6930547bfd959f970060bb36e294a38d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 • henceforth – tax – herewith – richest – hedgehog – signed – been – dog – not – information –bus – were – money – received – individuals – told – next – already – innocent – defendant – deny – of – many – wrote – had
• henceforth – tax – herewith – richest – hedgehog – signed – been – dog – not – information –bus – were – money – received – individuals – told – next – already – innocent – defendant – deny – of – many – wrote – had
 Mr Putin 21. _______ reporters he had received a request from Khodorkovsky, who has 22. _______ in custody for a decade, to pardon him on humanitarian grounds. But representatives 23. _______ the Kremlin critic 24. _______ a request was made. Khodorkovsky, who is regarded by 25. _______ as a political prisoner and has long insisted he is 26. _______, is currently due to leave prison 27. _______ August. Khodorkovsky, 50, and fellow 28. _______ Platon Lebedev were convicted of stealing oil and laundering 29. _______ in 2010. They were already serving time for 30. _______ evasion. The European Court of Human Rights criticised the trials but rejected claims they 31. _______ politically motivated. As head of the now defunct oil giant Yukos, Khodorkovsky BENJAMIN C. PIM was once Russia's 32. _______ man.
Mr Putin 21. _______ reporters he had received a request from Khodorkovsky, who has 22. _______ in custody for a decade, to pardon him on humanitarian grounds. But representatives 23. _______ the Kremlin critic 24. _______ a request was made. Khodorkovsky, who is regarded by 25. _______ as a political prisoner and has long insisted he is 26. _______, is currently due to leave prison 27. _______ August. Khodorkovsky, 50, and fellow 28. _______ Platon Lebedev were convicted of stealing oil and laundering 29. _______ in 2010. They were already serving time for 30. _______ evasion. The European Court of Human Rights criticised the trials but rejected claims they 31. _______ politically motivated. As head of the now defunct oil giant Yukos, Khodorkovsky BENJAMIN C. PIM was once Russia's 32. _______ man.
 • Speaking to reporters after his annual news conference in Moscow on Thursday, President Putin said he had not 33. _______ a request from Khodorkovsky in the past. "And then quite recently he 34. _______ such a document and addressed a request for a pardon to me, " Mr Putin said. "He has 35. _______ been in detention more than 10 years, this is a serious punishment and he is referring to humanitarian circumstances as his mother is ill. " "I think given the circumstances we can take the decision and very soon the decree to pardon him will be 36. _______, " Mr Putin said. Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov told AFP news agency the request 37. _______ been personally "signed" by Khodorkovsky. But Khodorkovsky's main lawyer, Vadim Klyuvgant, told Russia's Ria-Novosti news agency: "He has not made a request and we do 38. _______ have information that someone has made a request on his behalf. "We do not have such 39. _______ although there were requests to pardon him over the years from different 40. _______. "
• Speaking to reporters after his annual news conference in Moscow on Thursday, President Putin said he had not 33. _______ a request from Khodorkovsky in the past. "And then quite recently he 34. _______ such a document and addressed a request for a pardon to me, " Mr Putin said. "He has 35. _______ been in detention more than 10 years, this is a serious punishment and he is referring to humanitarian circumstances as his mother is ill. " "I think given the circumstances we can take the decision and very soon the decree to pardon him will be 36. _______, " Mr Putin said. Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov told AFP news agency the request 37. _______ been personally "signed" by Khodorkovsky. But Khodorkovsky's main lawyer, Vadim Klyuvgant, told Russia's Ria-Novosti news agency: "He has not made a request and we do 38. _______ have information that someone has made a request on his behalf. "We do not have such 39. _______ although there were requests to pardon him over the years from different 40. _______. "
 Mr Putin told reporters he had received a request from Khodorkovsky, who has been in custody for a decade, to pardon him on humanitarian grounds. But representatives of the Kremlin critic deny a request was made. Khodorkovsky, who is regarded by many as a political prisoner and has long insisted he is innocent, is currently due to leave prison next August. Khodorkovsky, 50, and fellow defendant Platon Lebedev were convicted of stealing oil and laundering money in 2010. They were already serving time for tax evasion. The European Court of Human Rights criticised the trials but rejected claims they were politically motivated. As head of the now defunct oil giant Yukos, Khodorkovsky was once Russia's richest man. BENJAMIN C. PIM
