2ecd0aba39c2b776b8ceb44527587412.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95
 HEPIX Summary CCR workshop LNGS – June 2008 Michele Michelotto INFN Padova HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 1
HEPIX Summary CCR workshop LNGS – June 2008 Michele Michelotto INFN Padova HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 1
 Service Pack 1 – Introduction • Service Pack 1 has been released on 15 th of February 2008 – It is already May and preparations for the upgrade are not finished – Very heavy • Installation might take even 2 hours • 3 reboots are needed – Strong prerequisites • Several other updates needs to be installed first (KB 949939, KB 937287, KB 935509, KB 938371 and eventually KB 938759) • Several drivers are not compatible with SP 1 (KB 948343) • Once installed – Performance and reliability are improved – No new feature HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 2
Service Pack 1 – Introduction • Service Pack 1 has been released on 15 th of February 2008 – It is already May and preparations for the upgrade are not finished – Very heavy • Installation might take even 2 hours • 3 reboots are needed – Strong prerequisites • Several other updates needs to be installed first (KB 949939, KB 937287, KB 935509, KB 938371 and eventually KB 938759) • Several drivers are not compatible with SP 1 (KB 948343) • Once installed – Performance and reliability are improved – No new feature HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 2
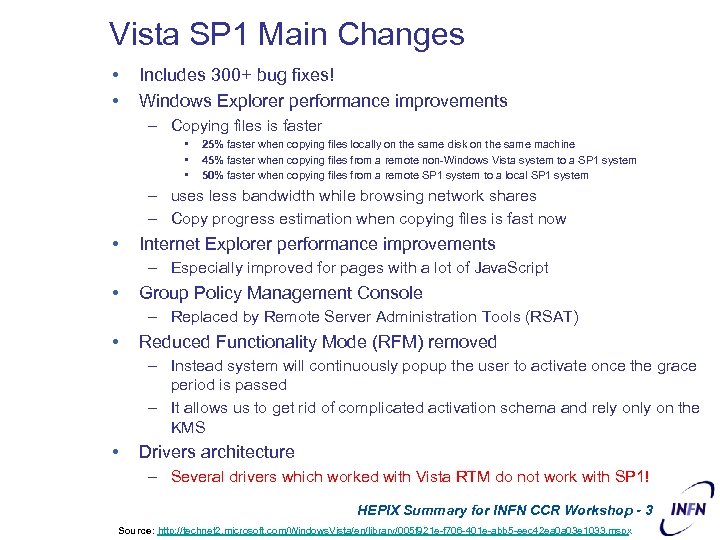 Vista SP 1 Main Changes • • Includes 300+ bug fixes! Windows Explorer performance improvements – Copying files is faster • • • 25% faster when copying files locally on the same disk on the same machine 45% faster when copying files from a remote non-Windows Vista system to a SP 1 system 50% faster when copying files from a remote SP 1 system to a local SP 1 system – uses less bandwidth while browsing network shares – Copy progress estimation when copying files is fast now • Internet Explorer performance improvements – Especially improved for pages with a lot of Java. Script • Group Policy Management Console – Replaced by Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) • Reduced Functionality Mode (RFM) removed – Instead system will continuously popup the user to activate once the grace period is passed – It allows us to get rid of complicated activation schema and rely on the KMS • Drivers architecture – Several drivers which worked with Vista RTM do not work with SP 1! HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 3 Source: http: //technet 2. microsoft. com/Windows. Vista/en/library/005 f 921 e-f 706 -401 e-abb 5 -eec 42 ea 0 a 03 e 1033. mspx
Vista SP 1 Main Changes • • Includes 300+ bug fixes! Windows Explorer performance improvements – Copying files is faster • • • 25% faster when copying files locally on the same disk on the same machine 45% faster when copying files from a remote non-Windows Vista system to a SP 1 system 50% faster when copying files from a remote SP 1 system to a local SP 1 system – uses less bandwidth while browsing network shares – Copy progress estimation when copying files is fast now • Internet Explorer performance improvements – Especially improved for pages with a lot of Java. Script • Group Policy Management Console – Replaced by Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) • Reduced Functionality Mode (RFM) removed – Instead system will continuously popup the user to activate once the grace period is passed – It allows us to get rid of complicated activation schema and rely on the KMS • Drivers architecture – Several drivers which worked with Vista RTM do not work with SP 1! HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 3 Source: http: //technet 2. microsoft. com/Windows. Vista/en/library/005 f 921 e-f 706 -401 e-abb 5 -eec 42 ea 0 a 03 e 1033. mspx
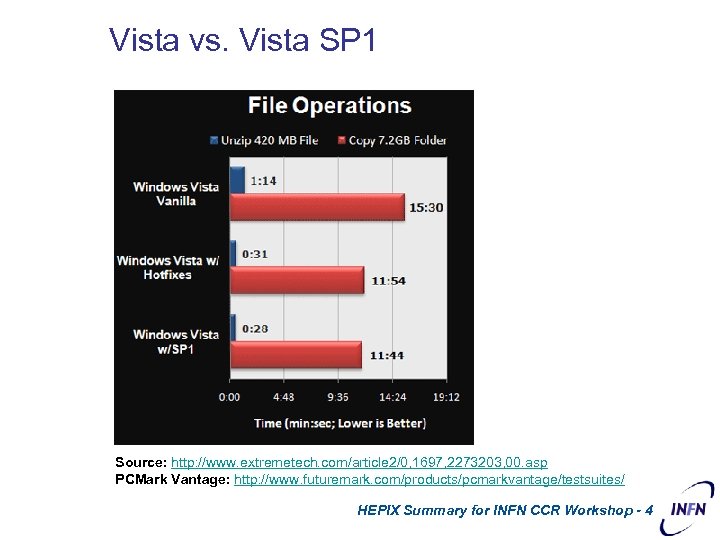 Vista vs. Vista SP 1 Source: http: //www. extremetech. com/article 2/0, 1697, 2273203, 00. asp PCMark Vantage: http: //www. futuremark. com/products/pcmarkvantage/testsuites/ HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 4
Vista vs. Vista SP 1 Source: http: //www. extremetech. com/article 2/0, 1697, 2273203, 00. asp PCMark Vantage: http: //www. futuremark. com/products/pcmarkvantage/testsuites/ HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 4
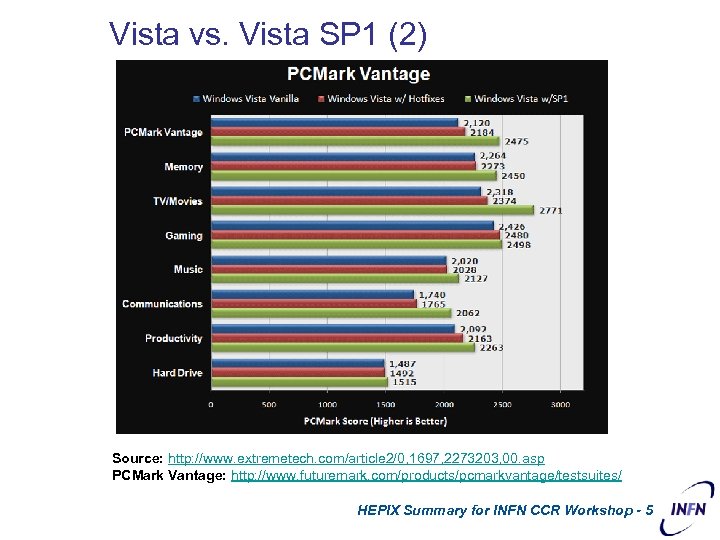 Vista vs. Vista SP 1 (2) Source: http: //www. extremetech. com/article 2/0, 1697, 2273203, 00. asp PCMark Vantage: http: //www. futuremark. com/products/pcmarkvantage/testsuites/ HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 5
Vista vs. Vista SP 1 (2) Source: http: //www. extremetech. com/article 2/0, 1697, 2273203, 00. asp PCMark Vantage: http: //www. futuremark. com/products/pcmarkvantage/testsuites/ HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 5
 Vista vs. XP Report by Principled Technologies: Responsiveness of Windows Vista ™, Windows Vista ™ SP 1, and Windows XP ™ on common business tasks http: //principledtechnologies. com/Clients/Reports/Microsoft/Vista. SP 1 XPVista. Bus. Resp 0208. pdf HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 6
Vista vs. XP Report by Principled Technologies: Responsiveness of Windows Vista ™, Windows Vista ™ SP 1, and Windows XP ™ on common business tasks http: //principledtechnologies. com/Clients/Reports/Microsoft/Vista. SP 1 XPVista. Bus. Resp 0208. pdf HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 6
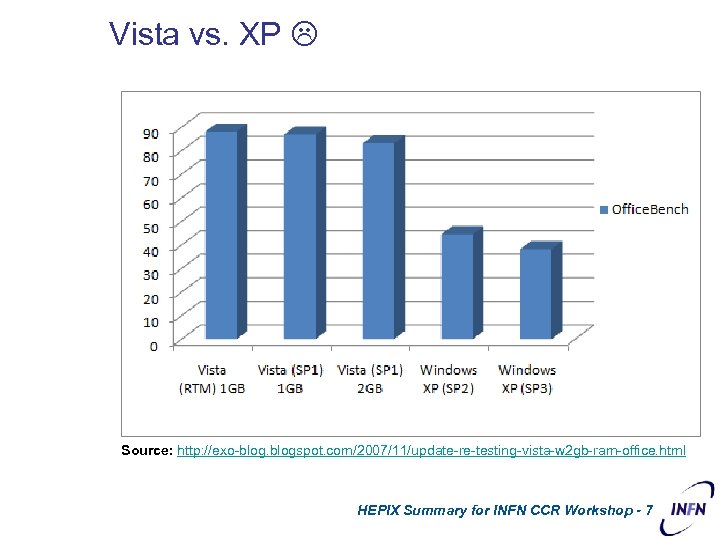 Vista vs. XP Source: http: //exo-blogspot. com/2007/11/update-re-testing-vista-w 2 gb-ram-office. html HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 7
Vista vs. XP Source: http: //exo-blogspot. com/2007/11/update-re-testing-vista-w 2 gb-ram-office. html HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 7
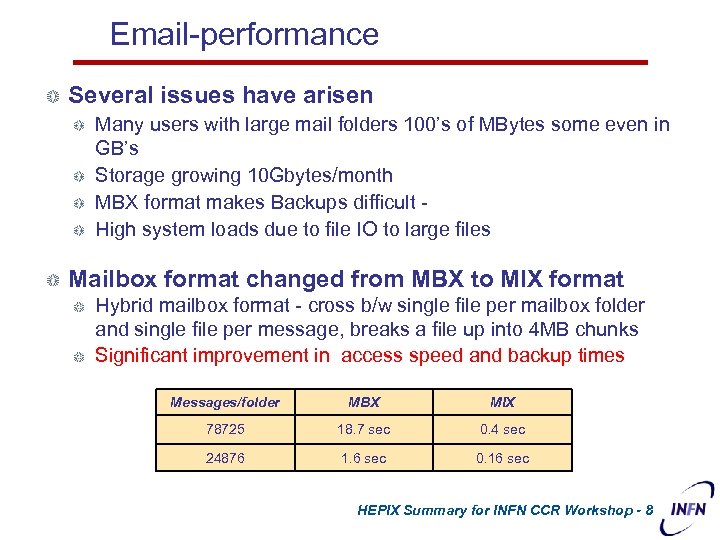 Email-performance Several issues have arisen Many users with large mail folders 100’s of MBytes some even in GB’s Storage growing 10 Gbytes/month MBX format makes Backups difficult - High system loads due to file IO to large files Mailbox format changed from MBX to MIX format Hybrid mailbox format - cross b/w single file per mailbox folder and single file per message, breaks a file up into 4 MB chunks Significant improvement in access speed and backup times Messages/folder MBX MIX 78725 18. 7 sec 0. 4 sec 24876 1. 6 sec 0. 16 sec HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 8
Email-performance Several issues have arisen Many users with large mail folders 100’s of MBytes some even in GB’s Storage growing 10 Gbytes/month MBX format makes Backups difficult - High system loads due to file IO to large files Mailbox format changed from MBX to MIX format Hybrid mailbox format - cross b/w single file per mailbox folder and single file per message, breaks a file up into 4 MB chunks Significant improvement in access speed and backup times Messages/folder MBX MIX 78725 18. 7 sec 0. 4 sec 24876 1. 6 sec 0. 16 sec HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 8
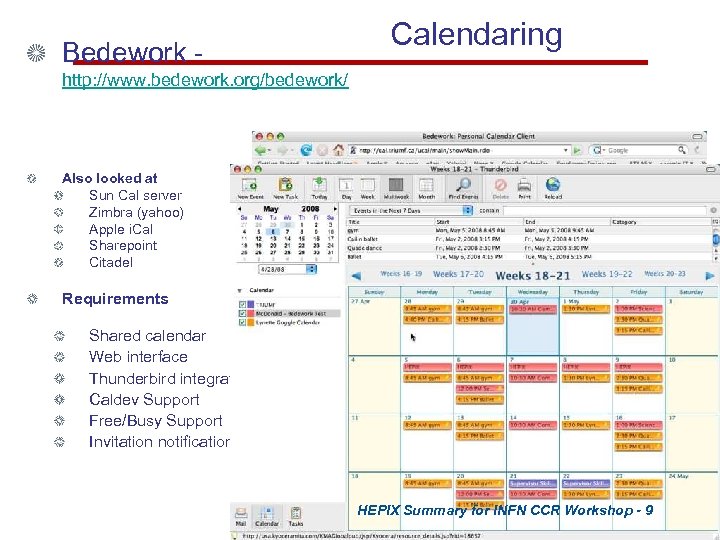 Bedework - Calendaring http: //www. bedework. org/bedework/ Also looked at Sun Cal server Zimbra (yahoo) Apple i. Cal Sharepoint Citadel Requirements Shared calendar Web interface Thunderbird integration Caldev Support Free/Busy Support Invitation notification HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 9
Bedework - Calendaring http: //www. bedework. org/bedework/ Also looked at Sun Cal server Zimbra (yahoo) Apple i. Cal Sharepoint Citadel Requirements Shared calendar Web interface Thunderbird integration Caldev Support Free/Busy Support Invitation notification HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 9
 What is IPv 6? • Same, same – Just like IPv 4 (which we all use) – “The stuff underneath TCP” – What you get when you do a dns lookup on a hostname
What is IPv 6? • Same, same – Just like IPv 4 (which we all use) – “The stuff underneath TCP” – What you get when you do a dns lookup on a hostname
 What is IPv 6? • But different. . – 128 -bit instead of 32 -bit – 2001: 6 b 0: e: 2018: 21 d: e 0 ff: fe 38: c 561 vs 130. 239. 18. 137 – Requires different syscalls for low-level (C, etc) programming (getaddrinfo instead of gethostbyname, etc) – Different DNS resource records • A for IPv 4 AAAA for IPv 6 • reverse zones also different
What is IPv 6? • But different. . – 128 -bit instead of 32 -bit – 2001: 6 b 0: e: 2018: 21 d: e 0 ff: fe 38: c 561 vs 130. 239. 18. 137 – Requires different syscalls for low-level (C, etc) programming (getaddrinfo instead of gethostbyname, etc) – Different DNS resource records • A for IPv 4 AAAA for IPv 6 • reverse zones also different
 Why should we care? • Even if most of us have plenty of IPv 4 – Prestige, status, technical excellence, fun, etc – User laptop on a conference only getting a IPv 6 address (and a broken webproxy or NAT for IPv 4 content) – Political/funding reasons (IPv 6 might be an important checkbox item) – IPv 4 address space might become worth $$$, without IPv 6 you can't sell off unused space
Why should we care? • Even if most of us have plenty of IPv 4 – Prestige, status, technical excellence, fun, etc – User laptop on a conference only getting a IPv 6 address (and a broken webproxy or NAT for IPv 4 content) – Political/funding reasons (IPv 6 might be an important checkbox item) – IPv 4 address space might become worth $$$, without IPv 6 you can't sell off unused space
 What worked? • OS support – But see “what needed work” for details • Mainstream software • Most “odd” software • Assuming that you run versions that aren't ancient – Our webserver is still on apache 1. 3. . .
