68f22f2830b63d012fbdc73f1b277ab0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

HEALTH CARE PROBLEMS IN PENITENTIARY SYSTEM REPUBLIC OF LITHUANIA PRISON DEPARTMENT UNDER THE MINISTRY OF JUSTICE OF THE REPUBLIC OF LITHUANIA
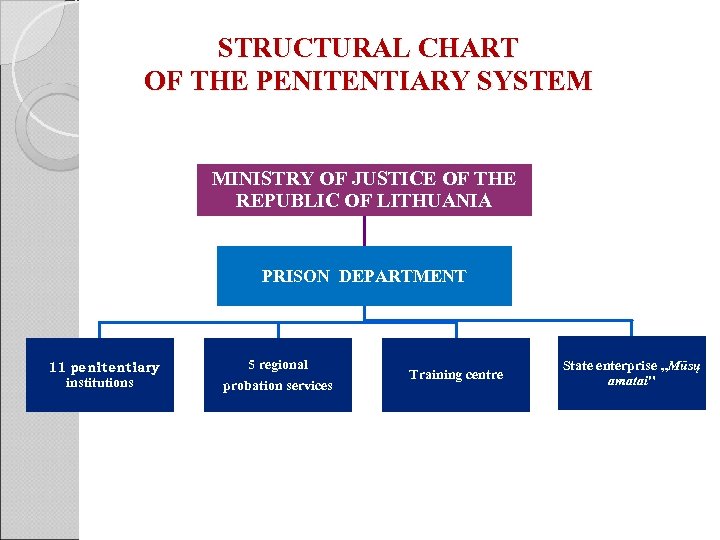
STRUCTURAL CHART OF THE PENITENTIARY SYSTEM MINISTRY OF JUSTICE OF THE REPUBLIC OF LITHUANIA PRISON DEPARTMENT 11 penitentiary institutions 5 regional probation services Training centre State enterprise „Mūsų amatai"
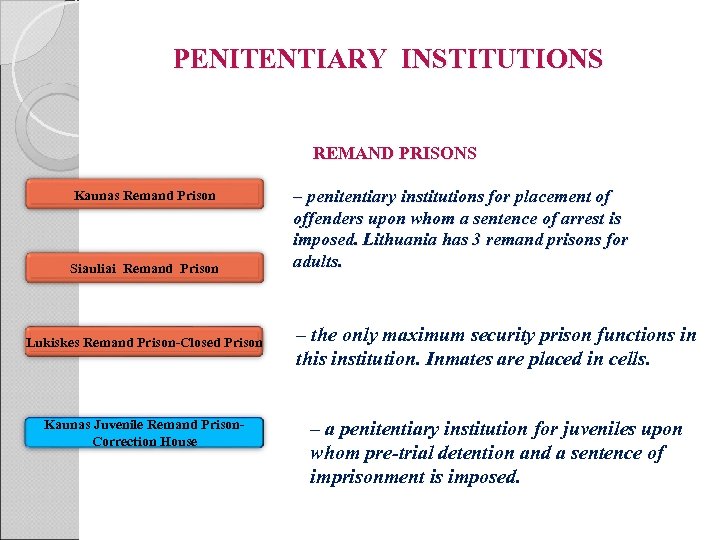
PENITENTIARY INSTITUTIONS REMAND PRISONS Kaunas Remand Prison Siauliai Remand Prison Lukiskes Remand Prison-Closed Prison Kaunas Juvenile Remand Prison. Correction House – penitentiary institutions for placement of offenders upon whom a sentence of arrest is imposed. Lithuania has 3 remand prisons for adults. – the only maximum security prison functions in this institution. Inmates are placed in cells. – a penitentiary institution for juveniles upon whom pre-trial detention and a sentence of imprisonment is imposed.
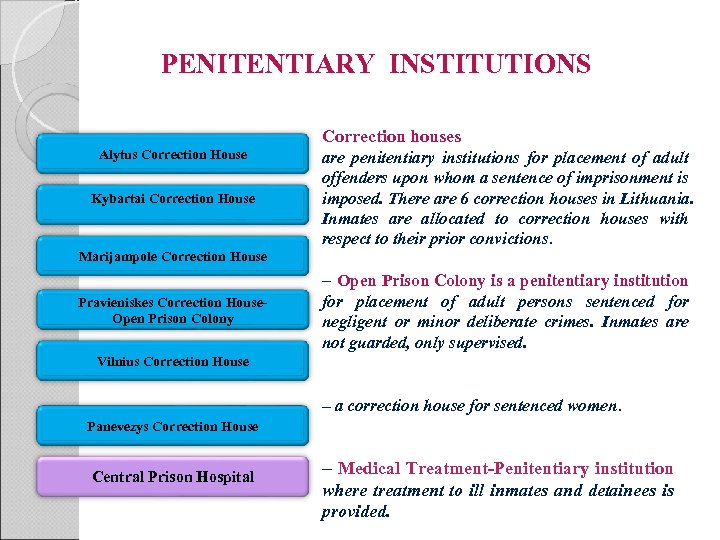
PENITENTIARY INSTITUTIONS Correction houses Alytus Correction House Kybartai Correction House are penitentiary institutions for placement of adult offenders upon whom a sentence of imprisonment is imposed. There are 6 correction houses in Lithuania. Inmates are allocated to correction houses with respect to their prior convictions. Marijampole Correction House – Open Prison Colony is a penitentiary institution Pravieniskes Correction House. Open Prison Colony for placement of adult persons sentenced for negligent or minor deliberate crimes. Inmates are not guarded, only supervised. Vilnius Correction House – a correction house for sentenced women. Panevezys Correction House Central Prison Hospital – Medical Treatment-Penitentiary institution where treatment to ill inmates and detainees is provided.

