c15c8735c5504aba0f335e7e16374dec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

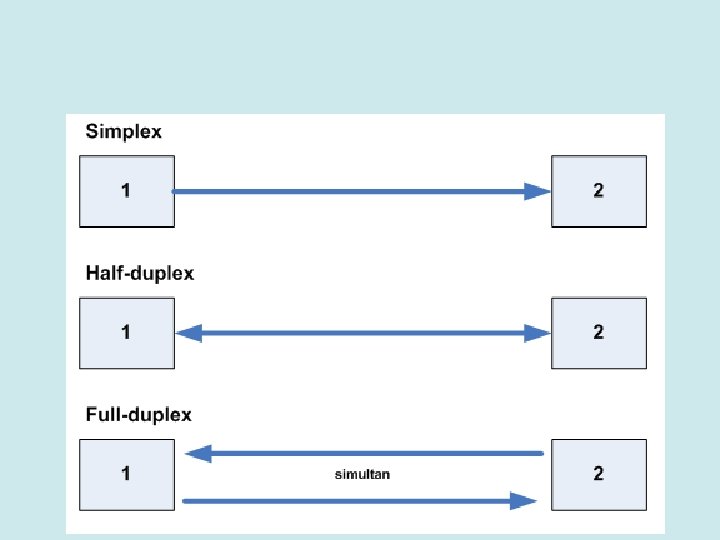
 HF Com Chapter 4 High Frequency Communications
HF Com Chapter 4 High Frequency Communications
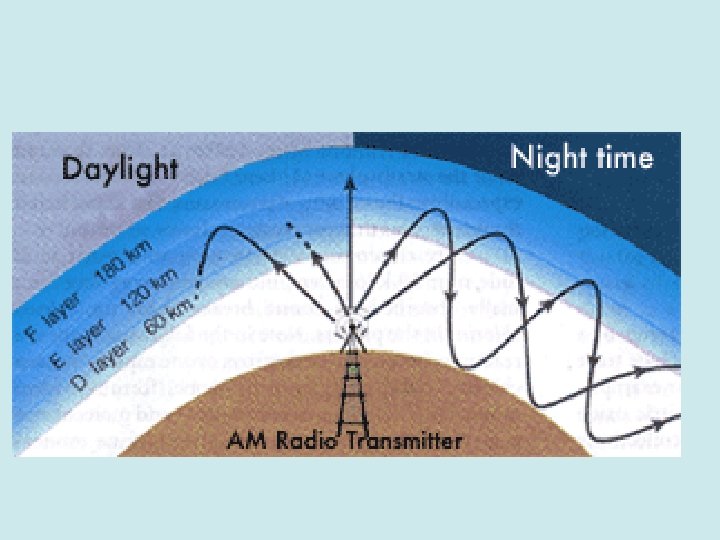
 Textbook page 23 When an airplane leaves the coastline for a transoceanic flight, it moves into a polar region or ventures over a remote area, it loses VHF communications. VHF signals are line of sight and cannot curve over the horizon. For long-range flight, the airplane switches to HF (High frequency) communications. Textbook page 23
Textbook page 23 When an airplane leaves the coastline for a transoceanic flight, it moves into a polar region or ventures over a remote area, it loses VHF communications. VHF signals are line of sight and cannot curve over the horizon. For long-range flight, the airplane switches to HF (High frequency) communications. Textbook page 23
 Radio Frequency (RF ) Very Low Frequency Medium Frequency High Frequency Very High Frequency Ultra High Frequency VLF LF MF HF VHF UHF 3 k. Hz -30 k. Hz - 300 k. Hz - 3 MHz - 300 MHz - 3 GHz Super High Frequency Extremely High Frequency SHF 3 GHz - 30 GHz EHF 30 GHz -300 GHz HF isn’t very High
Radio Frequency (RF ) Very Low Frequency Medium Frequency High Frequency Very High Frequency Ultra High Frequency VLF LF MF HF VHF UHF 3 k. Hz -30 k. Hz - 300 k. Hz - 3 MHz - 300 MHz - 3 GHz Super High Frequency Extremely High Frequency SHF 3 GHz - 30 GHz EHF 30 GHz -300 GHz HF isn’t very High
 HF Com Works by “skipping” through the ionosphere. Since the ionosphere is not constant, and changes between day and night and season to season, HF isn’t always reliable. Will eventually be replaced by satellite communications (SAT COM).
HF Com Works by “skipping” through the ionosphere. Since the ionosphere is not constant, and changes between day and night and season to season, HF isn’t always reliable. Will eventually be replaced by satellite communications (SAT COM).
