261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70
 Help Desk, Customer Service and Support With thanks to Rabih Neouchi William Luthi University of Alberta ICT-management Fall 2004 Wim De Bruyn, Bert Van Vreckem
Help Desk, Customer Service and Support With thanks to Rabih Neouchi William Luthi University of Alberta ICT-management Fall 2004 Wim De Bruyn, Bert Van Vreckem
 Outline n n n n Introduction to Help Desks Help Desk Case Logging Distributed Help Desks Examples of Help Desk Technologies Security Issues Future Trends (AI Approaches) Summary References
Outline n n n n Introduction to Help Desks Help Desk Case Logging Distributed Help Desks Examples of Help Desk Technologies Security Issues Future Trends (AI Approaches) Summary References
 Introduction to Help Desks n n n Motivation of Help Desks Architecture of Classic Models Problems in Classic Models Politics What Users Expect
Introduction to Help Desks n n n Motivation of Help Desks Architecture of Classic Models Problems in Classic Models Politics What Users Expect
 Motivation of Help Desks n n Cope with evolving technology As you increase complexity n n n Probability of failure grows exponentially The number of available technicians becomes limited Help desk operator’s expertise tend to diverge (do not overlap) Problem solving experience becomes distributed and changes over time Expertise needed exceeds resources available to end users Assist the user’s needs
Motivation of Help Desks n n Cope with evolving technology As you increase complexity n n n Probability of failure grows exponentially The number of available technicians becomes limited Help desk operator’s expertise tend to diverge (do not overlap) Problem solving experience becomes distributed and changes over time Expertise needed exceeds resources available to end users Assist the user’s needs
![Architecture of Classic Models Example of Support Layers [1] Architecture of Classic Models Example of Support Layers [1]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-5.jpg) Architecture of Classic Models Example of Support Layers [1]
Architecture of Classic Models Example of Support Layers [1]
![Architecture of Classic Models Call Flow in a Help Desk Structure [2] Architecture of Classic Models Call Flow in a Help Desk Structure [2]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-6.jpg) Architecture of Classic Models Call Flow in a Help Desk Structure [2]
Architecture of Classic Models Call Flow in a Help Desk Structure [2]
 Problems n n Handling support requests efficiently Efficient use of employee knowledge Reduction of maintenance costs Politics Potential Pitfalls of a Dispatcher [2]
Problems n n Handling support requests efficiently Efficient use of employee knowledge Reduction of maintenance costs Politics Potential Pitfalls of a Dispatcher [2]
![Politics [5] Politics [5]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-8.jpg) Politics [5]
Politics [5]
 What Users Expect n Help Desk Operators to provide n n n Guidelines on how to use products Maintenance tasks Solutions to problems: n n n In a short time With short notice Expertise in all product areas
What Users Expect n Help Desk Operators to provide n n n Guidelines on how to use products Maintenance tasks Solutions to problems: n n n In a short time With short notice Expertise in all product areas
 Help Desk Case Logging n n n n What is Case Logging? General Case Structure Why Log Cases? Help Desk Knowledge Repository Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) Case Reuse Knowledge Engineering of CBHD System
Help Desk Case Logging n n n n What is Case Logging? General Case Structure Why Log Cases? Help Desk Knowledge Repository Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) Case Reuse Knowledge Engineering of CBHD System
 What is Case Logging? n Store request and solutions for each help desk request case [3] n n n n Case Number Date User Help Desk Technician Assigned Problem Description Reason Solution Other Notes
What is Case Logging? n Store request and solutions for each help desk request case [3] n n n n Case Number Date User Help Desk Technician Assigned Problem Description Reason Solution Other Notes
![General Case Structure Help Desk Case [1] General Case Structure Help Desk Case [1]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-12.jpg) General Case Structure Help Desk Case [1]
General Case Structure Help Desk Case [1]
