6badda8d299d75de59fe42ba6d752c85.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Health Informatics Series Introduction to Health Informatics Mark H. Spohr, MD Health Care Informatics IER/HIS, World Health Organization, 20, Avenue Appia, CH-1211 Geneva 27 SWITZERLAND 1| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Health Informatics Series Introduction to Health Informatics Mark H. Spohr, MD Health Care Informatics IER/HIS, World Health Organization, 20, Avenue Appia, CH-1211 Geneva 27 SWITZERLAND 1| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Why Health Informatics? Health Informatics provides information to make decisions Better information leads to better decisions Health care, management, planning and policy all need good information 2| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Why Health Informatics? Health Informatics provides information to make decisions Better information leads to better decisions Health care, management, planning and policy all need good information 2| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Health Informatics The intersection of information science, computer science, and health care. It deals with the resources, devices and methods required to optimize the acquisition, storage, retrieval and use of information in health. 3| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Health Informatics The intersection of information science, computer science, and health care. It deals with the resources, devices and methods required to optimize the acquisition, storage, retrieval and use of information in health. 3| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Tools Health informatics tools include not only computers but also clinical guidelines, formal medical terminologies, and information and communication systems. 4| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Tools Health informatics tools include not only computers but also clinical guidelines, formal medical terminologies, and information and communication systems. 4| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 CDC Health Informatics CDC's National Center for Public Health Informatics (NCPHI) provides leadership in the application of information and computer science and technology to public health practice, research, and learning. – Electronic health record support of public health functions – Use of health care, population and other public health data in supporting public health systems and analyses – Basic capabilities that support public health practice such as statistical and health surveillance – Public Health decision support 5| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
CDC Health Informatics CDC's National Center for Public Health Informatics (NCPHI) provides leadership in the application of information and computer science and technology to public health practice, research, and learning. – Electronic health record support of public health functions – Use of health care, population and other public health data in supporting public health systems and analyses – Basic capabilities that support public health practice such as statistical and health surveillance – Public Health decision support 5| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 e. Health is a broad term for healthcare practice which is supported by electronic processes and communication. The term can encompass a range of services that are at the edge of medicine/healthcare and information technology. 6| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
e. Health is a broad term for healthcare practice which is supported by electronic processes and communication. The term can encompass a range of services that are at the edge of medicine/healthcare and information technology. 6| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 m. Health Mobile technologies such as mobile phones to collect and access health information. 7| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
