473f943d51271e7b1554e9b849a4644f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 HEART Trust/NTA Facilitator of 2030 Plan • Education for Employment International Forum: Global Perspective • Edmonton, Alberta, Canada • June 4, 2011 • Presenter- Ludlow Thompson, Sr. Director (Acting) NCTVET
HEART Trust/NTA Facilitator of 2030 Plan • Education for Employment International Forum: Global Perspective • Edmonton, Alberta, Canada • June 4, 2011 • Presenter- Ludlow Thompson, Sr. Director (Acting) NCTVET
 HEART Trust/National Training Agency • HEART : Human Employment and Resource Training Agency. Creation of HEART Act. 1982 – Three parts: 1) employment creation, 2) resource (human) training and 3) the trust fund. • Funding: 3% levy on employers(Wage Bill) • NTA (1991): The coordinator of the National Training System - empowered to use the funds from the Trust to support training at a national level. HEART PLUS every other training provider in Jamaica regardless of the certification level (1 -5) in every sector comprise the training system. • Tertiary IS included in the NTA: lawyers, doctors, engineers, pharmacists and any profession with a practical component.
HEART Trust/National Training Agency • HEART : Human Employment and Resource Training Agency. Creation of HEART Act. 1982 – Three parts: 1) employment creation, 2) resource (human) training and 3) the trust fund. • Funding: 3% levy on employers(Wage Bill) • NTA (1991): The coordinator of the National Training System - empowered to use the funds from the Trust to support training at a national level. HEART PLUS every other training provider in Jamaica regardless of the certification level (1 -5) in every sector comprise the training system. • Tertiary IS included in the NTA: lawyers, doctors, engineers, pharmacists and any profession with a practical component.
 HEART cont’d • • Staffing: 1700 employees (Technical, Instructional, Administrative) Asset base : $2 billion worth of assets Cost Centres: Sixty (including 28 institutions) Training Capacity: Approximately 80, 000 spaces Throughput : over 30, 000 graduates annually Training Projects Funded : Over 100 Community- Based Projects Training Modalities: Institution – based, Enterprise-based, Community- based, Distance Technology
HEART cont’d • • Staffing: 1700 employees (Technical, Instructional, Administrative) Asset base : $2 billion worth of assets Cost Centres: Sixty (including 28 institutions) Training Capacity: Approximately 80, 000 spaces Throughput : over 30, 000 graduates annually Training Projects Funded : Over 100 Community- Based Projects Training Modalities: Institution – based, Enterprise-based, Community- based, Distance Technology
 Context is Everything: CANTA , Regional & ILO Framework • HEART Trust/NTA is a member of: • CANTA and contributor to/implementer of CARICOM Regional TVET Strategies. • International Labour Organisation and its technical arm, CINTERFOR. • ILO has mandated that training must be used to achieve millennium development goal: poverty reduction. • It also mandates that DECENT and PRODUCTIVE WORK must be provided for all.
Context is Everything: CANTA , Regional & ILO Framework • HEART Trust/NTA is a member of: • CANTA and contributor to/implementer of CARICOM Regional TVET Strategies. • International Labour Organisation and its technical arm, CINTERFOR. • ILO has mandated that training must be used to achieve millennium development goal: poverty reduction. • It also mandates that DECENT and PRODUCTIVE WORK must be provided for all.
 Jamaica’s 2030 Development Plan Developed Vision: “Jamaica, the place of choice to live, work, raise families , and do business”. • • National Goals: Jamaicans are empowered to achieve their fullest potential. The Jamaican society is secure, cohesive and just. Jamaica’s economy is prosperous. Jamaica has a healthy natural environment.
Jamaica’s 2030 Development Plan Developed Vision: “Jamaica, the place of choice to live, work, raise families , and do business”. • • National Goals: Jamaicans are empowered to achieve their fullest potential. The Jamaican society is secure, cohesive and just. Jamaica’s economy is prosperous. Jamaica has a healthy natural environment.