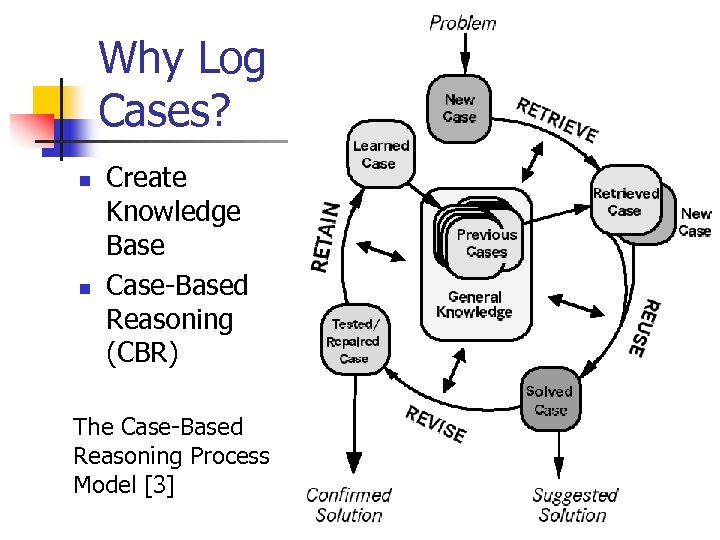 Why Log Cases? n n Create Knowledge Base Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) The Case-Based Reasoning Process Model [3]
Why Log Cases? n n Create Knowledge Base Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) The Case-Based Reasoning Process Model [3]
![Help Desk Knowledge Repository Knowledge acquisition and Transfer [1] Help Desk Knowledge Repository Knowledge acquisition and Transfer [1]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-14.jpg) Help Desk Knowledge Repository Knowledge acquisition and Transfer [1]
Help Desk Knowledge Repository Knowledge acquisition and Transfer [1]
 Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) n Idea: n n n Uses previous support cases and adapts them to solve new problems If no solution is found, a new case is entered into the KB Stores, shares and re-uses experiences
Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) n Idea: n n n Uses previous support cases and adapts them to solve new problems If no solution is found, a new case is entered into the KB Stores, shares and re-uses experiences
![Case Reuse Process of a case-based help desk system [3] Case Reuse Process of a case-based help desk system [3]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-16.jpg) Case Reuse Process of a case-based help desk system [3]
Case Reuse Process of a case-based help desk system [3]
![How to Knowledge Engineer a Case-Based Help Desk System Development Procedure [7] How to Knowledge Engineer a Case-Based Help Desk System Development Procedure [7]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-17.jpg) How to Knowledge Engineer a Case-Based Help Desk System Development Procedure [7]
How to Knowledge Engineer a Case-Based Help Desk System Development Procedure [7]
![Homer Case Example [3, 11] Homer Case Example [3, 11]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-18.jpg) Homer Case Example [3, 11]
Homer Case Example [3, 11]
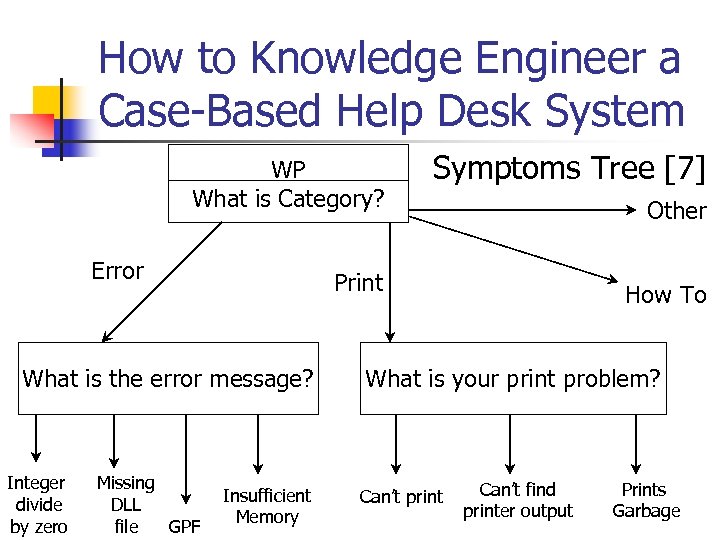 How to Knowledge Engineer a Case-Based Help Desk System WP What is Category? Symptoms Tree [7] Print How To Error What is the error message? Integer divide by zero Missing DLL file GPF Insufficient Memory Other What is your print problem? Can’t print Can’t find printer output Prints Garbage
How to Knowledge Engineer a Case-Based Help Desk System WP What is Category? Symptoms Tree [7] Print How To Error What is the error message? Integer divide by zero Missing DLL file GPF Insufficient Memory Other What is your print problem? Can’t print Can’t find printer output Prints Garbage
 Distributed Help Desk n n n Online Support Model Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Support Problem Prevention and Troubleshooting of Online Support Systems Centralized vs. Decentralized vs. Hybrid Call centers Customer Support Agents
Distributed Help Desk n n n Online Support Model Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Support Problem Prevention and Troubleshooting of Online Support Systems Centralized vs. Decentralized vs. Hybrid Call centers Customer Support Agents
![Online Support Models n Motivation n Long distance phone calls are [10]: n n Online Support Models n Motivation n Long distance phone calls are [10]: n n](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-21.jpg) Online Support Models n Motivation n Long distance phone calls are [10]: n n n Inefficient Ineffective Costly Time consuming Poor in quality
Online Support Models n Motivation n Long distance phone calls are [10]: n n n Inefficient Ineffective Costly Time consuming Poor in quality
![Online Support Model Generations [4] Online Support Model Generations [4]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-22.jpg) Online Support Model Generations [4]
Online Support Model Generations [4]
![First Generation n Informational First Generation Support Site [4] First Generation n Informational First Generation Support Site [4]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-23.jpg) First Generation n Informational First Generation Support Site [4]
First Generation n Informational First Generation Support Site [4]
![Second Generation n Conversational Second Generation Support Site [4] Second Generation n Conversational Second Generation Support Site [4]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-24.jpg) Second Generation n Conversational Second Generation Support Site [4]
