705b80cd194d4b0458d4cef135ac0a55.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

HEALTH SCIENCES: Open Access Databases BIOMED CENTRAL Dr. S. C. Jindal University of Delhi-India scjindal@du. ac. in

What is Open Access?

The new world of access to knowledge

OA in brief • No subscriptions = no barriers to access • Published articles immediately available online for free for everyone! • Copyright remains with the author • Major OA publishers - Article Processing Charges (APCs) • Support from funding bodies and governmental agencies

Advantages of open access • Very high visibility - Accessible from multiple sites - Indexed widely, eg Pub. Med - No barriers to dissemination • Quality - Acceptance rates based purely on the quality of the submissions

Open Access Publishing, Then and Now… 2000 2012 And many more…

Open access in 2012 • Over 7200 open access journals in the DOAJ • Over 1000 OA journals are indexed by ISI • Open access to research is now mandated in over 135 institutions and by over 50 funders • Submissions to OA journals grew by over 35% between 2009 and 2010 • OA firmly part of the mainstream
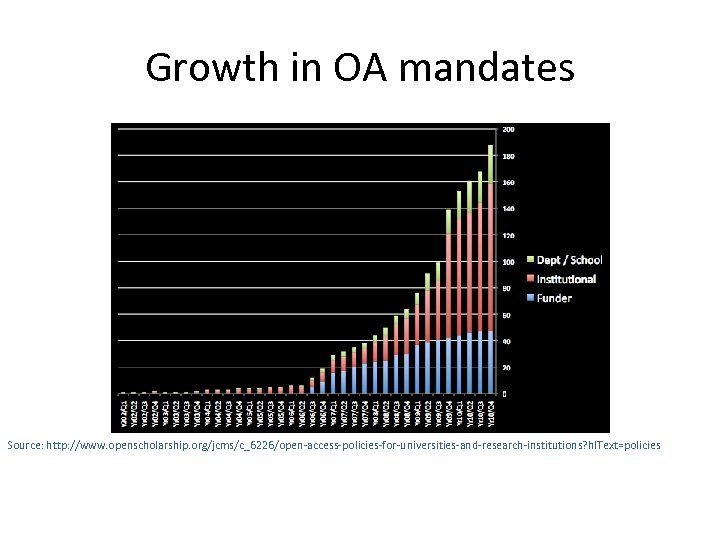
Growth in OA mandates Source: http: //www. openscholarship. org/jcms/c_6226/open-access-policies-for-universities-and-research-institutions? hl. Text=policies

Impact Factor journals: open access market growth

Difference between subscription and open access models • Both have – Editors, peer review, are indexed in ISI etc, have similar production processes, obey publication ethics • OA journals also – Allow the contents to be immediately freely available online everywhere in perpetuity • Different business models

The open access business model • Commonly financed by Article Processing Charges (APCs) usually paid by funders, institutions, societies, etc • Some open access journals have central support, so no charges for authors or readers • No charges for access
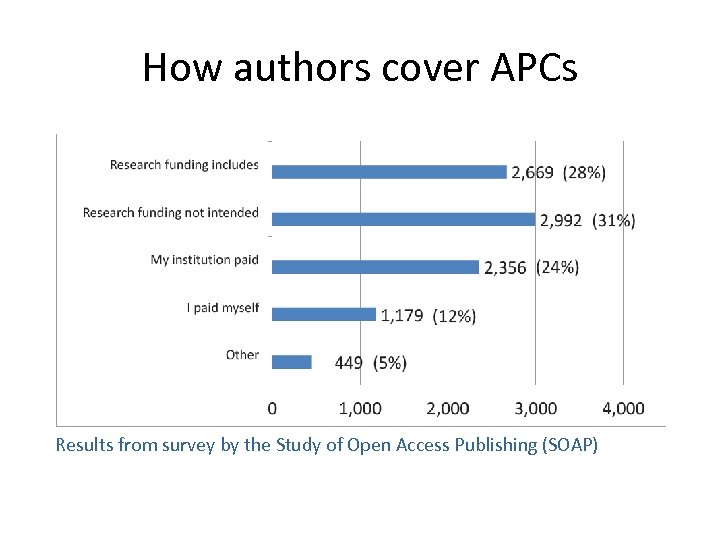
How authors cover APCs Results from survey by the Study of Open Access Publishing (SOAP)

