49b207ba1e6f11738116be457e4950e0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 179
 Hewlett-Packard Consulting ITIL Overview Session Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Hewlett-Packard Consulting ITIL Overview Session Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
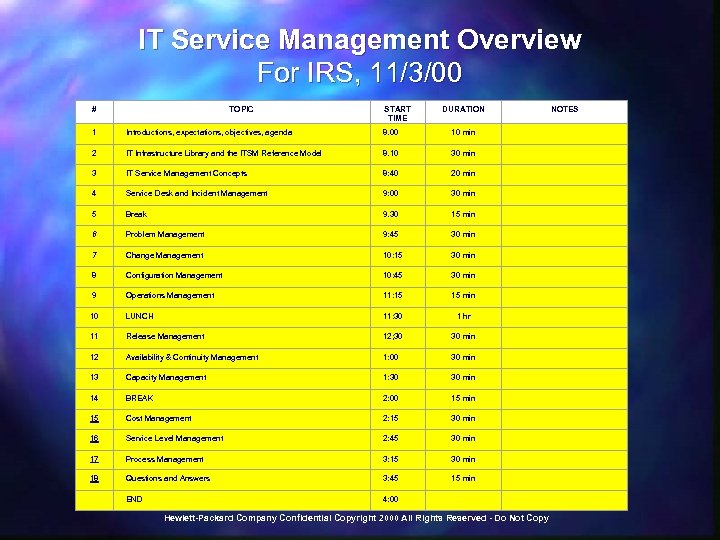 IT Service Management Overview For IRS, 11/3/00 # TOPIC START TIME DURATION NOTES 1 Introductions, expectations, objectives, agenda 8. 00 10 min 2 IT Infrastructure Library and the ITSM Reference Model 8. 10 30 min 3 IT Service Management Concepts 8: 40 20 min 4 Service Desk and Incident Management 9: 00 30 min 5 Break 9. 30 15 min 6 Problem Management 9: 45 30 min 7 Change Management 10: 15 30 min 8 Configuration Management 10: 45 30 min 9 Operations Management 11: 15 15 min 10 LUNCH 11: 30 1 hr 11 Release Management 12; 30 30 min 12 Availability & Continuity Management 1: 00 30 min 13 Capacity Management 1: 30 30 min 14 BREAK 2: 00 15 min 15 Cost Management 2: 15 30 min 16 Service Level Management 2: 45 30 min 17 Process Management 3: 15 30 min 18 Questions and Answers 3: 45 15 min END 4: 00 Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
IT Service Management Overview For IRS, 11/3/00 # TOPIC START TIME DURATION NOTES 1 Introductions, expectations, objectives, agenda 8. 00 10 min 2 IT Infrastructure Library and the ITSM Reference Model 8. 10 30 min 3 IT Service Management Concepts 8: 40 20 min 4 Service Desk and Incident Management 9: 00 30 min 5 Break 9. 30 15 min 6 Problem Management 9: 45 30 min 7 Change Management 10: 15 30 min 8 Configuration Management 10: 45 30 min 9 Operations Management 11: 15 15 min 10 LUNCH 11: 30 1 hr 11 Release Management 12; 30 30 min 12 Availability & Continuity Management 1: 00 30 min 13 Capacity Management 1: 30 30 min 14 BREAK 2: 00 15 min 15 Cost Management 2: 15 30 min 16 Service Level Management 2: 45 30 min 17 Process Management 3: 15 30 min 18 Questions and Answers 3: 45 15 min END 4: 00 Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session ITIL Overview: What is ITIL? Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session ITIL Overview: What is ITIL? Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 What is ITIL? n A set of books & modules, used as a complete code of best practice for IT Service Provision n A roadmap which defines the relationships between people, processes and infrastructure necessary for effective IT Service provision n The only comprehensive, publicly available guidance on IT Service Provision n Developed by the CCTA - British Government n International Certification Programs n In place since 1986 n Rewrite currently underway http: //www. itil. co. uk/ Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
What is ITIL? n A set of books & modules, used as a complete code of best practice for IT Service Provision n A roadmap which defines the relationships between people, processes and infrastructure necessary for effective IT Service provision n The only comprehensive, publicly available guidance on IT Service Provision n Developed by the CCTA - British Government n International Certification Programs n In place since 1986 n Rewrite currently underway http: //www. itil. co. uk/ Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Why Change? n n If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it! Need to deliver true 100% reliability within guaranteed hours of operation (most often 7 x 24) Even 99. 5% reliability in a 7 x 24 shop equals 306 hours of downtime Complexity of managing a complete extended supply chain to agreed upon service levels Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Why Change? n n If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it! Need to deliver true 100% reliability within guaranteed hours of operation (most often 7 x 24) Even 99. 5% reliability in a 7 x 24 shop equals 306 hours of downtime Complexity of managing a complete extended supply chain to agreed upon service levels Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 The ITIL User Community Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The ITIL User Community Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
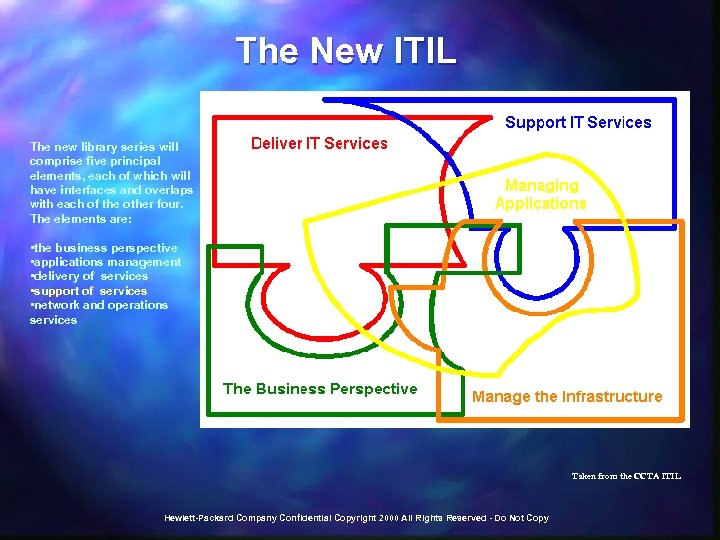 The New ITIL The new library series will comprise five principal elements, each of which will have interfaces and overlaps with each of the other four. The elements are: • the business perspective • applications management • delivery of services • support of services • network and operations services Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The New ITIL The new library series will comprise five principal elements, each of which will have interfaces and overlaps with each of the other four. The elements are: • the business perspective • applications management • delivery of services • support of services • network and operations services Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Service Support Processes n n n Service Desk, Incident Management, Problem Management, Change Management, Configuration Management, Release Management; Operational in nature; Provide control and stability to the IT infrastructure while remaining flexible to accommodate changes to business and time to market demands*. *Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Service Support Processes n n n Service Desk, Incident Management, Problem Management, Change Management, Configuration Management, Release Management; Operational in nature; Provide control and stability to the IT infrastructure while remaining flexible to accommodate changes to business and time to market demands*. *Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Service Delivery Processes n n Service Level Management, Capacity Management, Availability Management, Continuity Management, Financial Management for IT Services, Customer Relationship Management; More strategic in nature, with some operational activities; Provide quality to the delivery of IT services; Cannot be truly effective without the underlying support processes. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Service Delivery Processes n n Service Level Management, Capacity Management, Availability Management, Continuity Management, Financial Management for IT Services, Customer Relationship Management; More strategic in nature, with some operational activities; Provide quality to the delivery of IT services; Cannot be truly effective without the underlying support processes. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Why Implement ITIL? n n n n n Professionalism Focus on benefits to the customer/business Decision making metrics Clear points of contact Part of a QM strategy - focus on continuous improvement Cost reduction - based on the standardization of the expensive processes (20/80) Managing the infrastructure now in top 3 concerns Avoid reinventing the wheel Long term survival! Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Why Implement ITIL? n n n n n Professionalism Focus on benefits to the customer/business Decision making metrics Clear points of contact Part of a QM strategy - focus on continuous improvement Cost reduction - based on the standardization of the expensive processes (20/80) Managing the infrastructure now in top 3 concerns Avoid reinventing the wheel Long term survival! Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session ITIL Process Framework and Interconnections: HP ITSM Reference Model Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session ITIL Process Framework and Interconnections: HP ITSM Reference Model Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
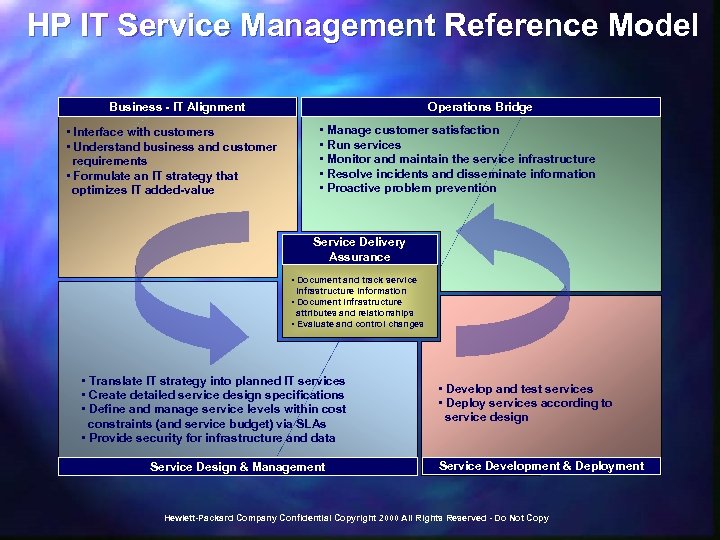 HP IT Service Management Reference Model Business - IT Alignment • Interface with customers • Understand business and customer requirements • Formulate an IT strategy that optimizes IT added-value Operations Bridge • Manage customer satisfaction • Run services • Monitor and maintain the service infrastructure • Resolve incidents and disseminate information • Proactive problem prevention Service Delivery Assurance • Document and track service infrastructure information • Document infrastructure attributes and relationships • Evaluate and control changes • Translate IT strategy into planned IT services • Create detailed service design specifications • Define and manage service levels within cost constraints (and service budget) via SLAs • Provide security for infrastructure and data Service Design & Management • Develop and test services • Deploy services according to service design Service Development & Deployment Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
HP IT Service Management Reference Model Business - IT Alignment • Interface with customers • Understand business and customer requirements • Formulate an IT strategy that optimizes IT added-value Operations Bridge • Manage customer satisfaction • Run services • Monitor and maintain the service infrastructure • Resolve incidents and disseminate information • Proactive problem prevention Service Delivery Assurance • Document and track service infrastructure information • Document infrastructure attributes and relationships • Evaluate and control changes • Translate IT strategy into planned IT services • Create detailed service design specifications • Define and manage service levels within cost constraints (and service budget) via SLAs • Provide security for infrastructure and data Service Design & Management • Develop and test services • Deploy services according to service design Service Development & Deployment Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
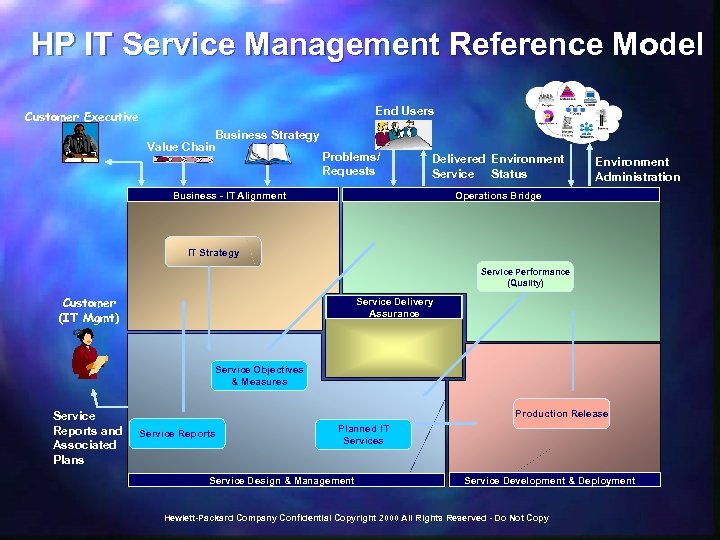 HP IT Service Management Reference Model End Users Customer Executive Business Strategy Value Chain Problems/ Requests Delivered Environment Service Status Business - IT Alignment Environment Administration Operations Bridge Service Delivery Assurance IT Strategy Service Performance (Quality) Customer (IT Mgmt) Service Delivery Assurance Service Objectives & Measures Service Reports and Associated Plans Production Release Service Reports Planned IT Services Service Design & Management Service Development & Deployment Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
HP IT Service Management Reference Model End Users Customer Executive Business Strategy Value Chain Problems/ Requests Delivered Environment Service Status Business - IT Alignment Environment Administration Operations Bridge Service Delivery Assurance IT Strategy Service Performance (Quality) Customer (IT Mgmt) Service Delivery Assurance Service Objectives & Measures Service Reports and Associated Plans Production Release Service Reports Planned IT Services Service Design & Management Service Development & Deployment Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
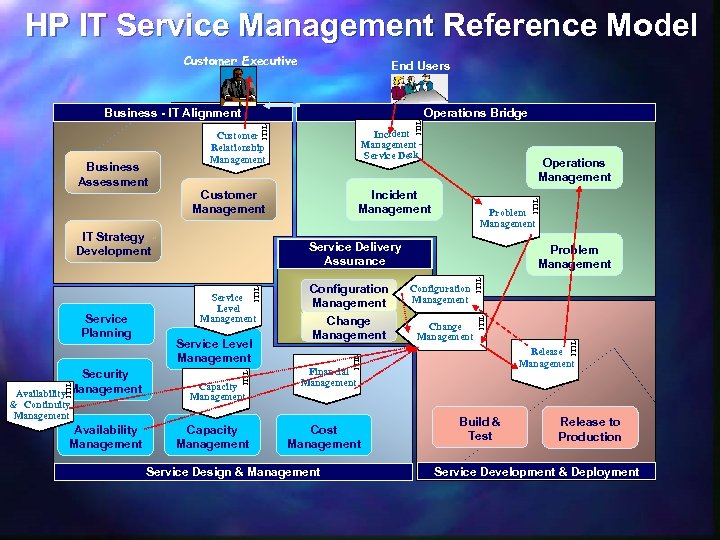 HP IT Service Management Reference Model Customer Executive End Users Operations Bridge Availability Management Service Level Management Capacity Management Configuration Management Change Management ITIL Service Level Management Problem Management ITIL & Continuity Management Problem Management Service Delivery Assurance ITIL Security Availability Management Incident Management Customer Management IT Strategy Development Service Planning Operations Management Service Delivery Assurance Release Management ITIL Business Assessment Incident Management Service Desk Customer Relationship Management Financial Management Cost Management Service Design & Management ITIL Business - IT Alignment Build & Test Release to Production Service Development & Deployment
HP IT Service Management Reference Model Customer Executive End Users Operations Bridge Availability Management Service Level Management Capacity Management Configuration Management Change Management ITIL Service Level Management Problem Management ITIL & Continuity Management Problem Management Service Delivery Assurance ITIL Security Availability Management Incident Management Customer Management IT Strategy Development Service Planning Operations Management Service Delivery Assurance Release Management ITIL Business Assessment Incident Management Service Desk Customer Relationship Management Financial Management Cost Management Service Design & Management ITIL Business - IT Alignment Build & Test Release to Production Service Development & Deployment
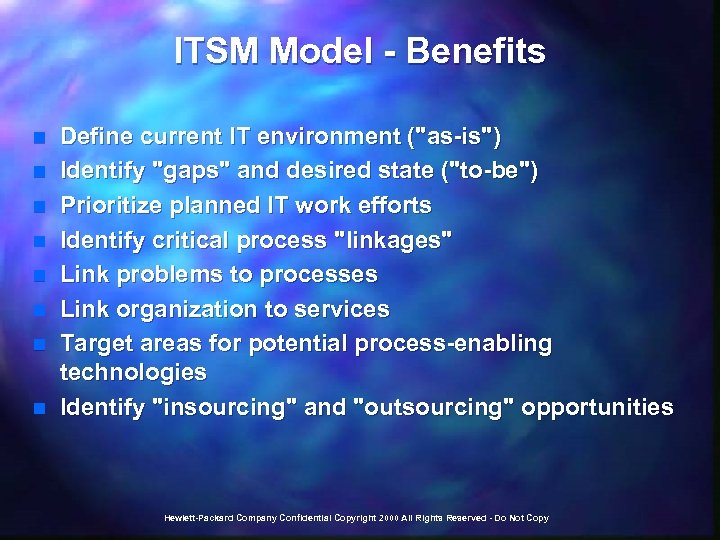 ITSM Model - Benefits n n n n Define current IT environment ("as-is") Identify "gaps" and desired state ("to-be") Prioritize planned IT work efforts Identify critical process "linkages" Link problems to processes Link organization to services Target areas for potential process-enabling technologies Identify "insourcing" and "outsourcing" opportunities Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITSM Model - Benefits n n n n Define current IT environment ("as-is") Identify "gaps" and desired state ("to-be") Prioritize planned IT work efforts Identify critical process "linkages" Link problems to processes Link organization to services Target areas for potential process-enabling technologies Identify "insourcing" and "outsourcing" opportunities Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session ITIL Overview: IT Service Management Concepts Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session ITIL Overview: IT Service Management Concepts Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 What is a Service? n n n A service is product or output of the IT operation to it’s customers. It is not an internal activity between departments. It is delivered to the customer and it’s performance must be measured at the customers interface point, not IT’s internal reference points. These measurements are called the service performance levels or service levels for short. There are three customer interface points for IT services n In the screen (Applications) n In the phone (Service and Service requests) n Face to Face (Installation, consulting, and New system development) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
What is a Service? n n n A service is product or output of the IT operation to it’s customers. It is not an internal activity between departments. It is delivered to the customer and it’s performance must be measured at the customers interface point, not IT’s internal reference points. These measurements are called the service performance levels or service levels for short. There are three customer interface points for IT services n In the screen (Applications) n In the phone (Service and Service requests) n Face to Face (Installation, consulting, and New system development) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
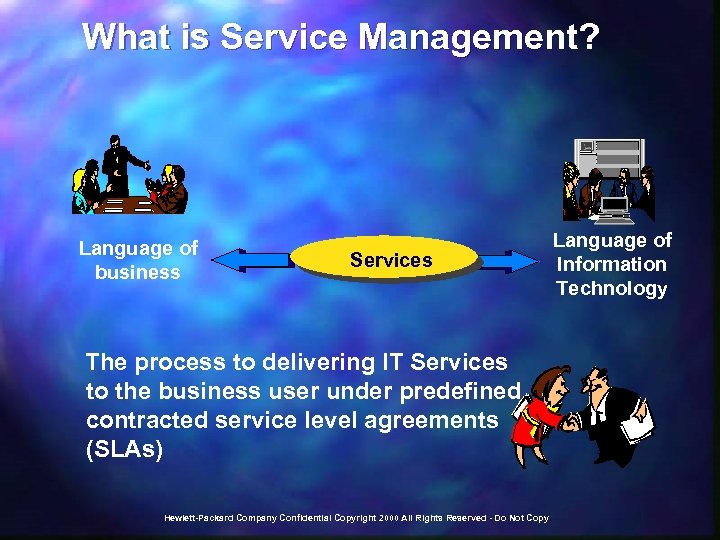 What is Service Management? Language of business Services The process to delivering IT Services to the business user under predefined, contracted service level agreements (SLAs) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Language of Information Technology
What is Service Management? Language of business Services The process to delivering IT Services to the business user under predefined, contracted service level agreements (SLAs) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Language of Information Technology
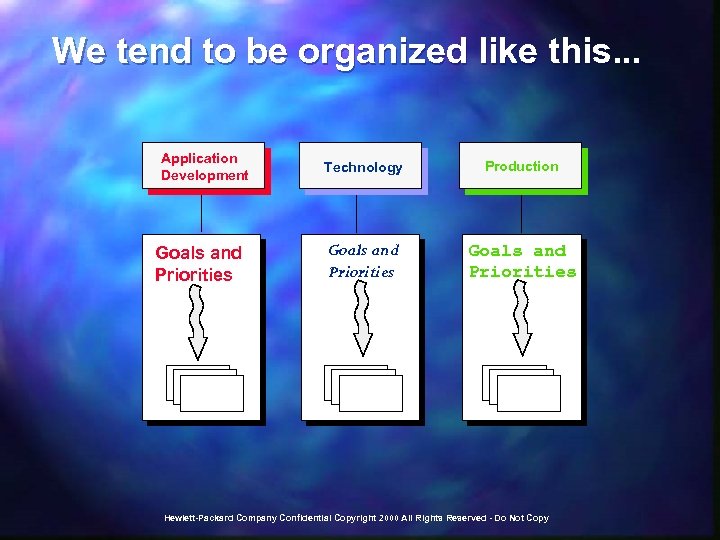 We tend to be organized like this. . . Application Development Goals and Priorities Technology Production Goals and Priorities Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
We tend to be organized like this. . . Application Development Goals and Priorities Technology Production Goals and Priorities Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 But our customers see us like this. . . Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
But our customers see us like this. . . Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
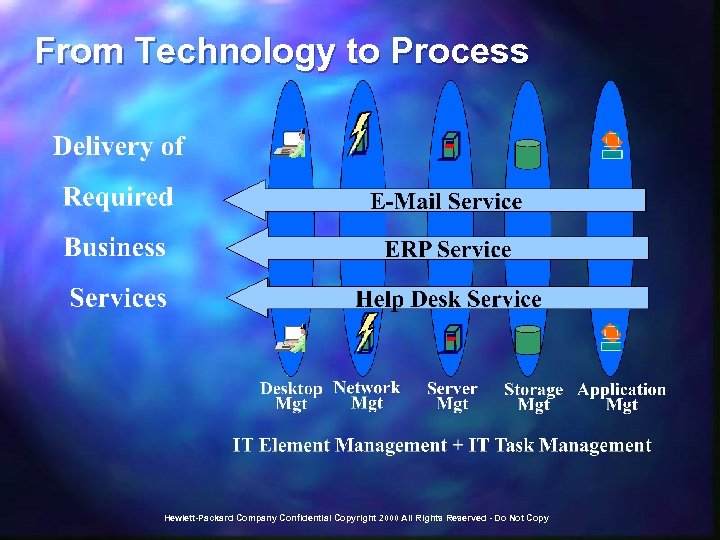 From Technology to Process Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
