ee055f8c4be326562d64c592e28767ef.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Helsinki University of Technology Dynamic Trust Management for Decision Making Systems using Context Aware Management/Policy Manager Architecture professor Hannu H. Kari Laboratory for Theoretical Computer Science Department of Computer Science and Engineering Helsinki University of Technology (HUT), Espoo, Finland email: Kari [at] tcs [dot] hut [dot] fi NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 1
Helsinki University of Technology Dynamic Trust Management for Decision Making Systems using Context Aware Management/Policy Manager Architecture professor Hannu H. Kari Laboratory for Theoretical Computer Science Department of Computer Science and Engineering Helsinki University of Technology (HUT), Espoo, Finland email: Kari [at] tcs [dot] hut [dot] fi NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 1
 Agenda Helsinki University of Technology • Context Aware Management/Policy Manager (CAM/PM) • Reliable delivery of content using multichannel distribution engine • Certificate revocation • Decision making • Stealth attacks on decision making • Conclusions NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 2
Agenda Helsinki University of Technology • Context Aware Management/Policy Manager (CAM/PM) • Reliable delivery of content using multichannel distribution engine • Certificate revocation • Decision making • Stealth attacks on decision making • Conclusions NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 2
 Helsinki University of Technology Context Aware Management/Policy Manager (CAM/PM) NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 3
Helsinki University of Technology Context Aware Management/Policy Manager (CAM/PM) NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 3
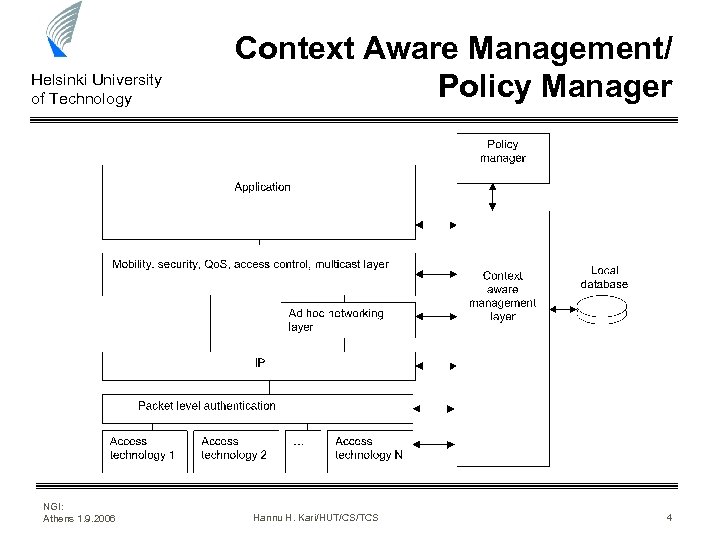 Helsinki University of Technology NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Context Aware Management/ Policy Manager Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 4
Helsinki University of Technology NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Context Aware Management/ Policy Manager Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 4
 Helsinki University of Technology Reliable delivery of content using multichannel distribution engine NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 5
