dfdbfc2f8499f208c6425225a1c6e244.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 Here is what Step 1 covers- did we get them all? • Production/function granulocyte, NK cells and macrophages/DC • Production/function of T cells, TCR, cytokines/chemokines • Production/function of B cells and PC, Ig structure, classes, molecular basis for specificity, receptors • Antigenicity/immunogenicity, host defenses(read Innate I), primary/secondary responses, passive transfer of immunity(all ways) • In vitro complement, other diagnostic tests and antigen antibody reactions • Mediators, complement, aa, histamine, NO and cytokines • MHC structure and function, RBC antigens. Transplantation • Vaccines, protective immunity, tumor immunity • Disease states like ID, HIV and pharmacological immunosuppression
Here is what Step 1 covers- did we get them all? • Production/function granulocyte, NK cells and macrophages/DC • Production/function of T cells, TCR, cytokines/chemokines • Production/function of B cells and PC, Ig structure, classes, molecular basis for specificity, receptors • Antigenicity/immunogenicity, host defenses(read Innate I), primary/secondary responses, passive transfer of immunity(all ways) • In vitro complement, other diagnostic tests and antigen antibody reactions • Mediators, complement, aa, histamine, NO and cytokines • MHC structure and function, RBC antigens. Transplantation • Vaccines, protective immunity, tumor immunity • Disease states like ID, HIV and pharmacological immunosuppression
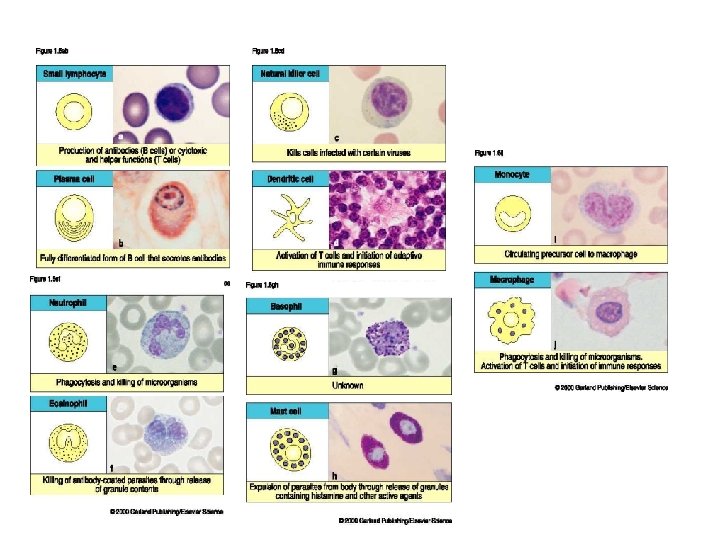
 INNATE IMMUNITY • NOT ANTIGEN SPECIFIC • HAS NO MEMORY • MEDIATED BY – NEUTROPHILS – MACROPHAGES/MONOCYTES – NATURAL KILLER CELLS – EOSINOPHILS – BASOPHILS/MAST CELLS – MANNOSE BINDING PROTEIN AND COMPLEMENT – PROSTAGLANDIN & KININ SYSTEMS INDISCRIMINATE DESTRUCTION
INNATE IMMUNITY • NOT ANTIGEN SPECIFIC • HAS NO MEMORY • MEDIATED BY – NEUTROPHILS – MACROPHAGES/MONOCYTES – NATURAL KILLER CELLS – EOSINOPHILS – BASOPHILS/MAST CELLS – MANNOSE BINDING PROTEIN AND COMPLEMENT – PROSTAGLANDIN & KININ SYSTEMS INDISCRIMINATE DESTRUCTION
