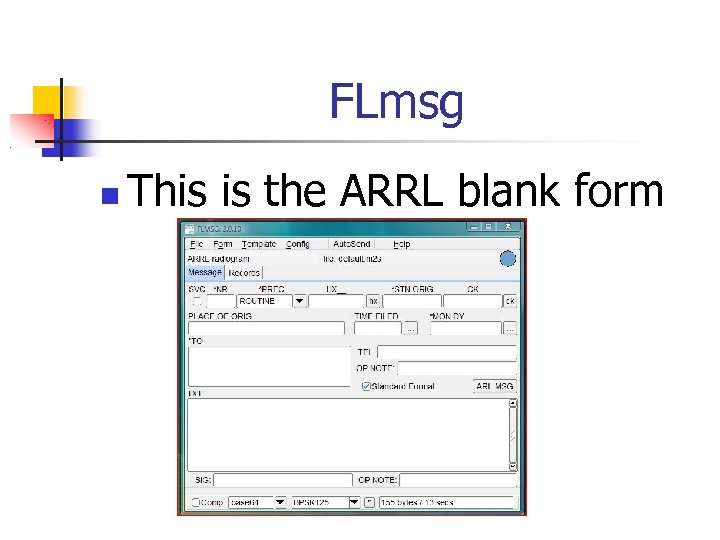 FLmsg This is the ARRL blank form
FLmsg This is the ARRL blank form
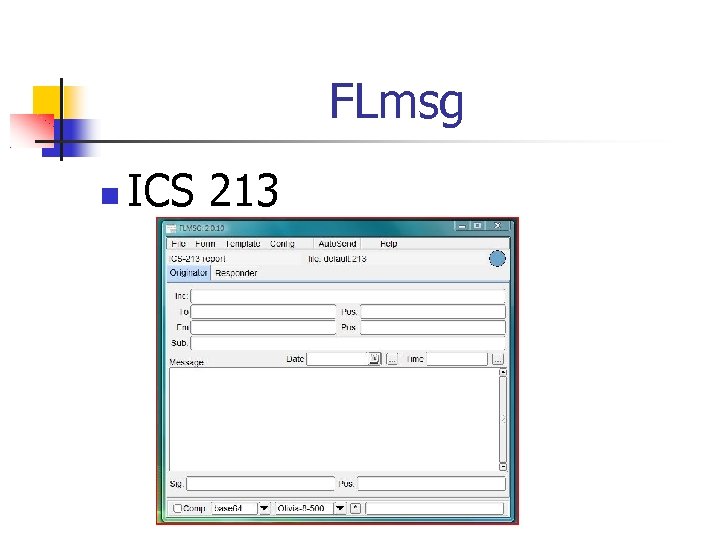 FLmsg ICS 213
FLmsg ICS 213
 Hardware Only 3 components needed Radio Computer Audio / PTT Interface Optionally a Computer Aided Tuning (CAT) interface Not required but nice to have if the radio supports it
Hardware Only 3 components needed Radio Computer Audio / PTT Interface Optionally a Computer Aided Tuning (CAT) interface Not required but nice to have if the radio supports it
 Hardware How much does it cost? Assuming you have the radio and computer……. Build your own interface from free to $25 Buy commercial interfaces from $60 -300
Hardware How much does it cost? Assuming you have the radio and computer……. Build your own interface from free to $25 Buy commercial interfaces from $60 -300
 Hardware Radio Almost any USB HF Transceiver Older mechanical analog VFO rigs may NOT be stable enough for narrow modes like PSK 31 but work well on modes like RTTY and SSTV. Newer radios with stable frequency synthesizers are best. Some high end rigs have PSK and RTTY built in!
Hardware Radio Almost any USB HF Transceiver Older mechanical analog VFO rigs may NOT be stable enough for narrow modes like PSK 31 but work well on modes like RTTY and SSTV. Newer radios with stable frequency synthesizers are best. Some high end rigs have PSK and RTTY built in!