 Strategic Sectors: • • • Agriculture Manufacturing Mining and Quarrying Construction Creative Industries Sport Information and Communication Technology Services Tourism
Strategic Sectors: • • • Agriculture Manufacturing Mining and Quarrying Construction Creative Industries Sport Information and Communication Technology Services Tourism
 Specific Outcomes That Enable HEART’s Work • Outcome 1: Establish and implement a sustainable mechanism for human resources • Outcome 2: Ensure that adequate and high quality education is provided with an emphasis on the interface with work and school. • Expand mechanisms to provide access to education and training for all, including unattached youth. • Establish a National Qualification Framework. • Strengthen mechanisms to align training with demands of the labour markets. • Outcome 3: Expand opportunities for the poor to engage in sustainable livelihoods. • Outcome 4: Preserve, develop and promote Jamaica’s cultural heritage. • Integrate Jamaica’s nation brand into developmental process. • Strengthen the role of sport in all aspects of national development.
Specific Outcomes That Enable HEART’s Work • Outcome 1: Establish and implement a sustainable mechanism for human resources • Outcome 2: Ensure that adequate and high quality education is provided with an emphasis on the interface with work and school. • Expand mechanisms to provide access to education and training for all, including unattached youth. • Establish a National Qualification Framework. • Strengthen mechanisms to align training with demands of the labour markets. • Outcome 3: Expand opportunities for the poor to engage in sustainable livelihoods. • Outcome 4: Preserve, develop and promote Jamaica’s cultural heritage. • Integrate Jamaica’s nation brand into developmental process. • Strengthen the role of sport in all aspects of national development.
 Outcome cont’d • Outcome 8: Use trade and foreign relations to create an enabling external environment for economic growth. • Develop an efficient labour market. • Develop the capabilities of Micro, Small and Mediumsized enterprises. • Outcome 11: Integrate science and technology into all areas of development. • Create a dynamic and responsive National Innovative System. • Outcome 12: Develop company sophistication and productivity. • Develop economic linkages and clusters. • Enhance the framework for competition among enterprises. • Outcome 15: Create vibrant and diversified rural areas.
Outcome cont’d • Outcome 8: Use trade and foreign relations to create an enabling external environment for economic growth. • Develop an efficient labour market. • Develop the capabilities of Micro, Small and Mediumsized enterprises. • Outcome 11: Integrate science and technology into all areas of development. • Create a dynamic and responsive National Innovative System. • Outcome 12: Develop company sophistication and productivity. • Develop economic linkages and clusters. • Enhance the framework for competition among enterprises. • Outcome 15: Create vibrant and diversified rural areas.
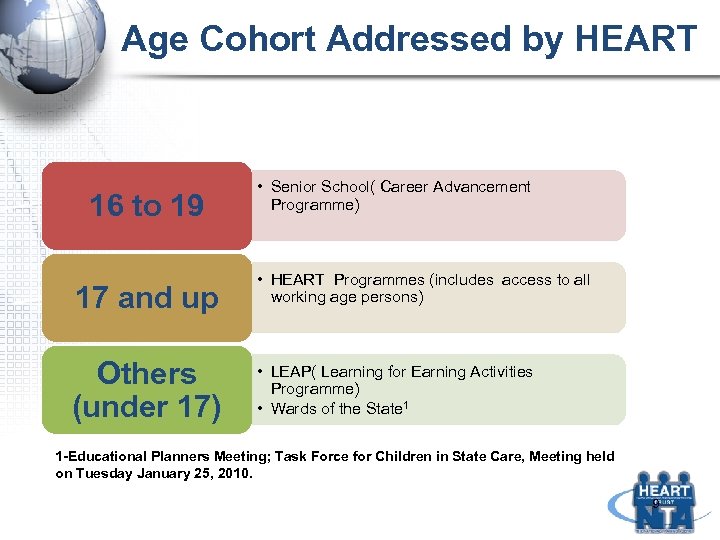 Age Cohort Addressed by HEART 16 to 19 17 and up Others (under 17) • Senior School( Career Advancement Programme) • HEART Programmes (includes access to all working age persons) • LEAP( Learning for Earning Activities Programme) • Wards of the State 1 1 -Educational Planners Meeting; Task Force for Children in State Care, Meeting held on Tuesday January 25, 2010. 9