Bio. Med Central Membership • For Bio. Med Central, Springer. Open and Chemistry Central journals • Institutions pay APCs in full or in part for their researchers • Over 380 Member institutions worldwide, including - Escola Nacional de Saúde Pública Sergio Arouca - Universidade Estadual Paulista • Ask your librarian to visit: http: //www. biomedcentral. com/libraries/membership

Bio. Med Central Open Access Charter • All published peer-reviewed research articles in Bio. Med Central journals are – Universally, freely accessible through Internet – In readable format – Immediately deposited in an international Open Access repository • eg Pub. Med Central • Authors/copyright owners must irrevocably grant to anyone the right to use, reproduce or disseminate the research article in its entirety or in part in perpetuity provided that – – No substantive errors are introduced Authorship attribution is correct Citation details are provided Bibliographic details are unchanged

Open Access Publishing: Basics • No subscription barriers • Journal costs covered by – Article Processing Charges • Typically paid by author's funder /institution and/or – Direct Institutional support of Journal

Why Open Access?

Traditional Scientific Publishing • Researchers – Conduct research – Write up results – Submit papers to Journals • Other researchers – Act as peer reviewers and editorial advisers • Publishers sell access to that research back to scientific community

Limitations of this Model • Contrary to the interests of: – Scientists doing research • Access, especially across disciplines, and in low income countries, is limited – Funders who pay for it • Often have no rights to access their own research articles – Society as a whole • Public has almost no access

Bio. Med Central • Independant publisher of peer-reviewed open access research • Costs covered by ‘Article Processing Charge’ • All research articles covered by Creative Commons licence – Launched first open access journals in 2000 – Now publishing over 150 open access journals – Over 12, 000 peer-reviewed open access articles published – Typically £ 750/$1300 or – Membership – Allowing free re-use

Bio. Med Central Publishing • All papers • Peer-reviewed in the ‘traditional’ way • All papers are permanently archived in Pub. Med Central, INIST and other international archives • Searchable and retrievable • All included in Pub. Med, Scirus, Google, Cross. Ref, HINARI • Some journals • Indexed in MEDLINE, Biosis, CAS • Tracked by ISI for citations • 33 tracked • 15 with impact factors

Bio. Med Central Journals • 60 BMC series journals – run by an in-house editorial team – cover all areas of Biology and Medicine – e. g. BMC Genetics, BMC Immunology, BMC Cancer • 70+ independant journals – run by external groups of scientists or societies – e. g. Malaria Journal, Respiratory Research, Retrovirology • Other titles which publish subscription-only commissioned content in addition to OA research – Arthritis Research & Therapy, Genome Biology, Breast Cancer Research, Critical Care

Journals with Impact Factors BMC Bioinformatics impact factor: 5. 42 Respiratory Research impact factor: 4. 03 Arthritis Research & Therapy impact factor: 4. 55 BMC Genomics impact factor: 3. 25 Critical Care impact factor: 3. 21 BMC Molecular Biology impact factor: 3. 12 Breast Cancer Research impact factor: 2. 98 BMC Cell Biology impact factor: 2. 62 BMC Cancer impact factor: 2. 29 BMC Infectious Diseases impact factor: 2. 07 BMC Public Health impact factor: 1. 55 BMC Health Services Research impact factor: 1. 23 BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders impact factor: 1. 00 BMC Genetics impact factor: 0. 92 Trials impact factor: 1. 70

Journals awaiting Impact Factors BMC Biotechnology impact factor due June 2007 BMC Evolutionary Biology impact factor due June 2006 BMC Gastroenterology impact factor due June 2006 BMC Medical Genetics impact factor due June 2008 BMC Microbiology impact factor due June 2007 BMC Neuroscience impact factor due June 2006 Journal of Translational Medicine impact factor due June 2008 BMC Plant Biology impact factor due June 2008 Retrovirology impact factor due June 2009 Malaria Journal impact factor due June 2006 Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology impact factor due June 2008 Genome Biology impact factor due June 2006 BMC Developmental Biology impact factor due June 2008 BMC Immunology impact factor due June 2008 BMC Neurology impact factor due June 2008 BMC Structural Biology impact factor due June 2008 Microbial Cell Factories impact factor due June 2008