Helsinki University of Technology Reliable delivery of content using multichannel distribution engine NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 5
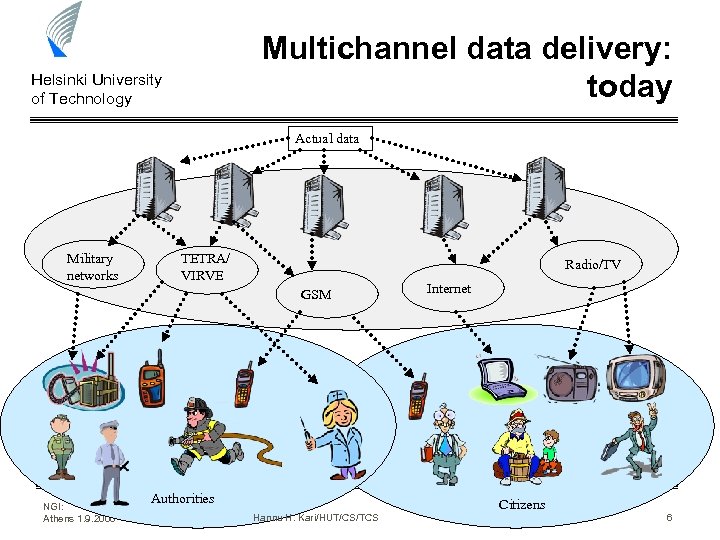 Multichannel data delivery: today Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Authorities Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS Internet Citizens 6
Multichannel data delivery: today Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Authorities Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS Internet Citizens 6
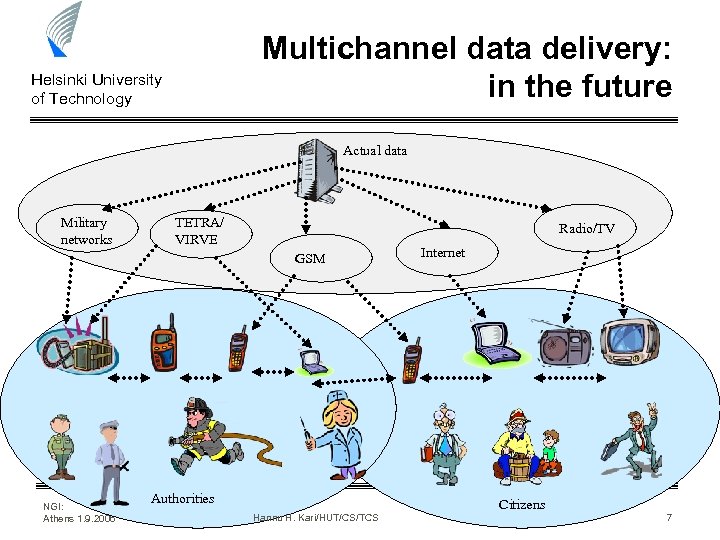 Multichannel data delivery: in the future Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Authorities Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS Internet Citizens 7
Multichannel data delivery: in the future Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Authorities Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS Internet Citizens 7
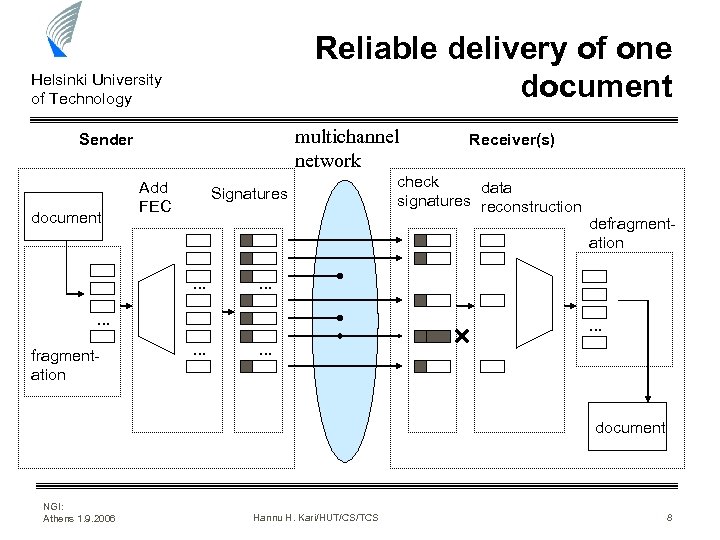 Reliable delivery of one document Helsinki University of Technology multichannel network Sender document Add FEC Signatures . . . check data signatures reconstruction defragmentation . . . fragmentation Receiver(s) . . document NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 8
Reliable delivery of one document Helsinki University of Technology multichannel network Sender document Add FEC Signatures . . . check data signatures reconstruction defragmentation . . . fragmentation Receiver(s) . . document NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 8
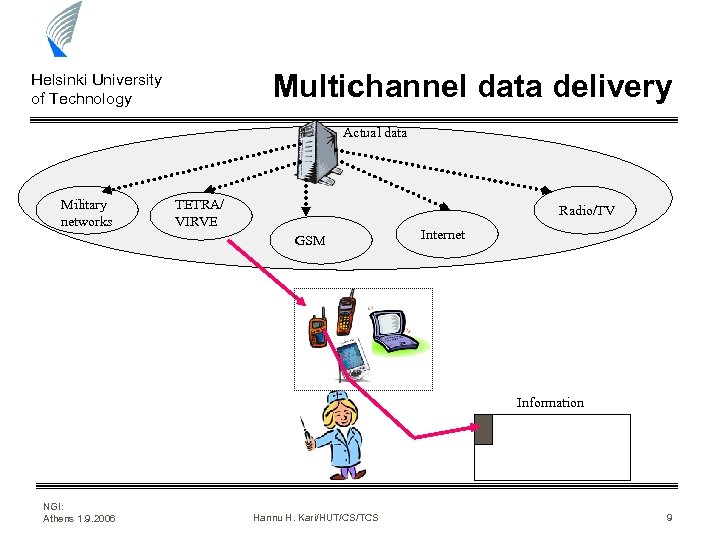 Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 9
Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 9
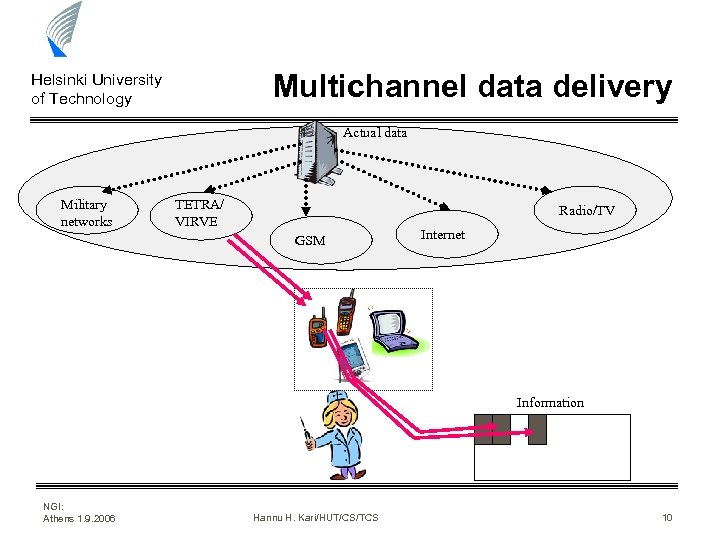 Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 10
Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 10
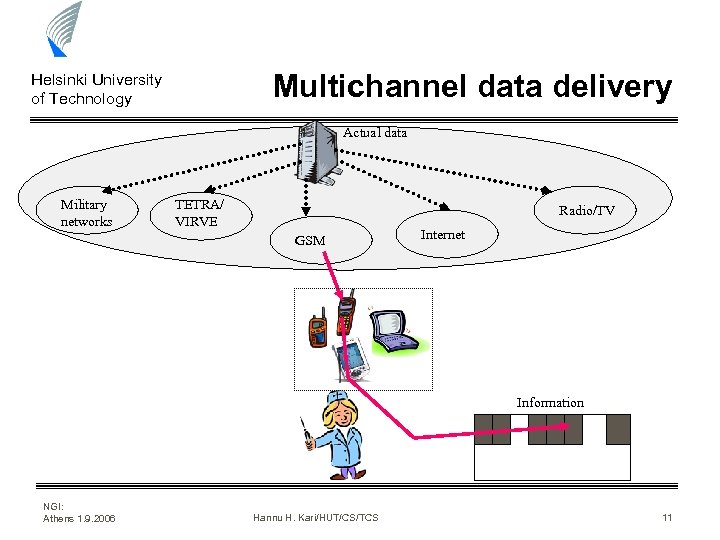 Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 11
Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 11
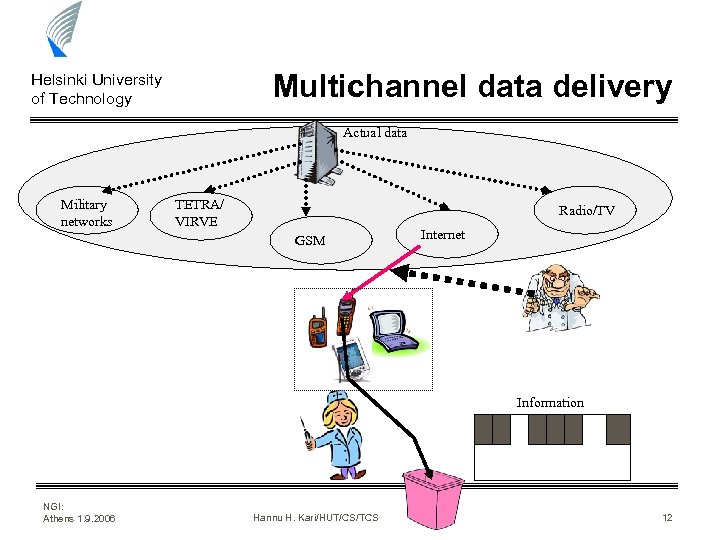 Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 12
Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 12
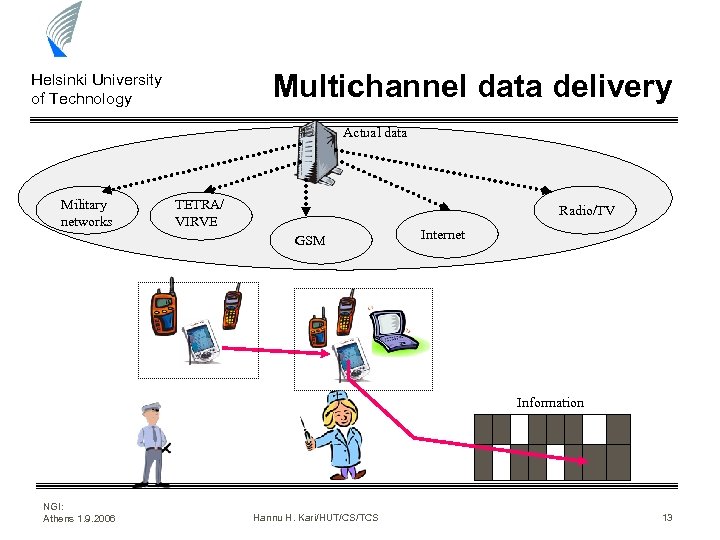 Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 13
Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 13
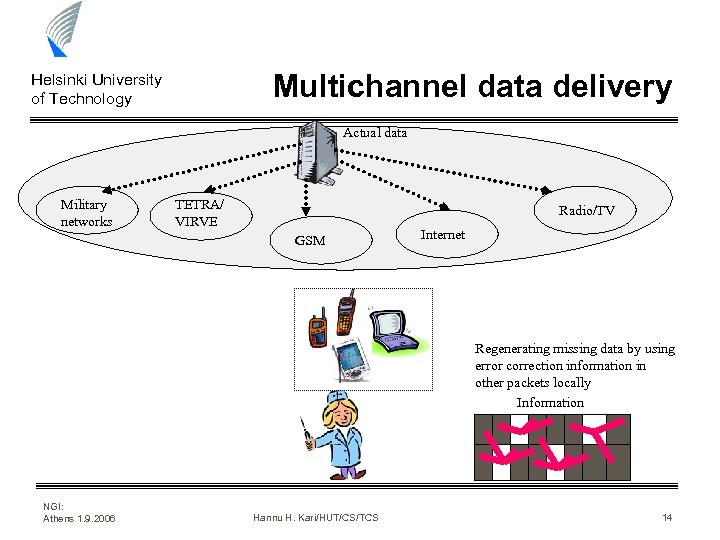 Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Regenerating missing data by using error correction information in other packets locally Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 14
Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet Regenerating missing data by using error correction information in other packets locally Information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 14
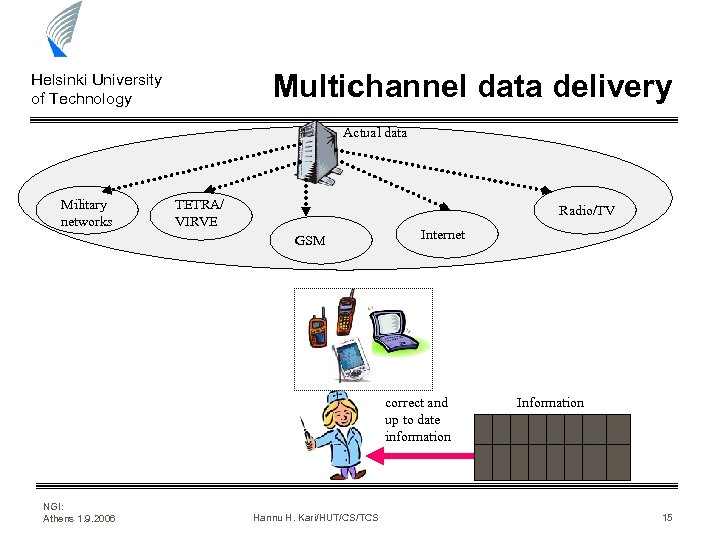 Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet correct and up to date information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS Information 15
Multichannel data delivery Helsinki University of Technology Actual data Military networks TETRA/ VIRVE Radio/TV GSM Internet correct and up to date information NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS Information 15
 Helsinki University of Technology Certificate revocation NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 16
Helsinki University of Technology Certificate revocation NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 16
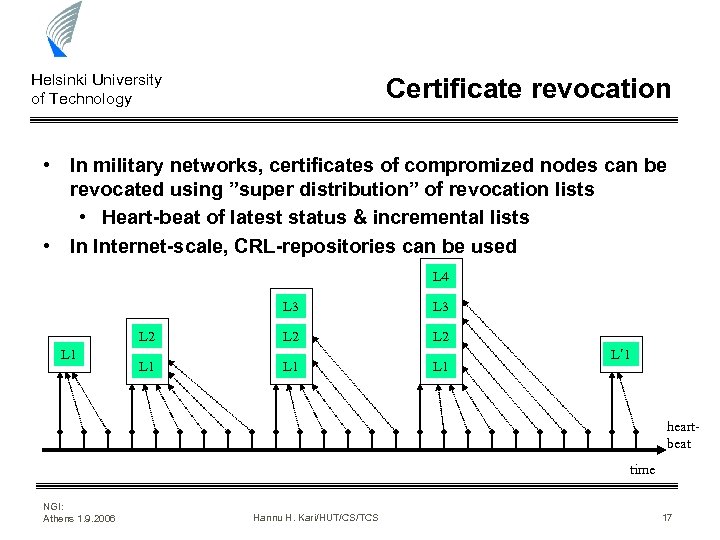 Helsinki University of Technology Certificate revocation • In military networks, certificates of compromized nodes can be revocated using ”super distribution” of revocation lists • Heart-beat of latest status & incremental lists • In Internet-scale, CRL-repositories can be used L 4 L 3 L 2 L 1 L 1 L´ 1 heartbeat time NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 17
Helsinki University of Technology Certificate revocation • In military networks, certificates of compromized nodes can be revocated using ”super distribution” of revocation lists • Heart-beat of latest status & incremental lists • In Internet-scale, CRL-repositories can be used L 4 L 3 L 2 L 1 L 1 L´ 1 heartbeat time NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 17
 Helsinki University of Technology Decision making NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 18
Helsinki University of Technology Decision making NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 18
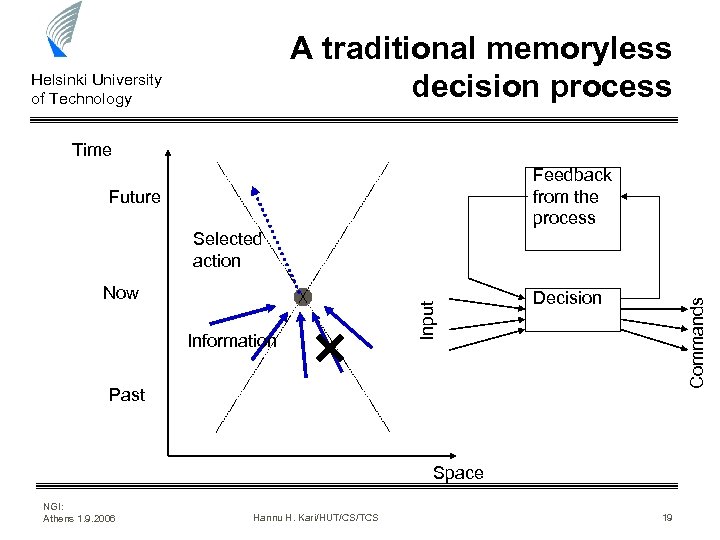 A traditional memoryless decision process Helsinki University of Technology Time Feedback from the process Future Information Decision Commands Now Input Selected action Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 19
A traditional memoryless decision process Helsinki University of Technology Time Feedback from the process Future Information Decision Commands Now Input Selected action Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 19