From Technology to Process Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Challenges to the IT Organization n n n n Contribution to solving business challenges – This means contributing earlier in the planning cycle A measurable contribution to the business value chain Service provision as opposed to IT product delivery A business like relationship A consistent and stable service Less emphasis on technology Meeting the new demands of IT as a utility Delivering 100% reliability 7 x 24 Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Challenges to the IT Organization n n n n Contribution to solving business challenges – This means contributing earlier in the planning cycle A measurable contribution to the business value chain Service provision as opposed to IT product delivery A business like relationship A consistent and stable service Less emphasis on technology Meeting the new demands of IT as a utility Delivering 100% reliability 7 x 24 Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session ITIL Service Support Processes Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session ITIL Service Support Processes Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session The Service Desk & the Incident Management Process Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session The Service Desk & the Incident Management Process Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Service Desk Objectives n n n To be the primary contact point for all: – Calls – Questions – Requests – Complaints – Remarks To restore the service as quickly as possible To manage the incident life-cycle (co-ordinating resolution) To support business activities To manage the Incident Process Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Service Desk Objectives n n n To be the primary contact point for all: – Calls – Questions – Requests – Complaints – Remarks To restore the service as quickly as possible To manage the incident life-cycle (co-ordinating resolution) To support business activities To manage the Incident Process Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
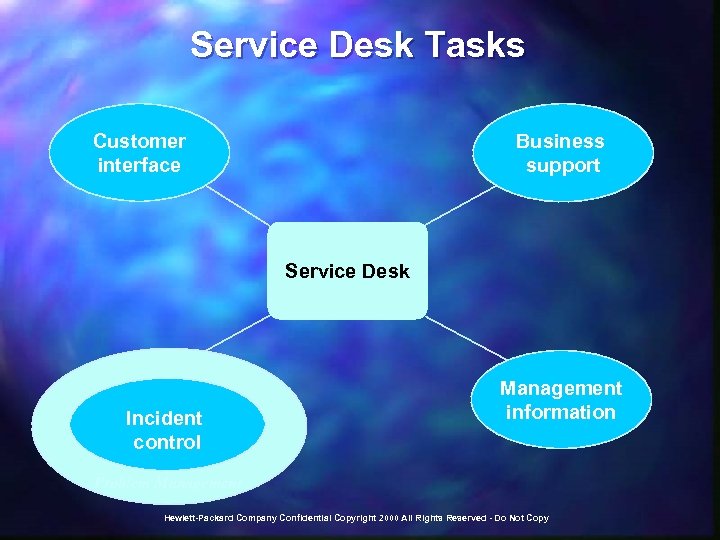 Service Desk Tasks Customer interface Business support Service Desk Incident control Management information Problem Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Service Desk Tasks Customer interface Business support Service Desk Incident control Management information Problem Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
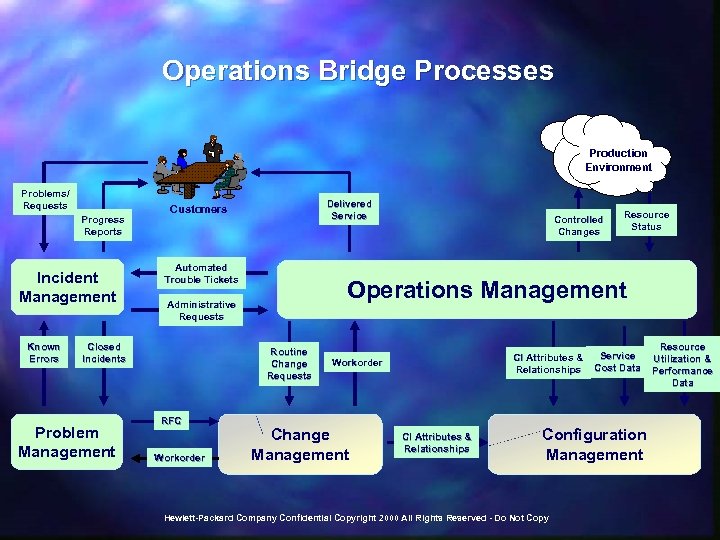 Operations Bridge Processes Production Environment Problems/ Requests Progress Reports Incident Management Known Errors Automated Trouble Tickets Routine Change Requests RFC Workorder Controlled Changes Resource Status Operations Management Administrative Requests Closed Incidents Problem Management Delivered Service Customers CI Attributes & Relationships Workorder Change Management CI Attributes & Relationships Service Cost Data Configuration Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Resource Utilization & Performance Data
Operations Bridge Processes Production Environment Problems/ Requests Progress Reports Incident Management Known Errors Automated Trouble Tickets Routine Change Requests RFC Workorder Controlled Changes Resource Status Operations Management Administrative Requests Closed Incidents Problem Management Delivered Service Customers CI Attributes & Relationships Workorder Change Management CI Attributes & Relationships Service Cost Data Configuration Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Resource Utilization & Performance Data
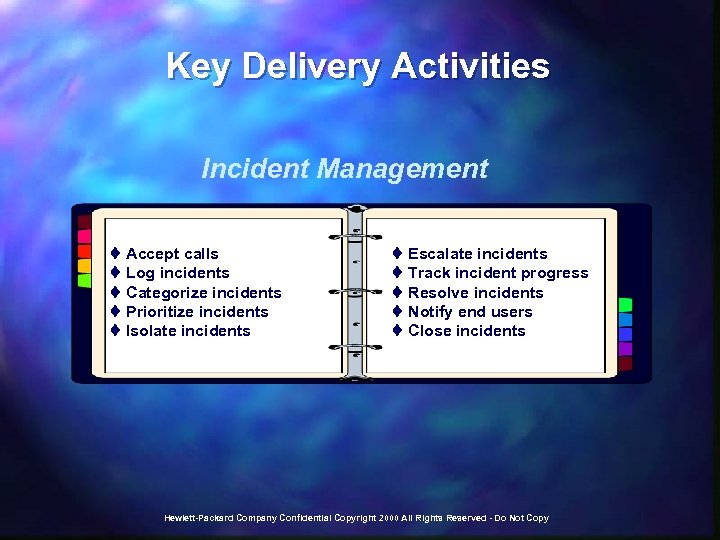 Key Delivery Activities Incident Management t Accept calls t Log incidents t Categorize incidents t Prioritize incidents t Isolate incidents t Escalate incidents t Track incident progress t Resolve incidents t Notify end users t Close incidents Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Key Delivery Activities Incident Management t Accept calls t Log incidents t Categorize incidents t Prioritize incidents t Isolate incidents t Escalate incidents t Track incident progress t Resolve incidents t Notify end users t Close incidents Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
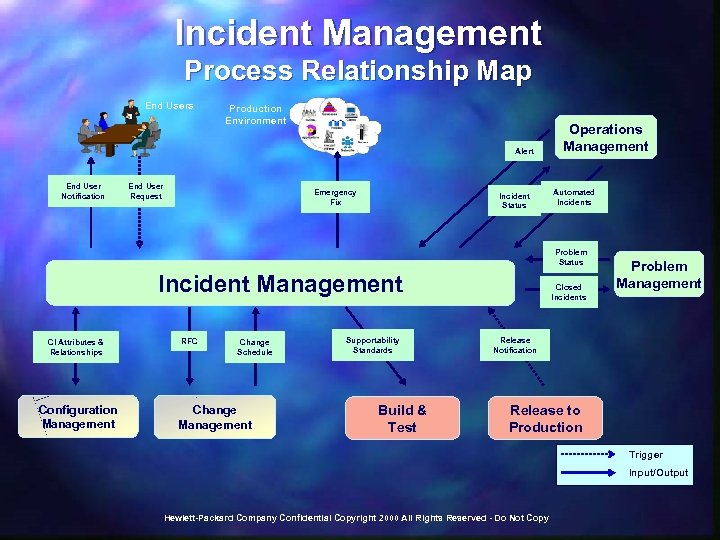 Incident Management Process Relationship Map End Users Production Environment Alert End User Notification End User Request Emergency Fix Incident Status Operations Management Automated Incidents Problem Status Incident Management CI Attributes & Relationships Configuration Management RFC Change Schedule Change Management Supportability Standards Build & Test Closed Incidents Problem Management Release Notification Release to Production Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Incident Management Process Relationship Map End Users Production Environment Alert End User Notification End User Request Emergency Fix Incident Status Operations Management Automated Incidents Problem Status Incident Management CI Attributes & Relationships Configuration Management RFC Change Schedule Change Management Supportability Standards Build & Test Closed Incidents Problem Management Release Notification Release to Production Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Incidents, Problems and Known Errors n n n Incident – Any event which is not part of the standard operation of a service and which causes or may cause an interruption to or a reduction in the quality of that service. Problem – The unknown root cause of one or more incidents (not necessarily known or solved at the time the incident is closed). Known Error – A condition that exists after the successful diagnosis of the root cause of a problem when it is confirmed that a CI is at fault. A work-around exists and is used to restore service until the error is removed by implementing a change. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Incidents, Problems and Known Errors n n n Incident – Any event which is not part of the standard operation of a service and which causes or may cause an interruption to or a reduction in the quality of that service. Problem – The unknown root cause of one or more incidents (not necessarily known or solved at the time the incident is closed). Known Error – A condition that exists after the successful diagnosis of the root cause of a problem when it is confirmed that a CI is at fault. A work-around exists and is used to restore service until the error is removed by implementing a change. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
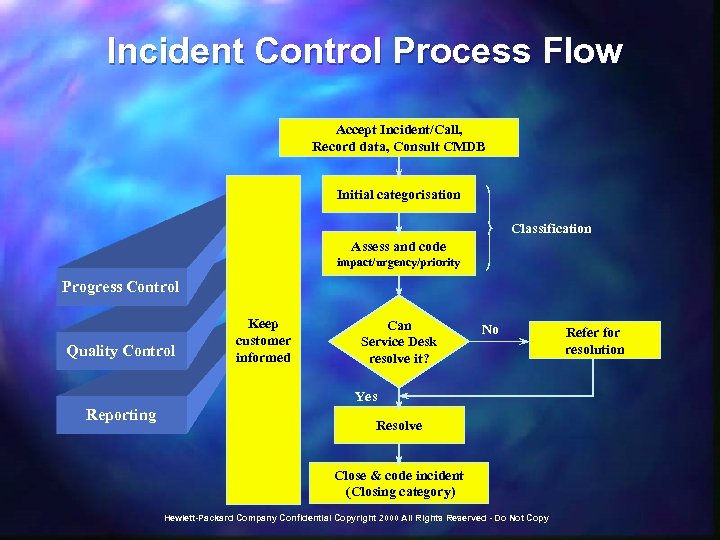 Incident Control Process Flow Accept Incident/Call, Record data, Consult CMDB Initial categorisation Classification Assess and code impact/urgency/priority Progress Control Quality Control Keep customer informed Can Service Desk resolve it? No Yes Reporting Resolve Close & code incident (Closing category) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Refer for resolution
Incident Control Process Flow Accept Incident/Call, Record data, Consult CMDB Initial categorisation Classification Assess and code impact/urgency/priority Progress Control Quality Control Keep customer informed Can Service Desk resolve it? No Yes Reporting Resolve Close & code incident (Closing category) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Refer for resolution
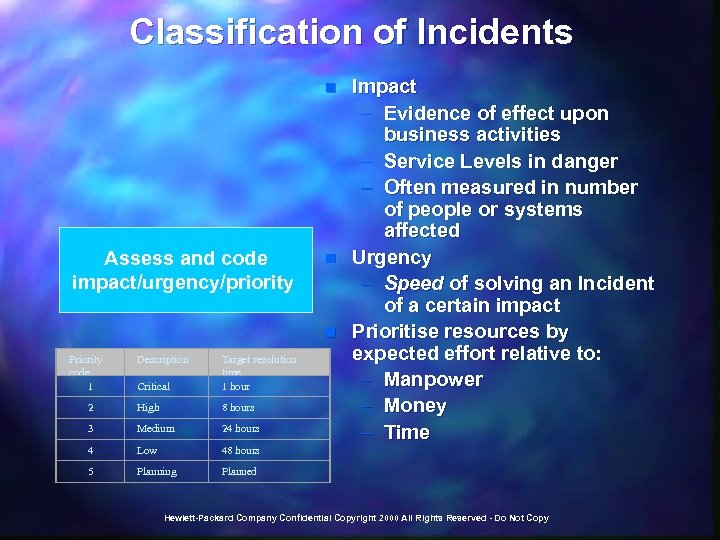 Classification of Incidents n Assess and code impact/urgency/priority n n Priority code 1 Description Critical Target resolution time 1 hour 2 High 8 hours 3 Medium 24 hours 4 Low 48 hours 5 Planning Impact – Evidence of effect upon business activities – Service Levels in danger – Often measured in number of people or systems affected Urgency – Speed of solving an Incident of a certain impact Prioritise resources by expected effort relative to: – Manpower – Money – Time Planned Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Classification of Incidents n Assess and code impact/urgency/priority n n Priority code 1 Description Critical Target resolution time 1 hour 2 High 8 hours 3 Medium 24 hours 4 Low 48 hours 5 Planning Impact – Evidence of effect upon business activities – Service Levels in danger – Often measured in number of people or systems affected Urgency – Speed of solving an Incident of a certain impact Prioritise resources by expected effort relative to: – Manpower – Money – Time Planned Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
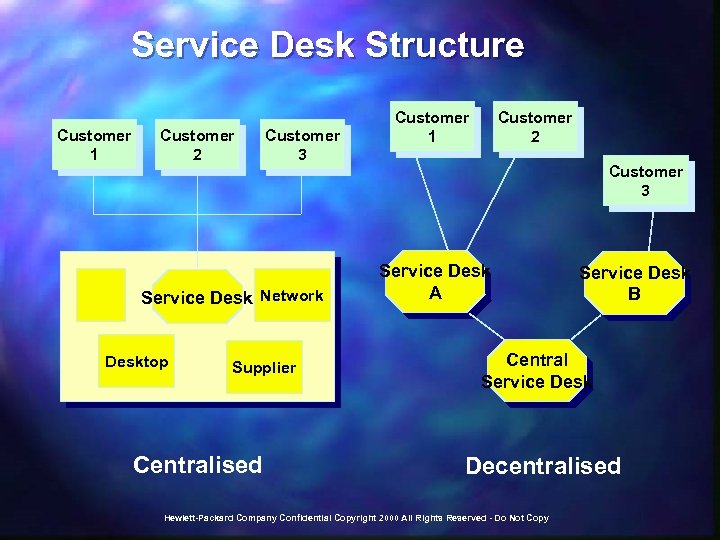 Service Desk Structure Customer 1 Customer 2 Customer 3 Service Desk Network Desktop Supplier Centralised Customer 1 Customer 2 Customer 3 Service Desk A Service Desk B Central Service Desk Decentralised Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Service Desk Structure Customer 1 Customer 2 Customer 3 Service Desk Network Desktop Supplier Centralised Customer 1 Customer 2 Customer 3 Service Desk A Service Desk B Central Service Desk Decentralised Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
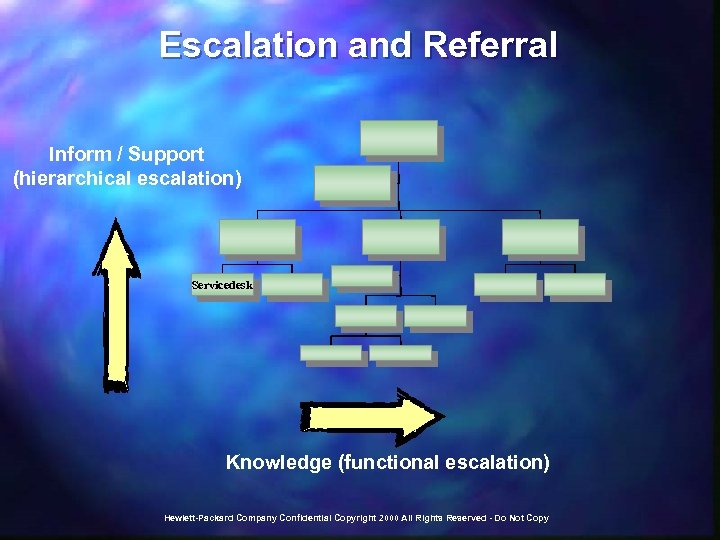 Escalation and Referral Inform / Support (hierarchical escalation) Servicedesk Knowledge (functional escalation) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Escalation and Referral Inform / Support (hierarchical escalation) Servicedesk Knowledge (functional escalation) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
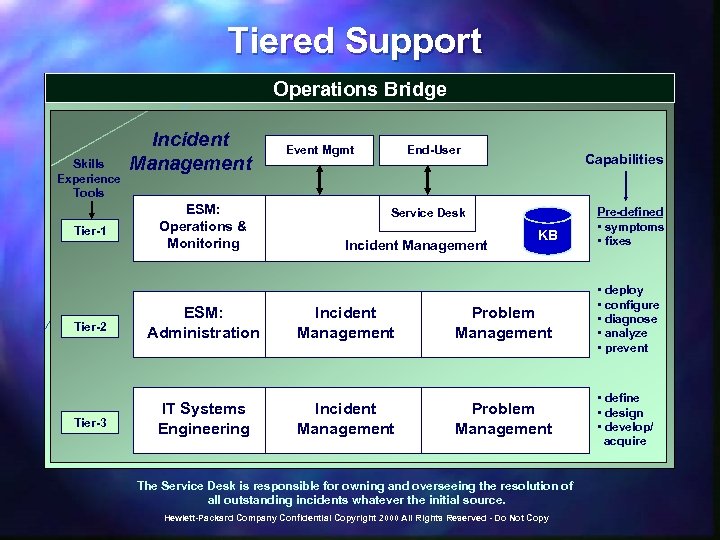 Tiered Support Operations Bridge Skills Experience Tools Tier-1 Incident Management ESM: Operations & Monitoring Event Mgmt End-User Capabilities Service Desk Incident Management KB Pre-defined • symptoms • fixes Tier-2 ESM: Administration Incident Management Problem Management • deploy • configure • diagnose • analyze • prevent Tier-3 IT Systems Engineering Incident Management Problem Management • define • design • develop/ acquire The Service Desk is responsible for owning and overseeing the resolution of all outstanding incidents whatever the initial source. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Tiered Support Operations Bridge Skills Experience Tools Tier-1 Incident Management ESM: Operations & Monitoring Event Mgmt End-User Capabilities Service Desk Incident Management KB Pre-defined • symptoms • fixes Tier-2 ESM: Administration Incident Management Problem Management • deploy • configure • diagnose • analyze • prevent Tier-3 IT Systems Engineering Incident Management Problem Management • define • design • develop/ acquire The Service Desk is responsible for owning and overseeing the resolution of all outstanding incidents whatever the initial source. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Service Desk Essentials n n n n Single point of contact/Restore service ASAP Tasks: Customer Interface, Business Support, Incident Control & Management Information Concentrates on incident lifecycle management Incident: (Expected) disruption to agreed service Priority determined by business impact and urgency Correct assessment of priorities enables the deployment of manpower and other resources to be in the best interests of the customer Escalation and referral Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Service Desk Essentials n n n n Single point of contact/Restore service ASAP Tasks: Customer Interface, Business Support, Incident Control & Management Information Concentrates on incident lifecycle management Incident: (Expected) disruption to agreed service Priority determined by business impact and urgency Correct assessment of priorities enables the deployment of manpower and other resources to be in the best interests of the customer Escalation and referral Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n Integrate with service level management. Place less emphasis on “pass-through” and more on “one and done. ” Place less emphasis on reducing IT's costs and more on increasing business effectiveness. Position Service Desk as the primary interface to IT and use it to increase IT credibility throughout lines of business. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n Integrate with service level management. Place less emphasis on “pass-through” and more on “one and done. ” Place less emphasis on reducing IT's costs and more on increasing business effectiveness. Position Service Desk as the primary interface to IT and use it to increase IT credibility throughout lines of business. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n n Better utilization and increased productivity of skilled staff Fewer incidents and user difficulties with business applications Reduction in times to respond to users and to resolve incidents Greater client focus Earlier and more effective identification of problem areas Higher levels of IT service availability Comprehensive and accurate management information about the quality of service and user support Information to the business of the “health” of business applications Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n n Better utilization and increased productivity of skilled staff Fewer incidents and user difficulties with business applications Reduction in times to respond to users and to resolve incidents Greater client focus Earlier and more effective identification of problem areas Higher levels of IT service availability Comprehensive and accurate management information about the quality of service and user support Information to the business of the “health” of business applications Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Common Roadblocks n n n n n How many Service Desks are enough? Interface and information sharing within large organizations Servicedesk is launched too early and gets swamped No process for functional escalation Tension between Servicedesk and other IT units Users try to bypass the system The director as Servicedesk Ineffective communication between development and Servicedesk (e. g. at roll-outs) Point solution impedes integration Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n n n How many Service Desks are enough? Interface and information sharing within large organizations Servicedesk is launched too early and gets swamped No process for functional escalation Tension between Servicedesk and other IT units Users try to bypass the system The director as Servicedesk Ineffective communication between development and Servicedesk (e. g. at roll-outs) Point solution impedes integration Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Problem Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Problem Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Problem Management Objectives What is a problem? A condition identified often because of multiple incidents that exhibit common symptoms. Problems can also be identified from a single significant incident, indicative of a single error, for which the cause is unknown, but for which the impact is significant. n n n Stabilizing IT services through: – Minimizing the consequences of incidents – Removal of the root causes of incidents – Prevention of incidents and problems Improving productive use of resources Ensure that previous information is documented in such a way that it is readily recyclable to front line and other second line staff Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Problem Management Objectives What is a problem? A condition identified often because of multiple incidents that exhibit common symptoms. Problems can also be identified from a single significant incident, indicative of a single error, for which the cause is unknown, but for which the impact is significant. n n n Stabilizing IT services through: – Minimizing the consequences of incidents – Removal of the root causes of incidents – Prevention of incidents and problems Improving productive use of resources Ensure that previous information is documented in such a way that it is readily recyclable to front line and other second line staff Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Problem Management Tasks Incident Management Problem control Problem Management Known Error control Management information RFCs Change Management Check after change Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Problem Management Tasks Incident Management Problem control Problem Management Known Error control Management information RFCs Change Management Check after change Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
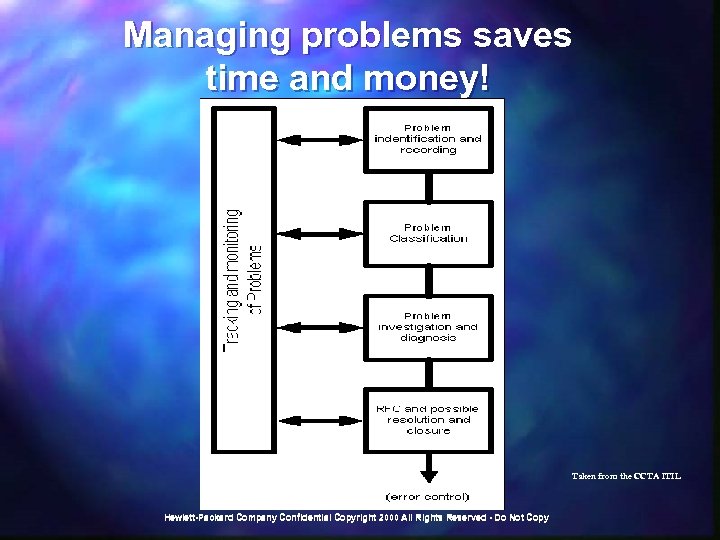 Managing problems saves time and money! Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Managing problems saves time and money! Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
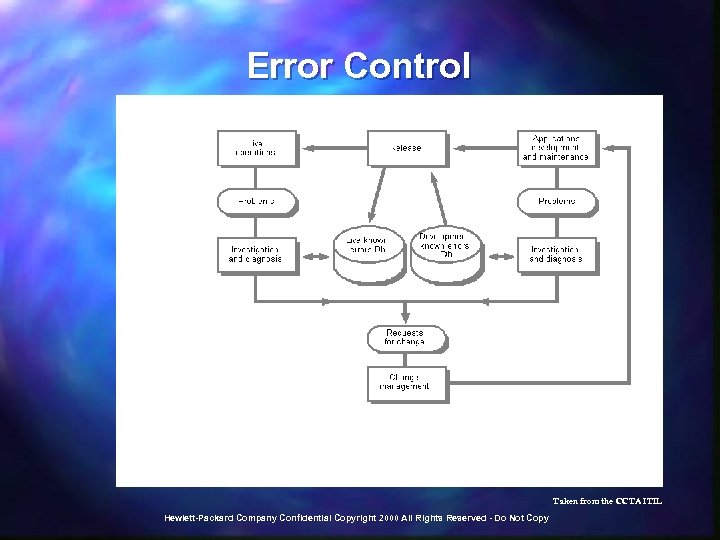 Error Control Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Error Control Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
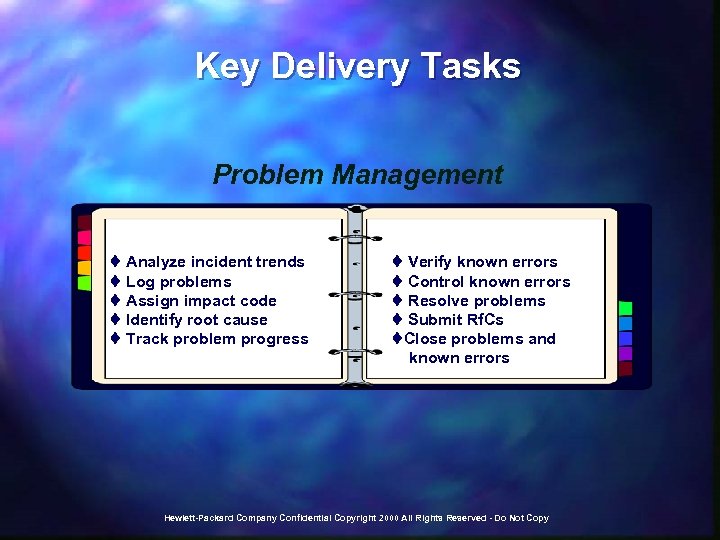 Key Delivery Tasks Problem Management t Analyze incident trends t Log problems t Assign impact code t Identify root cause t Track problem progress t Verify known errors t Control known errors t Resolve problems t Submit Rf. Cs t. Close problems and known errors Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Key Delivery Tasks Problem Management t Analyze incident trends t Log problems t Assign impact code t Identify root cause t Track problem progress t Verify known errors t Control known errors t Resolve problems t Submit Rf. Cs t. Close problems and known errors Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
