 Hernia
Hernia
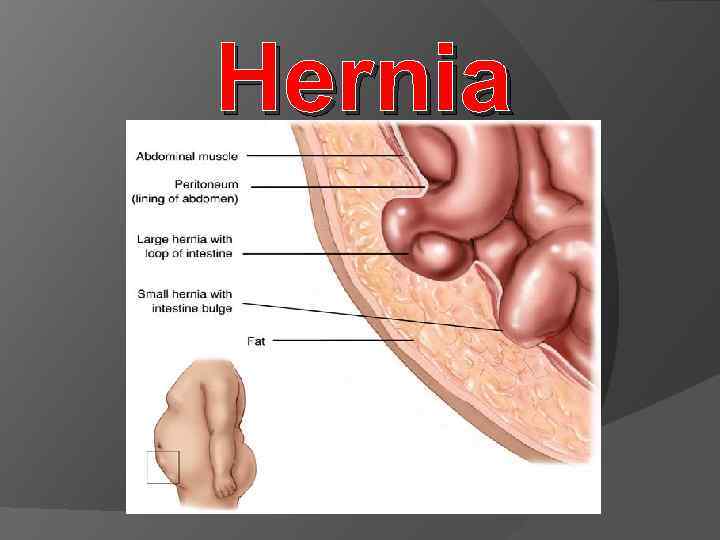
 What is hernia ? hernia is a sac formed by the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). The sac comes through a hole or weak area in the strong layer of the belly wall that surrounds the muscle. This layer is called the fascia.
What is hernia ? hernia is a sac formed by the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). The sac comes through a hole or weak area in the strong layer of the belly wall that surrounds the muscle. This layer is called the fascia.
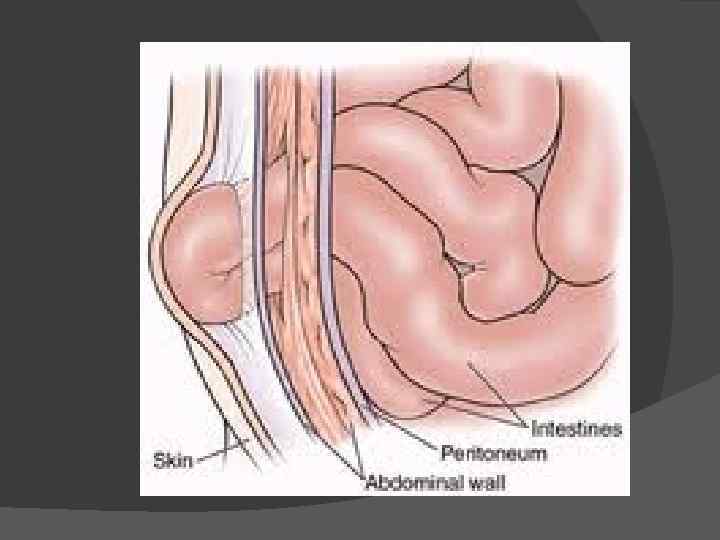
 Hernias are most common in the abdomen. However, they can also appear in the upper thigh, belly button, and groin regions. Though the majority of hernias are not immediately life threatening, they will not go away on their own and will require surgical correction to prevent potentially dangerous complications
Hernias are most common in the abdomen. However, they can also appear in the upper thigh, belly button, and groin regions. Though the majority of hernias are not immediately life threatening, they will not go away on their own and will require surgical correction to prevent potentially dangerous complications
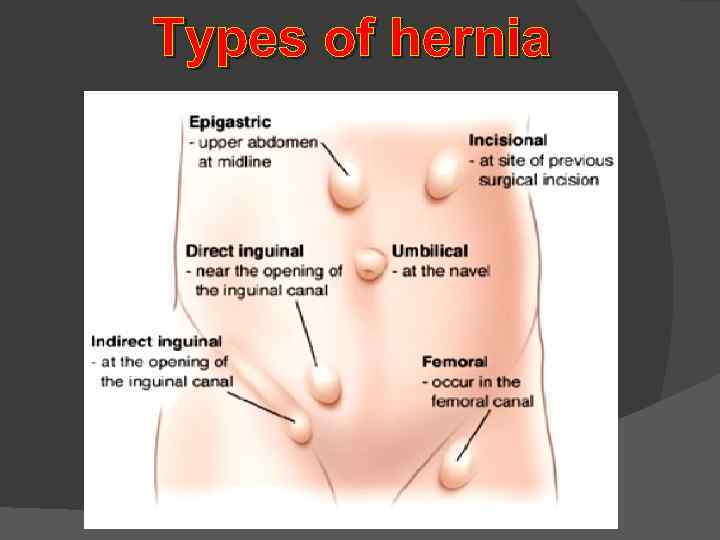 Types of hernia
Types of hernia
 Inguinal Hernias Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia, most commonly in men They occur in a part of the abdominal wall known as the inguinal canal, where a man's testicles must descend before birth. This leaves a natural defect called the internal inguinal ring that can develop into a hernia if it doesn't seal properly. As a result, the contents of the abdomen, such as intestine, may protrude through the opening, creating pain and/or a bulge.