Age Cohort Addressed by HEART 16 to 19 17 and up Others (under 17) • Senior School( Career Advancement Programme) • HEART Programmes (includes access to all working age persons) • LEAP( Learning for Earning Activities Programme) • Wards of the State 1 1 -Educational Planners Meeting; Task Force for Children in State Care, Meeting held on Tuesday January 25, 2010. 9
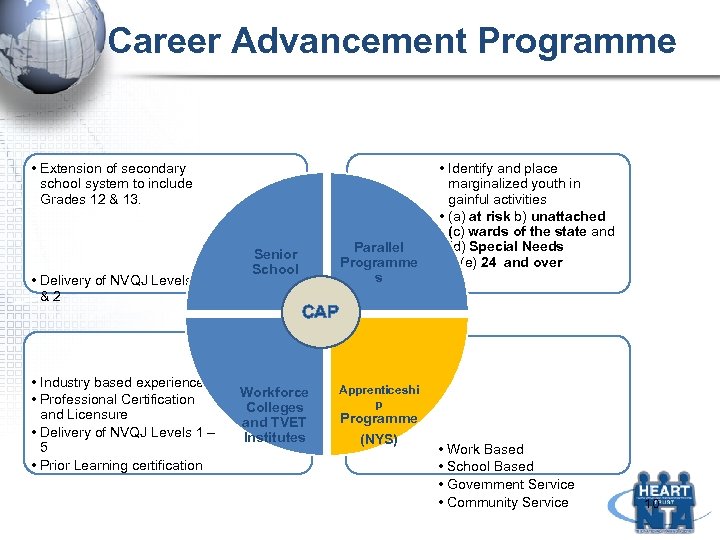 Career Advancement Programme • Extension of secondary school system to include Grades 12 & 13. • Delivery of NVQJ Levels 1 &2 • Industry based experience • Professional Certification and Licensure • Delivery of NVQJ Levels 1 – 5 • Prior Learning certification Parallel Programme s Senior School • Identify and place marginalized youth in gainful activities • (a) at risk b) unattached (c) wards of the state and (d) Special Needs e (e) 24 and over CAP Workforce Colleges and TVET Institutes Apprenticeshi p Programme (NYS) • Work Based • School Based • Government Service • Community Service 10
Career Advancement Programme • Extension of secondary school system to include Grades 12 & 13. • Delivery of NVQJ Levels 1 &2 • Industry based experience • Professional Certification and Licensure • Delivery of NVQJ Levels 1 – 5 • Prior Learning certification Parallel Programme s Senior School • Identify and place marginalized youth in gainful activities • (a) at risk b) unattached (c) wards of the state and (d) Special Needs e (e) 24 and over CAP Workforce Colleges and TVET Institutes Apprenticeshi p Programme (NYS) • Work Based • School Based • Government Service • Community Service 10
 NYS National Youth Service MOE Ministry of Education SDC Social Development Commission
NYS National Youth Service MOE Ministry of Education SDC Social Development Commission
 HEART’s MANDATE 1 Develop a programme for 1 At Risk Youth 2 Implement the Senior School programme 3 Within 3 years create 2 -3 Workforce Colleges 4 Rebrand HEART Trust Reposition HEART Trust as the National Training 5 Agency 1 - Board Meeting December 16, 2009 12
HEART’s MANDATE 1 Develop a programme for 1 At Risk Youth 2 Implement the Senior School programme 3 Within 3 years create 2 -3 Workforce Colleges 4 Rebrand HEART Trust Reposition HEART Trust as the National Training 5 Agency 1 - Board Meeting December 16, 2009 12
 Closing the Loop! • By focusing on the ILO mandate, the 2030 Plan and the HEART five year strategic plan, regional strategies the loop can be closed. • How? Training focuses on trade and competitiveness. By empowering the backward and forward supply chain supporting the ten strategic sectors in the 2030 plan, creating synergies, linkages and partnerships, HEART will ultimately increase innovation, productivity and competitiveness and the multiplier within the economy.
Closing the Loop! • By focusing on the ILO mandate, the 2030 Plan and the HEART five year strategic plan, regional strategies the loop can be closed. • How? Training focuses on trade and competitiveness. By empowering the backward and forward supply chain supporting the ten strategic sectors in the 2030 plan, creating synergies, linkages and partnerships, HEART will ultimately increase innovation, productivity and competitiveness and the multiplier within the economy.
