Heaven and hell.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Heaven (happiness) Virtue Hell (suffering or pain) Sin
Heaven (happiness) Virtue Hell (suffering or pain) Sin
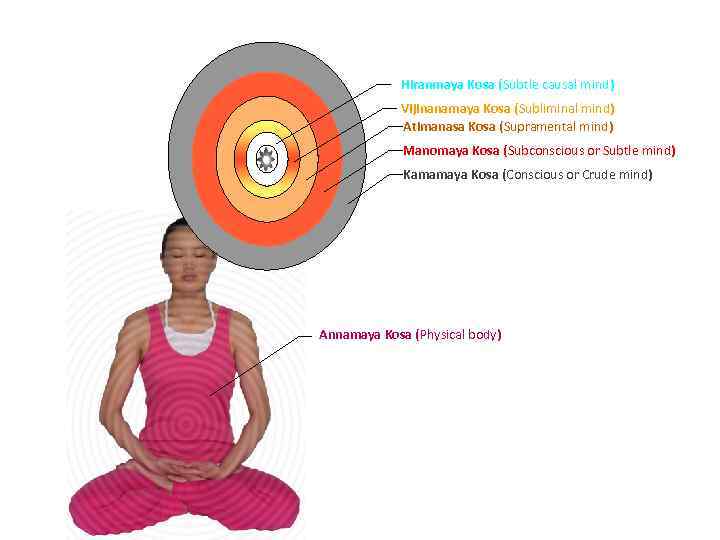 Hiranmaya Kosa (Subtle causal mind) Vijinanamaya Kosa (Subliminal mind) Atimanasa Kosa (Supramental mind) Manomaya Kosa (Subconscious or Subtle mind) Kamamaya Kosa (Conscious or Crude mind) Annamaya Kosa (Physical body)
Hiranmaya Kosa (Subtle causal mind) Vijinanamaya Kosa (Subliminal mind) Atimanasa Kosa (Supramental mind) Manomaya Kosa (Subconscious or Subtle mind) Kamamaya Kosa (Conscious or Crude mind) Annamaya Kosa (Physical body)
 Conscious mind (Crude mind) Kamamaya Kosa • The Conscious mind has three functions: 1. sensing external stimuli from the outside world through the five sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin); 2. having the desire/aversion on the basis of those stimuli; 3. acting to materialise those desires by using the five motor organs (hands, feet, vocal chord, sexual organ and digestive / excretory organ). • This layer of mind controls the organs and the instincts. It is the gateway to the external world.
Conscious mind (Crude mind) Kamamaya Kosa • The Conscious mind has three functions: 1. sensing external stimuli from the outside world through the five sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin); 2. having the desire/aversion on the basis of those stimuli; 3. acting to materialise those desires by using the five motor organs (hands, feet, vocal chord, sexual organ and digestive / excretory organ). • This layer of mind controls the organs and the instincts. It is the gateway to the external world.
 Subconscious mind (Subtle mind) Manomaya Kosa • The Subconscious mind has four functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. • • memory; contemplation or deep thinking; experience of pleasure and pain; dreaming. The vast majority of most people’s thinking goes on at this layer of the mind. The images that one perceives during dreams are thoughts that are stored in the Subconscious mind.
Subconscious mind (Subtle mind) Manomaya Kosa • The Subconscious mind has four functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. • • memory; contemplation or deep thinking; experience of pleasure and pain; dreaming. The vast majority of most people’s thinking goes on at this layer of the mind. The images that one perceives during dreams are thoughts that are stored in the Subconscious mind.
