e573e95a1ba06de1e8e7d960abe16213.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Health Information Exchange 101 Problem, Definitions, Value, Policy David C. Kendrick, MD, MPH Asst. Provost for Strategic Planning OUHSC

National perspective • At >17% of GDP, healthcare costs - out of control • Value delivered is limited– US ranks below most industrialized nations on quality metrics, despite spending more • Healthcare IT - part of the solution – prioritized and funded – American Recovery and Reinvestment Act • Patient Centered Medical Home gaining as the delivery model of choice

Healthcare Reform likely possible • Details change daily, but will probably might include – Coverage expansion for the uninsured, perhaps through a public plan or premium assistance programs – Emphasis on preventive care – More prominent role of the Patient Centered Medical Home – Emphasis on Healthcare IT
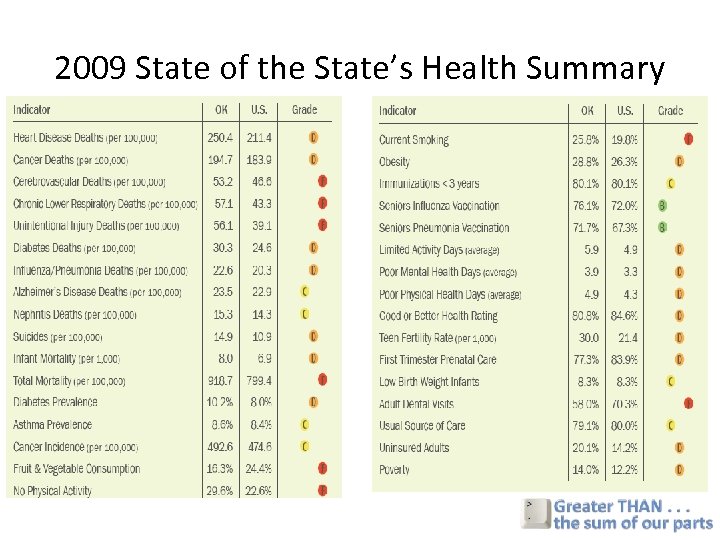
2009 State of the State’s Health Summary

Oklahoma is the only state where the death rate has gotten worse…. . Some Factors 1. Economic downturn healthy people and jobs left Oklahoma 2. Poverty remained 3. Heart Disease – (Diabetes) 4. Cancer 5. Access to Care Age-adjusted Death Rates Past 25 Years

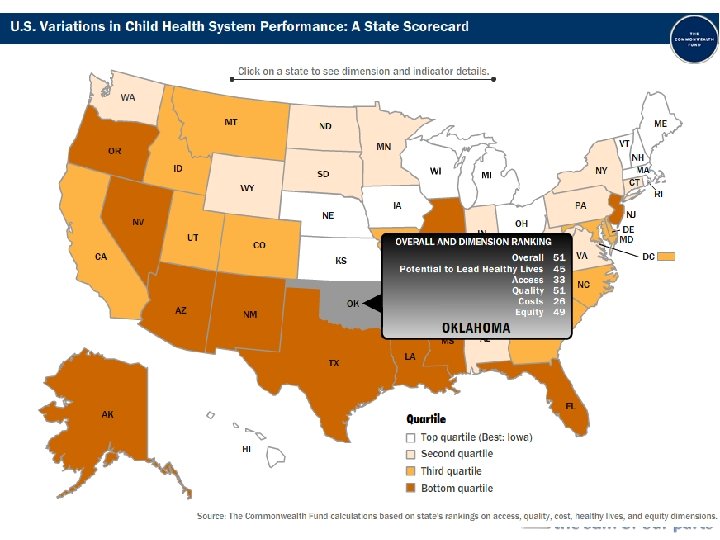
2007 COMMONWEALTH FUND Report State Scorecard Summary of Health System Performance

What WE CAN’T Do • “Grow” more doctors quickly • Create new hospitals overnight • Force patients to: –Exercise –Stop smoking –Lose weight

