83053caa513df08d7c79ab6162d0b24e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME Paul Cryer Programme Manager Department of Health
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME Paul Cryer Programme Manager Department of Health
 HCAI Technology Innovation Programme Aim – To speed up the development and adoption of new and novel medical device and/or cleaning related technologies to further help combat HCAIs Outcomes – Technology that the NHS needs – Products that add more clinical value at the front-line – More value per NHS £ spent on HCAI related technologies – Swifter development and adoption rates – A broader understanding of the evidence by the NHS and industry
HCAI Technology Innovation Programme Aim – To speed up the development and adoption of new and novel medical device and/or cleaning related technologies to further help combat HCAIs Outcomes – Technology that the NHS needs – Products that add more clinical value at the front-line – More value per NHS £ spent on HCAI related technologies – Swifter development and adoption rates – A broader understanding of the evidence by the NHS and industry
 www. clean-safe-care. nhs. uk - (technologies tab)
www. clean-safe-care. nhs. uk - (technologies tab)
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATIONPROGRAMME KEY STRANDS – The Rapid Review Panel ++ – NHS Smart Ideas Programmes – Design Bugs Out with the Design Council – Smart Solutions from SMEs – Product Surgeries for Innovators – The Science of Cleaning – Local Technology Reviews – Showcase Hospitals – Knowledge Networks – International HACI Technology Summit and Awards Programme – The Innovation Village
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATIONPROGRAMME KEY STRANDS – The Rapid Review Panel ++ – NHS Smart Ideas Programmes – Design Bugs Out with the Design Council – Smart Solutions from SMEs – Product Surgeries for Innovators – The Science of Cleaning – Local Technology Reviews – Showcase Hospitals – Knowledge Networks – International HACI Technology Summit and Awards Programme – The Innovation Village
 Main Causes of Healthcare Associated Infections in England • • • Gastrointestinal – 22% Urinary tract infection – 20% Lower respiratory tract infection - 20% Surgical site infection – 14% Skin and soft tissue infections – 10% Blood stream infections (bacteraemia) – 7%
Main Causes of Healthcare Associated Infections in England • • • Gastrointestinal – 22% Urinary tract infection – 20% Lower respiratory tract infection - 20% Surgical site infection – 14% Skin and soft tissue infections – 10% Blood stream infections (bacteraemia) – 7%
 Often the case for development and/or adoption is based on the economic case for infection avoidance 2. 39 The best estimate of treating healthcare associated infections therefore remains at least £ 1 billion, as quoted in our initial report in 2000 and our follow up in 2004. The cost of treating a healthcare associated infection varies, but ……. estimates that each avoidable healthcare associated infection costs the NHS £ 4, 300. The cost of treating a bloodstream infection such as MRSA is likely to be higher as length of stay is much longer.
Often the case for development and/or adoption is based on the economic case for infection avoidance 2. 39 The best estimate of treating healthcare associated infections therefore remains at least £ 1 billion, as quoted in our initial report in 2000 and our follow up in 2004. The cost of treating a healthcare associated infection varies, but ……. estimates that each avoidable healthcare associated infection costs the NHS £ 4, 300. The cost of treating a bloodstream infection such as MRSA is likely to be higher as length of stay is much longer.
 What works …… ? hand hygiene aseptic techniques prudent antibiotic prescribing.
What works …… ? hand hygiene aseptic techniques prudent antibiotic prescribing.
 How do we know what else works …….
How do we know what else works …….
 THE RAPID REVIEW PANEL We know if the basic science works because the Rapid Review Panel tells us … “provide a prompt assessment of new and novel equipment, materials and other products that may be of value to the NHS in improving hospital infection control and reducing hospital acquired infection”
THE RAPID REVIEW PANEL We know if the basic science works because the Rapid Review Panel tells us … “provide a prompt assessment of new and novel equipment, materials and other products that may be of value to the NHS in improving hospital infection control and reducing hospital acquired infection”
 However knowing that a technology works is not enough …….
However knowing that a technology works is not enough …….
