9e03ca7791764e211b42e443f1bfcf9c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Heating Systems
Heating Systems
 Thermal Energy on the Move: Conduction: the transfer of energy through matter by direct contact of particles § Pans on a stove transfer the heat by conduction to the food. Convection: the transfer of energy by the bulk movement of matter. § used with fluids: any material that flows (liquids & gases) Ocean and wind currents are a global form of convection Radiation: the transfer of energy in the form of waves. § The sun and a camp fire the side of you that faces the heat source is warmed but the other side can be cold. 1 -3
Thermal Energy on the Move: Conduction: the transfer of energy through matter by direct contact of particles § Pans on a stove transfer the heat by conduction to the food. Convection: the transfer of energy by the bulk movement of matter. § used with fluids: any material that flows (liquids & gases) Ocean and wind currents are a global form of convection Radiation: the transfer of energy in the form of waves. § The sun and a camp fire the side of you that faces the heat source is warmed but the other side can be cold. 1 -3
 Conventional Heating Systems: § All heating systems must have a source of energy. - Electricity -Fuels -Fossil Fuels: Oil, Natural Gas, LP -Biomass: Wood, Sawdust, Vegetable oil, etc - Solar (Active & Passive Systems) 4
Conventional Heating Systems: § All heating systems must have a source of energy. - Electricity -Fuels -Fossil Fuels: Oil, Natural Gas, LP -Biomass: Wood, Sawdust, Vegetable oil, etc - Solar (Active & Passive Systems) 4
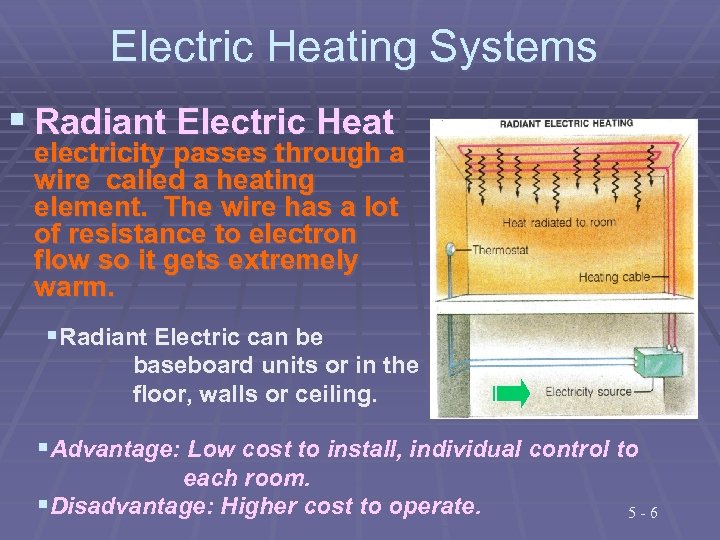 Electric Heating Systems § Radiant Electric Heat electricity passes through a wire called a heating element. The wire has a lot of resistance to electron flow so it gets extremely warm. §Radiant Electric can be baseboard units or in the floor, walls or ceiling. §Advantage: Low cost to install, individual control to each room. §Disadvantage: Higher cost to operate. 5 -6
Electric Heating Systems § Radiant Electric Heat electricity passes through a wire called a heating element. The wire has a lot of resistance to electron flow so it gets extremely warm. §Radiant Electric can be baseboard units or in the floor, walls or ceiling. §Advantage: Low cost to install, individual control to each room. §Disadvantage: Higher cost to operate. 5 -6
 Central Heating Systems: § A central heating system generates heat for an entire building or group of buildings from one location: § A furnace or boiler is used to convert fuel into heat. § Most common heat distribution systems. §Forced hot water §Forced hot air §Steam heat 7, 8
Central Heating Systems: § A central heating system generates heat for an entire building or group of buildings from one location: § A furnace or boiler is used to convert fuel into heat. § Most common heat distribution systems. §Forced hot water §Forced hot air §Steam heat 7, 8
 Hot Water Heating System: Forced-Water Systems: § § Common fuel sources – Natural Gas and Oil Water is heated in the furnace an a pump is used to move hot water through a series of pipes from the furnace to the areas to be heated. § The heated water will go to baseboards to obtain convection currents in the room or use radiant heating in a floor, wall or ceiling. § Advantage: More even heat, Furnace can supply domestic hot water, zone heating, often easier to adapt to solar hot water. Disadvantage: Slower to warm a space. § 9 - 12
Hot Water Heating System: Forced-Water Systems: § § Common fuel sources – Natural Gas and Oil Water is heated in the furnace an a pump is used to move hot water through a series of pipes from the furnace to the areas to be heated. § The heated water will go to baseboards to obtain convection currents in the room or use radiant heating in a floor, wall or ceiling. § Advantage: More even heat, Furnace can supply domestic hot water, zone heating, often easier to adapt to solar hot water. Disadvantage: Slower to warm a space. § 9 - 12
 Baseboards § Both Electrical and Hydronic baseboards have the heating element or copper pipe in the center of metal fins. § What is the purpose of the fins? Answer: Allow for more surface area to dissipate the heat from the heating element or the copper pipe full of hot water. Cool air near the floor gets warmed as it passes by the fins. As the air warms it will rise to the ceiling as part of convection currents that will circulate in the room.