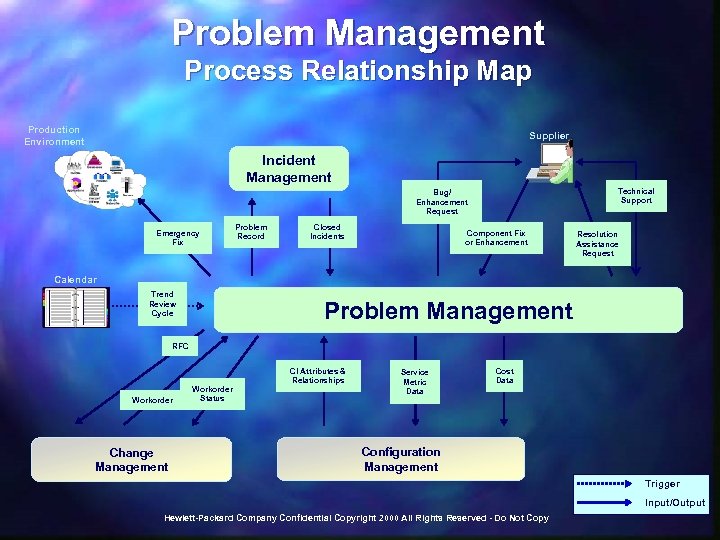 Problem Management Process Relationship Map Production Environment Supplier Incident Management Technical Support Bug/ Enhancement Request Emergency Fix Problem Record Closed Incidents Component Fix or Enhancement Resolution Assistance Request Calendar Trend Review Cycle Problem Management RFC Workorder Change Management Workorder Status CI Attributes & Relationships Service Metric Data Cost Data Configuration Management Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Problem Management Process Relationship Map Production Environment Supplier Incident Management Technical Support Bug/ Enhancement Request Emergency Fix Problem Record Closed Incidents Component Fix or Enhancement Resolution Assistance Request Calendar Trend Review Cycle Problem Management RFC Workorder Change Management Workorder Status CI Attributes & Relationships Service Metric Data Cost Data Configuration Management Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
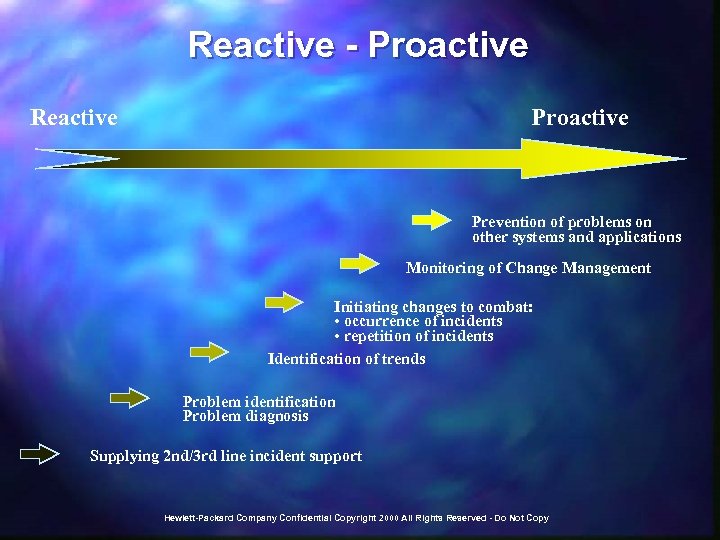 Reactive - Proactive Reactive Proactive Prevention of problems on other systems and applications Monitoring of Change Management Initiating changes to combat: • occurrence of incidents • repetition of incidents Identification of trends Problem identification Problem diagnosis Supplying 2 nd/3 rd line incident support Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Reactive - Proactive Reactive Proactive Prevention of problems on other systems and applications Monitoring of Change Management Initiating changes to combat: • occurrence of incidents • repetition of incidents Identification of trends Problem identification Problem diagnosis Supplying 2 nd/3 rd line incident support Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Problem Management Essentials n n n Objectives – Manage the problem life-cycle – Stabilizing services through: n Minimizing the consequences of incidents (the quick fix) n Removing the causes of incidents n Preventing occurrence of incidents and problems – Improving productive use of resources: Tasks – Problem Control, Error Control (including raising RFCs), Management information Reactive to proactive (stop problems occurring/recurring) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Problem Management Essentials n n n Objectives – Manage the problem life-cycle – Stabilizing services through: n Minimizing the consequences of incidents (the quick fix) n Removing the causes of incidents n Preventing occurrence of incidents and problems – Improving productive use of resources: Tasks – Problem Control, Error Control (including raising RFCs), Management information Reactive to proactive (stop problems occurring/recurring) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n n Separate incidents and problems into distinct areas of responsibility with separate metrics. Emphasize containment and prevention of incidents. Go beyond operational environment to encompass systems and infrastructure development as well. Skill people on methods for root cause analysis and problem solving. Separate the PM process from the management of the PM process. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n n Separate incidents and problems into distinct areas of responsibility with separate metrics. Emphasize containment and prevention of incidents. Go beyond operational environment to encompass systems and infrastructure development as well. Skill people on methods for root cause analysis and problem solving. Separate the PM process from the management of the PM process. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n It is a key part of an overall service improvement program It helps generate a cycle of rapidly increasing IT service quality. It is instrumental in reducing the number of incidents, leading to improve IT service quality. There will be a gradual reduction in the number and impact of problems and known errors as problems and errors that are resolved, stay resolved. The process is based on the concept of learning from past experience. There will be a better first time fix rate of incidents at the Service Desk, achieved via the capture, retention and availability of incident resolution and workaround data within a knowledge database available to the Service Desk at call logging. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n It is a key part of an overall service improvement program It helps generate a cycle of rapidly increasing IT service quality. It is instrumental in reducing the number of incidents, leading to improve IT service quality. There will be a gradual reduction in the number and impact of problems and known errors as problems and errors that are resolved, stay resolved. The process is based on the concept of learning from past experience. There will be a better first time fix rate of incidents at the Service Desk, achieved via the capture, retention and availability of incident resolution and workaround data within a knowledge database available to the Service Desk at call logging. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Common Roadblocks n n Allocating support staff resources to incident and problem management. Limited integration between point solution tools. Poor communications between systems development and error control in the live environment. Lack of discipline in support teams Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n Allocating support staff resources to incident and problem management. Limited integration between point solution tools. Poor communications between systems development and error control in the live environment. Lack of discipline in support teams Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Change Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Change Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Change Management Objective To implement approved changes efficiently, cost-effectively and with minimal risk to the existing and to the new IT infrastructure Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Change Management Objective To implement approved changes efficiently, cost-effectively and with minimal risk to the existing and to the new IT infrastructure Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
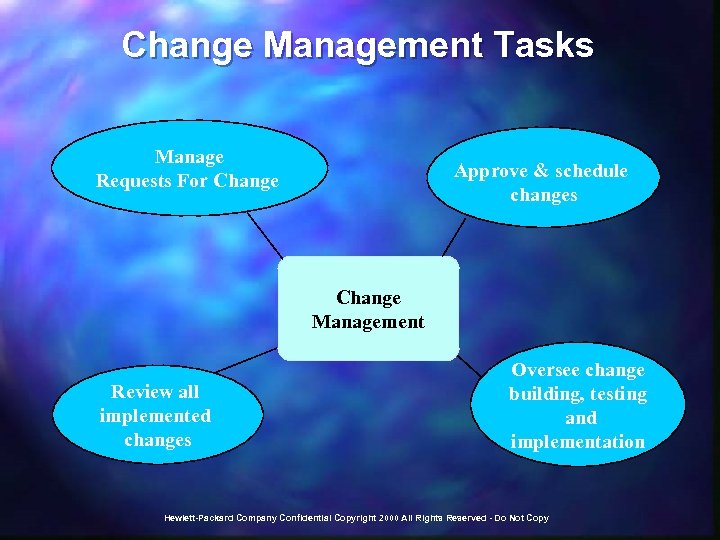 Change Management Tasks Manage Requests For Change Approve & schedule changes Change Management Review all implemented changes Oversee change building, testing and implementation Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Change Management Tasks Manage Requests For Change Approve & schedule changes Change Management Review all implemented changes Oversee change building, testing and implementation Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
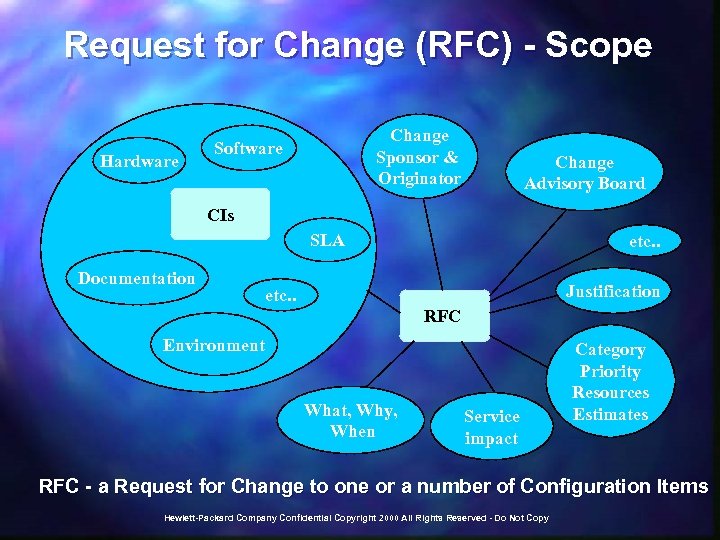 Request for Change (RFC) - Scope Hardware Change Sponsor & Originator Software Change Advisory Board CIs SLA Documentation etc. . Justification etc. . RFC Environment What, Why, When Service impact Category Priority Resources Estimates RFC - a Request for Change to one or a number of Configuration Items Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Request for Change (RFC) - Scope Hardware Change Sponsor & Originator Software Change Advisory Board CIs SLA Documentation etc. . Justification etc. . RFC Environment What, Why, When Service impact Category Priority Resources Estimates RFC - a Request for Change to one or a number of Configuration Items Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Impact of Change n n n Category 1 – Little impact on current services. The Change Manager is entitled to authorize this RFC. Category 2 – Clear impact on the services. The RFC must be discussed in the Change Advisory Board. The Change Manager requests advice on authorization and planning. Category 3 – Significant impact on the services and the business. Considerable manpower and/or resources needed. The RFC will have to be submitted to the board level. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Impact of Change n n n Category 1 – Little impact on current services. The Change Manager is entitled to authorize this RFC. Category 2 – Clear impact on the services. The RFC must be discussed in the Change Advisory Board. The Change Manager requests advice on authorization and planning. Category 3 – Significant impact on the services and the business. Considerable manpower and/or resources needed. The RFC will have to be submitted to the board level. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Priority Setting n n Urgent – Change necessary now (otherwise severe business impact) High – Change needed as soon as possible (potentially damaging) Medium – Change will solve irritating errors or missing functionality (can be scheduled) Low – Change leads to minor improvements (that are not contractually necessary) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Priority Setting n n Urgent – Change necessary now (otherwise severe business impact) High – Change needed as soon as possible (potentially damaging) Medium – Change will solve irritating errors or missing functionality (can be scheduled) Low – Change leads to minor improvements (that are not contractually necessary) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
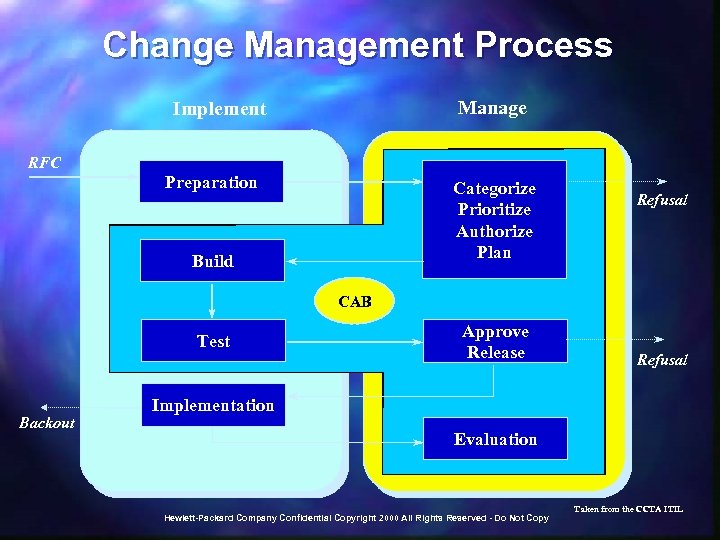 Change Management Process Manage Implement RFC Preparation Categorize Prioritize Authorize Plan Build Refusal CAB Test Backout Approve Release Refusal Implementation Evaluation Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Taken from the CCTA ITIL
Change Management Process Manage Implement RFC Preparation Categorize Prioritize Authorize Plan Build Refusal CAB Test Backout Approve Release Refusal Implementation Evaluation Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Taken from the CCTA ITIL
 Management of the Change “Management” of change requests means: • evaluating the change for appropriateness, scope, ownership • authorizing the request • setting priorities for requests • scheduling resources needed to effect the change • assessing risks associated with requested changes • managing change projects Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Management of the Change “Management” of change requests means: • evaluating the change for appropriateness, scope, ownership • authorizing the request • setting priorities for requests • scheduling resources needed to effect the change • assessing risks associated with requested changes • managing change projects Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Implementation of Changes Implementing change requests means: • breaking up change projects into work orders • assigning work orders to appropriate owners • ensuring that the changes will not have an adverse impact on the IT production environment • monitoring and tracking significant steps in the development and deployment of changes Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Implementation of Changes Implementing change requests means: • breaking up change projects into work orders • assigning work orders to appropriate owners • ensuring that the changes will not have an adverse impact on the IT production environment • monitoring and tracking significant steps in the development and deployment of changes Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
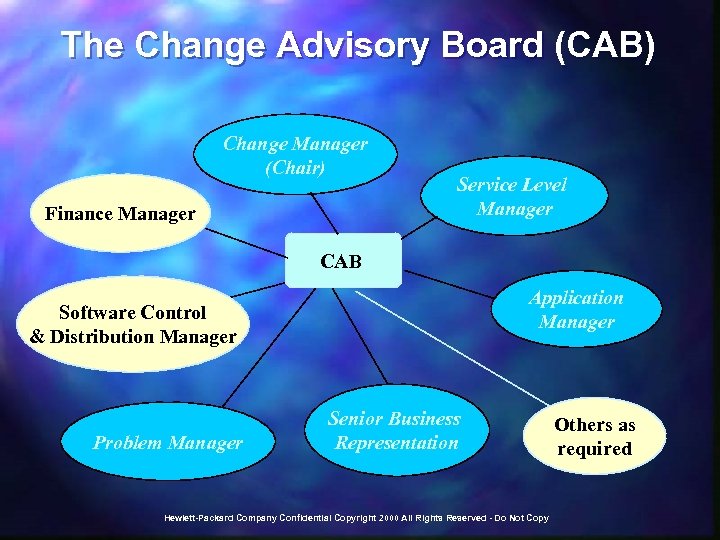 The Change Advisory Board (CAB) Change Manager (Chair) Finance Manager Service Level Manager CAB Application Manager Software Control & Distribution Manager Problem Manager Senior Business Representation Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Others as required
The Change Advisory Board (CAB) Change Manager (Chair) Finance Manager Service Level Manager CAB Application Manager Software Control & Distribution Manager Problem Manager Senior Business Representation Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Others as required
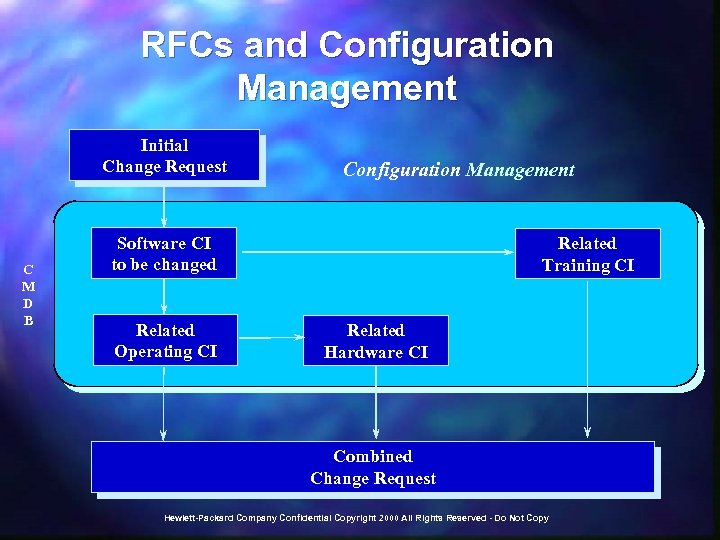 RFCs and Configuration Management Initial Change Request C M D B Configuration Management Software CI to be changed Related Operating CI Related Training CI Related Hardware CI Combined Change Request Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
RFCs and Configuration Management Initial Change Request C M D B Configuration Management Software CI to be changed Related Operating CI Related Training CI Related Hardware CI Combined Change Request Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Change Management Essentials – Objective n Only approved changes made, risk and cost minimized – Request For Change (RFC) n Applies to all IT infrastructure components – Tasks n Manage RFCs; approve & schedule changes; oversee change building, testing & implementation; business support – CAB and CAB/EC: n Membership n Advisory role n Assess impact, urgency & resources n Urgent changes – Urgency/Priority: urgent, high, medium, low – Impact category: no impact. . tremendous impact – Backout – Process always ends with a review of the change Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Change Management Essentials – Objective n Only approved changes made, risk and cost minimized – Request For Change (RFC) n Applies to all IT infrastructure components – Tasks n Manage RFCs; approve & schedule changes; oversee change building, testing & implementation; business support – CAB and CAB/EC: n Membership n Advisory role n Assess impact, urgency & resources n Urgent changes – Urgency/Priority: urgent, high, medium, low – Impact category: no impact. . tremendous impact – Backout – Process always ends with a review of the change Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
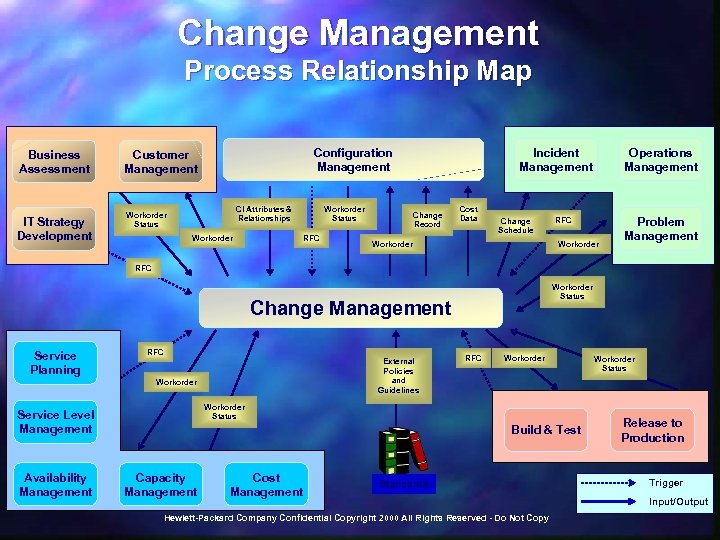 Change Management Process Relationship Map Business Assessment IT Strategy Development Configuration Management Customer Management CI Attributes & Relationships Workorder Status RFC Incident Management Change Record Cost Data Change Schedule Workorder Operations Management RFC Workorder Problem Management RFC Workorder Status Change Management Service Planning RFC External Policies and Guidelines Workorder Status Service Level Management Availability Management RFC Build & Test Capacity Management Cost Management Standards Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Workorder Status Release to Production Trigger Input/Output
Change Management Process Relationship Map Business Assessment IT Strategy Development Configuration Management Customer Management CI Attributes & Relationships Workorder Status RFC Incident Management Change Record Cost Data Change Schedule Workorder Operations Management RFC Workorder Problem Management RFC Workorder Status Change Management Service Planning RFC External Policies and Guidelines Workorder Status Service Level Management Availability Management RFC Build & Test Capacity Management Cost Management Standards Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Workorder Status Release to Production Trigger Input/Output
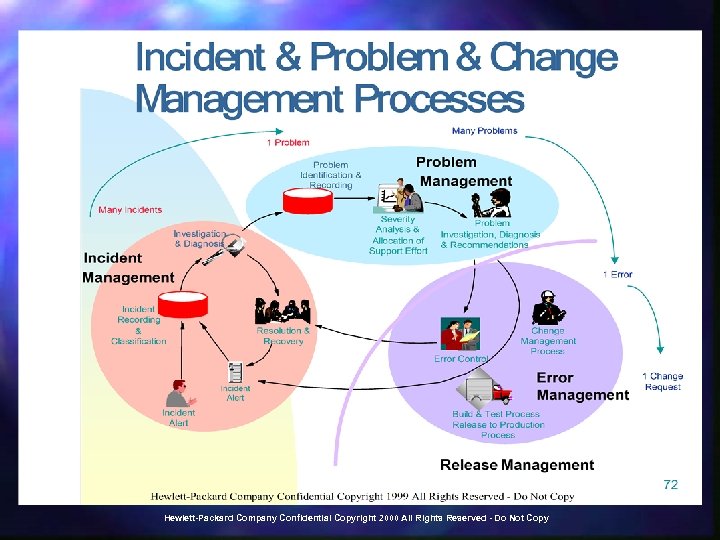 Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n n Integrate with Configuration Management and Software Control & Distribution. Go beyond operational environment to encompass systems and infrastructure development as well. Separate the process and the management of the process. Assign ownership of process as independently as possible of the line hierarchy. Plan for urgent changes rather than making urgent changes via the normal change procedure. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n n Integrate with Configuration Management and Software Control & Distribution. Go beyond operational environment to encompass systems and infrastructure development as well. Separate the process and the management of the process. Assign ownership of process as independently as possible of the line hierarchy. Plan for urgent changes rather than making urgent changes via the normal change procedure. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n n Less adverse impact of changes on services. Better up-front assessment of the costs of proposed changes. Reduction in the number of disruptive changes through packaging. Reduction in number of failed changes. Better communication with customers. Valuable management information. Increased productivity of customers and IT personnel. Ability to absorb a higher level of error-free change. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n n Less adverse impact of changes on services. Better up-front assessment of the costs of proposed changes. Reduction in the number of disruptive changes through packaging. Reduction in number of failed changes. Better communication with customers. Valuable management information. Increased productivity of customers and IT personnel. Ability to absorb a higher level of error-free change. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Common Roadblocks n n n Tracing life-cycle of a change, paper based systems overload easily Attempts to implement changes outside of procedure Involving outside suppliers Cultural clashes - acceptance of process discipline Excessive over-ruling for strategic expedience Over-zealousness can lead to analysis-paralysis Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n Tracing life-cycle of a change, paper based systems overload easily Attempts to implement changes outside of procedure Involving outside suppliers Cultural clashes - acceptance of process discipline Excessive over-ruling for strategic expedience Over-zealousness can lead to analysis-paralysis Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Configuration Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Configuration Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