 …… we also need to know Does it work By how much does it work What’s the overall in-use value and what barriers can we take away to improve adoption
…… we also need to know Does it work By how much does it work What’s the overall in-use value and what barriers can we take away to improve adoption
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME SHOWCASE HOSPITALS 1. The Royal Wolverhampton Hospitals NHS Trust 2. Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust 3. Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust 4. Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust 5. County Durham and Darlington NHS Foundation Trust 6. The Lewisham Hospital NHS Trust 7. Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust 8. Mid Essex Hospital Services NHS Trust
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME SHOWCASE HOSPITALS 1. The Royal Wolverhampton Hospitals NHS Trust 2. Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust 3. Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust 4. Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust 5. County Durham and Darlington NHS Foundation Trust 6. The Lewisham Hospital NHS Trust 7. Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust 8. Mid Essex Hospital Services NHS Trust
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME SHOWCASE HOSPITALS TECHNOLGY EVALUATIONS 2008/9 (RRP 1) 1. Bardex IC – silver alloy coated hydrogel catheters 2. Chlora. Prep – Enturia Insight Health Ltd 3. Bioquell Hydrogen Peroxide Vapour System 4. Convatec Flexiseal (faecal management system) 5. Hollister Zassi (bowel management system) 6. 3 M Clean. Trace ATP Testing 7. Integu. Seal (microbial sealant) Kimberly-Clark (2009/10)
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME SHOWCASE HOSPITALS TECHNOLGY EVALUATIONS 2008/9 (RRP 1) 1. Bardex IC – silver alloy coated hydrogel catheters 2. Chlora. Prep – Enturia Insight Health Ltd 3. Bioquell Hydrogen Peroxide Vapour System 4. Convatec Flexiseal (faecal management system) 5. Hollister Zassi (bowel management system) 6. 3 M Clean. Trace ATP Testing 7. Integu. Seal (microbial sealant) Kimberly-Clark (2009/10)
 www. clean-safe-care. nhs. uk - (technologies tab)
www. clean-safe-care. nhs. uk - (technologies tab)
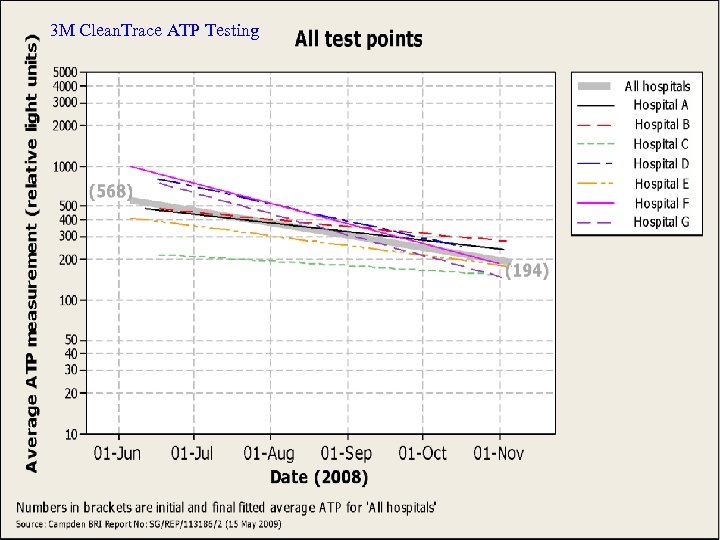 3 M Clean. Trace ATP Testing
3 M Clean. Trace ATP Testing
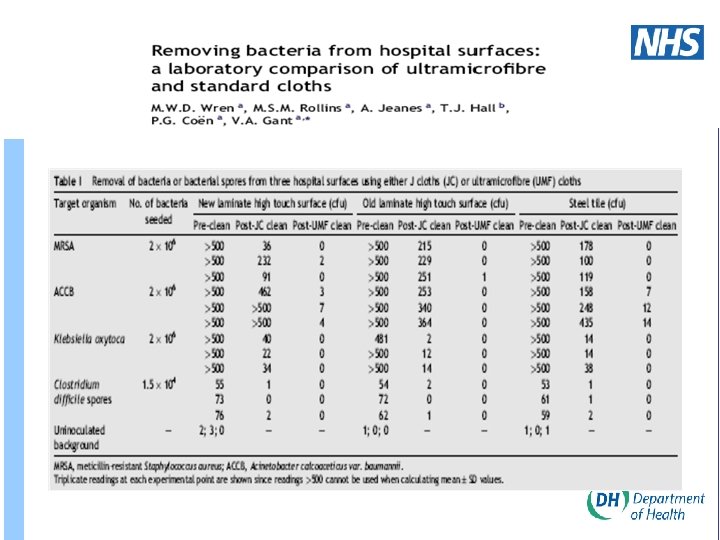
 More recently …. . and unpublished as yet • Three surfaces tested (ceramic, laminate and stainless steel) • Three organisms used (C. diff, E. coli and MRSA) • In three parts with the top 10 micro fibre cloths used by the NHS – comparison of individual cloth performance – how large a surface could be cleaned by a single cloth – prolonged washing performance
More recently …. . and unpublished as yet • Three surfaces tested (ceramic, laminate and stainless steel) • Three organisms used (C. diff, E. coli and MRSA) • In three parts with the top 10 micro fibre cloths used by the NHS – comparison of individual cloth performance – how large a surface could be cleaned by a single cloth – prolonged washing performance
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME “LOCAL TECHNOLOGY REVEIWS” 2009/10 SHOWCASE HOPSITALS – An infection control IT system (dashboard) into which other hospital information systems feed to consolidate data sets; – Rapid screening for C. Difficile to establish if patients get decolonisation treatment earlier than under current regimes; – The development of a hand hygiene educational DVD; – A citizens web site for local hospital information on infection advice and issues; – A review of infection issues associated with blood pressure cuffs – an informative study; – Service evaluation of a 2% chlorhexidine based infection resistant lines/site protector; – New hospital wide hand hygiene communications campaigns; – A new style dressings mat that provides multiple clean working surfaces. – Ultra sonics as a pre cleaning tool