PRISON POPULATION penitentiary On 30 Juni 2016 7051 inmates were placed in institutions, of them: – 552 detainees, awaiting court decision; – 6499 sentenced inmates (of them – 120 life sentenced, 159 sentenced to arrest); – 69 juveniles; – 323 women; – 107 foreign citizens. Prison population on 18 September 2016 - 7820 5
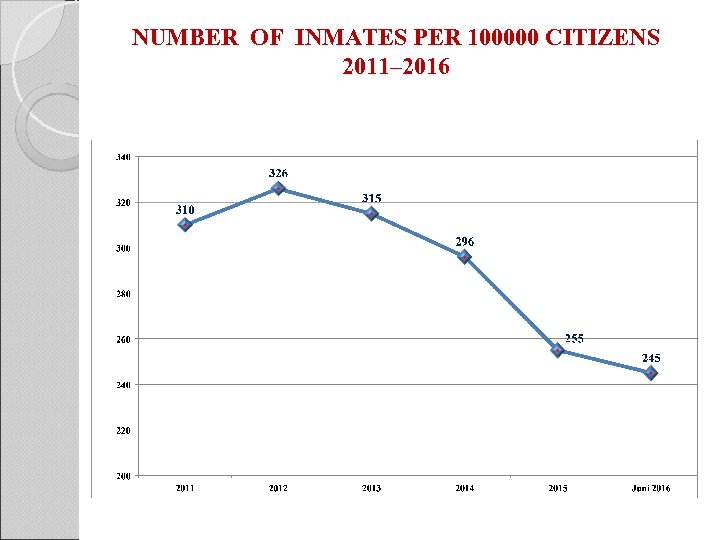
NUMBER OF INMATES PER 100000 CITIZENS 2011– 2016
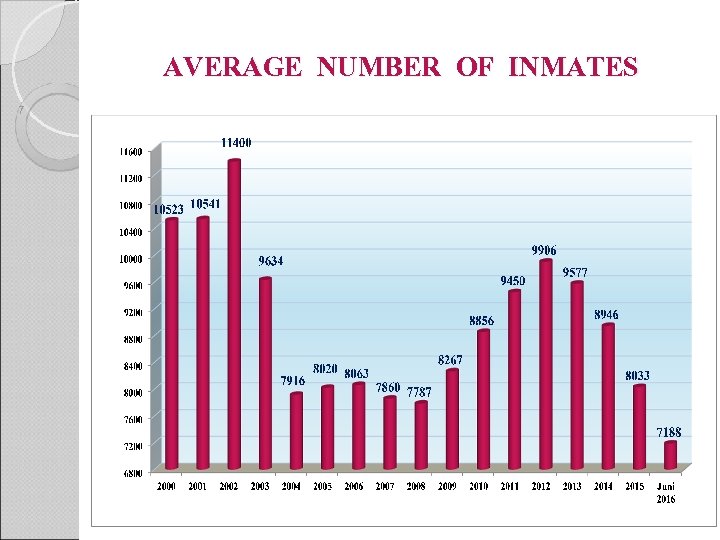
AVERAGE NUMBER OF INMATES 7
