fbd7e24de676435dece4e5f16b3d3d13.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 79
 HCI History – Part 1 of 2 Key people, events, ideas and paradigm shifts This material has been developed by Georgia Tech HCI faculty, and continues to evolve. Contributors include Gregory Abowd, Jim Foley, Diane Gromala, Elizabeth Mynatt, Jeff Pierce, Colin Potts, Chris Shaw, John Stasko, and Bruce Walker. This specific presentation also borrows from James Landay and Jason Hong at UC Berkeley. Comments directed to foley@cc. gatech. edu are encouraged. Permission is granted to use with acknowledgement 1 for non-profit purposes. Last revision: January 2004.
HCI History – Part 1 of 2 Key people, events, ideas and paradigm shifts This material has been developed by Georgia Tech HCI faculty, and continues to evolve. Contributors include Gregory Abowd, Jim Foley, Diane Gromala, Elizabeth Mynatt, Jeff Pierce, Colin Potts, Chris Shaw, John Stasko, and Bruce Walker. This specific presentation also borrows from James Landay and Jason Hong at UC Berkeley. Comments directed to foley@cc. gatech. edu are encouraged. Permission is granted to use with acknowledgement 1 for non-profit purposes. Last revision: January 2004.
 The Evolution of HCI • Series of technological advances lead to and are sometimes facilitated by a • Series of paradigm shifts that in turn are created by a • Series of key people and events 2
The Evolution of HCI • Series of technological advances lead to and are sometimes facilitated by a • Series of paradigm shifts that in turn are created by a • Series of key people and events 2
 Why study HCI’s history? • Understanding where you’ve come from can help a lot in figuring out where you’re going - repeat positive lessons • “Those who forget the past are condemned to repeat it” (Santayana)avoid negative lessons • Knowledge of an area implies an appreciation of its history 3
Why study HCI’s history? • Understanding where you’ve come from can help a lot in figuring out where you’re going - repeat positive lessons • “Those who forget the past are condemned to repeat it” (Santayana)avoid negative lessons • Knowledge of an area implies an appreciation of its history 3
 What are Paradigms • Predominant theoretical frameworks or scientific world views § e. g. , Aristotelian, Newtonian, Einsteinian (relativistic) paradigms in physics • Understanding HCI history is largely about understanding a series of paradigm shifts § Not all listed here are necessarily “paradigm” shifts, but are at least candidates § History will judge which are true shifts 4
What are Paradigms • Predominant theoretical frameworks or scientific world views § e. g. , Aristotelian, Newtonian, Einsteinian (relativistic) paradigms in physics • Understanding HCI history is largely about understanding a series of paradigm shifts § Not all listed here are necessarily “paradigm” shifts, but are at least candidates § History will judge which are true shifts 4
 Howard Rheingold – Tools for Thought • History of interactive breakthroughs § On-line at http: //www. rheingold. com/texts/tft/ • One of several good sources 5
Howard Rheingold – Tools for Thought • History of interactive breakthroughs § On-line at http: //www. rheingold. com/texts/tft/ • One of several good sources 5
 (Some of the) Key Technological Advances • Starting point § Computing in 1945 § Batch processing • Interactive graphics systems • Time sharing computers § One computer to many people • Internet 6
(Some of the) Key Technological Advances • Starting point § Computing in 1945 § Batch processing • Interactive graphics systems • Time sharing computers § One computer to many people • Internet 6
 More Key Technological Advances • The desk top / personal computer § One computer to one person • Inexpensive, low-power chips § Many computers to one person • Wireless connectivity 7
More Key Technological Advances • The desk top / personal computer § One computer to one person • Inexpensive, low-power chips § Many computers to one person • Wireless connectivity 7
 Paradigm Shifts – How We Use Computers • Interactive Computing - time sharing, Basic • WIMP Interfaces § Windows, Icons, Mouse, Pointing § Direct Manipulation § Metaphors • Hypertext / WWW • Computers for person-to-person communications – not just for computing § Email, CSCW 8