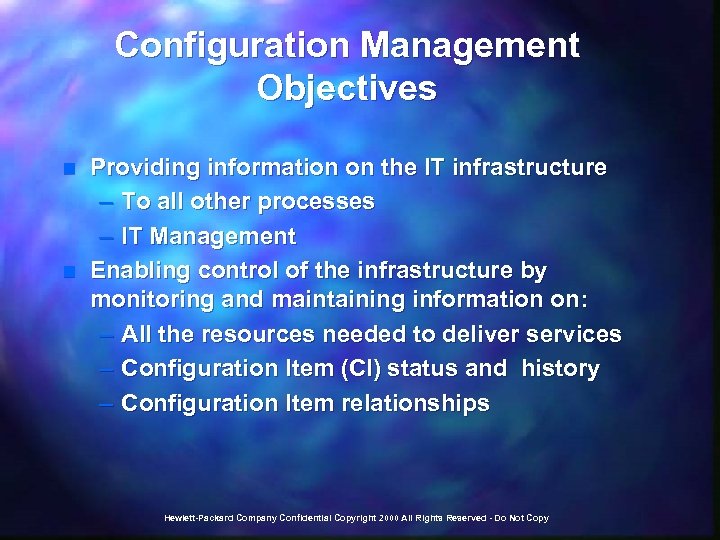 Configuration Management Objectives n n Providing information on the IT infrastructure – To all other processes – IT Management Enabling control of the infrastructure by monitoring and maintaining information on: – All the resources needed to deliver services – Configuration Item (CI) status and history – Configuration Item relationships Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Configuration Management Objectives n n Providing information on the IT infrastructure – To all other processes – IT Management Enabling control of the infrastructure by monitoring and maintaining information on: – All the resources needed to deliver services – Configuration Item (CI) status and history – Configuration Item relationships Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
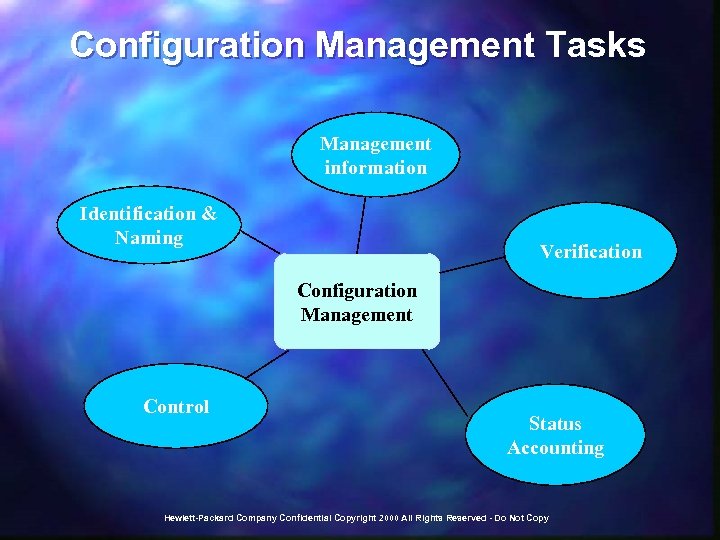 Configuration Management Tasks Management information Identification & Naming Verification Configuration Management Control Status Accounting Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Configuration Management Tasks Management information Identification & Naming Verification Configuration Management Control Status Accounting Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
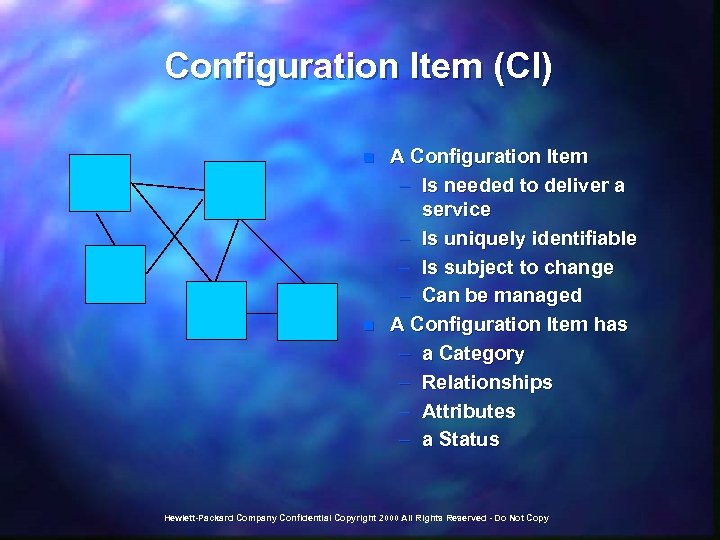 Configuration Item (CI) n n A Configuration Item – Is needed to deliver a service – Is uniquely identifiable – Is subject to change – Can be managed A Configuration Item has – a Category – Relationships – Attributes – a Status Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Configuration Item (CI) n n A Configuration Item – Is needed to deliver a service – Is uniquely identifiable – Is subject to change – Can be managed A Configuration Item has – a Category – Relationships – Attributes – a Status Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
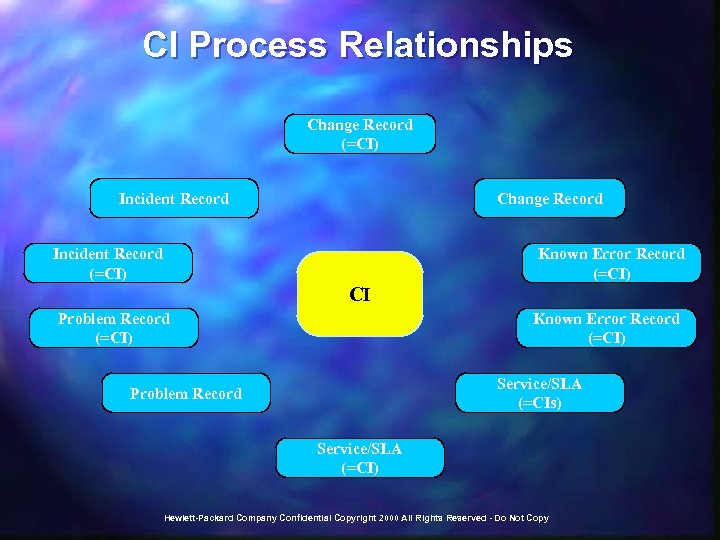 CI Process Relationships Change Record (=CI) Incident Record Change Record Incident Record (=CI) Known Error Record (=CI) CI Problem Record (=CI) Known Error Record (=CI) Service/SLA (=CIs) Problem Record Service/SLA (=CI) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
CI Process Relationships Change Record (=CI) Incident Record Change Record Incident Record (=CI) Known Error Record (=CI) CI Problem Record (=CI) Known Error Record (=CI) Service/SLA (=CIs) Problem Record Service/SLA (=CI) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
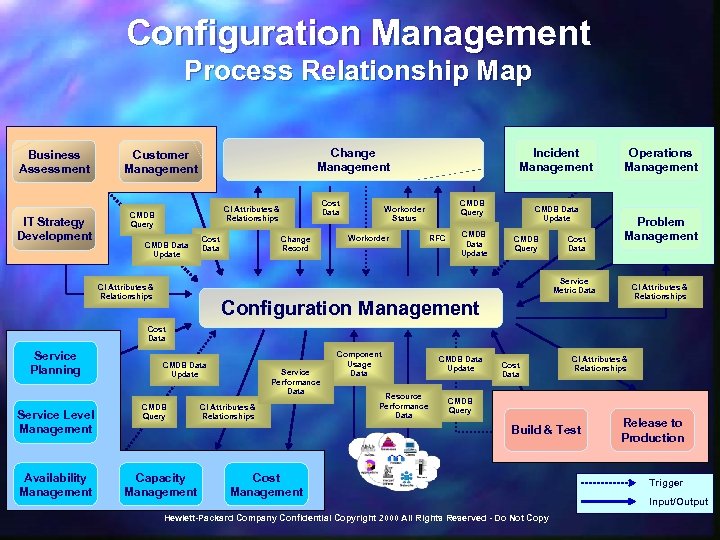 Configuration Management Process Relationship Map Business Assessment IT Strategy Development Change Management Customer Management Cost Data CI Attributes & Relationships CMDB Query CMDB Data Update Cost Data Change Record Incident Management CMDB Query Workorder Status Workorder RFC CMDB Data Update CMDB Query Cost Data Operations Management Problem Management Service Metric Data CI Attributes & Relationships Configuration Management Cost Data Service Planning Service Level Management Availability Management CMDB Data Update CMDB Query Service Performance Data CI Attributes & Relationships Component Usage Data Resource Performance Data CMDB Data Update Cost Data CI Attributes & Relationships CMDB Query Build & Test Capacity Management Cost Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Release to Production Trigger Input/Output
Configuration Management Process Relationship Map Business Assessment IT Strategy Development Change Management Customer Management Cost Data CI Attributes & Relationships CMDB Query CMDB Data Update Cost Data Change Record Incident Management CMDB Query Workorder Status Workorder RFC CMDB Data Update CMDB Query Cost Data Operations Management Problem Management Service Metric Data CI Attributes & Relationships Configuration Management Cost Data Service Planning Service Level Management Availability Management CMDB Data Update CMDB Query Service Performance Data CI Attributes & Relationships Component Usage Data Resource Performance Data CMDB Data Update Cost Data CI Attributes & Relationships CMDB Query Build & Test Capacity Management Cost Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Release to Production Trigger Input/Output
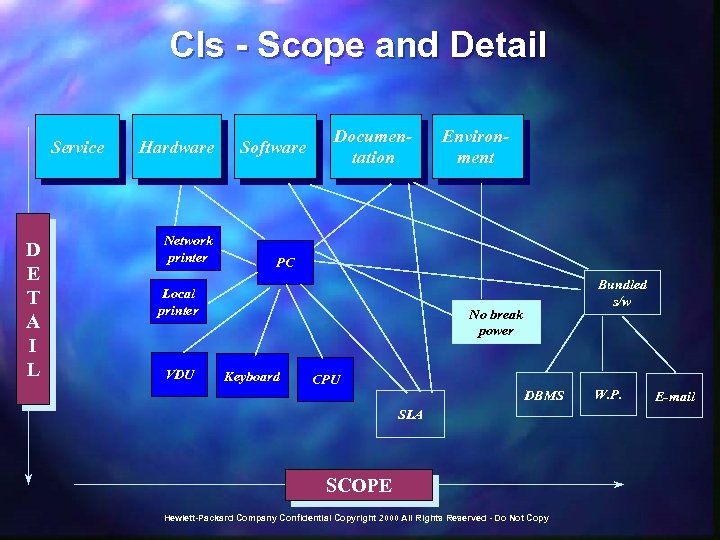 CIs - Scope and Detail Service D E T A I L Hardware Network printer Software Documentation PC Local printer VDU Environment Bundled s/w No break power Keyboard CPU DBMS SLA SCOPE Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy W. P. E-mail
CIs - Scope and Detail Service D E T A I L Hardware Network printer Software Documentation PC Local printer VDU Environment Bundled s/w No break power Keyboard CPU DBMS SLA SCOPE Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy W. P. E-mail
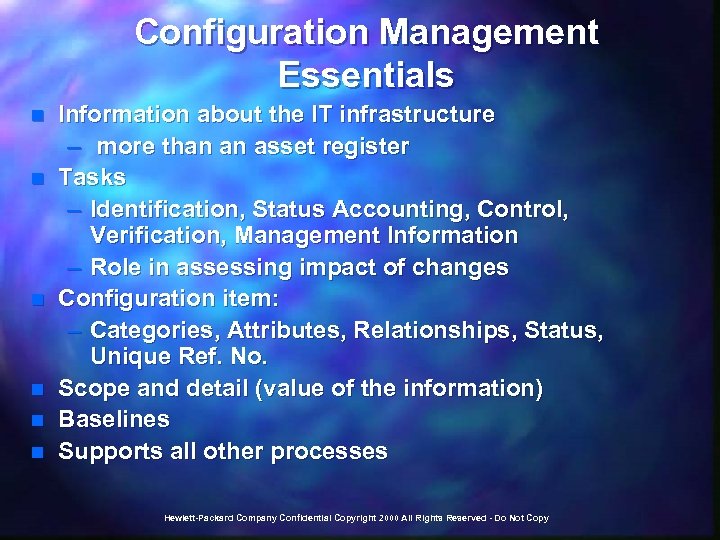 Configuration Management Essentials n n n Information about the IT infrastructure – more than an asset register Tasks – Identification, Status Accounting, Control, Verification, Management Information – Role in assessing impact of changes Configuration item: – Categories, Attributes, Relationships, Status, Unique Ref. No. Scope and detail (value of the information) Baselines Supports all other processes Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Configuration Management Essentials n n n Information about the IT infrastructure – more than an asset register Tasks – Identification, Status Accounting, Control, Verification, Management Information – Role in assessing impact of changes Configuration item: – Categories, Attributes, Relationships, Status, Unique Ref. No. Scope and detail (value of the information) Baselines Supports all other processes Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n n n Start early to establish the Configuration Management practice Build gradually based on perceived priorities Emphasize importance of build Careful tool selection Discipline (enforcement) to use Change Process when making changes Automated discovery tools with resource inventory capability for reconciliation Value proposition - "You can only control what you can measure, and not everything needs controlling" Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n n n Start early to establish the Configuration Management practice Build gradually based on perceived priorities Emphasize importance of build Careful tool selection Discipline (enforcement) to use Change Process when making changes Automated discovery tools with resource inventory capability for reconciliation Value proposition - "You can only control what you can measure, and not everything needs controlling" Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n n Improves asset management Reduces risks from changes Leads to more effective user support Improves security against malicious changes Facilitates compliance with legal obligations Supports budget process Facilitates service level management Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n n Improves asset management Reduces risks from changes Leads to more effective user support Improves security against malicious changes Facilitates compliance with legal obligations Supports budget process Facilitates service level management Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
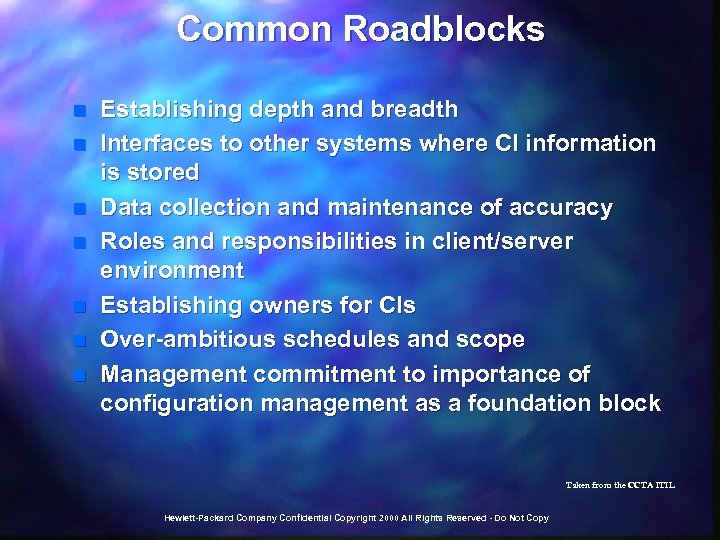 Common Roadblocks n n n n Establishing depth and breadth Interfaces to other systems where CI information is stored Data collection and maintenance of accuracy Roles and responsibilities in client/server environment Establishing owners for CIs Over-ambitious schedules and scope Management commitment to importance of configuration management as a foundation block Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n n Establishing depth and breadth Interfaces to other systems where CI information is stored Data collection and maintenance of accuracy Roles and responsibilities in client/server environment Establishing owners for CIs Over-ambitious schedules and scope Management commitment to importance of configuration management as a foundation block Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Operations Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Operations Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Key Delivery Activities These functions manage and perform normal day-to day processing activities within the IT production environment, required for IT service delivery and in accordance with agreed-upon service levels. t Schedule production processing t Monitor resource status and raise alerts t Manage output and print queue t Monitor performance t Manage backups t Manage data storage t Administer clients, servers, networks t Administer users t Administer Internet Protocol ("IP") addresses t Administer databases t Manage voice infrastructure t Maintain a secure IT infrastructure environment t Coordinate preventive maintenance t Track service delivery cost data t Track service metric data Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Key Delivery Activities These functions manage and perform normal day-to day processing activities within the IT production environment, required for IT service delivery and in accordance with agreed-upon service levels. t Schedule production processing t Monitor resource status and raise alerts t Manage output and print queue t Monitor performance t Manage backups t Manage data storage t Administer clients, servers, networks t Administer users t Administer Internet Protocol ("IP") addresses t Administer databases t Manage voice infrastructure t Maintain a secure IT infrastructure environment t Coordinate preventive maintenance t Track service delivery cost data t Track service metric data Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
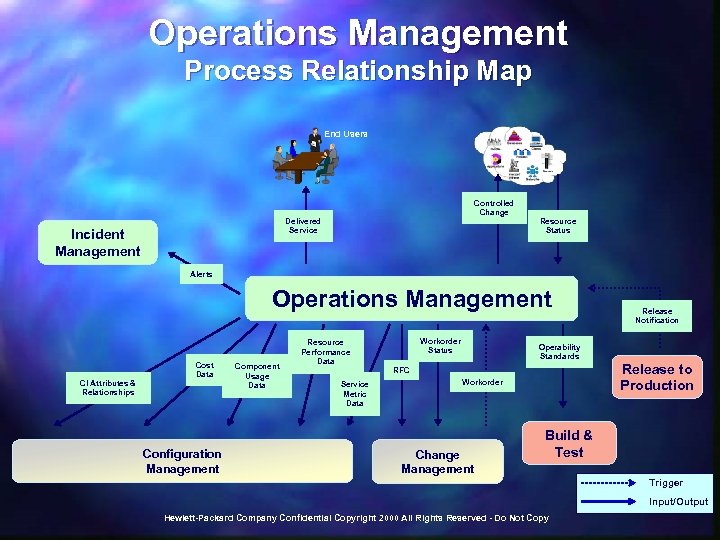 Operations Management Process Relationship Map End Users Controlled Change Delivered Service Incident Management Resource Status Alerts Operations Management CI Attributes & Relationships Cost Data Configuration Management Component Usage Data Resource Performance Data Service Metric Data Workorder Status Operability Standards RFC Workorder Change Management Release Notification Release to Production Build & Test Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Operations Management Process Relationship Map End Users Controlled Change Delivered Service Incident Management Resource Status Alerts Operations Management CI Attributes & Relationships Cost Data Configuration Management Component Usage Data Resource Performance Data Service Metric Data Workorder Status Operability Standards RFC Workorder Change Management Release Notification Release to Production Build & Test Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Release Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Release Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Build & Test This process develops and validates a functional version of a component, service function, or end-to-end service, and documents instructions for replication and implementation of a production copy as needed. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Build & Test This process develops and validates a functional version of a component, service function, or end-to-end service, and documents instructions for replication and implementation of a production copy as needed. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Build & Test t Acquire components and service functions t Develop application provision guidelines t Certify hardware/software t Construct service support and control mechanisms t Develop test plans and procedures t Perform prototype test setup t Perform prototype test t Perform unit test setup t Perform unit test t Perform pilot test setup t Perform pilot test t Document recovery procedures t Develop support procedures t Develop training design and plan t Develop training materials t Develop master blueprint Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Build & Test t Acquire components and service functions t Develop application provision guidelines t Certify hardware/software t Construct service support and control mechanisms t Develop test plans and procedures t Perform prototype test setup t Perform prototype test t Perform unit test setup t Perform unit test t Perform pilot test setup t Perform pilot test t Document recovery procedures t Develop support procedures t Develop training design and plan t Develop training materials t Develop master blueprint Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
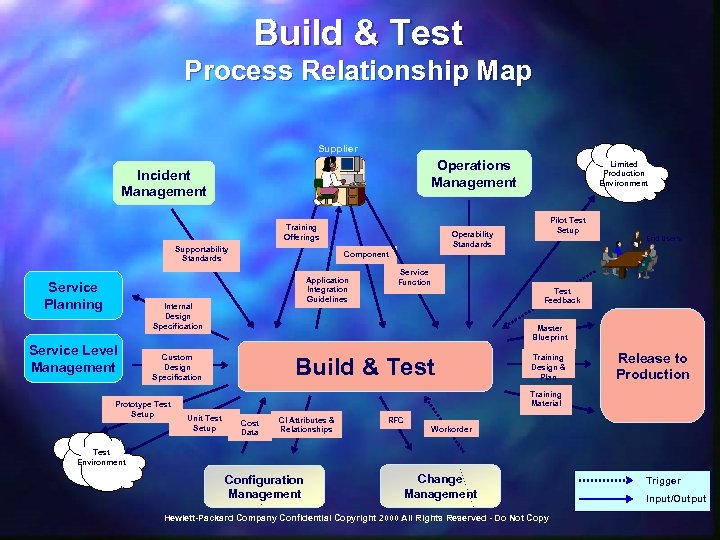 Build & Test Process Relationship Map Supplier Operations Management Incident Management Training Offerings Supportability Standards Service Planning Operability Standards Application Integration Guidelines End Users Service Function Test Feedback Master Blueprint Custom Design Specification Prototype Test Setup Pilot Test Setup Component Internal Design Specification Service Level Management Limited Production Environment Build & Test Training Design & Plan Release to Production Training Material Unit Test Setup Cost Data CI Attributes & Relationships RFC Workorder Test Environment Configuration Management Change Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Trigger Input/Output
Build & Test Process Relationship Map Supplier Operations Management Incident Management Training Offerings Supportability Standards Service Planning Operability Standards Application Integration Guidelines End Users Service Function Test Feedback Master Blueprint Custom Design Specification Prototype Test Setup Pilot Test Setup Component Internal Design Specification Service Level Management Limited Production Environment Build & Test Training Design & Plan Release to Production Training Material Unit Test Setup Cost Data CI Attributes & Relationships RFC Workorder Test Environment Configuration Management Change Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Trigger Input/Output
 Release to Production This process creates one or more production copies of a new or updated component, service function, or end-to-end service for a specific customer, based on a master blueprint (production plan). “Production copies” means assembling and integrating components, service functions, or end-to-end services in such a way as to duplicate (many times if need be) what has already been designed and tested by Build & Test. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Release to Production This process creates one or more production copies of a new or updated component, service function, or end-to-end service for a specific customer, based on a master blueprint (production plan). “Production copies” means assembling and integrating components, service functions, or end-to-end services in such a way as to duplicate (many times if need be) what has already been designed and tested by Build & Test. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Release to Production t Procure resources t Conduct IT staff, supplier training t Assemble components t Distribute components t Implement service support and control mechanisms t Implement component, service function or end-to-end service t Perform software administration t Conduct end user training t Establish production test scenarios t Perform production test setup t Perform production test t Perform end user acceptance test setup t Perform end user acceptance test t Activate service Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Release to Production t Procure resources t Conduct IT staff, supplier training t Assemble components t Distribute components t Implement service support and control mechanisms t Implement component, service function or end-to-end service t Perform software administration t Conduct end user training t Establish production test scenarios t Perform production test setup t Perform production test t Perform end user acceptance test setup t Perform end user acceptance test t Activate service Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
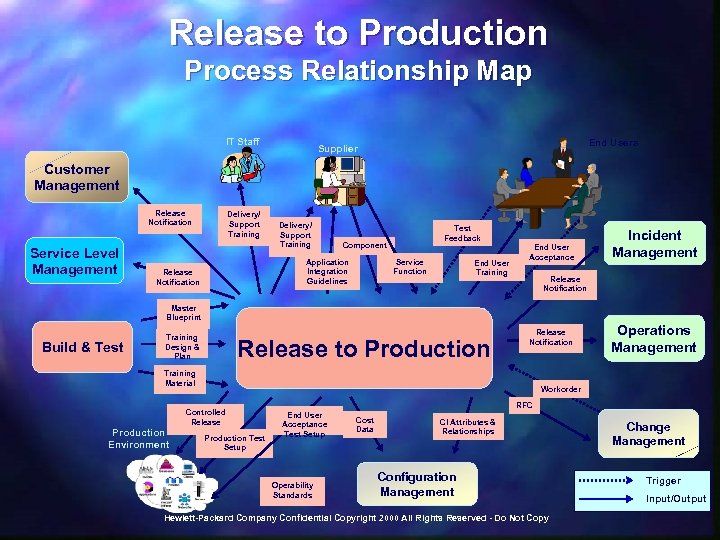 Release to Production Process Relationship Map IT Staff End Users Supplier Customer Management Release Notification Service Level Management Delivery/ Support Training Component Application Integration Guidelines Release Notification Test Feedback Service Function End User Training End User Acceptance Incident Management Release Notification Master Blueprint Build & Test Training Design & Plan Release to Production Release Notification Training Material Workorder Controlled Release Production Environment Operations Management Production Test Setup RFC End User Acceptance Test Setup Operability Standards Cost Data CI Attributes & Relationships Configuration Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Change Management Trigger Input/Output