Inguinal Hernias Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia, most commonly in men They occur in a part of the abdominal wall known as the inguinal canal, where a man's testicles must descend before birth. This leaves a natural defect called the internal inguinal ring that can develop into a hernia if it doesn't seal properly. As a result, the contents of the abdomen, such as intestine, may protrude through the opening, creating pain and/or a bulge.
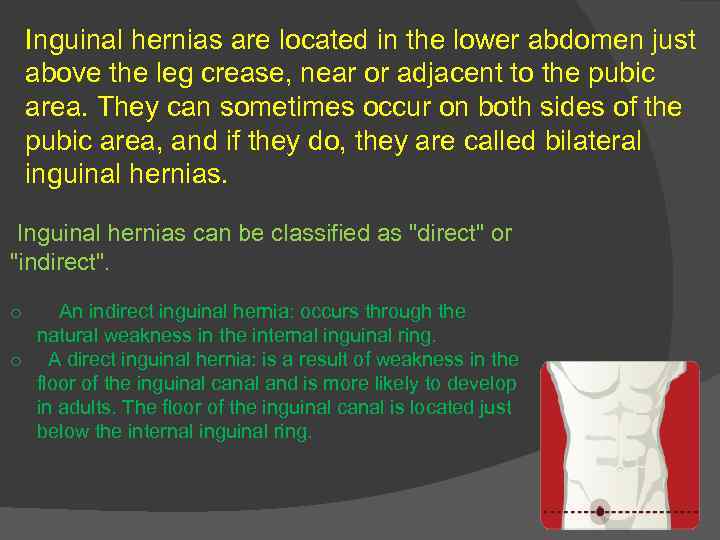 Inguinal hernias are located in the lower abdomen just above the leg crease, near or adjacent to the pubic area. They can sometimes occur on both sides of the pubic area, and if they do, they are called bilateral inguinal hernias. Inguinal hernias can be classified as "direct" or "indirect". An indirect inguinal hernia: occurs through the natural weakness in the internal inguinal ring. o A direct inguinal hernia: is a result of weakness in the floor of the inguinal canal and is more likely to develop in adults. The floor of the inguinal canal is located just below the internal inguinal ring. o
Inguinal hernias are located in the lower abdomen just above the leg crease, near or adjacent to the pubic area. They can sometimes occur on both sides of the pubic area, and if they do, they are called bilateral inguinal hernias. Inguinal hernias can be classified as "direct" or "indirect". An indirect inguinal hernia: occurs through the natural weakness in the internal inguinal ring. o A direct inguinal hernia: is a result of weakness in the floor of the inguinal canal and is more likely to develop in adults. The floor of the inguinal canal is located just below the internal inguinal ring. o
 Ventral Hernias: A hernia that appears in the abdomen at the site of a previous surgery is known as a ventral or incisional hernia. These hernias can appear weeks, months, or even years after surgery and can vary in size from small to very large and complex.
Ventral Hernias: A hernia that appears in the abdomen at the site of a previous surgery is known as a ventral or incisional hernia. These hernias can appear weeks, months, or even years after surgery and can vary in size from small to very large and complex.
 Femoral Hernias Femoral hernias, along with inguinal hernias are groin hernias. They are much more common in women but can occur in men. These hernias appear just below the groin crease and are usually the result of pregnancy and childbirth. A weakness in the lower groin allows an intestinal sac to drop into the femoral canal, These hernias are more prone than inguinal hernias to develop incarceration or strangulation as an early complication.