Second Generation n Conversational Second Generation Support Site [4]
![Third Generation n Decisional Third Generation Support Site [4] Third Generation n Decisional Third Generation Support Site [4]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-25.jpg) Third Generation n Decisional Third Generation Support Site [4]
Third Generation n Decisional Third Generation Support Site [4]
![Advantages of Online Support [4] n n n Self-service Remote access Single source access Advantages of Online Support [4] n n n Self-service Remote access Single source access](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-26.jpg) Advantages of Online Support [4] n n n Self-service Remote access Single source access Information sharing Assisted service Integration
Advantages of Online Support [4] n n n Self-service Remote access Single source access Information sharing Assisted service Integration
![Potential Disadvantages of Online Support [4] n n n n Not knowing your customers Potential Disadvantages of Online Support [4] n n n n Not knowing your customers](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-27.jpg) Potential Disadvantages of Online Support [4] n n n n Not knowing your customers Useless functions and information Outdated information Staff may not have skills for updating the site Poor Marketing Site does not change with organization Poor site design Negative impact on bottom line
Potential Disadvantages of Online Support [4] n n n n Not knowing your customers Useless functions and information Outdated information Staff may not have skills for updating the site Poor Marketing Site does not change with organization Poor site design Negative impact on bottom line
![Problem Prevention and Troubleshooting [4] n Problem symptoms: n n n At the earliest Problem Prevention and Troubleshooting [4] n Problem symptoms: n n n At the earliest](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-28.jpg) Problem Prevention and Troubleshooting [4] n Problem symptoms: n n n At the earliest stages During the scope definition During the staff selection and design Involving the functions and tools Involving the processes and implementation During site operation
Problem Prevention and Troubleshooting [4] n Problem symptoms: n n n At the earliest stages During the scope definition During the staff selection and design Involving the functions and tools Involving the processes and implementation During site operation
![Earliest Problem Symptoms [4] n “For heaven’s sake, everyone knows we need a support Earliest Problem Symptoms [4] n “For heaven’s sake, everyone knows we need a support](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-29.jpg) Earliest Problem Symptoms [4] n “For heaven’s sake, everyone knows we need a support site. Let’s just do it. ” Symptom Want to build site with no planning Eventual Results Negative support site Possible Causes No formal justification Prognosis and Suggestions Do a cost justification for Recovery Prevention Measure actual costs and return on investment
Earliest Problem Symptoms [4] n “For heaven’s sake, everyone knows we need a support site. Let’s just do it. ” Symptom Want to build site with no planning Eventual Results Negative support site Possible Causes No formal justification Prognosis and Suggestions Do a cost justification for Recovery Prevention Measure actual costs and return on investment
![Problem symptoms during scope definition [4] n “We want the site to eliminate all Problem symptoms during scope definition [4] n “We want the site to eliminate all](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-30.jpg) Problem symptoms during scope definition [4] n “We want the site to eliminate all other support, triple sales, bring world peace, and so on. ” Symptom Scope is unrealistic Eventual Results The site is late, over budget, and poorly implemented Possible Causes Stakeholders have unrealistic expectations Prognosis and Suggestions Negotiate with clients and present a cost for Recovery benefit analysis Prevention Make cost justifications mandatory
Problem symptoms during scope definition [4] n “We want the site to eliminate all other support, triple sales, bring world peace, and so on. ” Symptom Scope is unrealistic Eventual Results The site is late, over budget, and poorly implemented Possible Causes Stakeholders have unrealistic expectations Prognosis and Suggestions Negotiate with clients and present a cost for Recovery benefit analysis Prevention Make cost justifications mandatory