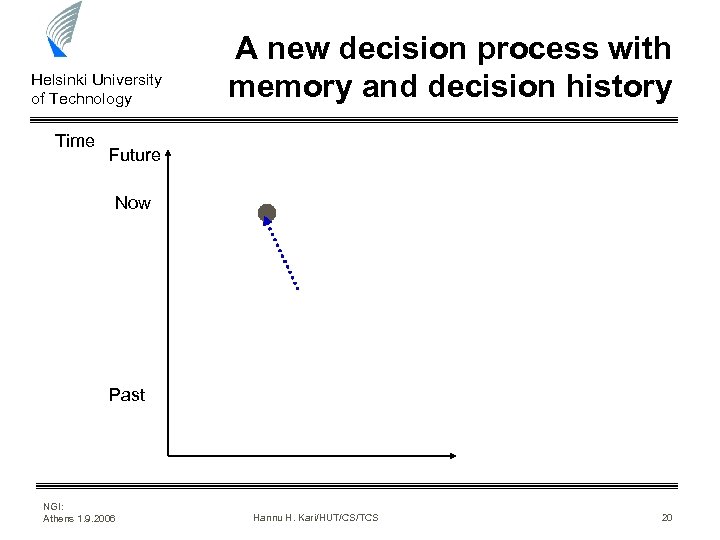 Helsinki University of Technology Time A new decision process with memory and decision history Future Now Past NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 20
Helsinki University of Technology Time A new decision process with memory and decision history Future Now Past NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 20
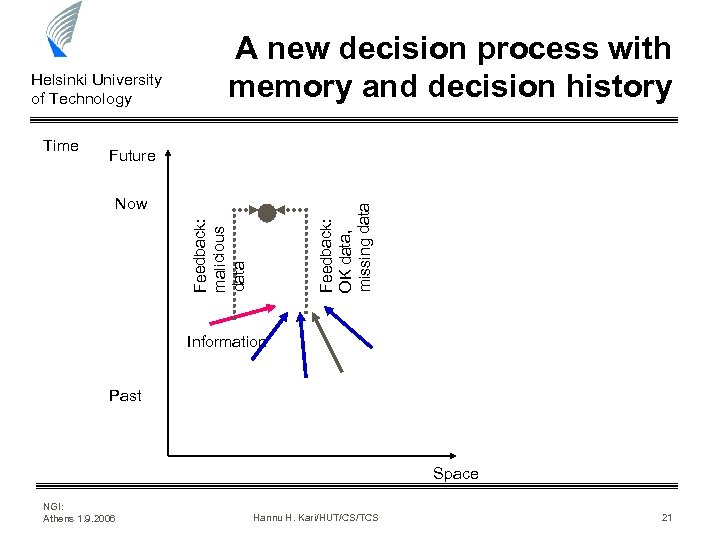 Helsinki University of Technology Time A new decision process with memory and decision history Future Feedback: malicious data Feedback: OK data, missing data Now Information Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 21
Helsinki University of Technology Time A new decision process with memory and decision history Future Feedback: malicious data Feedback: OK data, missing data Now Information Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 21
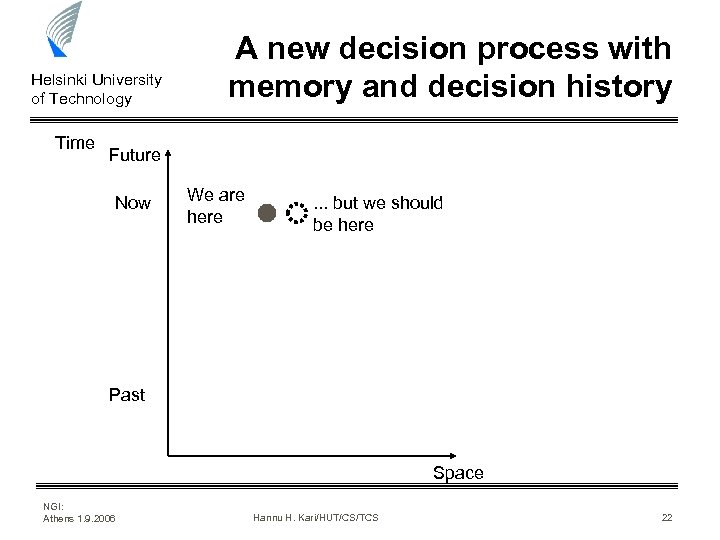 Helsinki University of Technology Time A new decision process with memory and decision history Future Now We are here . . . but we should be here Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 22
Helsinki University of Technology Time A new decision process with memory and decision history Future Now We are here . . . but we should be here Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 22
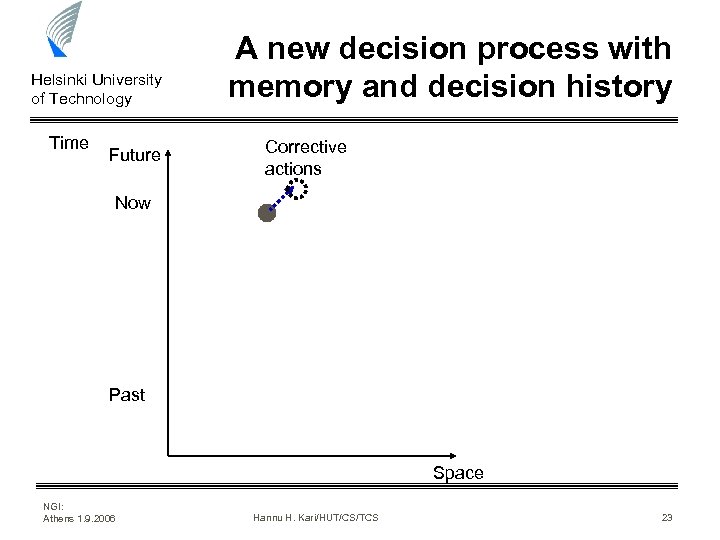 Helsinki University of Technology Time Future A new decision process with memory and decision history Corrective actions Now Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 23
Helsinki University of Technology Time Future A new decision process with memory and decision history Corrective actions Now Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 23
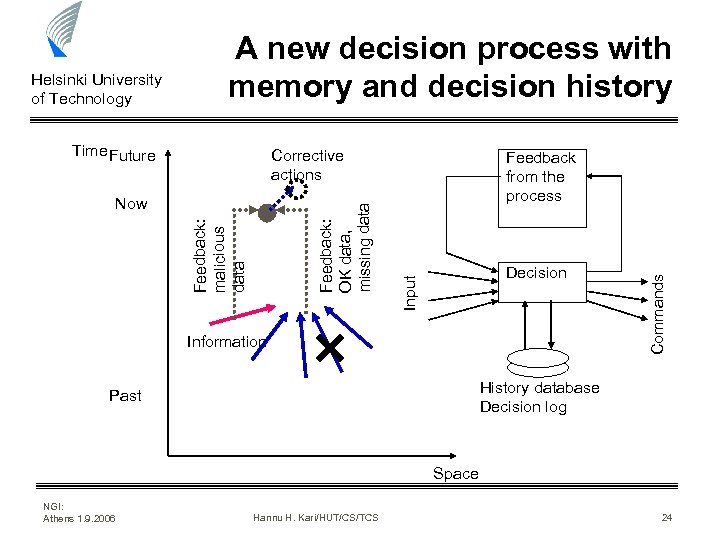 Corrective actions Feedback: malicious data Feedback: OK data, missing data Now Feedback from the process Decision Information Commands Time Future Input Helsinki University of Technology A new decision process with memory and decision history History database Decision log Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 24
Corrective actions Feedback: malicious data Feedback: OK data, missing data Now Feedback from the process Decision Information Commands Time Future Input Helsinki University of Technology A new decision process with memory and decision history History database Decision log Past Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 24
