3058fd1febd9504ce9ddff01ac817316.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Healthy Carbohydrates Presented by: Professor Steven P. Dion Salem State College Sport, Fitness and Leisure Studies Department

Where do they come from? n Photosynthesis Carbohydrates come from various plant sources Carbs are formed when water from the plants roots and carbon dioxide are absorbed into the leaves and combine in the presence of chlorophyll (green coloration) to produce glycogen / sugar. The glucose is then held as the fiber or fabric of the plants / fruits. u n n

Types of Carbohydrates n n n n Monosaccharides - glucose, fructose, galactose Disaccharides - maltose, sucrose, lactose Oligosaccharides – 10 -100 molecules of mono’s combined (fruits and veggies mostly) Polysaccharides - too many to list Glycogen - how animals store sugar Starches - pasta - rice - potatoes Fiber - bran - corn (husks)

Purpose / Role of carbs Brain’s primary fuel n Body energy n Protein sparing n Provides fiber in the diet n

Sources of Carbohydrates All plant products n Humans don’t produce carbs - but we can eat the animals that eat grasses / grains etc. n
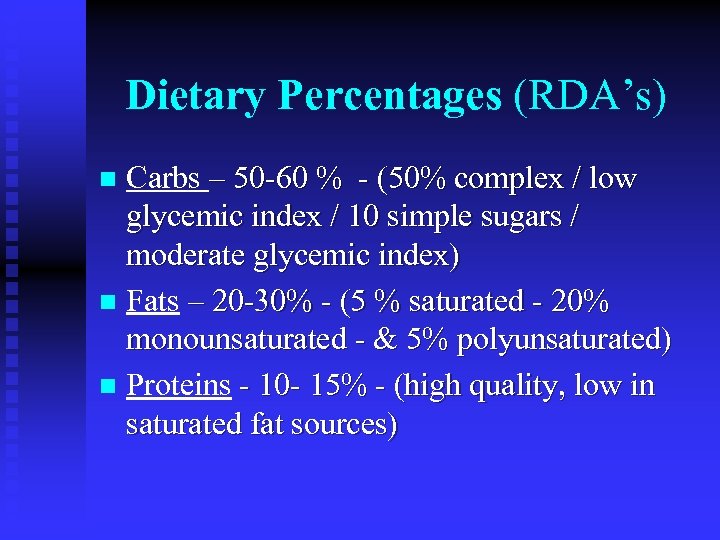
Dietary Percentages (RDA’s) Carbs – 50 -60 % - (50% complex / low glycemic index / 10 simple sugars / moderate glycemic index) n Fats – 20 -30% - (5 % saturated - 20% monounsaturated - & 5% polyunsaturated) n Proteins - 10 - 15% - (high quality, low in saturated fat sources) n

How much / many cals should we be getting from carbs? Average male needs 2000 calories per day n Average female needs 1800 calories per day n Each gram of carbohydrates has 4 calories n 60% of 2000 total calories = 1200 calories = 300 grams of carbs = 250 grams of complex and 50 grams of simple or moderate complex carbs. n

Choosing quality carbs “Glycemic Index” The rate of how fast a food (carb) turns into blood sugar / dextrose n Rated on a scale from 0 - 100 u 100 = pure glucose / blood sugar / dextrose n Examples: u Table sugar = 62 u Rice cake 72 n

Additional tips / suggestions n Eating more fiber – u Decreases cancer % u Cleanses the system / colon u Helps to remove fat from body u Gives bulk to stool u Helps remove harmful toxins u Decreases LDL Cholesterol

Additional tips / suggestions n Cooking tips: u Eat our pasta aldente u Slightly cook all veggies to help release their nutritional values u Buy quality grains: t The bread is heartier t Look for whole grain types t Just stay away from white floor (moderation)

Carbs and Athletic Performance Pre-Game Meals Carb loading Designed to pack more glycogen in the muscles n Stage 1: Depletion n Stage 2: n

n Stage 1: Depletion Phase Day 1 - exhausting exercise to deplete muscle glycogen in specific muscles t Only 60 -100 grams of carbs u Days 2, 3& 4 - low carb intake (60 -100) high protein and fat (preferably mono and polyunsaturated) consumption u n Stage u 2: Carbohydrate Loading Day 5, 6, & 7: High carb foods - normal protein and fats

Competition day 4 hours prior – consume 3 -5 grams / kg n 1 hour prior - 1 -2 grams / kg n 10 minutes prior - 50 -60 grams - 40 -50% solution n During exercise - 15 -20 grams every 20 minutes n

§ Pre and Post Race Choices § Doesn't' really matter what type of sugar - just as long as the serving is correct. u Fructose possibly better - digests slower - n Post Exercise u Take in. 7 grams/kg every 2 hours u Others say - immediately take in 50 -100 grams of glucose in a 20 -25% solution taken right after and then 50 grams each hour after for about 24 hours. u Endurance athletes - 500 -600 grams per day helps keep glycogen stores full. u Best if use complex carbs for replenishing - just as long as not exercising immediately again.

When do I need to carb load? Not necessary when doing 60 -90 minutes or less of continuous exercise n When it may be beneficial n For exercises lasting over 90 minutes - carb intake 1 - 4 hours prior shows benefits. n Intake of carbs 5 -10 minutes prior to a 2 hour or longer episode = better results (better performance at the end of activity) n

Drawbacks n n n If already hypoglycemic / diabetic this can cause adverse effects Additional water storage (bloating) = heavy feeling Too much fat or fiber intake can cause intestinal problems / stress More than 4 days of carb depletion can equal gluconeogenesis Mood alterations “Adding a gallon to a gas tank will not make the car go faster”

Thank you for coming! Any further questions?
3058fd1febd9504ce9ddff01ac817316.ppt