 Height Matters http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
Height Matters http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
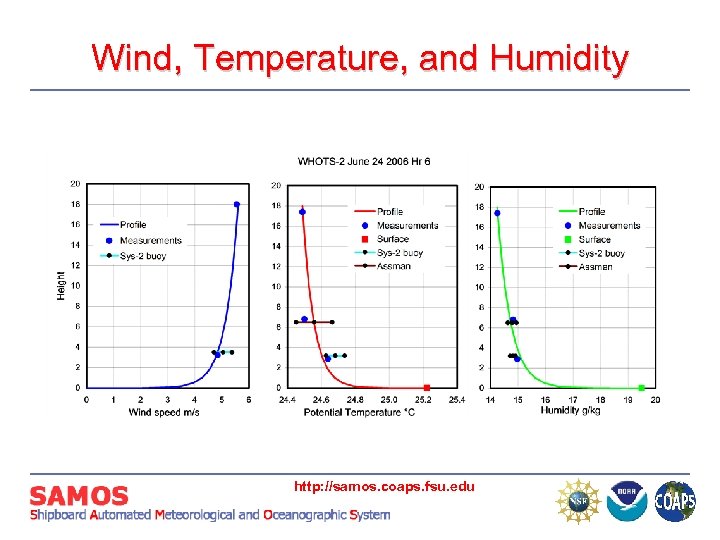 Wind, Temperature, and Humidity http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
Wind, Temperature, and Humidity http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
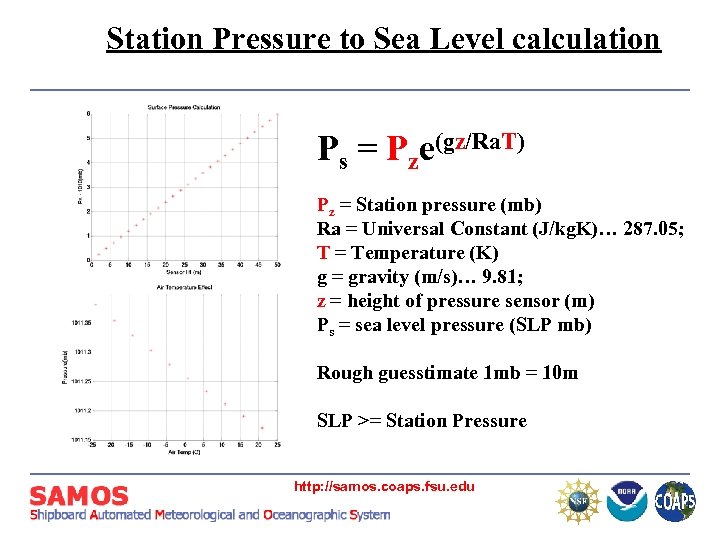 Station Pressure to Sea Level calculation Ps = Pze(gz/Ra. T) Pz = Station pressure (mb) Ra = Universal Constant (J/kg. K)… 287. 05; T = Temperature (K) g = gravity (m/s)… 9. 81; z = height of pressure sensor (m) Ps = sea level pressure (SLP mb) Rough guesstimate 1 mb = 10 m SLP >= Station Pressure http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
Station Pressure to Sea Level calculation Ps = Pze(gz/Ra. T) Pz = Station pressure (mb) Ra = Universal Constant (J/kg. K)… 287. 05; T = Temperature (K) g = gravity (m/s)… 9. 81; z = height of pressure sensor (m) Ps = sea level pressure (SLP mb) Rough guesstimate 1 mb = 10 m SLP >= Station Pressure http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