 Business Model – YESTERDAY. . . Section 1 – HEART Business Model VTCs Academies HEART Trust/NTA • Presentation to Board of Directors – The Day after tomorrow 3
Business Model – YESTERDAY. . . Section 1 – HEART Business Model VTCs Academies HEART Trust/NTA • Presentation to Board of Directors – The Day after tomorrow 3
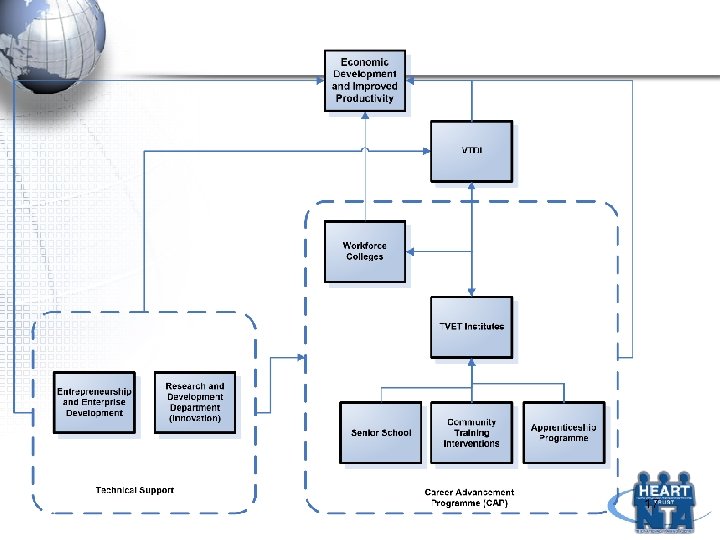
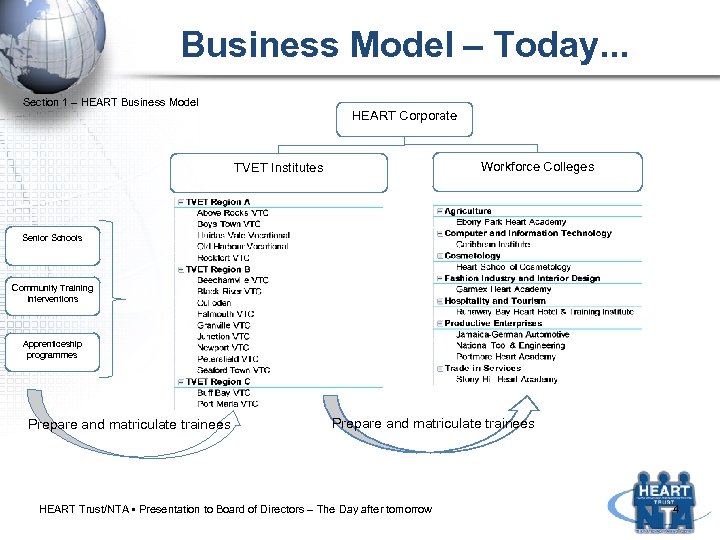 Business Model – Today. . . Section 1 – HEART Business Model HEART Corporate Workforce Colleges TVET Institutes Senior Schools Community Training Interventions Apprenticeship programmes Prepare and matriculate trainees HEART Trust/NTA • Presentation to Board of Directors – The Day after tomorrow 4
Business Model – Today. . . Section 1 – HEART Business Model HEART Corporate Workforce Colleges TVET Institutes Senior Schools Community Training Interventions Apprenticeship programmes Prepare and matriculate trainees HEART Trust/NTA • Presentation to Board of Directors – The Day after tomorrow 4
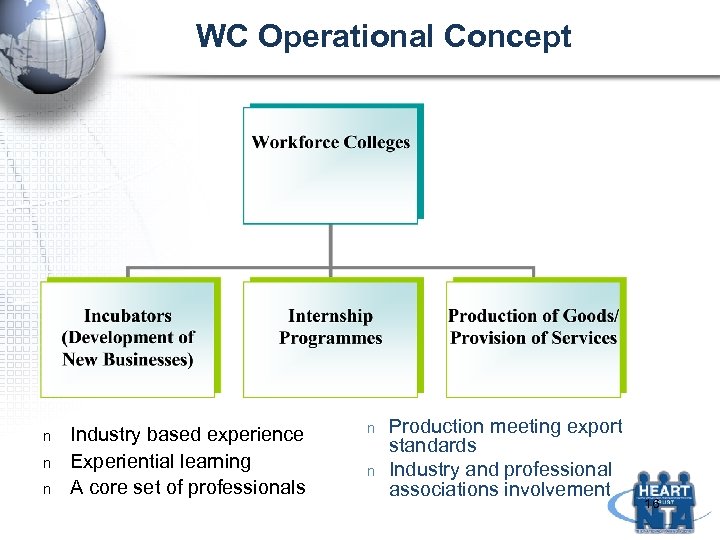 WC Operational Concept n n n Industry based experience Experiential learning A core set of professionals n n Production meeting export standards Industry and professional associations involvement 16
WC Operational Concept n n n Industry based experience Experiential learning A core set of professionals n n Production meeting export standards Industry and professional associations involvement 16
 17
17
 TRAINING INTERVENTIONS Marginalized Population: Youths at Risk Special Education Needs Wards of the State
TRAINING INTERVENTIONS Marginalized Population: Youths at Risk Special Education Needs Wards of the State
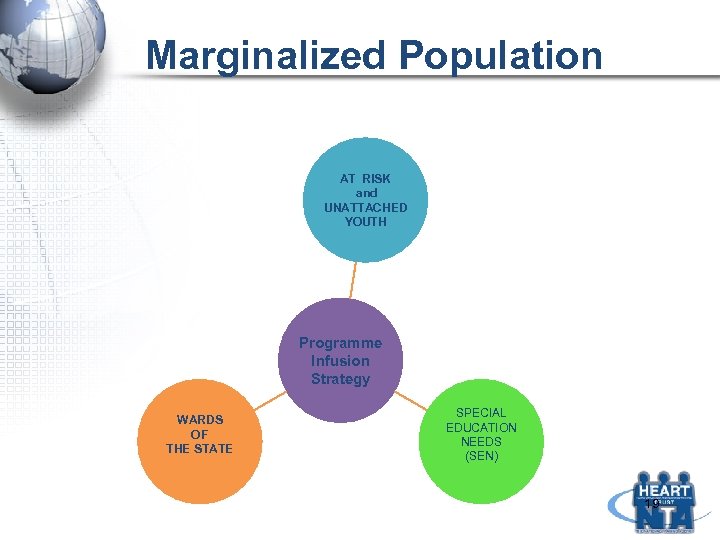 Marginalized Population AT RISK and UNATTACHED YOUTH Programme Infusion Strategy WARDS OF THE STATE SPECIAL EDUCATION NEEDS (SEN) 19
Marginalized Population AT RISK and UNATTACHED YOUTH Programme Infusion Strategy WARDS OF THE STATE SPECIAL EDUCATION NEEDS (SEN) 19
 Statistics • Unattached and at Risk Youth within age 14 to 24 age cohort account for approximate 70% of participants in the training programmes • In 2008, 19. 6% of the labour force had received some form of certification. • Females represents 75% of those formally trained. Females are three times more likely to be trained and outside the labour market
Statistics • Unattached and at Risk Youth within age 14 to 24 age cohort account for approximate 70% of participants in the training programmes • In 2008, 19. 6% of the labour force had received some form of certification. • Females represents 75% of those formally trained. Females are three times more likely to be trained and outside the labour market
 Statistic • Termination/Drop Out: • Enrolment: • Special Education Needs
Statistic • Termination/Drop Out: • Enrolment: • Special Education Needs