What We Can Do Leverage Technology • Complex populations • Limited Resources: –Create a lean healthcare system –Improve Care Coordination –Business case for: • Funding • Efficiency

Where to Focus? –Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) important, but. . . –Health Information Exchanges (HIEs) • immediate benefit and greater cost savings –Community-wide care coordination (CCC) • more benefit and cost savings

Physician Organization in Relation to Quality and Efficiency of Care The Commonwealth Fund, April 2008 Evidence Increasingly shows that improved “systemness” drives quality and efficiency System: a group of independent but interrelated elements Designed to work as a coherent entity

Where Will there be Savings? Majority: From the Exchange of Clinical Information among care providers Reduction in duplicate Dx procedures Prevention of Medical Error Source: Center for Information Technology Leadership 2005

Current Situation Hospitals (inpt) Payers Rx ER/UC Demographics Medical claims Pharmacy claims Case mgmt records Patient Safety Net Clinics and community agencies Imaging Doctor offices EHR Claims Rx Case mgmt Community outreach Other PCPs Manual connection (mail, fax) Electronic connection Labs Specialists Ancillary care PT/OT/Aud/Diet Public Health
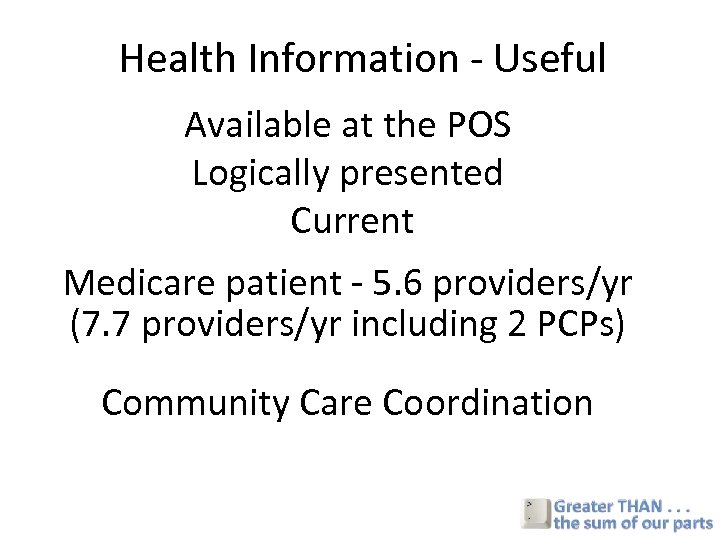
Health Information - Useful Available at the POS Logically presented Current Medicare patient - 5. 6 providers/yr (7. 7 providers/yr including 2 PCPs) Community Care Coordination
Definitions: EMR vs. HIE vs. HIO vs. CCC HIE

