5f2573e6da8c89af0a47b2dc640238f3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 HET CERTIFICAAT NEDERLANDS ALS VREEMDE TAAL oznur. karaca@arts. kuleuven. be Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, 23 September 2005
HET CERTIFICAAT NEDERLANDS ALS VREEMDE TAAL oznur. karaca@arts. kuleuven. be Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, 23 September 2005
 Introducing Two New Profiles for the Certificate Dutch as a Foreign Language
Introducing Two New Profiles for the Certificate Dutch as a Foreign Language
 THE CERTIFICATE OF DUTCH AS A FOREIGN LANGUAGE Administered worldwide Functional and task-based exams 4 domain-specific language examinations
THE CERTIFICATE OF DUTCH AS A FOREIGN LANGUAGE Administered worldwide Functional and task-based exams 4 domain-specific language examinations
 Principles of functional language use • Domain specific language use Being able to function with the target language in a certain cluster of situations • Based on highly contextualised needs
Principles of functional language use • Domain specific language use Being able to function with the target language in a certain cluster of situations • Based on highly contextualised needs
 The 4 Existing Domains 1. Tourist and informal language proficiency 2. Social language proficiency 3. Professional language proficiency 4. Academic language proficiency
The 4 Existing Domains 1. Tourist and informal language proficiency 2. Social language proficiency 3. Professional language proficiency 4. Academic language proficiency
 Additional Domains 5. Domain of Language Proficiency in Practically Oriented Professions (PTPB) intended for secondary school graduates who wish to start working as labourers or skilled workers (welders, electricians, lorry drivers, repairmen, …) in Dutch speaking territories.
Additional Domains 5. Domain of Language Proficiency in Practically Oriented Professions (PTPB) intended for secondary school graduates who wish to start working as labourers or skilled workers (welders, electricians, lorry drivers, repairmen, …) in Dutch speaking territories.
 Additional Domains 6. Domain of Language Proficiency in Higher Education (PTHO) Intended for secondary school graduates who wish to enroll at a university or other institute of higher education in Dutchspeaking territories, taking into account different branches of study.
Additional Domains 6. Domain of Language Proficiency in Higher Education (PTHO) Intended for secondary school graduates who wish to enroll at a university or other institute of higher education in Dutchspeaking territories, taking into account different branches of study.
 Conducting a needs analysis Presenting pupils with target language use situations Comparison with final achievement goals in schools in border regions Comparison with admittance requirements in institutes of higher education and companies in border regions
Conducting a needs analysis Presenting pupils with target language use situations Comparison with final achievement goals in schools in border regions Comparison with admittance requirements in institutes of higher education and companies in border regions
 Consulted Sources Framework Language and Intercultural Competencies – the Euregio competencies IHK-Zusatzqualifikation berufsorientierte Fremdsprache Arbeitzplatz Europa Compétences minimales et savoirs requis en langues modernes Admittance requirements of Flemish institutes of higher education
Consulted Sources Framework Language and Intercultural Competencies – the Euregio competencies IHK-Zusatzqualifikation berufsorientierte Fremdsprache Arbeitzplatz Europa Compétences minimales et savoirs requis en langues modernes Admittance requirements of Flemish institutes of higher education
 Bringing the data together Creating real-life language use situations Determining the language skills required in one such situation Label these with language use requirements SETTING NEW LANGUAGE PROFICIENCY REQUIREMENTS Comparison to the Common European Framework of Reference
Bringing the data together Creating real-life language use situations Determining the language skills required in one such situation Label these with language use requirements SETTING NEW LANGUAGE PROFICIENCY REQUIREMENTS Comparison to the Common European Framework of Reference
 Example of one language requirement description ( for PTPB) - Listening skills 1. Determining the language act: Can catch and follow the main thought 2. Determining the kind of text: In an Informative Text such as Instructions, Announcements, Etc. 3. Determining examples: - listening to instructions of the foreman - understanding a call via intercom to proceed to another room
Example of one language requirement description ( for PTPB) - Listening skills 1. Determining the language act: Can catch and follow the main thought 2. Determining the kind of text: In an Informative Text such as Instructions, Announcements, Etc. 3. Determining examples: - listening to instructions of the foreman - understanding a call via intercom to proceed to another room
 Examples of language tasks PTPB: • The employee is able to deal with an automatic answering machine. • The employee can fill out a repair invoice, having listened to a customer explaining what is wrong with an appliance. • The employee can fill out a work schedule in discussion with co-workers. • The employee can explain safety measures to a student in work placement. • . . .
Examples of language tasks PTPB: • The employee is able to deal with an automatic answering machine. • The employee can fill out a repair invoice, having listened to a customer explaining what is wrong with an appliance. • The employee can fill out a work schedule in discussion with co-workers. • The employee can explain safety measures to a student in work placement. • . . .
