9c47b6360652e170bd42aae5dbbd0d84.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Hem-Onc Emergencies Ratnoff/Weisman Katia Khoury PGY 3 S
Hem-Onc Emergencies Ratnoff/Weisman Katia Khoury PGY 3 S
 Outline S Welcome to Seidman S Helpful tips S Febrile neutropenia S Tumor lysis syndrome S Acute Chest S Acute leukemia S Cord compression
Outline S Welcome to Seidman S Helpful tips S Febrile neutropenia S Tumor lysis syndrome S Acute Chest S Acute leukemia S Cord compression
 Welcome to Seidman S Patients are sicker (mini-ICU) S Check your own pulse first S Do not hesitate to ask for help
Welcome to Seidman S Patients are sicker (mini-ICU) S Check your own pulse first S Do not hesitate to ask for help
 Welcome to Seidman S Ratnoff: Hem-Onc attending S Weisman: Hospitalist, consulting services S Cap is 8 per intern (10 with AI) S Interdisciplinary meetings on T Th at 1 pm (seniors) S Daily huddle on S 4 at 8 am (seniors) S Teaching Wednesdays at 1 pm
Welcome to Seidman S Ratnoff: Hem-Onc attending S Weisman: Hospitalist, consulting services S Cap is 8 per intern (10 with AI) S Interdisciplinary meetings on T Th at 1 pm (seniors) S Daily huddle on S 4 at 8 am (seniors) S Teaching Wednesdays at 1 pm
 Welcome to Seidman, and UH S x= floor number S Seidman floors: 63 xxx S Towers: 420 x 0 S Seidman 3 nutrition room: 4321* S Seidman 4 nutrition room: 1379* S Lakeside: 415 x 0 S Wolfgang: 63830 S Lakeside 55: 47405 S Seidman appointments: 43951 S ED: 43723 S Plasmapheresis is back at UH!
Welcome to Seidman, and UH S x= floor number S Seidman floors: 63 xxx S Towers: 420 x 0 S Seidman 3 nutrition room: 4321* S Seidman 4 nutrition room: 1379* S Lakeside: 415 x 0 S Wolfgang: 63830 S Lakeside 55: 47405 S Seidman appointments: 43951 S ED: 43723 S Plasmapheresis is back at UH!
 Oncologic History S Who is their oncologist? S When was their last chemo? (Check on EMR IV chemo) S What was their last chemo? (know your acronyms) S Did they get any medications with chemo? (G-CSF) S What is their previous oncologic course? S What access do they have? (mediport, PICC? ) S Sickle cell: check care path in portal and OARRS S Inform primary oncologist of patient’s admission
Oncologic History S Who is their oncologist? S When was their last chemo? (Check on EMR IV chemo) S What was their last chemo? (know your acronyms) S Did they get any medications with chemo? (G-CSF) S What is their previous oncologic course? S What access do they have? (mediport, PICC? ) S Sickle cell: check care path in portal and OARRS S Inform primary oncologist of patient’s admission
 Helpful tips S Write your consultants’ pagers and frequently used numbers on the board; it will help the whole team S Keep a small notebook with helpful and common numbers and tips you fill frequently use S Communicate with the nurses and social workers S Communicate with your patients and their families S Write clinical event notes with major updates
Helpful tips S Write your consultants’ pagers and frequently used numbers on the board; it will help the whole team S Keep a small notebook with helpful and common numbers and tips you fill frequently use S Communicate with the nurses and social workers S Communicate with your patients and their families S Write clinical event notes with major updates