Release to Production Process Relationship Map IT Staff End Users Supplier Customer Management Release Notification Service Level Management Delivery/ Support Training Component Application Integration Guidelines Release Notification Test Feedback Service Function End User Training End User Acceptance Incident Management Release Notification Master Blueprint Build & Test Training Design & Plan Release to Production Release Notification Training Material Workorder Controlled Release Production Environment Operations Management Production Test Setup RFC End User Acceptance Test Setup Operability Standards Cost Data CI Attributes & Relationships Configuration Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Change Management Trigger Input/Output
 Software Control & Distribution Objectives n Safeguard all software and related items n Ensure that only tested/correct versions of authorized software in use n Right software, right time, right place Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Software Control & Distribution Objectives n Safeguard all software and related items n Ensure that only tested/correct versions of authorized software in use n Right software, right time, right place Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
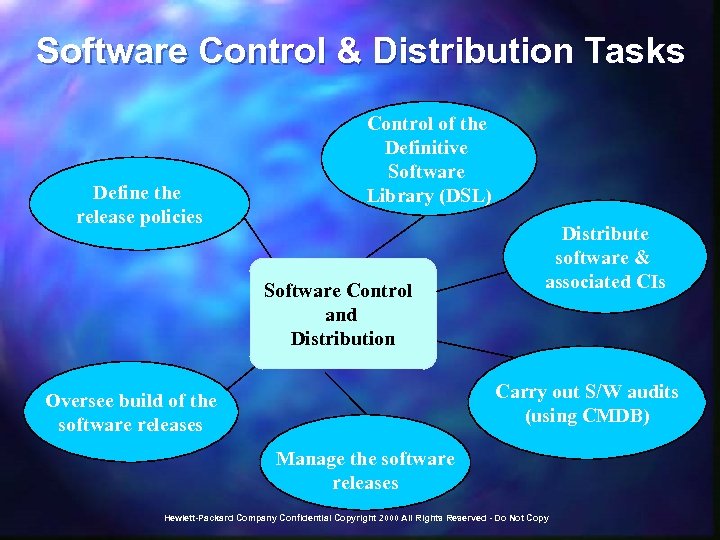 Software Control & Distribution Tasks Define the release policies Control of the Definitive Software Library (DSL) Software Control and Distribution Distribute software & associated CIs Carry out S/W audits (using CMDB) Oversee build of the software releases Manage the software releases Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Software Control & Distribution Tasks Define the release policies Control of the Definitive Software Library (DSL) Software Control and Distribution Distribute software & associated CIs Carry out S/W audits (using CMDB) Oversee build of the software releases Manage the software releases Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
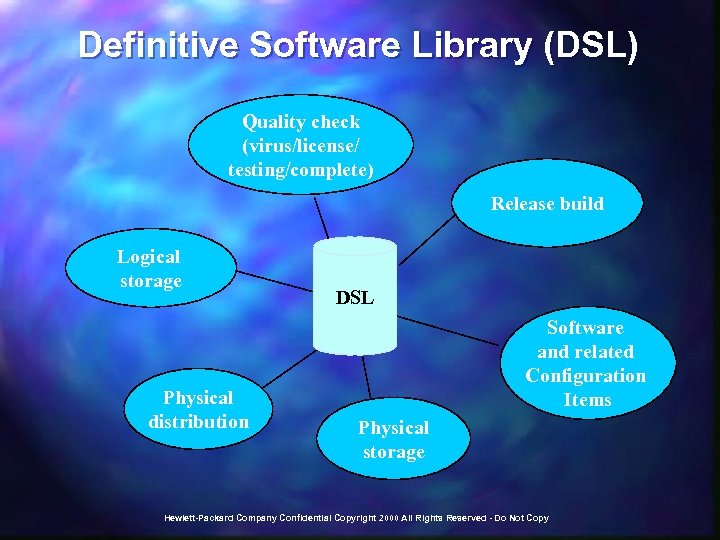 Definitive Software Library (DSL) Quality check (virus/license/ testing/complete) Release build Logical storage Physical distribution DSL Software and related Configuration Items Physical storage Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Definitive Software Library (DSL) Quality check (virus/license/ testing/complete) Release build Logical storage Physical distribution DSL Software and related Configuration Items Physical storage Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
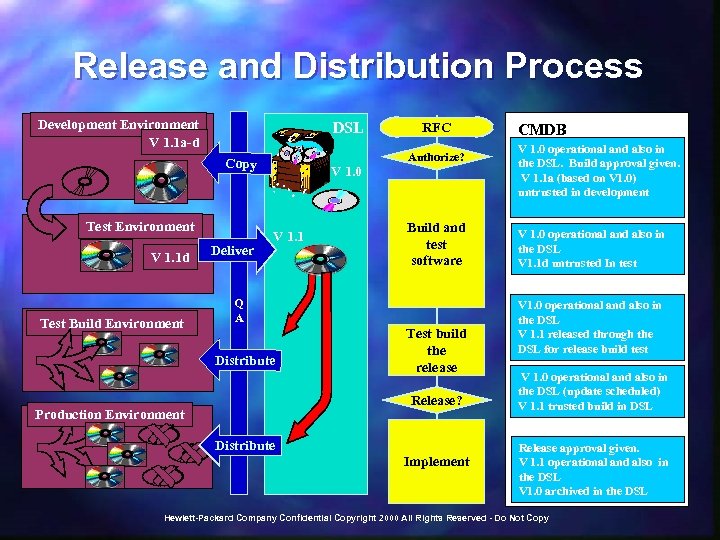 Release and Distribution Process Development Environment V 1. 1 a-d DSL Copy Test Environment V 1. 1 d Test Build Environment Deliver V 1. 0 V 1. 1 RFC Authorize? Build and test software Q A Distribute Test build the release Release? Production Environment Distribute Implement CMDB V 1. 0 operational and also in the DSL. Build approval given. V 1. 1 a (based on V 1. 0) untrusted in development V 1. 0 operational and also in the DSL V 1. 1 d untrusted In test V 1. 0 operational and also in the DSL V 1. 1 released through the DSL for release build test V 1. 0 operational and also in the DSL (update scheduled) V 1. 1 trusted build in DSL Release approval given. V 1. 1 operational and also in the DSL V 1. 0 archived in the DSL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Release and Distribution Process Development Environment V 1. 1 a-d DSL Copy Test Environment V 1. 1 d Test Build Environment Deliver V 1. 0 V 1. 1 RFC Authorize? Build and test software Q A Distribute Test build the release Release? Production Environment Distribute Implement CMDB V 1. 0 operational and also in the DSL. Build approval given. V 1. 1 a (based on V 1. 0) untrusted in development V 1. 0 operational and also in the DSL V 1. 1 d untrusted In test V 1. 0 operational and also in the DSL V 1. 1 released through the DSL for release build test V 1. 0 operational and also in the DSL (update scheduled) V 1. 1 trusted build in DSL Release approval given. V 1. 1 operational and also in the DSL V 1. 0 archived in the DSL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
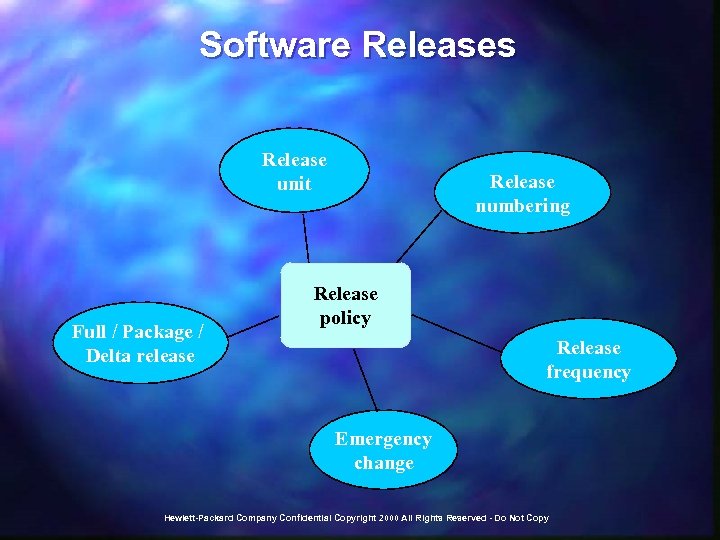 Software Releases Release unit Full / Package / Delta release Release numbering Release policy Release frequency Emergency change Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Software Releases Release unit Full / Package / Delta release Release numbering Release policy Release frequency Emergency change Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 SC & D Essentials n n n Objectives – Safeguard software Configuration Items (CIs) – Ensure only tested, authorized software is in the live environment Tasks – Control DSL, define release, build release, manage release, distribute s/w CIs, software audits DSL – Reliable versions of software Logical / physical storage Releases – Release unit, Full/package/delta releases, Numbering, Frequency Version control – Development, testing, live, archive Process – Software Control & Distribution (operational) – Change Management (control) – Configuration Management (control & administration) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
SC & D Essentials n n n Objectives – Safeguard software Configuration Items (CIs) – Ensure only tested, authorized software is in the live environment Tasks – Control DSL, define release, build release, manage release, distribute s/w CIs, software audits DSL – Reliable versions of software Logical / physical storage Releases – Release unit, Full/package/delta releases, Numbering, Frequency Version control – Development, testing, live, archive Process – Software Control & Distribution (operational) – Change Management (control) – Configuration Management (control & administration) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n n Physically store all operational software in a Definitive Software Library (DSL). Distribute all software from the DSL. Integrate SC&D with Configuration Management, Change Management and Process Integration. Control all software by release, version, and package policies. Separate the SC&D process from the management of the process. Include all procured software in SC&D's control. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n n Physically store all operational software in a Definitive Software Library (DSL). Distribute all software from the DSL. Integrate SC&D with Configuration Management, Change Management and Process Integration. Control all software by release, version, and package policies. Separate the SC&D process from the management of the process. Include all procured software in SC&D's control. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n n n The ability to maintain consistent software over many locations Detection and elimination of incorrect versions / unauthorized copies Guaranteed quality of 'live' software Ensures that errors corrected in one release do not return in a later release Better coordination of releases to avoid errors Software assets are properly and securely safeguarded Ability to build and control software used at remote sites from a central location Reduced likelihood of illegal copies of software Reduced opportunities for unnoticed introduction of viruses or other malicious software Baseline and trusted versions of software available for fallback reversions Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n n n The ability to maintain consistent software over many locations Detection and elimination of incorrect versions / unauthorized copies Guaranteed quality of 'live' software Ensures that errors corrected in one release do not return in a later release Better coordination of releases to avoid errors Software assets are properly and securely safeguarded Ability to build and control software used at remote sites from a central location Reduced likelihood of illegal copies of software Reduced opportunities for unnoticed introduction of viruses or other malicious software Baseline and trusted versions of software available for fallback reversions Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
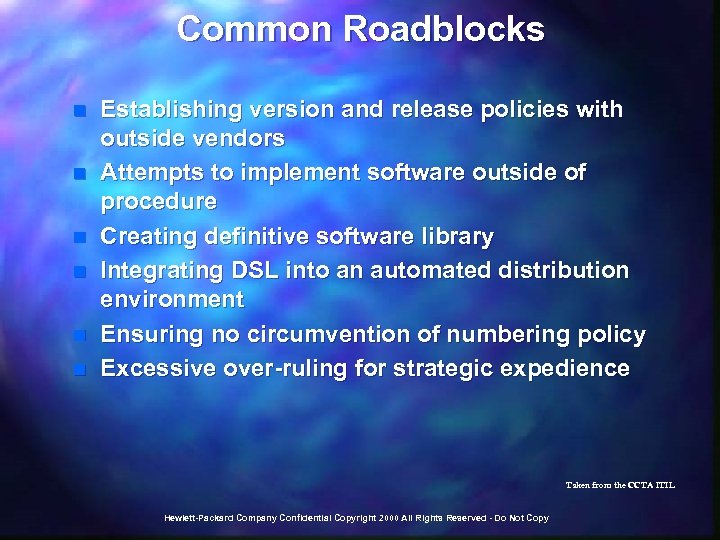 Common Roadblocks n n n Establishing version and release policies with outside vendors Attempts to implement software outside of procedure Creating definitive software library Integrating DSL into an automated distribution environment Ensuring no circumvention of numbering policy Excessive over-ruling for strategic expedience Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n Establishing version and release policies with outside vendors Attempts to implement software outside of procedure Creating definitive software library Integrating DSL into an automated distribution environment Ensuring no circumvention of numbering policy Excessive over-ruling for strategic expedience Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Availability Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Availability Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Availability Management Objectives n n To predict, plan for and manage the availability of services by ensuring that: – All services are underpinned by sufficient, reliable and properly maintained CIs – Where CIs are not supported internally there appropriate contractual arrangements with third party suppliers – Changes are proposed to prevent future loss of service availability Only then can IT organizations be certain of delivering the levels of availability agreed with customers in SLAs Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Availability Management Objectives n n To predict, plan for and manage the availability of services by ensuring that: – All services are underpinned by sufficient, reliable and properly maintained CIs – Where CIs are not supported internally there appropriate contractual arrangements with third party suppliers – Changes are proposed to prevent future loss of service availability Only then can IT organizations be certain of delivering the levels of availability agreed with customers in SLAs Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Aspects of Availability – reliability; n MTBF - average up-time – resilience; n freedom from failure – maintainability; n ability to keep IT in operation - OLAs – serviceability; n underpinning contracts – planning; – monitoring and reporting. – security Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Aspects of Availability – reliability; n MTBF - average up-time – resilience; n freedom from failure – maintainability; n ability to keep IT in operation - OLAs – serviceability; n underpinning contracts – planning; – monitoring and reporting. – security Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
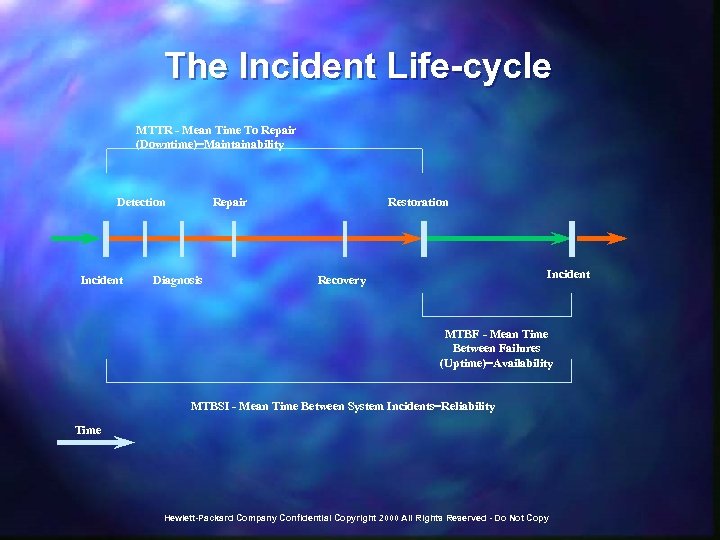 The Incident Life-cycle MTTR - Mean Time To Repair (Downtime)=Maintainability Detection Incident Repair Diagnosis Restoration Incident Recovery MTBF - Mean Time Between Failures (Uptime)=Availability MTBSI - Mean Time Between System Incidents=Reliability Time Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The Incident Life-cycle MTTR - Mean Time To Repair (Downtime)=Maintainability Detection Incident Repair Diagnosis Restoration Incident Recovery MTBF - Mean Time Between Failures (Uptime)=Availability MTBSI - Mean Time Between System Incidents=Reliability Time Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 When the customer cannot work “An IT service is not available to a customer if the functions that customer requires at that particular location cannot be used although the agreed conditions under which the IT service is supplied are being met” NB Simplistic calculation of % availability in the ITIL book is Agreed Service Hours - Downtime Agreed Service Hours X 100 1 But what does 98% Availability really mean ? Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
When the customer cannot work “An IT service is not available to a customer if the functions that customer requires at that particular location cannot be used although the agreed conditions under which the IT service is supplied are being met” NB Simplistic calculation of % availability in the ITIL book is Agreed Service Hours - Downtime Agreed Service Hours X 100 1 But what does 98% Availability really mean ? Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
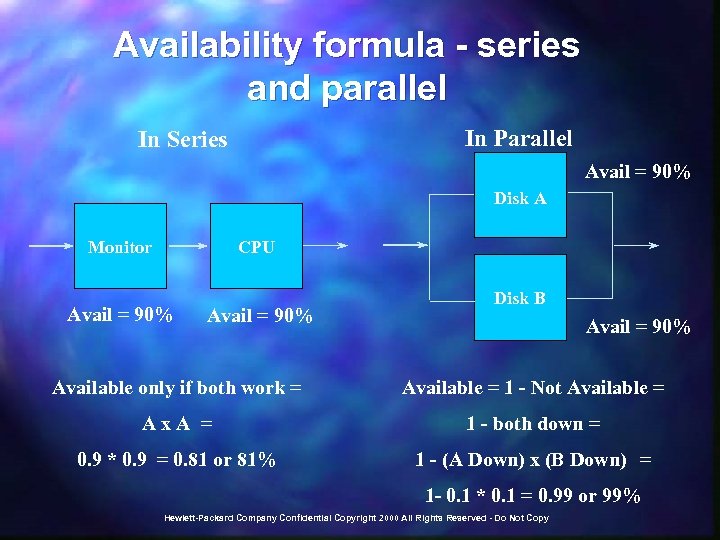 Availability formula - series and parallel In Parallel In Series Avail = 90% Disk A Monitor CPU Avail = 90% Disk B Avail = 90% Available only if both work = Available = 1 - Not Available = Ax. A = 1 - both down = 0. 9 * 0. 9 = 0. 81 or 81% 1 - (A Down) x (B Down) = 1 - 0. 1 * 0. 1 = 0. 99 or 99% Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Availability formula - series and parallel In Parallel In Series Avail = 90% Disk A Monitor CPU Avail = 90% Disk B Avail = 90% Available only if both work = Available = 1 - Not Available = Ax. A = 1 - both down = 0. 9 * 0. 9 = 0. 81 or 81% 1 - (A Down) x (B Down) = 1 - 0. 1 * 0. 1 = 0. 99 or 99% Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Availability Management Essentials n n n Purpose – Plan and manage CI availability Scope – Hardware, software, environment, etc. Assessing risk Calculating availability – MTBSI, MTTR, MTBF – % availability formulae Aspects – Reliability – Maintainability – Resilience – Serviceability – Security Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Availability Management Essentials n n n Purpose – Plan and manage CI availability Scope – Hardware, software, environment, etc. Assessing risk Calculating availability – MTBSI, MTTR, MTBF – % availability formulae Aspects – Reliability – Maintainability – Resilience – Serviceability – Security Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Key Delivery Activities t Determine reliability and serviceability requirements t Determine security requirements t Determine contingency requirements t Analyze service availability risks t Conduct gap analysis t Develop buy vs. build recommendations t Develop buy vs. build specifications t Establish supplier relationships t Analyze availability performance t Propose service improvements t Conduct supplier review t Rehears and review contingency plan Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Key Delivery Activities t Determine reliability and serviceability requirements t Determine security requirements t Determine contingency requirements t Analyze service availability risks t Conduct gap analysis t Develop buy vs. build recommendations t Develop buy vs. build specifications t Establish supplier relationships t Analyze availability performance t Propose service improvements t Conduct supplier review t Rehears and review contingency plan Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
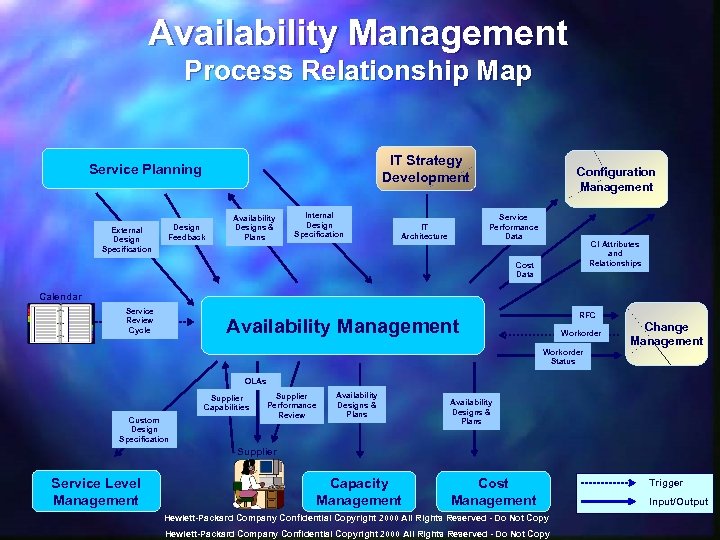 Availability Management Process Relationship Map IT Strategy Development Service Planning External Design Specification Design Feedback Availability Designs & Plans Internal Design Specification Configuration Management Service Performance Data IT Architecture CI Attributes and Relationships Cost Data Calendar Service Review Cycle RFC Availability Management Workorder Status Change Management OLAs Supplier Capabilities Custom Design Specification Supplier Performance Review Availability Designs & Plans Supplier Service Level Management Capacity Management Cost Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Trigger Input/Output
Availability Management Process Relationship Map IT Strategy Development Service Planning External Design Specification Design Feedback Availability Designs & Plans Internal Design Specification Configuration Management Service Performance Data IT Architecture CI Attributes and Relationships Cost Data Calendar Service Review Cycle RFC Availability Management Workorder Status Change Management OLAs Supplier Capabilities Custom Design Specification Supplier Performance Review Availability Designs & Plans Supplier Service Level Management Capacity Management Cost Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Trigger Input/Output
 Best Practices n n Separate design from measurement Don’t separate it from contingency planning & control. That in a way also is Availability Management Use in cooperation with capacity, cost, and contingency management Let this process set the norms for measurement. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n Separate design from measurement Don’t separate it from contingency planning & control. That in a way also is Availability Management Use in cooperation with capacity, cost, and contingency management Let this process set the norms for measurement. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Calculating the Cost of Unavailability Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Calculating the Cost of Unavailability Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