What worked? • OS support – But see “what needed work” for details • Mainstream software • Most “odd” software • Assuming that you run versions that aren't ancient – Our webserver is still on apache 1. 3. . .
 What needed work • DNS – Local zone management software needed to be extended to understand IPv 6 for both forward and reverse zones – Tell bind to listen to the appropriate IPv 6 interface, by default it seems to just listen on the IPv 4 interface • Log parsing scripts – Or anything else that needs to identify an IP address
What needed work • DNS – Local zone management software needed to be extended to understand IPv 6 for both forward and reverse zones – Tell bind to listen to the appropriate IPv 6 interface, by default it seems to just listen on the IPv 4 interface • Log parsing scripts – Or anything else that needs to identify an IP address
 What needed work? • Some odd software – In this case not so much, but some software still can't handle a IPv 6 address – This probably applies to lots of grid/HEP/HPC software though – Starting early makes it possible to enable it system by system, and not be rushed if some systems can't be dualstacked quickly
What needed work? • Some odd software – In this case not so much, but some software still can't handle a IPv 6 address – This probably applies to lots of grid/HEP/HPC software though – Starting early makes it possible to enable it system by system, and not be rushed if some systems can't be dualstacked quickly
 What needed work? • AIX sometimes forgets its IPv 6 interface – Might be a NIC driver bug (non-IBM card) • Linux NFS only speaks IPv 4 – Not a problem as long as you dual-stack, it will just use IPv 4 instead • Routing problems – Only noticed by a small minority, but really annoying when you want to have production-like availability of your services – Spontaneous loss of default route
What needed work? • AIX sometimes forgets its IPv 6 interface – Might be a NIC driver bug (non-IBM card) • Linux NFS only speaks IPv 4 – Not a problem as long as you dual-stack, it will just use IPv 4 instead • Routing problems – Only noticed by a small minority, but really annoying when you want to have production-like availability of your services – Spontaneous loss of default route
 What needed work? • Static IPv 6 adressing on Linux – – The Linux kernel is very eager to do addrconf You can turn it off by sysctl But! The sysctl is only accessable once the ipv 6 module is loaded and the interface is up – And at that point, Linux is doing the addrconf. . ,
What needed work? • Static IPv 6 adressing on Linux – – The Linux kernel is very eager to do addrconf You can turn it off by sysctl But! The sysctl is only accessable once the ipv 6 module is loaded and the interface is up – And at that point, Linux is doing the addrconf. . ,
 What needed work? • The solution, hack /etc/network/interfaces: iface eth 0 inet 6 static pre-up modprobe ipv 6 up /sbin/sysctl -q -w net. ipv 6. conf. eth 0. autoconf=0 address 2001: 6 b 0: e: 2018: : 137 netmask 64
What needed work? • The solution, hack /etc/network/interfaces: iface eth 0 inet 6 static pre-up modprobe ipv 6 up /sbin/sysctl -q -w net. ipv 6. conf. eth 0. autoconf=0 address 2001: 6 b 0: e: 2018: : 137 netmask 64
 LHC Networking T 0 -T 1 Status and Directions David Foster Head, Communications and Networks CERN Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 19 HEPIX May 2008
LHC Networking T 0 -T 1 Status and Directions David Foster Head, Communications and Networks CERN Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 19 HEPIX May 2008
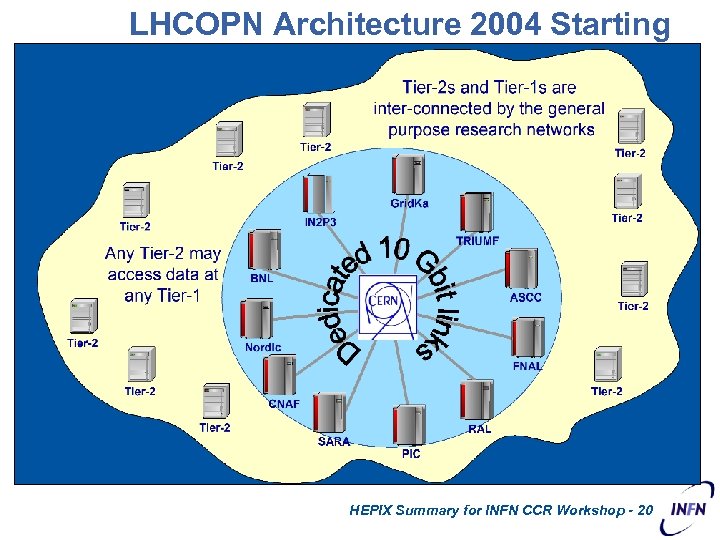 LHCOPN Architecture 2004 Starting Point HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 20 CERN – March 2007
LHCOPN Architecture 2004 Starting Point HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 20 CERN – March 2007
 Hybrid Networking Model • Infrastructure is provided by a number of initiatives: – – GEANT-2 Commercial Links Coordinated Infrastructures (USLHCNet, GLIF) NRENS + Research Networks (ESNet, I 2, Canarie etc) • Operated by the community – “Closed Club” of participants – Routers at the end points – Federated operational model • Evolving – Cross Border Fiber links playing an important role in resiliency. HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 21
Hybrid Networking Model • Infrastructure is provided by a number of initiatives: – – GEANT-2 Commercial Links Coordinated Infrastructures (USLHCNet, GLIF) NRENS + Research Networks (ESNet, I 2, Canarie etc) • Operated by the community – “Closed Club” of participants – Routers at the end points – Federated operational model • Evolving – Cross Border Fiber links playing an important role in resiliency. HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 21
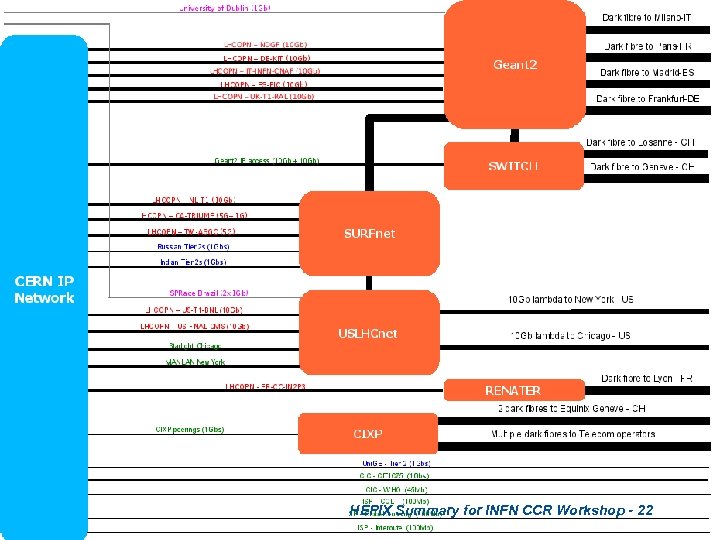 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 22
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 22
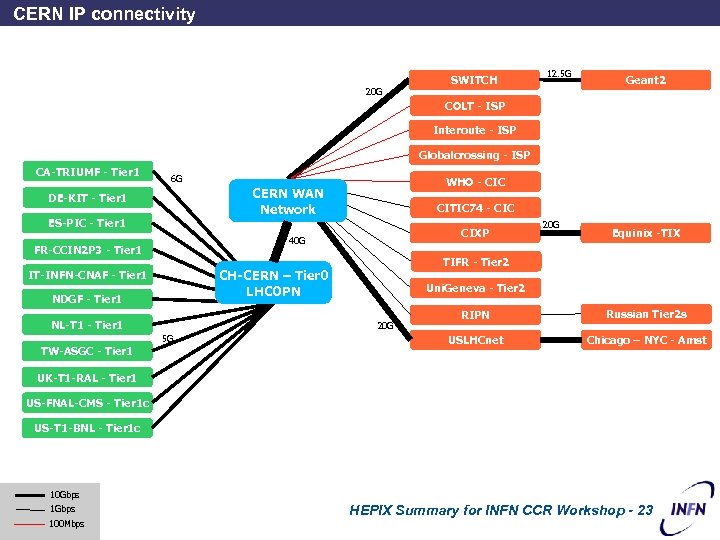 CERN IP connectivity 20 G SWITCH 12. 5 G Geant 2 COLT - ISP Interoute - ISP Globalcrossing - ISP CA-TRIUMF - Tier 1 6 G DE-KIT - Tier 1 ES-PIC - Tier 1 CITIC 74 - CIC CIXP 40 G FR-CCIN 2 P 3 - Tier 1 NDGF - Tier 1 NL-T 1 - Tier 1 Equinix -TIX Uni. Geneva - Tier 2 RIPN Russian Tier 2 s USLHCnet 20 G 5 G 20 G TIFR - Tier 2 CH-CERN – Tier 0 LHCOPN IT-INFN-CNAF - Tier 1 TW-ASGC - Tier 1 WHO - CIC CERN WAN Network Chicago – NYC - Amst UK-T 1 -RAL - Tier 1 US-FNAL-CMS - Tier 1 c US-T 1 -BNL - Tier 1 c 10 Gbps 100 Mbps HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 23
CERN IP connectivity 20 G SWITCH 12. 5 G Geant 2 COLT - ISP Interoute - ISP Globalcrossing - ISP CA-TRIUMF - Tier 1 6 G DE-KIT - Tier 1 ES-PIC - Tier 1 CITIC 74 - CIC CIXP 40 G FR-CCIN 2 P 3 - Tier 1 NDGF - Tier 1 NL-T 1 - Tier 1 Equinix -TIX Uni. Geneva - Tier 2 RIPN Russian Tier 2 s USLHCnet 20 G 5 G 20 G TIFR - Tier 2 CH-CERN – Tier 0 LHCOPN IT-INFN-CNAF - Tier 1 TW-ASGC - Tier 1 WHO - CIC CERN WAN Network Chicago – NYC - Amst UK-T 1 -RAL - Tier 1 US-FNAL-CMS - Tier 1 c US-T 1 -BNL - Tier 1 c 10 Gbps 100 Mbps HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 23
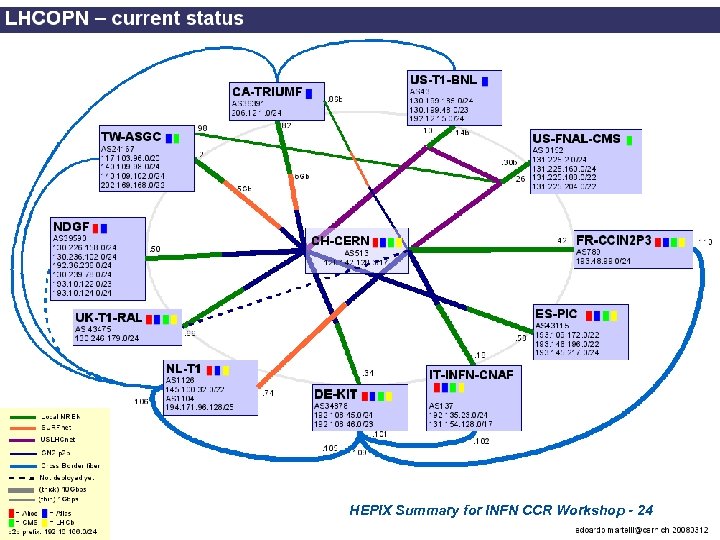 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 24
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 24