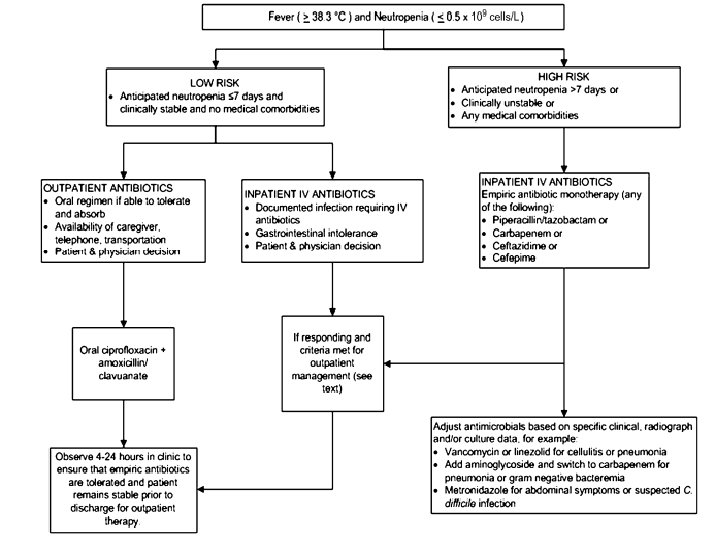
 Febrile Neutropenia S ANC<500 or ANC<1000 with expected nadir <500 over next 48 hours S T 38. 0 for >1 hour or T>38. 3 once S ANC=WBC count x neutrophils S Is patient HDS? Check set of vitals. Stable for floor? S Examine patient: any localizing symptoms? Any role for imaging? S Cultures STAT (2 sets bld cx peripheral, culture from lines or ports, sputum or stool cx/C Diff or wound cx as indicated), UA, UCx, CXR 2 view
Febrile Neutropenia S ANC<500 or ANC<1000 with expected nadir <500 over next 48 hours S T 38. 0 for >1 hour or T>38. 3 once S ANC=WBC count x neutrophils S Is patient HDS? Check set of vitals. Stable for floor? S Examine patient: any localizing symptoms? Any role for imaging? S Cultures STAT (2 sets bld cx peripheral, culture from lines or ports, sputum or stool cx/C Diff or wound cx as indicated), UA, UCx, CXR 2 view
 Febrile Neutropenia S Cover broadly (G+/G- /pseudomonas/fungals) TIME SENSITIVE S Check previous culture data (in portal) S Neutropenic diet, neutropenic precautions, CBC with differential
Febrile Neutropenia S Cover broadly (G+/G- /pseudomonas/fungals) TIME SENSITIVE S Check previous culture data (in portal) S Neutropenic diet, neutropenic precautions, CBC with differential
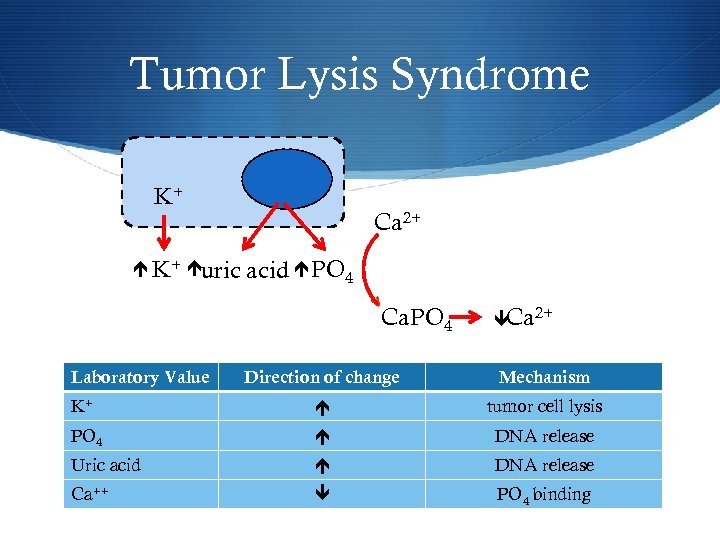 Tumor Lysis Syndrome K+ uric Ca 2+ acid PO 4 v Ca. PO 4 Laboratory Value Ca 2+ Direction of change Mechanism K+ tumor cell lysis PO 4 DNA release Uric acid DNA release Ca++ PO 4 binding
Tumor Lysis Syndrome K+ uric Ca 2+ acid PO 4 v Ca. PO 4 Laboratory Value Ca 2+ Direction of change Mechanism K+ tumor cell lysis PO 4 DNA release Uric acid DNA release Ca++ PO 4 binding
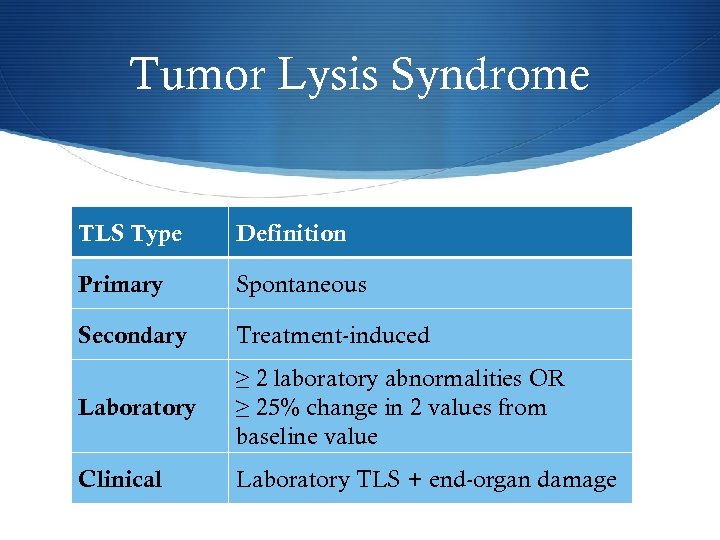 Tumor Lysis Syndrome TLS Type Definition Primary Spontaneous Secondary Treatment-induced Laboratory ≥ 2 laboratory abnormalities OR ≥ 25% change in 2 values from baseline value Clinical Laboratory TLS + end-organ damage
Tumor Lysis Syndrome TLS Type Definition Primary Spontaneous Secondary Treatment-induced Laboratory ≥ 2 laboratory abnormalities OR ≥ 25% change in 2 values from baseline value Clinical Laboratory TLS + end-organ damage
 Tumor Lysis Syndrome S Seen in high grade liquid tumors like leukemias with leukocytosis, high grade lymphomas, and some solid tumors like small cell lung ca S Clinical Features: weakness, arrhythmias, paralysis, acute renal failure, tetany, altered mental status, seizures S Treatment and prevention: fluids fluids S Rasburicase, HD, allopurinol S Check G 6 PD before administering rasburicase (risk of AHA, methemoglobinemia) S BID RFP, phos, ionized calcium, uric acid, LDH, PT/PTT S Keep UOP around 100 cc/hr
Tumor Lysis Syndrome S Seen in high grade liquid tumors like leukemias with leukocytosis, high grade lymphomas, and some solid tumors like small cell lung ca S Clinical Features: weakness, arrhythmias, paralysis, acute renal failure, tetany, altered mental status, seizures S Treatment and prevention: fluids fluids S Rasburicase, HD, allopurinol S Check G 6 PD before administering rasburicase (risk of AHA, methemoglobinemia) S BID RFP, phos, ionized calcium, uric acid, LDH, PT/PTT S Keep UOP around 100 cc/hr