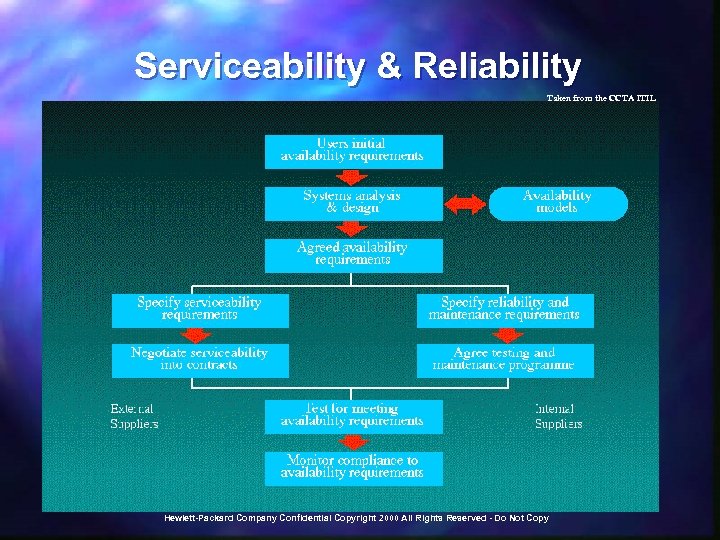 Serviceability & Reliability Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Serviceability & Reliability Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n Accurate baseline metrics, leading to more practical and accurate Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Accurate statistics leading to better supplier relations and support Improved quality and manageability of the IT infrastructure. Improved end user services by designing and meeting specific availability targets (SLAs) Improved service levels because of a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to problems Stronger cost justification and cost effectiveness of IT Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n Accurate baseline metrics, leading to more practical and accurate Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Accurate statistics leading to better supplier relations and support Improved quality and manageability of the IT infrastructure. Improved end user services by designing and meeting specific availability targets (SLAs) Improved service levels because of a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to problems Stronger cost justification and cost effectiveness of IT Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Common Roadblocks n n n Cost of Availability Management considered overhead and too expensive Difficult to quantify and cost users' availability requirements Hard to find experienced IT professionals Many tools needed to quantify baseline data Dependency on suppliers Understanding the IT infrastructure Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n Cost of Availability Management considered overhead and too expensive Difficult to quantify and cost users' availability requirements Hard to find experienced IT professionals Many tools needed to quantify baseline data Dependency on suppliers Understanding the IT infrastructure Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Contingency Planning Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Contingency Planning Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Why Plan? n n Increased business dependency on IT Reduced cost and time of recovery Cost to customer relationship Survival Many businesses fail within a year of suffering a major IT disaster! Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Why Plan? n n Increased business dependency on IT Reduced cost and time of recovery Cost to customer relationship Survival Many businesses fail within a year of suffering a major IT disaster! Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
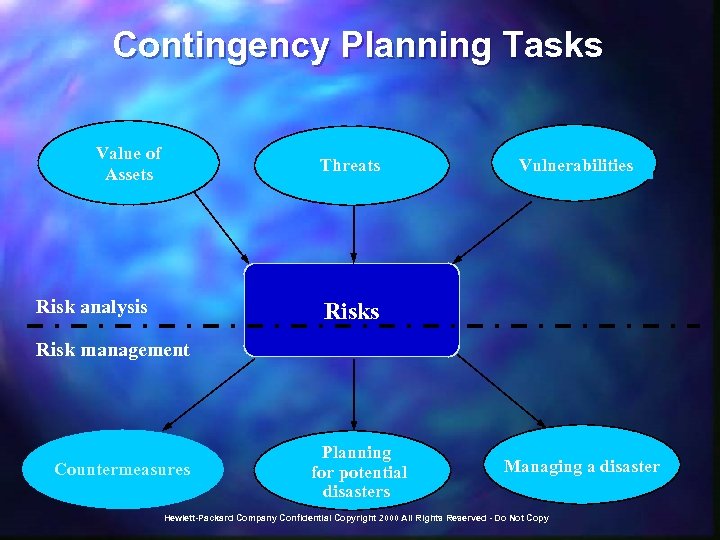 Contingency Planning Tasks Value of Assets Threats Risk analysis Vulnerabilities Risk management Countermeasures Planning for potential disasters Managing a disaster Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Contingency Planning Tasks Value of Assets Threats Risk analysis Vulnerabilities Risk management Countermeasures Planning for potential disasters Managing a disaster Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 The nine ITIL options 1. Do nothing 2. Clerical back-up 3. Reciprocal arrangement 4. Fortress approach 5. Cold start fixed 6. Cold start portable 7. Hot start internal 8. Hot start external 9. Hot start mobile Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The nine ITIL options 1. Do nothing 2. Clerical back-up 3. Reciprocal arrangement 4. Fortress approach 5. Cold start fixed 6. Cold start portable 7. Hot start internal 8. Hot start external 9. Hot start mobile Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 The seven sections of the plan 1. Administration 2. The IT infrastructure 3. IT infrastructure management & operating procedures 4. Personnel 5. Security 6. Contingency site 7. Return to normal Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The seven sections of the plan 1. Administration 2. The IT infrastructure 3. IT infrastructure management & operating procedures 4. Personnel 5. Security 6. Contingency site 7. Return to normal Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Test and Review Initially then every 6 to 12 months and after each disaster n Test it under realistic circumstances n Move / protect any live services first! n Review and change plan n What changes? New, more, less of: – Customers / services / SLRs / risks / – Dependencies / assets / CIs / staff / – Contracts / SLAs / countermeasures /. . … ALL change to be via the Change Advisory Board n Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Test and Review Initially then every 6 to 12 months and after each disaster n Test it under realistic circumstances n Move / protect any live services first! n Review and change plan n What changes? New, more, less of: – Customers / services / SLRs / risks / – Dependencies / assets / CIs / staff / – Contracts / SLAs / countermeasures /. . … ALL change to be via the Change Advisory Board n Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Contingency Planning Essentials n n Disasters will happen and will affect services! Assets/Threats/Vulnerabilities/Risks/Countermea sures Part of service planning & design The Contingency Plan – Assists in fast, controlled recovery – Must be given wide but controlled access – Contents (incl. Admin, Infrastructure, People, Return to normal) – Options (incl. Cold & Hot Start) – Must be tested regularly - without impacting the live service Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Contingency Planning Essentials n n Disasters will happen and will affect services! Assets/Threats/Vulnerabilities/Risks/Countermea sures Part of service planning & design The Contingency Plan – Assists in fast, controlled recovery – Must be given wide but controlled access – Contents (incl. Admin, Infrastructure, People, Return to normal) – Options (incl. Cold & Hot Start) – Must be tested regularly - without impacting the live service Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
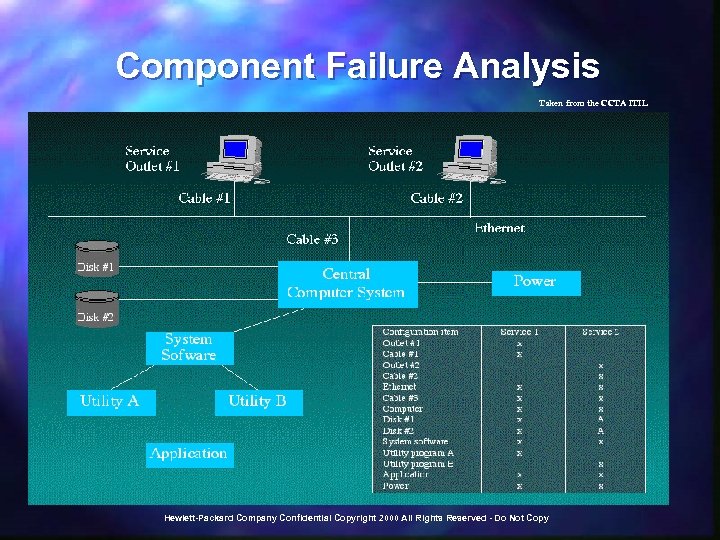 Component Failure Analysis Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Component Failure Analysis Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n Integrate with and base on thorough Risk Analysis and Management activities Apply the "If it's not worth protecting, it's not worth doing!" approach Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n Integrate with and base on thorough Risk Analysis and Management activities Apply the "If it's not worth protecting, it's not worth doing!" approach Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n Reduction the number of break and disasters that occur Reduction the impact of disasters that do occur Increased ability to recover from IT disasters in a controlled manner Reduction of lost time, providing greater continuity of service to users Minimal interruption to business Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n Reduction the number of break and disasters that occur Reduction the impact of disasters that do occur Increased ability to recover from IT disasters in a controlled manner Reduction of lost time, providing greater continuity of service to users Minimal interruption to business Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Common Roadblocks n n n Gaining commitment to staffing a Contingency Planning team Constrained to testing the plan on a production system Contingency Planning not included in departmental budgets Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n Gaining commitment to staffing a Contingency Planning team Constrained to testing the plan on a production system Contingency Planning not included in departmental budgets Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Capacity Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Capacity Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Capacity Management Objective To determine the right, cost justifiable, capacity of IT resources such that the Service Levels agreed with the business are achieved at the right time Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Capacity Management Objective To determine the right, cost justifiable, capacity of IT resources such that the Service Levels agreed with the business are achieved at the right time Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Key Delivery Activities t Inventory service resources t Characterize service workloads and demands t Configure capacity profile t Determine capacity requirements t Conduct gap analysis t Develop buy vs. build recommendations t Develop buy and build specifications t Analyze workload performance t Propose service improvements t Manage service demand Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Key Delivery Activities t Inventory service resources t Characterize service workloads and demands t Configure capacity profile t Determine capacity requirements t Conduct gap analysis t Develop buy vs. build recommendations t Develop buy and build specifications t Analyze workload performance t Propose service improvements t Manage service demand Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
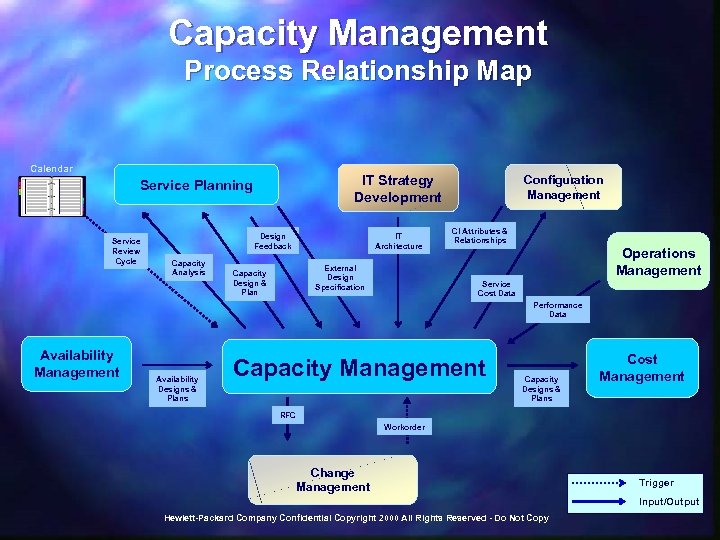 Capacity Management Process Relationship Map Calendar IT Strategy Development Service Planning Service Review Cycle Design Feedback Capacity Analysis IT Architecture External Design Specification Capacity Design & Plan Configuration Management CI Attributes & Relationships Operations Management Service Cost Data Performance Data Availability Management Availability Designs & Plans Capacity Management Capacity Designs & Plans Cost Management RFC Workorder Change Management Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Capacity Management Process Relationship Map Calendar IT Strategy Development Service Planning Service Review Cycle Design Feedback Capacity Analysis IT Architecture External Design Specification Capacity Design & Plan Configuration Management CI Attributes & Relationships Operations Management Service Cost Data Performance Data Availability Management Availability Designs & Plans Capacity Management Capacity Designs & Plans Cost Management RFC Workorder Change Management Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
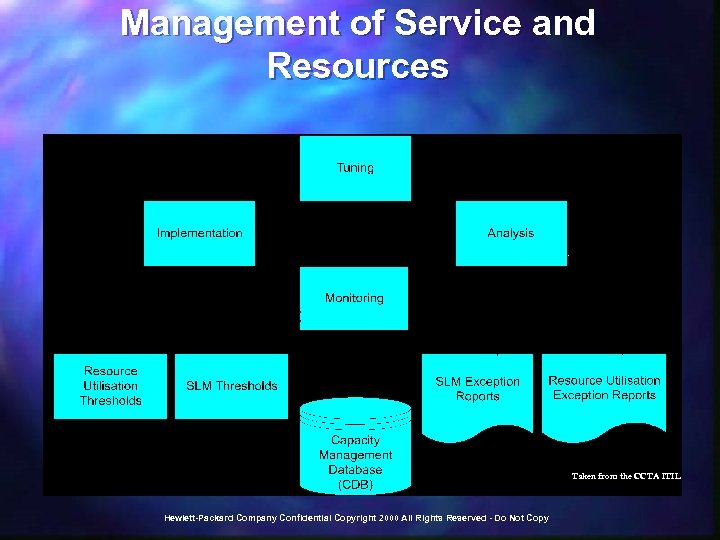 Management of Service and Resources Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Management of Service and Resources Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
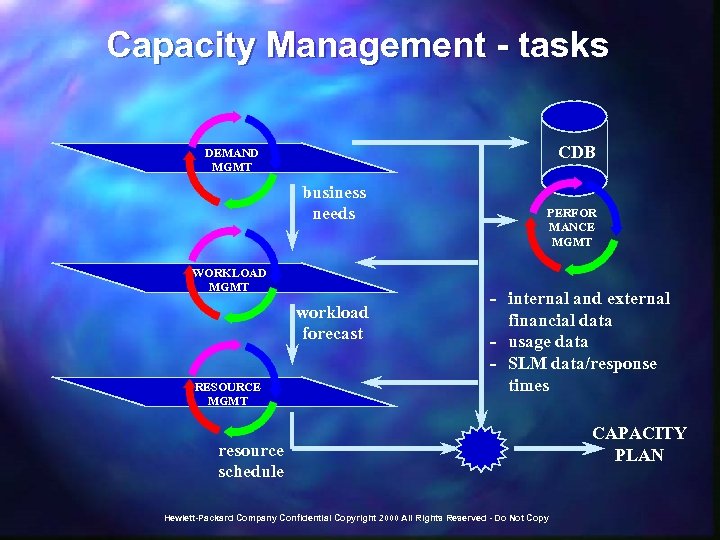 Capacity Management - tasks CDB DEMAND MGMT business needs WORKLOAD MGMT workload forecast RESOURCE MGMT PERFOR MANCE MGMT - internal and external financial data - usage data - SLM data/response times resource schedule Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy CAPACITY PLAN
Capacity Management - tasks CDB DEMAND MGMT business needs WORKLOAD MGMT workload forecast RESOURCE MGMT PERFOR MANCE MGMT - internal and external financial data - usage data - SLM data/response times resource schedule Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy CAPACITY PLAN
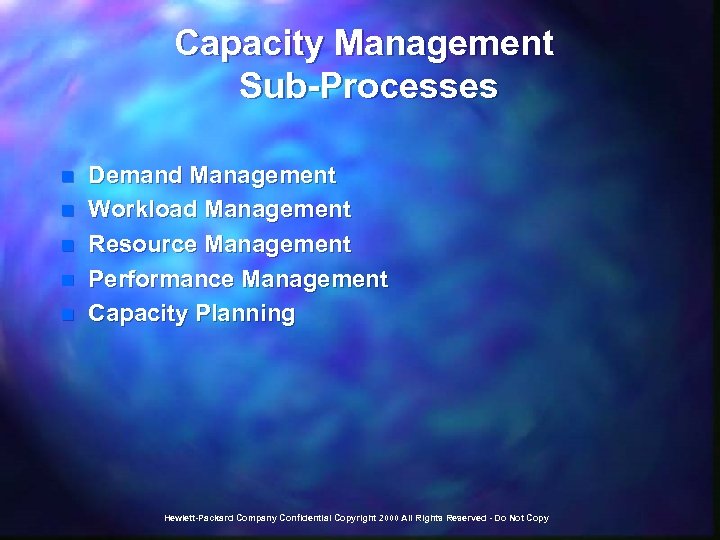 Capacity Management Sub-Processes n n n Demand Management Workload Management Resource Management Performance Management Capacity Planning Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Capacity Management Sub-Processes n n n Demand Management Workload Management Resource Management Performance Management Capacity Planning Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Capacity Management Essentials n n n From Customer Demands to Resources Demand - , Workload- , Resource Management Best Value for Money - Performance Management Capacity Planning Defining Thresholds and Monitoring Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Capacity Management Essentials n n n From Customer Demands to Resources Demand - , Workload- , Resource Management Best Value for Money - Performance Management Capacity Planning Defining Thresholds and Monitoring Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n Capacity requirements are demand-driven (linked to business) rather than reactive (derived from technology issues) Focus on customer "owned" metrics Basis in availability management Closely linked to cost management Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n Capacity requirements are demand-driven (linked to business) rather than reactive (derived from technology issues) Focus on customer "owned" metrics Basis in availability management Closely linked to cost management Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n n Ability to create and manage Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Reduced number of problems caused by lack of resources Increased end user satisfaction Increased system availability / resource utilization Improved capacity forecasting and budgeting capability Improved scheduling for upgrades and hardware installs Improved negotiating position Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n n Ability to create and manage Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Reduced number of problems caused by lack of resources Increased end user satisfaction Increased system availability / resource utilization Improved capacity forecasting and budgeting capability Improved scheduling for upgrades and hardware installs Improved negotiating position Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Common Roadblocks n n n Skill levels of capacity management staff Complexity of tools and tool integration Difficult to translate business requirements to system requirements to workloads Over-expectations of possible savings from implementing capacity management Difficult to manage customer expectations with respect to actual capacity and related costs Difficult to translate vendor benchmark results into realistic capacity characteristics in the production environment Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n Skill levels of capacity management staff Complexity of tools and tool integration Difficult to translate business requirements to system requirements to workloads Over-expectations of possible savings from implementing capacity management Difficult to manage customer expectations with respect to actual capacity and related costs Difficult to translate vendor benchmark results into realistic capacity characteristics in the production environment Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Cost Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Cost Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Cost Management Costing Charging Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Cost Management Costing Charging Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Costing Objectives To provide information about and control over the costs of delivering IT services that support customers’ business needs. Costing is a must! Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Costing Objectives To provide information about and control over the costs of delivering IT services that support customers’ business needs. Costing is a must! Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Input cost units recommended by ITIL n n n Equipment Cost Units Organization Cost Units Transfer Cost Units Accommodation Cost Units Software Cost Units (ECU) (OCU) (TCU) (ACU) (SCU) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Input cost units recommended by ITIL n n n Equipment Cost Units Organization Cost Units Transfer Cost Units Accommodation Cost Units Software Cost Units (ECU) (OCU) (TCU) (ACU) (SCU) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
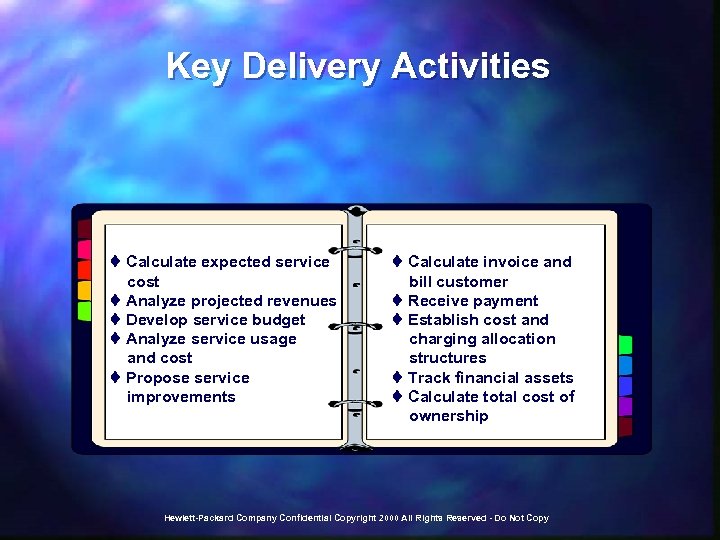 Key Delivery Activities t Calculate expected service cost t Analyze projected revenues t Develop service budget t Analyze service usage and cost t Propose service improvements t Calculate invoice and bill customer t Receive payment t Establish cost and charging allocation structures t Track financial assets t Calculate total cost of ownership Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Key Delivery Activities t Calculate expected service cost t Analyze projected revenues t Develop service budget t Analyze service usage and cost t Propose service improvements t Calculate invoice and bill customer t Receive payment t Establish cost and charging allocation structures t Track financial assets t Calculate total cost of ownership Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