Baseboards § Both Electrical and Hydronic baseboards have the heating element or copper pipe in the center of metal fins. § What is the purpose of the fins? Answer: Allow for more surface area to dissipate the heat from the heating element or the copper pipe full of hot water. Cool air near the floor gets warmed as it passes by the fins. As the air warms it will rise to the ceiling as part of convection currents that will circulate in the room.
 Forced Air Heating Systems: § Common fuel sources – Natural Gas, Oil, LP § A blower (fan) is used to move warmed air through a series of large ducts to vents in each room Warm air circulate by convection, cool air returns to the furnace to be reheated. § § § Advantage: Fast acting heat, Air ducts make it easier to install A/C, easy to add humidifiers and filters. Disadvantage: Heat tends vary frequently, tends to be dustier if not maintained. 14 - 17
Forced Air Heating Systems: § Common fuel sources – Natural Gas, Oil, LP § A blower (fan) is used to move warmed air through a series of large ducts to vents in each room Warm air circulate by convection, cool air returns to the furnace to be reheated. § § § Advantage: Fast acting heat, Air ducts make it easier to install A/C, easy to add humidifiers and filters. Disadvantage: Heat tends vary frequently, tends to be dustier if not maintained. 14 - 17
 Steam Heating Systems: § Common fuel sources – Natural Gas and Oil § § § Water is heated to above 100 C at which it turns to steam in a boiler not a furnace Steam, is under pressure, is forced to the convector in the rooms of the building. This causes convection currents. As the steam gives off its heat as it condenses and gravity returns water to the boiler. Advantage: Used often in larger building or campus. A large quantity of heat with little water (steam) Disadvantage: Higher temperatures are required this results in higher pressures in the pipes which can stress pipes and fittings. 19 - 21
Steam Heating Systems: § Common fuel sources – Natural Gas and Oil § § § Water is heated to above 100 C at which it turns to steam in a boiler not a furnace Steam, is under pressure, is forced to the convector in the rooms of the building. This causes convection currents. As the steam gives off its heat as it condenses and gravity returns water to the boiler. Advantage: Used often in larger building or campus. A large quantity of heat with little water (steam) Disadvantage: Higher temperatures are required this results in higher pressures in the pipes which can stress pipes and fittings. 19 - 21
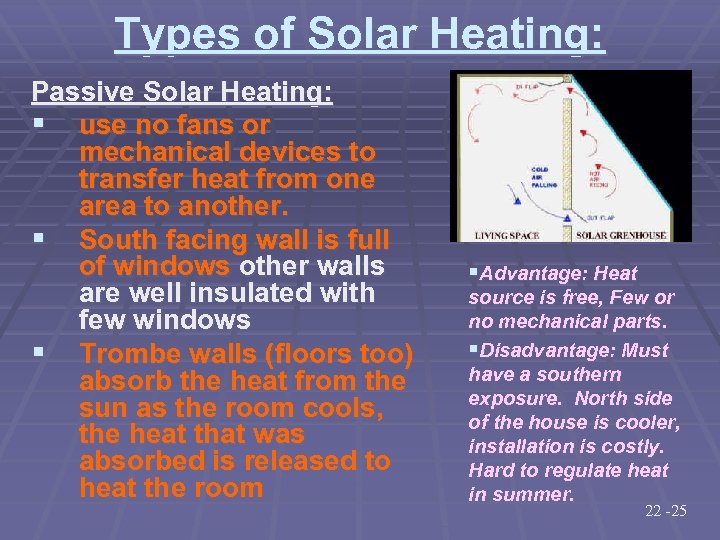 Types of Solar Heating: Passive Solar Heating: § use no fans or mechanical devices to transfer heat from one area to another. § South facing wall is full of windows other walls are well insulated with few windows § Trombe walls (floors too) absorb the heat from the sun as the room cools, the heat that was absorbed is released to heat the room §Advantage: Heat source is free, Few or no mechanical parts. §Disadvantage: Must have a southern exposure. North side of the house is cooler, installation is costly. Hard to regulate heat in summer. 22 -25