 Hardware Computer Big and fast not required Most “XP” computers work fine! Minimum Requirements Available USB or RS-232 port Sound Card 1 GHz CPU, 100 MB free RAM 300 MB Drive space Depends on software - YMMV
Hardware Computer Big and fast not required Most “XP” computers work fine! Minimum Requirements Available USB or RS-232 port Sound Card 1 GHz CPU, 100 MB free RAM 300 MB Drive space Depends on software - YMMV
 Interfaces Receive Start today with a simple attenuator cable Parts are about $10 at Radio Shack, cheaper elsewhere! wa 8 lmf. net/miscinfo/Univers al-Sound-Card-Cable. pdf
Interfaces Receive Start today with a simple attenuator cable Parts are about $10 at Radio Shack, cheaper elsewhere! wa 8 lmf. net/miscinfo/Univers al-Sound-Card-Cable. pdf
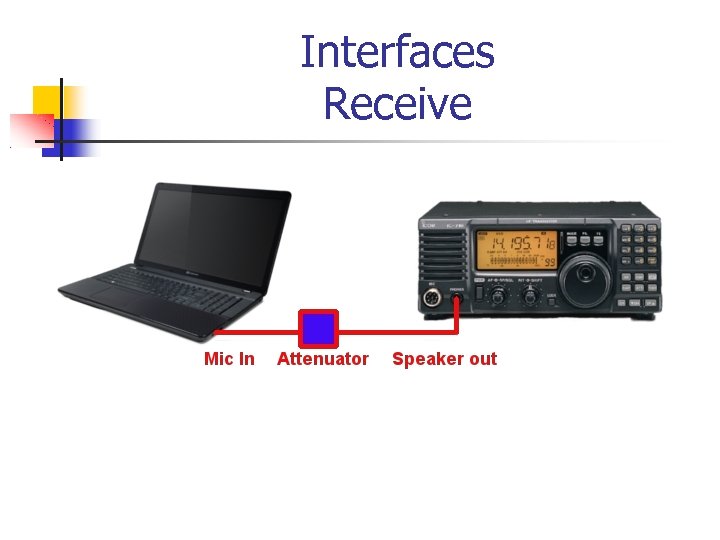 Interfaces Receive
Interfaces Receive
 Interfaces Transmitting is a little more complex PTT keying Isolate the audio to prevent ground loop issues
Interfaces Transmitting is a little more complex PTT keying Isolate the audio to prevent ground loop issues
 Interfaces Commercial Several Manufacturers MFJ West Mountain (Rig Blaster) Tiger. Tronics (Signal. Link) Some models include cables Other models require purchasing cables for your rig
Interfaces Commercial Several Manufacturers MFJ West Mountain (Rig Blaster) Tiger. Tronics (Signal. Link) Some models include cables Other models require purchasing cables for your rig
 Interfaces Commercial Better models include a sound card built in Your internal PC sound card is available for regular use Prices from $60 - $300
Interfaces Commercial Better models include a sound card built in Your internal PC sound card is available for regular use Prices from $60 - $300
 Interfaces Homebrew As basic as two 600 -600 ohm audio transformers, a few resistors, and a $1. 00 opto-isolator chip for PTT keying.
Interfaces Homebrew As basic as two 600 -600 ohm audio transformers, a few resistors, and a $1. 00 opto-isolator chip for PTT keying.