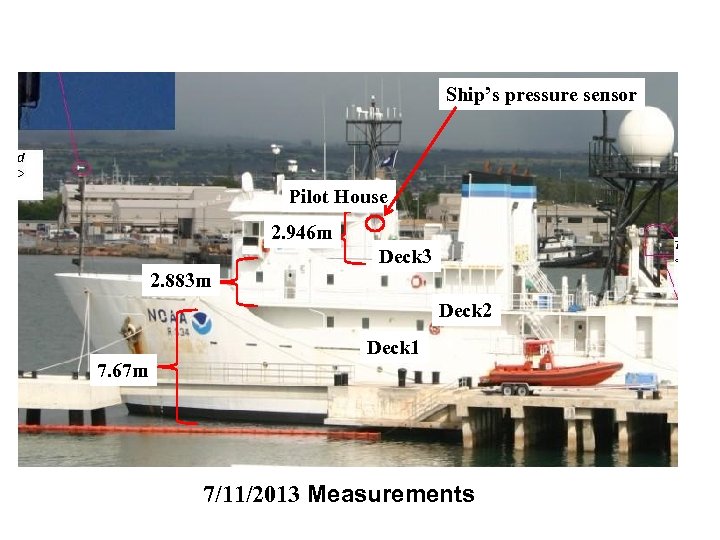 Ship’s pressure sensor Pilot House 2. 946 m Deck 3 2. 883 m Deck 2 Deck 1 7. 67 m 7/11/2013 Measurements
Ship’s pressure sensor Pilot House 2. 946 m Deck 3 2. 883 m Deck 2 Deck 1 7. 67 m 7/11/2013 Measurements
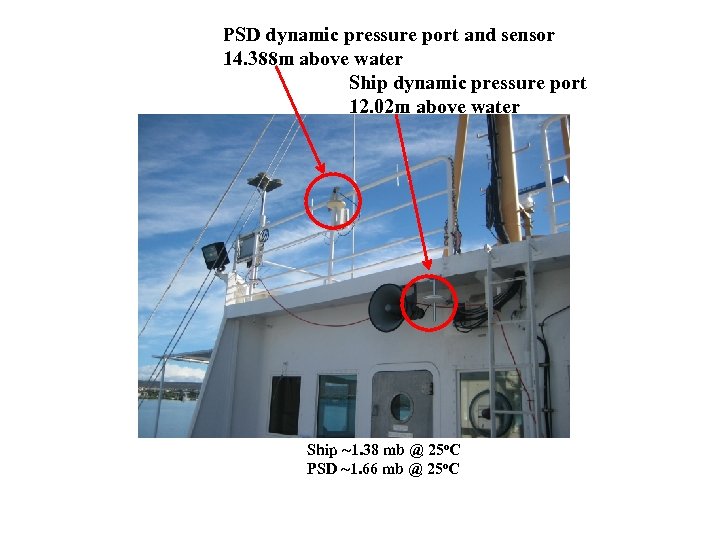 PSD dynamic pressure port and sensor 14. 388 m above water Ship dynamic pressure port 12. 02 m above water Ship ~1. 38 mb @ 25 o. C PSD ~1. 66 mb @ 25 o. C
PSD dynamic pressure port and sensor 14. 388 m above water Ship dynamic pressure port 12. 02 m above water Ship ~1. 38 mb @ 25 o. C PSD ~1. 66 mb @ 25 o. C
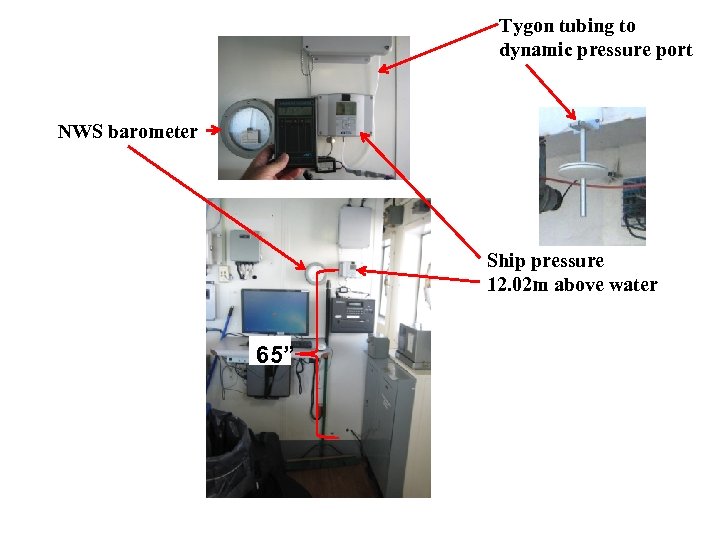 Tygon tubing to dynamic pressure port NWS barometer Ship pressure 12. 02 m above water 65”
Tygon tubing to dynamic pressure port NWS barometer Ship pressure 12. 02 m above water 65”
 PSD 3 Hand Held barometer Ship pressure sensor Prior to resetting Vaisala unit w/30 m offset
PSD 3 Hand Held barometer Ship pressure sensor Prior to resetting Vaisala unit w/30 m offset