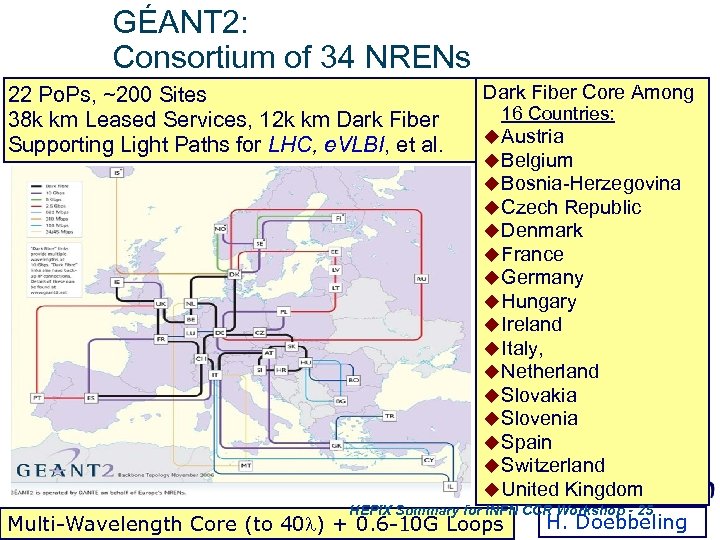 GÉANT 2: Consortium of 34 NRENs 22 Po. Ps, ~200 Sites 38 k km Leased Services, 12 k km Dark Fiber Supporting Light Paths for LHC, e. VLBI, et al. Dark Fiber Core Among 16 Countries: u Austria u Belgium u Bosnia-Herzegovina u Czech Republic u Denmark u France u Germany u Hungary u Ireland u Italy, u Netherland u Slovakia u Slovenia u Spain u Switzerland u United Kingdom HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 25 Multi-Wavelength Core (to 40 ) + 0. 6 -10 G Loops H. Doebbeling
GÉANT 2: Consortium of 34 NRENs 22 Po. Ps, ~200 Sites 38 k km Leased Services, 12 k km Dark Fiber Supporting Light Paths for LHC, e. VLBI, et al. Dark Fiber Core Among 16 Countries: u Austria u Belgium u Bosnia-Herzegovina u Czech Republic u Denmark u France u Germany u Hungary u Ireland u Italy, u Netherland u Slovakia u Slovenia u Spain u Switzerland u United Kingdom HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 25 Multi-Wavelength Core (to 40 ) + 0. 6 -10 G Loops H. Doebbeling
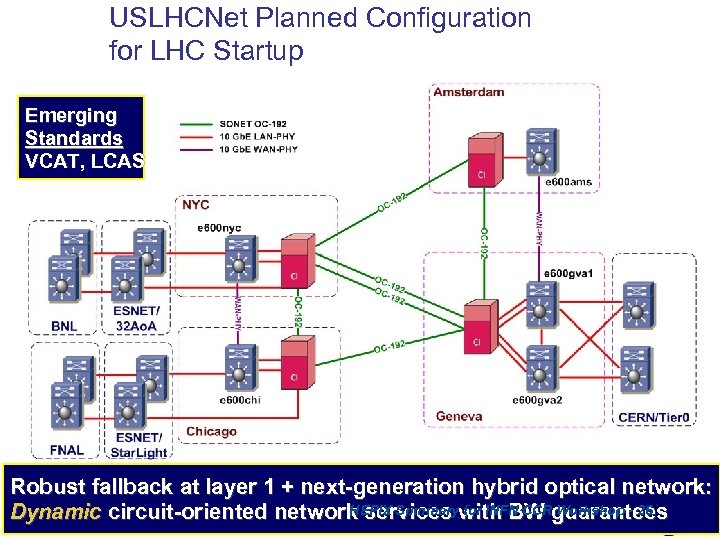 USLHCNet Planned Configuration for LHC Startup Emerging Standards VCAT, LCAS Robust fallback at layer 1 + next-generation hybrid optical network: HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 26 Dynamic circuit-oriented network services with BW guarantees 26
USLHCNet Planned Configuration for LHC Startup Emerging Standards VCAT, LCAS Robust fallback at layer 1 + next-generation hybrid optical network: HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 26 Dynamic circuit-oriented network services with BW guarantees 26
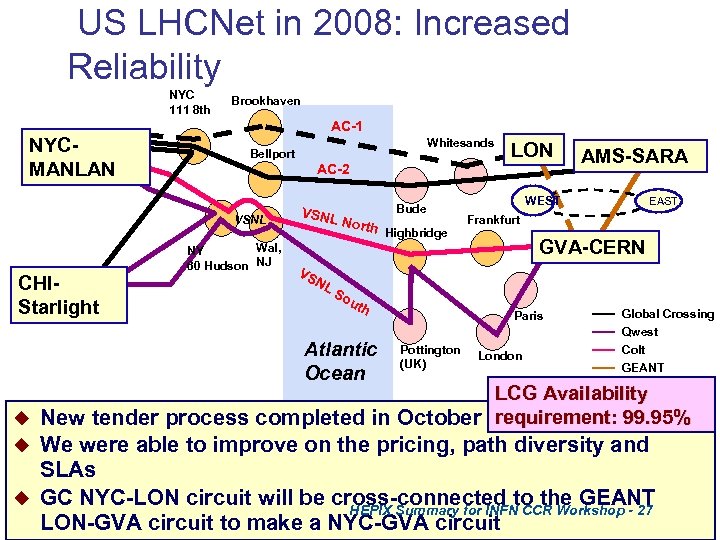 US LHCNet in 2008: Increased Reliability NYC 111 8 th Brookhaven AC-1 NYCMANLAN LON AC-2 VSNL CHIStarlight Whitesands Bellport Wal, NY 60 Hudson NJ VSNL North Bude Highbridge AMS-SARA WEST EAST Frankfurt GVA-CERN VS NL So uth Atlantic Ocean Paris Pottington (UK) London Global Crossing Qwest Colt GEANT LCG Availability u New tender process completed in October requirement: 99. 95% We were able to improve on the pricing, path diversity and SLAs u GC NYC-LON circuit will be cross-connected to the GEANT HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 27 LON-GVA circuit to make a NYC-GVA circuit 27 u
US LHCNet in 2008: Increased Reliability NYC 111 8 th Brookhaven AC-1 NYCMANLAN LON AC-2 VSNL CHIStarlight Whitesands Bellport Wal, NY 60 Hudson NJ VSNL North Bude Highbridge AMS-SARA WEST EAST Frankfurt GVA-CERN VS NL So uth Atlantic Ocean Paris Pottington (UK) London Global Crossing Qwest Colt GEANT LCG Availability u New tender process completed in October requirement: 99. 95% We were able to improve on the pricing, path diversity and SLAs u GC NYC-LON circuit will be cross-connected to the GEANT HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 27 LON-GVA circuit to make a NYC-GVA circuit 27 u
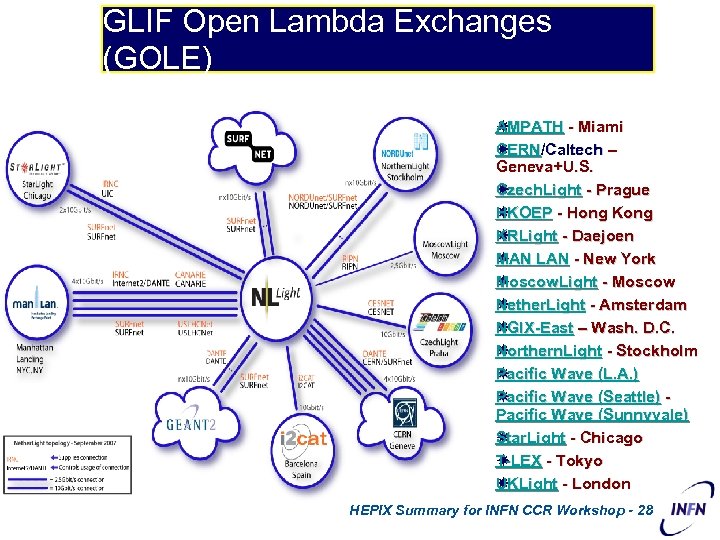 GLIF Open Lambda Exchanges (GOLE) AMPATH - Miami A CERN ERN/Caltech – C Geneva+U. S. Czech. Light - Prague C HKOEP - Hong Kong H KRLight - Daejoen K MAN AN LAN - New York M Moscow. Light - Moscow M Nether. Light - Amsterdam N NGIX-East – Wash. D. C. N Northern. Light - Stockholm N Pacific Wave (L. A. ) Pacific Wave (Seattle) Pacific Wave (Sunnyvale) Star. Light - Chicago Star. Light T-LEX - Tokyo T-LEX UKLight - London U HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 28 28
GLIF Open Lambda Exchanges (GOLE) AMPATH - Miami A CERN ERN/Caltech – C Geneva+U. S. Czech. Light - Prague C HKOEP - Hong Kong H KRLight - Daejoen K MAN AN LAN - New York M Moscow. Light - Moscow M Nether. Light - Amsterdam N NGIX-East – Wash. D. C. N Northern. Light - Stockholm N Pacific Wave (L. A. ) Pacific Wave (Seattle) Pacific Wave (Sunnyvale) Star. Light - Chicago Star. Light T-LEX - Tokyo T-LEX UKLight - London U HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 28 28
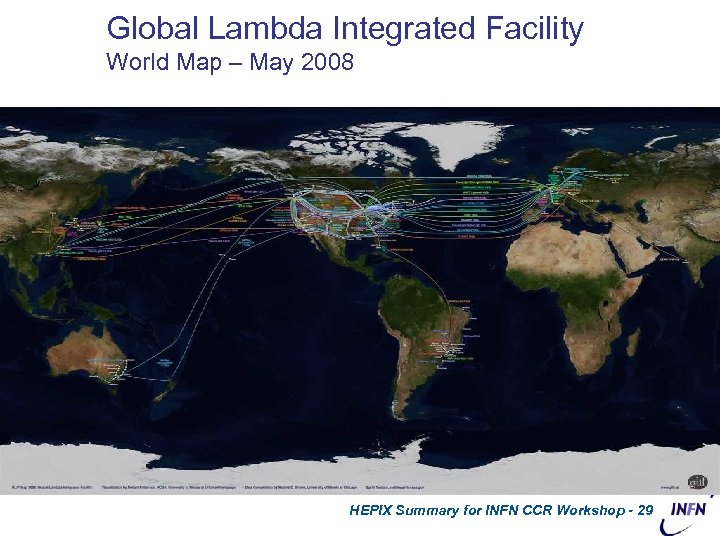 Global Lambda Integrated Facility World Map – May 2008 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 29
Global Lambda Integrated Facility World Map – May 2008 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 29
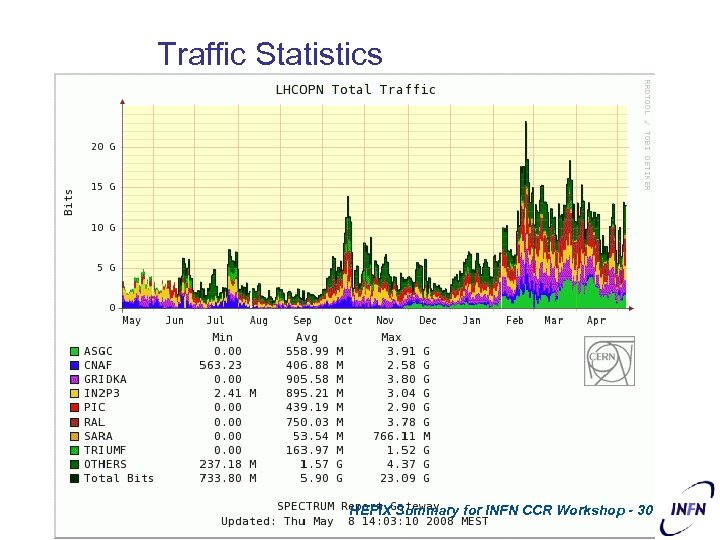 Traffic Statistics HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 30
Traffic Statistics HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 30
 Current Situation • T 0 -T 1 Network is operational and stable. – But, “The first principle is that you must not fool yourself, and you're the easiest person to fool. ” Richard Feynman • Several areas of weakness – Physical Path Routing – IP Backup – Operational Support – Monitoring HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 31
Current Situation • T 0 -T 1 Network is operational and stable. – But, “The first principle is that you must not fool yourself, and you're the easiest person to fool. ” Richard Feynman • Several areas of weakness – Physical Path Routing – IP Backup – Operational Support – Monitoring HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 31
 Physical Paths • Dante analysed the physical path routing for the OPN links. • The network had been built over time, taking in each case the most direct (and cheapest!) wavelength path in the GEANT network. • Analysis showed many common physical paths of fibers and wavelengths. • Re-routing of some wavelengths has been done. – More costly solution (more intervening equipment) – especially the path from Amsterdam -> CERN – 5 x 10 G on this path. HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 32
Physical Paths • Dante analysed the physical path routing for the OPN links. • The network had been built over time, taking in each case the most direct (and cheapest!) wavelength path in the GEANT network. • Analysis showed many common physical paths of fibers and wavelengths. • Re-routing of some wavelengths has been done. – More costly solution (more intervening equipment) – especially the path from Amsterdam -> CERN – 5 x 10 G on this path. HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 32
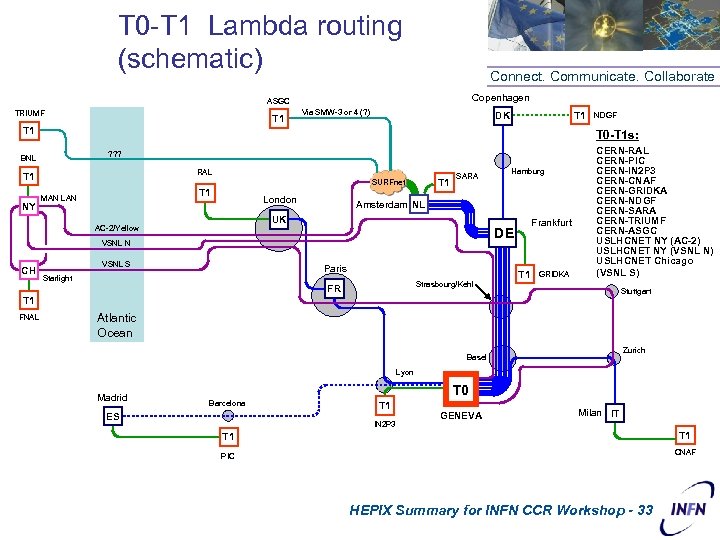 T 0 -T 1 Lambda routing (schematic) Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Copenhagen ASGC TRIUMF T 1 Via SMW-3 or 4 (? ) T 1 DK T 1 T 0 -T 1 s: ? ? ? BNL RAL T 1 NY T 1 SURFnet T 1 MAN London SARA Paris Starlight Frankfurt DE VSNL N VSNL S Hamburg Amsterdam NL UK AC-2/Yellow CH NDGF T 1 GRIDKA CERN-RAL CERN-PIC CERN-IN 2 P 3 CERN-CNAF CERN-GRIDKA CERN-NDGF CERN-SARA CERN-TRIUMF CERN-ASGC USLHCNET NY (AC-2) USLHCNET NY (VSNL N) USLHCNET Chicago (VSNL S) Strasbourg/Kehl FR Stuttgart T 1 FNAL Atlantic Ocean Zurich Basel Lyon Madrid T 0 Barcelona ES T 1 IN 2 P 3 GENEVA Milan IT T 1 CNAF PIC HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 33