Citation and Downloads • “Open access articles receive 50% more full-text accesses and PDF downloads than subscription-access articles. ” • Kenneth R. Fulton, PNAS Publisher • Independant study by CIBER found • “Senior authors believe downloads to be more credible measure of the usefulness of research then traditional citations. ” • http: //www. ucl. ac. uk/ciber_2005_survey_final. pdf
3. 5 million page views a month
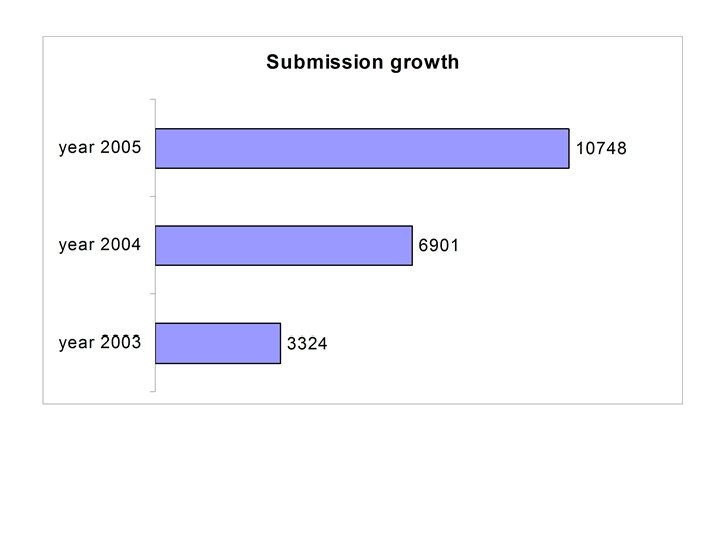
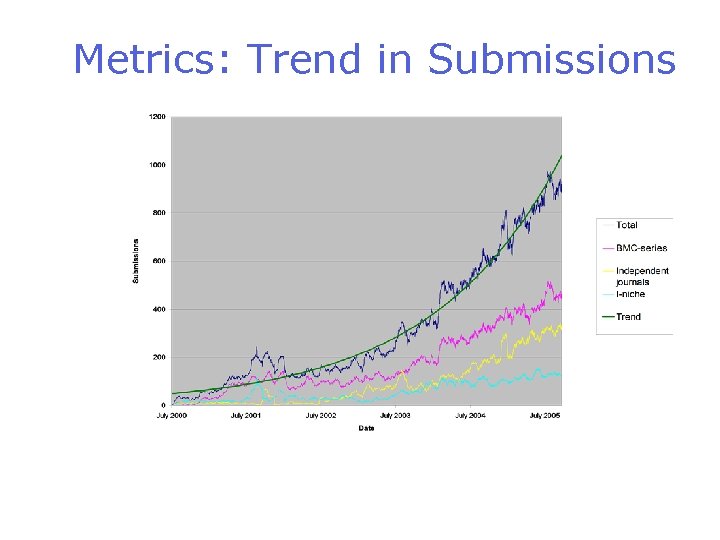
Metrics: Trend in Submissions