Mr Putin told reporters he had received a request from Khodorkovsky, who has been in custody for a decade, to pardon him on humanitarian grounds. But representatives of the Kremlin critic deny a request was made. Khodorkovsky, who is regarded by many as a political prisoner and has long insisted he is innocent, is currently due to leave prison next August. Khodorkovsky, 50, and fellow defendant Platon Lebedev were convicted of stealing oil and laundering money in 2010. They were already serving time for tax evasion. The European Court of Human Rights criticised the trials but rejected claims they were politically motivated. As head of the now defunct oil giant Yukos, Khodorkovsky was once Russia's richest man. BENJAMIN C. PIM
 Speaking to reporters after his annual news conference in Moscow on Thursday, President Putin said he had not received a request from Khodorkovsky in the past. "And then quite recently he wrote such a document and addressed a request for a pardon to me, " Mr Putin said. "He has already been in detention more than 10 years, this is a serious punishment and he is referring to humanitarian circumstances as his mother is ill. " "I think given the circumstances we can take the decision and very soon the decree to pardon him will be signed, " Mr Putin said. Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov told AFP news agency the request had been personally "signed" by Khodorkovsky. But Khodorkovsky's main lawyer, Vadim Klyuvgant, told Russia's Ria-Novosti news agency: "He has not made a request and we do not have information that someone has made a request on his behalf. "We do not have such information although there were requests to pardon him over the years from different individuals. "
Speaking to reporters after his annual news conference in Moscow on Thursday, President Putin said he had not received a request from Khodorkovsky in the past. "And then quite recently he wrote such a document and addressed a request for a pardon to me, " Mr Putin said. "He has already been in detention more than 10 years, this is a serious punishment and he is referring to humanitarian circumstances as his mother is ill. " "I think given the circumstances we can take the decision and very soon the decree to pardon him will be signed, " Mr Putin said. Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov told AFP news agency the request had been personally "signed" by Khodorkovsky. But Khodorkovsky's main lawyer, Vadim Klyuvgant, told Russia's Ria-Novosti news agency: "He has not made a request and we do not have information that someone has made a request on his behalf. "We do not have such information although there were requests to pardon him over the years from different individuals. "
 1. In order to solve traffic problems, governments should tax private car owners heavily and use the money to improve public transportation. What are the advantages and disadvantages of such a solution? 2. The percentage of overweight children in western society has increased by almost 20% in the last ten years. Discuss the causes and effects of this disturbing trend and offer a solution.
1. In order to solve traffic problems, governments should tax private car owners heavily and use the money to improve public transportation. What are the advantages and disadvantages of such a solution? 2. The percentage of overweight children in western society has increased by almost 20% in the last ten years. Discuss the causes and effects of this disturbing trend and offer a solution.
 Past time
Past time
 Describing events in the past Main events • The past simple is used to describe finished actions and events in the past. Susan went into the station and bought a ticket.
Describing events in the past Main events • The past simple is used to describe finished actions and events in the past. Susan went into the station and bought a ticket.
 Background description • The past continuous is used to describe actions in progress in the past. • It gives information about the background situation. There were a lot of people waiting in the station. Some were sleeping on the benches, and others were walking up and down. Susan was looking for Graham, so she didn't sit down.
Background description • The past continuous is used to describe actions in progress in the past. • It gives information about the background situation. There were a lot of people waiting in the station. Some were sleeping on the benches, and others were walking up and down. Susan was looking for Graham, so she didn't sit down.
 Past before past • The past perfect is used to make it clear that one past event happens before another past event. • We use the past perfect for the earlier event. By the time the train arrived, Susan had managed to push her way to the front of the crowd. When I arrived at work my boss had been there for 2 hours.
Past before past • The past perfect is used to make it clear that one past event happens before another past event. • We use the past perfect for the earlier event. By the time the train arrived, Susan had managed to push her way to the front of the crowd. When I arrived at work my boss had been there for 2 hours.