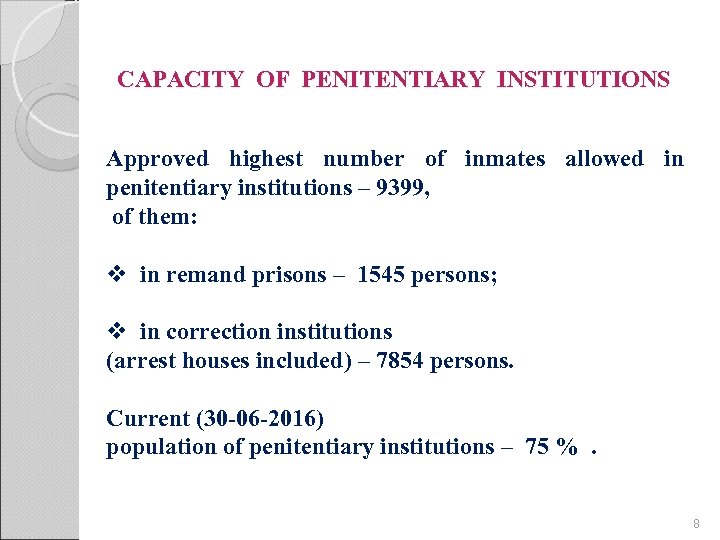
CAPACITY OF PENITENTIARY INSTITUTIONS Approved highest number of inmates allowed in penitentiary institutions – 9399, of them: v in remand prisons – 1545 persons; v in correction institutions (arrest houses included) – 7854 persons. Current (30 -06 -2016) population of penitentiary institutions – 75 % . 8
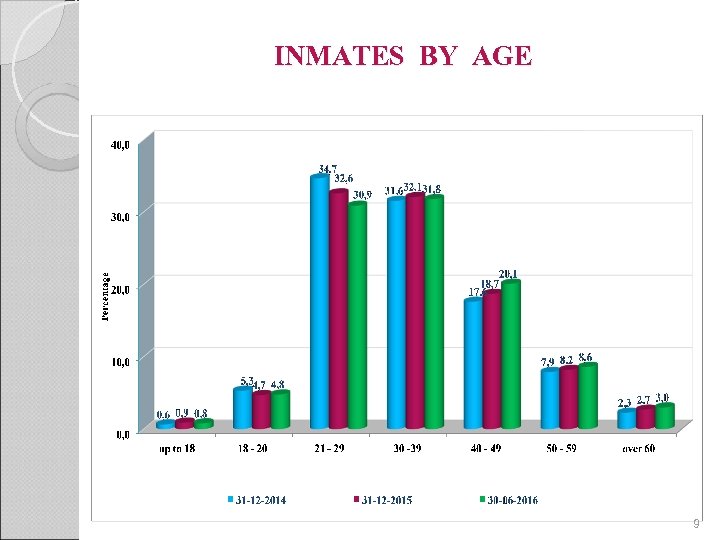
INMATES BY AGE 9
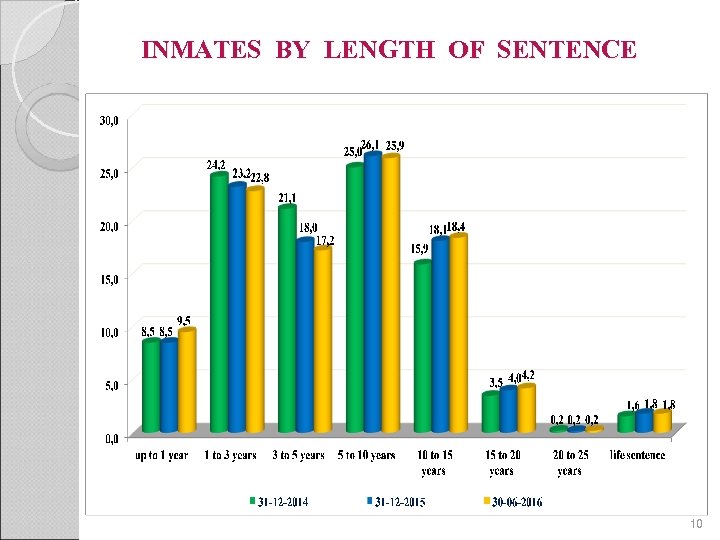
INMATES BY LENGTH OF SENTENCE 10