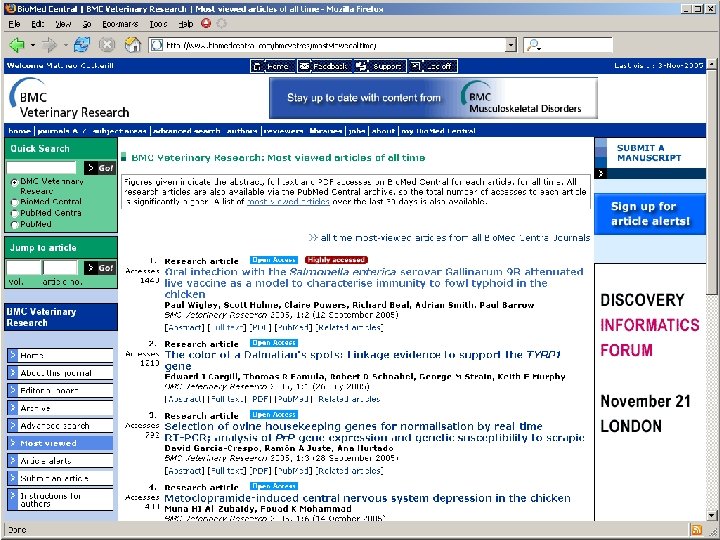
Most Viewed Articles
Visibility on Bio. Med Central • 500, 000 registrants • 450, 000 unique users per month • 280, 000+ Bio. Med Central email update recipients • 5 million page views per month • 2 million article downloads per month • Average article downloaded >1100 times in first 3 months
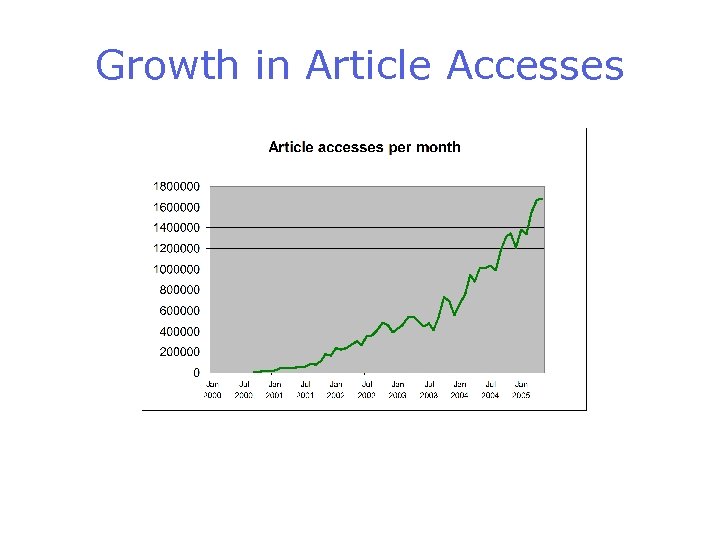
Growth in Article Accesses

Authors

Authors Embracing OA • Research community is now much aware of open access • Up 10 percentage points from 2004 • Fall in authors knowing nothing at all about open access (down 25 percentage points) • Authors publishing in OA up from 11% (2004) to 29% (2005) Independant study by CIBER: http: //www. ucl. ac. uk/ciber_2005_survey_final. pdf

What do Authors like about Bio. Med Central? • Speed with which article is included in Pub. Med/other abstracting/indexing services • Final appearance of article • Helpfulness of editorial staff • Speed of online manuscript submission system • Over 90% of authors would recommend to a colleague

Quotes from Author Survey “You have the best online submission system I have used until now. ” BMC Bioinformatics author, Germany “The submission process is the simplest to navigate through. Congratulations!” BMC Pharmacology author, Canada “The submission process is extremely user friendly and excellent. ” Mohamed Mitwally, USA “Submission on line was excellent and easy to do. Congratulations on getting this right. Good work!” Arthritis Research & Therapy author, New Zealand “I hugely appreciate the ability to use powerpoint files for submission! Generally an extremely easy system to use. ” BMC Cancer author, UK “I could not be more pleased with the process. I look forward to publishing in open access journals in the future. ” BMC Evolutionary Biology author, USA “I am very pleased with the ease of submission. I love that the copyright remains in my hands so that I can use my figures etc as I wish. ” Journal of Translational Medicine author, Germany

Making it Pay: the Economics of Open Access Publishing

Macro-economics • Open access publishing involves no new costs • From the perspective of the research community as a whole, switching to an Open Access publishing model is affordable and desirable, as it – Costs no more than the current model – Delivers more (universal access and reuse)

Micro-economics • Library budgets already stretched, paying the costs of the current publishing model through subscriptions • Costs of traditional system are mostly invisible to authors, whereas article processing charges are an obstacle for authors • During a transitional period, moves towards open access may involve additional costs