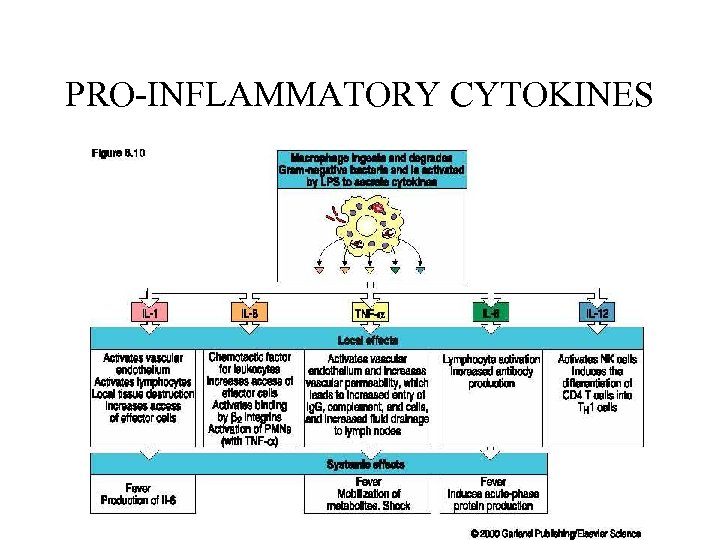 PRO-INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES
PRO-INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES
 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY • ANTIGEN SPECIFIC • CLONAL EXPANSION • AMPLIFIES AN IMMUNE RESPONSE AFTER A SPECIFIC RECEPTOR INTERACTION • INTEGRATES THE INNATE RESPONSE INTO THE REACTION • MEMORY OF THE ENCOUNTER
ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY • ANTIGEN SPECIFIC • CLONAL EXPANSION • AMPLIFIES AN IMMUNE RESPONSE AFTER A SPECIFIC RECEPTOR INTERACTION • INTEGRATES THE INNATE RESPONSE INTO THE REACTION • MEMORY OF THE ENCOUNTER
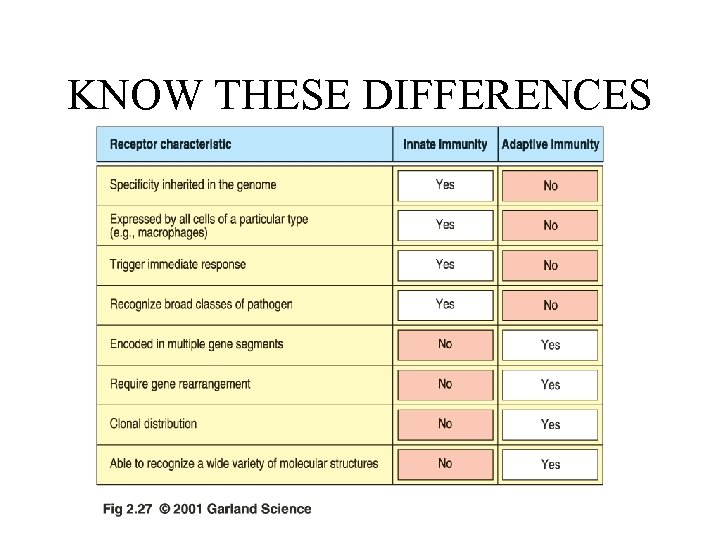 KNOW THESE DIFFERENCES
KNOW THESE DIFFERENCES
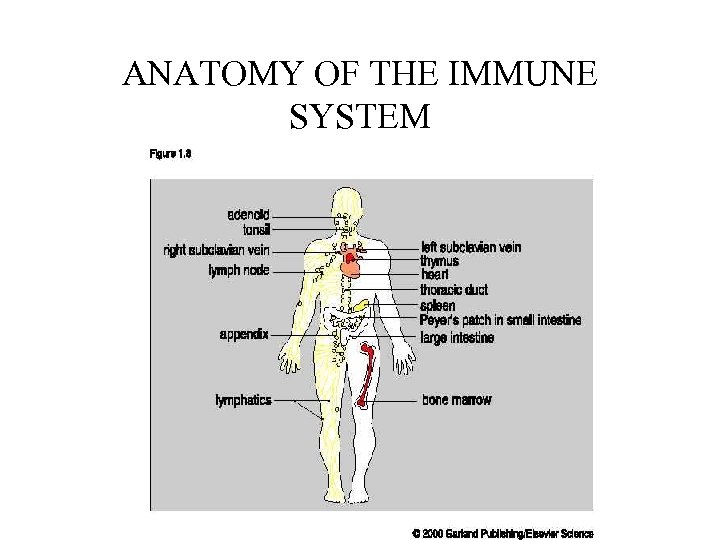 ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
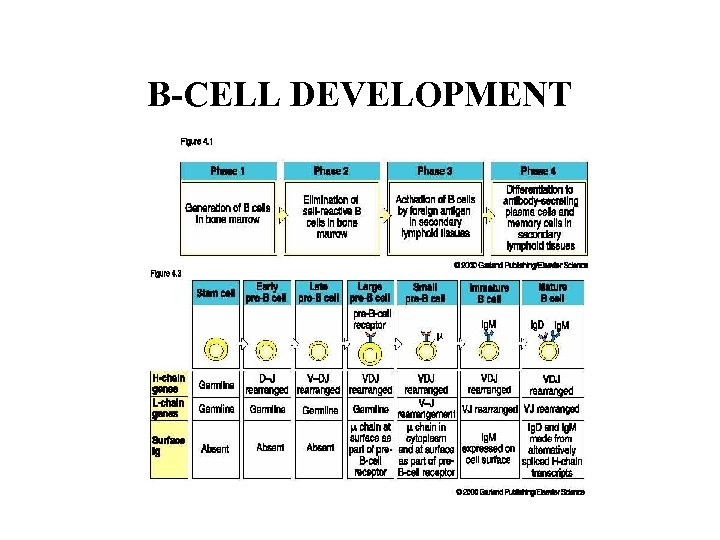 B-CELL DEVELOPMENT
B-CELL DEVELOPMENT
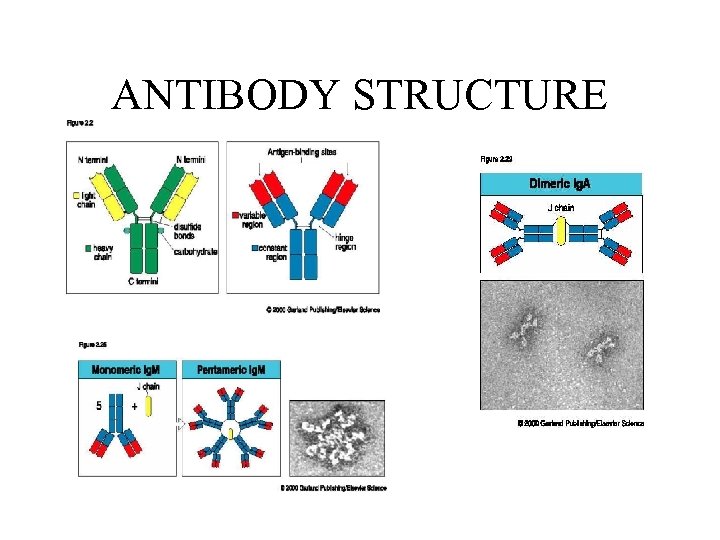 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE
ANTIBODY STRUCTURE
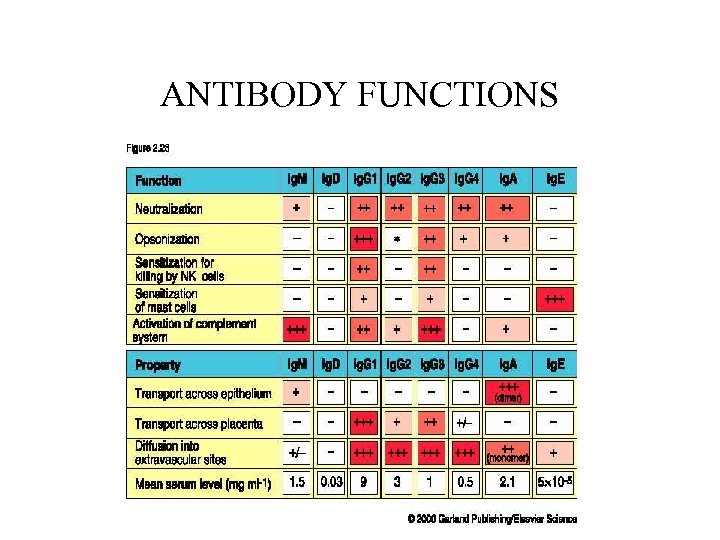 ANTIBODY FUNCTIONS
ANTIBODY FUNCTIONS
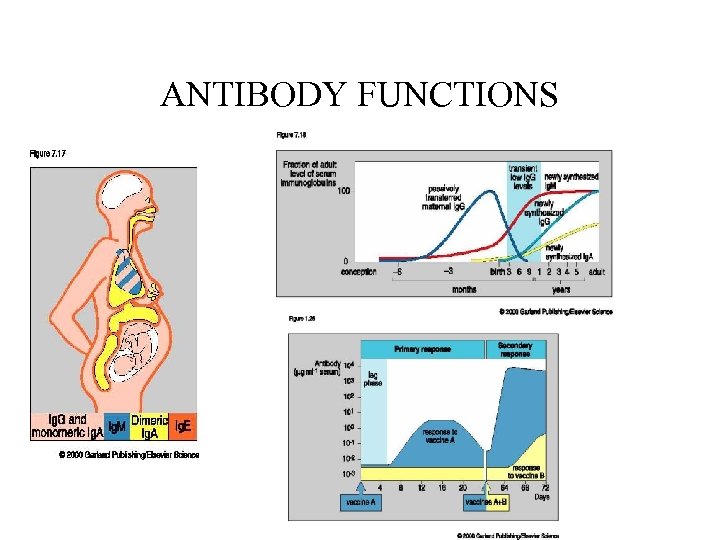 ANTIBODY FUNCTIONS
ANTIBODY FUNCTIONS
 COMPLEMENT • FLUID PHASE AMPLIFIER OF INNATE AND ANTIBODY MEDIATED RESPONSES • THREE ARMS – ALTERNATE-BACTERIAL CELL WALLS – MANNOSE BINDING-BACTERIAL CELL WALLS and MBP – DIRECT(CLASSIC)-SPECIFIC Ag/Ab REACTIONS
COMPLEMENT • FLUID PHASE AMPLIFIER OF INNATE AND ANTIBODY MEDIATED RESPONSES • THREE ARMS – ALTERNATE-BACTERIAL CELL WALLS – MANNOSE BINDING-BACTERIAL CELL WALLS and MBP – DIRECT(CLASSIC)-SPECIFIC Ag/Ab REACTIONS
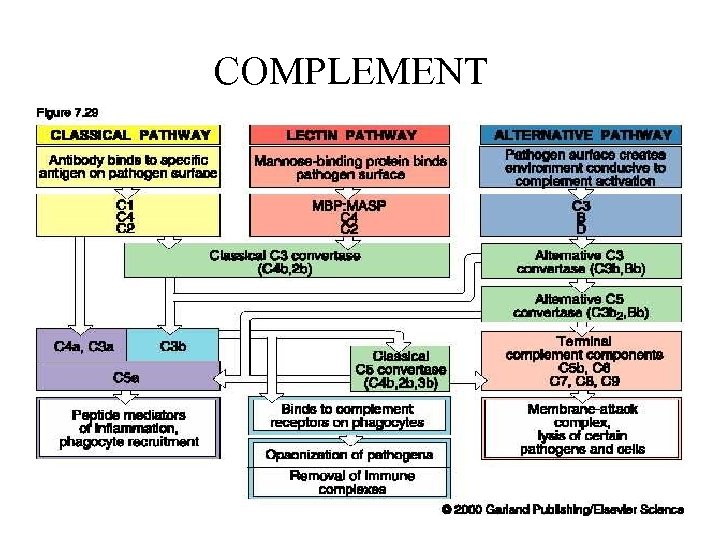 COMPLEMENT
COMPLEMENT
 COMPLEMENT • ENZYME ACTIVATED CASCADE WITH GENERATION OF INFLAMMATORY AND REGULATORY FRAGMENTS • ACTIVATES INFLAMMATORY CELLS BY SPECIFIC RECEPTOR INTERACTIONS • HAS IMPORTANT IMMUNOREGULATORY AND IMMUNE COMPLEX DISPOSAL ROLES • Measured by serum C 3 and C 4, total hemolysis and individual components