Paradigm Shifts – How We Use Computers • Interactive Computing - time sharing, Basic • WIMP Interfaces § Windows, Icons, Mouse, Pointing § Direct Manipulation § Metaphors • Hypertext / WWW • Computers for person-to-person communications – not just for computing § Email, CSCW 8
 More Paradigm Shifts • • Multimodal interfaces Immersive (VR) interfaces Ubiquitous computing Mobile computing 9
More Paradigm Shifts • • Multimodal interfaces Immersive (VR) interfaces Ubiquitous computing Mobile computing 9
 (Some of the) Key People and Events • People § § § § § Vannevar Bush Doug Engelbart Ivan Sutherland J. R. (Lick) Licklider Alan Kay Ted Nelson Nicholas Negroponte Mark Weiser Jaron Lanier • Events § Founding of Xerox PARC § Lisa / Macintosh 10
(Some of the) Key People and Events • People § § § § § Vannevar Bush Doug Engelbart Ivan Sutherland J. R. (Lick) Licklider Alan Kay Ted Nelson Nicholas Negroponte Mark Weiser Jaron Lanier • Events § Founding of Xerox PARC § Lisa / Macintosh 10
 Telling the Story • Key Technological Advances • Key Paradigm Shifts • Key People and Events • Interleaved in more or less chronological order 11
Telling the Story • Key Technological Advances • Key Paradigm Shifts • Key People and Events • Interleaved in more or less chronological order 11
 In the Very Beginning • Digital computer grounded in ideas from 1700’s & 1800’s • Technology became available in the 1940’s and 1950’s 12
In the Very Beginning • Digital computer grounded in ideas from 1700’s & 1800’s • Technology became available in the 1940’s and 1950’s 12
 In the Beginning – Computing in 1945 • Harvard Mark I • 55 feet long, 8 feet high, 5 tons Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley, Picture from http: //piano. dsi. uminho. pt/m useuv/indexmark. htm 13
In the Beginning – Computing in 1945 • Harvard Mark I • 55 feet long, 8 feet high, 5 tons Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley, Picture from http: //piano. dsi. uminho. pt/m useuv/indexmark. htm 13
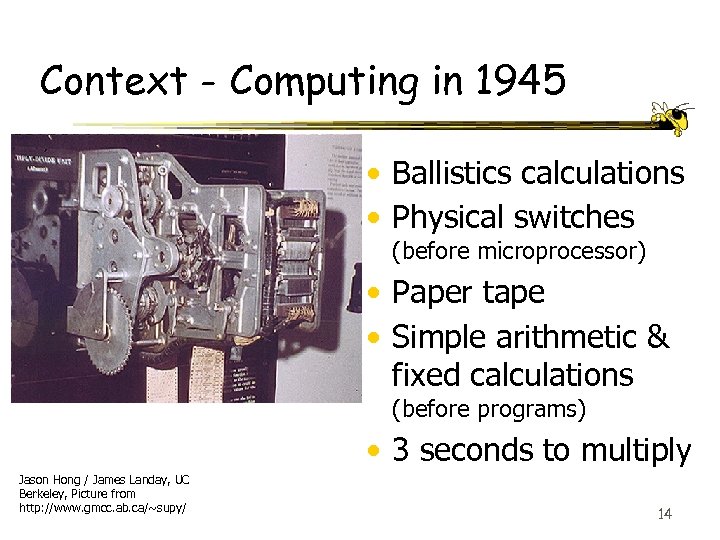 Context - Computing in 1945 • Ballistics calculations • Physical switches (before microprocessor) • Paper tape • Simple arithmetic & fixed calculations (before programs) • 3 seconds to multiply Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley, Picture from http: //www. gmcc. ab. ca/~supy/ 14
Context - Computing in 1945 • Ballistics calculations • Physical switches (before microprocessor) • Paper tape • Simple arithmetic & fixed calculations (before programs) • 3 seconds to multiply Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley, Picture from http: //www. gmcc. ab. ca/~supy/ 14
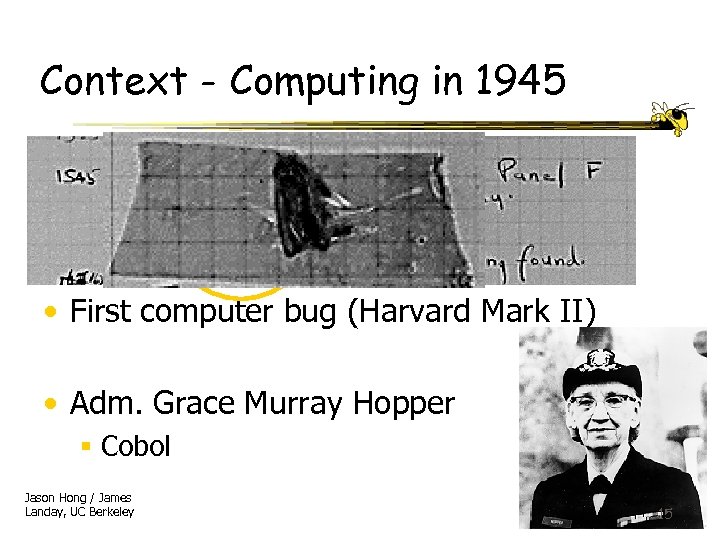 Context - Computing in 1945 • First computer bug (Harvard Mark II) • Adm. Grace Murray Hopper § Cobol Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley 15
Context - Computing in 1945 • First computer bug (Harvard Mark II) • Adm. Grace Murray Hopper § Cobol Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley 15
 Innovator: Vannevar Bush • “As We May Think” - 1945 Atlantic Monthly § “…publication has been extended far beyond our present ability to make real use of the record. ” • Postulated Memex device § Stores all records/articles/communications § Items retrieved by indexing, keywords, cross references (now called hyperlinks) § (Envisioned as microfilm, not computer) • Interactive and nonlinear components are key • http: //www. theatlantic. com/unbound/flashbks/computer /bushf. htm 16
Innovator: Vannevar Bush • “As We May Think” - 1945 Atlantic Monthly § “…publication has been extended far beyond our present ability to make real use of the record. ” • Postulated Memex device § Stores all records/articles/communications § Items retrieved by indexing, keywords, cross references (now called hyperlinks) § (Envisioned as microfilm, not computer) • Interactive and nonlinear components are key • http: //www. theatlantic. com/unbound/flashbks/computer /bushf. htm 16
 More About Vannevar Bush • Name rhymes with "Beaver" • MIT faculty member • Coordinated WWII effort with 6000 US scientists • Social contract for science § federal government funds universities § universities do basic research § research helps economy & national defense 17