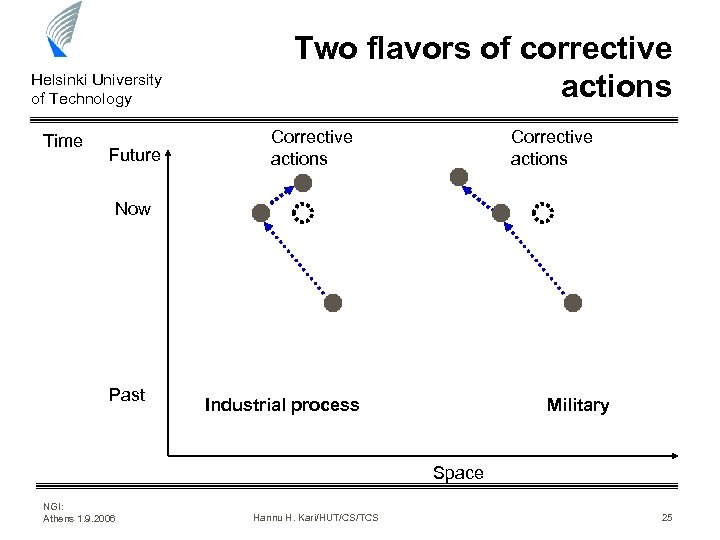 Helsinki University of Technology Time Future Two flavors of corrective actions Corrective actions Now Past Industrial process Military Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 25
Helsinki University of Technology Time Future Two flavors of corrective actions Corrective actions Now Past Industrial process Military Space NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 25
 Helsinki University of Technology Stealth attacks on decision making NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 26
Helsinki University of Technology Stealth attacks on decision making NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 26
 Attack flavors Helsinki University of Technology • Brute force attack • Radical distortion of the enemy’s decision making • Usable only once • E. g. , • Military operation at transition phase • Surgical attack • Minimal effort, usually undetectable, reusable • E. g. , • Stock market manipulation • Stealth attack against decision making NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 27
Attack flavors Helsinki University of Technology • Brute force attack • Radical distortion of the enemy’s decision making • Usable only once • E. g. , • Military operation at transition phase • Surgical attack • Minimal effort, usually undetectable, reusable • E. g. , • Stock market manipulation • Stealth attack against decision making NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 27
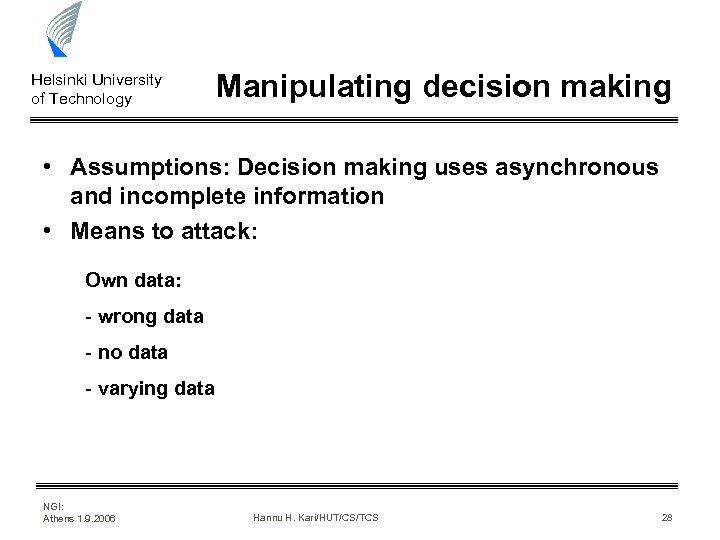 Helsinki University of Technology Manipulating decision making • Assumptions: Decision making uses asynchronous and incomplete information • Means to attack: Own data: - wrong data - no data - varying data NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 28
Helsinki University of Technology Manipulating decision making • Assumptions: Decision making uses asynchronous and incomplete information • Means to attack: Own data: - wrong data - no data - varying data NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 28
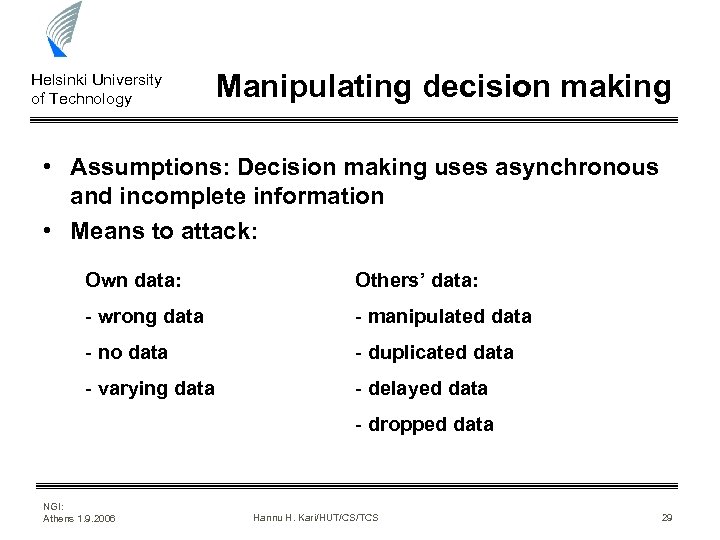 Helsinki University of Technology Manipulating decision making • Assumptions: Decision making uses asynchronous and incomplete information • Means to attack: Own data: Others’ data: - wrong data - manipulated data - no data - duplicated data - varying data - delayed data - dropped data NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 29