 Antenna Tuning via Antenna Coupler Uses ¼ wave antenna. However with varying frequencies this could be impractical as the lower frequencies could require an antenna > 100 feet long. The Autotune system eliminates the need for long antennas by using tuning circuits in the antenna coupler to electrically match up, thus enabling the use of a short-fixed length antenna. Textbook page 24 “Coupler”
Antenna Tuning via Antenna Coupler Uses ¼ wave antenna. However with varying frequencies this could be impractical as the lower frequencies could require an antenna > 100 feet long. The Autotune system eliminates the need for long antennas by using tuning circuits in the antenna coupler to electrically match up, thus enabling the use of a short-fixed length antenna. Textbook page 24 “Coupler”
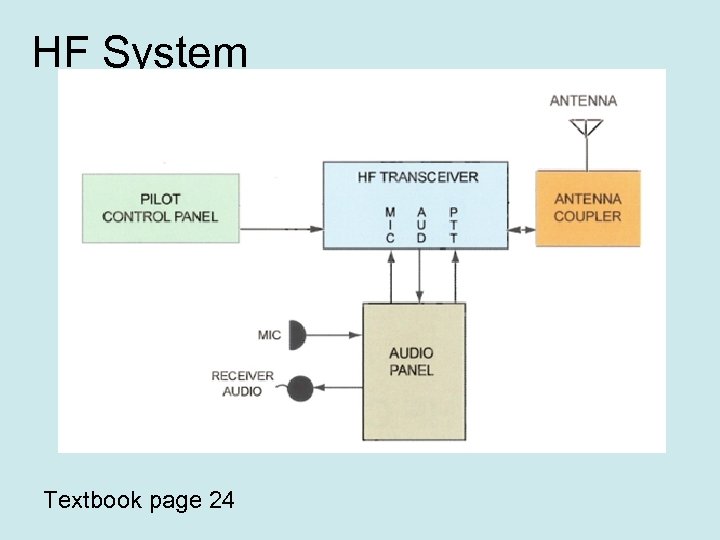 HF System Textbook page 24
HF System Textbook page 24
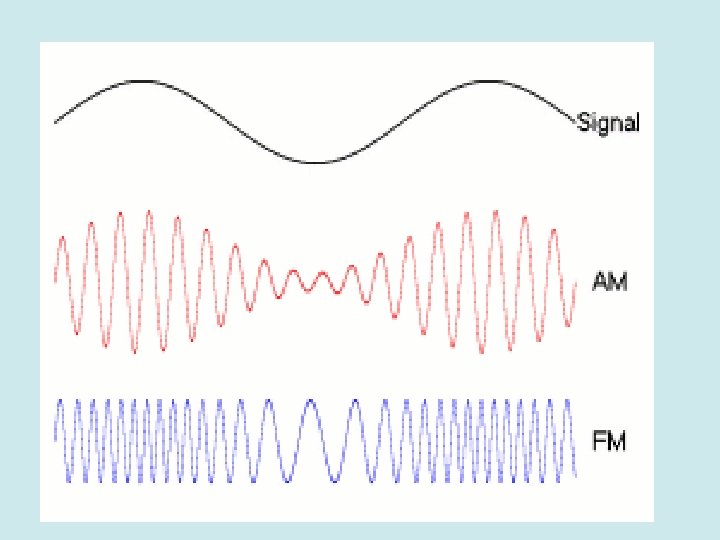
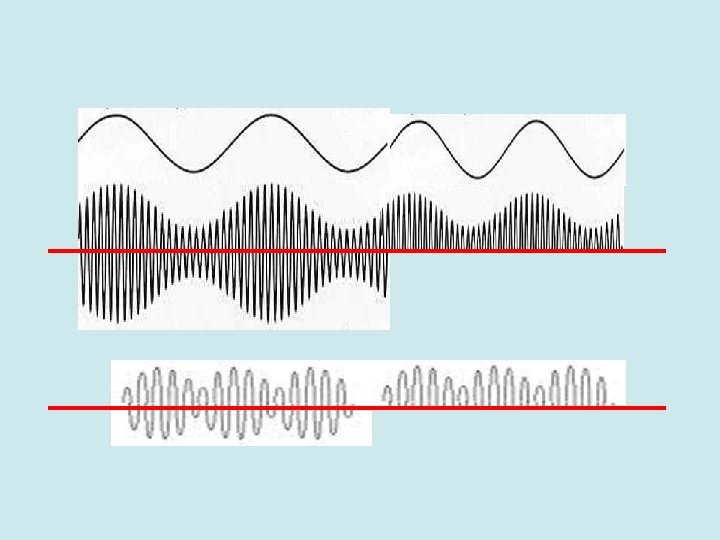
 Single Sideband (SSB) HF radio transmits using AM (amplitude modulation). AM has 3 components: The RF carrier, and an upper (USB) and lower (LSB) sideband. Originally, most of the power was lost in the carrier in AM. Since voice audio only uses the sidebands, modern transmitters direct the transmitter power into one sideband thus not losing it in the carrier signal. Textbook page 25
Single Sideband (SSB) HF radio transmits using AM (amplitude modulation). AM has 3 components: The RF carrier, and an upper (USB) and lower (LSB) sideband. Originally, most of the power was lost in the carrier in AM. Since voice audio only uses the sidebands, modern transmitters direct the transmitter power into one sideband thus not losing it in the carrier signal. Textbook page 25
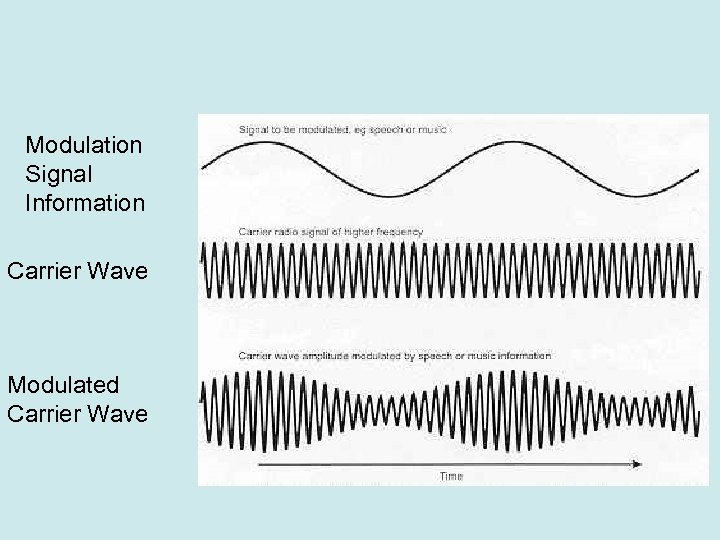 Modulation Signal Information Carrier Wave Modulated Carrier Wave
Modulation Signal Information Carrier Wave Modulated Carrier Wave
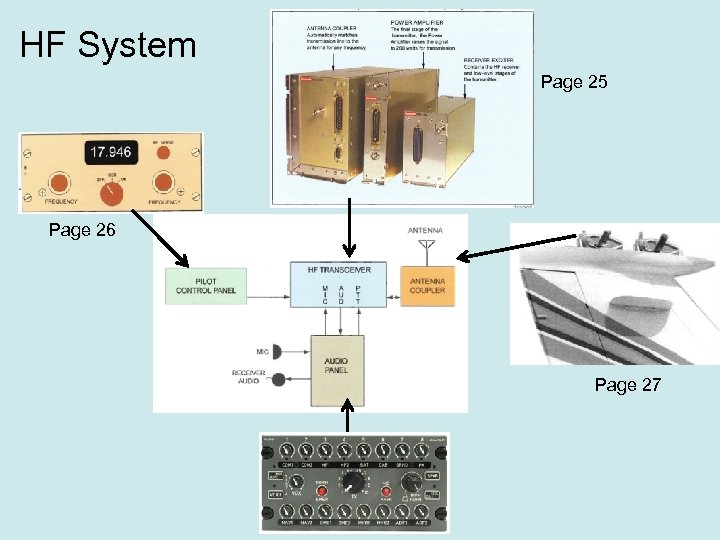 HF System Page 25 Page 26 Page 27
HF System Page 25 Page 26 Page 27