More About Vannevar Bush • Name rhymes with "Beaver" • MIT faculty member • Coordinated WWII effort with 6000 US scientists • Social contract for science § federal government funds universities § universities do basic research § research helps economy & national defense 17
 “As We May Think” • Futuristic inventions / trends § § § Wearable cameras for photographic records Encyclopedia Britanica for a nickel Automatic transcripts of speech Memex, Trails of discovery Direct capture of nerve impulses 18
“As We May Think” • Futuristic inventions / trends § § § Wearable cameras for photographic records Encyclopedia Britanica for a nickel Automatic transcripts of speech Memex, Trails of discovery Direct capture of nerve impulses 18
 As We May Think • Very optimistic about future § Technology could help society § Technology could manage flood of info • Bush – one of most informed people of his time § Look at trends, guess where we're going • If you read it § Which feature is your favorite? Why? § Which feature is your least favorite? Why? § What was he right about? Wrong about? 19
As We May Think • Very optimistic about future § Technology could help society § Technology could manage flood of info • Bush – one of most informed people of his time § Look at trends, guess where we're going • If you read it § Which feature is your favorite? Why? § Which feature is your least favorite? Why? § What was he right about? Wrong about? 19
 As We May Think • Some have come true § Increased specialization § Flood of information § Faster / Cheaper / Smaller / More reliable • Some he missed or we are still waiting § § Microphotography? Digital technologies? Non-science / Non-office apps? Memex? 20
As We May Think • Some have come true § Increased specialization § Flood of information § Faster / Cheaper / Smaller / More reliable • Some he missed or we are still waiting § § Microphotography? Digital technologies? Non-science / Non-office apps? Memex? 20
 As We May Think • Not so much predicting future as "inventing it" by publishing article § hypertext § wearable memory aid • Use technology to augment human intellectual abilities • New kinds of technology lead to new kinds of human/machine & human/human interaction • Be aware that science/engineering can impact society 21
As We May Think • Not so much predicting future as "inventing it" by publishing article § hypertext § wearable memory aid • Use technology to augment human intellectual abilities • New kinds of technology lead to new kinds of human/machine & human/human interaction • Be aware that science/engineering can impact society 21
 Context - Computing in 1960 s • • Transistor (1948) ARPA (1958) Timesharing (1950 s) Terminals and keyboards • Computers still primarily scientists and engineers Vacuum Tube for Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley 22
Context - Computing in 1960 s • • Transistor (1948) ARPA (1958) Timesharing (1950 s) Terminals and keyboards • Computers still primarily scientists and engineers Vacuum Tube for Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley 22
 Batch Processing • Computer had one task, performed sequentially • No “interaction” between operator and computer after starting the run • Punch cards, tapes for input • Serial operations 23
Batch Processing • Computer had one task, performed sequentially • No “interaction” between operator and computer after starting the run • Punch cards, tapes for input • Serial operations 23
 Innovator: J. R. Licklider • 1960 - Postulated “man-computer symbiosis” • Couple human brains and computing machines tightly to revolutionize information handling 24
Innovator: J. R. Licklider • 1960 - Postulated “man-computer symbiosis” • Couple human brains and computing machines tightly to revolutionize information handling 24
 Technological Advance: Interactive Graphics • More suitable medium than paper - picture worth a thousand words • Sutherland’s Sketch. Pad as landmark system • Start of Direct Manipulation • Computers used for visualizing and manipulating data 25