Femoral Hernias Femoral hernias, along with inguinal hernias are groin hernias. They are much more common in women but can occur in men. These hernias appear just below the groin crease and are usually the result of pregnancy and childbirth. A weakness in the lower groin allows an intestinal sac to drop into the femoral canal, These hernias are more prone than inguinal hernias to develop incarceration or strangulation as an early complication.
 Umbilical Hernias: Umbilical hernias occur near the bellybutton or navel, which has a natural weakness from the blood vessels of the umbilical cord. These hernias may occur in infants at or just after birth and may resolve by three or four years of age. However, the area of weakness can persist throughout life and can occur in men, women, and children at any time. In adults, umbilical hernias will not resolve and may progressively worsen over time and need surgical treatment. They are sometimes caused by abdominal pressure due to being overweight, excessive coughing, or pregnancy.
Umbilical Hernias: Umbilical hernias occur near the bellybutton or navel, which has a natural weakness from the blood vessels of the umbilical cord. These hernias may occur in infants at or just after birth and may resolve by three or four years of age. However, the area of weakness can persist throughout life and can occur in men, women, and children at any time. In adults, umbilical hernias will not resolve and may progressively worsen over time and need surgical treatment. They are sometimes caused by abdominal pressure due to being overweight, excessive coughing, or pregnancy.
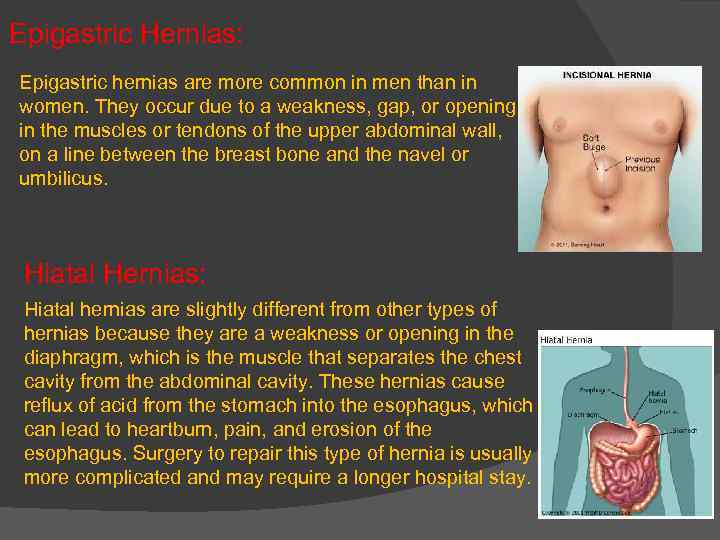 Epigastric Hernias: Epigastric hernias are more common in men than in women. They occur due to a weakness, gap, or opening in the muscles or tendons of the upper abdominal wall, on a line between the breast bone and the navel or umbilicus. Hiatal Hernias: Hiatal hernias are slightly different from other types of hernias because they are a weakness or opening in the diaphragm, which is the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. These hernias cause reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus, which can lead to heartburn, pain, and erosion of the esophagus. Surgery to repair this type of hernia is usually more complicated and may require a longer hospital stay.
Epigastric Hernias: Epigastric hernias are more common in men than in women. They occur due to a weakness, gap, or opening in the muscles or tendons of the upper abdominal wall, on a line between the breast bone and the navel or umbilicus. Hiatal Hernias: Hiatal hernias are slightly different from other types of hernias because they are a weakness or opening in the diaphragm, which is the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. These hernias cause reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus, which can lead to heartburn, pain, and erosion of the esophagus. Surgery to repair this type of hernia is usually more complicated and may require a longer hospital stay.