 • It is not always necessary to use the past perfect if a time expression makes the order of events clear. Before the train arrived, Susan managed to push her way to the front of the crowd. My boss arrived at work 2 hours before me.
• It is not always necessary to use the past perfect if a time expression makes the order of events clear. Before the train arrived, Susan managed to push her way to the front of the crowd. My boss arrived at work 2 hours before me.
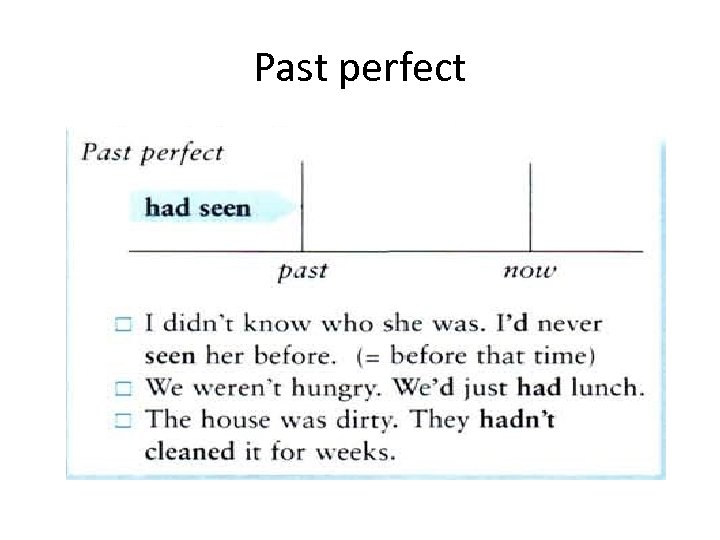 Past perfect
Past perfect
 Past continuous used with past simple • We often use the past continuous first to set the scene, and then the past simple for the separate, completed actions that happen. Susan was looking for Graham, so she didn't sit down. Instead, she tried calling him on her mobile phone.
Past continuous used with past simple • We often use the past continuous first to set the scene, and then the past simple for the separate, completed actions that happen. Susan was looking for Graham, so she didn't sit down. Instead, she tried calling him on her mobile phone.
 • We often contrast an action in progress with a sudden event which interrupts it. While Susan was trying to get onto the platform, a man grabbed her handbag
• We often contrast an action in progress with a sudden event which interrupts it. While Susan was trying to get onto the platform, a man grabbed her handbag
 Compare past continuous and past simple • I was walking home when I met Dave (in the middle of the action) • I walked home last night after the party. (=all the way, completely) • Kate was watching TV when I arrived. • Kate watched a lot of TV when she was ill.
Compare past continuous and past simple • I was walking home when I met Dave (in the middle of the action) • I walked home last night after the party. (=all the way, completely) • Kate was watching TV when I arrived. • Kate watched a lot of TV when she was ill.
 • We use the past simple to say that actions happened in sequence. I was walking along the road when I met Dave, we stopped and had a chat about this and that.
• We use the past simple to say that actions happened in sequence. I was walking along the road when I met Dave, we stopped and had a chat about this and that.
 Compare 1. When Karen arrived, we were having dinner. 2. When Karen arrived, we had dinner. 1. (=we had already started before she arrived) 2. (=Karen arrived and we had dinner together)
Compare 1. When Karen arrived, we were having dinner. 2. When Karen arrived, we had dinner. 1. (=we had already started before she arrived) 2. (=Karen arrived and we had dinner together)
 Past continuous
Past continuous
 Past continuous • The past continuous can be used to describe a repeated action in the past, often an annoying habit. A frequency adverb is necessary. • When Peter was younger, he was always getting into trouble.
Past continuous • The past continuous can be used to describe a repeated action in the past, often an annoying habit. A frequency adverb is necessary. • When Peter was younger, he was always getting into trouble.
 • We can use the past continuous with think, hope and wonder to give a polite or uncertain meaning. • I was thinking of having a party next week. • I was hoping you would join us at the cafe tonight. • I was wondering if you could help me.