Technological Advance: Interactive Graphics • More suitable medium than paper - picture worth a thousand words • Sutherland’s Sketch. Pad as landmark system • Start of Direct Manipulation • Computers used for visualizing and manipulating data 25
 Innovator: Ivan Sutherland • Sketch. Pad - 1963 Ph. D thesis at MIT § § § § Hierarchy - pictures & subpictures Master picture with instances (ie, OOP) Constraints Icons Copying Light pen input device Recursive operations 26
Innovator: Ivan Sutherland • Sketch. Pad - 1963 Ph. D thesis at MIT § § § § Hierarchy - pictures & subpictures Master picture with instances (ie, OOP) Constraints Icons Copying Light pen input device Recursive operations 26
 Technological Advance / Paradigm Shift: Time Sharing • (Mid 1960 s) • Command line - teletypes, then “glass teletypes” • Computers still too expensive for individuals timesharing § increased accessibility § interactive systems, not jobs § text processing, editing § email, shared file system Need for HCI* * There was an unrecognized need for HCI in the design of programming languages 27
Technological Advance / Paradigm Shift: Time Sharing • (Mid 1960 s) • Command line - teletypes, then “glass teletypes” • Computers still too expensive for individuals timesharing § increased accessibility § interactive systems, not jobs § text processing, editing § email, shared file system Need for HCI* * There was an unrecognized need for HCI in the design of programming languages 27
 The Ubiquitous ASR 33 Teletype • ASR: Automatic Send / Receive • Save programs on punched paper tape • The first direct humancomputer interface experience for many in the 1960 s • About 10 characters per second - 110 bps 28
The Ubiquitous ASR 33 Teletype • ASR: Automatic Send / Receive • Save programs on punched paper tape • The first direct humancomputer interface experience for many in the 1960 s • About 10 characters per second - 110 bps 28
 The Ubiquitous Glass Teletype • 24 x 80 characters • Up to 19, 200 bps (Wow was big stuff!) Source: http: //www. columbia. edu/acis/history/vt 100. html 29
The Ubiquitous Glass Teletype • 24 x 80 characters • Up to 19, 200 bps (Wow was big stuff!) Source: http: //www. columbia. edu/acis/history/vt 100. html 29
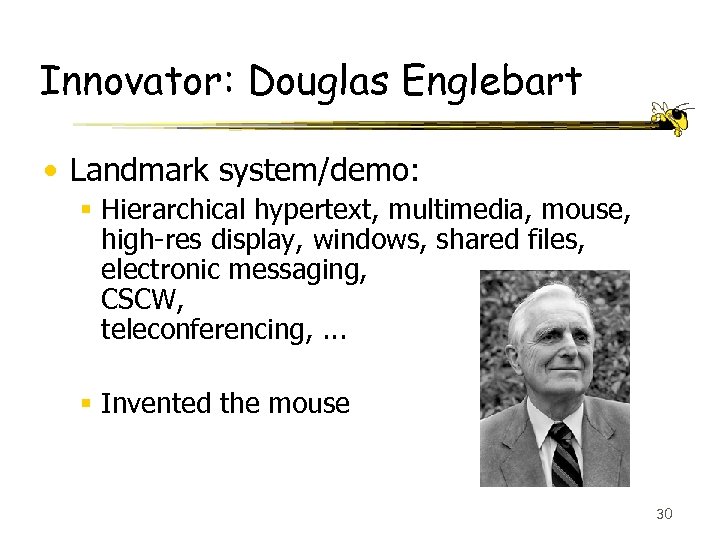 Innovator: Douglas Englebart • Landmark system/demo: § Hierarchical hypertext, multimedia, mouse, high-res display, windows, shared files, electronic messaging, CSCW, teleconferencing, . . . § Invented the mouse 30
Innovator: Douglas Englebart • Landmark system/demo: § Hierarchical hypertext, multimedia, mouse, high-res display, windows, shared files, electronic messaging, CSCW, teleconferencing, . . . § Invented the mouse 30
 Augmenting Human Intellect • 1968 Fall Joint Computer Conference (SF) • Video of NLS (o. NLine System) • All this took place before § Unix and C (1970 s) § ARPAnet (1969) & later Internet http: //sloan. stanford. edu/ Mouse. Site/Mouse. Site. Pg 1. html 31
Augmenting Human Intellect • 1968 Fall Joint Computer Conference (SF) • Video of NLS (o. NLine System) • All this took place before § Unix and C (1970 s) § ARPAnet (1969) & later Internet http: //sloan. stanford. edu/ Mouse. Site/Mouse. Site. Pg 1. html 31
 About Doug Engelbart • Graduate of Berkeley (EE '55) § "bi-stable gaseous plasma digital devices" • Stanford Research Institute (SRI) § Augmentation Research Center • 1962 Paper "Conceptual Model for Augmenting Human Intellect" § Complexity of problems increasing § Need better ways of solving problems Picture from www. bootstrap. org 32
About Doug Engelbart • Graduate of Berkeley (EE '55) § "bi-stable gaseous plasma digital devices" • Stanford Research Institute (SRI) § Augmentation Research Center • 1962 Paper "Conceptual Model for Augmenting Human Intellect" § Complexity of problems increasing § Need better ways of solving problems Picture from www. bootstrap. org 32
 Engelbart NLS Video 33
Engelbart NLS Video 33
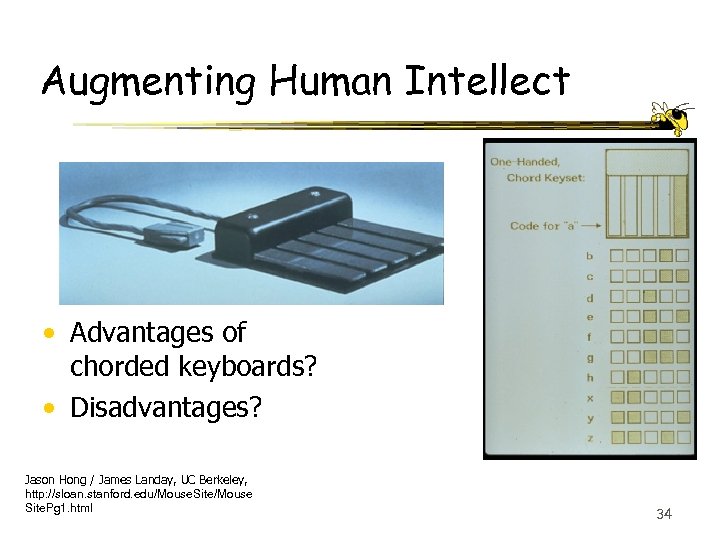 Augmenting Human Intellect • Advantages of chorded keyboards? • Disadvantages? Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley, http: //sloan. stanford. edu/Mouse. Site/Mouse Site. Pg 1. html 34
Augmenting Human Intellect • Advantages of chorded keyboards? • Disadvantages? Jason Hong / James Landay, UC Berkeley, http: //sloan. stanford. edu/Mouse. Site/Mouse Site. Pg 1. html 34