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME “LOCAL TECHNOLOGY REVEIWS” 2009/10 SHOWCASE HOPSITALS – An infection control IT system (dashboard) into which other hospital information systems feed to consolidate data sets; – Rapid screening for C. Difficile to establish if patients get decolonisation treatment earlier than under current regimes; – The development of a hand hygiene educational DVD; – A citizens web site for local hospital information on infection advice and issues; – A review of infection issues associated with blood pressure cuffs – an informative study; – Service evaluation of a 2% chlorhexidine based infection resistant lines/site protector; – New hospital wide hand hygiene communications campaigns; – A new style dressings mat that provides multiple clean working surfaces. – Ultra sonics as a pre cleaning tool
 The environment as a key vector for infection…. . the role of cleaning
The environment as a key vector for infection…. . the role of cleaning

 Risks to patients from equipment and environment • High Risk - anything that enters a normally sterile body area (Sterilised) • Medium - anything in contact with intact mucous membrane (Sterilised, heat disinfected, chemical disinfected only if thermolabile) • Low - anything in contact with intact skin (Sterilised, heat or chemical disinfected, cleaned (socially) • Minimal - items not normally in contact with a patient (Cleaned; disinfected in exceptional circumstances) Peter Hoffman Consultant Clinical Scientist Laboratory of Healthcare-associated Infection Health Protection Agency
Risks to patients from equipment and environment • High Risk - anything that enters a normally sterile body area (Sterilised) • Medium - anything in contact with intact mucous membrane (Sterilised, heat disinfected, chemical disinfected only if thermolabile) • Low - anything in contact with intact skin (Sterilised, heat or chemical disinfected, cleaned (socially) • Minimal - items not normally in contact with a patient (Cleaned; disinfected in exceptional circumstances) Peter Hoffman Consultant Clinical Scientist Laboratory of Healthcare-associated Infection Health Protection Agency
 • The ability to kill a particular target microbe is a starting point for consideration but other factors need to be taken into account. Examples: – Inactivation by organic matter – Inability to penetrate lumps, clots, dried organic matter – Inadequate coverage (improper immersion, air bubble, poor coverage etc. ) – Contact time, including time to drying Peter Hoffman Consultant Clinical Scientist Laboratory of Healthcare-associated Infection Health Protection Agency
• The ability to kill a particular target microbe is a starting point for consideration but other factors need to be taken into account. Examples: – Inactivation by organic matter – Inability to penetrate lumps, clots, dried organic matter – Inadequate coverage (improper immersion, air bubble, poor coverage etc. ) – Contact time, including time to drying Peter Hoffman Consultant Clinical Scientist Laboratory of Healthcare-associated Infection Health Protection Agency
 Key Issues – – – How are colonies sustained and hosted? How do pathogens move from one host or location to another? What turns colonisation into infection and who is most vulnerable? How can pathogens be destroyed or deactivated? Can the movement of pathogens be inhibited or prevented? Nigel Tomlinson. Principal Scientific Advisor DH Estates and Facilities
Key Issues – – – How are colonies sustained and hosted? How do pathogens move from one host or location to another? What turns colonisation into infection and who is most vulnerable? How can pathogens be destroyed or deactivated? Can the movement of pathogens be inhibited or prevented? Nigel Tomlinson. Principal Scientific Advisor DH Estates and Facilities