 Acute Chest S Both routine and life threatening admissions will involve pain S Care path and OARRS S CBC, CMP, retic, LDH, bilirubin S CXR S UA/ UCx, Bld cx if indicated
Acute Chest S Both routine and life threatening admissions will involve pain S Care path and OARRS S CBC, CMP, retic, LDH, bilirubin S CXR S UA/ UCx, Bld cx if indicated
 Acute Chest S Hypoxia, chest pain, and new infiltrate on CXR S Red flags: Hgb<2 g below baseline, RR>22, Sa 02<92%, worst HA of life (SAH), new LUQ pain (spl sequestration), fever S Treatment: T&S, pain control, good IV access, urgent heme consult, consider MICU for exchange transfusion S Can use simple transfusion to bridge to exchange transfusion while waiting for MICU bed (does not remove Hgb S)
Acute Chest S Hypoxia, chest pain, and new infiltrate on CXR S Red flags: Hgb<2 g below baseline, RR>22, Sa 02<92%, worst HA of life (SAH), new LUQ pain (spl sequestration), fever S Treatment: T&S, pain control, good IV access, urgent heme consult, consider MICU for exchange transfusion S Can use simple transfusion to bridge to exchange transfusion while waiting for MICU bed (does not remove Hgb S)
 Acute Leukemias (blast crisis) S You do not have to diagnose acute leukemia, just suspect it in the appropriate clinical setting, conduct the workup, and support patients S Clinical presentation: malaise, infection, bleeding (thrombocytopenia, DIC), TLS, hypoxia, leukostasis (high blast count hyperviscosity decreased tissue perfusion MI, ARDS, bowel ischemia, CVA, retinal hemorrhages) S Culture on admission, even if afebrile and asymptomatic S CBC with diff, peripheral smear, peripheral flow cytometry, coags, fibrinogen, D-dimer, RFP S Involve consultants early!
Acute Leukemias (blast crisis) S You do not have to diagnose acute leukemia, just suspect it in the appropriate clinical setting, conduct the workup, and support patients S Clinical presentation: malaise, infection, bleeding (thrombocytopenia, DIC), TLS, hypoxia, leukostasis (high blast count hyperviscosity decreased tissue perfusion MI, ARDS, bowel ischemia, CVA, retinal hemorrhages) S Culture on admission, even if afebrile and asymptomatic S CBC with diff, peripheral smear, peripheral flow cytometry, coags, fibrinogen, D-dimer, RFP S Involve consultants early!
 Cord compression S Patients may not present with pain, and symptoms may be underwhelming S Obtain a good history and neurologic exam S Steroids: dexamethasone 10 mg STAT then 4 mg q 6 (IV or PO) S Consulting teams: ortho/ neurosurgery, radiation oncology S Pain control S **Cord compression protocol at UH
Cord compression S Patients may not present with pain, and symptoms may be underwhelming S Obtain a good history and neurologic exam S Steroids: dexamethasone 10 mg STAT then 4 mg q 6 (IV or PO) S Consulting teams: ortho/ neurosurgery, radiation oncology S Pain control S **Cord compression protocol at UH