 The definition of sin and virtue varies from country to country. ie. suicide is sin in England India but it is not a sin in Japan. To bath in Ganges is virtue in India
The definition of sin and virtue varies from country to country. ie. suicide is sin in England India but it is not a sin in Japan. To bath in Ganges is virtue in India
![for a Sha kta [devotee of Shakti] eating meat is not a sin, but for a Sha kta [devotee of Shakti] eating meat is not a sin, but](https://present5.com/presentation/-31665812_132746969/image-6.jpg) for a Sha kta [devotee of Shakti] eating meat is not a sin, but for a Vaes n ava [Vaishnavite, devotee of Vis n u] even to see an animal being slaughtered is a sin; he or she cannot even think of eating meat.
for a Sha kta [devotee of Shakti] eating meat is not a sin, but for a Vaes n ava [Vaishnavite, devotee of Vis n u] even to see an animal being slaughtered is a sin; he or she cannot even think of eating meat.
 Krs n a Dvaepa yana. He was the author of the eighteen Pura n as: As t adashapura n es u Vya sasya vacanadvayam Paropaka rah pun ya ya Parapiir an am pa pa ya [The two most important words in all of Vyasa’s eighteen Pura n as are paropaka rah – doing good is virtue – and parapiir an am – doing bad is vice. ]
Krs n a Dvaepa yana. He was the author of the eighteen Pura n as: As t adashapura n es u Vya sasya vacanadvayam Paropaka rah pun ya ya Parapiir an am pa pa ya [The two most important words in all of Vyasa’s eighteen Pura n as are paropaka rah – doing good is virtue – and parapiir an am – doing bad is vice. ]
 Pun ya means that action which leads to one´s physical, psychic and spiritual well-being. Pápa means that action which leads to one´s physical, psychic and spiritual degeneration.
Pun ya means that action which leads to one´s physical, psychic and spiritual well-being. Pápa means that action which leads to one´s physical, psychic and spiritual degeneration.
 Two types of pápa. 1. Pátaka 2. Pratyaváya. 1. If one does something which should not be done, such as stealing, telling lies, etc, it is called “pa taka”. It is an action which harms others. 2. If one fails to do that which should be done, such as not feeding the poor or not serving the sick, it is called “pratyava ya”
Two types of pápa. 1. Pátaka 2. Pratyaváya. 1. If one does something which should not be done, such as stealing, telling lies, etc, it is called “pa taka”. It is an action which harms others. 2. If one fails to do that which should be done, such as not feeding the poor or not serving the sick, it is called “pratyava ya”
 3 -types of Pátaki 1. Pataki 2. Atipátaki 3. Mahápátaki Pataki- still something and after returning ask for punishment.
3 -types of Pátaki 1. Pataki 2. Atipátaki 3. Mahápátaki Pataki- still something and after returning ask for punishment.
 Damage which can never be compensated for. Suppose you cut off someone´s fingers: they can never be replaced. Such an action is called “atipa taka”. And when you cause heavy damage which can never be compensated for and which has a recurring bad influence on others, it is called “mahapa taka”. Suppose an unscrupulous businessman adulterates black pepper with papaya seeds.
Damage which can never be compensated for. Suppose you cut off someone´s fingers: they can never be replaced. Such an action is called “atipa taka”. And when you cause heavy damage which can never be compensated for and which has a recurring bad influence on others, it is called “mahapa taka”. Suppose an unscrupulous businessman adulterates black pepper with papaya seeds.
 Two types of pun ya: pratyaks a pun ya and apratyaks a pun ya – direct and indirect virtue. • direct virtue, is acquired when one performs an action such as feeding the hungry or serving the infirm. • Indirect virtue is acquired when one� s service has a recurring effect, such as service to the society, planting trees, etc.
Two types of pun ya: pratyaks a pun ya and apratyaks a pun ya – direct and indirect virtue. • direct virtue, is acquired when one performs an action such as feeding the hungry or serving the infirm. • Indirect virtue is acquired when one� s service has a recurring effect, such as service to the society, planting trees, etc.
 Three causes of Sin 1) shortage of physical and psychic resources 2) non-utilization of over-accumulated physical and psychic resources 3) stagnancy
Three causes of Sin 1) shortage of physical and psychic resources 2) non-utilization of over-accumulated physical and psychic resources 3) stagnancy


