Lecture-MSU-PREZ-HSP-2011.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 72

HEAT SHOCK PROTEINS IN BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE Igor Malyshev Department of Pathophysiology Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry

BIOLOGICAL AND MEDICAL ASPECTS OF HEAT SHOCK PROTEINS (HSP) • 1. HSP 70 functions in a normal cell • 2. HSP 70 functions in a damaged cell • 3. Mechanisms of HSP 70 synthesis activation • 4. HSP 70 in immunity responses • 5. HSP 70 in carcinogenesis • 6. HSP 70 in protecting the brain in Alzheimer disease • 7. HSP 70 in protecting the heart
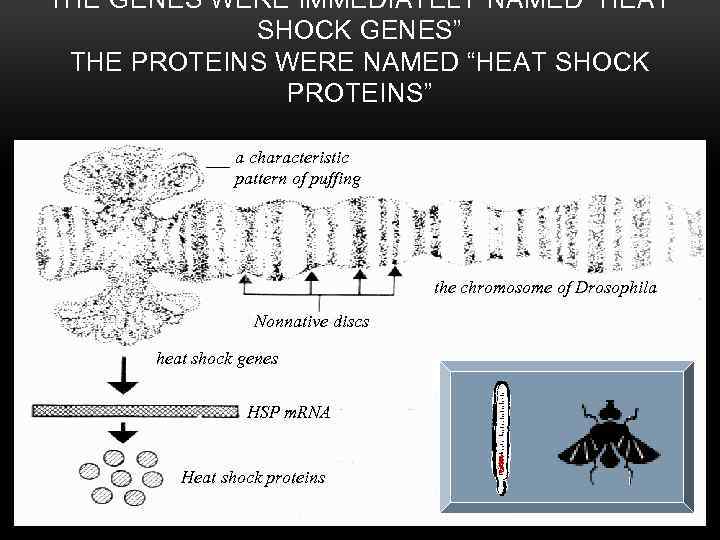
THE GENES WERE IMMEDIATELY NAMED “HEAT SHOCK GENES” THE PROTEINS WERE NAMED “HEAT SHOCK PROTEINS” a characteristic pattern of puffing the chromosome of Drosophila Nonnative discs heat shock genes HSP m. RNA Heat shock proteins
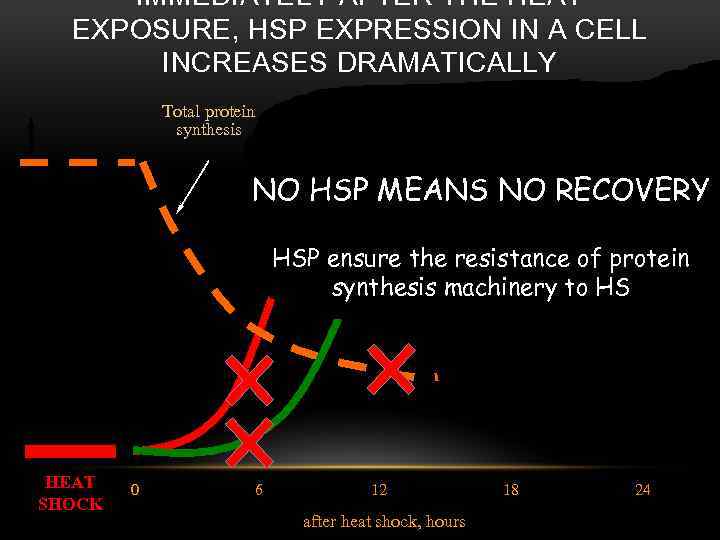
IMMEDIATELY AFTER THE HEAT EXPOSURE, HSP EXPRESSION IN A CELL INCREASES DRAMATICALLY Total protein synthesis HSP 70 in cytoplasm HSP 70 in nucleus NO HSP MEANS NO RECOVERY The HSP content in the nucleus gradually decreases, while it increases in the cytoplasm HSP ensure the resistance of protein synthesis machinery to HS The damaged nucleolar structure, as well as the disturbed general protein synthesis completely recover Most of HSP is contained in the nucleus among the damaged preribosomes HEAT SHOCK 0 6 12 after heat shock, hours 18 24
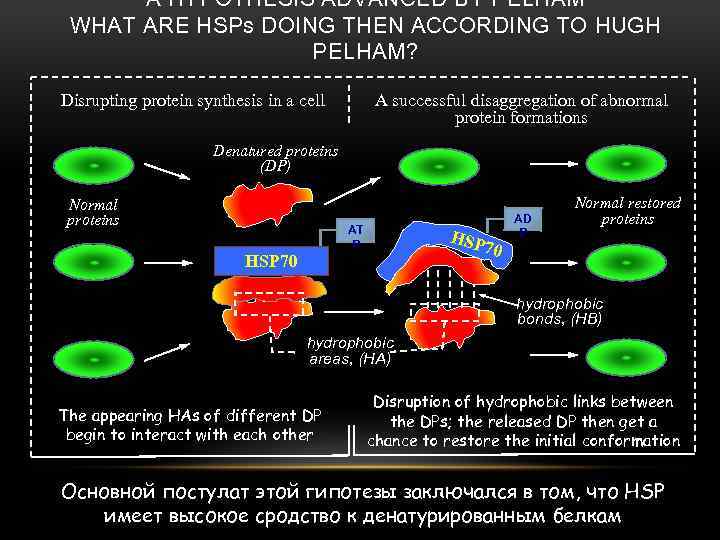
A HYPOTHESIS ADVANCED BY PELHAM WHAT ARE HSPs DOING THEN ACCORDING TO HUGH PELHAM? Disrupting protein synthesis in a cell A successful disaggregation of abnormal protein formations Denatured proteins (DP) Normal proteins AT P HSP 70 AD P Normal restored proteins hydrophobic bonds, (HB) hydrophobic areas, (HA) The appearing HAs of different DP begin to interact with each other Disruption of hydrophobic links between the DPs; the released DP then get a chance to restore the initial conformation Основной постулат этой гипотезы заключался в том, что HSP имеет высокое сродство к денатурированным белкам
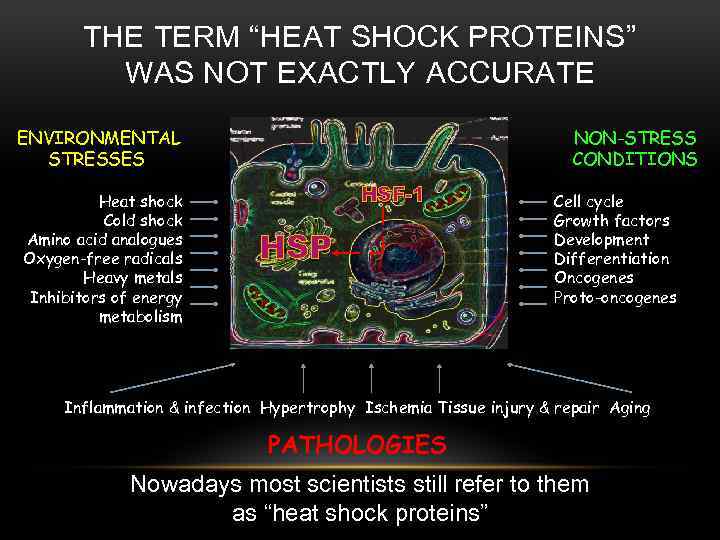
THE TERM “HEAT SHOCK PROTEINS” WAS NOT EXACTLY ACCURATE ENVIRONMENTAL STRESSES Heat shock Cold shock Amino acid analogues Oxygen-free radicals Heavy metals Inhibitors of energy metabolism NON-STRESS CONDITIONS HSF-1 HSP Cell cycle Growth factors Development Differentiation Oncogenes Proto-oncogenes Inflammation & infection Hypertrophy Ischemia Tissue injury & repair Aging PATHOLOGIES Nowadays most scientists still refer to them as “heat shock proteins”

HEAT SHOCK PROTEINS ARE FOUND IN ALL LIVING ORGANISMS, FROM VIRUSES TO PRIMATES • Evolutionarily HSPs are highly conservative proteins. Homology in the amino acid composition of HSP in bacteria and in humans reaches 60%. • By now HSPs with molecular weight of 28, 32, 40, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110 k. Da have been discovered.

HSP 70 FAMILY INCLUDES PROTEINS WHOSE SYNTHESIS IS STIMULATED BY STRESS, AND WHOSE GENES CONTAIN A MARKER NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE, THE HSE: CT-GAA-TTC-AG” HSP 70 family: • • Constituitive HSP 70: a high basal level and are weakly induced by stress. Inducible HSP 70: absent in the intact conditions, while their expression increases under stress. Hsp 70 can be found in any part of a cell: HSP • in the cytoplasm, • the nucleus, • mitochondria, HSP • endoplasmic reticulum • any other organelles HSP HSP 70: basically everywhere HSP where a protein unfolding happens: HSP protein translocation through membranes, • HSP in m. RNA translation, • HSP • protein delivery to sites of degradation, • the assembly and disassembly of macromolecular complexes, • genes induction and apoptosis
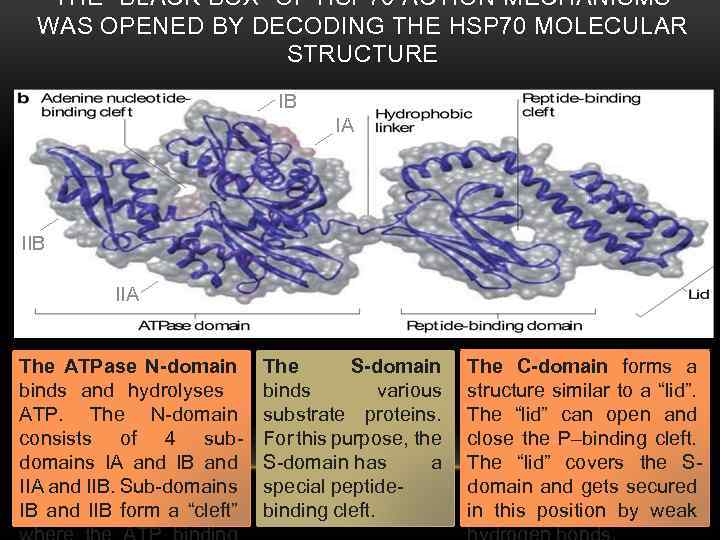
THE “BLACK BOX” OF HSP 70 ACTION MECHANISMS WAS OPENED BY DECODING THE HSP 70 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE IB IA IIB IIA The ATPase N-domain binds and hydrolyses ATP. The N-domain consists of 4 subdomains IA and IB and IIA and IIB. Sub-domains IB and IIB form a “cleft” The S-domain binds various substrate proteins. For this purpose, the S-domain has a special peptidebinding cleft. The C-domain forms a structure similar to a “lid”. The “lid” can open and close the P–binding cleft. The “lid” covers the Sdomain and gets secured in this position by weak
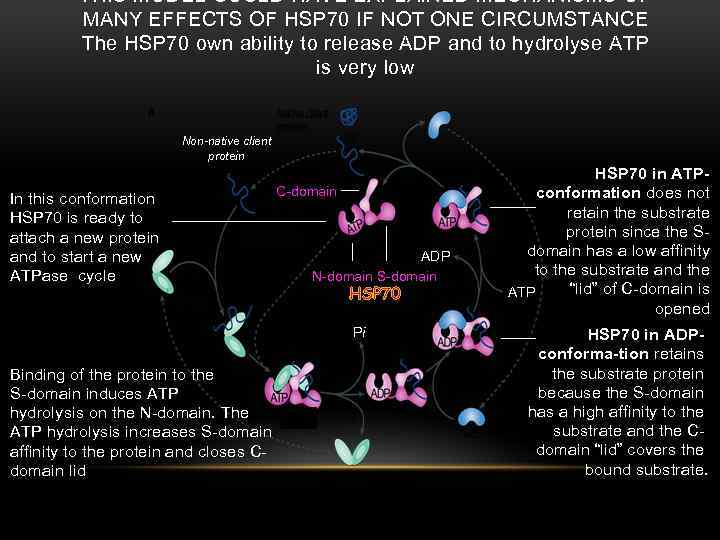
THIS MODEL COULD HAVE EXPLAINED MECHANISMS OF MANY EFFECTS OF HSP 70 IF NOT ONE CIRCUMSTANCE The HSP 70 own ability to release ADP and to hydrolyse ATP is very low Non-native client protein In this conformation HSP 70 is ready to attach a new protein and to start a new ATPase cycle C-domain ADP N-domain S-domain HSP 70 Pi Binding of the protein to the S-domain induces ATP hydrolysis on the N-domain. The ATP hydrolysis increases S-domain affinity to the protein and closes Cdomain lid HSP 70 in ATPconformation does not retain the substrate protein since the Sdomain has a low affinity to the substrate and the “lid” of C-domain is ATP opened HSP 70 in ADPconforma-tion retains the substrate protein because the S-domain has a high affinity to the substrate and the Cdomain “lid” covers the bound substrate.