 Review Q&A Chapter 4 HF Com 4. 1 Why are High Frequency communications not as reliable as VHF? Answer: Because HF depends on varying atmospheric conditions to work. 4. 2 What is the advantage of “Autotune”? Answer: It allows for a short-fixed antenna and eliminates the need for the pilot to tune the radio. 4. 3 Why is SSB (single sideband) more efficient than conventional AM radio? Answer: It directs the transmitter power to the sideband thus eliminating losses in the carrier signal. 4. 4 What made HF datalink possible? Answer: Improved filtering technology. 4. 5 What are 3 major components of an HF LRU? Answer: Antenna Coupler, Power Amplifier, and Receiver-Exciter.
Review Q&A Chapter 4 HF Com 4. 1 Why are High Frequency communications not as reliable as VHF? Answer: Because HF depends on varying atmospheric conditions to work. 4. 2 What is the advantage of “Autotune”? Answer: It allows for a short-fixed antenna and eliminates the need for the pilot to tune the radio. 4. 3 Why is SSB (single sideband) more efficient than conventional AM radio? Answer: It directs the transmitter power to the sideband thus eliminating losses in the carrier signal. 4. 4 What made HF datalink possible? Answer: Improved filtering technology. 4. 5 What are 3 major components of an HF LRU? Answer: Antenna Coupler, Power Amplifier, and Receiver-Exciter.
 Review Q&A Chapter 4 HF Com 4. 5 What are 3 major components of an HF LRU? Answer: Antenna Coupler, Power Amplifier, and Receiver-Exciter 4. 6 Name 2 advantages of HF datalink. Answer: Lower pilot workload, Shorter Message Transmission time, Lower channel access time, Less Training for flight crew, Relieves congestion on voice frequencies, Automatic selection of frequency & data rates, Less vulnerability to human error, Automatically detects and corrects errors, can operate in noisier environments, Increases HF traffic capability, assured communications link, automatic air/ground HF linkage with lower acquisition cost compared to SATCOM, improved voice/data quality and datalink messages are not written or sensitive to verbal language. 4. 7 What is the purpose of an HF antenna coupler? Answer: To tune the antenna 4. 8 Where is the HF antenna mounted on many airliners? Answer: In the vertical stabilizer.