T 0 -T 1 Lambda routing (schematic) Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Copenhagen ASGC TRIUMF T 1 Via SMW-3 or 4 (? ) T 1 DK T 1 T 0 -T 1 s: ? ? ? BNL RAL T 1 NY T 1 SURFnet T 1 MAN London SARA Paris Starlight Frankfurt DE VSNL N VSNL S Hamburg Amsterdam NL UK AC-2/Yellow CH NDGF T 1 GRIDKA CERN-RAL CERN-PIC CERN-IN 2 P 3 CERN-CNAF CERN-GRIDKA CERN-NDGF CERN-SARA CERN-TRIUMF CERN-ASGC USLHCNET NY (AC-2) USLHCNET NY (VSNL N) USLHCNET Chicago (VSNL S) Strasbourg/Kehl FR Stuttgart T 1 FNAL Atlantic Ocean Zurich Basel Lyon Madrid T 0 Barcelona ES T 1 IN 2 P 3 GENEVA Milan IT T 1 CNAF PIC HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 33
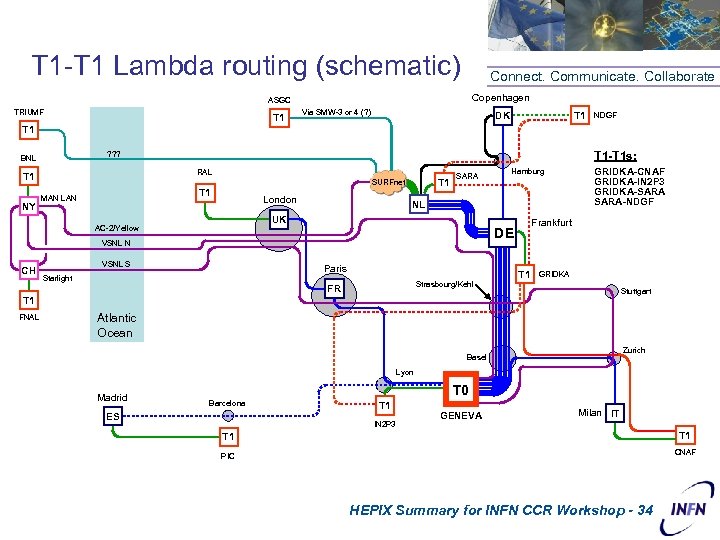 T 1 -T 1 Lambda routing (schematic) Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Copenhagen ASGC TRIUMF T 1 Via SMW-3 or 4 (? ) T 1 DK NDGF T 1 RAL T 1 NY T 1 -T 1 s: ? ? ? BNL T 1 SURFnet T 1 MAN London SARA NL UK AC-2/Yellow VSNL S Paris Starlight GRIDKA-CNAF GRIDKA-IN 2 P 3 GRIDKA-SARA-NDGF Frankfurt DE VSNL N CH Hamburg T 1 GRIDKA Strasbourg/Kehl FR Stuttgart T 1 FNAL Atlantic Ocean Zurich Basel Lyon Madrid T 0 Barcelona ES T 1 IN 2 P 3 GENEVA Milan IT T 1 CNAF PIC HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 34
T 1 -T 1 Lambda routing (schematic) Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Copenhagen ASGC TRIUMF T 1 Via SMW-3 or 4 (? ) T 1 DK NDGF T 1 RAL T 1 NY T 1 -T 1 s: ? ? ? BNL T 1 SURFnet T 1 MAN London SARA NL UK AC-2/Yellow VSNL S Paris Starlight GRIDKA-CNAF GRIDKA-IN 2 P 3 GRIDKA-SARA-NDGF Frankfurt DE VSNL N CH Hamburg T 1 GRIDKA Strasbourg/Kehl FR Stuttgart T 1 FNAL Atlantic Ocean Zurich Basel Lyon Madrid T 0 Barcelona ES T 1 IN 2 P 3 GENEVA Milan IT T 1 CNAF PIC HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 34
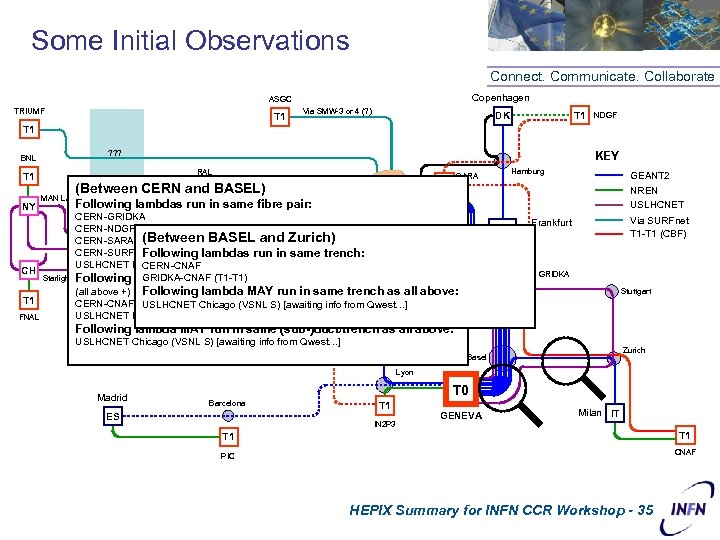 Some Initial Observations Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Copenhagen ASGC TRIUMF T 1 Via SMW-3 or 4 (? ) T 1 DK NDGF T 1 ? ? ? BNL T 1 NY CH T 1 FNAL KEY RAL (Between CERN and BASEL) T 1 MAN London Following lambdas run in same fibre pair: Starlight SARA T 1 SURFnet Hamburg GEANT 2 NREN USLHCNET NL CERN-GRIDKA UK AC-2/Yellow CERN-NDGF CERN-SARA (Between BASEL and Zurich) VSNL N CERN-SURFnet-TRIUMF/ASGC (x 2) run in same trench: Following lambdas VSNL S CERN-CNAF USLHCNET NY (AC-2) Paris GRIDKA-CNAF (T 1 -T 1) Following lambdas run in same (sub-)duct/trench: Strasbourg/Kehl FR (all above +) Following lambda MAY run in same trench as all above: CERN-CNAF USLHCNET Chicago (VSNL S) [awaiting info from Qwest…] USLHCNET NY (VSNL N) [supplier is COLT] Atlantic Via SURFnet T 1 -T 1 (CBF) Frankfurt DE T 1 GRIDKA Stuttgart Following lambda MAY run in same (sub-)duct/trench as all above: Ocean USLHCNET Chicago (VSNL S) [awaiting info from Qwest…] Zurich Basel Lyon Madrid T 0 Barcelona ES T 1 IN 2 P 3 GENEVA Milan IT T 1 CNAF PIC HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 35
Some Initial Observations Connect. Communicate. Collaborate Copenhagen ASGC TRIUMF T 1 Via SMW-3 or 4 (? ) T 1 DK NDGF T 1 ? ? ? BNL T 1 NY CH T 1 FNAL KEY RAL (Between CERN and BASEL) T 1 MAN London Following lambdas run in same fibre pair: Starlight SARA T 1 SURFnet Hamburg GEANT 2 NREN USLHCNET NL CERN-GRIDKA UK AC-2/Yellow CERN-NDGF CERN-SARA (Between BASEL and Zurich) VSNL N CERN-SURFnet-TRIUMF/ASGC (x 2) run in same trench: Following lambdas VSNL S CERN-CNAF USLHCNET NY (AC-2) Paris GRIDKA-CNAF (T 1 -T 1) Following lambdas run in same (sub-)duct/trench: Strasbourg/Kehl FR (all above +) Following lambda MAY run in same trench as all above: CERN-CNAF USLHCNET Chicago (VSNL S) [awaiting info from Qwest…] USLHCNET NY (VSNL N) [supplier is COLT] Atlantic Via SURFnet T 1 -T 1 (CBF) Frankfurt DE T 1 GRIDKA Stuttgart Following lambda MAY run in same (sub-)duct/trench as all above: Ocean USLHCNET Chicago (VSNL S) [awaiting info from Qwest…] Zurich Basel Lyon Madrid T 0 Barcelona ES T 1 IN 2 P 3 GENEVA Milan IT T 1 CNAF PIC HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 35
 IP Backup • In case of failures, degraded service may be expected. – This is not yet quantified on a “per failure” basis. • The IP configuration needs to be validated – Some failures have indeed produced successful failover. – Tests executed this month (9 th April) • Some sites still have no physical backup paths – PIC (difficult) and RAL (some possibilities)7 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 36
IP Backup • In case of failures, degraded service may be expected. – This is not yet quantified on a “per failure” basis. • The IP configuration needs to be validated – Some failures have indeed produced successful failover. – Tests executed this month (9 th April) • Some sites still have no physical backup paths – PIC (difficult) and RAL (some possibilities)7 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 36
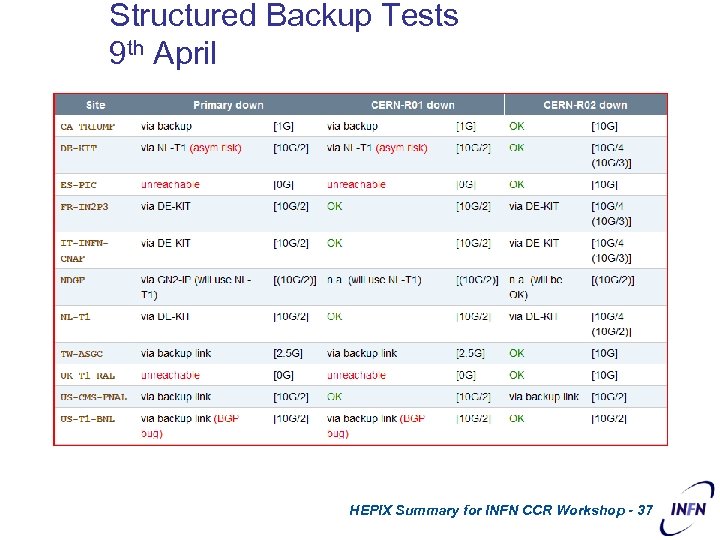 Structured Backup Tests 9 th April HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 37 CERN – March 2007
Structured Backup Tests 9 th April HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 37 CERN – March 2007
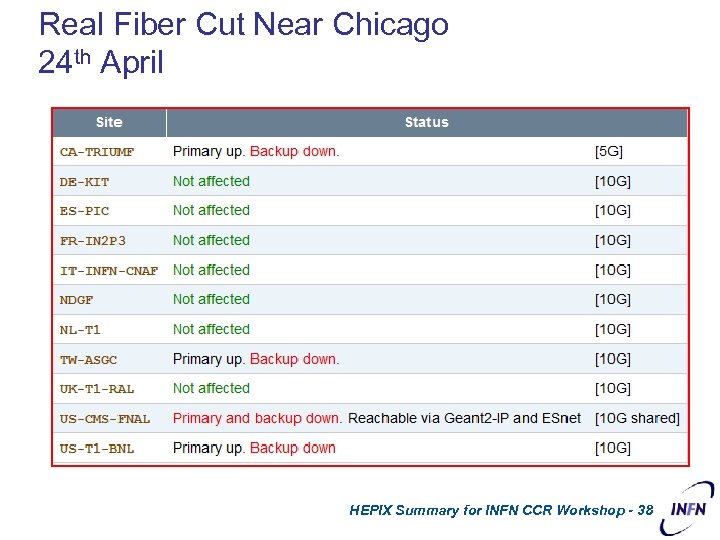 Real Fiber Cut Near Chicago 24 th April HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 38 CERN – March 2007
Real Fiber Cut Near Chicago 24 th April HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 38 CERN – March 2007
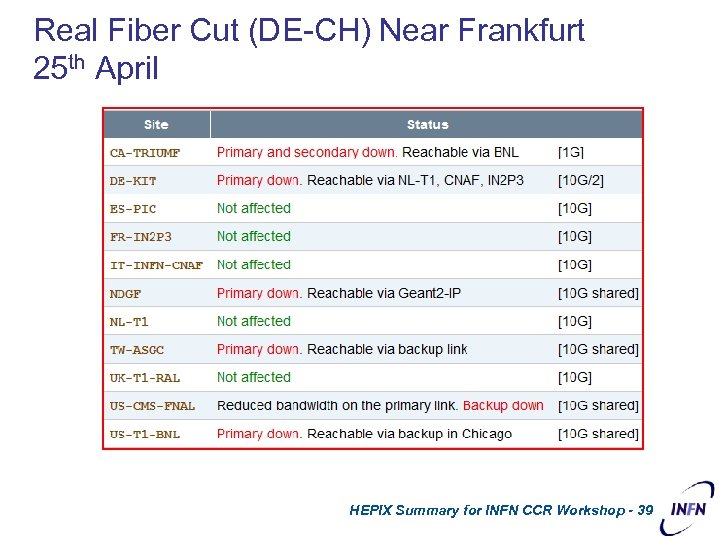 Real Fiber Cut (DE-CH) Near Frankfurt 25 th April HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 39 CERN – March 2007
Real Fiber Cut (DE-CH) Near Frankfurt 25 th April HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 39 CERN – March 2007
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 40
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 40
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 41
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 41
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 42
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 42
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 43
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 43
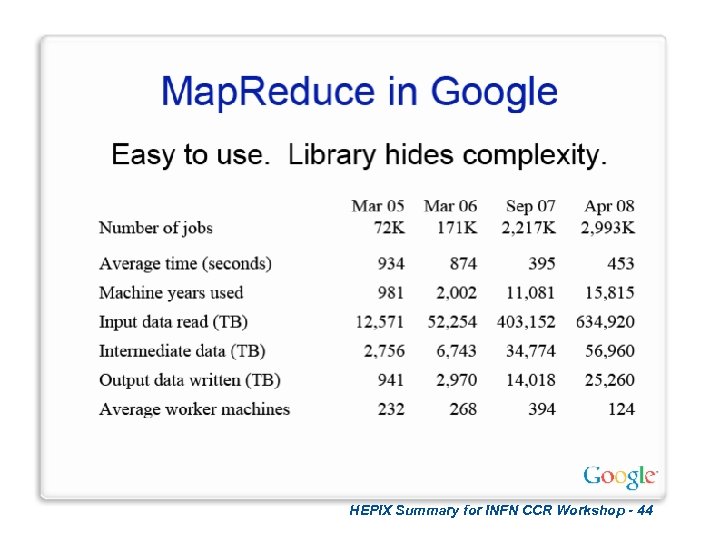 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 44
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 44
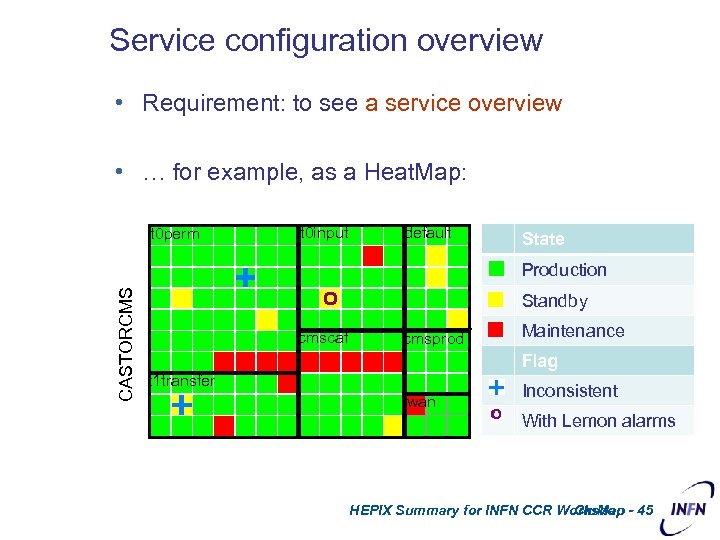 Service configuration overview • Requirement: to see a service overview • … for example, as a Heat. Map: t 0 perm t 0 input default State CASTORCMS Production Standby cmscaf cmsprod Maintenance Flag t 1 transfer wan Inconsistent With Lemon alarms HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 45 Clu. Man