COMPLEMENT • ENZYME ACTIVATED CASCADE WITH GENERATION OF INFLAMMATORY AND REGULATORY FRAGMENTS • ACTIVATES INFLAMMATORY CELLS BY SPECIFIC RECEPTOR INTERACTIONS • HAS IMPORTANT IMMUNOREGULATORY AND IMMUNE COMPLEX DISPOSAL ROLES • Measured by serum C 3 and C 4, total hemolysis and individual components
 COMPLEMENT-RELATED DISEASES • Rare • C 1 esterase deficiency with angioneurotic edema • Deficiencies in the direct sequence associated with IC diseases like SLE • Homozygous C 3 is lethal • Deficiencies in the alternate path very rare • Individual component deficiency after C 5 associated with Neisserial bacteremia
COMPLEMENT-RELATED DISEASES • Rare • C 1 esterase deficiency with angioneurotic edema • Deficiencies in the direct sequence associated with IC diseases like SLE • Homozygous C 3 is lethal • Deficiencies in the alternate path very rare • Individual component deficiency after C 5 associated with Neisserial bacteremia
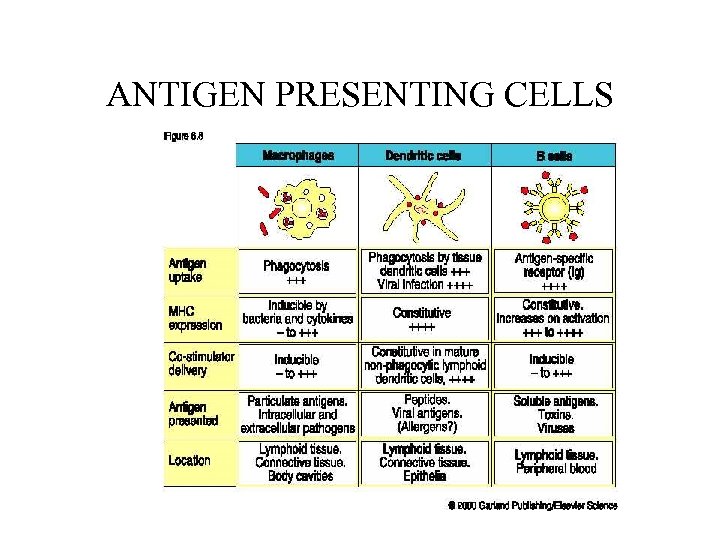 ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS
ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS
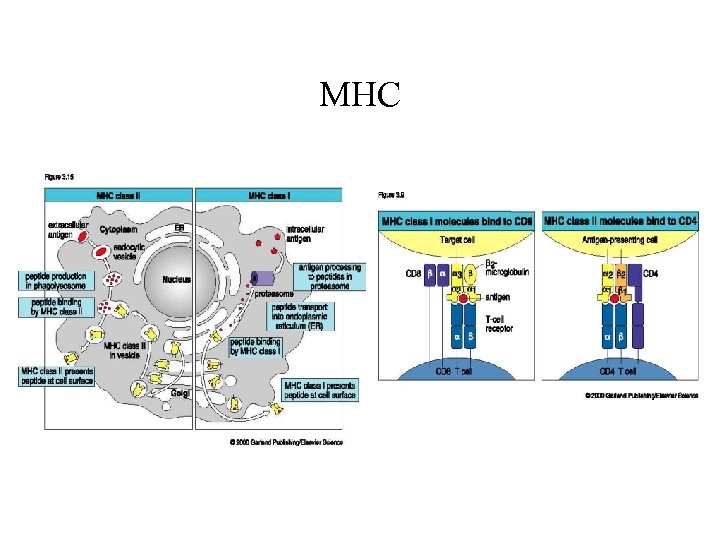 MHC
MHC
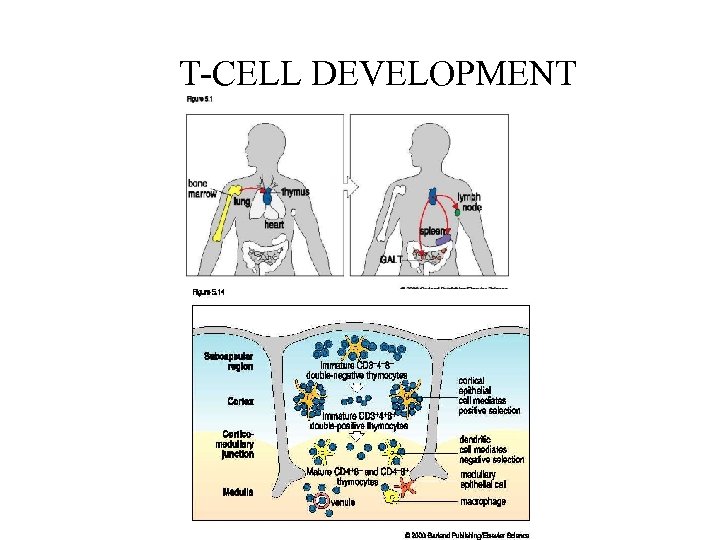 T-CELL DEVELOPMENT
T-CELL DEVELOPMENT
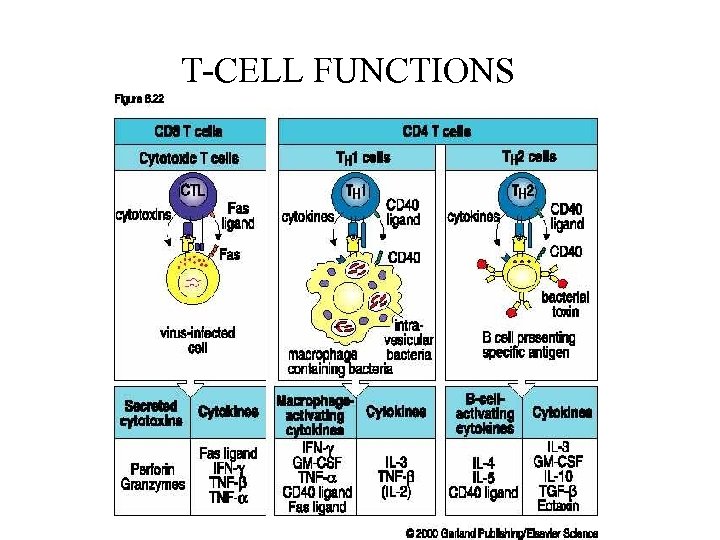
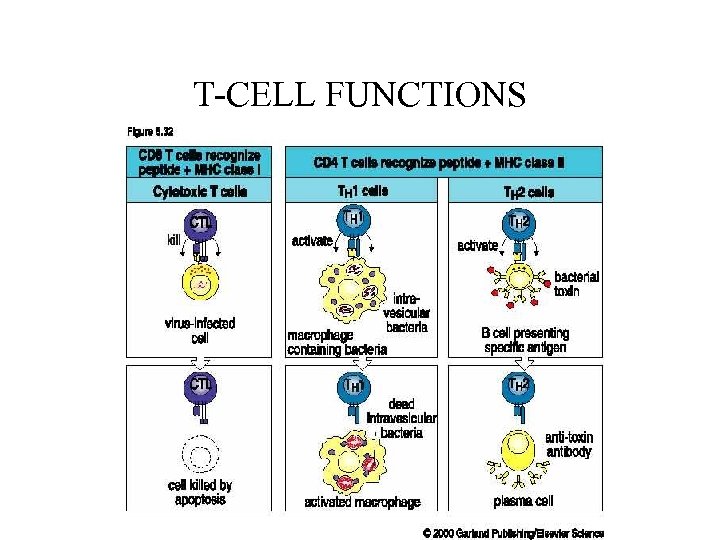 T-CELL FUNCTIONS
T-CELL FUNCTIONS
 QUESTIONS • • • From stem cell to T cell why the thymus CD 4 versus CD 8 gamma delts versus alpha bets peripheral blood CDs to remember………. – 3, 4, 8, 25, 19, 16, 20,
QUESTIONS • • • From stem cell to T cell why the thymus CD 4 versus CD 8 gamma delts versus alpha bets peripheral blood CDs to remember………. – 3, 4, 8, 25, 19, 16, 20,
 MORE CYTOKINES TO REMEMBER Il-12, INF- and IL-2 =TH 1 response IL-4 =TH 2 response & antibody formation IL-10, IL- 4 = suppression of Th 1 INF- = suppression of TH 2 IL-8 = neutrophils IL-5= eosinophils TGF- = healing IL-6 = fever and cachexia TNF- =inflammation (RA), sepsis and SIRS, monoclonals available to inhibit some syndromes