Review Q&A Chapter 4 HF Com 4. 5 What are 3 major components of an HF LRU? Answer: Antenna Coupler, Power Amplifier, and Receiver-Exciter 4. 6 Name 2 advantages of HF datalink. Answer: Lower pilot workload, Shorter Message Transmission time, Lower channel access time, Less Training for flight crew, Relieves congestion on voice frequencies, Automatic selection of frequency & data rates, Less vulnerability to human error, Automatically detects and corrects errors, can operate in noisier environments, Increases HF traffic capability, assured communications link, automatic air/ground HF linkage with lower acquisition cost compared to SATCOM, improved voice/data quality and datalink messages are not written or sensitive to verbal language. 4. 7 What is the purpose of an HF antenna coupler? Answer: To tune the antenna 4. 8 Where is the HF antenna mounted on many airliners? Answer: In the vertical stabilizer.
 Sat. Com Chapter 5 Satellite Communications
Sat. Com Chapter 5 Satellite Communications
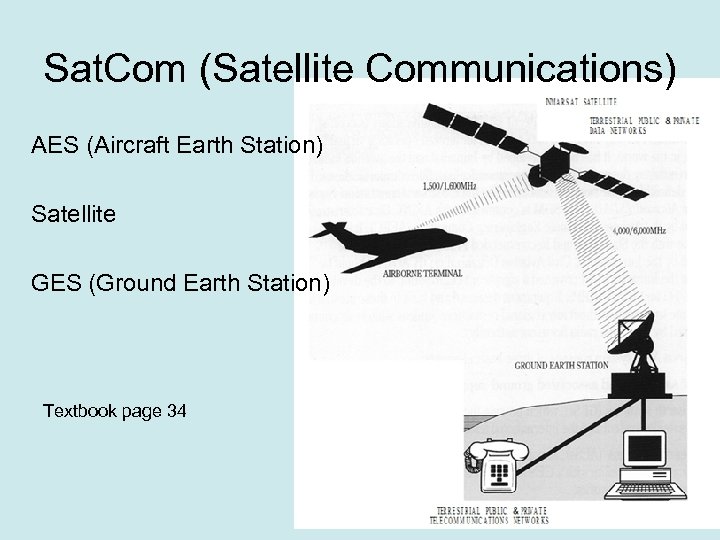 Sat. Com (Satellite Communications) AES (Aircraft Earth Station) Satellite GES (Ground Earth Station) Textbook page 34
Sat. Com (Satellite Communications) AES (Aircraft Earth Station) Satellite GES (Ground Earth Station) Textbook page 34
 Sat. Com (Satellite Communications) • http: //orbitaldebris. jsc. nasa. gov/photogallery/beehives. html
Sat. Com (Satellite Communications) • http: //orbitaldebris. jsc. nasa. gov/photogallery/beehives. html