Service configuration overview • Requirement: to see a service overview • … for example, as a Heat. Map: t 0 perm t 0 input default State CASTORCMS Production Standby cmscaf cmsprod Maintenance Flag t 1 transfer wan Inconsistent With Lemon alarms HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 45 Clu. Man
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 46
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 46
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 47
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 47
 Status of the LHC HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 48 48
Status of the LHC HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 48 48
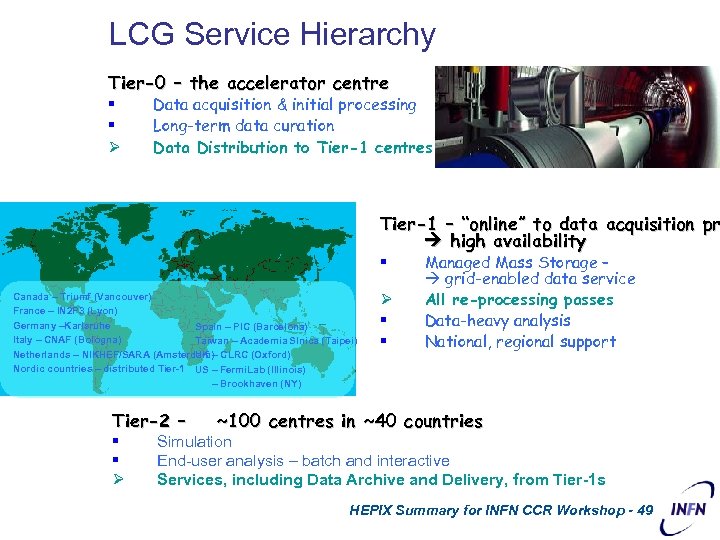 LCG Service Hierarchy Tier-0 – the accelerator centre § § Ø Data acquisition & initial processing Long-term data curation Data Distribution to Tier-1 centres Tier-1 – “online” to data acquisition pr high availability § Canada – Triumf (Vancouver) France – IN 2 P 3 (Lyon) Germany –Karlsruhe Spain – PIC (Barcelona) Italy – CNAF (Bologna) Taiwan – Academia SInica (Taipei) Netherlands – NIKHEF/SARA (Amsterdam) CLRC (Oxford) UK – Nordic countries – distributed Tier-1 US – Fermi. Lab (Illinois) Ø § § Managed Mass Storage – grid-enabled data service All re-processing passes Data-heavy analysis National, regional support – Brookhaven (NY) Tier-2 – § § Ø ~100 centres in ~40 countries Simulation End-user analysis – batch and interactive Services, including Data Archive and Delivery, from Tier-1 s HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 49
LCG Service Hierarchy Tier-0 – the accelerator centre § § Ø Data acquisition & initial processing Long-term data curation Data Distribution to Tier-1 centres Tier-1 – “online” to data acquisition pr high availability § Canada – Triumf (Vancouver) France – IN 2 P 3 (Lyon) Germany –Karlsruhe Spain – PIC (Barcelona) Italy – CNAF (Bologna) Taiwan – Academia SInica (Taipei) Netherlands – NIKHEF/SARA (Amsterdam) CLRC (Oxford) UK – Nordic countries – distributed Tier-1 US – Fermi. Lab (Illinois) Ø § § Managed Mass Storage – grid-enabled data service All re-processing passes Data-heavy analysis National, regional support – Brookhaven (NY) Tier-2 – § § Ø ~100 centres in ~40 countries Simulation End-user analysis – batch and interactive Services, including Data Archive and Delivery, from Tier-1 s HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 49
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 50
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 50
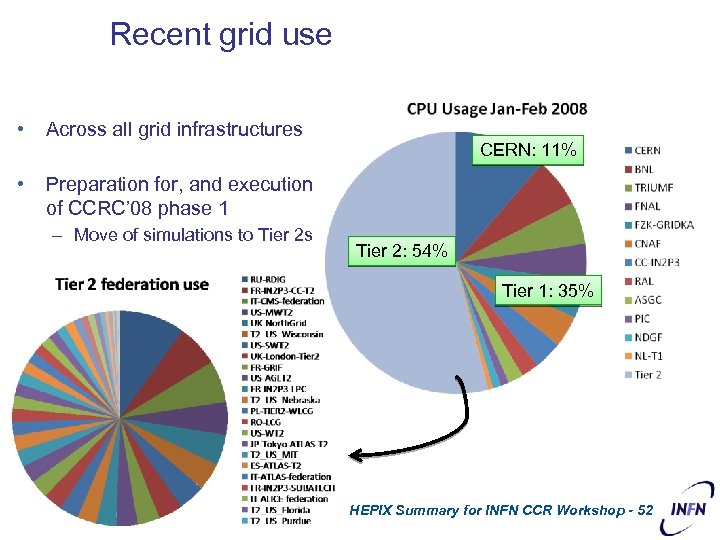 Recent grid use • Across all grid infrastructures • Preparation for, and execution of CCRC’ 08 phase 1 – Move of simulations to Tier 2 s CERN: 11% Tier 2: 54% Tier 1: 35% HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 52
Recent grid use • Across all grid infrastructures • Preparation for, and execution of CCRC’ 08 phase 1 – Move of simulations to Tier 2 s CERN: 11% Tier 2: 54% Tier 1: 35% HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 52
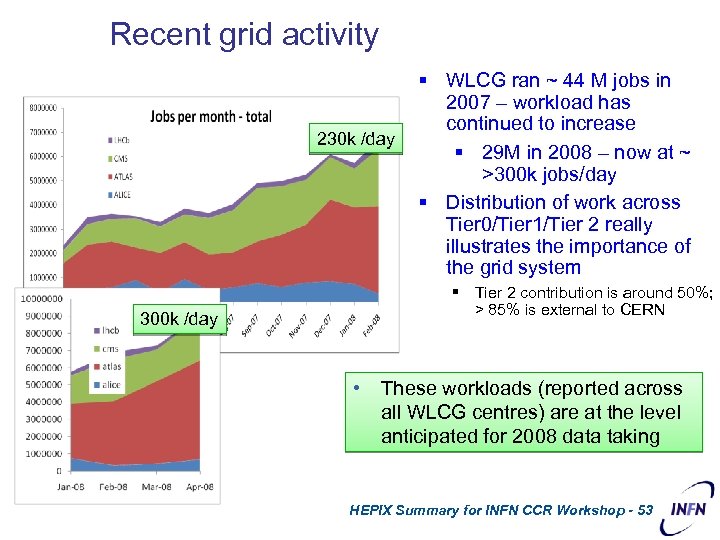 Recent grid activity 230 k /day § WLCG ran ~ 44 M jobs in 2007 – workload has continued to increase § 29 M in 2008 – now at ~ >300 k jobs/day § Distribution of work across Tier 0/Tier 1/Tier 2 really illustrates the importance of the grid system § Tier 2 contribution is around 50%; > 85% is external to CERN 300 k /day • These workloads (reported across all WLCG centres) are at the level anticipated for 2008 data taking HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 53
Recent grid activity 230 k /day § WLCG ran ~ 44 M jobs in 2007 – workload has continued to increase § 29 M in 2008 – now at ~ >300 k jobs/day § Distribution of work across Tier 0/Tier 1/Tier 2 really illustrates the importance of the grid system § Tier 2 contribution is around 50%; > 85% is external to CERN 300 k /day • These workloads (reported across all WLCG centres) are at the level anticipated for 2008 data taking HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 53
 Combined Computing Readiness Challenge – CCRC’ 08 • Objective was to show that we can run together (4 experiments, all sites) at 2008 production scale: – All functions, from DAQ Tier 0 Tier 1 s Tier 2 s • Two challenge phases were foreseen: 1. Feb: not all 2008 resources in place – still adapting to new versions of some services (e. g. SRM) & experiment s/w 2. May: all 2008 resources in place – full 2008 workload, all aspects of experiments’ production chains • Agreed on specific targets and metrics – helped integrate different aspects of the service q Explicit “scaling factors” set by the experiments for each functional block (e. g. data rates, # jobs, etc. ) q Targets for “critical services” defined by experiments – essential for production, with analysis of impact of service degradation / interruption q WLCG “Mo. U targets” – services to be provided by sites, target availability, time to intervene / resolve problems … HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 54
Combined Computing Readiness Challenge – CCRC’ 08 • Objective was to show that we can run together (4 experiments, all sites) at 2008 production scale: – All functions, from DAQ Tier 0 Tier 1 s Tier 2 s • Two challenge phases were foreseen: 1. Feb: not all 2008 resources in place – still adapting to new versions of some services (e. g. SRM) & experiment s/w 2. May: all 2008 resources in place – full 2008 workload, all aspects of experiments’ production chains • Agreed on specific targets and metrics – helped integrate different aspects of the service q Explicit “scaling factors” set by the experiments for each functional block (e. g. data rates, # jobs, etc. ) q Targets for “critical services” defined by experiments – essential for production, with analysis of impact of service degradation / interruption q WLCG “Mo. U targets” – services to be provided by sites, target availability, time to intervene / resolve problems … HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 54
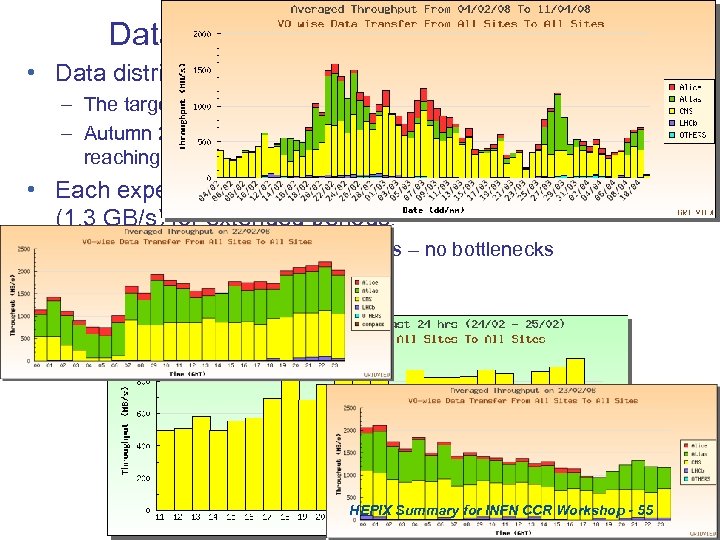 Data transfer • Data distribution from CERN to Tier-1 sites – The target rate was achieved in 2006 under test conditions – Autumn 2007 & CCRC’ 08 under more realistic experiment testing, reaching & sustaining target rate with ATLAS and CMS active • Each experiment sustained in excess of the target rates (1. 3 GB/s) for extended periods. – Peak aggregate rates over 2. 1 GB/s – no bottlenecks • All Tier 1 sites were included HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 55