MORE CYTOKINES TO REMEMBER Il-12, INF- and IL-2 =TH 1 response IL-4 =TH 2 response & antibody formation IL-10, IL- 4 = suppression of Th 1 INF- = suppression of TH 2 IL-8 = neutrophils IL-5= eosinophils TGF- = healing IL-6 = fever and cachexia TNF- =inflammation (RA), sepsis and SIRS, monoclonals available to inhibit some syndromes
 MHC • • Co-dominant alleles Present on Chromosome 6 in humans A, B, C loci are Class I D loci are class II and control immune responses and rejection
MHC • • Co-dominant alleles Present on Chromosome 6 in humans A, B, C loci are Class I D loci are class II and control immune responses and rejection
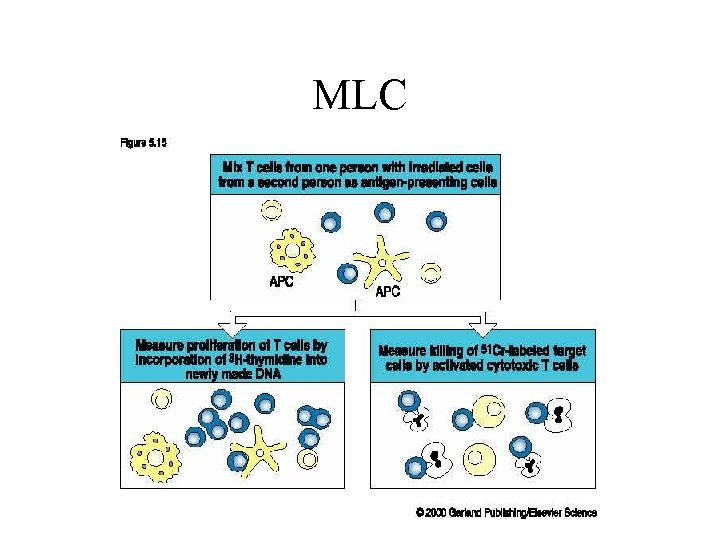 MLC
MLC
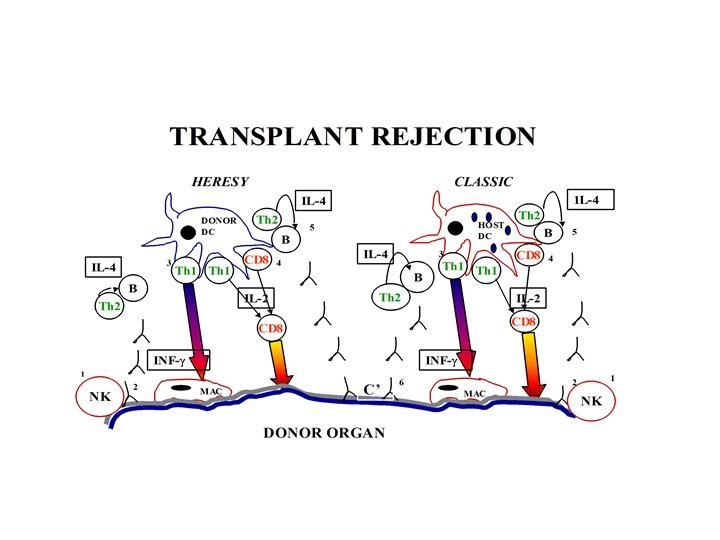
 TRANSPLANT TYPES • • Autograft Isograft Allograft (also known as Homograft) Xenograft
TRANSPLANT TYPES • • Autograft Isograft Allograft (also known as Homograft) Xenograft
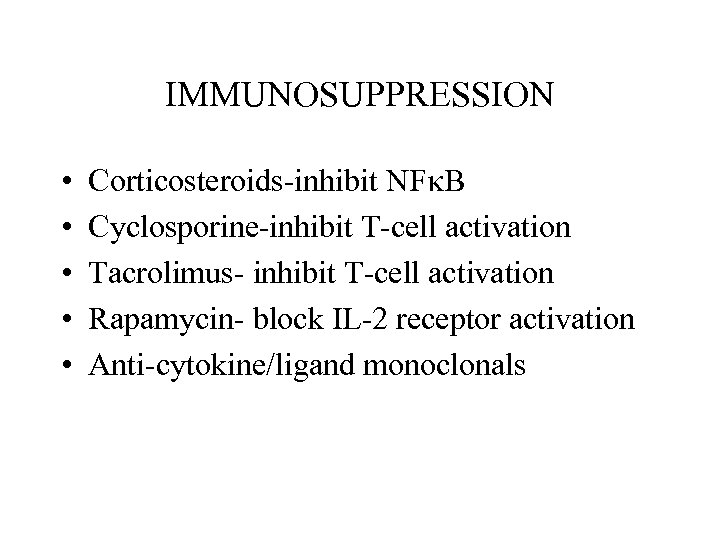 IMMUNOSUPPRESSION • • • Corticosteroids-inhibit NF B Cyclosporine-inhibit T-cell activation Tacrolimus- inhibit T-cell activation Rapamycin- block IL-2 receptor activation Anti-cytokine/ligand monoclonals
IMMUNOSUPPRESSION • • • Corticosteroids-inhibit NF B Cyclosporine-inhibit T-cell activation Tacrolimus- inhibit T-cell activation Rapamycin- block IL-2 receptor activation Anti-cytokine/ligand monoclonals
 PREDICT THE TYPE OF INFECTION • Pure B cell…encapsulated bacteria and systemic spread of GI viruses. . frequent after 6 mos of age • “pure” T cell…. TB, fungi, pneumocystis since helper function is lost…occurs at birth. B cell infections will not occur until maternal antibody gone-approx 6 mos • B & T cell. . at birth, severe and fatal if not transplanted • CGD –neutrophil inability to kill bacterial that produce catalase. . esp staph • cytokine. . IL-12, Interferon gamma, IL-4