HSP 70 FUNCTIONS IN A NORMAL CELL
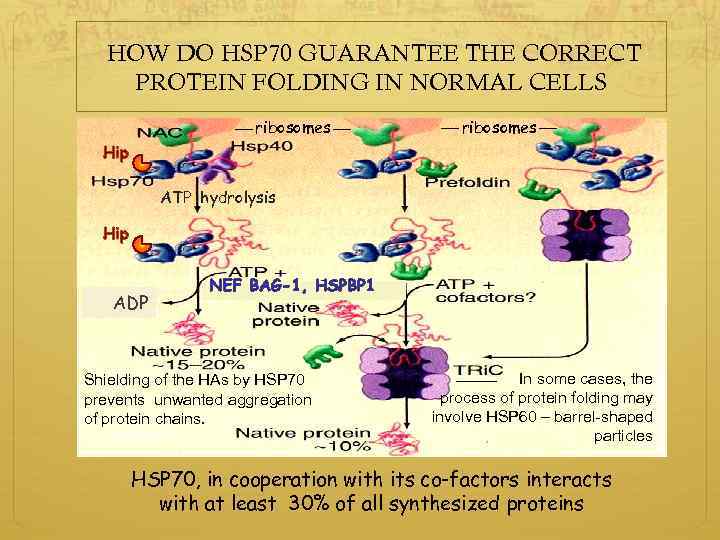
HOW DO HSP 70 GUARANTEE THE CORRECT PROTEIN FOLDING IN NORMAL CELLS ribosomes Hip ATP hydrolysis Hip ADP Shielding of the HAs by HSP 70 prevents unwanted aggregation of protein chains. In some cases, the process of protein folding may involve HSP 60 – barrel-shaped particles HSP 70, in cooperation with its co-factors interacts with at least 30% of all synthesized proteins
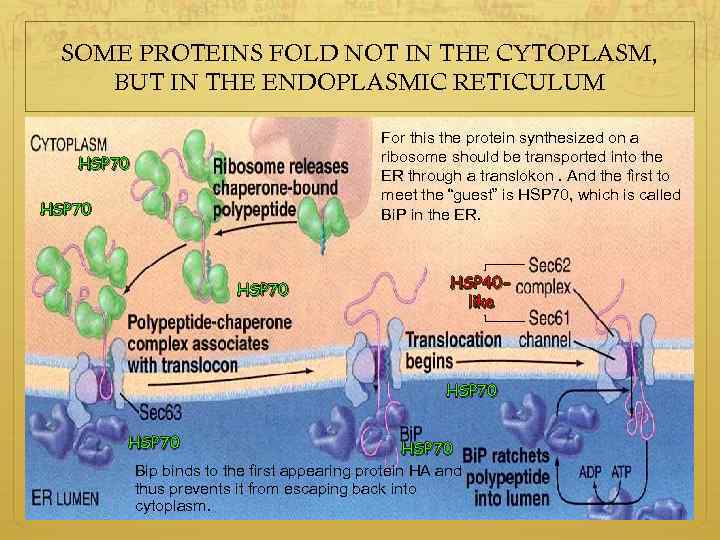
SOME PROTEINS FOLD NOT IN THE CYTOPLASM, BUT IN THE ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM For this the protein synthesized on a ribosome should be transported into the ER through a translokon. And the first to meet the “guest” is HSP 70, which is called Bi. P in the ER. HSP 70 HSP 40 like HSP 70 Bip binds to the first appearing protein HA and thus prevents it from escaping back into cytoplasm.
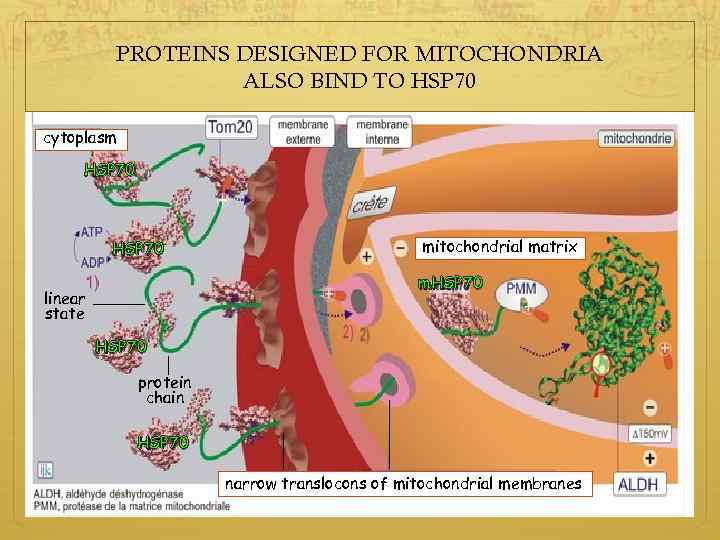
PROTEINS DESIGNED FOR MITOCHONDRIA ALSO BIND TO HSP 70 cytoplasm HSP 70 mitochondrial matrix m. HSP 70 linear state HSP 70 protein chain HSP 70 narrow translocons of mitochondrial membranes
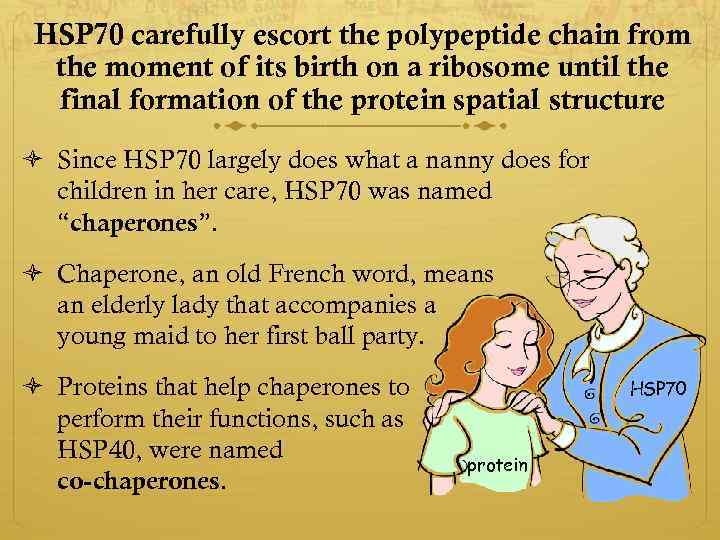
HSP 70 carefully escort the polypeptide chain from the moment of its birth on a ribosome until the final formation of the protein spatial structure Since HSP 70 largely does what a nanny does for children in her care, HSP 70 was named “chaperones”. Chaperone, an old French word, means an elderly lady that accompanies a young maid to her first ball party. Proteins that help chaperones to perform their functions, such as HSP 40, were named co-chaperones. HSP 70 protein