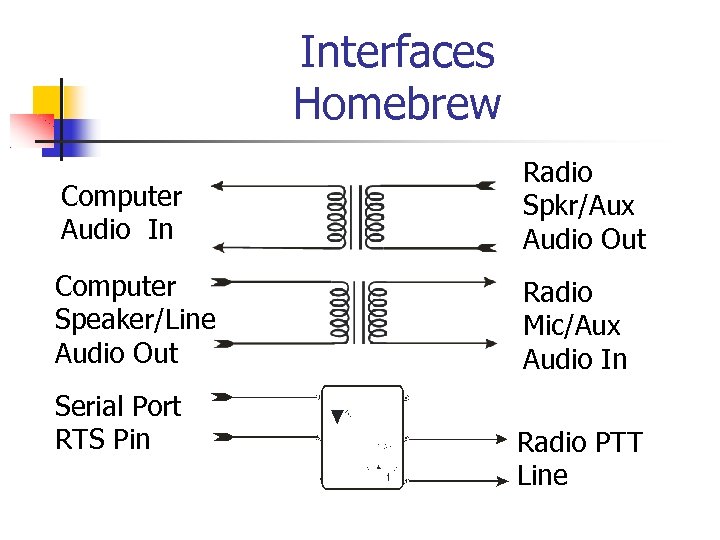 Interfaces Homebrew Computer Audio In Radio Spkr/Aux Audio Out Computer Speaker/Line Audio Out Radio Mic/Aux Audio In Serial Port RTS Pin Radio PTT Line
Interfaces Homebrew Computer Audio In Radio Spkr/Aux Audio Out Computer Speaker/Line Audio Out Radio Mic/Aux Audio In Serial Port RTS Pin Radio PTT Line
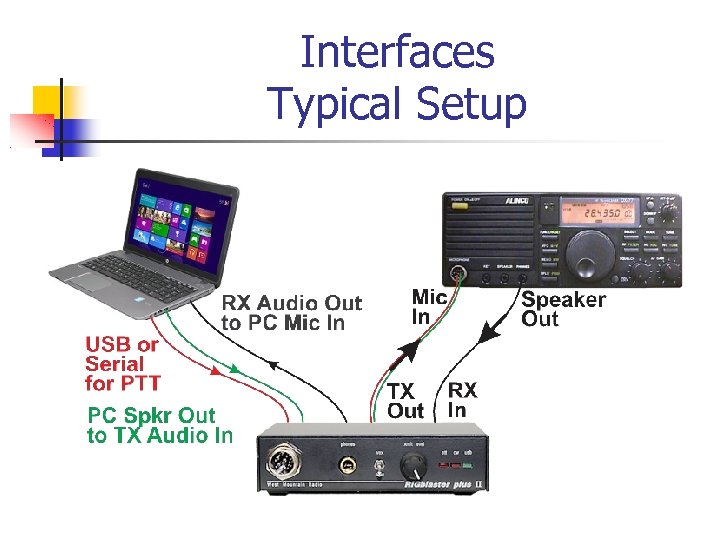 Interfaces Typical Setup
Interfaces Typical Setup
 Tips and Tricks Power Reduce your power! Unlike SSB, these modes either run at 100% duty cycle, or use multiple tones sensitive to intermodulation distortion! Be kind to your finals! Keep peak power out well below key-down CW maximum to minimize distortion. Keep ALC to zero Turn off speech processing or compression
Tips and Tricks Power Reduce your power! Unlike SSB, these modes either run at 100% duty cycle, or use multiple tones sensitive to intermodulation distortion! Be kind to your finals! Keep peak power out well below key-down CW maximum to minimize distortion. Keep ALC to zero Turn off speech processing or compression
 Tips and Tricks Jacks Use the Auxiliary, Accessory, “Data”, or “Packet” jacks on the radio. Most radios from the major manufacturers have one or more of these jacks on the rear panel May have constant audio input, output, and PTT lines
Tips and Tricks Jacks Use the Auxiliary, Accessory, “Data”, or “Packet” jacks on the radio. Most radios from the major manufacturers have one or more of these jacks on the rear panel May have constant audio input, output, and PTT lines
 Tips and Tricks Jacks Typical Jacks 6 -pin Mini-DIN 13 -Pin Full-size DIN
Tips and Tricks Jacks Typical Jacks 6 -pin Mini-DIN 13 -Pin Full-size DIN
 Tips and Tricks Jacks No need to adjust the volume or mic gain all the time No need to unplug the speaker to hear the radio No need to swap the mic in and out You may need a mic switch!
Tips and Tricks Jacks No need to adjust the volume or mic gain all the time No need to unplug the speaker to hear the radio No need to swap the mic in and out You may need a mic switch!