Data transfer • Data distribution from CERN to Tier-1 sites – The target rate was achieved in 2006 under test conditions – Autumn 2007 & CCRC’ 08 under more realistic experiment testing, reaching & sustaining target rate with ATLAS and CMS active • Each experiment sustained in excess of the target rates (1. 3 GB/s) for extended periods. – Peak aggregate rates over 2. 1 GB/s – no bottlenecks • All Tier 1 sites were included HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 55
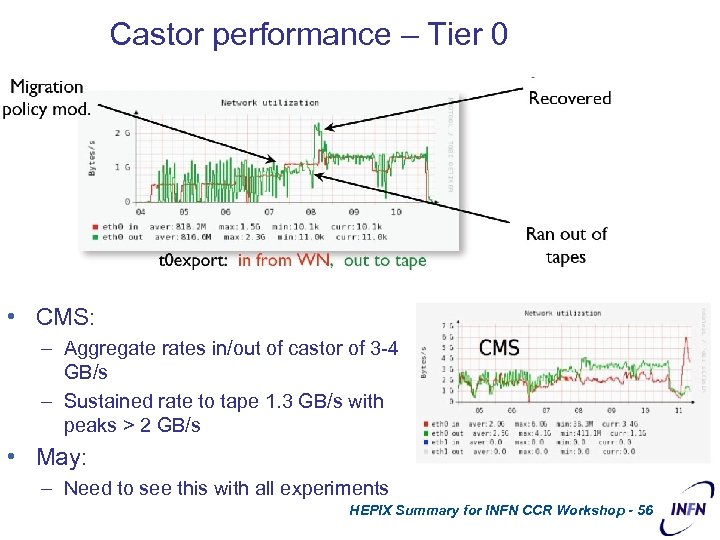 Castor performance – Tier 0 • CMS: – Aggregate rates in/out of castor of 3 -4 GB/s – Sustained rate to tape 1. 3 GB/s with peaks > 2 GB/s • May: – Need to see this with all experiments HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 56
Castor performance – Tier 0 • CMS: – Aggregate rates in/out of castor of 3 -4 GB/s – Sustained rate to tape 1. 3 GB/s with peaks > 2 GB/s • May: – Need to see this with all experiments HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 56
 Resource ramp up for 2008 • CPU: – Most Tier 1 sites will have full 2008 pledges in place for 1 May – Total of 36725 KSi 2 K. – Largest missing is +2500 at NL-T 1 due Nov. • Disk and tape – Many sites will catch up later in the year as need expands: – 2008 disk requirements are 23 PB with 15. 5 PB expected by 1 May – 2008 tape requirements are 24 PB with 15 PB expected by 1 May. • May run of CCRC’ 08 at 55% only requires +1 PB of disk and +1. 5 PB of tape (mostly reusable) so should have no resource problems. • Full status of resource installation will be reported at CRRB in April. • Many sites had problems with procurement process/ vendor delivery/ faulty equipment Ø These issues must be taken into account in future – the process is long, but yearly deadlines are important HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 57
Resource ramp up for 2008 • CPU: – Most Tier 1 sites will have full 2008 pledges in place for 1 May – Total of 36725 KSi 2 K. – Largest missing is +2500 at NL-T 1 due Nov. • Disk and tape – Many sites will catch up later in the year as need expands: – 2008 disk requirements are 23 PB with 15. 5 PB expected by 1 May – 2008 tape requirements are 24 PB with 15 PB expected by 1 May. • May run of CCRC’ 08 at 55% only requires +1 PB of disk and +1. 5 PB of tape (mostly reusable) so should have no resource problems. • Full status of resource installation will be reported at CRRB in April. • Many sites had problems with procurement process/ vendor delivery/ faulty equipment Ø These issues must be taken into account in future – the process is long, but yearly deadlines are important HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 57
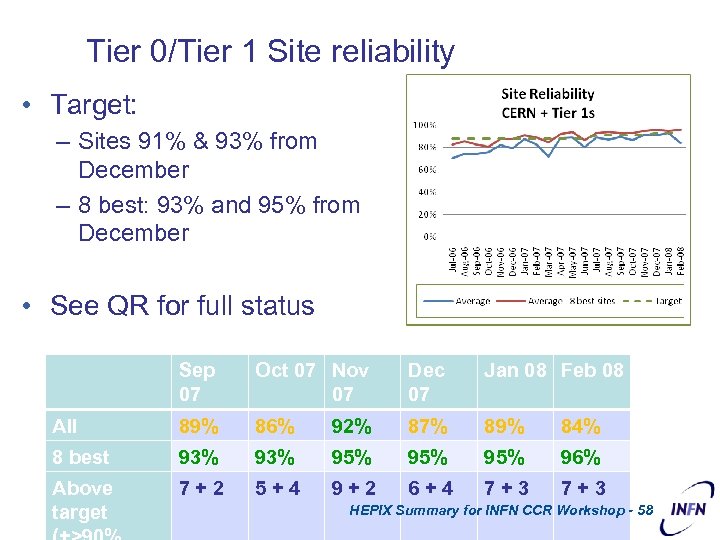 Tier 0/Tier 1 Site reliability • Target: – Sites 91% & 93% from December – 8 best: 93% and 95% from December • See QR for full status Sep 07 Oct 07 Nov 07 Dec 07 Jan 08 Feb 08 All 89% 86% 92% 87% 89% 84% 8 best 93% 95% 95% 96% Above target 7+2 5+4 9+2 6+4 7+3 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 58
Tier 0/Tier 1 Site reliability • Target: – Sites 91% & 93% from December – 8 best: 93% and 95% from December • See QR for full status Sep 07 Oct 07 Nov 07 Dec 07 Jan 08 Feb 08 All 89% 86% 92% 87% 89% 84% 8 best 93% 95% 95% 96% Above target 7+2 5+4 9+2 6+4 7+3 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 58
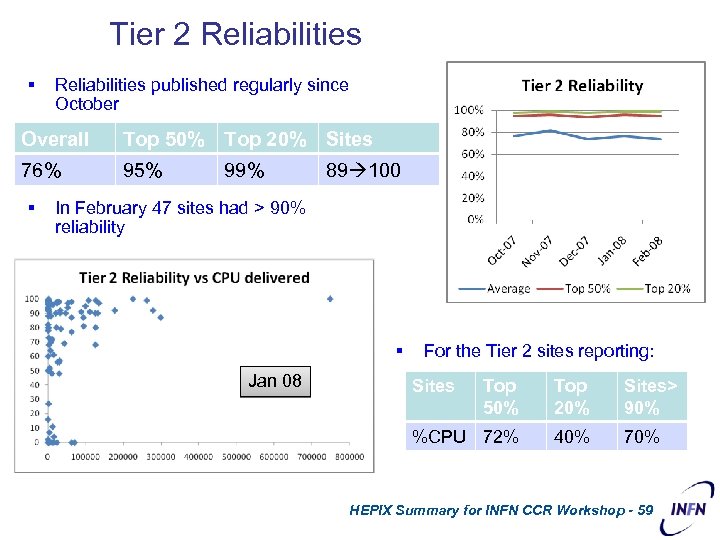 Tier 2 Reliabilities § Reliabilities published regularly since October Overall Top 50% Top 20% Sites 76% 95% § 99% 89 100 In February 47 sites had > 90% reliability § Jan 08 For the Tier 2 sites reporting: Sites Top 50% Top 20% Sites> 90% %CPU 72% 40% 70% HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 59
Tier 2 Reliabilities § Reliabilities published regularly since October Overall Top 50% Top 20% Sites 76% 95% § 99% 89 100 In February 47 sites had > 90% reliability § Jan 08 For the Tier 2 sites reporting: Sites Top 50% Top 20% Sites> 90% %CPU 72% 40% 70% HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 59
 Reliability. . . • Site reliability/availability affects resource delivery and usability of a site – This has been the outstanding problem for a long time (slow improvement of reliability) • Addressed through human oversight (Grid Operator on Duty). . . – Teams of experts on duty to flag problems and follow up with sites • In place since late 2004; effort intensive • Instrumental in stabilisation and gradual improvement of reliability • Unsustainable in the long term • . . . and though better monitoring. . . – – Monitoring tools (many!) Aggregating information Understanding (visualising) the data Automation HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 60
Reliability. . . • Site reliability/availability affects resource delivery and usability of a site – This has been the outstanding problem for a long time (slow improvement of reliability) • Addressed through human oversight (Grid Operator on Duty). . . – Teams of experts on duty to flag problems and follow up with sites • In place since late 2004; effort intensive • Instrumental in stabilisation and gradual improvement of reliability • Unsustainable in the long term • . . . and though better monitoring. . . – – Monitoring tools (many!) Aggregating information Understanding (visualising) the data Automation HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 60
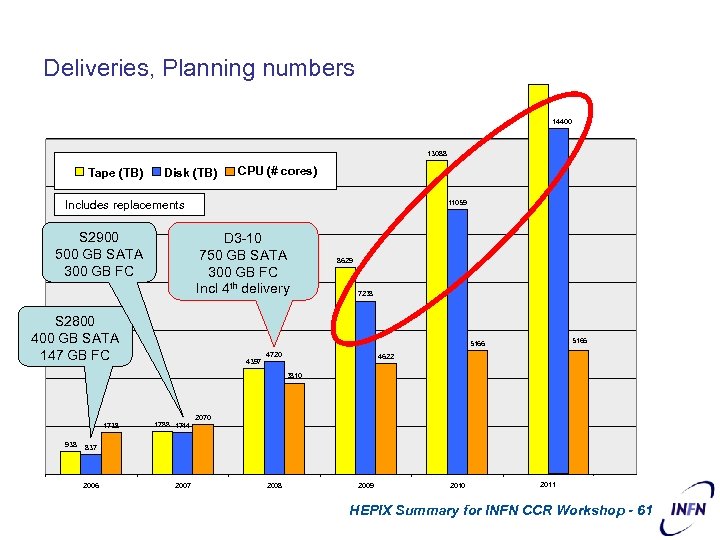 Deliveries, Planning numbers 14400 13088 Tape (TB) Disk (TB) CPU (# cores) Includes replacements S 2900 500 GB SATA 300 GB FC 11059 D 3 -10 750 GB SATA 300 GB FC Incl 4 th delivery S 2800 400 GB SATA 147 GB FC 8629 7238 5166 4397 4720 4622 3810 1738 938 1788 1744 2070 837 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 61
Deliveries, Planning numbers 14400 13088 Tape (TB) Disk (TB) CPU (# cores) Includes replacements S 2900 500 GB SATA 300 GB FC 11059 D 3 -10 750 GB SATA 300 GB FC Incl 4 th delivery S 2800 400 GB SATA 147 GB FC 8629 7238 5166 4397 4720 4622 3810 1738 938 1788 1744 2070 837 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 61
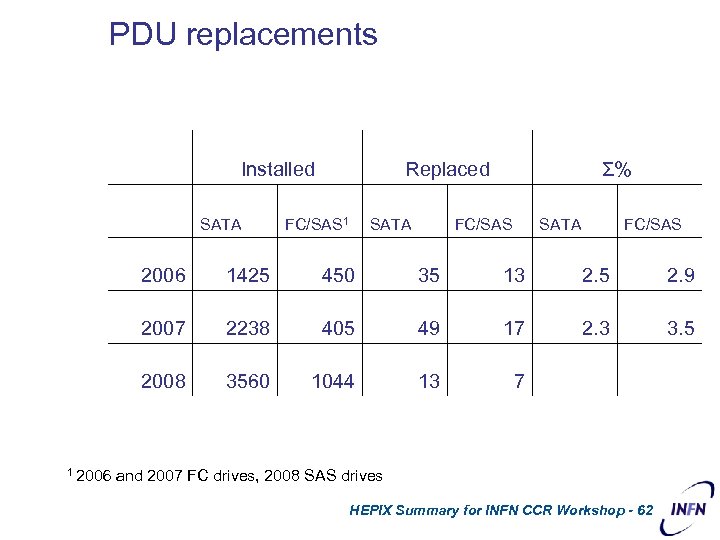 PDU replacements Installed SATA Replaced FC/SAS 1 SATA Σ% FC/SAS SATA FC/SAS 2006 1425 450 35 13 2. 5 2. 9 2007 2238 405 49 17 2. 3 3. 5 2008 3560 1044 13 7 1 2006 and 2007 FC drives, 2008 SAS drives HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 62