HSP 70 participate in two of them, namely PROTEASOMAL AND LYSOSOMAL DEGRADATION Unfortunately, protein folding and re-folding sometimes occurs with errors: that leads to emergence of non-functional proteins or proteins harmful to the cell Fortunately, the nature provided several ways of disposing such old, mutant or poorly folded proteins
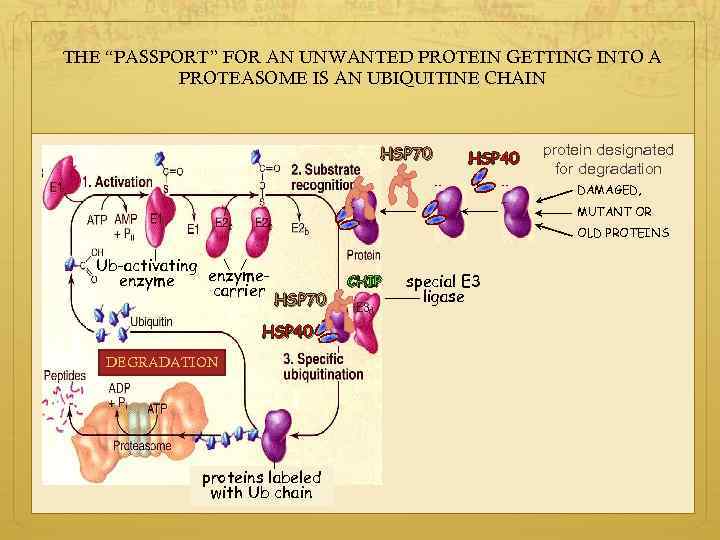
THE “PASSPORT” FOR AN UNWANTED PROTEIN GETTING INTO A PROTEASOME IS AN UBIQUITINE CHAIN HSP 70 HSP 40 protein designated for degradation DAMAGED, MUTANT OR OLD PROTEINS Ub-activating enzyme carrier HSP 70 HSP 40 DEGRADATION proteins labeled with Ub chain CHIP special E 3 ligase
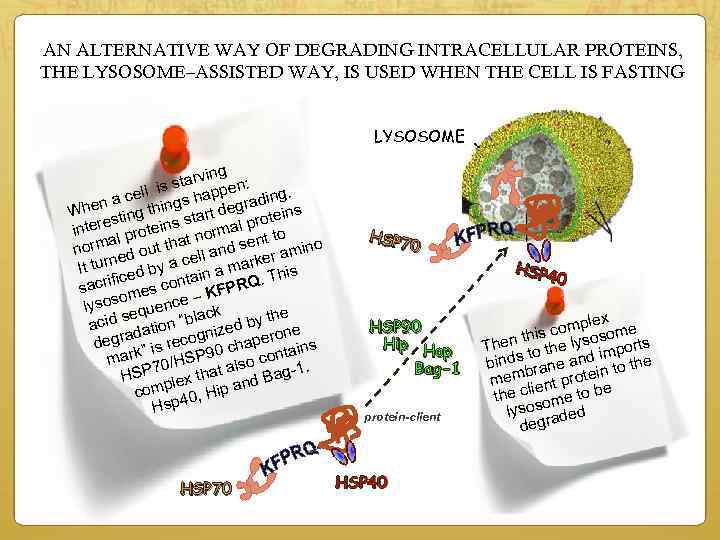
AN ALTERNATIVE WAY OF DEGRADING INTRACELLULAR PROTEINS, THE LYSOSOME–ASSISTED WAY, IS USED WHEN THE CELL IS FASTING LYSOSOME ving star pen: ll is. a ce hings hap egrading en ns t d Wh sting t star al protei e s r inte al protein t norm t to rm tha and sen amino no out rned by a cell marker It tu ced This ain a acrifi es cont KFPRQ. s om – lysos equence ck s la the acid dation “b ized by ne n o a degr ” is recog 0 chaper ains t 9 rk ma 70/HSP t also con 1. P a g HS mplex th and Ba ip o c sp 40, H H HSP 70 HSP 7 0 HSP 90 Hip Hop Bag-1 protein-client HSP 40 HSP 4 0 lex comp some his hen t the lyso ports T to im binds rane and to the n b mem ient protei e l the c ome to b s lyso raded g de
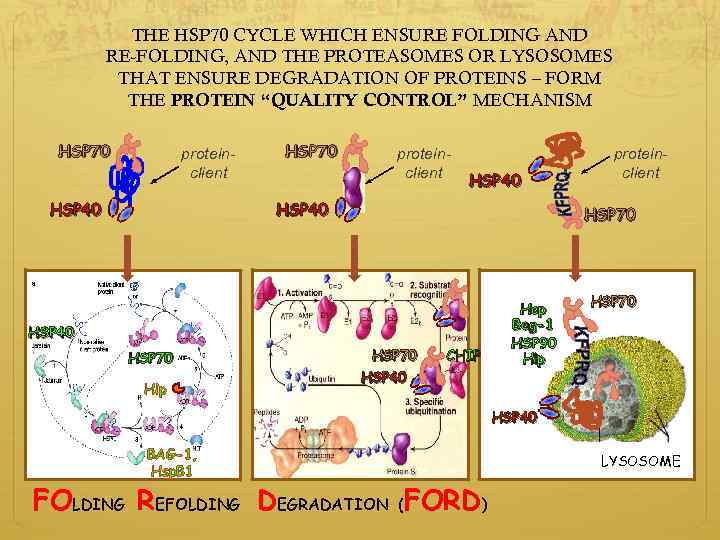
THE HSP 70 CYCLE WHICH ENSURE FOLDING AND RE-FOLDING, AND THE PROTEASOMES OR LYSOSOMES THAT ENSURE DEGRADATION OF PROTEINS – FORM THE PROTEIN “QUALITY CONTROL” MECHANISM HSP 70 proteinclient HSP 40 HSP 70 Hip HSP 70 CHIP HSP 40 protein-client BAG-1, Hsp. B 1 proteinclient FOLDING REFOLDING DEGRADATION (FORD) Hop Bag-1 HSP 90 Hip HSP 70 HSP 40 LYSOSOME

WHAT WE HAVE LEARNT ABOUT HSP 70 FUNCTIONS IN NORMAL CELLS 1. Благодаря трех-доменной структуре HSP 70 образуют АТФ-азный цикл, сопряженный с присоединением и отсоединением белка-клиента. 2. АТФ-азный цикл HSP 70 формирует механизм фолдинга и рефолдинга белка. 3. HSP 70 распознает необратимо поврежденные белки и посылает на деградацию в протеосомы, а белки с блоком KFPRQ в лизосомы.

HSP 70 FUNCTIONS IN A DAMAGED CELL

TO MAINTAIN THE PROTEIN HOMEOSTASIS IN A DAMAGED CELL, THE FORD MACHINERY (PROTEIN QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM) USES SEVERAL APPROACHES HSP 70 can prevent formation of aggregates If the aggregates have already formed, HSP 70 can disaggregate them and restore the protein If the protein cannot be restored, FORD degrades it
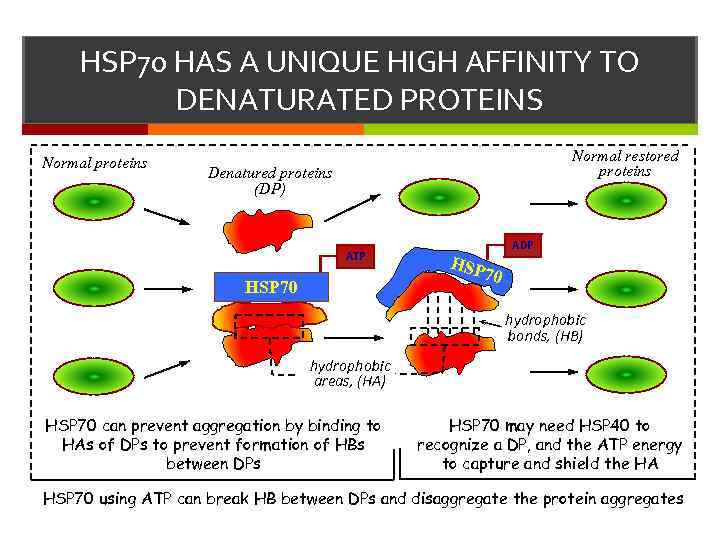
HSP 70 HAS A UNIQUE HIGH AFFINITY TO DENATURATED PROTEINS Normal proteins Normal restored proteins Denatured proteins (DP) ATP HSP 70 ADP HSP 70 hydrophobic bonds, (HB) hydrophobic areas, (HA) HSP 70 can prevent aggregation by binding to HAs of DPs to prevent formation of HBs between DPs HSP 70 may need HSP 40 to recognize a DP, and the ATP energy to capture and shield the HA HSP 70 using ATP can break HB between DPs and disaggregate the protein aggregates
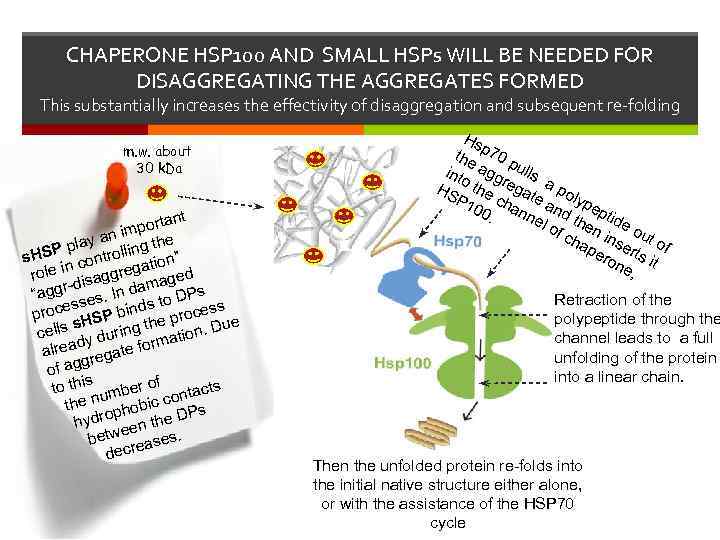
CHAPERONE HSP 100 AND SMALL HSPs WILL BE NEEDED FOR DISAGGREGATING THE AGGREGATES FORMED This substantially increases the effectivity of disaggregation and subsequent re-folding m. w. about 30 k. Da nt porta an im play olling the P s. HS n contr n” i gatio d role -disaggre mage r a “agg ses. In d to DPs s s s proce HSP bind e proces e th s. Du cells y during ation d rm alrea regate fo g of ag s to thi umber of ntacts n co the ophobic Ps ydr he D h en t etwe ases. b ecre d Hs the p 70 p int agg ulls o r HS the egat a po P 1 cha e a lype n 00. nnel d th ptide e of ch n ins out o ap ero erts i f ne t , Retraction of the polypeptide through the channel leads to a full unfolding of the protein into a linear chain. Then the unfolded protein re-folds into the initial native structure either alone, or with the assistance of the HSP 70 cycle
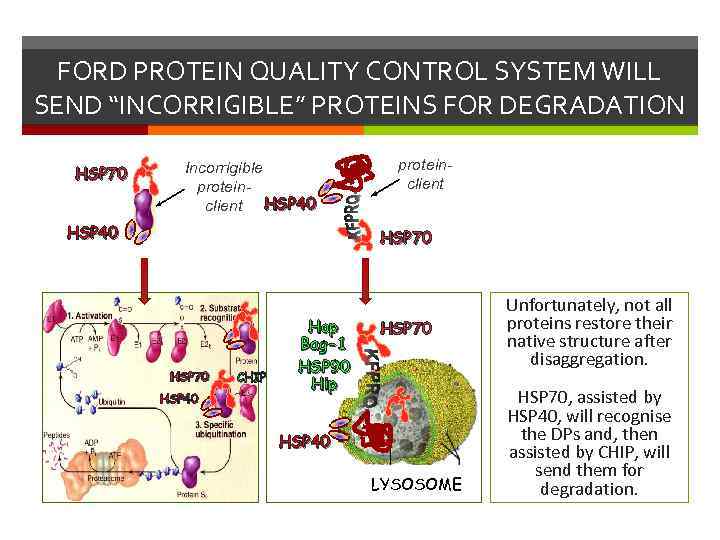
FORD PROTEIN QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM WILL SEND “INCORRIGIBLE” PROTEINS FOR DEGRADATION HSP 70 Incorrigible proteinclient HSP 40 proteinclient HSP 70 HSP 40 protein-client CHIP Hop Bag-1 HSP 90 Hip HSP 70 HSP 40 LYSOSOME Unfortunately, not all proteins restore their native structure after disaggregation. HSP 70, assisted by HSP 40, will recognise the DPs and, then assisted by CHIP, will send them for degradation.
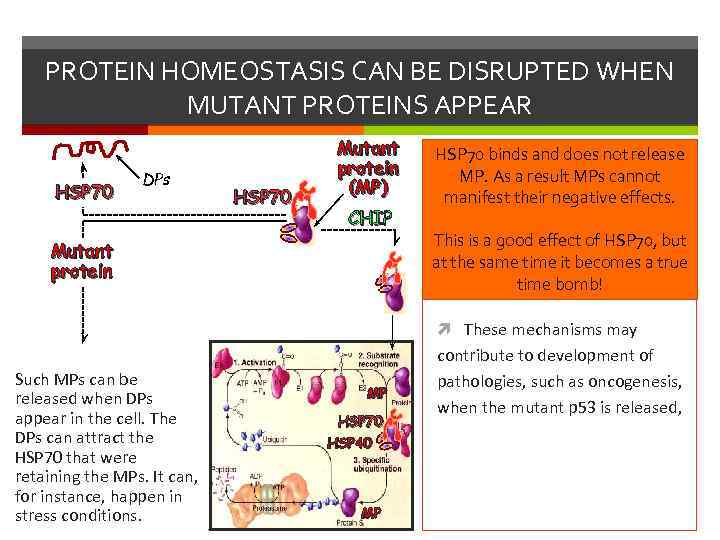
PROTEIN HOMEOSTASIS CAN BE DISRUPTED WHEN MUTANT PROTEINS APPEAR HSP 70 DPs HSP 70 Mutant protein (MP) CHIP Mutant protein HSP 70 binds and does not release MP. As a result MPs cannot manifest their negative effects. This is a good effect of HSP 70, but at the same time it becomes a true time bomb! These mechanisms may Such MPs can be released when DPs appear in the cell. The DPs can attract the HSP 70 that were retaining the MPs. It can, for instance, happen in stress conditions. MP HSP 70 HSP 40 MP contribute to development of pathologies, such as oncogenesis, when the mutant p 53 is released,
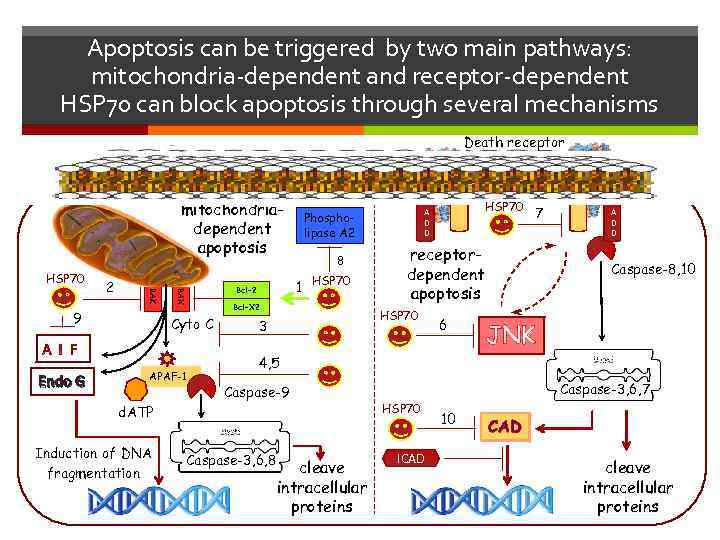
Apoptosis can be triggered by two main pathways: mitochondria-dependent and receptor-dependent HSP 70 can block apoptosis through several mechanisms Death receptor mitochondriadependent apoptosis HSP 70 9 Endo G BAX BAK 2 Cyto C APAF-1 Phospholipase A 2 8 1 Bcl-2 HSP 70 Bcl-X 2 HSP 70 7 receptordependent apoptosis HSP 70 3 6 F A D D Caspase-8, 10 JNK 4, 5 Caspase-9 d. ATP Induction of DNA fragmentation F A D D Caspase-3, 6, 8 cleave intracellular proteins Caspase-3, 6, 7 HSP 70 ICAD 10 CAD cleave intracellular proteins

WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNT TODAY 1. To maintain protein homeostasis in a damage cell, FORD prevents protein aggregation, disaggregates formed aggregates, and degrades irreparable proteins. 2. HSP 70 can deposit MPs. However, such MTs can be released when DPs appear in cell. 3. HSP 70 blocks apoptosis by inhibiting the release of proapoptotic factors from mitochondria; inhibiting AIF, caspase-9 and JNK, as well as by increasing the Bcl-2 level and decreasing the Bax level. GENERAL CONCLUSION: HSP 70 maintains the protein homeostasis and protects the damaged cell

WHAT ARE THE MECHANISMS REGULATING HSP 70 SYNTHESIS?
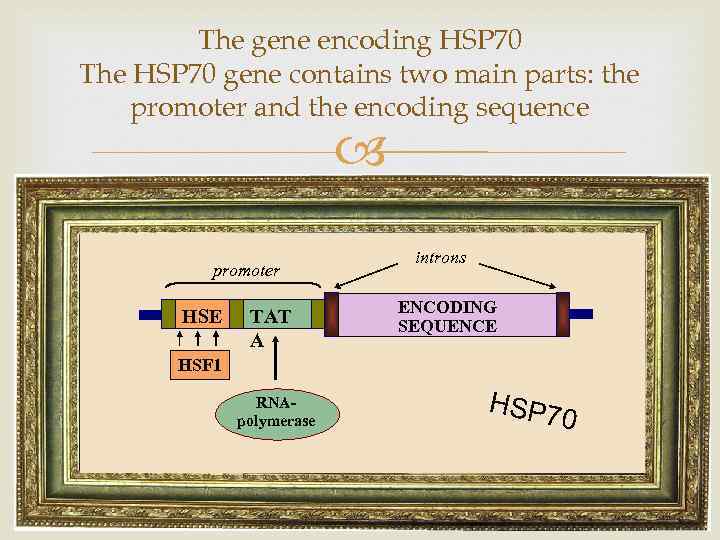
The gene encoding HSP 70 The HSP 70 gene contains two main parts: the promoter and the encoding sequence promoter HSE TAT A introns ENCODING SEQUENCE HSF 1 RNApolymerase HSP 7 0
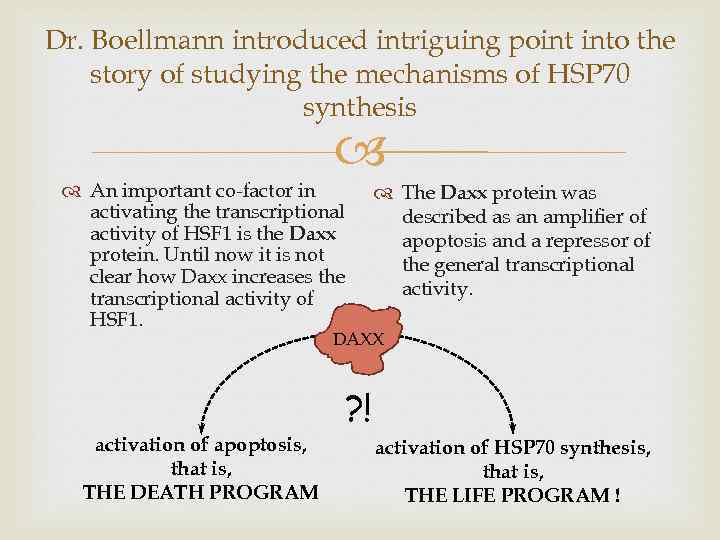
Dr. Boellmann introduced intriguing point into the story of studying the mechanisms of HSP 70 synthesis An important co-factor in activating the transcriptional activity of HSF 1 is the Daxx protein. Until now it is not clear how Daxx increases the transcriptional activity of HSF 1. The Daxx protein was described as an amplifier of apoptosis and a repressor of the general transcriptional activity. DAXX ? ! activation of apoptosis, that is, THE DEATH PROGRAM activation of HSP 70 synthesis, that is, THE LIFE PROGRAM !


Let us summarize what we have learnt today about the mechanisms of activation and inactivation of HSP 70 synthesis 1. The element of hsp 70 gene promoter, HSE plays a key role in the activation of HSP 70 gene transcription. The HSE interaction with the HSF 1 activates the expression of HSP 70 gene. 2. In a normal cell, HSF 1 occurs in cytoplasm in the inactive monomer state. The inactive state of HSF 1 monomer is maintained by HSP 70 and HSP 40. 3. Activation of the HSF 1 goes in two steps: 1) emerging denatured proteins induce removal of HSP 70 from HSF-1, trimerization of the HSF 1, and HSF 1 binding to DNA. 2) the hyperphosphorylation of HSF-1 takes place, and the transcription of hsp 70 gene is activated. 4. Cessation of HSP 70 synthesis are due to the fact that HSP 70 bind to active HSF 1, inhibit its transcriptional activity and disconnect it from DNA.

HSP 70 IN IMMUNE RESPONSES
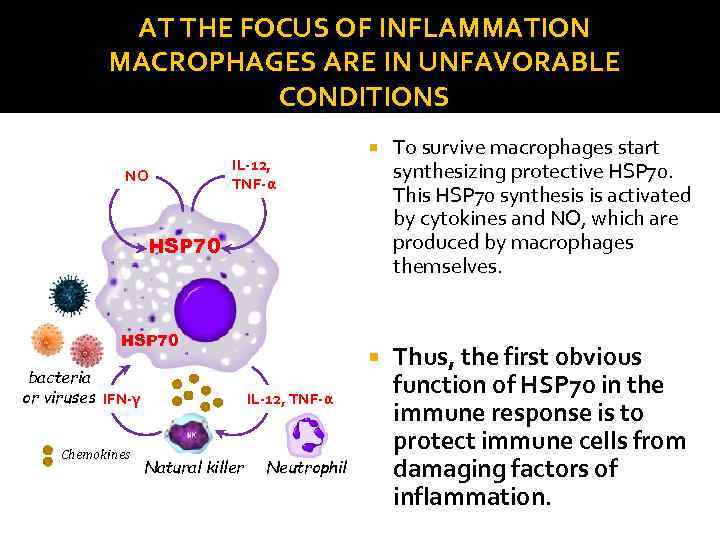
AT THE FOCUS OF INFLAMMATION MACROPHAGES ARE IN UNFAVORABLE CONDITIONS NO To survive macrophages start synthesizing protective HSP 70. This HSP 70 synthesis is activated by cytokines and NO, which are produced by macrophages themselves. IL-12, TNF-α Thus, the first obvious function of HSP 70 in the immune response is to protect immune cells from damaging factors of inflammation. HSP 70 bacteria or viruses IFN-γ Chemokines IL-12, TNF-α Natural killer Neutrophil
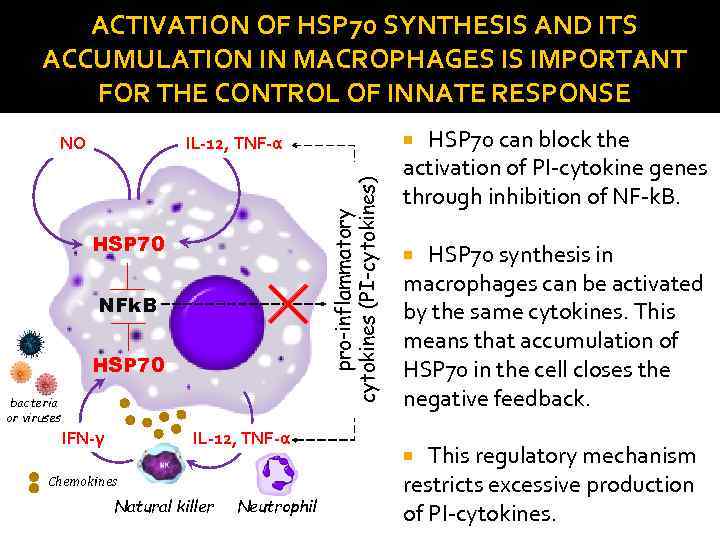
ACTIVATION OF HSP 70 SYNTHESIS AND ITS ACCUMULATION IN MACROPHAGES IS IMPORTANT FOR THE CONTROL OF INNATE RESPONSE HSP 70 NFk. B HSP 70 bacteria or viruses IFN-γ IL-12, TNF-α Chemokines Natural killer Neutrophil HSP 70 can block the activation of PI-cytokine genes through inhibition of NF-k. B. IL-12, TNF-α pro-inflammatory cytokines (PI-cytokines) NO HSP 70 synthesis in macrophages can be activated by the same cytokines. This means that accumulation of HSP 70 in the cell closes the negative feedback. This regulatory mechanism restricts excessive production of PI-cytokines.
Hsp 70 также обнаруживаются на поверхности нормальных, инфицированных, опухолевых клеток и даже в кровотоке HSP 70