PREDICT THE TYPE OF INFECTION • Pure B cell…encapsulated bacteria and systemic spread of GI viruses. . frequent after 6 mos of age • “pure” T cell…. TB, fungi, pneumocystis since helper function is lost…occurs at birth. B cell infections will not occur until maternal antibody gone-approx 6 mos • B & T cell. . at birth, severe and fatal if not transplanted • CGD –neutrophil inability to kill bacterial that produce catalase. . esp staph • cytokine. . IL-12, Interferon gamma, IL-4
 DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH TCELL DEFICIENCY • • HIV/AIDS THYMIC APLASIA SENESCENCE BIRTH WISKOTT-ALDRICH ATAXIA-TELANGIECTASIA TREATMENT
DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH TCELL DEFICIENCY • • HIV/AIDS THYMIC APLASIA SENESCENCE BIRTH WISKOTT-ALDRICH ATAXIA-TELANGIECTASIA TREATMENT
 DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH BCELL DEFICIENCY • X-LINKED AGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA • COMMON VARIABLE IMMUNODEFICIENCY • SELECTIVE Ig. A DEFICIENCY • CLL • HYPER Ig. M SYNDROME • TREATMENT
DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH BCELL DEFICIENCY • X-LINKED AGAMMAGLOBULINEMIA • COMMON VARIABLE IMMUNODEFICIENCY • SELECTIVE Ig. A DEFICIENCY • CLL • HYPER Ig. M SYNDROME • TREATMENT
 DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH T & B CELL DEFICIENCY • SCID • THERAPY: – STEM CELL TRANSPLANTS – BMT – GENE REPLACEMENT- recent problems with the retroviral vector insertion has led to leukemia
DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH T & B CELL DEFICIENCY • SCID • THERAPY: – STEM CELL TRANSPLANTS – BMT – GENE REPLACEMENT- recent problems with the retroviral vector insertion has led to leukemia
 TESTING IMMUNE FUNCTION • B-CELLS – SERUM IG LEVELS – ELECTROPHORECTIC DETECTION OF CLONALITY – ENUMERATION OF B-CELLS – DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIBODIES – IMMUNOHISTOPATHOLOGIC
TESTING IMMUNE FUNCTION • B-CELLS – SERUM IG LEVELS – ELECTROPHORECTIC DETECTION OF CLONALITY – ENUMERATION OF B-CELLS – DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIBODIES – IMMUNOHISTOPATHOLOGIC
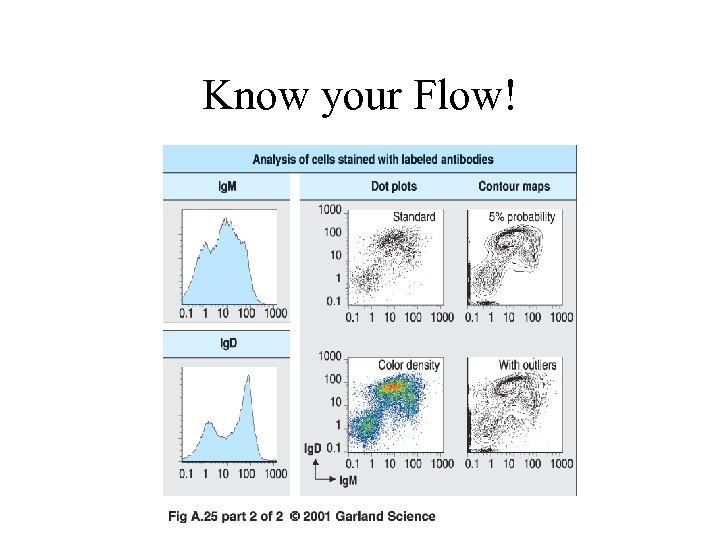 Know your Flow!