![Problem Symptoms during Staff Selection and Design [4] n “Jim can set up the Problem Symptoms during Staff Selection and Design [4] n “Jim can set up the](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-31.jpg) Problem Symptoms during Staff Selection and Design [4] n “Jim can set up the knowledge base. He’s a whiz at HTML. ” Symptom Person does not know about knowledge bases Eventual Results Knowledge base’s information is incorrect or unclear Possible Causes Perception technical wizards can do anything Prognosis and Suggestions Train the person or find a more suitable for Recovery candidate Prevention Have appropriate people trained in knowledge bases
Problem Symptoms during Staff Selection and Design [4] n “Jim can set up the knowledge base. He’s a whiz at HTML. ” Symptom Person does not know about knowledge bases Eventual Results Knowledge base’s information is incorrect or unclear Possible Causes Perception technical wizards can do anything Prognosis and Suggestions Train the person or find a more suitable for Recovery candidate Prevention Have appropriate people trained in knowledge bases
![Problem symptoms involving functions and tools [4] n “Let’s build our own tools. It Problem symptoms involving functions and tools [4] n “Let’s build our own tools. It](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-32.jpg) Problem symptoms involving functions and tools [4] n “Let’s build our own tools. It can’t be that hard. ” Symptom Want to create tools rather than buy them Eventual Results Project is late and over budget Possible Causes A lack of understanding of tool functionality and complexity Prognosis and Suggestions Scrap it and buy something that works or do for Recovery proper research and analysis for construction Prevention Do thorough analysis of tool requirements
Problem symptoms involving functions and tools [4] n “Let’s build our own tools. It can’t be that hard. ” Symptom Want to create tools rather than buy them Eventual Results Project is late and over budget Possible Causes A lack of understanding of tool functionality and complexity Prognosis and Suggestions Scrap it and buy something that works or do for Recovery proper research and analysis for construction Prevention Do thorough analysis of tool requirements
![Problem symptoms involving processes & implementation [4] n “We can’t really test this stuff Problem symptoms involving processes & implementation [4] n “We can’t really test this stuff](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-33.jpg) Problem symptoms involving processes & implementation [4] n “We can’t really test this stuff until our site is up. ” Symptom Site goes into production without being tested Eventual Results Customers experience problems Possible Causes You don’t know how to test the site Prognosis and Suggestions Poor. Outsource extra help while you test the for Recovery site to fix problems Prevention Make testing mandatory for each site iteration
Problem symptoms involving processes & implementation [4] n “We can’t really test this stuff until our site is up. ” Symptom Site goes into production without being tested Eventual Results Customers experience problems Possible Causes You don’t know how to test the site Prognosis and Suggestions Poor. Outsource extra help while you test the for Recovery site to fix problems Prevention Make testing mandatory for each site iteration
![Problem symptoms during site operation [4] n “Jenna can manage the site along with Problem symptoms during site operation [4] n “Jenna can manage the site along with](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-34.jpg) Problem symptoms during site operation [4] n “Jenna can manage the site along with the four other departments she manages. ” Symptom Site manager does not have time for the site Eventual Results Diminished return and usefulness Possible Causes Lack of understanding or staff shortages Prognosis and Suggestions Create a cost justification for management to for Recovery hire more people for the site Prevention Define site management requirements and create a job description