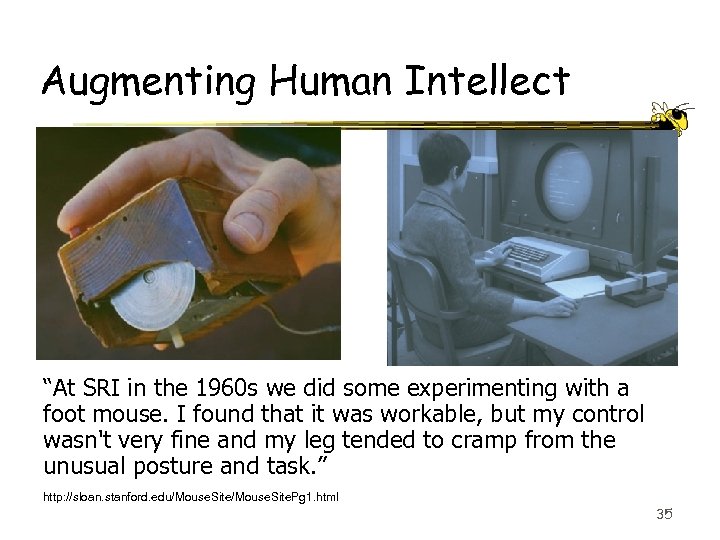 Augmenting Human Intellect “At SRI in the 1960 s we did some experimenting with a foot mouse. I found that it was workable, but my control wasn't very fine and my leg tended to cramp from the unusual posture and task. ” http: //sloan. stanford. edu/Mouse. Site. Pg 1. html 35
Augmenting Human Intellect “At SRI in the 1960 s we did some experimenting with a foot mouse. I found that it was workable, but my control wasn't very fine and my leg tended to cramp from the unusual posture and task. ” http: //sloan. stanford. edu/Mouse. Site. Pg 1. html 35
 Augmenting Human Intellect Chorded Keyboard Early 3 -button mouse 36
Augmenting Human Intellect Chorded Keyboard Early 3 -button mouse 36
 Augmenting Human Intellect • Discussion, if you watched the video • What did we just see? § Interaction devices § Interaction styles § Applications 37
Augmenting Human Intellect • Discussion, if you watched the video • What did we just see? § Interaction devices § Interaction styles § Applications 37
 Augmenting Human Intellect • • First mouse First groupware (shared screen First hypertext teleconferencing) First word processing First context. First 2 D editing and sensitive help windows • First document version First distributed client-server control Many, many more! 38
Augmenting Human Intellect • • First mouse First groupware (shared screen First hypertext teleconferencing) First word processing First context. First 2 D editing and sensitive help windows • First document version First distributed client-server control Many, many more! 38
 Augmentation not Automation "I tell people: look, you can spend all you want on building smart agents and smart tools…" "I'd bet that if you then give those to twenty people with no special training, and if you let me take twenty people and really condition and train them especially to learn how to harness the tools…" "The people with the training will always outdo the people for whom the computers were supposed to do the work. " 39
Augmentation not Automation "I tell people: look, you can spend all you want on building smart agents and smart tools…" "I'd bet that if you then give those to twenty people with no special training, and if you let me take twenty people and really condition and train them especially to learn how to harness the tools…" "The people with the training will always outdo the people for whom the computers were supposed to do the work. " 39
 Augmenting Human Intellect • • • Example: Roman Numerals vs Arabic What is XCI + III? Now what is XCI x III? What is 91 * 3? New kinds of artifacts, languages, methodologies, and training can enable us to do things we couldn't do before or simplify what we already do 40
Augmenting Human Intellect • • • Example: Roman Numerals vs Arabic What is XCI + III? Now what is XCI x III? What is 91 * 3? New kinds of artifacts, languages, methodologies, and training can enable us to do things we couldn't do before or simplify what we already do 40
 End of Part 1 of 2 41
End of Part 1 of 2 41
 HCI History Part 2 of 2 Key people, events, ideas and paradigm shifts This material has been developed by Georgia Tech HCI faculty, and continues to evolve. Contributors include Gregory Abowd, Jim Foley, Diane Gromala, Elizabeth Mynatt, Jeff Pierce, Colin Potts, Chris Shaw, John Stasko, and Bruce Walker. This specific presentation also borrows from James Landay and Jason Hong at UC Berkeley. Comments directed to foley@cc. gatech. edu are encouraged. Permission is granted to use with acknowledgement 42 for non-profit purposes. Last revision: August 2004.
HCI History Part 2 of 2 Key people, events, ideas and paradigm shifts This material has been developed by Georgia Tech HCI faculty, and continues to evolve. Contributors include Gregory Abowd, Jim Foley, Diane Gromala, Elizabeth Mynatt, Jeff Pierce, Colin Potts, Chris Shaw, John Stasko, and Bruce Walker. This specific presentation also borrows from James Landay and Jason Hong at UC Berkeley. Comments directed to foley@cc. gatech. edu are encouraged. Permission is granted to use with acknowledgement 42 for non-profit purposes. Last revision: August 2004.