Helsinki University of Technology Manipulating decision making • Assumptions: Decision making uses asynchronous and incomplete information • Means to attack: Own data: Others’ data: - wrong data - manipulated data - no data - duplicated data - varying data - delayed data - dropped data NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 29
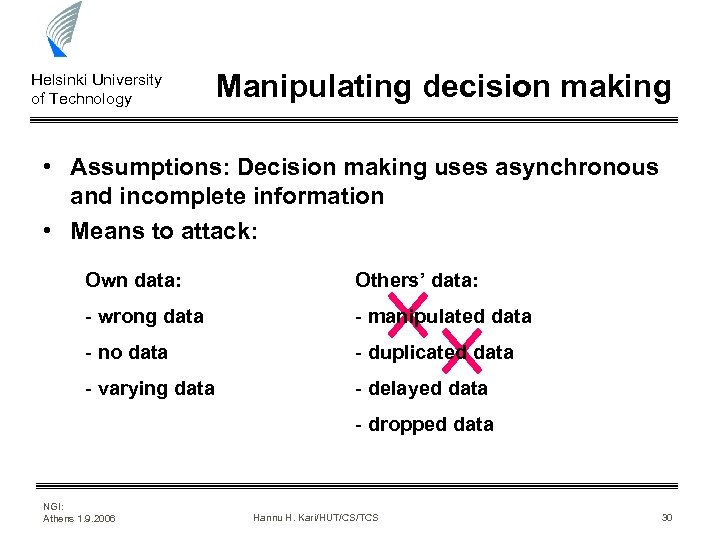 Helsinki University of Technology Manipulating decision making • Assumptions: Decision making uses asynchronous and incomplete information • Means to attack: Own data: Others’ data: - wrong data - manipulated data - no data - duplicated data - varying data - delayed data - dropped data NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 30
Helsinki University of Technology Manipulating decision making • Assumptions: Decision making uses asynchronous and incomplete information • Means to attack: Own data: Others’ data: - wrong data - manipulated data - no data - duplicated data - varying data - delayed data - dropped data NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 30
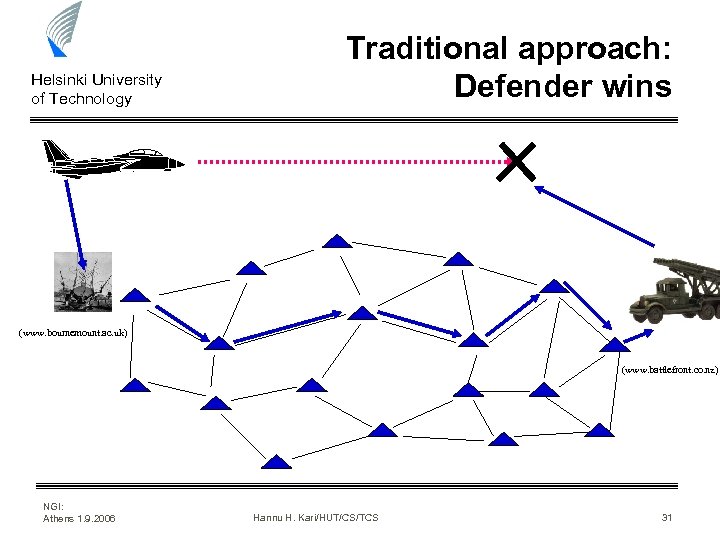 Helsinki University of Technology Traditional approach: Defender wins (www. bournemount. ac. uk) (www. battlefront. co. nz) NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 31
Helsinki University of Technology Traditional approach: Defender wins (www. bournemount. ac. uk) (www. battlefront. co. nz) NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 31
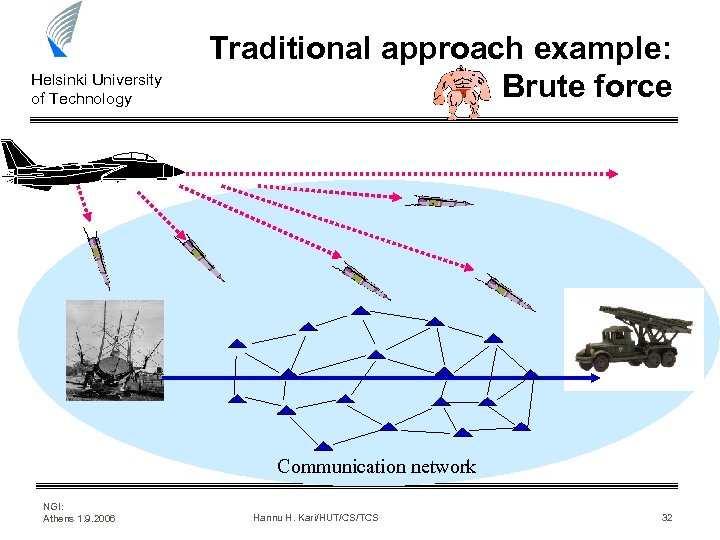 Helsinki University of Technology Traditional approach example: Brute force Communication network NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 32
Helsinki University of Technology Traditional approach example: Brute force Communication network NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 32
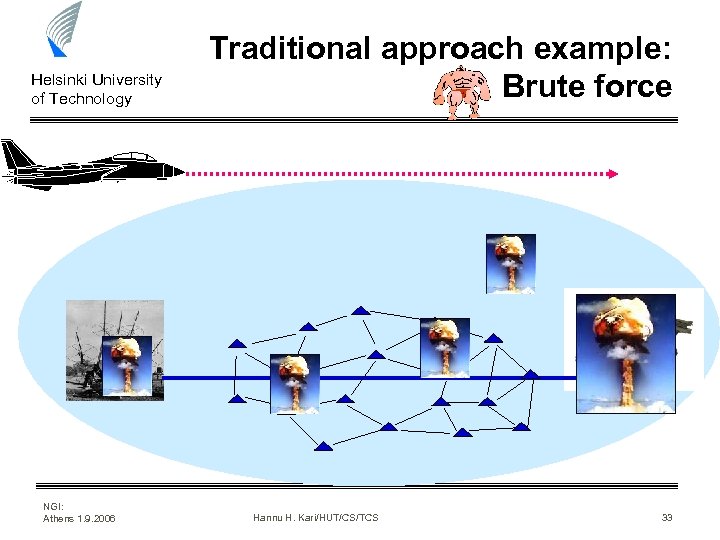 Helsinki University of Technology Traditional approach example: Brute force www. battlefront. co. nz NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 33
Helsinki University of Technology Traditional approach example: Brute force www. battlefront. co. nz NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 33
 Helsinki University of Technology Definition of a stealth attack (against computer network) • Network seems to operate under normal operating principles • At any time, behavior of all nodes (especially malevolent nodes) is according to expectations • Malevolent nodes do not generate any significant extra traffic • Attack may be external or internal • Results • Important messages are lost/delayed • Enemy can reuse the same attack again and again • Benevolent nodes may be blamed for misbehavior NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 34