Problem symptoms during site operation [4] n “Jenna can manage the site along with the four other departments she manages. ” Symptom Site manager does not have time for the site Eventual Results Diminished return and usefulness Possible Causes Lack of understanding or staff shortages Prognosis and Suggestions Create a cost justification for management to for Recovery hire more people for the site Prevention Define site management requirements and create a job description
 Centralized vs. Decentralized vs. Hybrid n n n Centralized Decentralized Hybrid
Centralized vs. Decentralized vs. Hybrid n n n Centralized Decentralized Hybrid
 Centralized Help Desk n Advantage n n Collaboration Disadvantage n May not be responsive to local needs
Centralized Help Desk n Advantage n n Collaboration Disadvantage n May not be responsive to local needs
 Decentralized Help Desk n Advantage n n Each unit can serve local needs Disadvantage n May produced inefficiencies and redundancies
Decentralized Help Desk n Advantage n n Each unit can serve local needs Disadvantage n May produced inefficiencies and redundancies
 Hybrid Approach n Tuft’s IT Support Services Model n n Takes best from both worlds “A seven person support team is funded by the central IT organization but ‘lives’ in the University’s local units’’ [8] Collaborative support team Whole university’s IT needs and local interests are served
Hybrid Approach n Tuft’s IT Support Services Model n n Takes best from both worlds “A seven person support team is funded by the central IT organization but ‘lives’ in the University’s local units’’ [8] Collaborative support team Whole university’s IT needs and local interests are served
 Call Centers n n n Telephony call centers Web-based using telephone and Web-based multimedia call centers
Call Centers n n n Telephony call centers Web-based using telephone and Web-based multimedia call centers
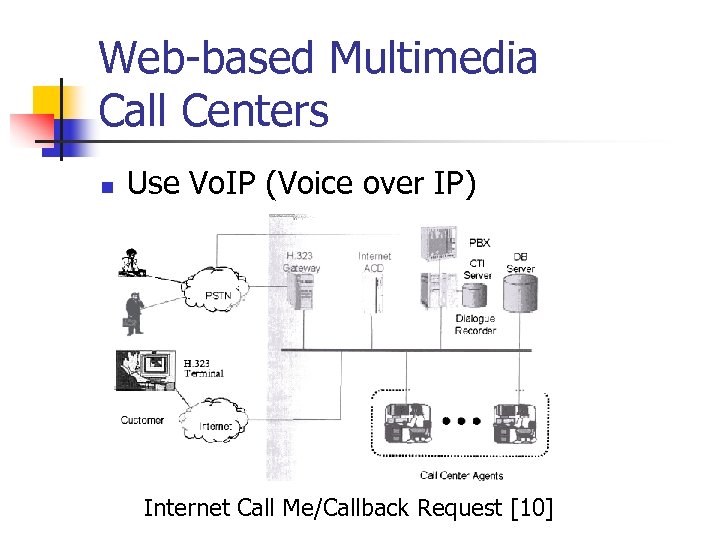 Web-based Multimedia Call Centers n Use Vo. IP (Voice over IP) Internet Call Me/Callback Request [10]
Web-based Multimedia Call Centers n Use Vo. IP (Voice over IP) Internet Call Me/Callback Request [10]
 Customer Support Agents n Callback services n n n Audiovisual interaction with help desks Co-browsing and multimedia presentations Three way teleconferences (customer, agent, another customer) Customer support agent for an e-commerce site [10]
Customer Support Agents n Callback services n n n Audiovisual interaction with help desks Co-browsing and multimedia presentations Three way teleconferences (customer, agent, another customer) Customer support agent for an e-commerce site [10]
 Examples of Help Desk Technologies n n Avrasoft Size. Master Help. Desk People. Soft Help. Desk Blue Ocean Track-It! HOMER
Examples of Help Desk Technologies n n Avrasoft Size. Master Help. Desk People. Soft Help. Desk Blue Ocean Track-It! HOMER
![Size. Master Help. Desk [14] n http: //www. avrasoft. com/sizemaster/ Size. Master Help. Desk [14] n http: //www. avrasoft. com/sizemaster/](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-43.jpg) Size. Master Help. Desk [14] n http: //www. avrasoft. com/sizemaster/
Size. Master Help. Desk [14] n http: //www. avrasoft. com/sizemaster/
![People. Soft Help. Desk [15] n http: //www. peoplesoft. com/corp/en/products /line/crm/help_desk/features. asp People. Soft Help. Desk [15] n http: //www. peoplesoft. com/corp/en/products /line/crm/help_desk/features. asp](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-44.jpg) People. Soft Help. Desk [15] n http: //www. peoplesoft. com/corp/en/products /line/crm/help_desk/features. asp
People. Soft Help. Desk [15] n http: //www. peoplesoft. com/corp/en/products /line/crm/help_desk/features. asp
![Blue Ocean Track-It [16] n http: //www. blueocean. com/smallbusiness/tw ebinfo. htm Blue Ocean Track-It [16] n http: //www. blueocean. com/smallbusiness/tw ebinfo. htm](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-45.jpg) Blue Ocean Track-It [16] n http: //www. blueocean. com/smallbusiness/tw ebinfo. htm
Blue Ocean Track-It [16] n http: //www. blueocean. com/smallbusiness/tw ebinfo. htm
 The HOMER System n HOMER: HOtline Mit ERfahrung Hotline with Experience CAD/CAM Help Desk Daimler-Benz
The HOMER System n HOMER: HOtline Mit ERfahrung Hotline with Experience CAD/CAM Help Desk Daimler-Benz
![The HOMER Architecture [1, 11] Domain Modelling [1] The HOMER Architecture [1, 11] Domain Modelling [1]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-47.jpg) The HOMER Architecture [1, 11] Domain Modelling [1]
The HOMER Architecture [1, 11] Domain Modelling [1]