Paying for Open Access: examples

Who Pays the Cost of Publication? • Some Bio. Med Central journals cover the cost of publication themselves – Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry – Chinese Medicine – Chiropractic & Osteopathy • For other Bio. Med Central journals, payment typically comes from the authors funder or institution

Government • EC Report calls for change in science publishing – Set up EU policy mandating EC-funded research to be made open access – Aim at a level playing field – Allocate money to libraries for subscription journals and for author pays journals http: //europa. eu. int/rapid/press. Releases. Action. do? reference=IP/06/ 414 • House of Commons(UK) Inquiry into Scientific Publishing – UK research funding bodies mandate free access to all their research findings – Research Councils each establish a fund to which their funded researchers can apply should they wish to publish their articles using the author-pays model http: //www. publications. parliament. uk/pa/cm 200304/cmselect/cms ctech/39902. htm

Institutional Membership • Two basic models for institutions – Full membership • Institution agrees to pay for every article published by one of their authors, at a discounted rate – Supporters' membership • Institution pays a flat rate, and in return, authors get a discount, but must still organize payment of their own APCs
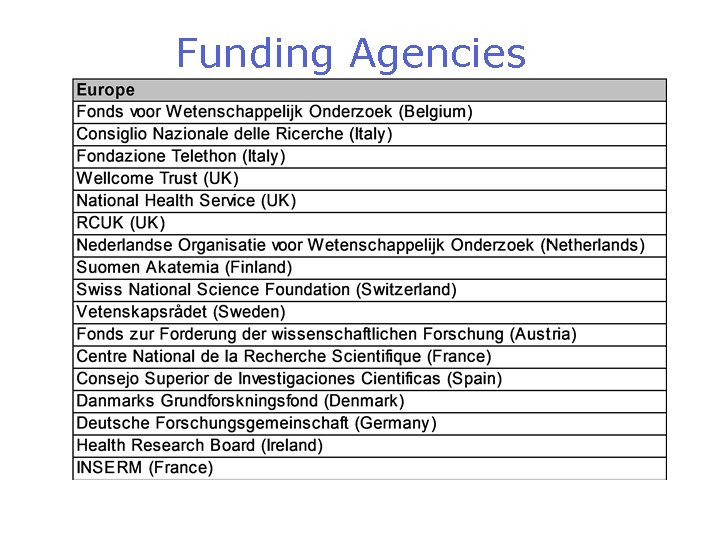
Funding Agencies
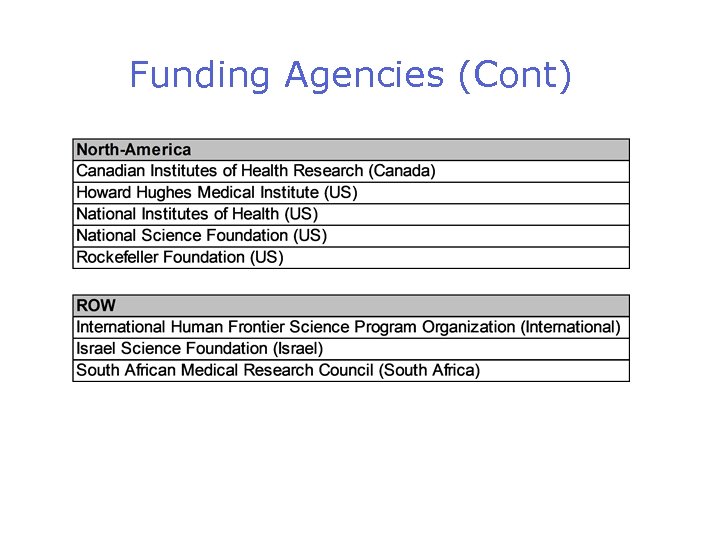
Funding Agencies (Cont)

Institutional membership More than 400 institutions are members of Bio. Med Central, including, to name just a few: • • • • Cal. Tech Cancer Research UK Columbia University Cornell University of California Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard University INSERM Imperial College Institut Pasteur John Innes Centre Johns Hopkins University Kyoto University Max Planck Institutes Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center • • • • MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology National Institutes of Health National Institute for Medical Research NHS England Princeton University Rockefeller University TIGR TSRI Tufts University Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute University of Wisconsin World Health Organization Yale University