 Implementation of At Risk Prorgammes • LEAP Centre addresses: • Adolescents age 15 -17 (especially males) who have a high drop-out rate from the formal school system. • Street children syndrome and articulate a goal to rehabilitate into the formal education system and main streaming into society. • Behavior modification needs of at risk youths. • Provision of training opportunities and development of unattached and at risk youth and promote Life Long Learning
Implementation of At Risk Prorgammes • LEAP Centre addresses: • Adolescents age 15 -17 (especially males) who have a high drop-out rate from the formal school system. • Street children syndrome and articulate a goal to rehabilitate into the formal education system and main streaming into society. • Behavior modification needs of at risk youths. • Provision of training opportunities and development of unattached and at risk youth and promote Life Long Learning
 AT Risk Programmes contd. • Community-Based Projects: • Provide funding and other support to Community-Based NGOs treating with; -Special Education Needs – mentally and physically challenged, the blind, hearing impaired, multiple disabilities. Training Programmes include: Art & Craft, Paper Making, Carving, Cosmetology, Housekeeping, Garment Food Preparation, Data Operation, Office Administration
AT Risk Programmes contd. • Community-Based Projects: • Provide funding and other support to Community-Based NGOs treating with; -Special Education Needs – mentally and physically challenged, the blind, hearing impaired, multiple disabilities. Training Programmes include: Art & Craft, Paper Making, Carving, Cosmetology, Housekeeping, Garment Food Preparation, Data Operation, Office Administration
 Wards of the State • Training intervention in place to provide support to children in the care and protection of the state. The strategy is to ensure that such children can successfully transition to society and become productive citizens. Interventions are in the forms of: • Curricula and other training materials • Development/up-skilling of staff • Assessment and Certification • Remediation • Career Development • Training Facilities
Wards of the State • Training intervention in place to provide support to children in the care and protection of the state. The strategy is to ensure that such children can successfully transition to society and become productive citizens. Interventions are in the forms of: • Curricula and other training materials • Development/up-skilling of staff • Assessment and Certification • Remediation • Career Development • Training Facilities
 Policy Framework for Special Education Needs(SEN) • Policy on Special Education Needs is in place to drive the Heart/NTA’s contribution to this segment of the population. The policy focuses on: • Resource support to the sector • Programme offerings • Appropriate Physical Facilities • Appropriate technology support • Certification