Types of Solar Heating: Passive Solar Heating: § use no fans or mechanical devices to transfer heat from one area to another. § South facing wall is full of windows other walls are well insulated with few windows § Trombe walls (floors too) absorb the heat from the sun as the room cools, the heat that was absorbed is released to heat the room §Advantage: Heat source is free, Few or no mechanical parts. §Disadvantage: Must have a southern exposure. North side of the house is cooler, installation is costly. Hard to regulate heat in summer. 22 -25
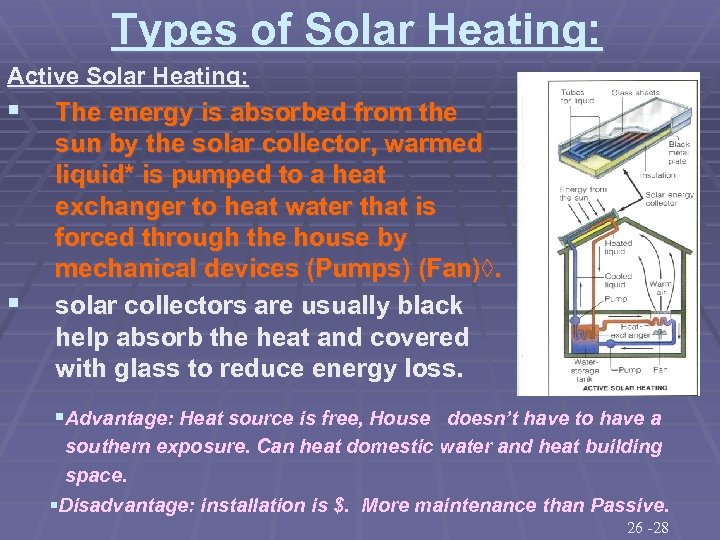 Types of Solar Heating: Active Solar Heating: § § The energy is absorbed from the sun by the solar collector, warmed liquid* is pumped to a heat exchanger to heat water that is forced through the house by mechanical devices (Pumps) (Fan)◊. solar collectors are usually black help absorb the heat and covered with glass to reduce energy loss. §Advantage: Heat source is free, House doesn’t have to have a southern exposure. Can heat domestic water and heat building space. §Disadvantage: installation is $. More maintenance than Passive. 26 -28
Types of Solar Heating: Active Solar Heating: § § The energy is absorbed from the sun by the solar collector, warmed liquid* is pumped to a heat exchanger to heat water that is forced through the house by mechanical devices (Pumps) (Fan)◊. solar collectors are usually black help absorb the heat and covered with glass to reduce energy loss. §Advantage: Heat source is free, House doesn’t have to have a southern exposure. Can heat domestic water and heat building space. §Disadvantage: installation is $. More maintenance than Passive. 26 -28
 R-VALUE § The R-value is the measure of resistance to heat loss through a material. § Greater the R-value, the more effective the insulation is. Preventing heat loss in winter and preventing heat gain in summer. § Two materials that have the same R-value indicates similar insulation performance The amount of material may vary.
R-VALUE § The R-value is the measure of resistance to heat loss through a material. § Greater the R-value, the more effective the insulation is. Preventing heat loss in winter and preventing heat gain in summer. § Two materials that have the same R-value indicates similar insulation performance The amount of material may vary.
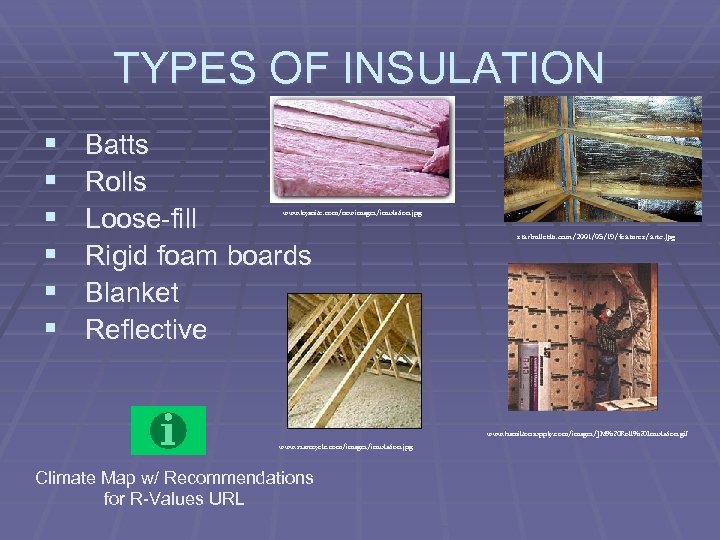 TYPES OF INSULATION § § § Batts Rolls Loose-fill Rigid foam boards Blanket Reflective www. kyanite. com/newimages/insulation. jpg starbulletin. com/2001/05/19/features/artc. jpg www. hamiltonsupply. com/images/JM%20 Roll%20 Insulation. gif www. rsarecycle. com/images/insulation. jpg Climate Map w/ Recommendations for R-Values URL
TYPES OF INSULATION § § § Batts Rolls Loose-fill Rigid foam boards Blanket Reflective www. kyanite. com/newimages/insulation. jpg starbulletin. com/2001/05/19/features/artc. jpg www. hamiltonsupply. com/images/JM%20 Roll%20 Insulation. gif www. rsarecycle. com/images/insulation. jpg Climate Map w/ Recommendations for R-Values URL
 Vapor Barriers § A vapor barrier is a material that reduces the rate at which water vapor can move through a material. § Warm air tends to hold water vapor. § The moisture that is in the air condenses on the first cold surface it encounters. If this surface is within an exterior wall cavity, wet insulation and framing will be the result.