Endogenous HSP 70 exposed on the outer surface of cell membranes contribute to the development of innate and adaptive responses Microbial and human HSP are highly conservative. This is why extracellular Hsp 70 may trigger a strong immune response. Immune cells can recognize HSP 70 on the cell surface. For instance, on the surface of tumor cells, HSP 70 are recognized by NK cells, DCs and T- cells. It is due to this recognition that NK cells kill tumor cells, while DCs and T-cells get activated.
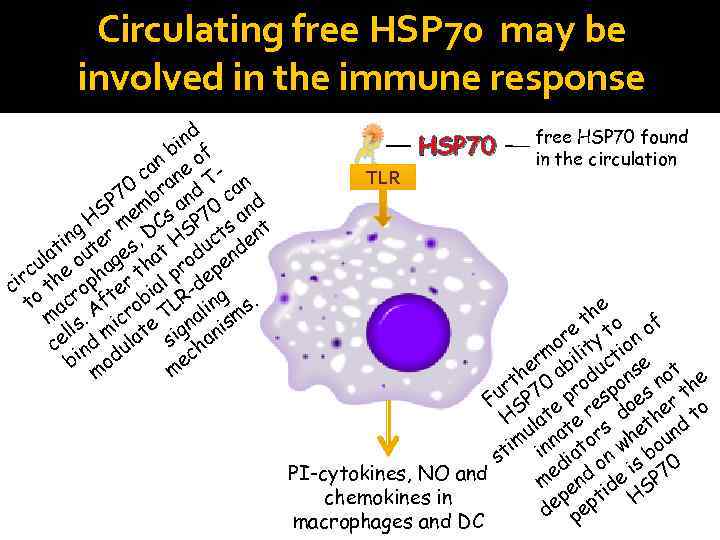
Circulating free HSP 70 may be involved in the immune response d in f b n eo ca an T- n 0 r a P 7 mb and 0 c nd HS me Cs P 7 s a t g in ter s, D HS uct den t la ou ge hat rod en u rc the pha r t l p dep ci o ro fte bia R- ng. t ac A ro L li s m ls. ic e T na ism el d m ulat sig han c in ec b od m m HSP 70 TLR free HSP 70 found in the circulation e th o of e t or ity ion m l t er abi uc se ot h rt 70 rod pon s n the Fu SP e p res oe er o d h t H lat te s het nd u a r im inn ato w bou st di d on is 70 e PI-cytokines, NO and m en ide SP chemokines in ep ept H d p macrophages and DC
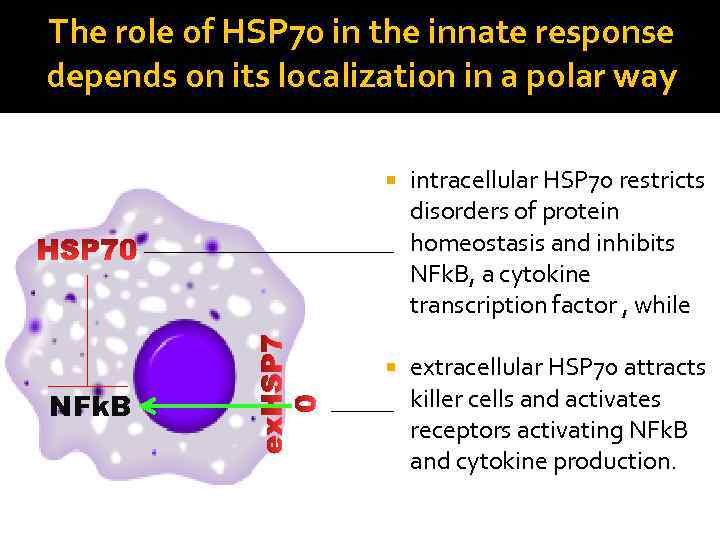
The role of HSP 70 in the innate response depends on its localization in a polar way NFk. B intracellular HSP 70 restricts disorders of protein homeostasis and inhibits NFk. B, a cytokine transcription factor , while extracellular HSP 70 attracts killer cells and activates receptors activating NFk. B and cytokine production.

HSP 70 PLAYS AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN THE ADAPTIVE RESPONSE, HSP 70 plays the most significant role in the antigen presentation. HSP 70 may be involved in the antigen presentation at three key stages of this process: 1) of formation of the complex with an antigen, 2) of antigen delivery to and transfer into the APCs 3) of intracellular delivery of antigens to the MHC class I
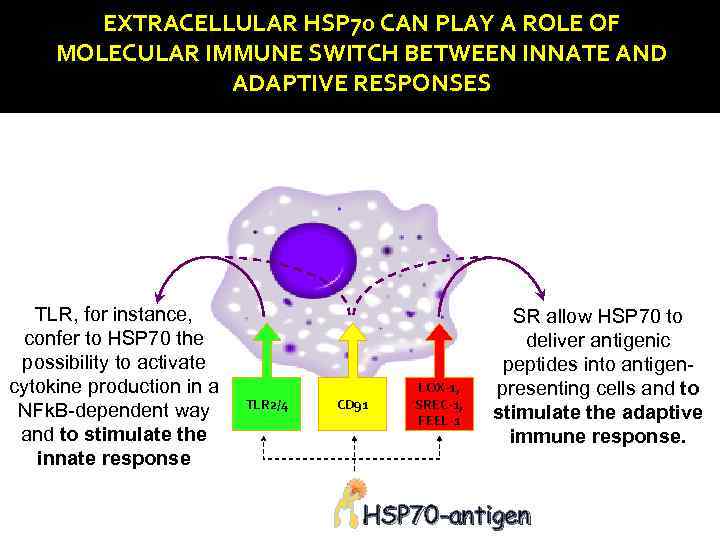
EXTRACELLULAR HSP 70 CAN PLAY A ROLE OF MOLECULAR IMMUNE SWITCH BETWEEN INNATE AND ADAPTIVE RESPONSES TLR, for instance, confer to HSP 70 the possibility to activate cytokine production in a NFk. B-dependent way and to stimulate the innate response TLR 2/4 CD 91 LOX-1, SREC-1, FEEL-1 SR allow HSP 70 to deliver antigenic peptides into antigenpresenting cells and to stimulate the adaptive immune response. HSP 70 -antigen

ЧТО МЫ УЗНАЛИ О РОЛИ HSP 70 В ИММУНИТЕТЕ: 1. Внутриклеточные HSP 70 защищают клетку и ограничивают продукцию цитокинов, тогда как внеклеточные, напротив стимулируют продукцию цитокинов и маркируют клетки на уничтожение. 2. Сигнальные TL-рецепторы помогают HSP 70 активировать продукцию цитокинов и стимулировать врожденный ответ, тогда как захватывающие SR рецепторы помогают HSP 70 доставлять антигены в антигенпрезентирующие клетки и стимулируют адаптивный ответ.

ROLE OF HSP 70 IN CARCINOGENESIS
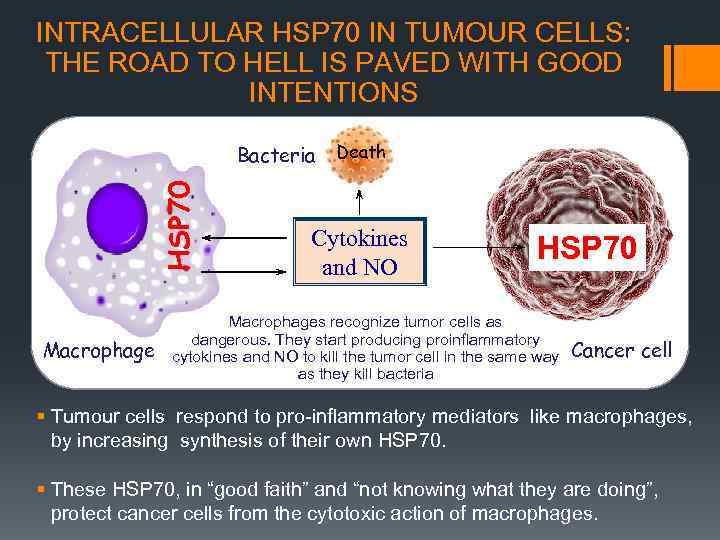
INTRACELLULAR HSP 70 IN TUMOUR CELLS: THE ROAD TO HELL IS PAVED WITH GOOD INTENTIONS HSP 70 Bacteria Macrophage Death Cytokines and NO HSP 70 Macrophages recognize tumor cells as dangerous. They start producing proinflammatory cytokines and NO to kill the tumor cell in the same way as they kill bacteria Cancer cell Tumour cells respond to pro-inflammatory mediators like macrophages, by increasing synthesis of their own HSP 70. These HSP 70, in “good faith” and “not knowing what they are doing”, protect cancer cells from the cytotoxic action of macrophages.
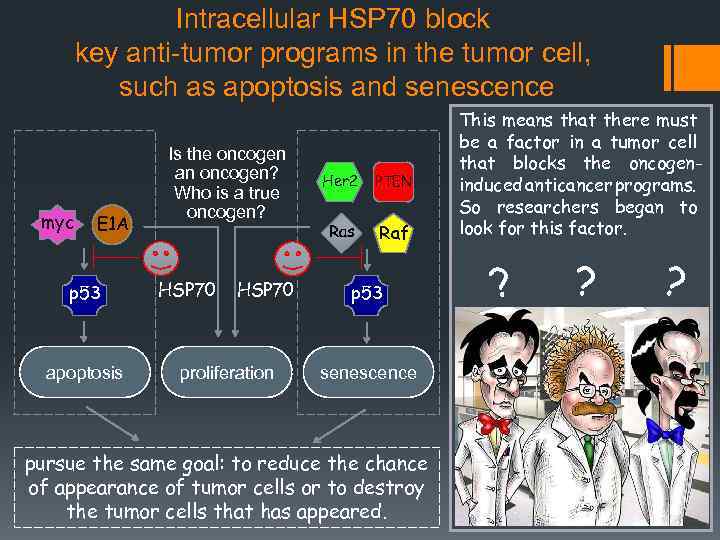
Intracellular HSP 70 block key anti-tumor programs in the tumor cell, such as apoptosis and senescence myc E 1 A p 53 apoptosis Is the oncogen an oncogen? Who is a true oncogen? HSP 70 proliferation Her 2 PTEN Ras Raf p 53 senescence pursue the same goal: to reduce the chance of appearance of tumor cells or to destroy the tumor cells that has appeared. This means that there must It was precisely the oncogenes be a factor in a tumor cell that could activate apoptosis in that blocks the oncogentumor cells, as myc or E 1 A do induced anticancer programs. or to trigger senescence, as So researchers began Ras, Her-2, PTEN, Raf do. to look for this factor. ? ? ? The oncogenes trigger both these anti-oncogene programs through activation of p 53. For a normal cell it is quite appropriate, because this protects the cell from spontaneous malignancy during the action of normal growth factors. But tumor cells apparently bypass this obstacle.
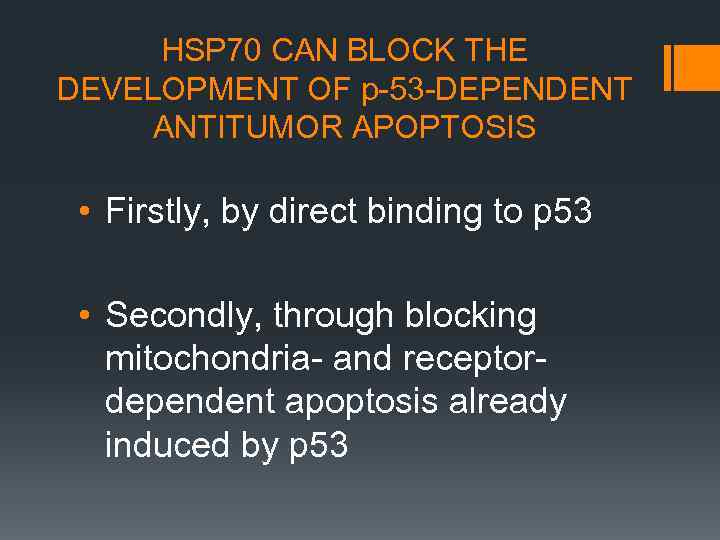
HSP 70 CAN BLOCK THE DEVELOPMENT OF р-53 -DEPENDENT ANTITUMOR APOPTOSIS • Firstly, by direct binding to p 53 • Secondly, through blocking mitochondria- and receptordependent apoptosis already induced by p 53
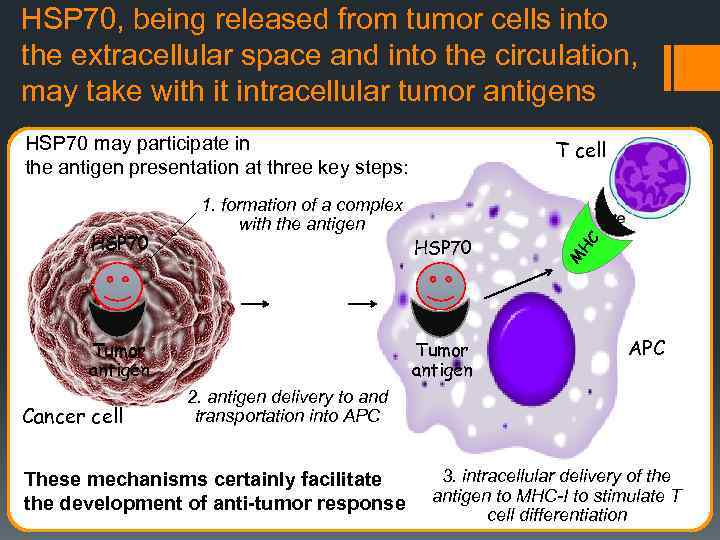
HSP 70, being released from tumor cells into the extracellular space and into the circulation, may take with it intracellular tumor antigens HSP 70 may participate in the antigen presentation at three key steps: T cell HSP 70 Tumor antigen Cancer cell Tumor antigen M HC HSP 70 1. formation of a complex with the antigen APC 2. antigen delivery to and transportation into APC These mechanisms certainly facilitate the development of anti-tumor response 3. intracellular delivery of the antigen to MHC-I to stimulate T cell differentiation
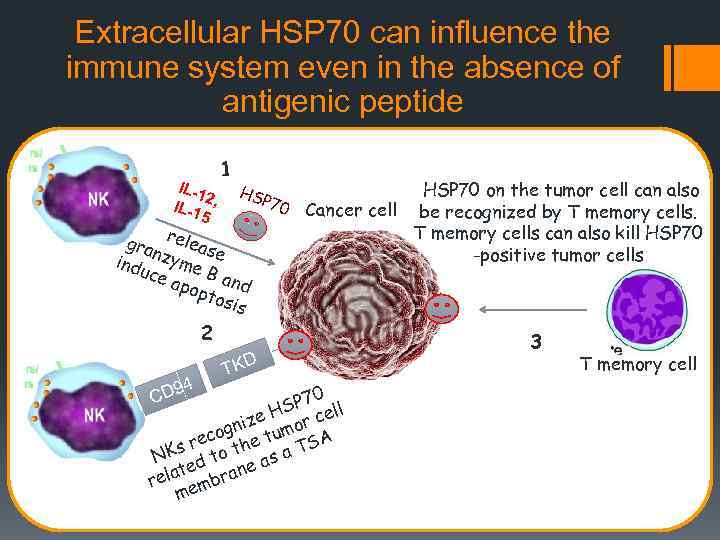
Extracellular HSP 70 can influence the immune system even in the absence of antigenic peptide IL - 1 2 IL-1 , 5 1 HS P 70 gra releas n e indu zyme ce a B an d pop tos is HSP 70 on the tumor cell can also Cancer cell be recognized by T memory cells can also kill HSP 70 -positive tumor cells 2 D 94 C TKD 0 SP 7 ell H nize umor c g eco he t TSA r NKs d to t as a te ne rela embra m 3 T memory cell