 Modes of Execution in HOMER n User Driven Mode n n Operator is experienced System Driven Mode n Operator lacks experience User Driven Mode [1]
Modes of Execution in HOMER n User Driven Mode n n Operator is experienced System Driven Mode n Operator lacks experience User Driven Mode [1]
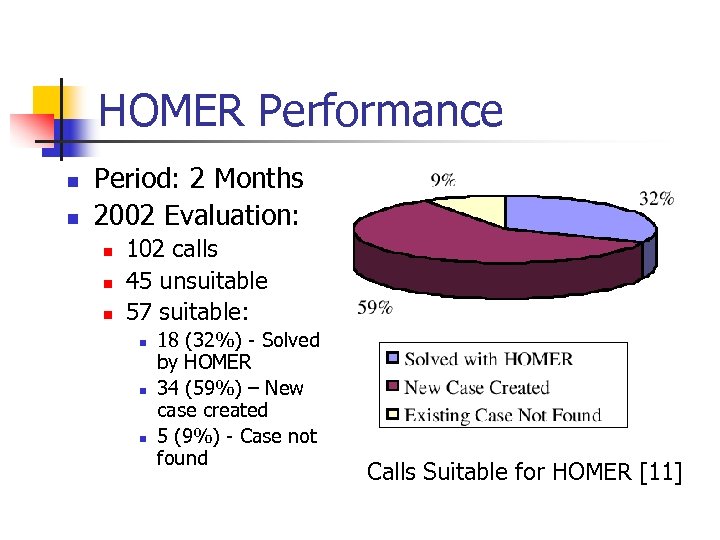 HOMER Performance n n Period: 2 Months 2002 Evaluation: n n n 102 calls 45 unsuitable 57 suitable: n n n 18 (32%) - Solved by HOMER 34 (59%) – New case created 5 (9%) - Case not found Calls Suitable for HOMER [11]
HOMER Performance n n Period: 2 Months 2002 Evaluation: n n n 102 calls 45 unsuitable 57 suitable: n n n 18 (32%) - Solved by HOMER 34 (59%) – New case created 5 (9%) - Case not found Calls Suitable for HOMER [11]
![HOMER Performance Call Resolution Time [11] HOMER Performance Call Resolution Time [11]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-50.jpg) HOMER Performance Call Resolution Time [11]
HOMER Performance Call Resolution Time [11]
![HOMER Along Product Lines Methodology Benefits [11] HOMER Along Product Lines Methodology Benefits [11]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-51.jpg) HOMER Along Product Lines Methodology Benefits [11]
HOMER Along Product Lines Methodology Benefits [11]
![HOMER Along Product Lines Methodology Benefits [11] HOMER Along Product Lines Methodology Benefits [11]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-52.jpg) HOMER Along Product Lines Methodology Benefits [11]
HOMER Along Product Lines Methodology Benefits [11]
 Security Issues n n Help Desk assisting in identification of incidents Vendors n n n Confidentiality Privacy User Threats n n Malicious users Denial of Service Attacks
Security Issues n n Help Desk assisting in identification of incidents Vendors n n n Confidentiality Privacy User Threats n n Malicious users Denial of Service Attacks
![Security Issues n Identification of Incidents [13] n n Potential incidents are identified by Security Issues n Identification of Incidents [13] n n Potential incidents are identified by](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-54.jpg) Security Issues n Identification of Incidents [13] n n Potential incidents are identified by user community First call goes to Help Desk A properly trained staff can identify incidents from calls or requests (cases) Help Desk staff must capture information so incidents can be dealt with swiftly
Security Issues n Identification of Incidents [13] n n Potential incidents are identified by user community First call goes to Help Desk A properly trained staff can identify incidents from calls or requests (cases) Help Desk staff must capture information so incidents can be dealt with swiftly
 Future Trends (AI Approaches) n Automatic Assignment of Technicians n n NL Agents for Help Desk Requests n n n Information Retrieval Natural language driven automated help desks ANN (Artificial Neural Networks) CBR-ANN (Web. Service System) n Hybrid case-based reasoning combined with ANN approach for machine fault diagnosis
Future Trends (AI Approaches) n Automatic Assignment of Technicians n n NL Agents for Help Desk Requests n n n Information Retrieval Natural language driven automated help desks ANN (Artificial Neural Networks) CBR-ANN (Web. Service System) n Hybrid case-based reasoning combined with ANN approach for machine fault diagnosis
![Automatic Assignment of Technicians Process Flow [9] Automatic Assignment of Technicians Process Flow [9]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-56.jpg) Automatic Assignment of Technicians Process Flow [9]
Automatic Assignment of Technicians Process Flow [9]
 Automatic Assignment of Technicians n IR techniques n n n Parsing Stop word removal Keyword matching Keyword weighting Model Stages n n n User report analysis Selection of Technician Refine selection with assignment rules
Automatic Assignment of Technicians n IR techniques n n n Parsing Stop word removal Keyword matching Keyword weighting Model Stages n n n User report analysis Selection of Technician Refine selection with assignment rules
 Automatic Assignment Results n Study conducted in 2002: n n 48% of the system assigned cases were better than human experts’ 92% of system cases were good or better [9]
Automatic Assignment Results n Study conducted in 2002: n n 48% of the system assigned cases were better than human experts’ 92% of system cases were good or better [9]