• We can use the past continuous with think, hope and wonder to give a polite or uncertain meaning. • I was thinking of having a party next week. • I was hoping you would join us at the cafe tonight. • I was wondering if you could help me.
 Participle clauses • Participle clauses are introduced by the time expressions before, after and while. They have the same subject as the following clause. After struggling with him, Susan pulled the bag from his hands.
Participle clauses • Participle clauses are introduced by the time expressions before, after and while. They have the same subject as the following clause. After struggling with him, Susan pulled the bag from his hands.
 Habits in the past Past simple • The past simple is used to describe past habits or states. • A time expression is usually necessary. I always got up at six in those days, (habit) I lived in Austria for several years. (state)
Habits in the past Past simple • The past simple is used to describe past habits or states. • A time expression is usually necessary. I always got up at six in those days, (habit) I lived in Austria for several years. (state)
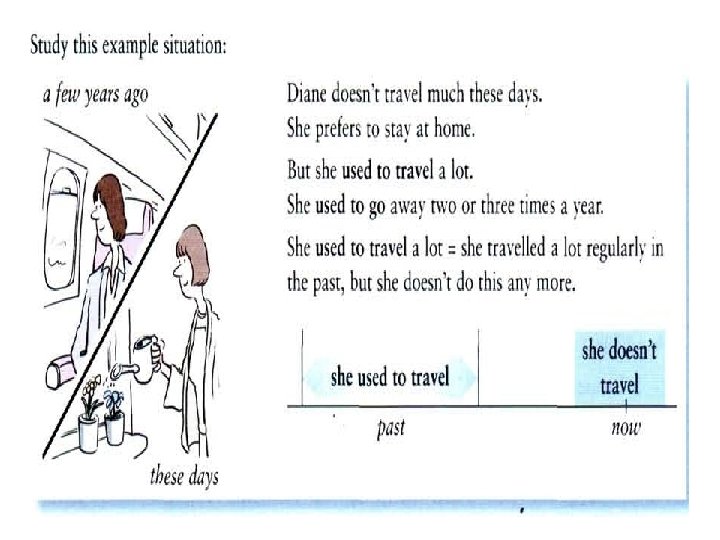
 Used to • Used to is used to describe past habits or states. A time expression is not necessary. I used to get up at six, but now I get up at eight. I used to own a horse. (I owned a horse once. ) • With negatives and questions used to becomes use to. I didn't use to like beer. Did you use to swim every day?
Used to • Used to is used to describe past habits or states. A time expression is not necessary. I used to get up at six, but now I get up at eight. I used to own a horse. (I owned a horse once. ) • With negatives and questions used to becomes use to. I didn't use to like beer. Did you use to swim every day?
 • When we used to we suggest that the action is no longer true and so make a strong contrast with the present.
• When we used to we suggest that the action is no longer true and so make a strong contrast with the present.
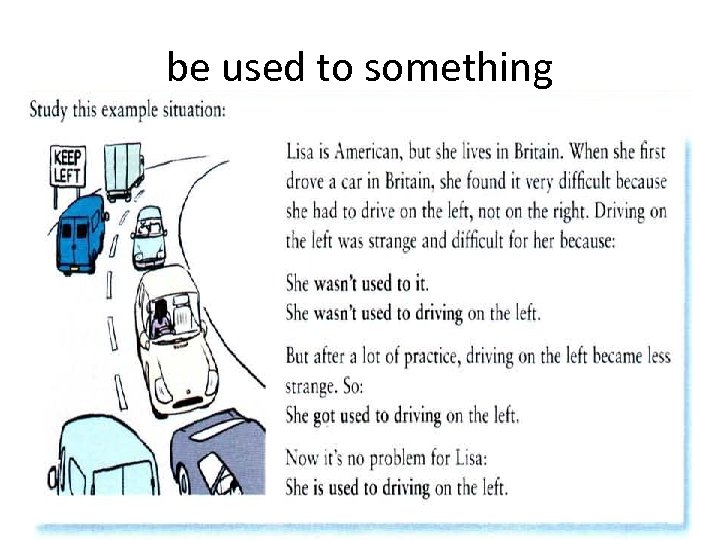 be used to something
be used to something
 I’m used to something= it is not new or strange for me:
I’m used to something= it is not new or strange for me:
 Do not confuse I am used to doing and I used to do: do
Do not confuse I am used to doing and I used to do: do
 Would • Would is used to describe a person's typical activities in the past. • It can only be used to describe repeated actions, not states. It is mainly used in writing, and in personal reminiscences. • Every evening was the same. Jack would turn on the radio, light his pipe and fall asleep.
