e38839ec7df302254de8bb60183b0972.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Herbert Hoover “Rugged Individualism” • He believed that Americans did not want a hand out. • His Laissez faire polices were supported by his advisors.

Hoover-Volunteerism/Taxes • “Volunteerism” • He asked companies to work together to solve problems (no layoffs). • After initially lowering taxes, he then raised them.

Reconstruction Finance Corporation • Government would make loans to banks, RR, and farm cooperatives. . • It was a trickle down approach. • Too little late. • https: //www. youtub e. com/watch? v=i 0 H t. VHYTTs 0

Federal Reserve Policies • The Fed raised interest rates after the crash and made it harder to get loans from banks. • There was a cash shortage during depression.

Vocabulary • Speculation- risky gambles on stock market • Buying “on the margin”- putting a small amount down when purchasing stock and getting a loan usually from a broker for the rest.

Reasons Farmers did not Prosper • WWI over nobody to buy surplus. • Prices low • Boycotts of U. S. products due to Tariffs. • No Bailout
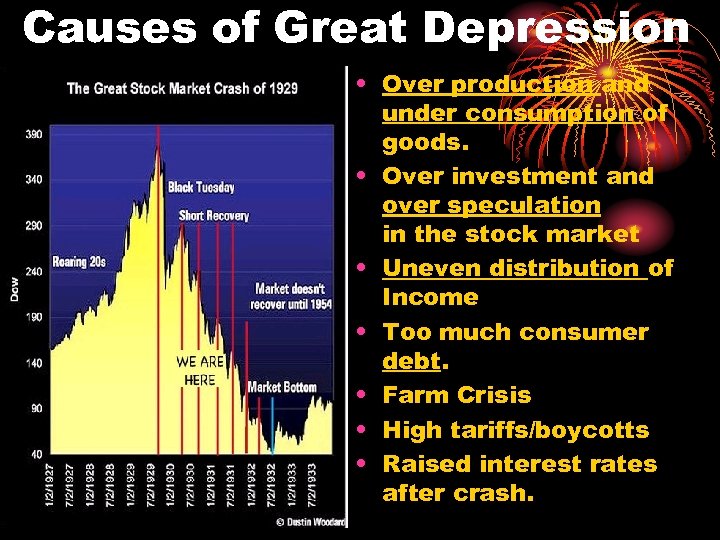
Causes of Great Depression • Over production and under consumption of goods. • Over investment and over speculation in the stock market • Uneven distribution of Income • Too much consumer debt. • Farm Crisis • High tariffs/boycotts • Raised interest rates after crash.

Bonus Army WWI Veterans want bonus early! • Senate says no bonus in 1932 • Hoover has to clear them out. 3 killed • Senate votes bill down

The Dust Bowl 1933 • Led to mass refugees from the middle of our country. • Many went to California and were seen as unwanted because of a tough job market • “Okies”
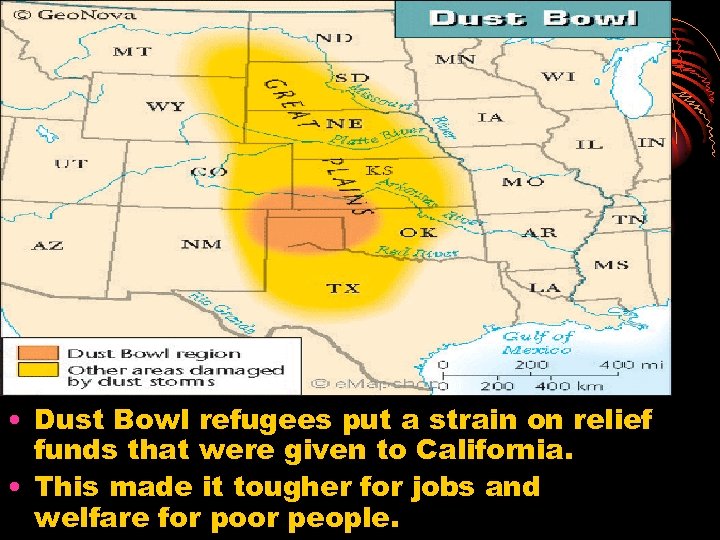
• Dust Bowl refugees put a strain on relief funds that were given to California. • This made it tougher for jobs and welfare for poor people.

Dust Bowl Refugees effect on California • There is a greater demand on available relief funds for Californians. • This causes Californians to get upset. There is less welfare and job programs to help poor.

Effects of Depression • • • Homelessness Bank failures Hunger Unemployment Hardship Government bigger!!!!!

FDR’S New Deal • His “New Deal” was based on his belief that the government needed to take a more active role in regulating the economy. • Relief, Recovery, Reform

FDR and the Bank Holiday • FDR tried to fix banks first. • He declares a bank holiday and sends in government inspectors. • Only “healthy banks” open. • Tried to increase confidence.

Federal Deposit Insurance Company • FDIC: government now insures your deposits up to a certain amount • We still have it today.

Securities and Exchange Commission • The SEC regulates the Stock market. • Its their job to prevent fraud and protect investors

Tennessee Valley Authority/ Problems • Gov. supported hydroelectric works project that helped employ many people in the Tennessee Valley area. • Many business groups opposed the TVA because they believed that it unfairly competed with private power companies.

Agricultural Adjustment Act • Paid farmers to produce less • Government is trying to raise prices • Later voted down in Supreme Court as unconstitutional

Works Progress Administration • Put artists, teachers and construction workers to work • Provided aid for students in the form of work-study programs

Civilian Conservation Corps • Put young men 1825 to work • Conservation of resources • Soil, trees, national parks • Involved every U. S. state

FERA • Federal Emergency Relief Act • Our first direct relief for the needy. • Beginning of Welfare. • “Priming the pump. ”

Left wing critics • Huey long and Francis. Townsend wanted the government to do more. Long promoted the Share our wealth program. Townsend wanted more for elderly.

Right wing critics of New Deal • Right-wing critics of FDR’s New Deal said that programs, such as the CCC, Social Security Act and WPA, would cause Americans to become too dependent on government help.

Effect of New Deal on Workers • A lasting effect of the Great Depression and New deal on American workers was that their rights were protected ; especially the right to unionize.

Wagner Act • provided a board to supervise conditions and union rights. • It guaranteed collective bargaining or the right of unions to work out deals with management.

Francis Perkins • 1 st woman to serve on Presidential Cabinet as the Secretary of Labor

New Deal Coalition • FDR’s supporters, who included farmers, laborers, African Americans, New immigrants, ethnic minorities, women, progressives and intellectuals.

CIO • Labor union that organized industrial workers from 1935 to 1955.


Social Security • Social Security, one of the major New Deal programs, was designed to help the unemployed and the elderly. • Some people argued that it would make people too dependent on the government.

The New Deal Chapter 10 Big Ideas • The federal government gets bigger and expands regulatory power • Welfare, unemployment, workers benefits, public works projects, banking reform, and housing programs • It doesn’t end depression. WWII does!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! • It did put many people to work and put systems into place designed to keep this from happening again
e38839ec7df302254de8bb60183b0972.ppt