HSP 70 ВЫПОЛНЯЕТ АЛЬТЕРНАТИВНЫЕ ФУНКЦИИ В ЗАВИСИМОСТИ ОТ ЛОКАЛИЗАЦИИ Внутриклеточный HSP 70, «не понимая» защищает раковую клетку и подавляет антиопухолевые программы апоптоза и старения. Экстраклеточный HSP 70 как сбежавший из раковой тюрьмы пленник рассказывает природным киллерам и Т клеткам, об истинном положени дел, о том, что клетка хоть и своя, но она раковая и ее надо уничтожить.

ROLE OF HSP 70 IN PROTECTION OF THE BRAIN IN ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
Alzheimer's is a neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system • Alzheimer's disease, long before the biological death of the body, gradually robs a person of the most important thing that makes him Homo Sapiens, • of his memory, • the ability to establish causal relationships, • to perceive and analyze new information, • to recognize friends and relatives.
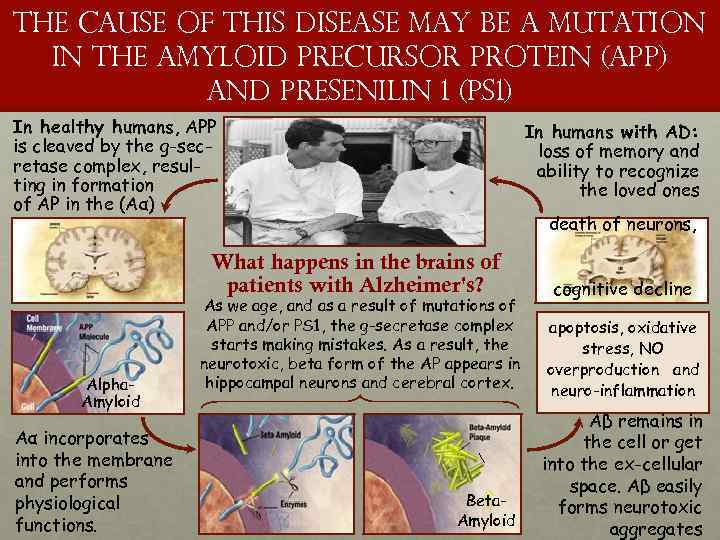
the cause of this disease may be a mutation in the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin 1 (PS 1) In healthy humans, APP is cleaved by the g-secretase complex, resulting in formation of AP in the (Aα) In humans with AD: loss of memory and ability to recognize the loved ones death of neurons, What happens in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's? Alpha. Amyloid Aα incorporates into the membrane and performs physiological functions. As we age, and as a result of mutations of APP and/or PS 1, the g-secretase complex starts making mistakes. As a result, the neurotoxic, beta form of the AP appears in hippocampal neurons and cerebral cortex. Beta. Amyloid cognitive decline apoptosis, oxidative stress, NO overproduction and neuro-inflammation Aβ remains in the cell or get into the ex-cellular space. Aβ easily forms neurotoxic aggregates
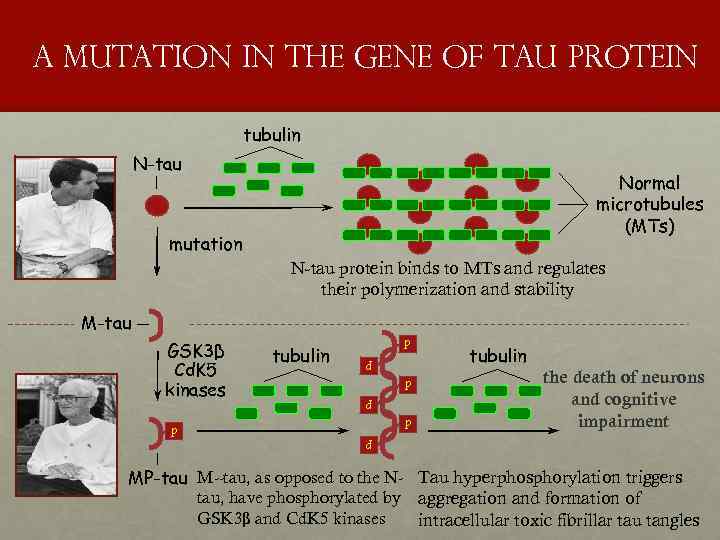
a mutation in the gene of tau protein tubulin N-tau Normal microtubules (MTs) mutation N-tau protein binds to MTs and regulates their polymerization and stability M-tau p p tubulin p p GSK 3β Cd. K 5 kinases p p tubulin the death of neurons and cognitive impairment p MP-tau M--tau, as opposed to the N- Tau hyperphosphorylation triggers tau, have phosphorylated by aggregation and formation of GSK 3β and Cd. K 5 kinases intracellular toxic fibrillar tau tangles