Helsinki University of Technology Definition of a stealth attack (against computer network) • Network seems to operate under normal operating principles • At any time, behavior of all nodes (especially malevolent nodes) is according to expectations • Malevolent nodes do not generate any significant extra traffic • Attack may be external or internal • Results • Important messages are lost/delayed • Enemy can reuse the same attack again and again • Benevolent nodes may be blamed for misbehavior NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 34
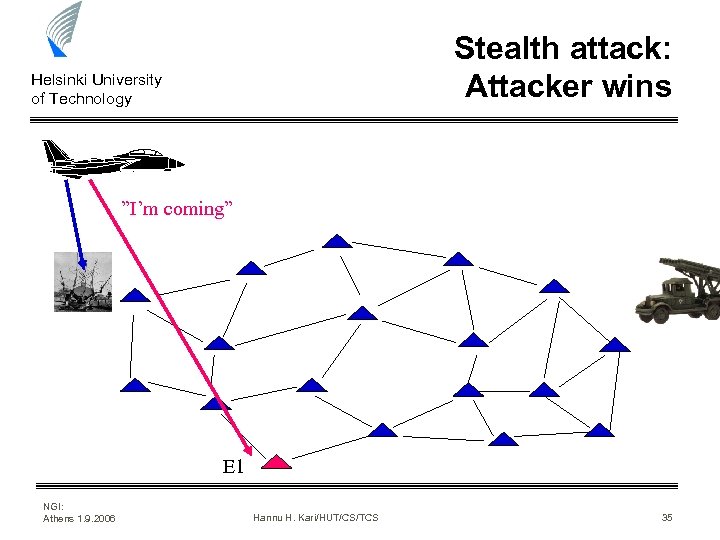 Stealth attack: Attacker wins Helsinki University of Technology ”I’m coming” E 1 NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 35
Stealth attack: Attacker wins Helsinki University of Technology ”I’m coming” E 1 NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 35
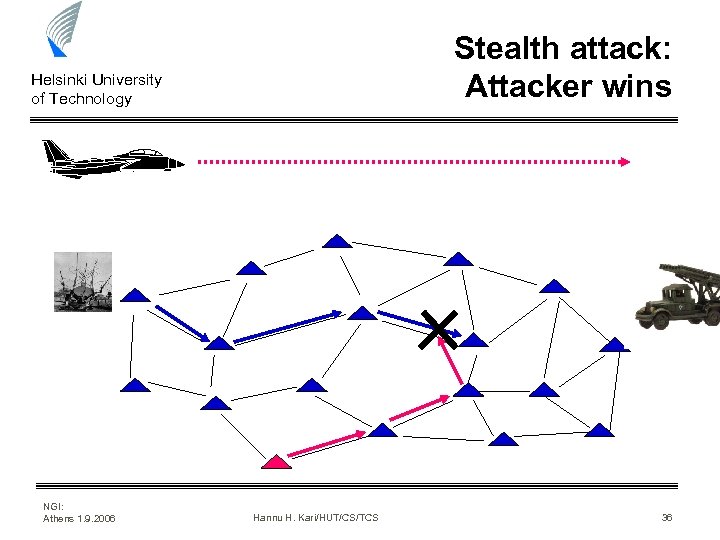 Stealth attack: Attacker wins Helsinki University of Technology NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 36
Stealth attack: Attacker wins Helsinki University of Technology NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 36
 Helsinki University of Technology Stealth attack methods • It is the matter of information superiority • When we know, in advance, what will happen in the defender’s network, we can easily block the traffic with minimum effort • Few seconds/fraction of seconds is enough to gain the advantage • Attack can resemble to a ordinary network anomaly that may occur occasionally • Defender thinks that ”it was Mr. Murphy again” NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 37
Helsinki University of Technology Stealth attack methods • It is the matter of information superiority • When we know, in advance, what will happen in the defender’s network, we can easily block the traffic with minimum effort • Few seconds/fraction of seconds is enough to gain the advantage • Attack can resemble to a ordinary network anomaly that may occur occasionally • Defender thinks that ”it was Mr. Murphy again” NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 37