FUNDING Lithuanian penitentiary system is financed from the state budget. In 2015 the penitentiary system was allocated approx. 64272 thousand Eur from the state budget. Certain social rehabilitation programs, enhancement of human resources, performance upgrading of correction inspections are funded from the Structural Funds of the European Union, Norwegian Financial Mechanism and other funds. 11

COSTS PER 1 INMATE IN PENITENTIARY INSTITUTION PER DAY (IN EUR) 12

HEALTHCARE IN PRISONS SYSTEM I level (in pre-trial prison and Correction houses): Family doctor or Internist and psychiatrist, dentist, dermatologist, TB doctor. II level (Prison hospital) III level healthcare in public healthcare institution

LEGISLATIVE BASIS FOR INFECTIUOS DISEASES CONTROL One of the main legal acts regulating the control of infections in penitentiary institutions is the Procedure on preventive examination for infections qualified as risky and of high risk of persons held in the institutions subordinate to the Prison department under the Ministry of Justice approved by the joint order of 19 March 2013 No V-276/1 R-85 of the Minister of Health care of the Republic of Lithuania and the Minister of Justice of the Republic of Lithuania

PREVENTIVE EXAMINATION FOR INFECTIONS 92 -95 percent of inmates is checked for the prevention of infectious diseases (or their agents carrying) every year: ◦ number of preventive tests in 2015 for tuberculosis 10 917 for HIV 12 716 for other communicable diseases 6 990 2018 -03 -19 15

In 2011 Lithuanian penitentiary system bought modern mobile digital Xray machine. It makes possibillity to diagnose pulmonary tuberculosis in early stage and prescribe proper treatment.