Societies Launching open access journals with Bio. Med Central: • Geochemical Transactions - Geochemistry Division of the American Chemical Society • Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica - Veterinary Associations of the Nordic Countries • Chiropractic & Osteopathy - Chiropractic & Osteopathic College of Australasia • Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases - subunit of INSERM • Chinese Medicine - International Society of Chinese Medicine • Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research Chinese Speaking Orthopaedic Society • Bio. Psycho. Social Medicine - Japanese Society of Psychosomatic Medicine

Funders that Explicitly Allow APCs to be Paid from Grants Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Canada) Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (France) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas (Spain) Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (Italy) Danmarks Grundforskningsfond (Denmark) Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Germany) Fondazione Telethon (Italy) Fonds zur Forderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Austria) Fonds voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Belgium) Health Research Board (Ireland) Howard Hughes Medical Institute (US) International Human Frontier Science Program Organization (International) Israel Science Foundation (Israel) National Health Service (UK) National Institutes of Health (US) National Science Foundation (US) Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Netherlands) Rockefeller Foundation (US) South African Medical Research Council (South Africa) Suomen Akatemia (Finland) Swiss National Science Foundation (Switzerland) Vetenskapsrådet (Sweden) Wellcome Trust (UK)
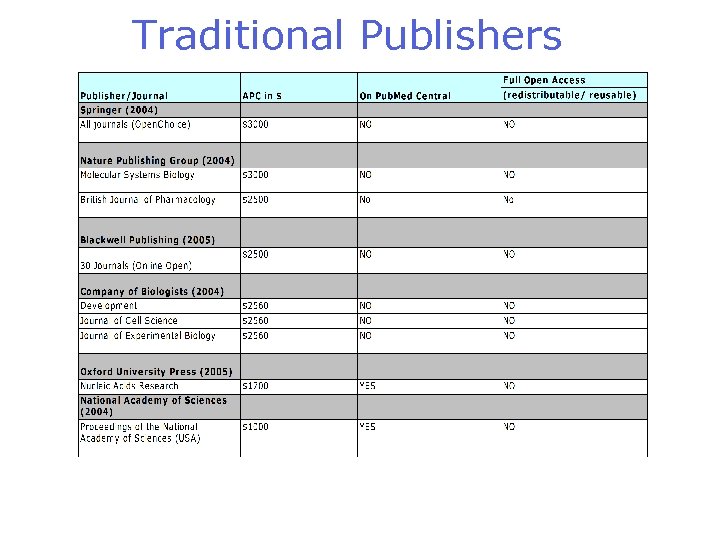
Traditional Publishers
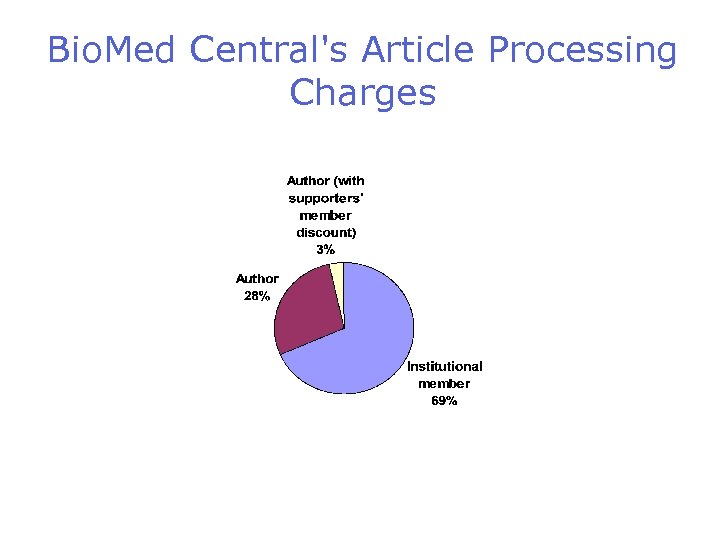
Bio. Med Central's Article Processing Charges
705b80cd194d4b0458d4cef135ac0a55.ppt