Know your Flow!
 TESTING IMMUNE FUNCTION • T-CELLS – IN VIVO SKIN TESTING- will not be valid in patients with malnutrition, on steroids etc – ENUMERATION OF T-CELLS-can be misleading because doesn’t reflect tissue distribution – IMMUNOHISTOPATHOLOGIC – IN VITRO FUNCTIONS- rarely needed
TESTING IMMUNE FUNCTION • T-CELLS – IN VIVO SKIN TESTING- will not be valid in patients with malnutrition, on steroids etc – ENUMERATION OF T-CELLS-can be misleading because doesn’t reflect tissue distribution – IMMUNOHISTOPATHOLOGIC – IN VITRO FUNCTIONS- rarely needed
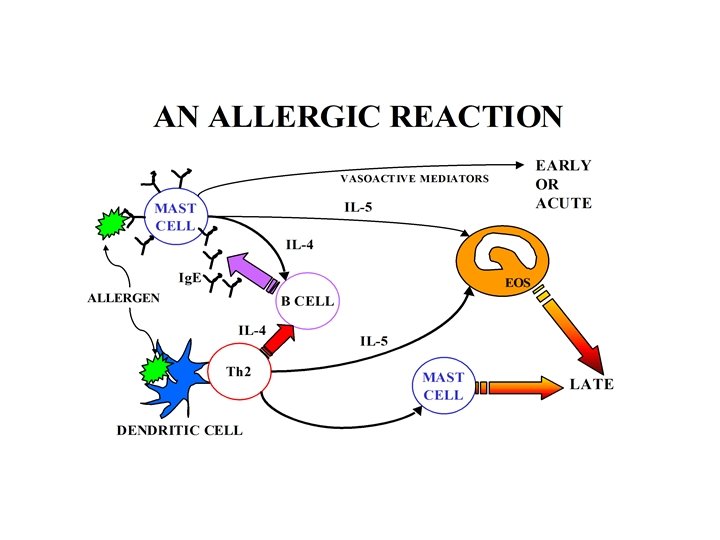
 HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS • TYPE I- Atopy, asthma & anaphylaxis • TYPE II-Antibody to cell structuresimmune thrombocytopenia, AIHA • TYPE III- Immune complex diseases. SLE is prototype • TYPE IV- Delayed hypersensitivitysarcoidosis
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS • TYPE I- Atopy, asthma & anaphylaxis • TYPE II-Antibody to cell structuresimmune thrombocytopenia, AIHA • TYPE III- Immune complex diseases. SLE is prototype • TYPE IV- Delayed hypersensitivitysarcoidosis
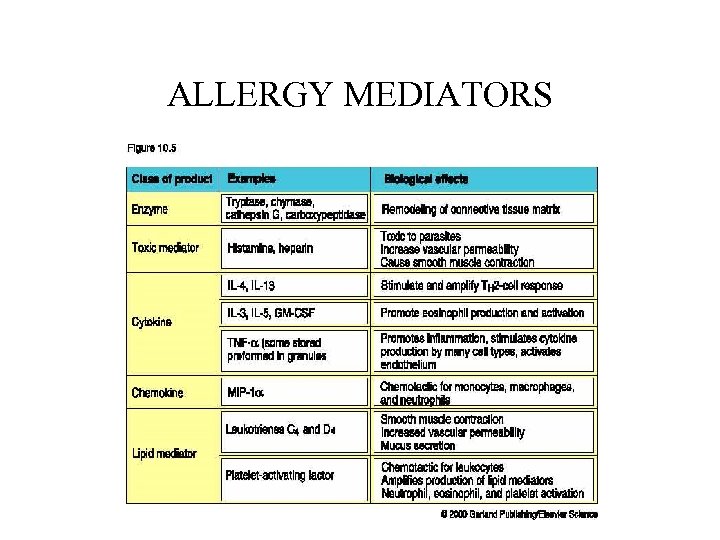 ALLERGY MEDIATORS
ALLERGY MEDIATORS
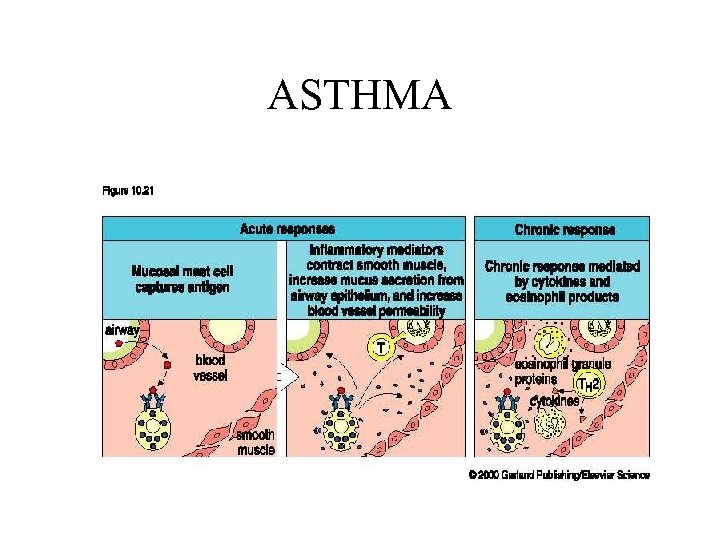 ASTHMA
ASTHMA
 Asthma • Limited early exposure to infections-socalled hygiene hypothesis • Obesity • Genes – Maternal 11 for Ig. E increase – T-bet gene abnormalitiesfor deficient INF- – IL-13
Asthma • Limited early exposure to infections-socalled hygiene hypothesis • Obesity • Genes – Maternal 11 for Ig. E increase – T-bet gene abnormalitiesfor deficient INF- – IL-13
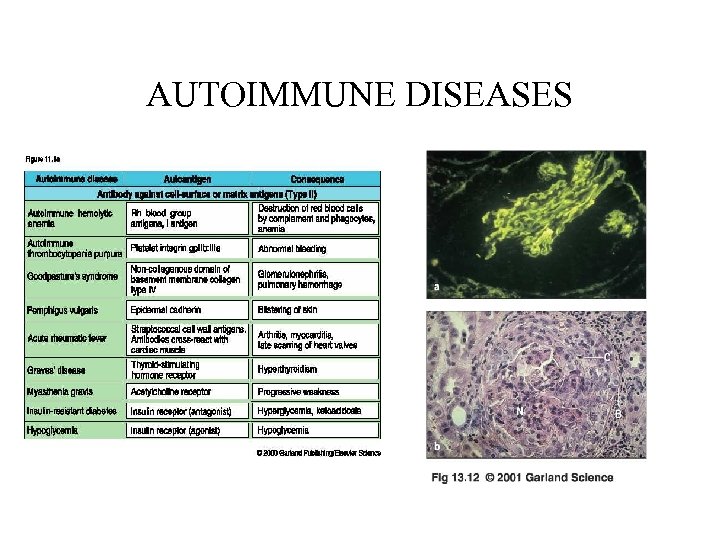 AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
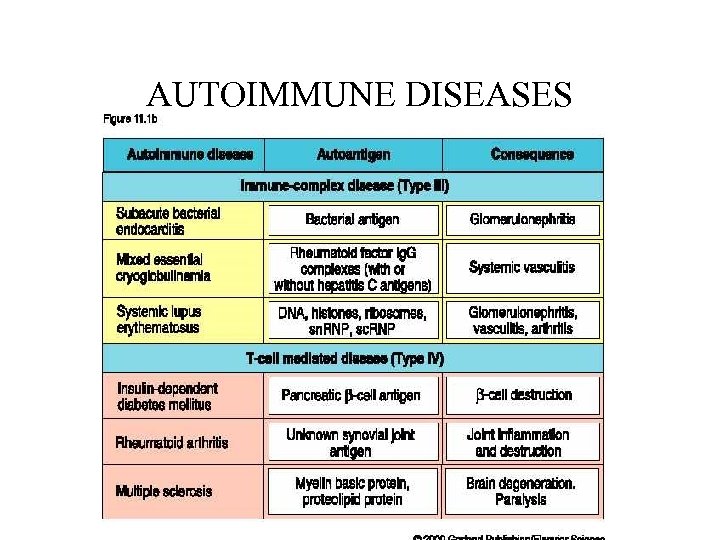 AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
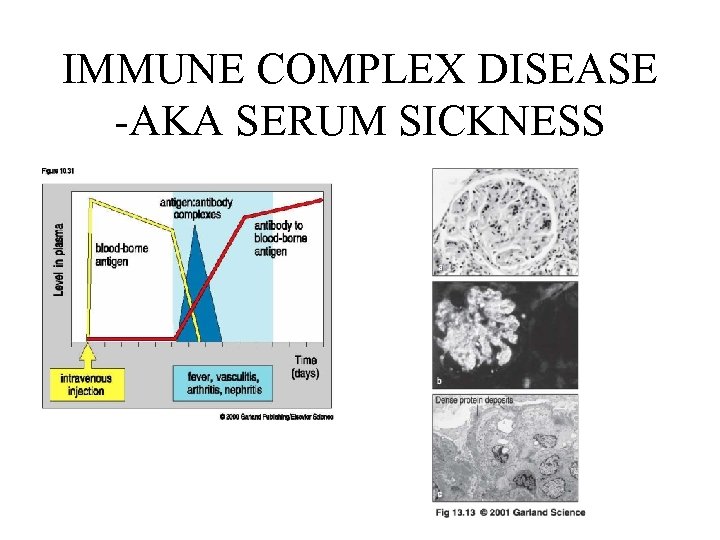 IMMUNE COMPLEX DISEASE -AKA SERUM SICKNESS
IMMUNE COMPLEX DISEASE -AKA SERUM SICKNESS
 AUTOANTOBODIES • SLE– ANA is a SCREENING TEST ONLY(HIGH SENSITIVITY, LOW SPECIFICITY) – double stranded(ds/native) DNA correlates loosely with renal disease, very specific – Sm very specific for SLE-low sensitivity – Histone- present in drug induced lupus but also SLE and other diseases – Ribonucleoprotein (RNP)- associated with mixed connective tissue disease
AUTOANTOBODIES • SLE– ANA is a SCREENING TEST ONLY(HIGH SENSITIVITY, LOW SPECIFICITY) – double stranded(ds/native) DNA correlates loosely with renal disease, very specific – Sm very specific for SLE-low sensitivity – Histone- present in drug induced lupus but also SLE and other diseases – Ribonucleoprotein (RNP)- associated with mixed connective tissue disease