Vapor Barriers § A vapor barrier is a material that reduces the rate at which water vapor can move through a material. § Warm air tends to hold water vapor. § The moisture that is in the air condenses on the first cold surface it encounters. If this surface is within an exterior wall cavity, wet insulation and framing will be the result.
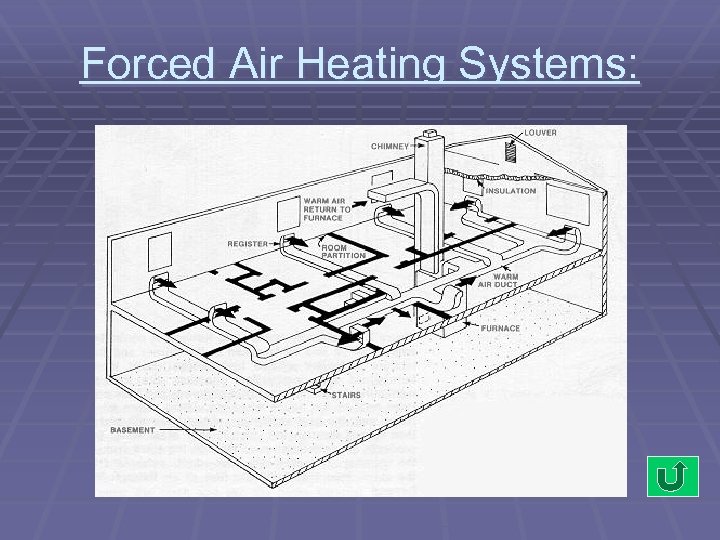 Forced Air Heating Systems:
Forced Air Heating Systems:
 Hydronic Perimeter Heating System
Hydronic Perimeter Heating System
 Radiant - Floor Installation oikos. com/esb/48/ radiantheat. html Baseboard - Convection www. butlerrec. com/
Radiant - Floor Installation oikos. com/esb/48/ radiantheat. html Baseboard - Convection www. butlerrec. com/
 www. h 2 oplumbing. com/services/ services. htm
www. h 2 oplumbing. com/services/ services. htm
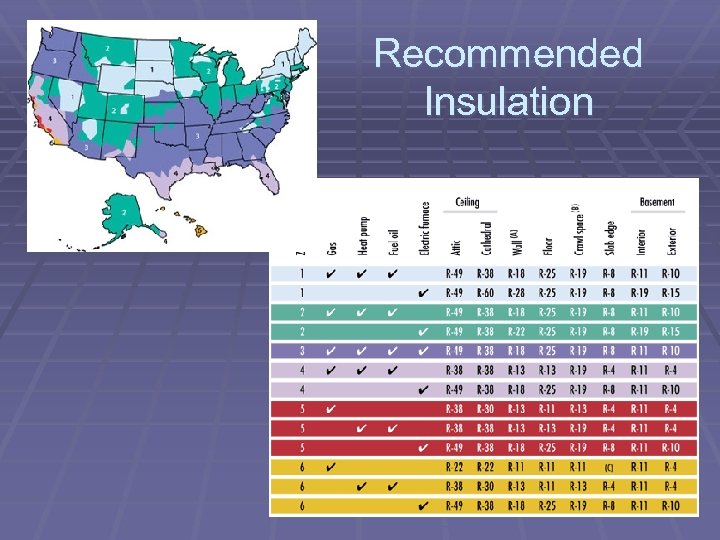 Recommended Insulation
Recommended Insulation