 Examples of language tasks PTHO: • The student is able to take part in a discussion at a forum, concerning the subject of his studies. • The student is able to take notes during a radio broadcast, in preparation of an oral presentation. • The student can summarize an elaborate text on a known subject. • …
Examples of language tasks PTHO: • The student is able to take part in a discussion at a forum, concerning the subject of his studies. • The student is able to take notes during a radio broadcast, in preparation of an oral presentation. • The student can summarize an elaborate text on a known subject. • …
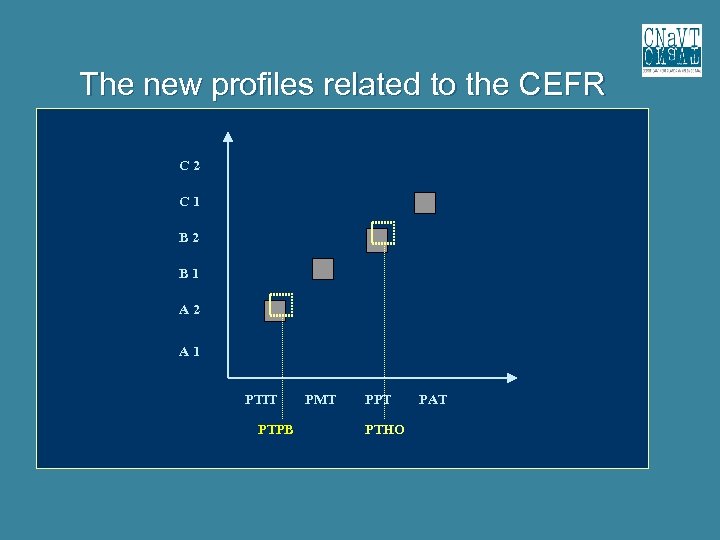 The new profiles related to the CEFR C 2 C 1 B 2 B 1 A 2 A 1 PTIT PTPB PMT PPT PTHO PAT
The new profiles related to the CEFR C 2 C 1 B 2 B 1 A 2 A 1 PTIT PTPB PMT PPT PTHO PAT
 Conducting a pilot exam • 120 students in Germany • Primarily last year students • Testing reading, listening, writing, and speaking skills.
Conducting a pilot exam • 120 students in Germany • Primarily last year students • Testing reading, listening, writing, and speaking skills.
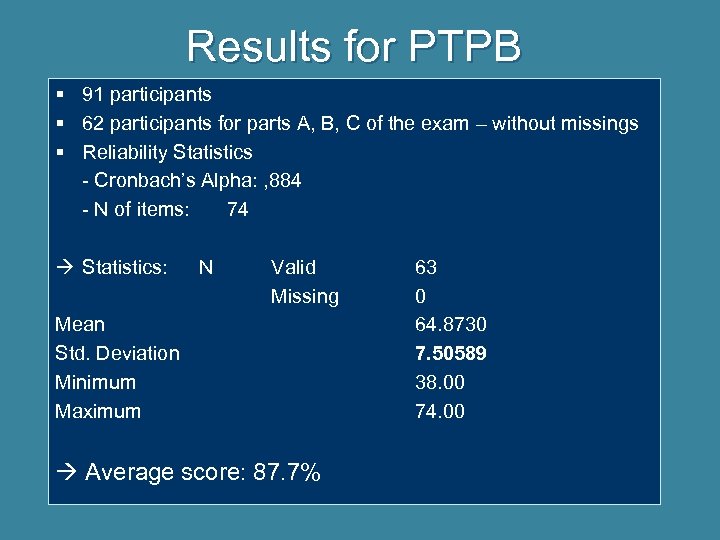 Results for PTPB § 91 participants § 62 participants for parts A, B, C of the exam – without missings § Reliability Statistics - Cronbach’s Alpha: , 884 - N of items: 74 Statistics: N Valid Missing Mean Std. Deviation Minimum Maximum Average score: 87. 7% 63 0 64. 8730 7. 50589 38. 00 74. 00
Results for PTPB § 91 participants § 62 participants for parts A, B, C of the exam – without missings § Reliability Statistics - Cronbach’s Alpha: , 884 - N of items: 74 Statistics: N Valid Missing Mean Std. Deviation Minimum Maximum Average score: 87. 7% 63 0 64. 8730 7. 50589 38. 00 74. 00
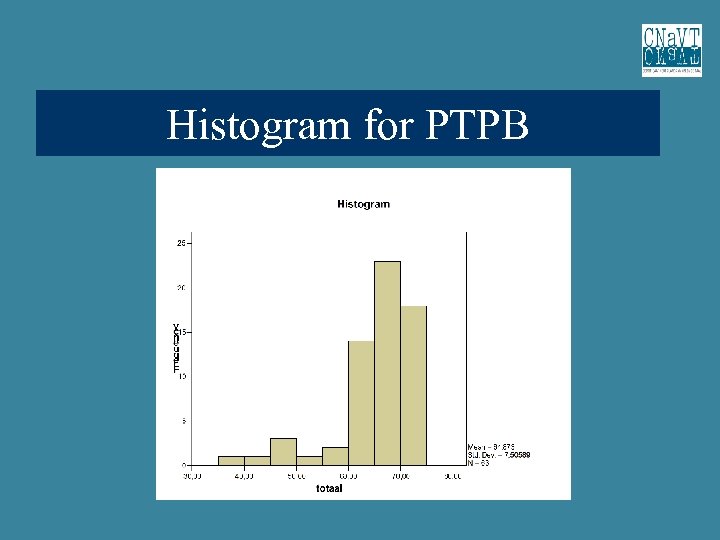 Histogram for PTPB
Histogram for PTPB
 QUESTIONS?
QUESTIONS?