 AUTOANTOBODIES – ANCA • c. ANCA high specificity for Wegeners Granulomatosus • p. ANCA found in some glomerulonephritis, microscopic vasculitis and other vasculitis Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis……anti-JO-1 SS-A(Ro)/SS-B(La)- Sjogren syndrome, congenital heart block
AUTOANTOBODIES – ANCA • c. ANCA high specificity for Wegeners Granulomatosus • p. ANCA found in some glomerulonephritis, microscopic vasculitis and other vasculitis Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis……anti-JO-1 SS-A(Ro)/SS-B(La)- Sjogren syndrome, congenital heart block
 MORE AUTOANTIBODIES • Scleroderma – SCL-70( aka anti-topoisomerase) specific but very low sensitivity – Centromere-high sensitivity for CREST(limited scleroderma) and codes for presence of pulmonary hypertension
MORE AUTOANTIBODIES • Scleroderma – SCL-70( aka anti-topoisomerase) specific but very low sensitivity – Centromere-high sensitivity for CREST(limited scleroderma) and codes for presence of pulmonary hypertension
 Other Autoantibodies to remember • Anti. Ac. R- myasthenia • Anti-endomysial- Sprue (anti gliadin) • Rheumatoid factor- not specific for RA
Other Autoantibodies to remember • Anti. Ac. R- myasthenia • Anti-endomysial- Sprue (anti gliadin) • Rheumatoid factor- not specific for RA
 Acute Phase reactants • C-reactive Protein • • Most accurate indicator of an inflammatory reaction Proxy for IL-6 May correlate independently of Lipids for CA High likelihood something about CRP will be on Boards!. . especially as independent indicator of coronary artery disease Transferrin, ceruloplasmin, C 3, haptoglobin increase with infection, albumin and hemoglobin decrease
Acute Phase reactants • C-reactive Protein • • Most accurate indicator of an inflammatory reaction Proxy for IL-6 May correlate independently of Lipids for CA High likelihood something about CRP will be on Boards!. . especially as independent indicator of coronary artery disease Transferrin, ceruloplasmin, C 3, haptoglobin increase with infection, albumin and hemoglobin decrease
 HLA ASSOCIATIONS WITH SPECIFIC DISEASES • • • Ankylosing spondylitis-B 27………………. 90 RR* Reactive Arthropathy-B 27. ………………. . . 40 Rheumatoid Arthritis-DR 4. ………………. . . 4 Behcet’s-B 51. ……………… 4 SLE-DR 3. …………………. . 6 IDDM-DR 3, 4………………. 6 Dermatitis Herpetiformis-DR 3. ……………. 16 MS-DR 2…………………. 4 Goodpastures-DR 2…………… 16 Birdshot Retinochoroidopathy-A 29. ………. 109** – *…remember the caveats, ** …. . for that extra point