 Tips and Tricks Jacks Some radios have an audio out line in the microphone jack. This can help reduce extra cables.
Tips and Tricks Jacks Some radios have an audio out line in the microphone jack. This can help reduce extra cables.
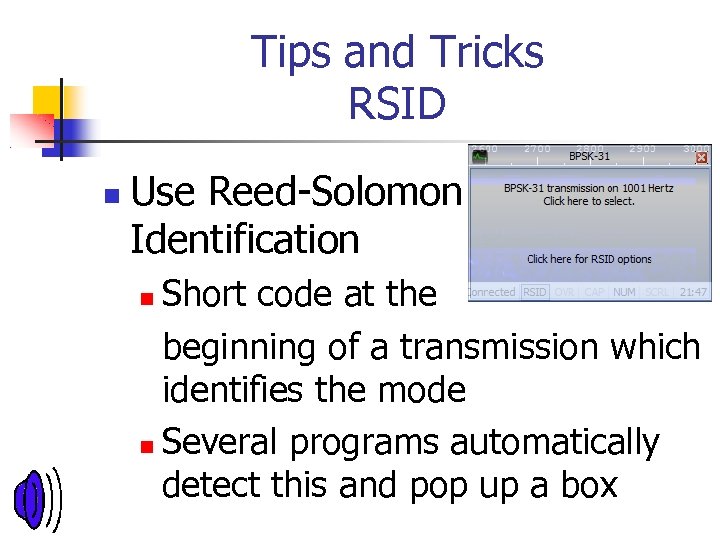 Tips and Tricks RSID Use Reed-Solomon Identification Short code at the beginning of a transmission which identifies the mode Several programs automatically detect this and pop up a box
Tips and Tricks RSID Use Reed-Solomon Identification Short code at the beginning of a transmission which identifies the mode Several programs automatically detect this and pop up a box
 Tips and Tricks Sound Device Check your sound card settings in the control panel! Turn off special effects Turn off pass-thru or “Listen to this device” modes Set rate to 16 bit 48000 Hz
Tips and Tricks Sound Device Check your sound card settings in the control panel! Turn off special effects Turn off pass-thru or “Listen to this device” modes Set rate to 16 bit 48000 Hz
 Tips and Tricks Sound Device Use the mixer to adjust your transmit audio using a dummy load and short 510 second intervals
Tips and Tricks Sound Device Use the mixer to adjust your transmit audio using a dummy load and short 510 second intervals
 Tips and Tricks References Commercial Sites Software: Ham Radio Deluxe V 6 www. hrdsoftwarellc. com Interfaces MFJ Rig. Blaster Signal. Link www. mfjenterprises. com www. westmountainradio. com www. tigertronics. com
Tips and Tricks References Commercial Sites Software: Ham Radio Deluxe V 6 www. hrdsoftwarellc. com Interfaces MFJ Rig. Blaster Signal. Link www. mfjenterprises. com www. westmountainradio. com www. tigertronics. com
 Local Digital Traffic Nets Kentucky Digital Net 3. 585 m. Hz 8/500 Olivia Wednesday 7 PM
Local Digital Traffic Nets Kentucky Digital Net 3. 585 m. Hz 8/500 Olivia Wednesday 7 PM
 Local Digital Traffic Nets Michigan Digital Traffic Net 3. 583 m. Hz 8/500 8 PM Tues, Thurs, Sat. State nets welcome out of state stations
Local Digital Traffic Nets Michigan Digital Traffic Net 3. 583 m. Hz 8/500 8 PM Tues, Thurs, Sat. State nets welcome out of state stations
 Local Digital Traffic Nets Ohio Digital Net: 3. 580 m. Hz, 8 tones 500 hz (8/500) Tues at 8 PM
Local Digital Traffic Nets Ohio Digital Net: 3. 580 m. Hz, 8 tones 500 hz (8/500) Tues at 8 PM
 Questions?
Questions?