ШЕСТЬ МЕХАНИЗМОВ НЕЙРОПРОТЕКТОРНОГО ЭФФЕКТА HSP 70 1) дизагрегация и деградация внутриклеточных βамилоидных агрегатов, 2) дизагрегация внеклеточных β-амилоидных агрегатов, 3) выведение β-амилоида из межклеточного пространства, 4) ограничение гиперфосфорилирования тау-белка, дисагрегация и деградация аномальных tau белков, 5) ограничение гиперпродукции NO и 6) ограничение апоптоза.
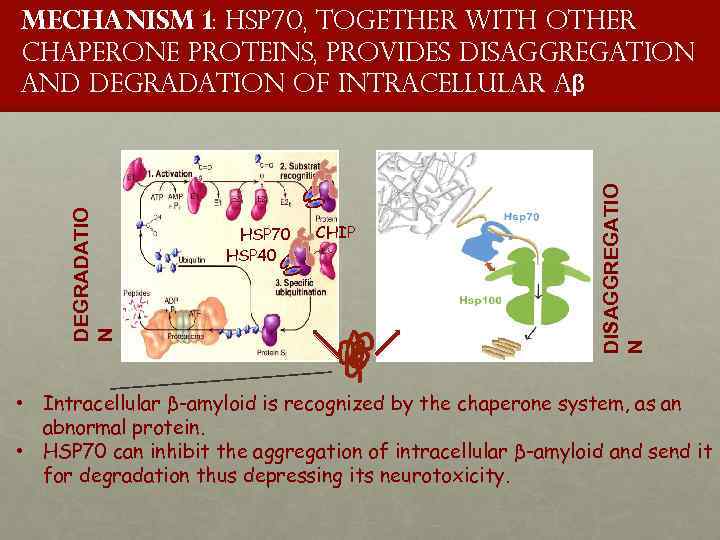
HSP 70 HSP 40 proteinclient CHIP DISAGGREGATIO N DEGRADATIO N Mechanism 1: HSP 70, together with other chaperone proteins, provides disaggregation and degradation of intracellular Aβ • Intracellular β-amyloid is recognized by the chaperone system, as an abnormal protein. • HSP 70 can inhibit the aggregation of intracellular β-amyloid and send it for degradation thus depressing its neurotoxicity.
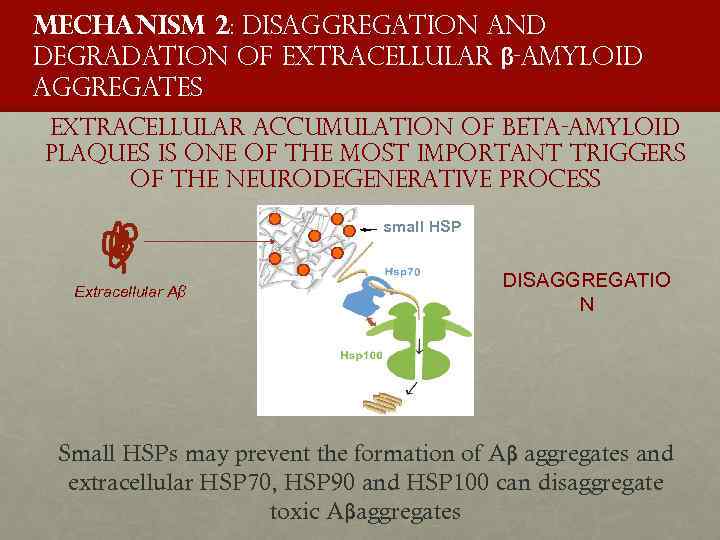
Mechanism 2: disaggregation and degradation of extracellular β-amyloid aggregates extracellular accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques is one of the most important triggers of the neurodegenerative process small HSP Extracellular Aβ DISAGGREGATIO N Small HSPs may prevent the formation of Aβ aggregates and extracellular HSP 70, HSP 90 and HSP 100 can disaggregate toxic Aβaggregates
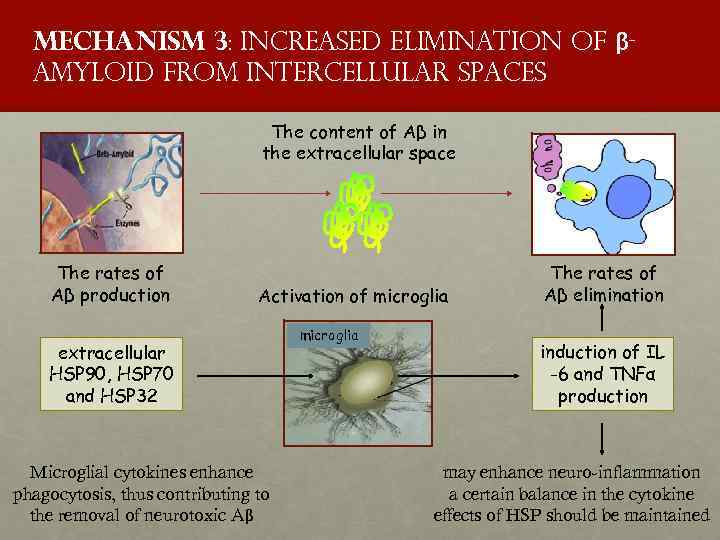
Mechanism 3: increased elimination of βamyloid from intercellular spaces The content of Aβ in the extracellular space The rates of Aβ production Activation of microglia extracellular HSP 90, HSP 70 and HSP 32 Microglial cytokines enhance phagocytosis, thus contributing to the removal of neurotoxic Aβ microglia The rates of Aβ elimination induction of IL -6 and TNFα production may enhance neuro-inflammation a certain balance in the cytokine effects of HSP should be maintained
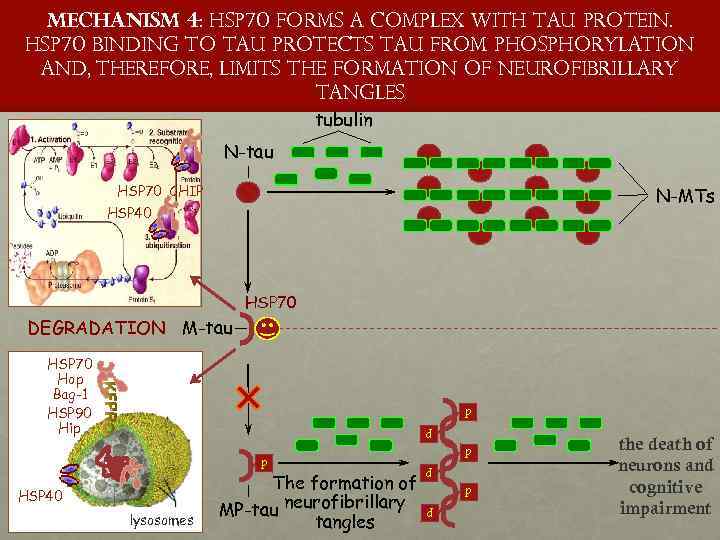
Mechanism 4: HSP 70 forms a complex with tau protein. HSP 70 binding to tau protects tau from phosphorylation and, therefore, limits the formation of neurofibrillary tangles tubulin N-tau HSP 70 CHIP N-MTs HSP 40 proteinclient HSP 70 DEGRADATION M-tau HSP 70 Hop Bag-1 HSP 90 LYSOSO ME Hip p p lysosomes The formation of MP-tau neurofibrillary tangles p p HSP 40 p p p the death of neurons and cognitive impairment
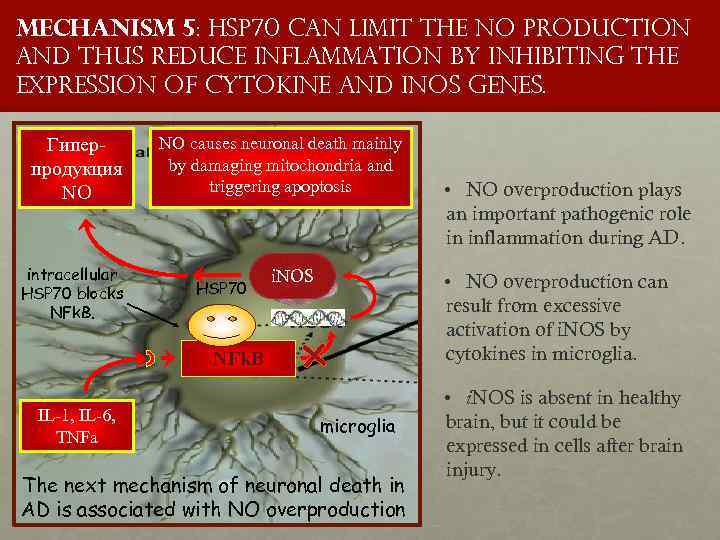
Mechanism 5: HSP 70 CAN limit the NO production and thus reduce inflammation by inhibiting the expression of cytokine and i. NOS genes. Гиперпродукция NO intracellular HSP 70 blocks NFk. B. NO causes neuronal death mainly by damaging mitochondria and triggering apoptosis HSP 70 i. NOS • NO overproduction can result from excessive activation of i. NOS by cytokines in microglia. NFk. B IL-1, IL-6, TNFa • NO overproduction plays an important pathogenic role in inflammation during AD. microglia The next mechanism of neuronal death in AD is associated with NO overproduction • i. NOS is absent in healthy brain, but it could be expressed in cells after brain injury.
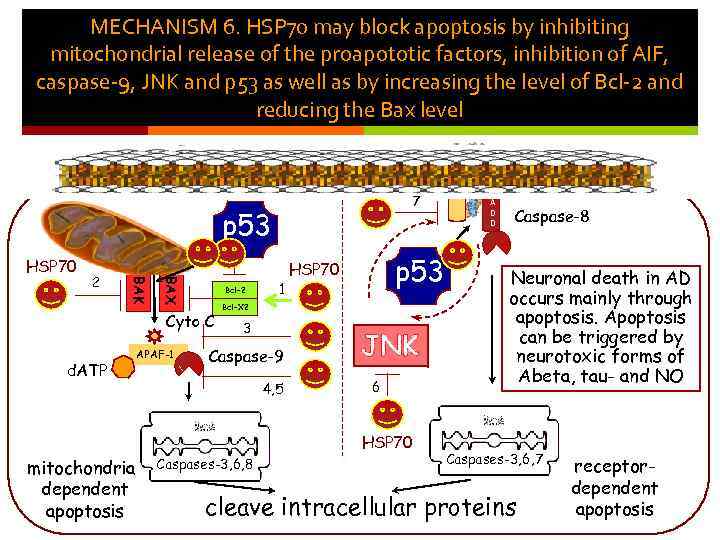
MECHANISM 6. HSP 70 may block apoptosis by inhibiting mitochondrial release of the proapototic factors, inhibition of AIF, caspase-9, JNK and p 53 as well as by increasing the level of Bcl-2 and reducing the Bax level 7 p 53 BAK 2 BAX HSP 70 Bcl-2 Cyto C d. ATP APAF-1 1 p 53 HSP 70 Bcl-X 2 3 Caspase-9 4, 5 JNK 6 HSP 70 mitochondriadependent apoptosis Caspases-3, 6, 8 F A D D Caspase-8 Neuronal death in AD occurs mainly through apoptosis. Apoptosis can be triggered by neurotoxic forms of Abeta, tau- and NO Caspases-3, 6, 7 cleave intracellular proteins receptordependent apoptosis

CONCLUSION HSP 70 is an important endogenous FACTOR for protection of neurons in Alzheimer's disease
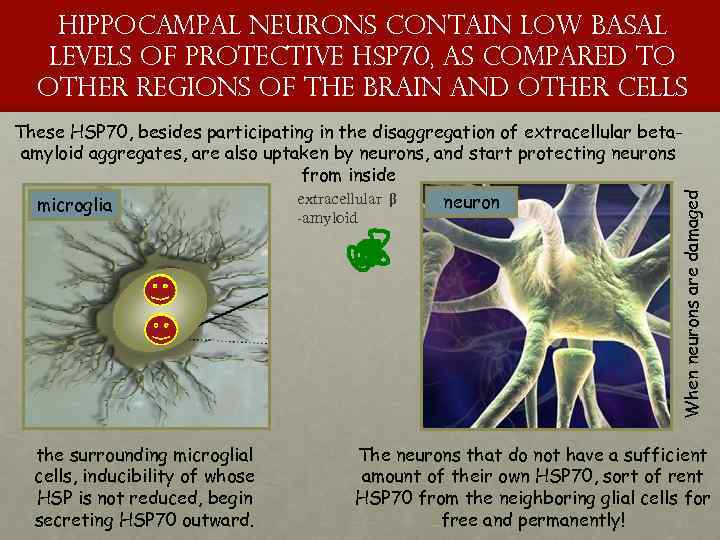
hippocampal neurons contain low basal levels of protective HSP 70, as compared to other regions of the brain and other cells -amyloid the surrounding microglial cells, inducibility of whose HSP is not reduced, begin secreting HSP 70 outward. When neurons are damaged These HSP 70, besides participating in the disaggregation of extracellular betaamyloid aggregates, are also uptaken by neurons, and start protecting neurons from inside extracellular β neuron microglia The neurons that do not have a sufficient amount of their own HSP 70, sort of rent HSP 70 from the neighboring glial cells for free and permanently!