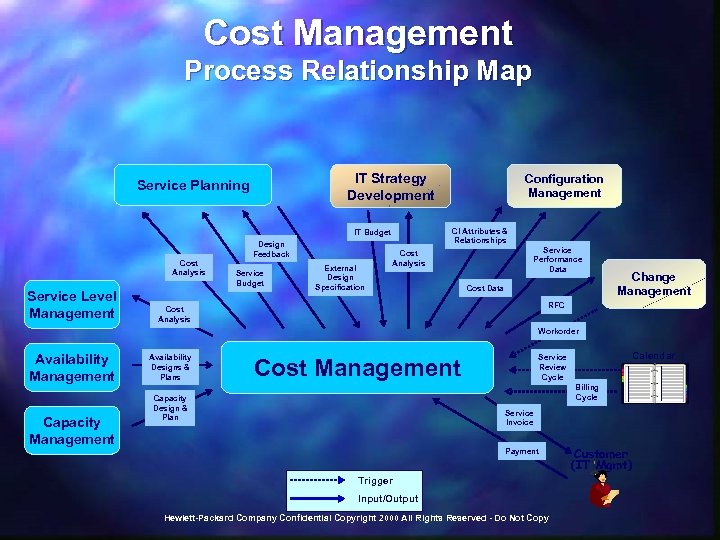 Cost Management Process Relationship Map IT Strategy Development Service Planning CI Attributes & Relationships IT Budget Cost Analysis Service Level Management Design Feedback Service Budget External Design Specification Configuration Management Service Performance Data Cost Analysis Cost Data Change Management RFC Cost Analysis Workorder Availability Management Capacity Management Availability Designs & Plans Calendar Service Review Cycle Cost Management Billing Cycle Capacity Design & Plan Service Invoice Payment Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Customer (IT Mgmt)
Cost Management Process Relationship Map IT Strategy Development Service Planning CI Attributes & Relationships IT Budget Cost Analysis Service Level Management Design Feedback Service Budget External Design Specification Configuration Management Service Performance Data Cost Analysis Cost Data Change Management RFC Cost Analysis Workorder Availability Management Capacity Management Availability Designs & Plans Calendar Service Review Cycle Cost Management Billing Cycle Capacity Design & Plan Service Invoice Payment Trigger Input/Output Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Customer (IT Mgmt)
 Different Cost Types n n n Fixed, unaffected by the level of usage Variable, varying according to the level of usage Direct, usage specific to one service Indirect or overhead, usage not specific to one service Capital, not diminished by usage Revenue or running, diminish with usage Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Different Cost Types n n n Fixed, unaffected by the level of usage Variable, varying according to the level of usage Direct, usage specific to one service Indirect or overhead, usage not specific to one service Capital, not diminished by usage Revenue or running, diminish with usage Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Charging Objectives n n n Recover from customers the full costs of the IT services provided Ensure that customers are aware of the costs they impose on IT Ensure that providers have an incentive to deliver an agreed quality and quantity of economic and effective services Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Charging Objectives n n n Recover from customers the full costs of the IT services provided Ensure that customers are aware of the costs they impose on IT Ensure that providers have an incentive to deliver an agreed quality and quantity of economic and effective services Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Charging & Pricing Options Charging n No charging n Notional Charging n Actual Charging Pricing n Recover of costs n Cost price plus n Market prices Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Charging & Pricing Options Charging n No charging n Notional Charging n Actual Charging Pricing n Recover of costs n Cost price plus n Market prices Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Cost Management Essentials n Costing – – – n Knowing & understanding costs Needed to manage changes Input cost units (Equip, Org, Trans, Accom, S/W) Input cost types (F/V, D/I, Cap/Rev) Output business cost units Need for good estimates of business workloads Charging (but not policy) – Determine charges in SLAs – Influence customer behavior – Charging does not affect costs n General – – Sound stewardship Minimize risk in decision making Estimating, planning, budgeting Targets & measures Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Cost Management Essentials n Costing – – – n Knowing & understanding costs Needed to manage changes Input cost units (Equip, Org, Trans, Accom, S/W) Input cost types (F/V, D/I, Cap/Rev) Output business cost units Need for good estimates of business workloads Charging (but not policy) – Determine charges in SLAs – Influence customer behavior – Charging does not affect costs n General – – Sound stewardship Minimize risk in decision making Estimating, planning, budgeting Targets & measures Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
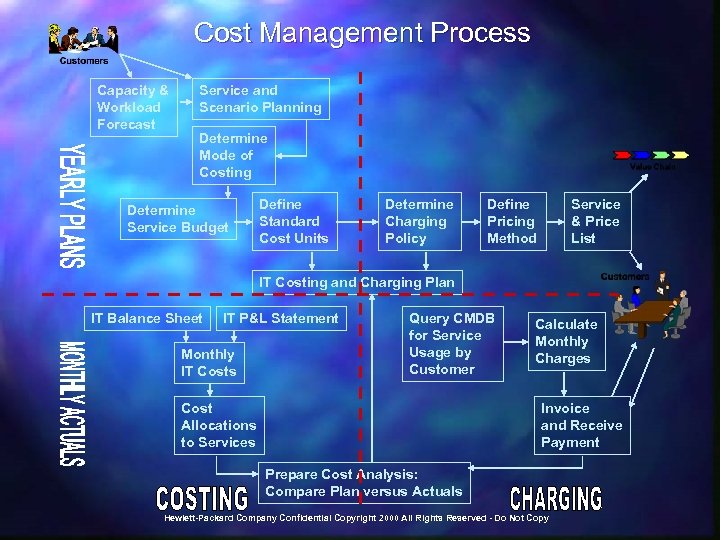 Cost Management Process Capacity & Workload Forecast Service and Scenario Planning Determine Mode of Costing Determine Service Budget Define Standard Cost Units Determine Charging Policy Define Pricing Method Service & Price List IT Costing and Charging Plan IT Balance Sheet IT P&L Statement Monthly IT Costs Query CMDB for Service Usage by Customer Cost Allocations to Services Calculate Monthly Charges Invoice and Receive Payment Prepare Cost Analysis: Compare Plan versus Actuals Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Cost Management Process Capacity & Workload Forecast Service and Scenario Planning Determine Mode of Costing Determine Service Budget Define Standard Cost Units Determine Charging Policy Define Pricing Method Service & Price List IT Costing and Charging Plan IT Balance Sheet IT P&L Statement Monthly IT Costs Query CMDB for Service Usage by Customer Cost Allocations to Services Calculate Monthly Charges Invoice and Receive Payment Prepare Cost Analysis: Compare Plan versus Actuals Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n Clear distinction between costing and charging Linked to availability management, capacity management, and configuration management Customer-based charging Financing, benchmarking, and investments are seen as important disciplines Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n Clear distinction between costing and charging Linked to availability management, capacity management, and configuration management Customer-based charging Financing, benchmarking, and investments are seen as important disciplines Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits Costing helps the IT Services Manager to. . . n base decisions about the services to be provided on assessments of cost-effectiveness, service by services n make more business-like decisions about IT services and their related investments n provide information to justify IT expenditures n plan and budget with confidence n understand the costs of failing to take advantage of strategic opportunities to justify the required expenditure (thereby providing value-added productivity) n help the users understand the costs associated with the services that they utilize Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits Costing helps the IT Services Manager to. . . n base decisions about the services to be provided on assessments of cost-effectiveness, service by services n make more business-like decisions about IT services and their related investments n provide information to justify IT expenditures n plan and budget with confidence n understand the costs of failing to take advantage of strategic opportunities to justify the required expenditure (thereby providing value-added productivity) n help the users understand the costs associated with the services that they utilize Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Common Roadblocks n n n Skill levels of cost management staff, especially finding professionals with accounting and IT experience Political aspects of cost allocation Monitoring can be expensive Difficult to identify and determine customerbased charges Integration across functions and tools is essential for real leverage Lack of clear IS strategy and objectives Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n Skill levels of cost management staff, especially finding professionals with accounting and IT experience Political aspects of cost allocation Monitoring can be expensive Difficult to identify and determine customerbased charges Integration across functions and tools is essential for real leverage Lack of clear IS strategy and objectives Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Service Level Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Service Level Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Service Level Management Balance between: Demand for IT services By: – Knowing the requirements of the business – Knowing the capabilities of IT Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Supply of IT services
Service Level Management Balance between: Demand for IT services By: – Knowing the requirements of the business – Knowing the capabilities of IT Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Supply of IT services
 Service Level Management Objectives n n n n Business-like relationship between customer and supplier Improved specification and understanding of service requirements Greater flexibility and responsiveness in service provision Balance customer demands and cost of services provision Measurable service levels Quality improvement (continuous review) Objective conflict resolution Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Service Level Management Objectives n n n n Business-like relationship between customer and supplier Improved specification and understanding of service requirements Greater flexibility and responsiveness in service provision Balance customer demands and cost of services provision Measurable service levels Quality improvement (continuous review) Objective conflict resolution Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
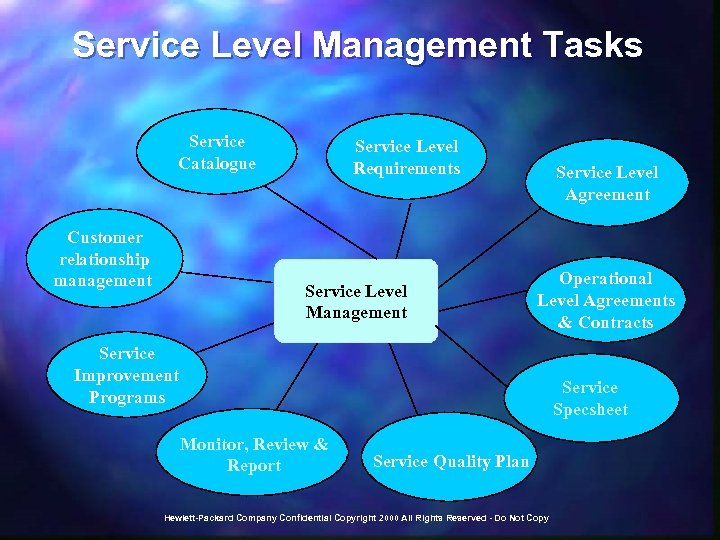 Service Level Management Tasks Service Catalogue Customer relationship management Service Level Requirements Service Level Management Service Level Agreement Operational Level Agreements & Contracts Service Improvement Programs Service Specsheet Monitor, Review & Report Service Quality Plan Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Service Level Management Tasks Service Catalogue Customer relationship management Service Level Requirements Service Level Management Service Level Agreement Operational Level Agreements & Contracts Service Improvement Programs Service Specsheet Monitor, Review & Report Service Quality Plan Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Key Delivery Activities t Assess customer-specific service requirements t Map standard services to requirements t Define customer services t Negotiate and document SLA t Establish service performance cycle t Design custom services t Analyze customer specific service level performance t Create customer reports t Conduct service performance review t Propose service improvements (customer specific) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Key Delivery Activities t Assess customer-specific service requirements t Map standard services to requirements t Define customer services t Negotiate and document SLA t Establish service performance cycle t Design custom services t Analyze customer specific service level performance t Create customer reports t Conduct service performance review t Propose service improvements (customer specific) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
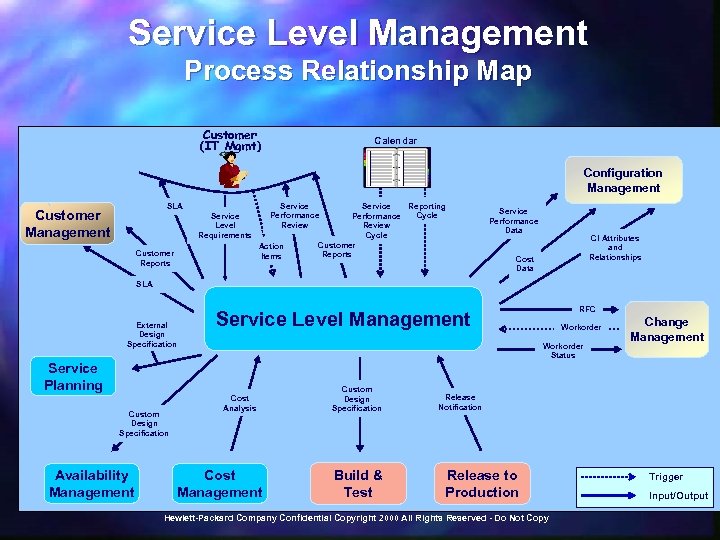 Service Level Management Process Relationship Map Customer (IT Mgmt) Calendar Configuration Management Service Performance Review SLA Customer Management Service Level Requirements Action Items Customer Reports Reporting Service Cycle Performance Review Cycle Customer Reports Service Performance Data CI Attributes and Relationships Cost Data SLA External Design Specification Availability Management Workorder Status Service Planning Custom Design Specification RFC Service Level Management Cost Analysis Cost Management Custom Design Specification Build & Test Change Management Release Notification Release to Production Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Trigger Input/Output
Service Level Management Process Relationship Map Customer (IT Mgmt) Calendar Configuration Management Service Performance Review SLA Customer Management Service Level Requirements Action Items Customer Reports Reporting Service Cycle Performance Review Cycle Customer Reports Service Performance Data CI Attributes and Relationships Cost Data SLA External Design Specification Availability Management Workorder Status Service Planning Custom Design Specification RFC Service Level Management Cost Analysis Cost Management Custom Design Specification Build & Test Change Management Release Notification Release to Production Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy Trigger Input/Output
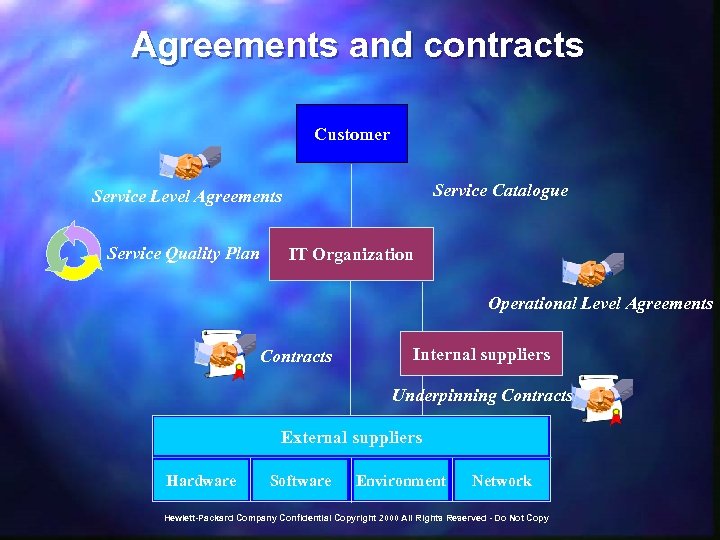 Agreements and contracts Customer Service Catalogue Service Level Agreements Service Quality Plan IT Organization Operational Level Agreements Contracts Internal suppliers Underpinning Contracts External suppliers Hardware Software Environment Network Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Agreements and contracts Customer Service Catalogue Service Level Agreements Service Quality Plan IT Organization Operational Level Agreements Contracts Internal suppliers Underpinning Contracts External suppliers Hardware Software Environment Network Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
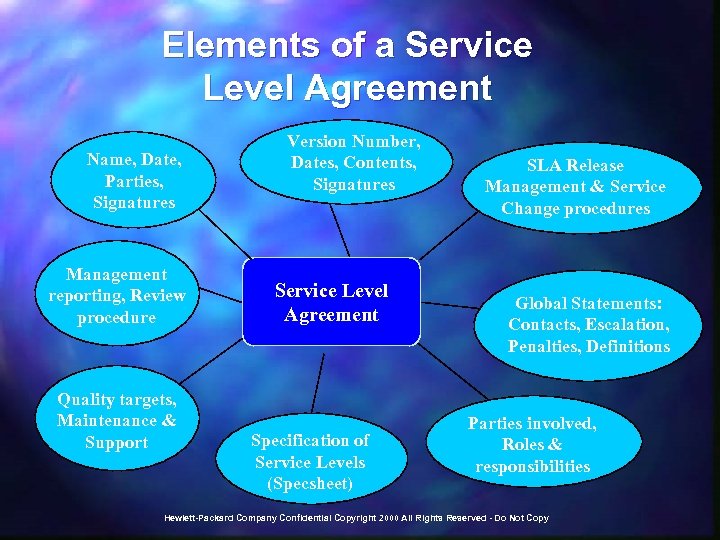 Elements of a Service Level Agreement Name, Date, Parties, Signatures Management reporting, Review procedure Quality targets, Maintenance & Support Version Number, Dates, Contents, Signatures Service Level Agreement Specification of Service Levels (Specsheet) SLA Release Management & Service Change procedures Global Statements: Contacts, Escalation, Penalties, Definitions Parties involved, Roles & responsibilities Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Elements of a Service Level Agreement Name, Date, Parties, Signatures Management reporting, Review procedure Quality targets, Maintenance & Support Version Number, Dates, Contents, Signatures Service Level Agreement Specification of Service Levels (Specsheet) SLA Release Management & Service Change procedures Global Statements: Contacts, Escalation, Penalties, Definitions Parties involved, Roles & responsibilities Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
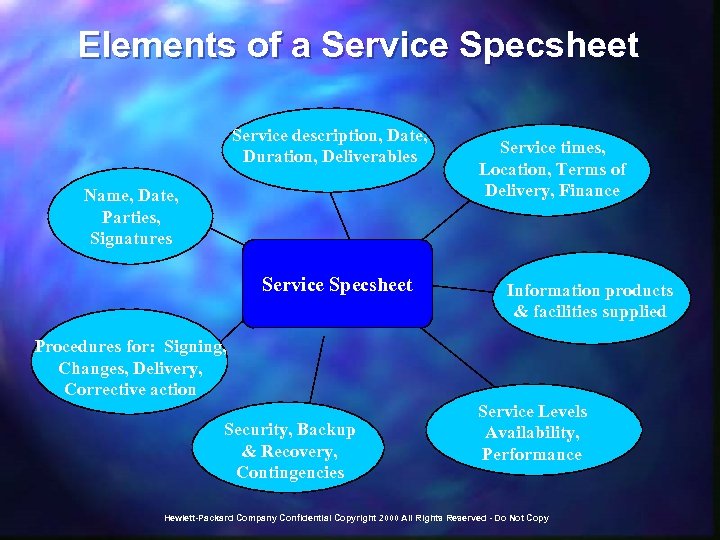 Elements of a Service Specsheet Service description, Date, Duration, Deliverables Name, Date, Parties, Signatures Service Specsheet Service times, Location, Terms of Delivery, Finance Information products & facilities supplied Procedures for: Signing, Changes, Delivery, Corrective action Security, Backup & Recovery, Contingencies Service Levels Availability, Performance Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Elements of a Service Specsheet Service description, Date, Duration, Deliverables Name, Date, Parties, Signatures Service Specsheet Service times, Location, Terms of Delivery, Finance Information products & facilities supplied Procedures for: Signing, Changes, Delivery, Corrective action Security, Backup & Recovery, Contingencies Service Levels Availability, Performance Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Service Level Management Essentials (1) n n n We need to understand what we mean by “Service Management” Objectives Improve service quality (customer dependence) – Measurable service levels – Balance between customer demand IT capabilities n Tasks – – – n Manage customer relationships Create / maintain Service Catalogue Determine SLRs; Negotiate, prepare & monitor Service Charter, SLAs & OLAs and Service Improvement/Quality plans Minimum requirements for an agreement – Period, service description, throughput, availability, response times, signature Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Service Level Management Essentials (1) n n n We need to understand what we mean by “Service Management” Objectives Improve service quality (customer dependence) – Measurable service levels – Balance between customer demand IT capabilities n Tasks – – – n Manage customer relationships Create / maintain Service Catalogue Determine SLRs; Negotiate, prepare & monitor Service Charter, SLAs & OLAs and Service Improvement/Quality plans Minimum requirements for an agreement – Period, service description, throughput, availability, response times, signature Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Service Level Management Essentials (2) n General – Ideally contracts are based on targets in the SLA – SLAs must take account of underpinning contracts where these already exist – SLAs can be organized by service or by customer n The new generation of service management tools allow SLAs to overlap, usually defaulting to the higher level of service. – SLAs must be monitored regularly and reviewed regularly n Monitor to see if service is being delivered to specification n Review to see if service specification is still appropriate. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Service Level Management Essentials (2) n General – Ideally contracts are based on targets in the SLA – SLAs must take account of underpinning contracts where these already exist – SLAs can be organized by service or by customer n The new generation of service management tools allow SLAs to overlap, usually defaulting to the higher level of service. – SLAs must be monitored regularly and reviewed regularly n Monitor to see if service is being delivered to specification n Review to see if service specification is still appropriate. Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Best Practices n n n n Emphasize contribution to business success as opposed to IT realities. Distinguish clearly between Service Level Management (process) and Service Level Agreements (contract). Base cost recovery on SLA as opposed to uniform chargeback. Construct SLAs with and for business units using common language. Implement Service Level Management to start at design and end with measurement of a service. Establish SLAs only within the context of a Service Level Management discipline. Formulate contractual relationships with (internal) suppliers to be consistent with SLAs. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Best Practices n n n n Emphasize contribution to business success as opposed to IT realities. Distinguish clearly between Service Level Management (process) and Service Level Agreements (contract). Base cost recovery on SLA as opposed to uniform chargeback. Construct SLAs with and for business units using common language. Implement Service Level Management to start at design and end with measurement of a service. Establish SLAs only within the context of a Service Level Management discipline. Formulate contractual relationships with (internal) suppliers to be consistent with SLAs. Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Business Benefits n n n n Establish more business-like relationships through measurable and realistic service level agreements. Accurately balance the service requirements of customers against the costs and complexity of providing those services. Accurately specify IT resources. Reduce unpredictable demand. Cut procurement costs through better information for on time negotiations with suppliers. Establish baseline for service improvements for greater customer satisfaction. Facilitate quick and objective resolution of disputes Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Business Benefits n n n n Establish more business-like relationships through measurable and realistic service level agreements. Accurately balance the service requirements of customers against the costs and complexity of providing those services. Accurately specify IT resources. Reduce unpredictable demand. Cut procurement costs through better information for on time negotiations with suppliers. Establish baseline for service improvements for greater customer satisfaction. Facilitate quick and objective resolution of disputes Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Common Roadblocks n n n n Customers have difficulty identifying requirements IT has difficulty identifying the customer Necessary disciplines are often not in place or not integrated with Service Level Management Differences between costing and charging not always appreciated by internal clients Investment often in a broad-based budget and not focused on a specific SLA, makes improvement difficult Managers often over-ambitious but not willing to invest in underpinning processes Lack of discipline in support teams Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Common Roadblocks n n n n Customers have difficulty identifying requirements IT has difficulty identifying the customer Necessary disciplines are often not in place or not integrated with Service Level Management Differences between costing and charging not always appreciated by internal clients Investment often in a broad-based budget and not focused on a specific SLA, makes improvement difficult Managers often over-ambitious but not willing to invest in underpinning processes Lack of discipline in support teams Taken from the CCTA ITIL Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Process Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Process Management Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
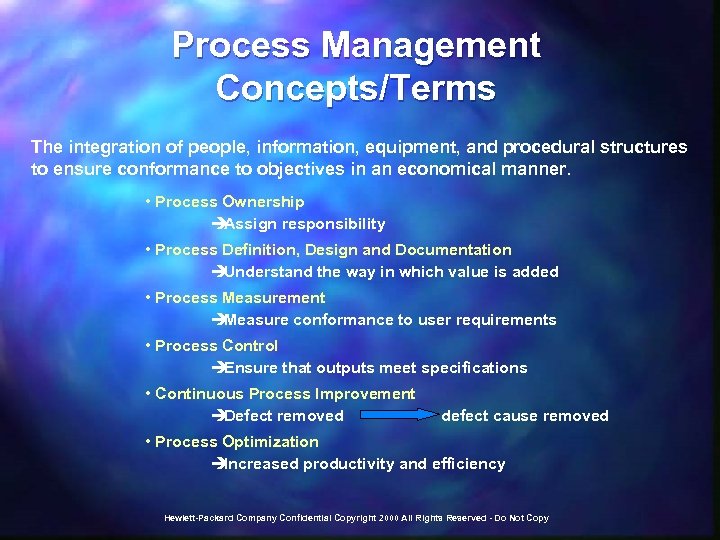 Process Management Concepts/Terms The integration of people, information, equipment, and procedural structures to ensure conformance to objectives in an economical manner. • Process Ownership è Assign responsibility • Process Definition, Design and Documentation è Understand the way in which value is added • Process Measurement è Measure conformance to user requirements • Process Control è Ensure that outputs meet specifications • Continuous Process Improvement è Defect removed defect cause removed • Process Optimization è Increased productivity and efficiency Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Process Management Concepts/Terms The integration of people, information, equipment, and procedural structures to ensure conformance to objectives in an economical manner. • Process Ownership è Assign responsibility • Process Definition, Design and Documentation è Understand the way in which value is added • Process Measurement è Measure conformance to user requirements • Process Control è Ensure that outputs meet specifications • Continuous Process Improvement è Defect removed defect cause removed • Process Optimization è Increased productivity and efficiency Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 The Target Solution. . . IT Service Management “A business-driven approach to reengineering IT, focused on delivering IT services to business users at agreed upon service quality and cost targets” Bringing together. . . • People • Process • Technology Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The Target Solution. . . IT Service Management “A business-driven approach to reengineering IT, focused on delivering IT services to business users at agreed upon service quality and cost targets” Bringing together. . . • People • Process • Technology Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
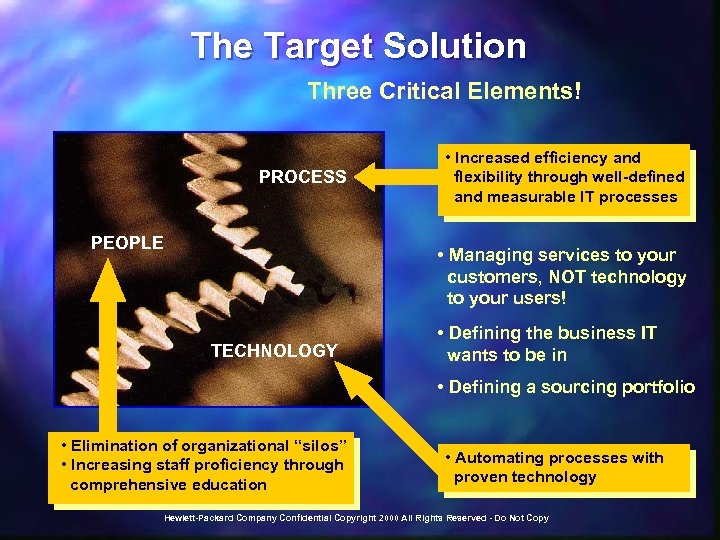 The Target Solution Three Critical Elements! PROCESS PEOPLE • Increased efficiency and flexibility through well-defined and measurable IT processes • Managing services to your customers, NOT technology to your users! TECHNOLOGY • Defining the business IT wants to be in • Defining a sourcing portfolio • Elimination of organizational “silos” • Increasing staff proficiency through comprehensive education • Automating processes with proven technology Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The Target Solution Three Critical Elements! PROCESS PEOPLE • Increased efficiency and flexibility through well-defined and measurable IT processes • Managing services to your customers, NOT technology to your users! TECHNOLOGY • Defining the business IT wants to be in • Defining a sourcing portfolio • Elimination of organizational “silos” • Increasing staff proficiency through comprehensive education • Automating processes with proven technology Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 The Importance of Process It’s all about process STABILITY! What do Customers Want? • An IT environment that is stable • An IT environment that can be continuously improved Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The Importance of Process It’s all about process STABILITY! What do Customers Want? • An IT environment that is stable • An IT environment that can be continuously improved Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
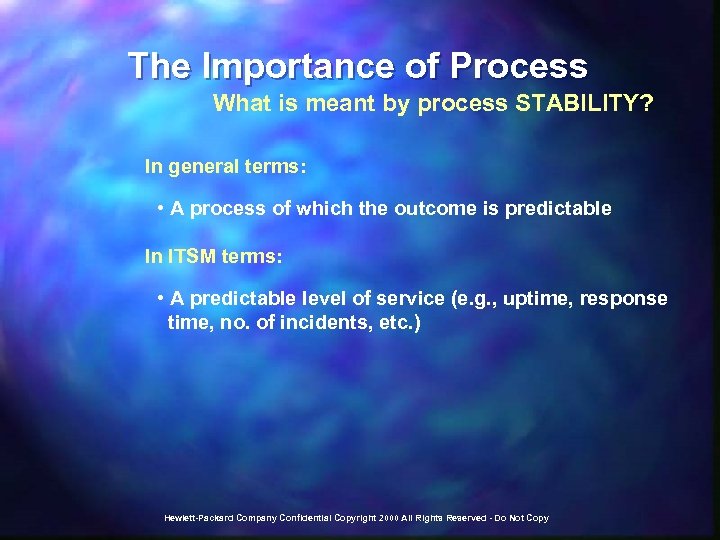 The Importance of Process What is meant by process STABILITY? In general terms: • A process of which the outcome is predictable In ITSM terms: • A predictable level of service (e. g. , uptime, response time, no. of incidents, etc. ) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The Importance of Process What is meant by process STABILITY? In general terms: • A process of which the outcome is predictable In ITSM terms: • A predictable level of service (e. g. , uptime, response time, no. of incidents, etc. ) Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 The Importance of Process Why is process STABILITY important? Stable IT processes means: • Service levels can be negotiated • Staff focus can move from “defense” towards process improvement • forecasting can now be done in earnest Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The Importance of Process Why is process STABILITY important? Stable IT processes means: • Service levels can be negotiated • Staff focus can move from “defense” towards process improvement • forecasting can now be done in earnest Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 The Importance of Process Think about it! • Most organizations recognize the importance of stability and continuous improvement • And many organizations actively try to achieve stability and improve on a continuous basis • But – only the most advanced organizations are capable of achieving and maintaining stability, and improving their performance Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The Importance of Process Think about it! • Most organizations recognize the importance of stability and continuous improvement • And many organizations actively try to achieve stability and improve on a continuous basis • But – only the most advanced organizations are capable of achieving and maintaining stability, and improving their performance Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
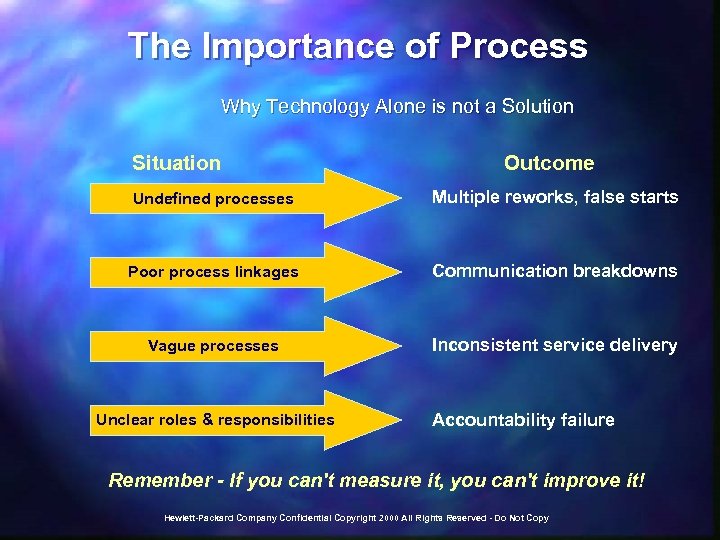 The Importance of Process Why Technology Alone is not a Solution Situation Outcome Undefined processes Multiple reworks, false starts Poor process linkages Communication breakdowns Vague processes Inconsistent service delivery Unclear roles & responsibilities Accountability failure Remember - If you can't measure it, you can't improve it! Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
The Importance of Process Why Technology Alone is not a Solution Situation Outcome Undefined processes Multiple reworks, false starts Poor process linkages Communication breakdowns Vague processes Inconsistent service delivery Unclear roles & responsibilities Accountability failure Remember - If you can't measure it, you can't improve it! Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
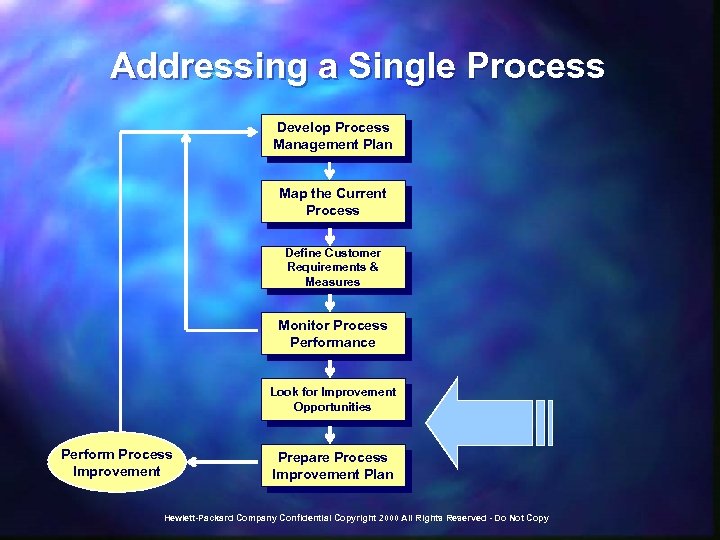 Addressing a Single Process Develop Process Management Plan Map the Current Process Define Customer Requirements & Measures Monitor Process Performance Look for Improvement Opportunities Perform Process Improvement Prepare Process Improvement Plan Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Addressing a Single Process Develop Process Management Plan Map the Current Process Define Customer Requirements & Measures Monitor Process Performance Look for Improvement Opportunities Perform Process Improvement Prepare Process Improvement Plan Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 Data Driven Decisions n n n “If you don’t measure it, you can’t manage it” “If you don’t measure it, you can’t improve it” “If you don’t measure it, you probably don’t care” “If you can’t influence it, then don’t measure it” “Not everything that can be measured counts, not everything that counts can be measured” Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Data Driven Decisions n n n “If you don’t measure it, you can’t manage it” “If you don’t measure it, you can’t improve it” “If you don’t measure it, you probably don’t care” “If you can’t influence it, then don’t measure it” “Not everything that can be measured counts, not everything that counts can be measured” Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
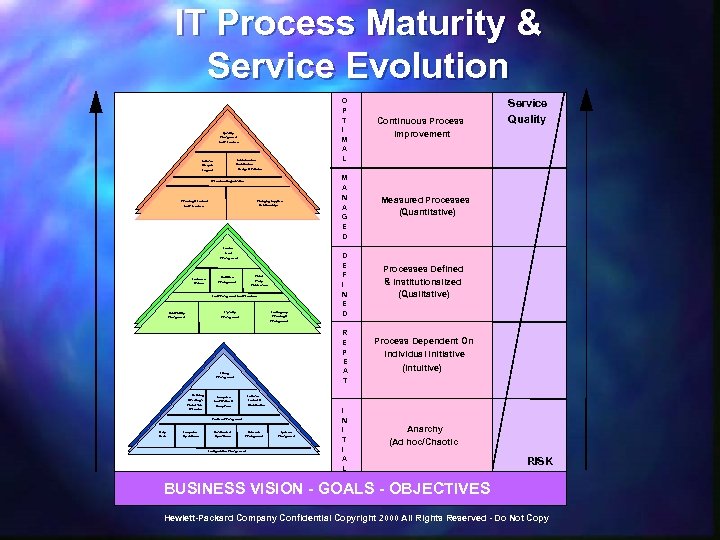 IT Process Maturity & Service Evolution O P T I M A L Quality Management for IT Services Software Infrastructure Lifecycle Architecture Continuous Process Improvement Service Quality Design & Policies Support IT Services Organization Managing Supplier Planning & Control Relationships for IT Services M A N A G E D Measured Processes (Quantitative) D E F I N E D Processes Defined & Institutionalized (Qualitative) Service Level Management Customer Liaison Third Facilities Party Management Maintenance Cost Management for IT Services Availability Contingency Capacity Management Planning & Management R E P E A T Change Management Defining & Testing a Marketable Process Dependent On Individual Initiative (Intuitive) Software Computer Control & Installation & Distribution Acceptance IT Service Problem Management Help Computer Unattended Network Systems Desk Operations Management Configuration Management I N I T I A L Anarchy (Ad hoc/Chaotic RISK BUSINESS VISION - GOALS - OBJECTIVES Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
IT Process Maturity & Service Evolution O P T I M A L Quality Management for IT Services Software Infrastructure Lifecycle Architecture Continuous Process Improvement Service Quality Design & Policies Support IT Services Organization Managing Supplier Planning & Control Relationships for IT Services M A N A G E D Measured Processes (Quantitative) D E F I N E D Processes Defined & Institutionalized (Qualitative) Service Level Management Customer Liaison Third Facilities Party Management Maintenance Cost Management for IT Services Availability Contingency Capacity Management Planning & Management R E P E A T Change Management Defining & Testing a Marketable Process Dependent On Individual Initiative (Intuitive) Software Computer Control & Installation & Distribution Acceptance IT Service Problem Management Help Computer Unattended Network Systems Desk Operations Management Configuration Management I N I T I A L Anarchy (Ad hoc/Chaotic RISK BUSINESS VISION - GOALS - OBJECTIVES Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
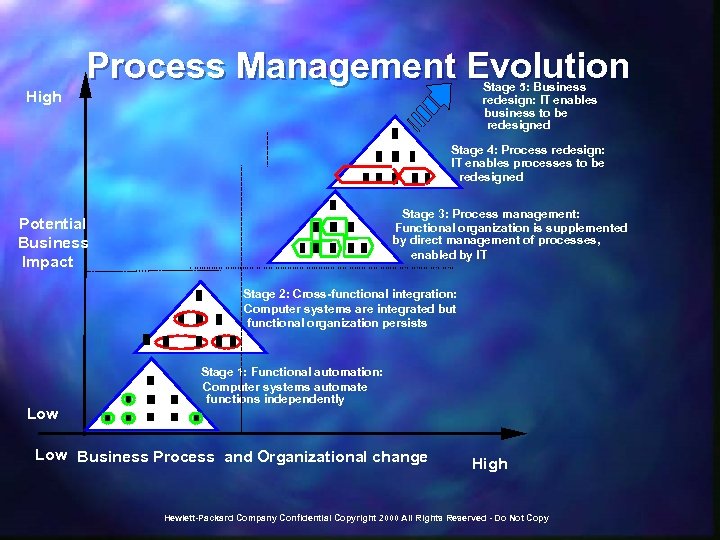 Process Management Evolution Stage 5: Business redesign: IT enables business to be redesigned High Potential Business Impact Low Stage 4: Process redesign: IT enables processes to be redesigned Stage 3: Process management: Functional organization is supplemented by direct management of processes, enabled by IT Stage 2: Cross-functional integration: Computer systems are integrated but functional organization persists Stage 1: Functional automation: Computer systems automate functions independently Low Business Process and Organizational change High Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Process Management Evolution Stage 5: Business redesign: IT enables business to be redesigned High Potential Business Impact Low Stage 4: Process redesign: IT enables processes to be redesigned Stage 3: Process management: Functional organization is supplemented by direct management of processes, enabled by IT Stage 2: Cross-functional integration: Computer systems are integrated but functional organization persists Stage 1: Functional automation: Computer systems automate functions independently Low Business Process and Organizational change High Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
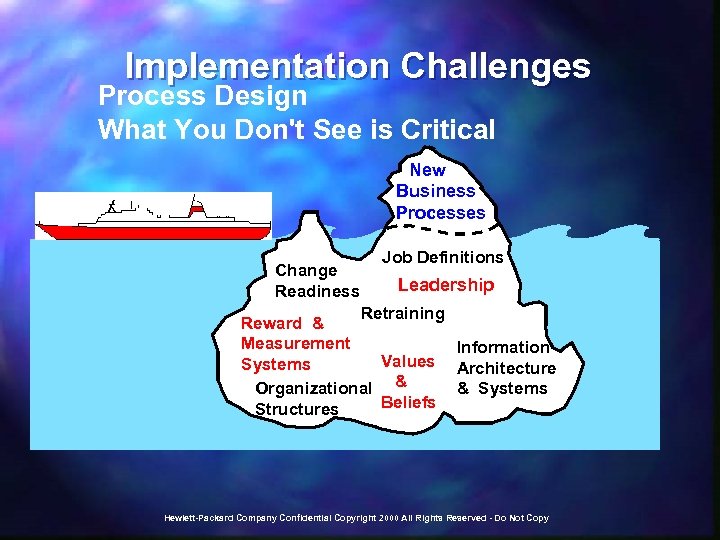 Implementation Challenges Process Design What You Don't See is Critical New Business Processes Change Readiness Job Definitions Leadership Retraining Reward & Measurement Information Values Architecture Systems & Systems Organizational & Beliefs Structures Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
Implementation Challenges Process Design What You Don't See is Critical New Business Processes Change Readiness Job Definitions Leadership Retraining Reward & Measurement Information Values Architecture Systems & Systems Organizational & Beliefs Structures Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 From IT to Utility…. Implementation Challenges Loss of Autonomy n Decisions must be made in light of the environment as a whole Increase in Accountability n Accountable for service level impact of decisions on environment as a whole Shift in Power from Application to Infrastructure n Application providers must plug into the known state infrastructure and do not have the power to change it at will Changes to Employee Value Proposition change from paying the best fire fighters the most to those who proactively prevent fires from occurring in the first place - (911 to 411) n Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
From IT to Utility…. Implementation Challenges Loss of Autonomy n Decisions must be made in light of the environment as a whole Increase in Accountability n Accountable for service level impact of decisions on environment as a whole Shift in Power from Application to Infrastructure n Application providers must plug into the known state infrastructure and do not have the power to change it at will Changes to Employee Value Proposition change from paying the best fire fighters the most to those who proactively prevent fires from occurring in the first place - (911 to 411) n Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
 ITIL Overview Session Questions and Answers Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy
ITIL Overview Session Questions and Answers Hewlett-Packard Company Confidential Copyright 2000 All Rights Reserved - Do Not Copy