PDU replacements Installed SATA Replaced FC/SAS 1 SATA Σ% FC/SAS SATA FC/SAS 2006 1425 450 35 13 2. 5 2. 9 2007 2238 405 49 17 2. 3 3. 5 2008 3560 1044 13 7 1 2006 and 2007 FC drives, 2008 SAS drives HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 62
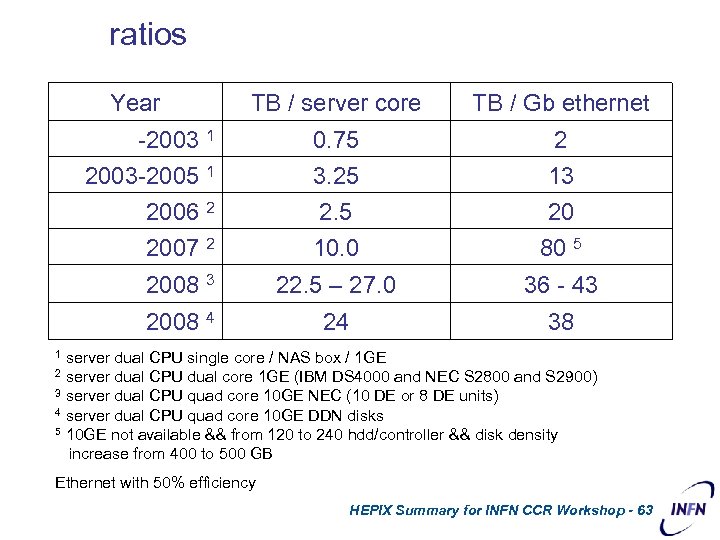 ratios Year TB / server core TB / Gb ethernet -2003 1 2003 -2005 1 2006 2 0. 75 3. 25 2. 5 2 13 20 2007 2 10. 0 80 5 2008 3 22. 5 – 27. 0 36 - 43 2008 4 24 38 1 server dual CPU single core / NAS box / 1 GE 2 server dual CPU dual core 1 GE (IBM DS 4000 and NEC S 2800 and S 2900) 3 server dual CPU quad core 10 GE NEC (10 DE or 8 DE units) 4 server dual CPU quad core 10 GE DDN disks 5 10 GE not available && from 120 to 240 hdd/controller && disk density increase from 400 to 500 GB Ethernet with 50% efficiency HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 63
ratios Year TB / server core TB / Gb ethernet -2003 1 2003 -2005 1 2006 2 0. 75 3. 25 2. 5 2 13 20 2007 2 10. 0 80 5 2008 3 22. 5 – 27. 0 36 - 43 2008 4 24 38 1 server dual CPU single core / NAS box / 1 GE 2 server dual CPU dual core 1 GE (IBM DS 4000 and NEC S 2800 and S 2900) 3 server dual CPU quad core 10 GE NEC (10 DE or 8 DE units) 4 server dual CPU quad core 10 GE DDN disks 5 10 GE not available && from 120 to 240 hdd/controller && disk density increase from 400 to 500 GB Ethernet with 50% efficiency HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 63
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 64
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 64
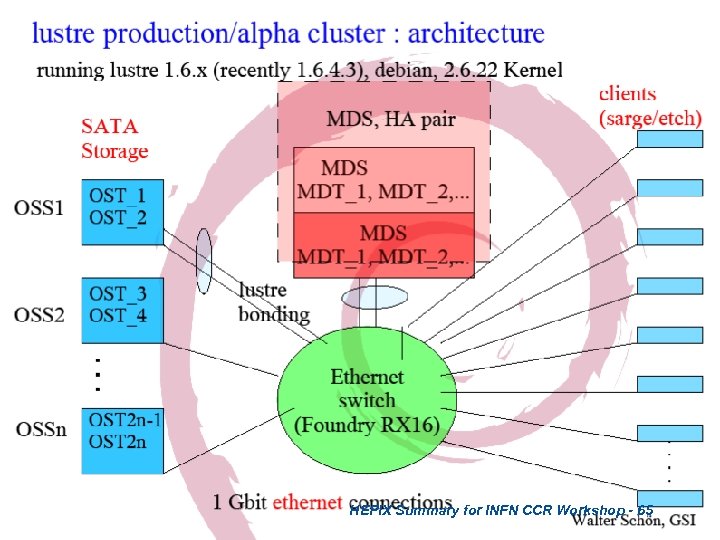 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 65
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 65
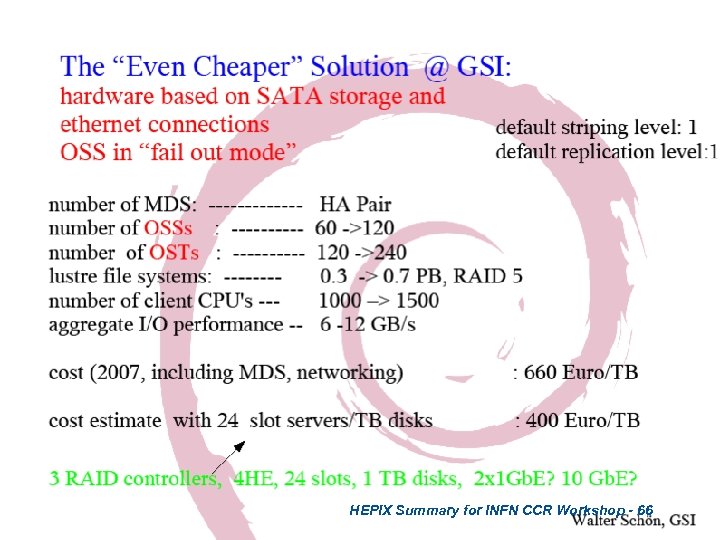 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 66
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 66
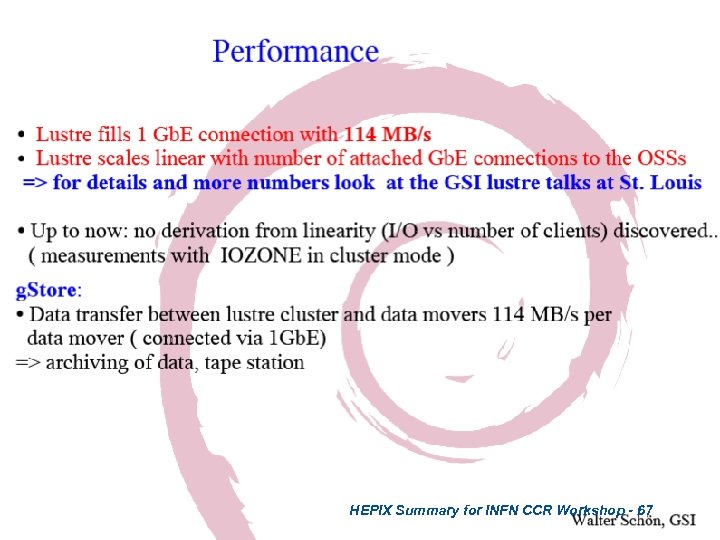 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 67
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 67
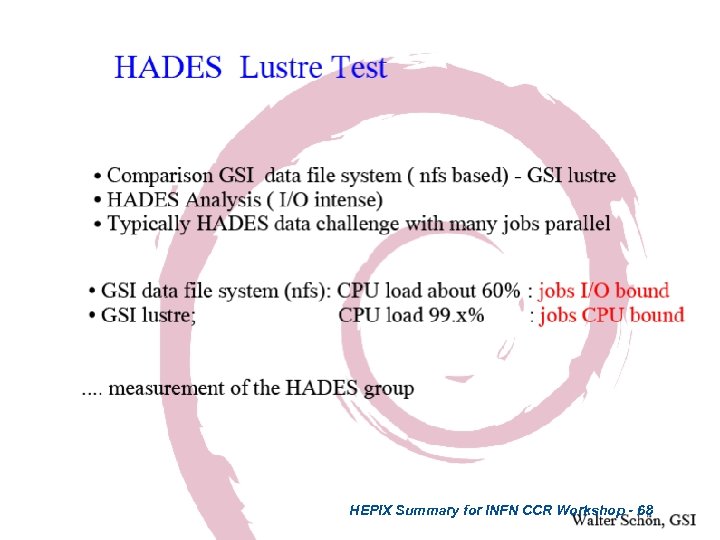 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 68
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 68
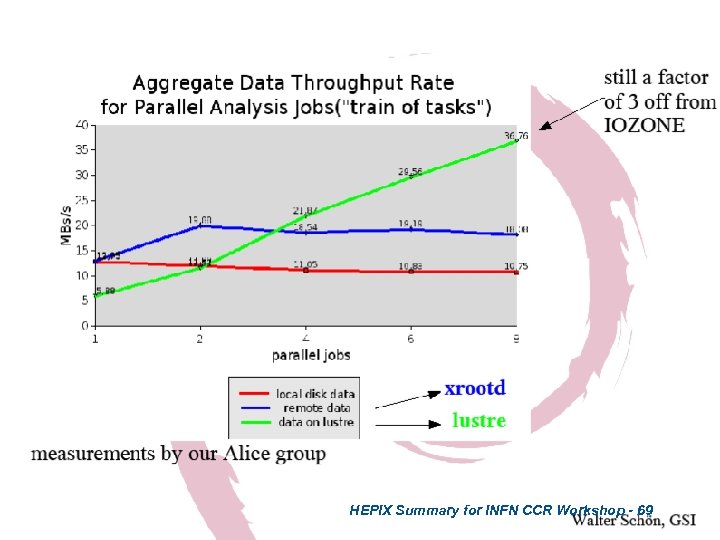 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 69
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 69
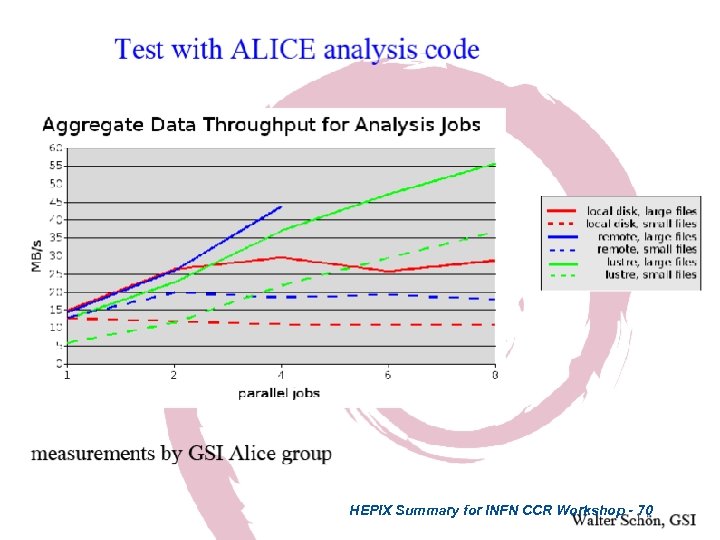 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 70
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 70
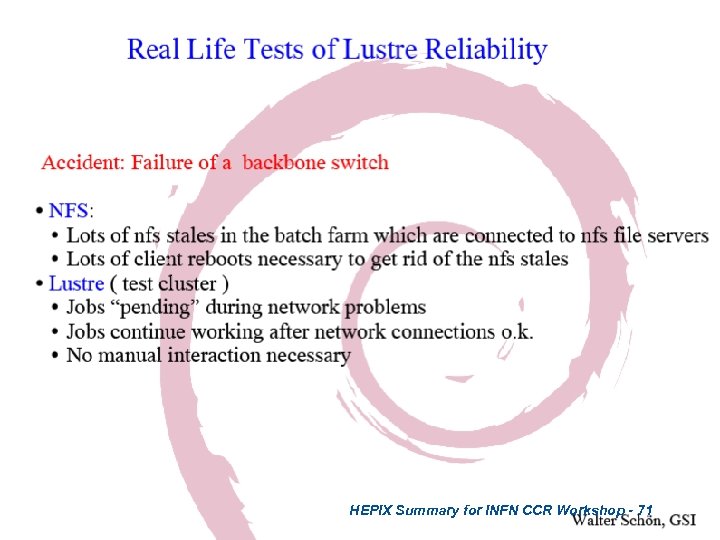 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 71
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 71
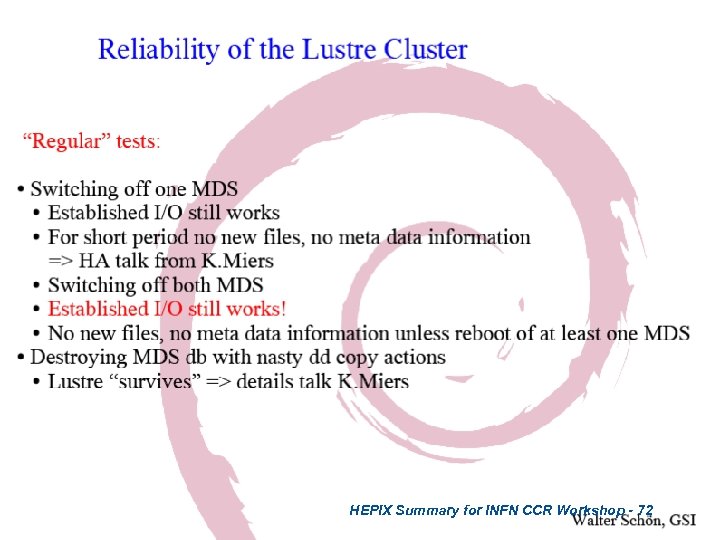 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 72
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 72
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 73
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 73
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 74
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 74
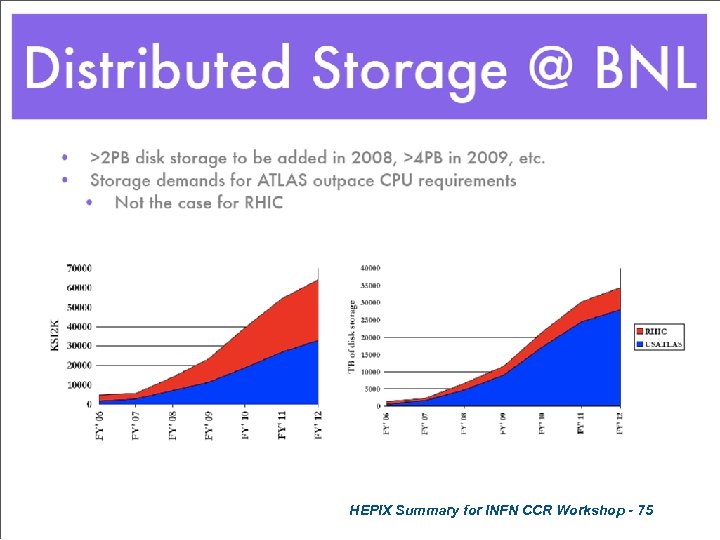 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 75
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 75
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 76
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 76
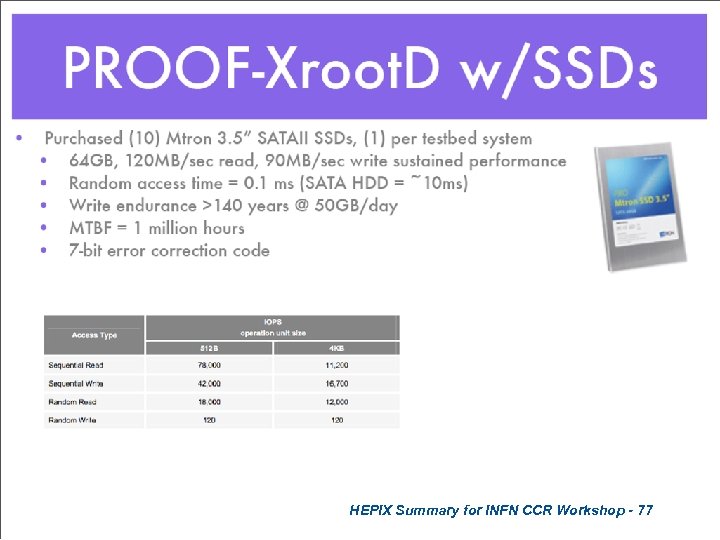 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 77
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 77
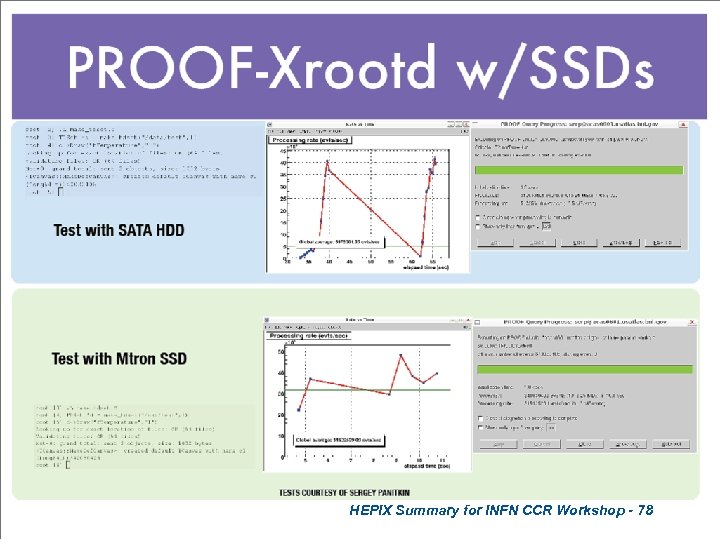 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 78
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 78
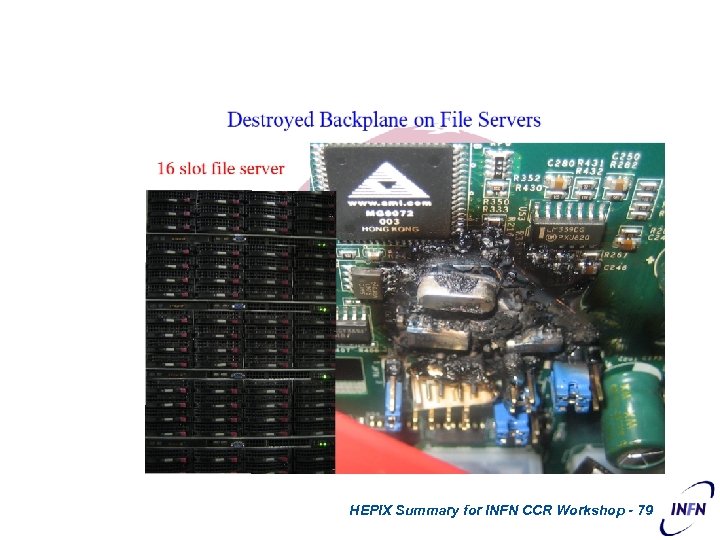 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 79
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 79
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 80
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 80
 Web (in)security update • IFRAME injection attacks continue – Inserts IFRAME HTML tags into web pages – Loads malware from another site into this IFRAME – Relies on finding vulnerable web servers • Unfortunately they are not difficult to find! – Targets vulnerabilities in Web browsers and plug-ins • E. g. vulnerabilities in media players are common • Insufficient file protections are targets – Including AFS file space – check if your ACLs are too open! – Used for hosting inappropriate content (malware, SPAM, …) – Automated tools post to open forums, blogs, wikis, guestbooks, etc. . . • http: //pandalabs. pandasecurity. com/archive/XRumer. aspx HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 81
Web (in)security update • IFRAME injection attacks continue – Inserts IFRAME HTML tags into web pages – Loads malware from another site into this IFRAME – Relies on finding vulnerable web servers • Unfortunately they are not difficult to find! – Targets vulnerabilities in Web browsers and plug-ins • E. g. vulnerabilities in media players are common • Insufficient file protections are targets – Including AFS file space – check if your ACLs are too open! – Used for hosting inappropriate content (malware, SPAM, …) – Automated tools post to open forums, blogs, wikis, guestbooks, etc. . . • http: //pandalabs. pandasecurity. com/archive/XRumer. aspx HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 81
 Malware Distribution Networks • Report by Google on drive-by-download attacks: – http: //research. google. com/archive/provos-2008 a. pdf – avoiding the dark corners of the Internet does not limit exposure to malware – state-of-the-art anti-virus engines are lacking in their ability to protect against drive-by downloads – users may be lured into the malware distribution networks by content served through online Ads • e. g. http: //www. theregister. co. uk/2008/04/28/yahoo_serves_rogue_ads/ – 1. 3% of the incoming search queries to Google's search engine return at least one link to a malicious site HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 82
Malware Distribution Networks • Report by Google on drive-by-download attacks: – http: //research. google. com/archive/provos-2008 a. pdf – avoiding the dark corners of the Internet does not limit exposure to malware – state-of-the-art anti-virus engines are lacking in their ability to protect against drive-by downloads – users may be lured into the malware distribution networks by content served through online Ads • e. g. http: //www. theregister. co. uk/2008/04/28/yahoo_serves_rogue_ads/ – 1. 3% of the incoming search queries to Google's search engine return at least one link to a malicious site HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 82