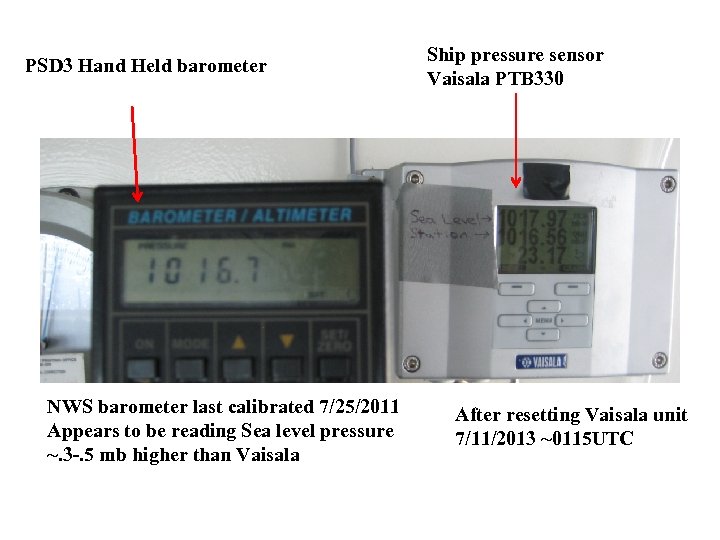 PSD 3 Hand Held barometer NWS barometer last calibrated 7/25/2011 Appears to be reading Sea level pressure ~. 3 -. 5 mb higher than Vaisala Ship pressure sensor Vaisala PTB 330 After resetting Vaisala unit 7/11/2013 ~0115 UTC
PSD 3 Hand Held barometer NWS barometer last calibrated 7/25/2011 Appears to be reading Sea level pressure ~. 3 -. 5 mb higher than Vaisala Ship pressure sensor Vaisala PTB 330 After resetting Vaisala unit 7/11/2013 ~0115 UTC
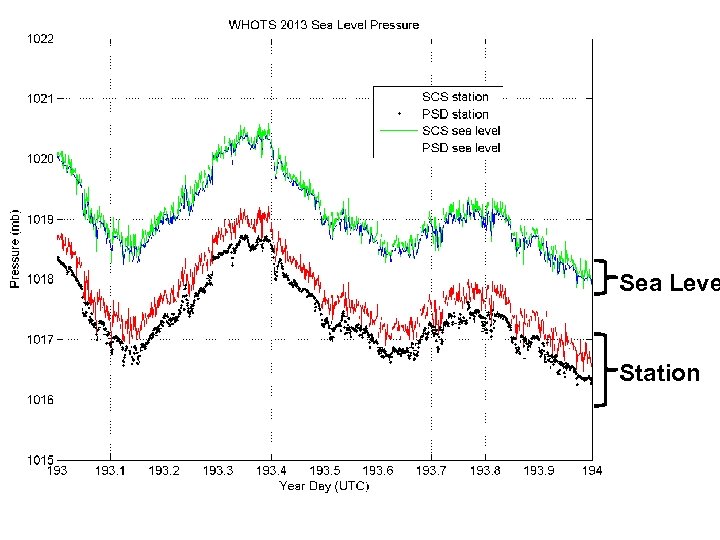 Sea Leve Station
Sea Leve Station
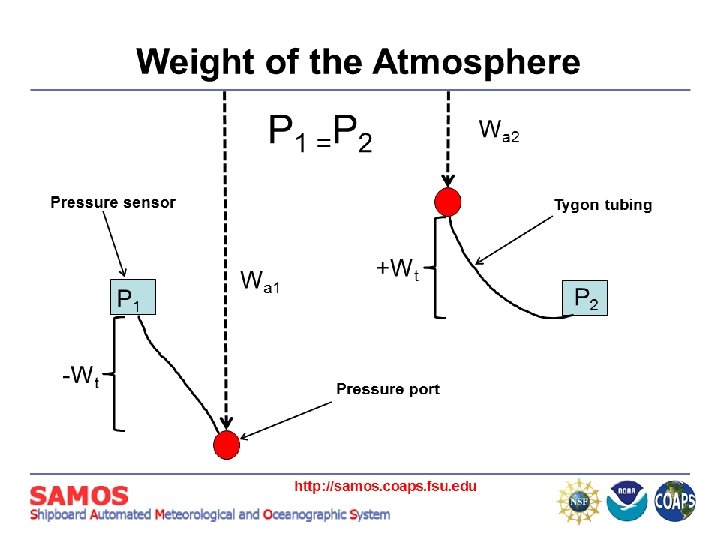 Pressure http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
Pressure http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
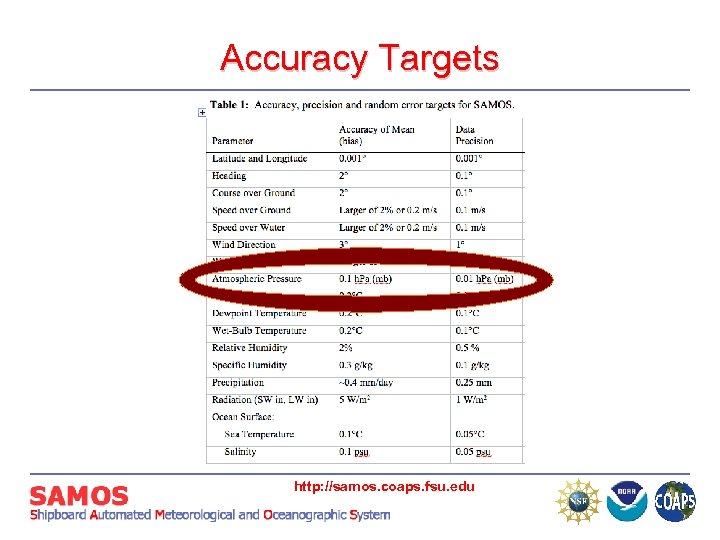 Accuracy Targets http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
Accuracy Targets http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
 Applying Heights in the Field Image Courtesy NOAA OAR http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