![NL Agent Help Desks NL Help Desk Architecture [6] n Main components n n NL Agent Help Desks NL Help Desk Architecture [6] n Main components n n](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-59.jpg) NL Agent Help Desks NL Help Desk Architecture [6] n Main components n n n Textual input analysis Request additional information from user, if needed Propose solution and verify
NL Agent Help Desks NL Help Desk Architecture [6] n Main components n n n Textual input analysis Request additional information from user, if needed Propose solution and verify
 NL Agent Results n n NL interfaces are user friendly Generic system that can be adapted to different media: n n Email driven systems Web based chat Telephony services Expect significant reduction in maintenance costs [6]
NL Agent Results n n NL interfaces are user friendly Generic system that can be adapted to different media: n n Email driven systems Web based chat Telephony services Expect significant reduction in maintenance costs [6]
![Web. Service System [12] Web. Service System [12]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-61.jpg) Web. Service System [12]
Web. Service System [12]
![CBR-ANN Help Desks Fault Diagnosis Engine [12] CBR-ANN Help Desks Fault Diagnosis Engine [12]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-62.jpg) CBR-ANN Help Desks Fault Diagnosis Engine [12]
CBR-ANN Help Desks Fault Diagnosis Engine [12]
![CBR-ANN Results n Trained with inputs and solutions from a knowledge base [12] CBR-ANN Results n Trained with inputs and solutions from a knowledge base [12]](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-63.jpg) CBR-ANN Results n Trained with inputs and solutions from a knowledge base [12]
CBR-ANN Results n Trained with inputs and solutions from a knowledge base [12]
 Summary n Help Desk Importance n n As complexity increases, systems are more vulnerable to failure User support is necessary to increase productivity Poor support strategies place burden on service agents Support should not be neglected n Problems should be dealt with fast and resource-efficient strategies
Summary n Help Desk Importance n n As complexity increases, systems are more vulnerable to failure User support is necessary to increase productivity Poor support strategies place burden on service agents Support should not be neglected n Problems should be dealt with fast and resource-efficient strategies
 Summary (continued) n Whenever dealing with a CBR (OO) system: n n n Case-base enables n n Should log all your cases Continuous knowledge acquisition and maintenance are necessary Access Reuse Knowledge extension Gains n n n Availability of solutions to previous problems Knowledge is cumulated and preserved Problem solving time is optimized
Summary (continued) n Whenever dealing with a CBR (OO) system: n n n Case-base enables n n Should log all your cases Continuous knowledge acquisition and maintenance are necessary Access Reuse Knowledge extension Gains n n n Availability of solutions to previous problems Knowledge is cumulated and preserved Problem solving time is optimized
 Summary (continued) n Distributed Help Desks n n Online support models Call centers
Summary (continued) n Distributed Help Desks n n Online support models Call centers
![References n n n n [1] Mehmet Göker et. al. The Development of HOMER: References n n n n [1] Mehmet Göker et. al. The Development of HOMER:](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-67.jpg) References n n n n [1] Mehmet Göker et. al. The Development of HOMER: A Case-Based CAD/CAM Help-Desk Support Tool. LNCS, Vol. 1488, pp 346 -357, 1998. [2] Barbara Czegel. Running an Effective Help Desk. John Wiley & Sons. 1998. [3] Mehmet Göker and Thomas Roth-Berghofer. Development and Utilization of a Case-Based Help-Desk Support System in a Corporate Environment. LNAI, Vol. 1650, pp 132 -146, 1999. [4] Barbara Czegel. Technical Support on the Web: Designing and Managing an Effective E-Support. John Wiley & Sons. 2001. [5] Keith Patching and Robina Chatham. Corporate Politics for IT Managers: How to Get Streetwise. Butterworth-Heinemann. 2000 [6] Melanie Knapp and Jens Woch. Towards a Natural Language Driven Automated Help Desk. LNCS, Vol. 2276, pp 96 -105, 2002. [7] Christine W. Chan et. al. Knowledge engineering for an intelligent case-based system for help desk operations. Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 18, No. 2, pp 125 -132, 2000.