Health Information Organization RHIO Greatest Value Your Data is Local (CCC) Business Model - Self Supporting Stakeholders/Users Quality, Safety & Efficient Delivery Govern, Sets Rules Statewide Network of Networks Disaster Bioterrorism National (NHIN) Public Health
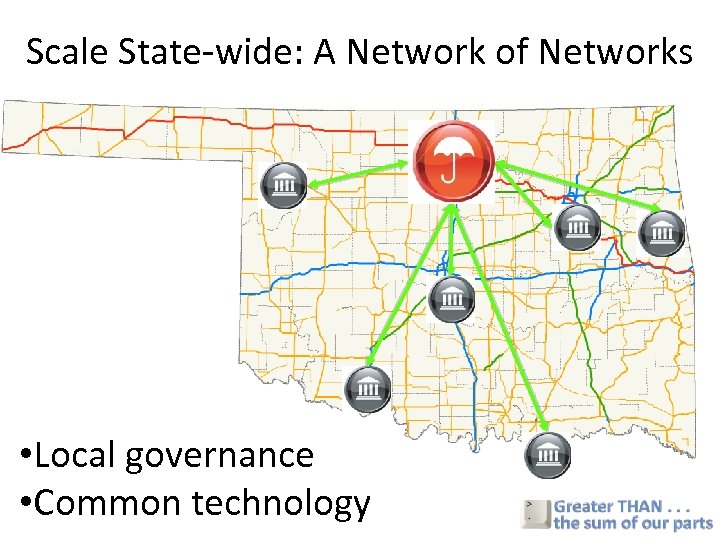
Scale State-wide: A Network of Networks • Local governance • Common technology
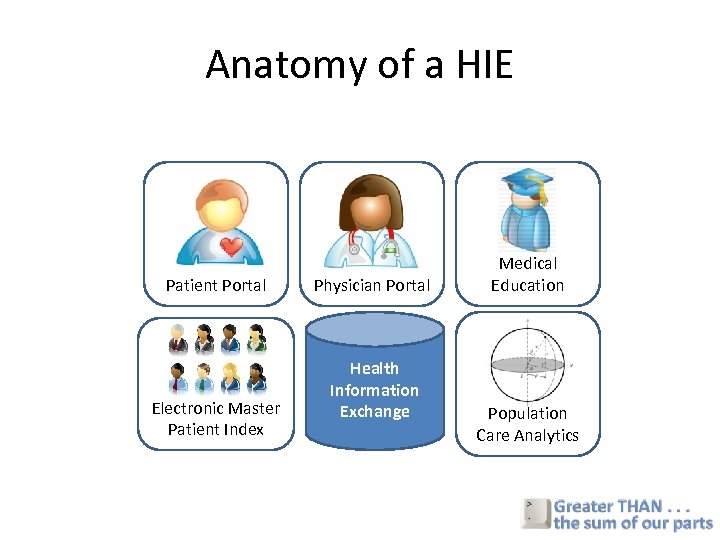
Anatomy of a HIE Patient Portal Electronic Master Patient Index Physician Portal Health Information Exchange Medical Education Population Care Analytics
Anatomy: Detailed Version • HIE - Central Data Repository for a core set of clinical variables • e. MPI - Master Patient Index tracks unique patients and ensures data integrity • Community Order Entry/Physician Portal- Centralized system coordinating orders, referrals, consultations, radiology and diagnostic tests, PT/OT, etc. • Decision analytics - Tools and algorithms for patient identification, prioritizing patients for interventions, prioritizing appropriate interventions each patient • Patient Portal - gives patients access to their own