EPIDEMIOLOGY OF TUBERCULOSIS IN PRISON SYSTEM OF LITHUANIA
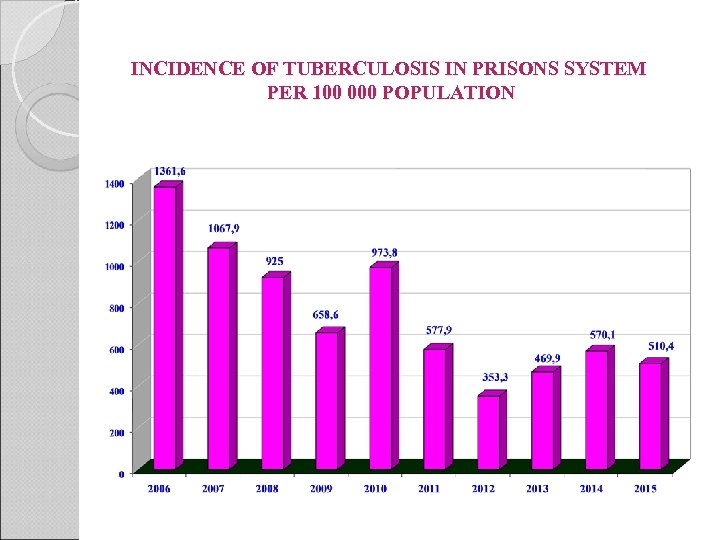
INCIDENCE OF TUBERCULOSIS IN PRISONS SYSTEM PER 100 000 POPULATION
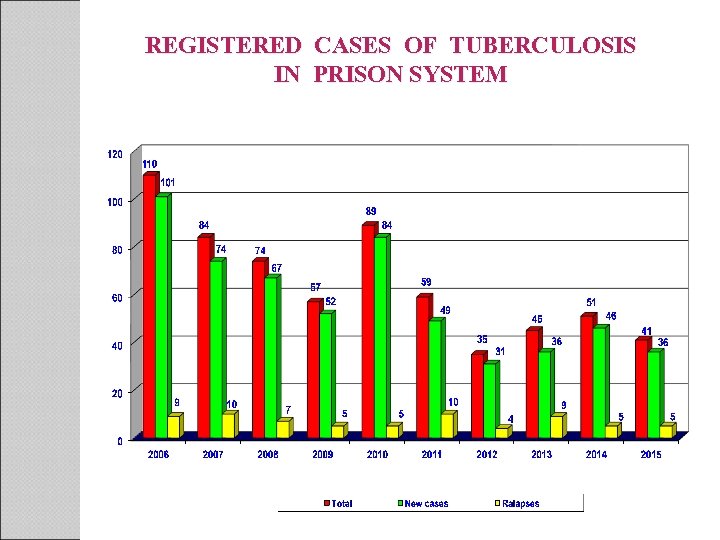
REGISTERED CASES OF TUBERCULOSIS IN PRISON SYSTEM
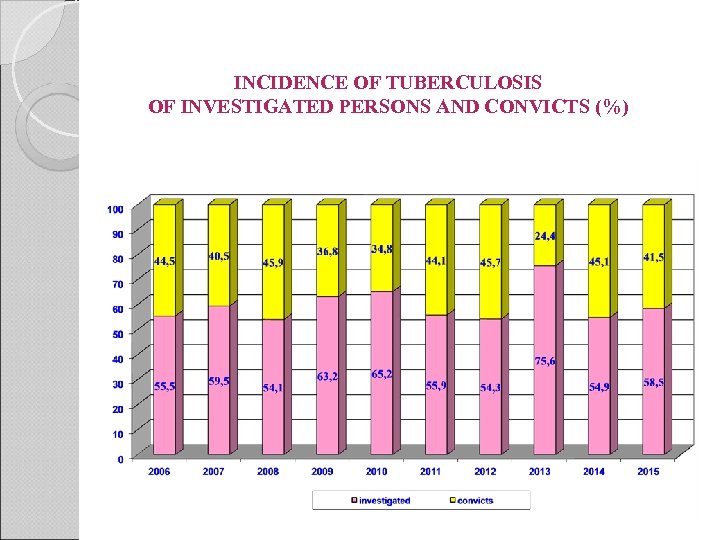
INCIDENCE OF TUBERCULOSIS OF INVESTIGATED PERSONS AND CONVICTS (%)
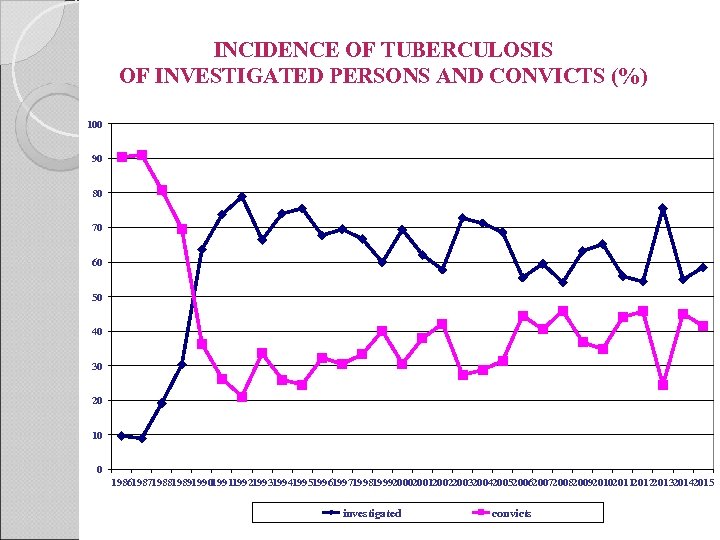
INCIDENCE OF TUBERCULOSIS OF INVESTIGATED PERSONS AND CONVICTS (%) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 198619871988198919901991199219931994199519961997199819992000200120022003200420052006200720082009201020112012201320142015 investigated convicts

CURRENT PROBLEM The level of TB incidence in penitentiary institutions fluctuates either up or down, but the trend that more than 50 percent of incidence if viewed on the incidence structural chart is comprised of “TB brought in from the outside”, i. e. , a disease which is revealed only during preventive medical examination upon an offender‘s entrance to a remand prison, remains.