 Acquired vs Congenital Hernias: (causes) Hernias can also be classified by when they occur. A person may be born with a hernia, or a hernia may be acquired from daily activity. o Acquired hernias are caused by the wear and tear of living, such as childbirth, weight gain, and other muscle strain , chronic cough, ascites, peritoneal dialysis, pregnancy, and lifting. Congenital hernias are present from birth and happen at points of weakness in the abdominal wall. Children's hernias are almost always congenital. Reducible vs Non-reducible Hernias: A hernia with a bulge can be classified based on whether or not the bulge can be flattened. A reducible hernia is a hernia with a bulge that flattens out when you lie down or push against it gently. This type of hernia is not an immediate danger to a person’s health, although it may be painful and worsen over time if left untreated. o A non-reducible hernia occurs when the loop of the intestine becomes trapped and a person loses the ability to make the bulge flatten out. Nonreducible hernias are often very painful and require prompt medical attention. Which can lead to strangulated hernia. o
Acquired vs Congenital Hernias: (causes) Hernias can also be classified by when they occur. A person may be born with a hernia, or a hernia may be acquired from daily activity. o Acquired hernias are caused by the wear and tear of living, such as childbirth, weight gain, and other muscle strain , chronic cough, ascites, peritoneal dialysis, pregnancy, and lifting. Congenital hernias are present from birth and happen at points of weakness in the abdominal wall. Children's hernias are almost always congenital. Reducible vs Non-reducible Hernias: A hernia with a bulge can be classified based on whether or not the bulge can be flattened. A reducible hernia is a hernia with a bulge that flattens out when you lie down or push against it gently. This type of hernia is not an immediate danger to a person’s health, although it may be painful and worsen over time if left untreated. o A non-reducible hernia occurs when the loop of the intestine becomes trapped and a person loses the ability to make the bulge flatten out. Nonreducible hernias are often very painful and require prompt medical attention. Which can lead to strangulated hernia. o
 Symptoms: There are usually no symptoms. Some people have discomfort or pain. The discomfort may be worse when you stand, strain, or lift heavy objects. In time, most people will complain about a bump that is sore and growing. If a hernia gets bigger, it may get stuck inside the hole and lose its blood supply. This is called "strangulation. Other common symptoms of an inguinal hernia include: 1. feeling of heaviness in the abdomen 2. nausea, vomiting or fever
Symptoms: There are usually no symptoms. Some people have discomfort or pain. The discomfort may be worse when you stand, strain, or lift heavy objects. In time, most people will complain about a bump that is sore and growing. If a hernia gets bigger, it may get stuck inside the hole and lose its blood supply. This is called "strangulation. Other common symptoms of an inguinal hernia include: 1. feeling of heaviness in the abdomen 2. nausea, vomiting or fever
 Diagnose: o physical examination. we may feel for a bulge in the abdomen or groin that gets larger when you stand, cough, or strain. o barium X-ray or endoscopy in case of hiatal hernia o Ultrasound in case of umbilical hernia (especially in child)
Diagnose: o physical examination. we may feel for a bulge in the abdomen or groin that gets larger when you stand, cough, or strain. o barium X-ray or endoscopy in case of hiatal hernia o Ultrasound in case of umbilical hernia (especially in child)
 Treatment: Based on the size of your hernia and the severity of the symptoms, it maw not need treatment. we may simply monitor the hernia for possible complications. The symptoms of a hiatal hernia can often be treated by simply changing the diet. Avoid large or heavy meals, don’t lie down or bend over after a meal, and keep your body weight in a healthy range. If these changes in diet do not eliminate the discomfort, we may need surgery to correct the hernia.
Treatment: Based on the size of your hernia and the severity of the symptoms, it maw not need treatment. we may simply monitor the hernia for possible complications. The symptoms of a hiatal hernia can often be treated by simply changing the diet. Avoid large or heavy meals, don’t lie down or bend over after a meal, and keep your body weight in a healthy range. If these changes in diet do not eliminate the discomfort, we may need surgery to correct the hernia.
 Surgery: if the hernia is growing larger or causing pain, we may decide that it’s best to operate. Your doctor may repair your hernia by sewing the hole in the abdominal wall closed during surgery. However, the more common treatment for hernias is to patch the hole with surgical mesh. We can repaire the hernia either with: o laparoscopic surgery. o open surgery.
Surgery: if the hernia is growing larger or causing pain, we may decide that it’s best to operate. Your doctor may repair your hernia by sewing the hole in the abdominal wall closed during surgery. However, the more common treatment for hernias is to patch the hole with surgical mesh. We can repaire the hernia either with: o laparoscopic surgery. o open surgery.
 Thank you Ali Maan Attallah G-413
Thank you Ali Maan Attallah G-413