Policy Framework for Special Education Needs(SEN) • Policy on Special Education Needs is in place to drive the Heart/NTA’s contribution to this segment of the population. The policy focuses on: • Resource support to the sector • Programme offerings • Appropriate Physical Facilities • Appropriate technology support • Certification
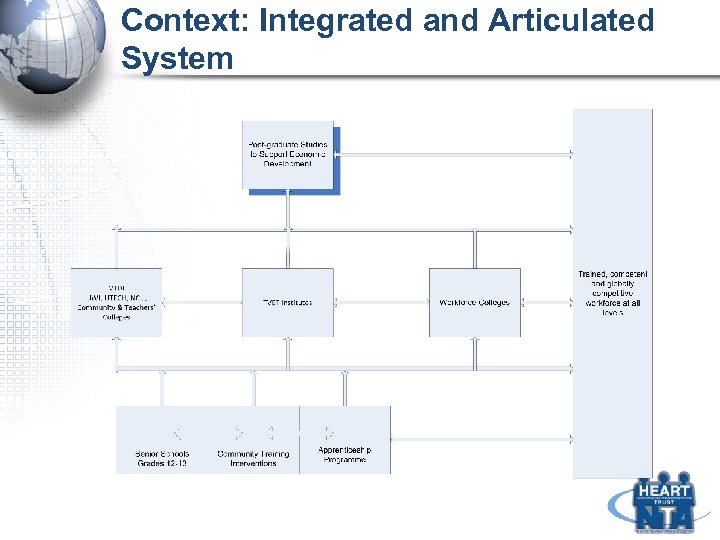 Context: Integrated and Articulated System
Context: Integrated and Articulated System
 The Result • The strategic development of human capital, economic development and social stability in Jamaica for the purpose of attracting inward investment while facilitating competitiveness aimed at export. 27
The Result • The strategic development of human capital, economic development and social stability in Jamaica for the purpose of attracting inward investment while facilitating competitiveness aimed at export. 27
 Challenges/Bottlenecks • • • Image/Perception of TVET among stakeholders Secured Funding Absence of national policy and consensus on TVET Legislative arrangement Inadequate supply of competent TVET professionals Appropriate resources: technology, training spaces, training materials • Industry collaboration (obtaining industry buy-in) • Literacy and Numeracy levels
Challenges/Bottlenecks • • • Image/Perception of TVET among stakeholders Secured Funding Absence of national policy and consensus on TVET Legislative arrangement Inadequate supply of competent TVET professionals Appropriate resources: technology, training spaces, training materials • Industry collaboration (obtaining industry buy-in) • Literacy and Numeracy levels
 Bottlenecks (cont’d) • National Qualification Framework to support Articulation and Credit Transfers • Inadequate Research and Development Mechanism • Labour Market Information System(particularly to emerging jobs identification) • Rapidly changing market dynamics and its impact on programme planning
Bottlenecks (cont’d) • National Qualification Framework to support Articulation and Credit Transfers • Inadequate Research and Development Mechanism • Labour Market Information System(particularly to emerging jobs identification) • Rapidly changing market dynamics and its impact on programme planning
 Support Required • Capacitation for the development of staff involved in delivery of instruction, institutional management, programme design and development, assessment and development, quality management systems. • Technology appropriate to support designs, development and delivery of instruction and online assessment systems • Institutional strengthening for Workforce Colleges and TVET Institutes • Entrepreneurial Development(Incubators)
Support Required • Capacitation for the development of staff involved in delivery of instruction, institutional management, programme design and development, assessment and development, quality management systems. • Technology appropriate to support designs, development and delivery of instruction and online assessment systems • Institutional strengthening for Workforce Colleges and TVET Institutes • Entrepreneurial Development(Incubators)