PREVALENCE OF TUBERCULOSIS IN PRISONS OF LITHUANIA (total No) 2018 -03 -19 23

SOCIO-DEMOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTIC An inmate/detainee ill with tuberculosis is a young man: out of 36 new cases and of tuberculosis in 2015 – only 1 women; Men by age: 15 -24 years old 2 25 -34 years old 15 35 -44 years old 11 45 -54 years old 5 55 -64 years old 2 Use of alcohol: rarely 59, 6 percent abused 40, 7 percent
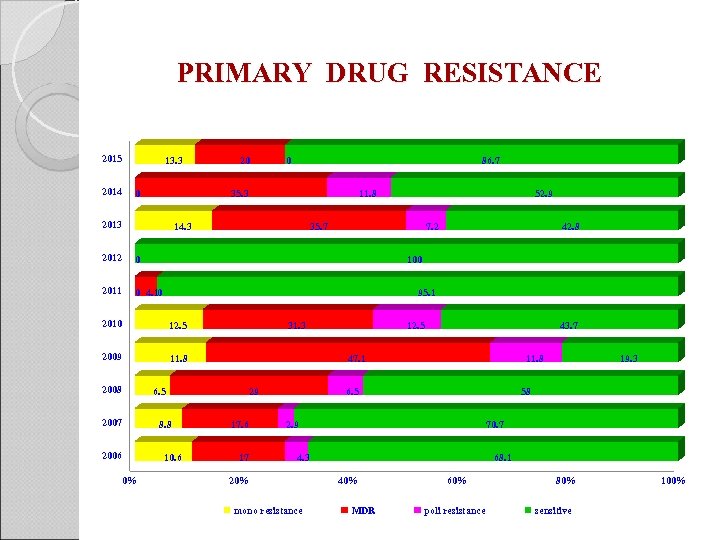
PRIMARY DRUG RESISTANCE 2015 2014 13. 3 0 20 0 86. 7 35. 3 2013 11. 8 14. 3 2012 35. 7 7. 2 0 2011 0 4. 10 95. 1 12. 5 2009 11. 8 31. 3 8. 8 2006 10. 6 0% 12. 5 43. 7 47. 1 6. 5 2007 42. 8 100 2010 2008 52. 9 29 17. 6 17 11. 8 6. 5 58 2. 9 70. 7 4. 3 20% mono resistance 19. 3 68. 1 40% MDR 60% poli resistance 80% sensitive 100%

CURRENT PROBLEM The problem of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in penitentiary institutions increases year by year. More offenders keep returning to penitentiary institutions with previously diagnosed tuberculosis and having terminated the treatment that ensues multidrug-resistance.
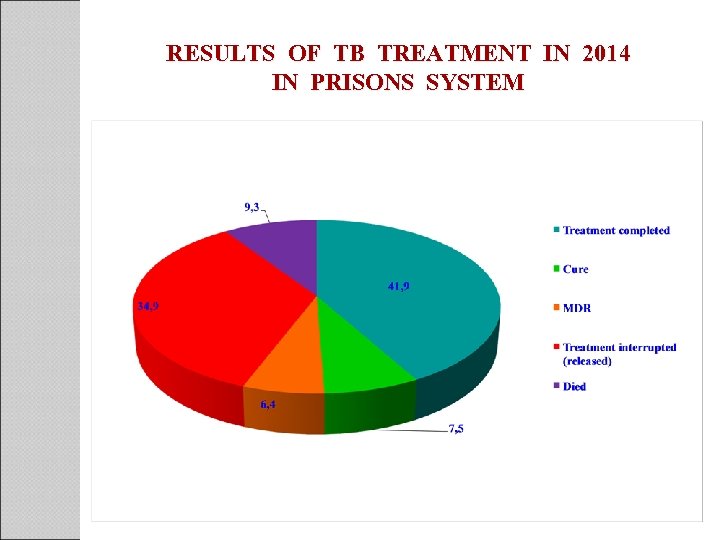
RESULTS OF TB TREATMENT IN 2014 IN PRISONS SYSTEM
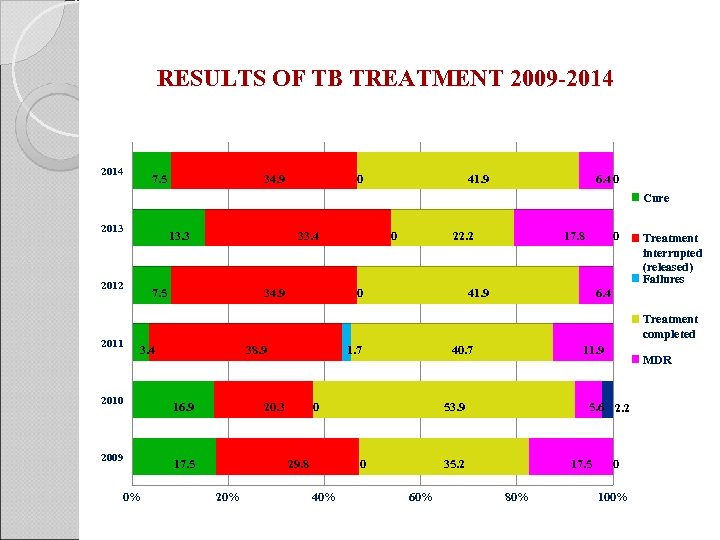
RESULTS OF TB TREATMENT 2009 -2014 7. 5 34. 9 0 41. 9 6. 4 0 Cure 2013 13. 3 2012 33. 4 7. 5 34. 9 0 22. 2 0 17. 8 0 41. 9 Treatment interrupted (released) Failures 6. 4 2011 Treatment completed 3. 4 2010 38. 9 16. 9 2009 20. 3 17. 5 0% 1. 7 0 29. 8 20% 40. 7 53. 9 0 40% 11. 9 5. 6 2. 2 35. 2 60% MDR 17. 5 80% 0 100%