 http: //www. duncanaviation. aero/homepage. php http: //www. duncanaviation. aero/straighttalk/index. php
http: //www. duncanaviation. aero/homepage. php http: //www. duncanaviation. aero/straighttalk/index. php
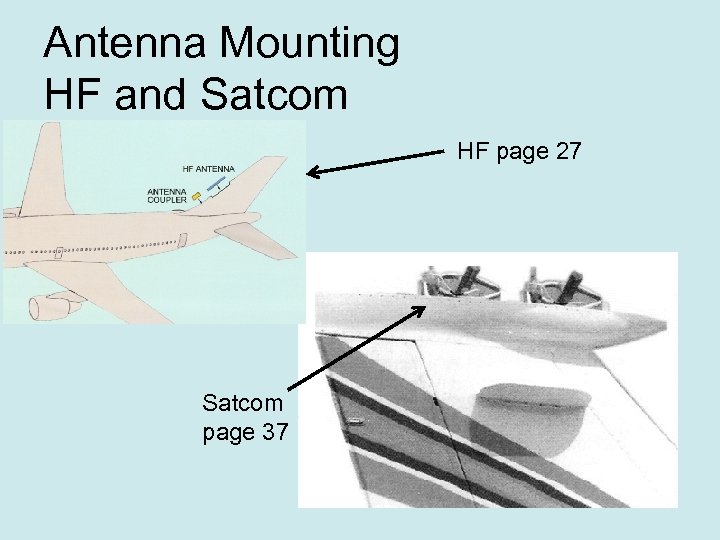 Antenna Mounting HF and Satcom HF page 27 Satcom page 37
Antenna Mounting HF and Satcom HF page 27 Satcom page 37
 VHF Comm Antennas
VHF Comm Antennas
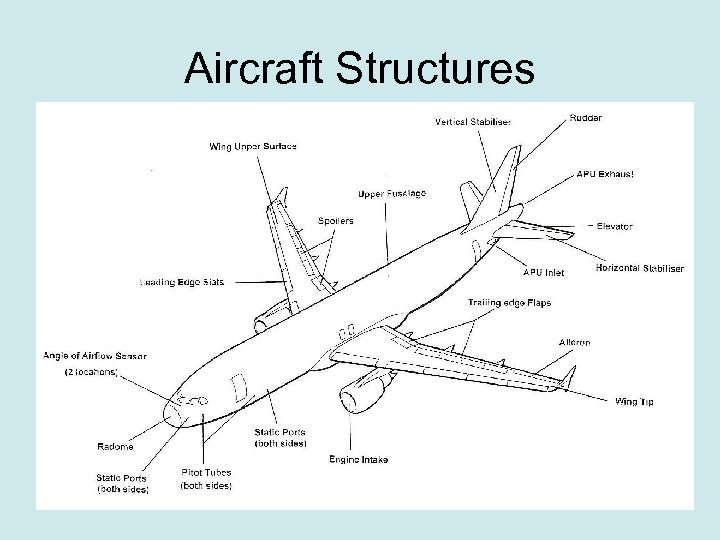 Aircraft Structures
Aircraft Structures
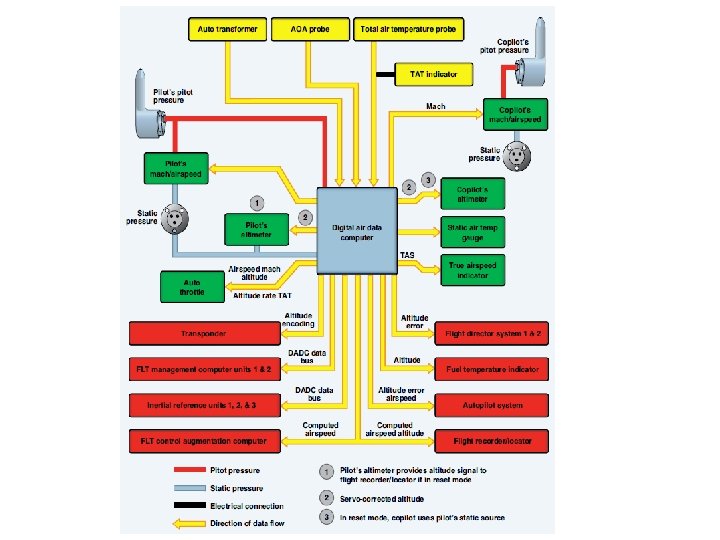
 Pitot-Static System Some of the most important flight instruments derive their indications from measuring air pressure. Gathering and distributing various air pressures for flight instrumentation is the function of the pitot-static system. FAA H 8083 -31 Vol 2 Page 10 -12