References n n n n [1] Mehmet Göker et. al. The Development of HOMER: A Case-Based CAD/CAM Help-Desk Support Tool. LNCS, Vol. 1488, pp 346 -357, 1998. [2] Barbara Czegel. Running an Effective Help Desk. John Wiley & Sons. 1998. [3] Mehmet Göker and Thomas Roth-Berghofer. Development and Utilization of a Case-Based Help-Desk Support System in a Corporate Environment. LNAI, Vol. 1650, pp 132 -146, 1999. [4] Barbara Czegel. Technical Support on the Web: Designing and Managing an Effective E-Support. John Wiley & Sons. 2001. [5] Keith Patching and Robina Chatham. Corporate Politics for IT Managers: How to Get Streetwise. Butterworth-Heinemann. 2000 [6] Melanie Knapp and Jens Woch. Towards a Natural Language Driven Automated Help Desk. LNCS, Vol. 2276, pp 96 -105, 2002. [7] Christine W. Chan et. al. Knowledge engineering for an intelligent case-based system for help desk operations. Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 18, No. 2, pp 125 -132, 2000.
![References (continued) n n n [8] Kathleen Cummings. Reinventing Support Services: Transcending the Centralized-Decentralized References (continued) n n n [8] Kathleen Cummings. Reinventing Support Services: Transcending the Centralized-Decentralized](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-68.jpg) References (continued) n n n [8] Kathleen Cummings. Reinventing Support Services: Transcending the Centralized-Decentralized Support Model Debate. In Proc. SIGUCCS’ 02, pp 232 -233, 2002. [9] Avinoam Lazarov and Peter Shoval. A rule-based system for automatic assignment of technicians to service faults. Decision Support Systems, Vol. 32. pp 343 -360, 2002. [10] Doo-Hyun Kim et. al. Collaborative Multimedia Architecture and Advanced Internet Call Center. In Proc. ICOIN’ 01, pp 246 -250, 2001. [11] Ralph Bergmann. Experience Management for Self-Service and Help-Desk Support. LNAI, Vol. 2432, pp 315 -346, 2002. [12] S. C. Hui et. al. A web-based intelligent fault diagnosis system for customer service support, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp 537 -548, 2001. [13] Eric Maiwald and William Sieglein. Security Planning & Disaster Recovery. Osborne/Mc. Graw-Hill. 2002.
References (continued) n n n [8] Kathleen Cummings. Reinventing Support Services: Transcending the Centralized-Decentralized Support Model Debate. In Proc. SIGUCCS’ 02, pp 232 -233, 2002. [9] Avinoam Lazarov and Peter Shoval. A rule-based system for automatic assignment of technicians to service faults. Decision Support Systems, Vol. 32. pp 343 -360, 2002. [10] Doo-Hyun Kim et. al. Collaborative Multimedia Architecture and Advanced Internet Call Center. In Proc. ICOIN’ 01, pp 246 -250, 2001. [11] Ralph Bergmann. Experience Management for Self-Service and Help-Desk Support. LNAI, Vol. 2432, pp 315 -346, 2002. [12] S. C. Hui et. al. A web-based intelligent fault diagnosis system for customer service support, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp 537 -548, 2001. [13] Eric Maiwald and William Sieglein. Security Planning & Disaster Recovery. Osborne/Mc. Graw-Hill. 2002.
![References (continued) n n [14] Size. Master Help Desk. Avrasoft Corporation, 2003. http: //www. References (continued) n n [14] Size. Master Help Desk. Avrasoft Corporation, 2003. http: //www.](https://present5.com/presentation/261e8d318754eec5adfa636618be80e7/image-69.jpg) References (continued) n n [14] Size. Master Help Desk. Avrasoft Corporation, 2003. http: //www. avrasoft. com/sizemaster/ [15] People. Soft Inc. Help Desk. People. Soft, 2003. http: //www. peoplesoft. com/corp/en/products/line/crm/help_desk/featu res. asp [16] Track-It! Demo. Blue Ocean Software Inc. , 2002. http: //www. blueocean. com/smallbusiness/twebinfo. htm Rabih Neouchi William Luthi CMPUT 660 Winter 2003, University of Alberta
References (continued) n n [14] Size. Master Help Desk. Avrasoft Corporation, 2003. http: //www. avrasoft. com/sizemaster/ [15] People. Soft Inc. Help Desk. People. Soft, 2003. http: //www. peoplesoft. com/corp/en/products/line/crm/help_desk/featu res. asp [16] Track-It! Demo. Blue Ocean Software Inc. , 2002. http: //www. blueocean. com/smallbusiness/twebinfo. htm Rabih Neouchi William Luthi CMPUT 660 Winter 2003, University of Alberta
 Questions & Answers
Questions & Answers