THE ROLE OF HSP 70 IN PROTECTING THE HEART
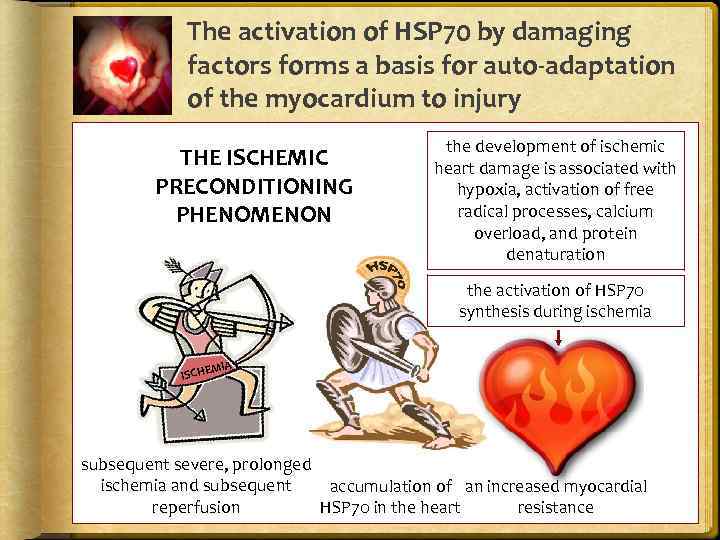
The activation of HSP 70 by damaging factors forms a basis for auto-adaptation of the myocardium to injury THE ISCHEMIC PRECONDITIONING PHENOMENON the development of ischemic heart damage is associated with hypoxia, activation of free radical processes, calcium overload, and protein denaturation the activation of HSP 70 synthesis during ischemia MIA ISCHE subsequent severe, prolonged ischemia and subsequent accumulation of an increased myocardial reperfusion HSP 70 in the heart resistance
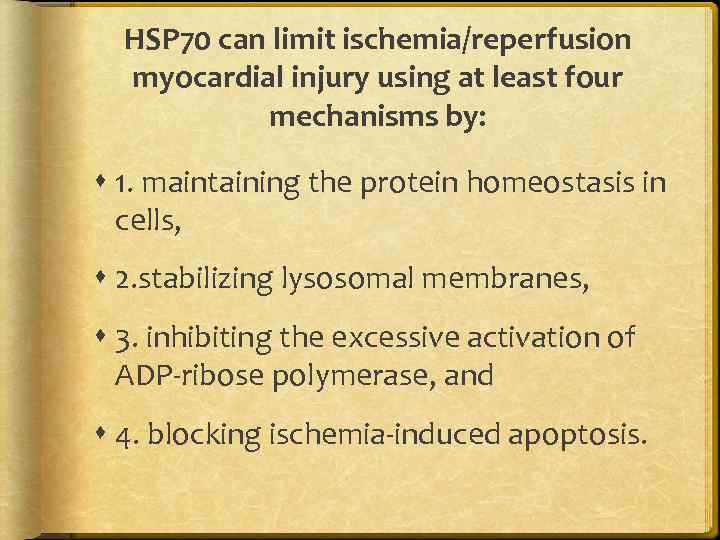
HSP 70 can limit ischemia/reperfusion myocardial injury using at least four mechanisms by: 1. maintaining the protein homeostasis in cells, 2. stabilizing lysosomal membranes, 3. inhibiting the excessive activation of ADP-ribose polymerase, and 4. blocking ischemia-induced apoptosis.
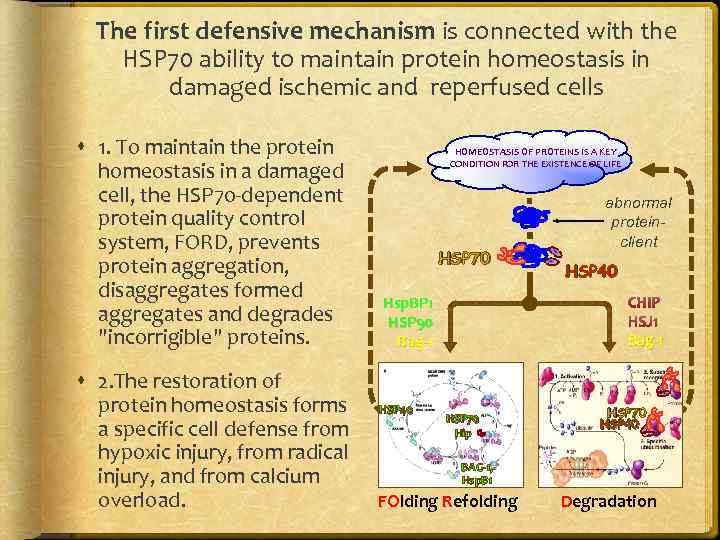
The first defensive mechanism is connected with the HSP 70 ability to maintain protein homeostasis in damaged ischemic and reperfused cells 1. To maintain the protein homeostasis in a damaged cell, the HSP 70 -dependent protein quality control system, FORD, prevents protein aggregation, disaggregates formed aggregates and degrades "incorrigible" proteins. 2. The restoration of protein homeostasis forms a specific cell defense from hypoxic injury, from radical injury, and from calcium overload. HOMEOSTASIS OF PROTEINS IS A KEY CONDITION FOR THE EXISTENCE OF LIFE HSP 70 HSP 40 CHIP HSJ 1 Bag-1 Hsp. BP 1 HSP 90 Bag-1 HSP 40 abnormal proteinclient HSP 70 Hip BAG-1, Hsp. B 1 FOlding Refolding HSP 70 HSP 40 proteinclient Degradation
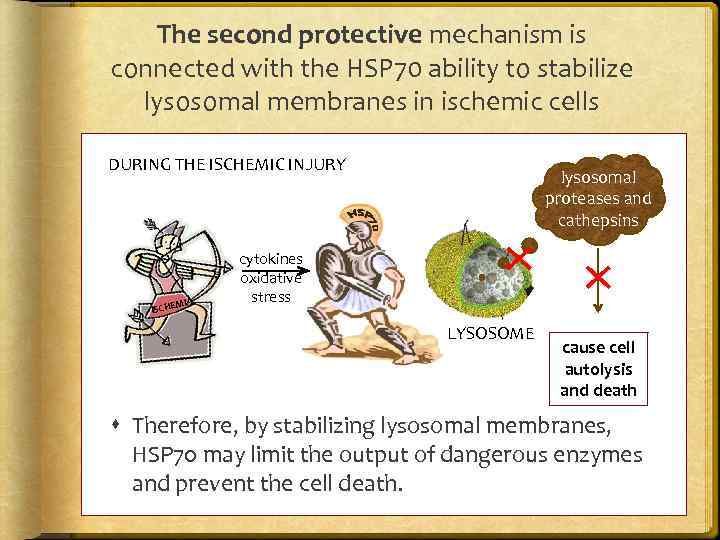
The second protective mechanism is connected with the HSP 70 ability to stabilize lysosomal membranes in ischemic cells DURING THE ISCHEMIC INJURY MIA ISCHE lysosomal proteases and cathepsins cytokines oxidative stress LYSOSOME cause cell autolysis and death Therefore, by stabilizing lysosomal membranes, HSP 70 may limit the output of dangerous enzymes and prevent the cell death.
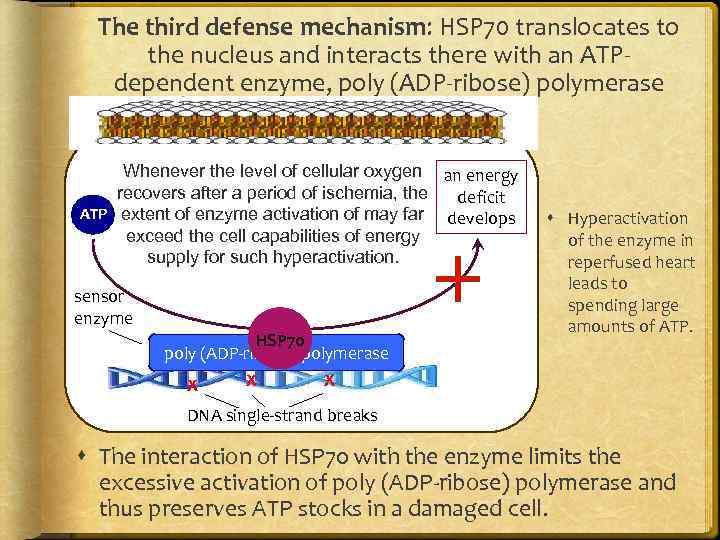
The third defense mechanism: HSP 70 translocates to the nucleus and interacts there with an ATPdependent enzyme, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase Whenever the level of cellular oxygen an energy recovers after a period of ischemia, the deficit ATP extent of enzyme activation of may far develops exceed the cell capabilities of energy supply for such hyperactivation. sensor enzyme HSP 70 poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase X X Hyperactivation of the enzyme in reperfused heart leads to spending large amounts of ATP. X DNA single-strand breaks The interaction of HSP 70 with the enzyme limits the excessive activation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase and thus preserves ATP stocks in a damaged cell.
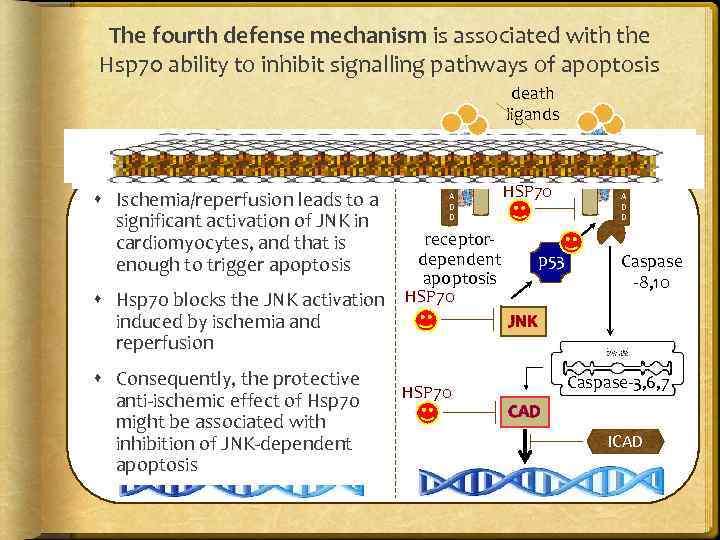
The fourth defense mechanism is associated with the Hsp 70 ability to inhibit signalling pathways of apoptosis death ligands mitochondriadependent apoptosis Bcl-2 BAX BAK Ischemia/reperfusion leads. Phosphoto a lipase A 2 p 53 significant activation of JNK in cardiomyocytes, and that is 8 HSP 70 enough to trigger apoptosis 1 2 Bcl-X 2 Endo G APAF-1 receptordependent apoptosis HSP 70 p 53 F A D D Caspase -8, 10 JNK ` HSP 70 9 Hsp 70 blocks the JNK 3 activation Cyto C induced by ischemia and 4 reperfusion F A D D 5 Consequently, the protective d. ATP Caspase-9 anti-ischemic effect of Hsp 70 DNA might be associated with fragmentation inhibition of. Caspase-3, 6, 8 JNK-dependent apoptosis HSP 70 Caspase-3, 6, 7 CAD ICAD

CONCLUSION Experimental and clinical data suggest that intracellular Hsp 70 protects the myocardium from ischemia/reperfusion injuries
Lecture-MSU-PREZ-HSP-2011.pptx