Pitot-Static System Some of the most important flight instruments derive their indications from measuring air pressure. Gathering and distributing various air pressures for flight instrumentation is the function of the pitot-static system. FAA H 8083 -31 Vol 2 Page 10 -12
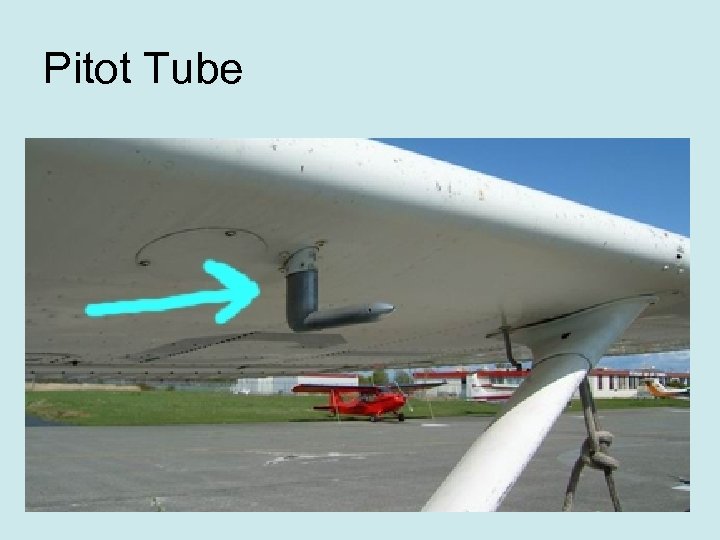 Pitot Tube
Pitot Tube
 Pitot Tube
Pitot Tube
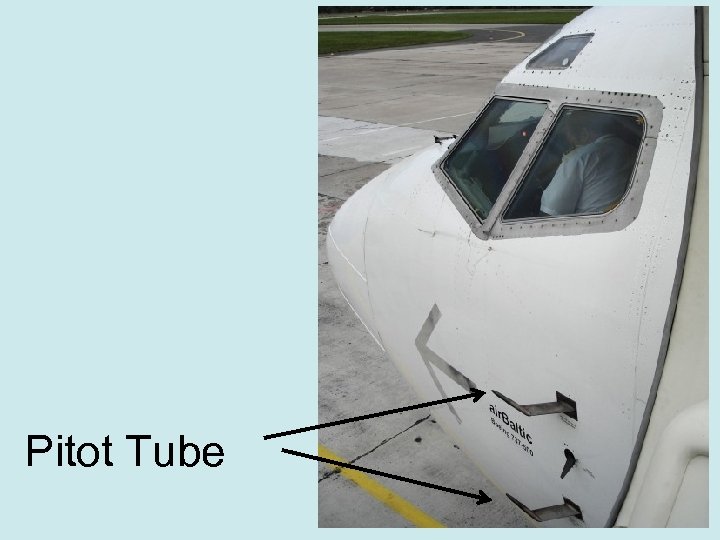 Pitot Tube
Pitot Tube
 Static Port
Static Port
 AOA Sensor
AOA Sensor
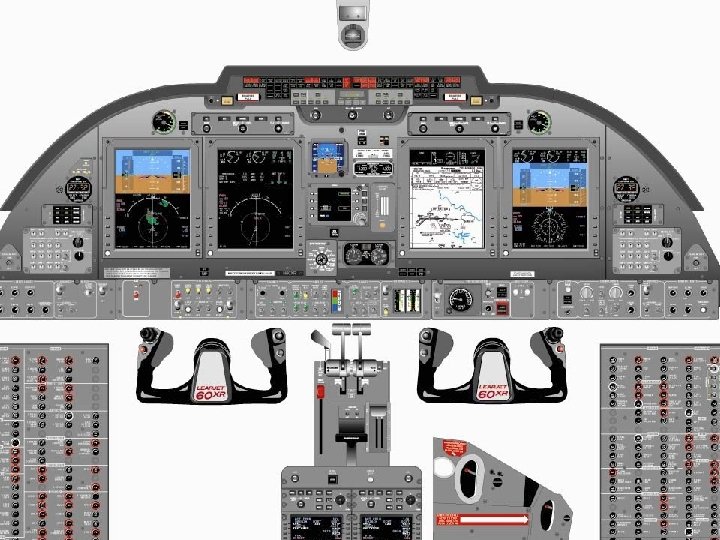
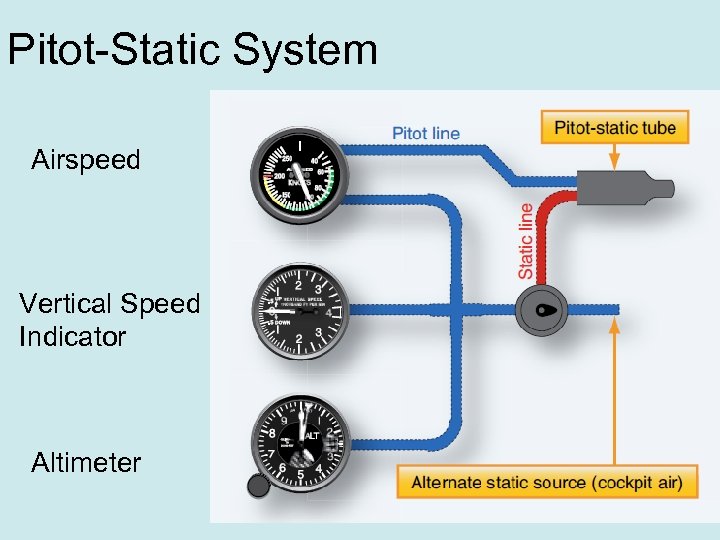 Pitot-Static System Airspeed Vertical Speed Indicator Altimeter
Pitot-Static System Airspeed Vertical Speed Indicator Altimeter
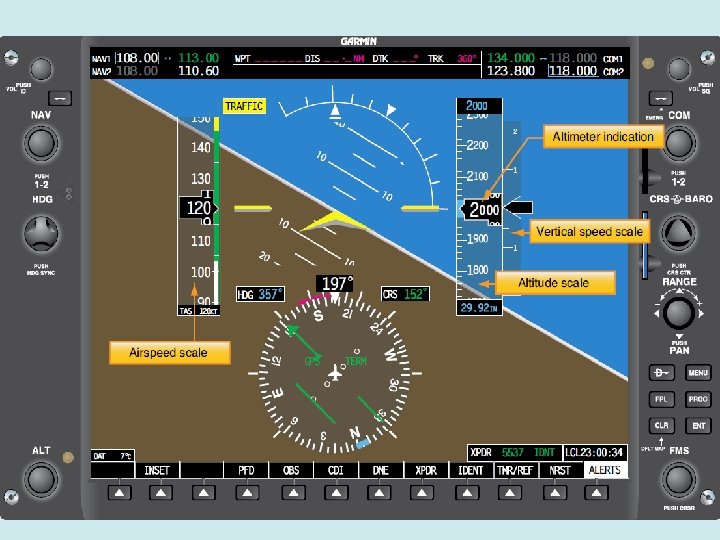
 6 Pack or Basic “T” Textbook page 157
6 Pack or Basic “T” Textbook page 157