 Web security advice • Require secure coding practices – Especially (but not only) for custom built web applications – http: //cern. ch/security/webapps/ • Educate users that web surfing has risks – Advertising, photos and videos can and do regularly contain malware – Be cautious of links in IM, Blogs and Online forums (e. g. social networking). Attackers have matured beyond using SPAM – Rich content and plug-ins increase chances of attacks – Even reputable sites can serve 3 rd party content, e. g. advertising • Consider blockers for Java. Script and advertising – e. g. No. Script and Ad. Block for Firefox – Disadvantages are that frequent updates are required and users need to understand what is being blocked and why HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 83
Web security advice • Require secure coding practices – Especially (but not only) for custom built web applications – http: //cern. ch/security/webapps/ • Educate users that web surfing has risks – Advertising, photos and videos can and do regularly contain malware – Be cautious of links in IM, Blogs and Online forums (e. g. social networking). Attackers have matured beyond using SPAM – Rich content and plug-ins increase chances of attacks – Even reputable sites can serve 3 rd party content, e. g. advertising • Consider blockers for Java. Script and advertising – e. g. No. Script and Ad. Block for Firefox – Disadvantages are that frequent updates are required and users need to understand what is being blocked and why HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 83
 Advice on securing Windows computers Centrally managing computers can help: • Ensure patching for applications as well as the operating system • Ensure anti-virus runs correctly and pattern files kept updated • Configure secure defaults, especially for web browsers • Only use privileges for actions that require them • 90% of compromised Windows computers at CERN in 2007 were privately managed – e. g. laptops owned privately or by outside institutes – => Centrally managed computers were more secure HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 84
Advice on securing Windows computers Centrally managing computers can help: • Ensure patching for applications as well as the operating system • Ensure anti-virus runs correctly and pattern files kept updated • Configure secure defaults, especially for web browsers • Only use privileges for actions that require them • 90% of compromised Windows computers at CERN in 2007 were privately managed – e. g. laptops owned privately or by outside institutes – => Centrally managed computers were more secure HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 84
 Control System Cyber Security in HEP • First workshop held during ICALEPCS 2007 • Located in Knoxville, Tennessee, on 15 Oct 2007 • Participants from several sites • KEK, FNAL, SLAC, STFC, . . . • Useful discussion and information exchange • Defence in depth is a common approach • Summary paper and talk linked from • http: //indico. cern. ch/conference. Display. py? conf. Id=13367 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 85
Control System Cyber Security in HEP • First workshop held during ICALEPCS 2007 • Located in Knoxville, Tennessee, on 15 Oct 2007 • Participants from several sites • KEK, FNAL, SLAC, STFC, . . . • Useful discussion and information exchange • Defence in depth is a common approach • Summary paper and talk linked from • http: //indico. cern. ch/conference. Display. py? conf. Id=13367 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 85
 Some conclusions… • The Internet world is not becoming a safer place • Attacks are becoming more targeted – Driven by money and criminal activity – e. g. compromised computers, accounts and data can be sold – Phishing targets passwords, personal data, credit card details, … • Secure coding practices are essential – Custom built software, especially web apps, are a growing target • Privately managed computers/applications can increase risks – Applications, plug-ins etc need to be patched (not just the OS) – Centralised management makes it easier to keep computers secure • Users need to be alert for malware – Via links in IM, Blogs, Online forums (e. g. social networking), … – In photos, videos, advertising, documents, … – Relying solely on anti-virus software is not sufficient HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 86
Some conclusions… • The Internet world is not becoming a safer place • Attacks are becoming more targeted – Driven by money and criminal activity – e. g. compromised computers, accounts and data can be sold – Phishing targets passwords, personal data, credit card details, … • Secure coding practices are essential – Custom built software, especially web apps, are a growing target • Privately managed computers/applications can increase risks – Applications, plug-ins etc need to be patched (not just the OS) – Centralised management makes it easier to keep computers secure • Users need to be alert for malware – Via links in IM, Blogs, Online forums (e. g. social networking), … – In photos, videos, advertising, documents, … – Relying solely on anti-virus software is not sufficient HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 86
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 87
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 87
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 88
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 88
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 89
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 89
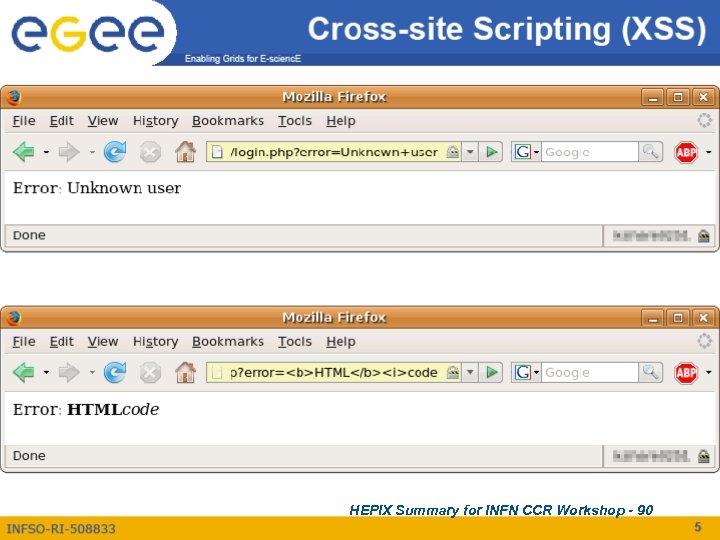 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 90
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 90
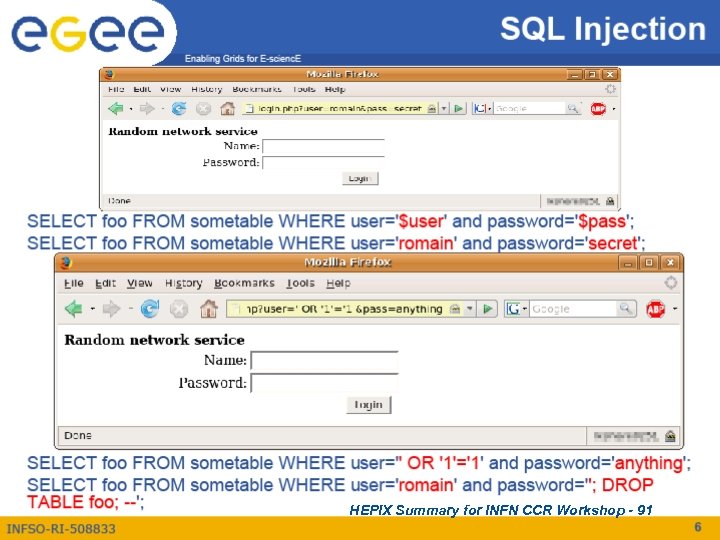 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 91
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 91
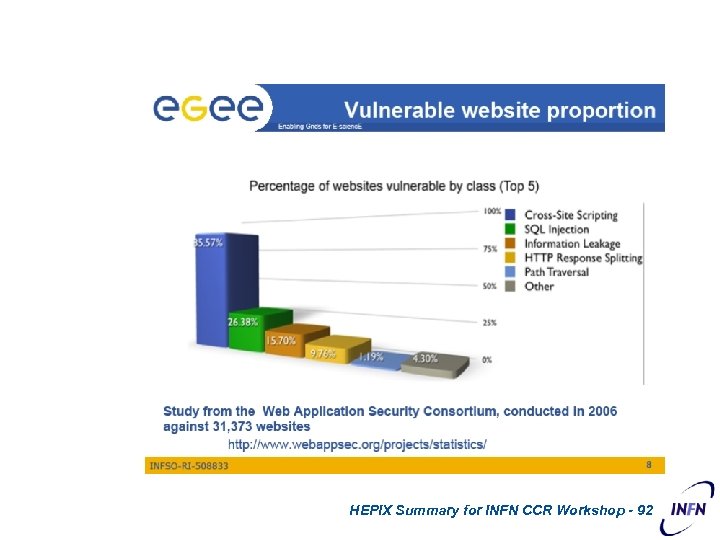 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 92
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 92
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 93
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 93
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 94
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 94
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 95
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 95
 HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 96
HEPIX Summary for INFN CCR Workshop - 96