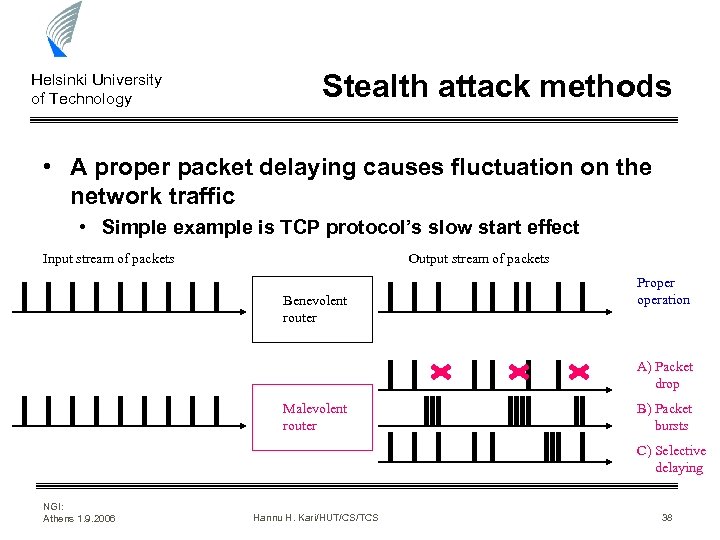 Helsinki University of Technology Stealth attack methods • A proper packet delaying causes fluctuation on the network traffic • Simple example is TCP protocol’s slow start effect Input stream of packets Output stream of packets Benevolent router Properation A) Packet drop Malevolent router B) Packet bursts C) Selective delaying NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 38
Helsinki University of Technology Stealth attack methods • A proper packet delaying causes fluctuation on the network traffic • Simple example is TCP protocol’s slow start effect Input stream of packets Output stream of packets Benevolent router Properation A) Packet drop Malevolent router B) Packet bursts C) Selective delaying NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 38
 Helsinki University of Technology Conclusions NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 39
Helsinki University of Technology Conclusions NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 39
 Conclusions Helsinki University of Technology • • • Information integrity protection • Security solutions can guarantee information integrity • . . . but not that we get all necessary data Þ Decision making can be done with accurate, but partial information CAM/PM • Computers need rule-based decision making system • Rules can be dynamically updated Þ We can change dynamically nodes’ behavior A new decision making system is needed • It shall be capable of remaking decisions when previous decisions were made based on wrong or incomplete information. Þ We can to redo our decision if we have been misinformed NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 40
Conclusions Helsinki University of Technology • • • Information integrity protection • Security solutions can guarantee information integrity • . . . but not that we get all necessary data Þ Decision making can be done with accurate, but partial information CAM/PM • Computers need rule-based decision making system • Rules can be dynamically updated Þ We can change dynamically nodes’ behavior A new decision making system is needed • It shall be capable of remaking decisions when previous decisions were made based on wrong or incomplete information. Þ We can to redo our decision if we have been misinformed NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 40
 Helsinki University of Technology Thank you, Questions? NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 41
Helsinki University of Technology Thank you, Questions? NGI: Athens 1. 9. 2006 Hannu H. Kari/HUT/CS/TCS 41