Would • Would is used to describe a person's typical activities in the past. • It can only be used to describe repeated actions, not states. It is mainly used in writing, and in personal reminiscences. • Every evening was the same. Jack would turn on the radio, light his pipe and fall asleep.
 choose the most suitable verb form in each sentence. a) I suddenly remembered that I forgot/had forgotten my keys. b) While Diana watched/was watching her favourite television programme, there was a power-cut. c) Tom used to live/is used to live in the house at the end of the street. d) Who was driving/drove the car at the time of the accident? e) By the time Sheila got back, Chris went/had gone.
choose the most suitable verb form in each sentence. a) I suddenly remembered that I forgot/had forgotten my keys. b) While Diana watched/was watching her favourite television programme, there was a power-cut. c) Tom used to live/is used to live in the house at the end of the street. d) Who was driving/drove the car at the time of the accident? e) By the time Sheila got back, Chris went/had gone.
 f) David ate/had eaten Japanese food before, so he knew what to order. g) I did/was doing some shopping yesterday, when I saw that Dutch friend of yours. h) I used to like/was liking sweets much more than I do now. i) What exactly were you doing/did you do when I came into your office yesterday? j) Laura missed the party because no-one was telling/had told her about it. k) Tanya was being/used to be a doctor.
f) David ate/had eaten Japanese food before, so he knew what to order. g) I did/was doing some shopping yesterday, when I saw that Dutch friend of yours. h) I used to like/was liking sweets much more than I do now. i) What exactly were you doing/did you do when I came into your office yesterday? j) Laura missed the party because no-one was telling/had told her about it. k) Tanya was being/used to be a doctor.
 answers
answers
 Put each verb in brackets into a suitable past verb form. Only use the past perfect where this is absolutely necessary a) While I (try) __to get my car started, a passing car (stop) __and the driver (offer)__ to help me. b) The police (pay)__ no attention to Clare's complaint because she (phone)__ them so many times before. c) Mary (not wear)__ her glasses at the time, so she (not notice) __what kind of car the man (drive) __.
Put each verb in brackets into a suitable past verb form. Only use the past perfect where this is absolutely necessary a) While I (try) __to get my car started, a passing car (stop) __and the driver (offer)__ to help me. b) The police (pay)__ no attention to Clare's complaint because she (phone)__ them so many times before. c) Mary (not wear)__ her glasses at the time, so she (not notice) __what kind of car the man (drive) __.
 d) Nick (lie)__ down on the grass for a while, next to some tourists who (feed)__ the ducks. e) Tony (admit)__ that he (hit)__ the other car, but said that he (not damage)__ it. f) Sorry, I (not listen)__ to you. I (think)__about something else. g) Helen (feel)__ very tired, and when she (finish) __ her work, she (fall)__ asleep.
d) Nick (lie)__ down on the grass for a while, next to some tourists who (feed)__ the ducks. e) Tony (admit)__ that he (hit)__ the other car, but said that he (not damage)__ it. f) Sorry, I (not listen)__ to you. I (think)__about something else. g) Helen (feel)__ very tired, and when she (finish) __ her work, she (fall)__ asleep.
 h) The police (get)__ to Clare's house as fast as they could, but the burglars (disappear)__ i) I (phone)__ you last night but you (not answer)___. What (you do) ___? j) We (not go)__ out yesterday because it (rain)__.
h) The police (get)__ to Clare's house as fast as they could, but the burglars (disappear)__ i) I (phone)__ you last night but you (not answer)___. What (you do) ___? j) We (not go)__ out yesterday because it (rain)__.
 answers
answers