 The Evolution of HCI • Series of technological advances lead to and are sometimes facilitated by a • Series of paradigm shifts that in turn are created by a • Series of key people and events 43
The Evolution of HCI • Series of technological advances lead to and are sometimes facilitated by a • Series of paradigm shifts that in turn are created by a • Series of key people and events 43
 Paradigm: Personal Computer • System is more powerful if it’s easier to use • Small, powerful machine dedicated to individual use • Made possible by single-chip processor and less semiconductor memory - drives down costs Moore’s Law 44
Paradigm: Personal Computer • System is more powerful if it’s easier to use • Small, powerful machine dedicated to individual use • Made possible by single-chip processor and less semiconductor memory - drives down costs Moore’s Law 44
 Early Personal Computers • 1975 IBM 5100 • 1977 Radio Shack TRS-80 45
Early Personal Computers • 1975 IBM 5100 • 1977 Radio Shack TRS-80 45
 Early Personal Computers • 1997 Apple II • 1979 Visi. Calc - “killer app” for Apple II • 1981 IBM XT/AT 46
Early Personal Computers • 1997 Apple II • 1979 Visi. Calc - “killer app” for Apple II • 1981 IBM XT/AT 46
 The dawn of the PC & GUI Xerox PARC - 1970 • Established 1970 § Bob Taylor heads CSL - Computer Systems Lab • Goal: “The Paperless Office” § Are we there yet? • “Inventing the future” § Researchers using their new creations as their own tools - bootstrapping 47
The dawn of the PC & GUI Xerox PARC - 1970 • Established 1970 § Bob Taylor heads CSL - Computer Systems Lab • Goal: “The Paperless Office” § Are we there yet? • “Inventing the future” § Researchers using their new creations as their own tools - bootstrapping 47
 PARC Hardware Milestones • Laser printer 1971 § Gary Starkweather • Ethernet 1973 § Bob Metcalfe • Alto personal computer 1973 § Chuck Thacker § Ed Mc. Creight, Chuck Thacker, Butler Lampson, Bob Sproull, and Dave Boggs • Real-time windowing operations (Bit. Blt) 1973 § Dan Ingalls 48
PARC Hardware Milestones • Laser printer 1971 § Gary Starkweather • Ethernet 1973 § Bob Metcalfe • Alto personal computer 1973 § Chuck Thacker § Ed Mc. Creight, Chuck Thacker, Butler Lampson, Bob Sproull, and Dave Boggs • Real-time windowing operations (Bit. Blt) 1973 § Dan Ingalls 48
 Xerox PARC – The Alto - 1973 • First personal computer! • 808 x 606 raster bitmapped display • 3 -button mouse, keyboard • Ethernet • Merges printing, display and networking 49
Xerox PARC – The Alto - 1973 • First personal computer! • 808 x 606 raster bitmapped display • 3 -button mouse, keyboard • Ethernet • Merges printing, display and networking 49
 PARC Software Milestones • Bravo WYSIWYG text editor/formatter 1974 § Butler Lampson and Charles Simonyi • Gypsy text editor with GUI and modeless cut and paste editing 1975 § Larry Tessler and Timothy Mott • Draw drawing program 1975 § William Newman • Superpaint program 1974 -75 § Dick Shoup 50
PARC Software Milestones • Bravo WYSIWYG text editor/formatter 1974 § Butler Lampson and Charles Simonyi • Gypsy text editor with GUI and modeless cut and paste editing 1975 § Larry Tessler and Timothy Mott • Draw drawing program 1975 § William Newman • Superpaint program 1974 -75 § Dick Shoup 50
 Innovator: Alan Kay • • • Dynabook - Notebook sized computer loaded with multimedia and can store everything @PARC Personal computing Desktop interface Overlapping windows 51
Innovator: Alan Kay • • • Dynabook - Notebook sized computer loaded with multimedia and can store everything @PARC Personal computing Desktop interface Overlapping windows 51
 HCI Researchers at Xerox PARC in 1970 s and early 1980 s • • Stu Card Tom Moran George Robertson David Smith Bill Verplank Jeff Johnson …… 52
HCI Researchers at Xerox PARC in 1970 s and early 1980 s • • Stu Card Tom Moran George Robertson David Smith Bill Verplank Jeff Johnson …… 52
 Paradigm: WIMP / GUI • Windows, Icons, Menus, Pointers • Graphical User Interface • Timesharing=multi-user; now we need multitasking • WIMP interface allows you to do several things simultaneously • Has become the familiar GUI interface • Xerox Alto & Star; Perq, Lisa, Macintosh, … 53
Paradigm: WIMP / GUI • Windows, Icons, Menus, Pointers • Graphical User Interface • Timesharing=multi-user; now we need multitasking • WIMP interface allows you to do several things simultaneously • Has become the familiar GUI interface • Xerox Alto & Star; Perq, Lisa, Macintosh, … 53
 Xerox Star - 1981 • First commercial PC designed for “business professionals” § desktop metaphor, pointing, WYSIWYG, high degree of consistency and simplicity • First system based on usability engineering § Paper prototyping and analysis § Usability testing and iterative refinement 54