m. Health Mobile technologies such as mobile phones to collect and access health information. 7| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Informatics ≠ IT Information Technology is not Informatics Information technology is hardware & software. • IT is to nouns, as informatics is to verbs. • Informatics helps IT ‘work appropriately. ’ 8| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Informatics ≠ IT Information Technology is not Informatics Information technology is hardware & software. • IT is to nouns, as informatics is to verbs. • Informatics helps IT ‘work appropriately. ’ 8| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Key Elements of Informatics Acquisition Storage Communication Manipulation Display 9| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Key Elements of Informatics Acquisition Storage Communication Manipulation Display 9| Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
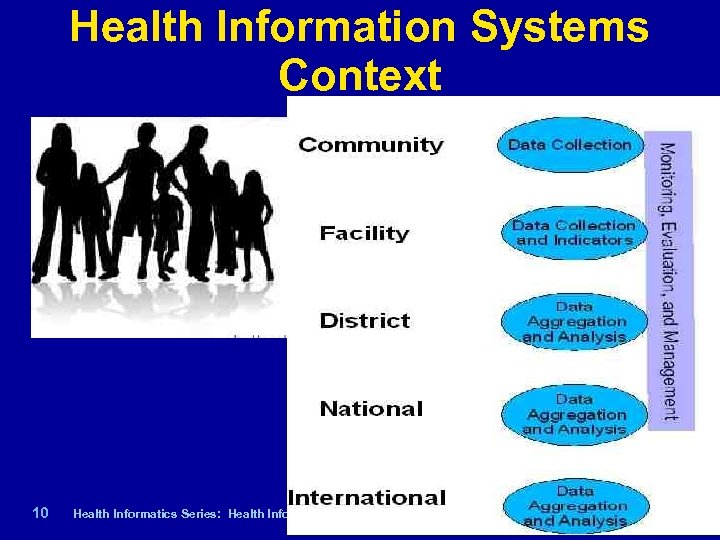 Health Information Systems Context 10 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Health Information Systems Context 10 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Health Informatics Principles Use drives data Interoperability using open standards Incremental development and strengthening of systems Enterprise Architecture approach Collaborative Communities 11 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Health Informatics Principles Use drives data Interoperability using open standards Incremental development and strengthening of systems Enterprise Architecture approach Collaborative Communities 11 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
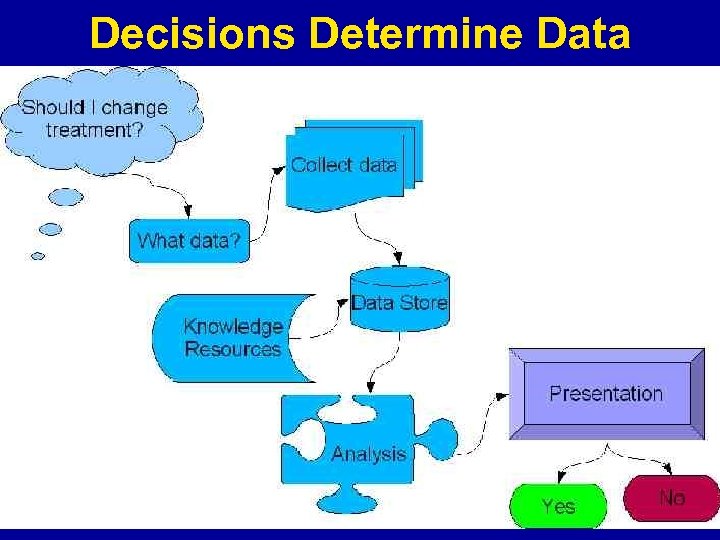 Decisions Determine Data 12 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Decisions Determine Data 12 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Incremental strengthening of systems You always have legacy systems The goal should not be to implement a single system but to encourage the development of interoperable systems. If it works, enhance it! Much easier to make continuous small improvements than to re-design and re 13 -implement the entire system | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Incremental strengthening of systems You always have legacy systems The goal should not be to implement a single system but to encourage the development of interoperable systems. If it works, enhance it! Much easier to make continuous small improvements than to re-design and re 13 -implement the entire system | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
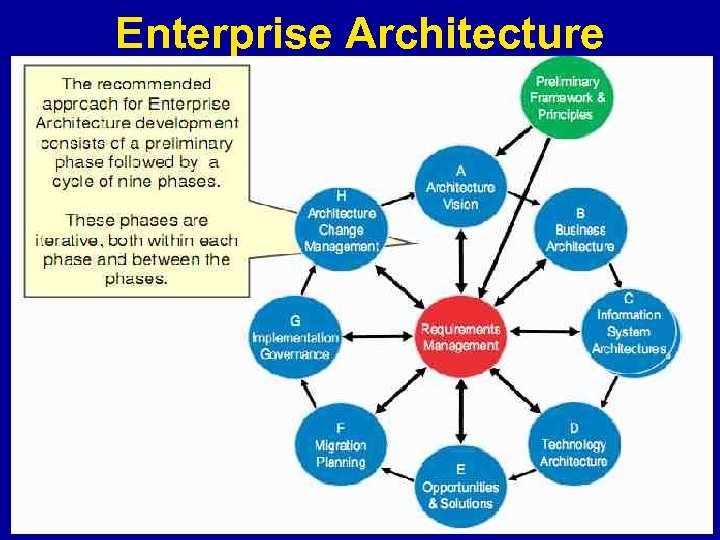 Enterprise Architecture 14 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Enterprise Architecture 14 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Encourage open systems 15 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Encourage open systems 15 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Make vs. Buy… Or Modify Buy Software – May not be an exact fit to your needs Build Software – Long expensive process not guaranteed to succeed. Modify – Start with open source software that you can modify – Modified software to meet your exact requirements – Everyone benefits from your investment in the software 16 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Make vs. Buy… Or Modify Buy Software – May not be an exact fit to your needs Build Software – Long expensive process not guaranteed to succeed. Modify – Start with open source software that you can modify – Modified software to meet your exact requirements – Everyone benefits from your investment in the software 16 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
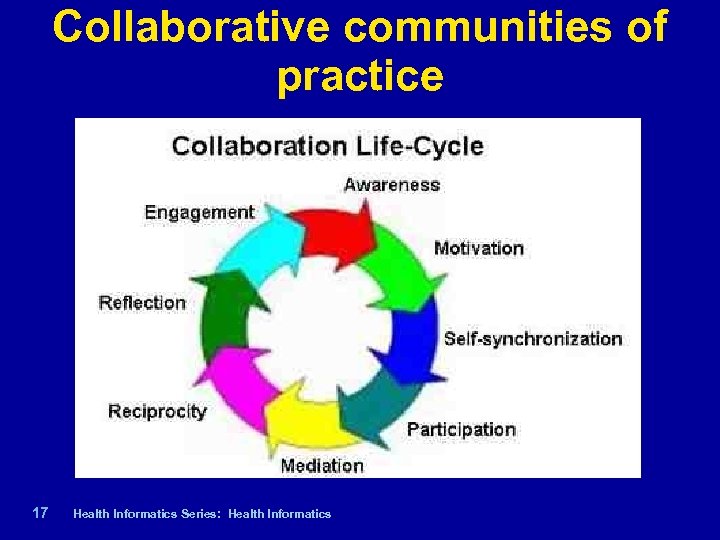 Collaborative communities of practice 17 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Collaborative communities of practice 17 | Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
 Health Informatics Series Mark H. Spohr, MD – email: mhspohr@gmail. com Lectures in this series: – – – 18 | Introduction to Health Informatics Enterprise Architecture Interoperability National Health Information Systems Patient Identifiers Software Selection Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics
Health Informatics Series Mark H. Spohr, MD – email: mhspohr@gmail. com Lectures in this series: – – – 18 | Introduction to Health Informatics Enterprise Architecture Interoperability National Health Information Systems Patient Identifiers Software Selection Health Informatics Series: Health Informatics