community health records, ability to communicate with their providers: – e. Visits, Schedule requests, Refill requests, Patient educational materials, Self-care logs (BP, BS, asthma, etc. ), Health Risk Assessments (Depression screen, Cardiac risk), Review records shared across the community • Comprehensive clinical education support – Trainee portfolios, Evaluations, Delivery of relevant didactic educational materials
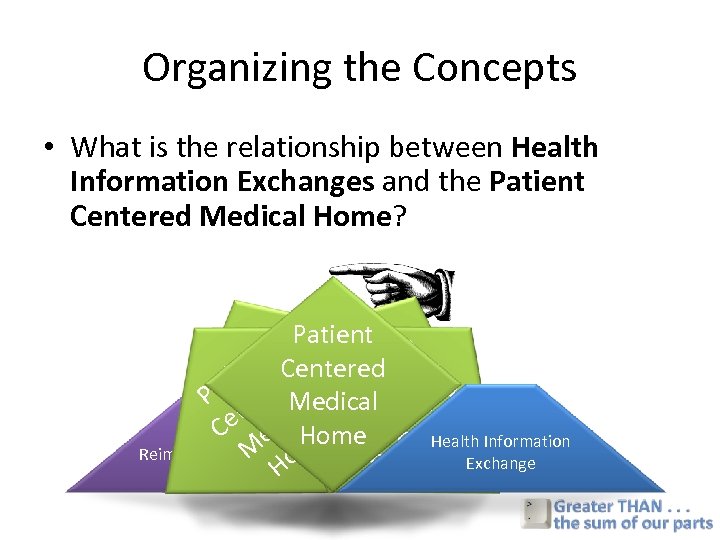
Organizing the Concepts • What is the relationship between Health Information Exchanges and the Patient Centered Medical Home? Pa P t n. Patient tien ntie. Centered atie a Pe t edred. Cen n ti nrte M Mt ere Pa Cee Medical tere t t dacal edec d il e e. H i en Mdic He i dac d C Health Information la Health Information Homem e om ome l m o M HExchange e Reimbursement Exchange Ho Model
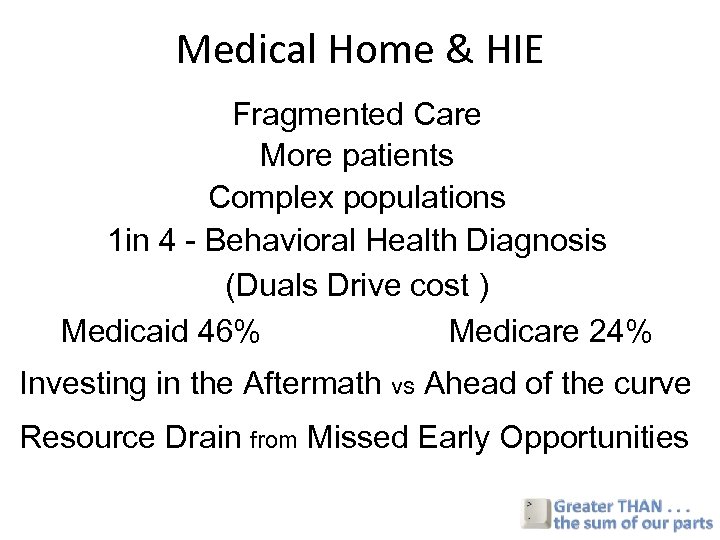
Medical Home & HIE Fragmented Care More patients Complex populations 1 in 4 - Behavioral Health Diagnosis (Duals Drive cost ) Medicaid 46% Medicare 24% Investing in the Aftermath vs Ahead of the curve Resource Drain from Missed Early Opportunities