Applying Heights in the Field Image Courtesy NOAA OAR http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
 Questions? http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
Questions? http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
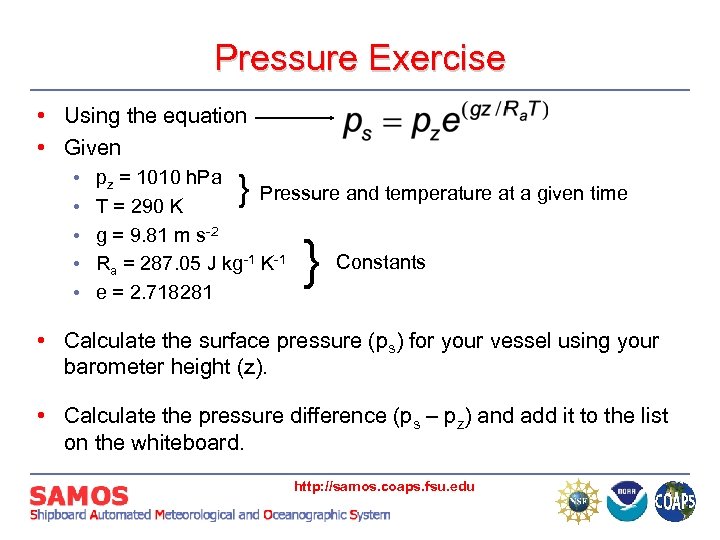 Pressure Exercise • Using the equation • Given • • • pz = 1010 h. Pa Pressure and temperature at a given time T = 290 K g = 9. 81 m s-2 Constants Ra = 287. 05 J kg-1 K-1 e = 2. 718281 } } • Calculate the surface pressure (ps) for your vessel using your barometer height (z). • Calculate the pressure difference (ps – pz) and add it to the list on the whiteboard. http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu
Pressure Exercise • Using the equation • Given • • • pz = 1010 h. Pa Pressure and temperature at a given time T = 290 K g = 9. 81 m s-2 Constants Ra = 287. 05 J kg-1 K-1 e = 2. 718281 } } • Calculate the surface pressure (ps) for your vessel using your barometer height (z). • Calculate the pressure difference (ps – pz) and add it to the list on the whiteboard. http: //samos. coaps. fsu. edu