Xerox Star - 1981 • First commercial PC designed for “business professionals” § desktop metaphor, pointing, WYSIWYG, high degree of consistency and simplicity • First system based on usability engineering § Paper prototyping and analysis § Usability testing and iterative refinement 54
 Xerox Star Desktop 55
Xerox Star Desktop 55
 Xerox Star - 1981 • Commercial flop § $15 k cost § closed architecture § lacking key functionality (spreadsheet) • Video - the Star in use 56
Xerox Star - 1981 • Commercial flop § $15 k cost § closed architecture § lacking key functionality (spreadsheet) • Video - the Star in use 56
 Apple Lisa - 1982 • Based on ideas of Star • More personal rather than office tool § Still $$$ - $10 K to $12 K • Failure 57
Apple Lisa - 1982 • Based on ideas of Star • More personal rather than office tool § Still $$$ - $10 K to $12 K • Failure 57
 Apple Macintosh - 1984 • Aggressive pricing § $2500 • Good interface guidelines • Third party applications • Great graphics, laser printer 58
Apple Macintosh - 1984 • Aggressive pricing § $2500 • Good interface guidelines • Third party applications • Great graphics, laser printer 58
 Paradigm: Direct Manipulation • ‘ 82 Shneiderman describes appeal of rapidlydeveloping graphically-based interaction § § § object visibility incremental action and rapid feedback reversibility encourages exploration replace language with action syntactic correctness of all actions • WYSIWYG, Apple Mac 59
Paradigm: Direct Manipulation • ‘ 82 Shneiderman describes appeal of rapidlydeveloping graphically-based interaction § § § object visibility incremental action and rapid feedback reversibility encourages exploration replace language with action syntactic correctness of all actions • WYSIWYG, Apple Mac 59
 Paradigm: Metaphor • All use is problem-solving or learning to some extent • Relating computing to real-world activity is effective learning mechanism § File management on office desktop § Financial analysis as spreadsheets • The tension between literalism & magic § Eject disk or CD on Mac by dragging to trash can 60
Paradigm: Metaphor • All use is problem-solving or learning to some extent • Relating computing to real-world activity is effective learning mechanism § File management on office desktop § Financial analysis as spreadsheets • The tension between literalism & magic § Eject disk or CD on Mac by dragging to trash can 60
 Paradigm/Technology – Personto-Person Communications • Enabled by several technologies § Ethernet and TCP/IP protocol § Personal computer § Telephone network and modems • And by killer-app software § Email, Instant Messaging, Chat, Bulletin Boards • CSCW - conferencing, shared white boards – Not quite yet a killer-app • Micro-sociological phenomenon are central to successes (and failures) 61
Paradigm/Technology – Personto-Person Communications • Enabled by several technologies § Ethernet and TCP/IP protocol § Personal computer § Telephone network and modems • And by killer-app software § Email, Instant Messaging, Chat, Bulletin Boards • CSCW - conferencing, shared white boards – Not quite yet a killer-app • Micro-sociological phenomenon are central to successes (and failures) 61
 Paradigm: CSCW • • Computer-Supported Cooperative Work No longer single user/single system Micro-social aspects are crucial E-mail as prominent success but other groupware still not widely used 62
Paradigm: CSCW • • Computer-Supported Cooperative Work No longer single user/single system Micro-social aspects are crucial E-mail as prominent success but other groupware still not widely used 62
 Paradigm: Hypertext • Think of information not as linear flow but as interconnected nodes • Bush’s MEMEX gave the idea in 1945 • Nelson coined term in 1965 • Engelbart’s NLS did it in 1965 • WWW in ’ 93 was the real launch 63
Paradigm: Hypertext • Think of information not as linear flow but as interconnected nodes • Bush’s MEMEX gave the idea in 1945 • Nelson coined term in 1965 • Engelbart’s NLS did it in 1965 • WWW in ’ 93 was the real launch 63
 Innovator: Ted Nelson • Computers can help people, not just business • Coined and popularized “hypertext” term (1965) 64
Innovator: Ted Nelson • Computers can help people, not just business • Coined and popularized “hypertext” term (1965) 64
 Ted Nelson’s Book(s) 65
Ted Nelson’s Book(s) 65
 The World-Wide Web • Two Key Components § URL = Uniform Resource Locator § Browser • Tim Brenners-Lee did both • See http: //www. w 3. org/History. html for more web history 66
The World-Wide Web • Two Key Components § URL = Uniform Resource Locator § Browser • Tim Brenners-Lee did both • See http: //www. w 3. org/History. html for more web history 66
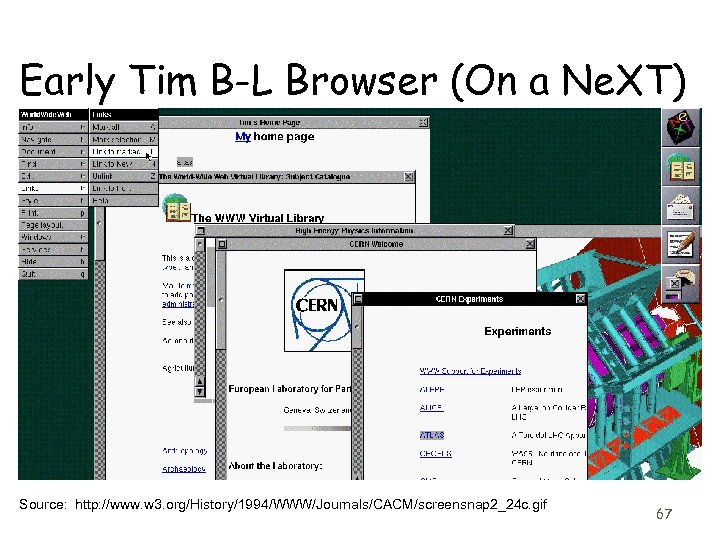 Early Tim B-L Browser (On a Ne. XT) Source: http: //www. w 3. org/History/1994/WWW/Journals/CACM/screensnap 2_24 c. gif 67
Early Tim B-L Browser (On a Ne. XT) Source: http: //www. w 3. org/History/1994/WWW/Journals/CACM/screensnap 2_24 c. gif 67