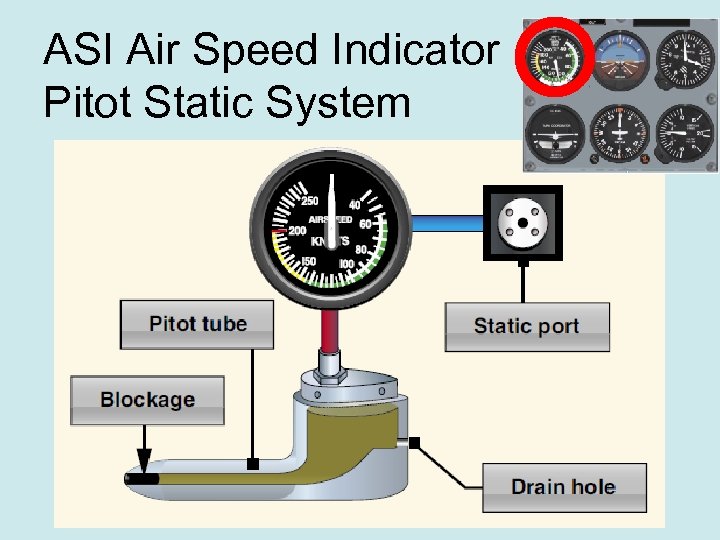 ASI Air Speed Indicator Pitot Static System
ASI Air Speed Indicator Pitot Static System
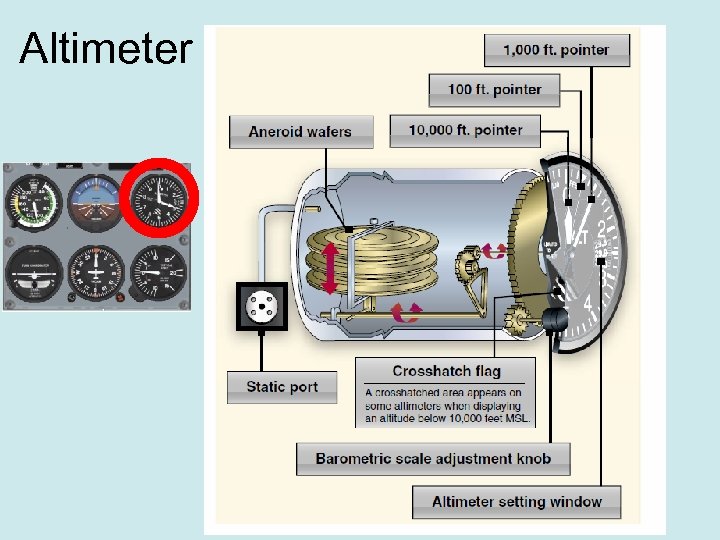 Altimeter
Altimeter
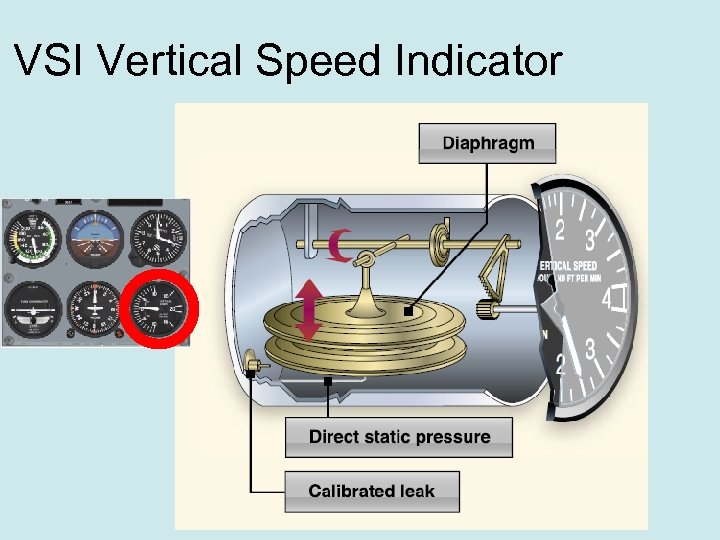 VSI Vertical Speed Indicator
VSI Vertical Speed Indicator
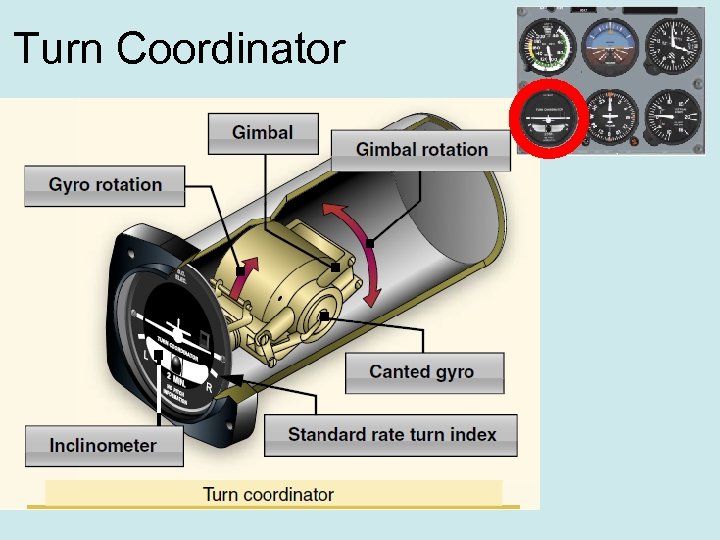 Turn Coordinator
Turn Coordinator
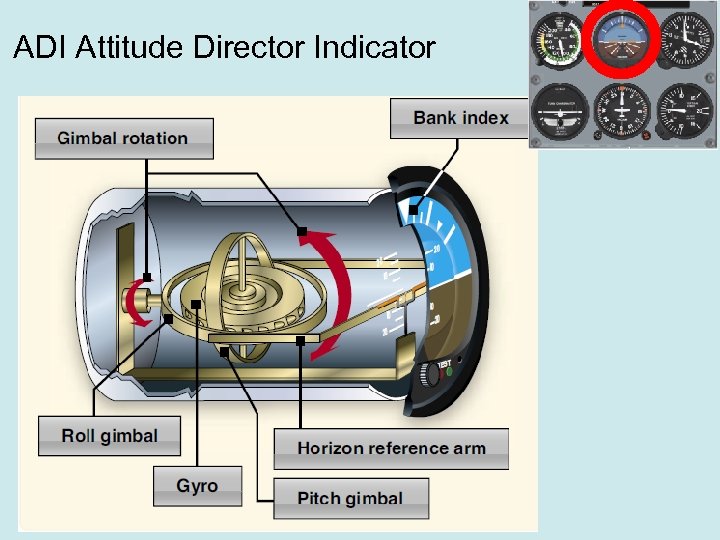 ADI Attitude Director Indicator
ADI Attitude Director Indicator
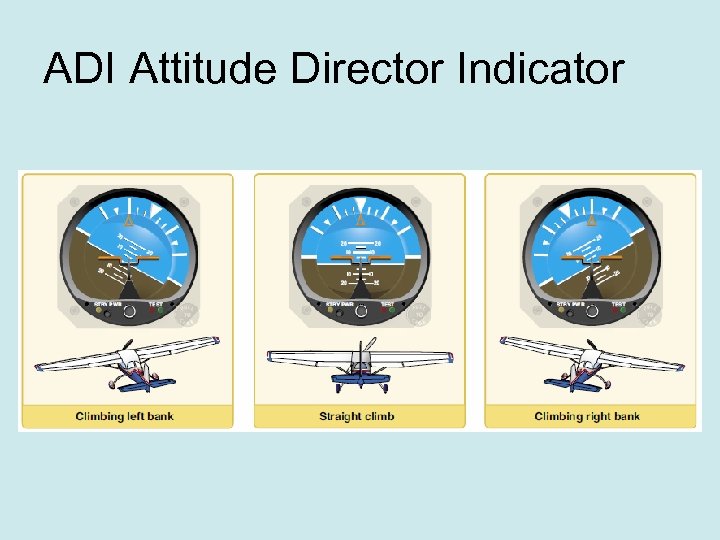 ADI Attitude Director Indicator
ADI Attitude Director Indicator
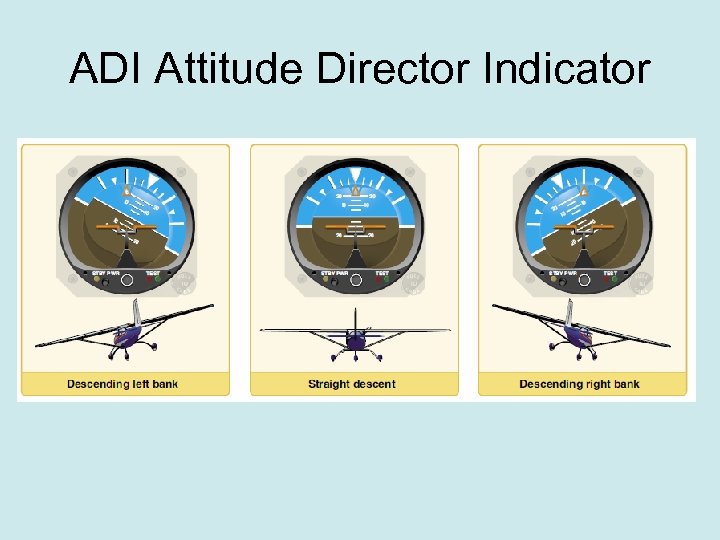 ADI Attitude Director Indicator
ADI Attitude Director Indicator

 6 Pack or Basic “T” Textbook page 157
6 Pack or Basic “T” Textbook page 157