HLA ASSOCIATIONS WITH SPECIFIC DISEASES • • • Ankylosing spondylitis-B 27………………. 90 RR* Reactive Arthropathy-B 27. ………………. . . 40 Rheumatoid Arthritis-DR 4. ………………. . . 4 Behcet’s-B 51. ……………… 4 SLE-DR 3. …………………. . 6 IDDM-DR 3, 4………………. 6 Dermatitis Herpetiformis-DR 3. ……………. 16 MS-DR 2…………………. 4 Goodpastures-DR 2…………… 16 Birdshot Retinochoroidopathy-A 29. ………. 109** – *…remember the caveats, ** …. . for that extra point
 TERMS TO REMEMBER • • ANTIGEN IMMUNOGEN EPITOPE HAPTEN ADJUVANT STEM CELLS PRIMARY AND SECONDARY IMMUNE RESPONSE
TERMS TO REMEMBER • • ANTIGEN IMMUNOGEN EPITOPE HAPTEN ADJUVANT STEM CELLS PRIMARY AND SECONDARY IMMUNE RESPONSE
 TERMS TO REMEMBER • • INNATE(AKA NATURAL) ADAPTIVE(SPECIFIC OR ACTIVE) CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY HUMORAL/ANTIBODY IMMUNITY PASSIVE IMMUNIZATION ACTIVE IMMUNIZATION ARTHUS REACTION
TERMS TO REMEMBER • • INNATE(AKA NATURAL) ADAPTIVE(SPECIFIC OR ACTIVE) CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY HUMORAL/ANTIBODY IMMUNITY PASSIVE IMMUNIZATION ACTIVE IMMUNIZATION ARTHUS REACTION
 TERMS TO REMEMBER • • ISOTYPE IDIOTYPE MONOCLONAL SYNGENEIC ALLOGRAFT AUTOGRAFT ELISA & RIA
TERMS TO REMEMBER • • ISOTYPE IDIOTYPE MONOCLONAL SYNGENEIC ALLOGRAFT AUTOGRAFT ELISA & RIA
 Here is what Step 1 covers- did we get them all? • Production/function granulocyte, NK cells and macrophages/DC • Production/function of T cells, TCR, cytokines/chemokines • Production/function of B cells and PC, Ig structure, classes, molecular basis for specificity, receptors • Antigenicity/immunogenicity, host defenses(read Innate I), primary/secondary responses, passive transfer of immunity(all ways) • In vitro complement, other diagnostic tests and antigen antibody reactions • Mediators, complement, aa, histamine, NO and cytokines • MHC structure and function, RBC antigens. Transplantation • Vaccines, protective immunity, tumor immunity • Disease states like ID, HIV and pharmacological immunosuppression
Here is what Step 1 covers- did we get them all? • Production/function granulocyte, NK cells and macrophages/DC • Production/function of T cells, TCR, cytokines/chemokines • Production/function of B cells and PC, Ig structure, classes, molecular basis for specificity, receptors • Antigenicity/immunogenicity, host defenses(read Innate I), primary/secondary responses, passive transfer of immunity(all ways) • In vitro complement, other diagnostic tests and antigen antibody reactions • Mediators, complement, aa, histamine, NO and cytokines • MHC structure and function, RBC antigens. Transplantation • Vaccines, protective immunity, tumor immunity • Disease states like ID, HIV and pharmacological immunosuppression
 T-CELL FUNCTIONS
T-CELL FUNCTIONS
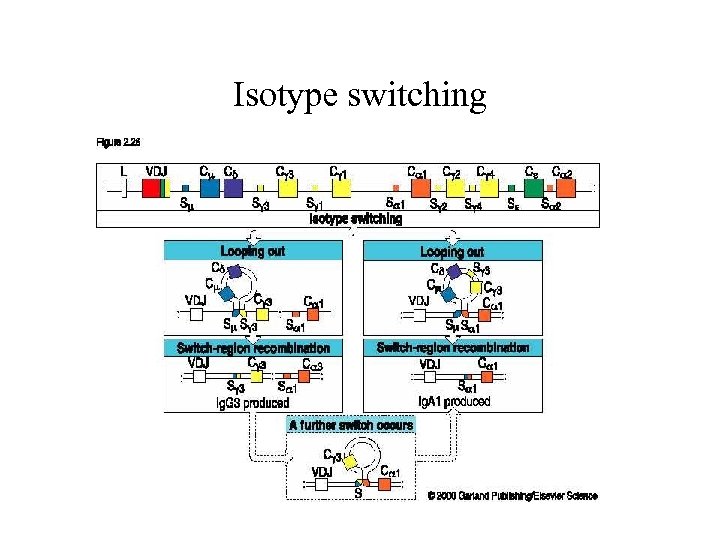 Isotype switching
Isotype switching