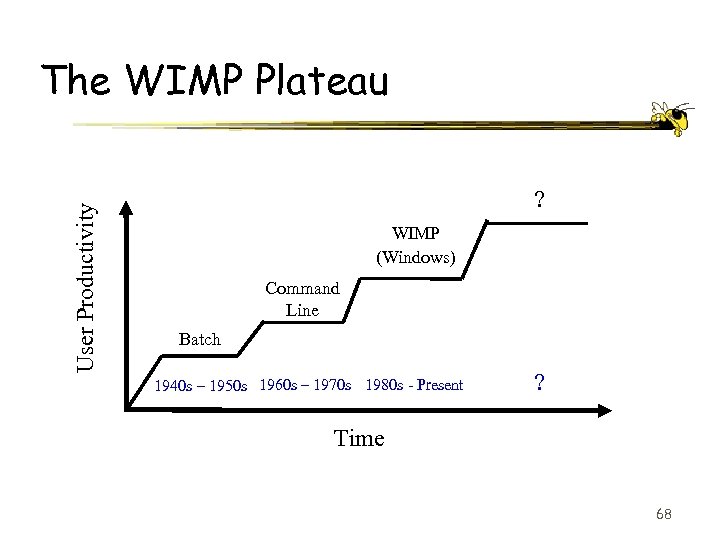 User Productivity The WIMP Plateau ? WIMP (Windows) Command Line Batch 1940 s – 1950 s 1960 s – 1970 s 1980 s - Present ? Time 68
User Productivity The WIMP Plateau ? WIMP (Windows) Command Line Batch 1940 s – 1950 s 1960 s – 1970 s 1980 s - Present ? Time 68
 Paradigm: Multi-modality • Mode is a human communication channel § Not just the senses – e. g. speech and non-speech audio are two modes • Emphasis on simultaneous use of multiple channels for I/O 69
Paradigm: Multi-modality • Mode is a human communication channel § Not just the senses – e. g. speech and non-speech audio are two modes • Emphasis on simultaneous use of multiple channels for I/O 69
 Innovator: Nicholas Negroponte • MIT Architecture Machine Group § ’ 69 -’ 80 s - prior to Media Lab • Ideas § wall-sized displays, video disks, AI in interfaces (agents), speech recognition, multimedia with hypertext § Put That There (Video) 70
Innovator: Nicholas Negroponte • MIT Architecture Machine Group § ’ 69 -’ 80 s - prior to Media Lab • Ideas § wall-sized displays, video disks, AI in interfaces (agents), speech recognition, multimedia with hypertext § Put That There (Video) 70
 Paradigm: Speech / Agents • Actions do not always speak louder than words • Interface as mediator or agent • Language paradigm • How good does it need to be? § “Tricks”, vocabulary, domains • How “human” do we want it to be? § (HAL, Bob, Paper. Clip) 71
Paradigm: Speech / Agents • Actions do not always speak louder than words • Interface as mediator or agent • Language paradigm • How good does it need to be? § “Tricks”, vocabulary, domains • How “human” do we want it to be? § (HAL, Bob, Paper. Clip) 71
 Innovator: Mark Weiser • Introduced notion of Ubiquitous Computing and Calm Technology § It’s everywhere, but recedes quietly into background • Was CTO of Xerox PARC • Died too early 72
Innovator: Mark Weiser • Introduced notion of Ubiquitous Computing and Calm Technology § It’s everywhere, but recedes quietly into background • Was CTO of Xerox PARC • Died too early 72
 Paradigm: Ubiquitous Computing • Person is no longer user of single device but occupant of computationally-rich environment • "Ubiquitous computing names the third wave in computing, just now beginning. First were mainframes, each shared by lots of people. Now we are in the personal computing era, person and machine staring uneasily at each other across the desktop. Next comes ubiquitous computing, or the age of calm technology, when technology recedes into the background of our lives. ” - Marki Weiser, circa 1988 • Can no longer neglect macro-social aspects 73
Paradigm: Ubiquitous Computing • Person is no longer user of single device but occupant of computationally-rich environment • "Ubiquitous computing names the third wave in computing, just now beginning. First were mainframes, each shared by lots of people. Now we are in the personal computing era, person and machine staring uneasily at each other across the desktop. Next comes ubiquitous computing, or the age of calm technology, when technology recedes into the background of our lives. ” - Marki Weiser, circa 1988 • Can no longer neglect macro-social aspects 73
 Computing is Everywhere, . . . • From the desk-top to the set-top to the palm-top to the flip-top to the wrist-top… Dick Tracy ®&© 1999 Tribune Media Services, Inc 74
Computing is Everywhere, . . . • From the desk-top to the set-top to the palm-top to the flip-top to the wrist-top… Dick Tracy ®&© 1999 Tribune Media Services, Inc 74
 Paradigm: VR & 3 D Interaction • Create immersion by § Realistic appearance, interaction, behavior • Draw on spatial memory, proprioception, kinesthesis, two-handed interaction 75
Paradigm: VR & 3 D Interaction • Create immersion by § Realistic appearance, interaction, behavior • Draw on spatial memory, proprioception, kinesthesis, two-handed interaction 75
 Paradigm: Mobile Computing • Devices used in a variety of contexts • Employ sensors to understand how user is working with devices • Wireless communication • PDAs, Cell Phones, GPSs, etc etc 76
Paradigm: Mobile Computing • Devices used in a variety of contexts • Employ sensors to understand how user is working with devices • Wireless communication • PDAs, Cell Phones, GPSs, etc etc 76
 What Next? • What are the next paradigm shifts? • What are the next technical innovations? • Who knows? I don’t • But, more importantly, 77
What Next? • What are the next paradigm shifts? • What are the next technical innovations? • Who knows? I don’t • But, more importantly, 77
 Who Will… • Drive future technical breakthroughs? • Lead future paradigm shifts? • It just might be YOU! 78
Who Will… • Drive future technical breakthroughs? • Lead future paradigm shifts? • It just might be YOU! 78
 The End 79
The End 79