CURRENT PROBLEM Released patients who have not completed the treatment course sooner or later are registered in the category of terminated treatment and stimulate the development not only of MDR but also of X-DR tuberculosis.
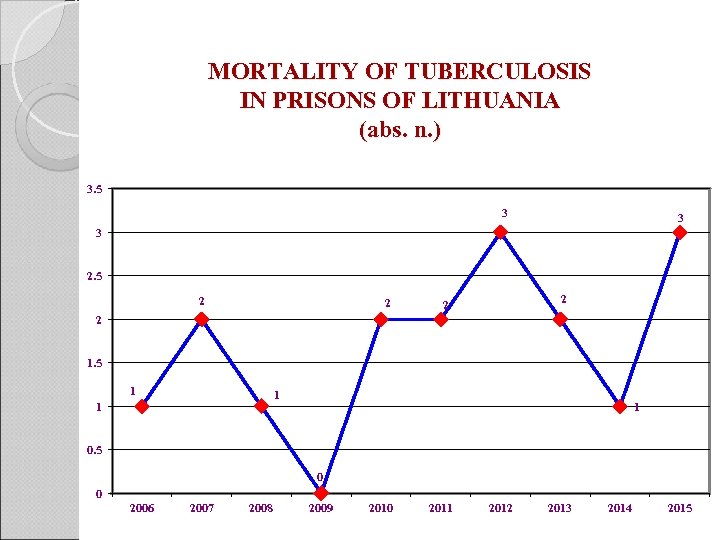
MORTALITY OF TUBERCULOSIS IN PRISONS OF LITHUANIA (abs. n. ) 3. 5 3 3 3 2. 5 2 2 2 1. 5 1 1 0. 5 0 0 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015

Strategy of TB prevention, treatment, and control in Prison system for 2017 -2022 (Approved by the order of 22 August 2016 No V-289 of the Director of Prison department under the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Lithuania) 31

HIV/AIDS EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SITUATION IN PRISON SYSTEM OF LITHUANIA

HIV INFECTION IN PRISONS • Daily number of prisoners in penitentiary institutions who are HIV infected or ill with AIDS amounts to 300 -310 (about 3, 5 per cent of all inmates): on 1 st of september 2016 the number was 245 • More than 1200 (about 65 per cent) HIV infected persons of the country have experience of imprisonment (served their term in prison)

COUNSELING AND TESTING OF PRISONERS FOR HIV Testing for HIV in prison: for prisoners (detainees/sentenced) upon their arrival to places of detention and imprisonment, also to Central Prison Hospital from police arrest houses or before transfering from one correction house to other; 4 weeks after 1 st testing (after their arrival to remand prisons and correction house); once per year – all inmates in correction houses; according epidemiological or medical indications.

HIV CASES DETECTED IN PRISONS OF LITHUANIA

THANK YOU FOR YOUR KIND ATTENTION Prison Department under the Ministry of Justice Republic of Lithuania L. Sapiegos st. 1, Vilnius Tel. (+370 5) 271 9003/82 Fax. (+370 5) 275 2778 Email: kaldep@kaldep. lt 36
68f22f2830b63d012fbdc73f1b277ab0.ppt