Medical Home Goals Integrated Systems More Efficient Use of Resources Identify & Prioritize patients for Intervention (ahead of the curve) Link Providers - Coordinate Care Raise Quality - Evidence Based Guidelines Identify Quality issues & Make Rapid Changes

Have we given this any thought? • 2004: Harvard Center for IT Leadership published a report on the value of health information exchange • $77 B in annual savings through Health IT • Prompted, in part, the creation of the Office of the National Coordinator for Healthcare IT (ONCHIT), the Health IT “Czar” • 2006: GKFF commissioned an OK-specific evaluation of the value of HIE

Motivation • Clinicians have incomplete knowledge of their patients – Relevant patient data not available in 81% of ambulatory visits – 18% of medical errors that lead to ADEs due to missing patient information. Tang 1994 Leape JAMA 1995 • Medicare patients see an average of 5. 6 different providers each year= 5. 6 silos of data • What is the value of HIE for Oklahoma and specifically for the Tulsa region?

HIE Expert Panelists • • • David Brailer, MD, Ph. D – Santa Barbara County Care Data Exchange, Health Technology Center William Braithwaite, MD, Ph. D – Independent consultant, “Dr HIPAA” Paul Carpenter, MD – Associate Professor of Medicine, Endocrinology-Metabolism and Health Informatics Research, Mayo Clinic Daniel Friedman, Ph. D – Independent public health consultant Robert Miller, Ph. D – Associate Professor of Health Economics, UCSF Arnold Milstein, MD, MPH – Pacific Business Group on Health, Mercer Consulting, Leapfrog Group J Marc Overhage, MD, Ph. D – Regenstrief Institute, Associate Professor of Medicine, Indiana University Scott Young, MD – Senior Clinical Advisor, Office of Clinical Standards and Quality, CMS Kepa Zubeldia, MD – President and CEO, Claredi Corporation
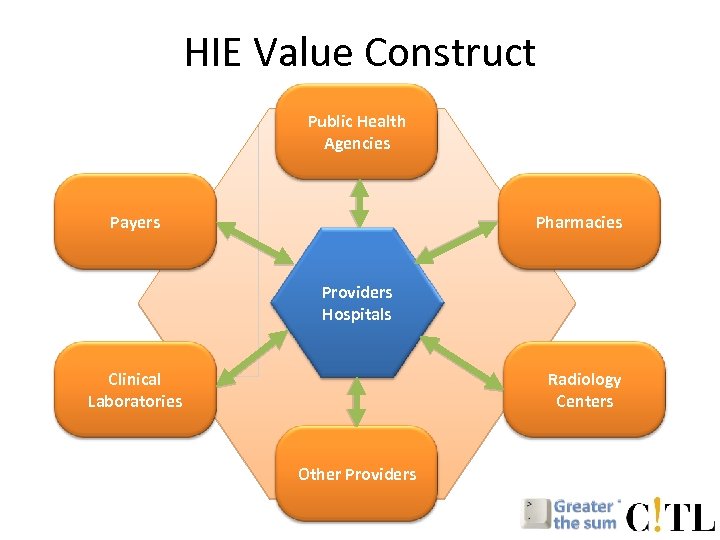
HIE Value Construct Public Health Agencies Payers Pharmacies Providers Hospitals Clinical Laboratories Radiology Centers Other Providers
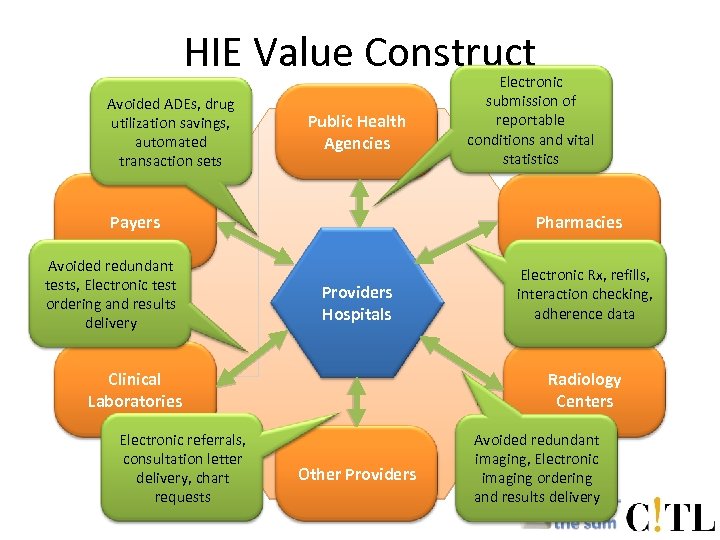
HIE Value Construct Avoided ADEs, drug utilization savings, automated transaction sets Public Health Agencies Payers Avoided redundant tests, Electronic test ordering and results delivery Pharmacies Providers Hospitals Clinical Laboratories Electronic referrals, consultation letter delivery, chart requests Electronic submission of reportable conditions and vital statistics Electronic Rx, refills, interaction checking, adherence data Radiology Centers Other Providers Avoided redundant imaging, Electronic imaging ordering and results delivery

What about funding? • One time: – ARRA stimulus dollars – Other grants • Ongoing: – Business model must be developed – ROI by stakeholder will drive the business model
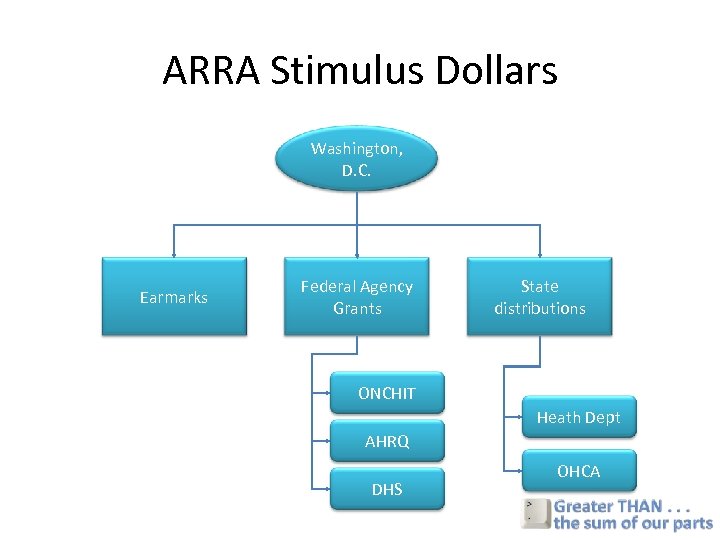
ARRA Stimulus Dollars Washington, D. C. Earmarks Federal Agency Grants State distributions ONCHIT Heath Dept AHRQ DHS OHCA

Opportunity: Stimulus Package • Federal Agencies offering – $20 B for healthcare IT, $3 B short term and $300 M immediately – $1 B for comparative effectiveness research – $1. 5 B for community health centers • Much will be distributed through grant process • Will be highly competitive • Many other communities have been in this game for years • Our communities must – Be unified behind a well-developed plan of action – We must build the coalition now Greater Tulsa Health Access Network

From the final ARRA: In order to be eligible for Stimulus Grants • Must be a qualified State-designated entity – Designated by State as eligible to receive awards – Non-profit entity – Clear objectives to use Healthcare information technology to improve care quality and efficiency through secure data exchange – Adopt non-discrimination and conflict of interest policies – Broad stakeholder representation on governing board
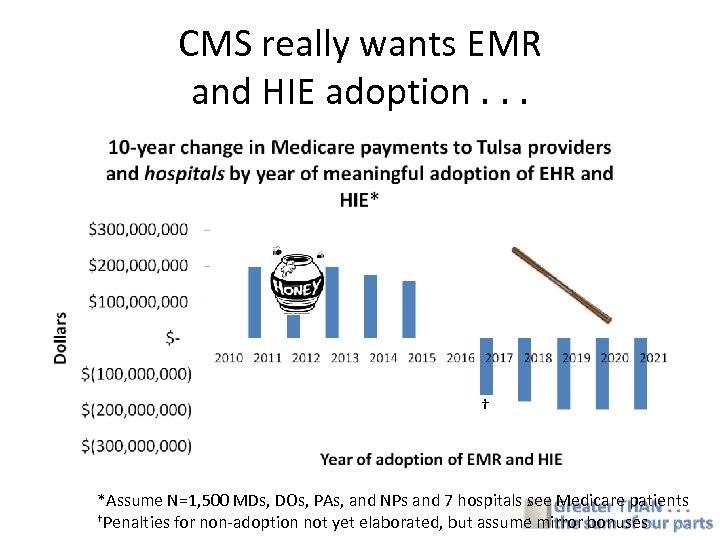
CMS really wants EMR and HIE adoption. . . † *Assume N=1, 500 MDs, DOs, PAs, and NPs and 7 hospitals see Medicare patients †Penalties for non-adoption not yet elaborated, but assume mirror bonuses

From the final ARRA: Regional organization must include • Providers, including those focused on low-income and underserved • Health plans • Patient and consumer organizations • HIT vendors • Healthcare purchasers and employers • Public health agencies • Universities • Clinical researchers • Other staff who use HIT

National: Meaningful Use guidance • In order to qualify for bonus payments (and avoid penalties) – By 2011, the following must be exchanged: • Doctors: Problem lists, medication lists, allergies, test results • Hospitals: Discharge summaries, procedures, problem lists, medication lists, allergies, and test results – By 2013, the following must be exchanged: • Doctors: Share all care transition data across the community electronically • Hospitals: Share all care transition data electronically
e573e95a1ba06de1e8e7d960abe16213.ppt