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE …. for better targeted cleaning – Testing disinfectant products used in the NHS for efficacy against C. Difficile spores – Testing micro fibre – which work and how well? – Identifying the higher risk areas around the ward in terms of bacterial contamination and which surfaces attract which types of bacteria most. – How and which bacteria move around the ward area the most and what are the principle routes for transmission. – Knowing more about why people do and do not wash their hands before/after patient contact
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE …. for better targeted cleaning – Testing disinfectant products used in the NHS for efficacy against C. Difficile spores – Testing micro fibre – which work and how well? – Identifying the higher risk areas around the ward in terms of bacterial contamination and which surfaces attract which types of bacteria most. – How and which bacteria move around the ward area the most and what are the principle routes for transmission. – Knowing more about why people do and do not wash their hands before/after patient contact
 Ultra Sonics
Ultra Sonics
 Hand Hygiene
Hand Hygiene
 Our specially formulated CHGbased handwashing solutions for use in your Resurgent equipment. Contains skin conditioning agents.
Our specially formulated CHGbased handwashing solutions for use in your Resurgent equipment. Contains skin conditioning agents.

 Design Bugs Out…. . what’s it all about? “If things are designed to be cleaned more easily and made from materials that are more easily cleaned then they are likely to get cleaned better and be cleaner more often”
Design Bugs Out…. . what’s it all about? “If things are designed to be cleaned more easily and made from materials that are more easily cleaned then they are likely to get cleaned better and be cleaner more often”
 National launch of prototypes April 2009
National launch of prototypes April 2009
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME SMART SOLUTIONS
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME SMART SOLUTIONS
 Forward Look
Forward Look
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME …. new ways of helping fight infection – New style hand cleansing systems – Affordable point of care rapid screening for MRSA in <30 minutes (and C. difficile) – Non toxic sporicidal cleansing agent – “life beyond chlorine” – Pathogen detection in the healthcare environment – alarms (visual, colour, noise etc) when bio load reaches a predefined limit e. g. – Disinfection of the entire patient bed area in one process giving the public confidence of “near infection free beds”. – More automated cleaning – especially for side rooms
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME …. new ways of helping fight infection – New style hand cleansing systems – Affordable point of care rapid screening for MRSA in <30 minutes (and C. difficile) – Non toxic sporicidal cleansing agent – “life beyond chlorine” – Pathogen detection in the healthcare environment – alarms (visual, colour, noise etc) when bio load reaches a predefined limit e. g. – Disinfection of the entire patient bed area in one process giving the public confidence of “near infection free beds”. – More automated cleaning – especially for side rooms
 HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME NHS “SMART IDEAS” PROGRAMME The way that C. difficile and MRSA bacteria spread are different – therefore as a general principle for C. Difficile we want to keep the bacteria in a known space and with MRSA we want to minimise person-person contact …. in the making! – Two styles of temporary isolation facility for patients with C. Difficile and MRSA – Portable hand wash facility – New style infection reducing toilet/commode – Air door
HCAI TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION PROGRAMME NHS “SMART IDEAS” PROGRAMME The way that C. difficile and MRSA bacteria spread are different – therefore as a general principle for C. Difficile we want to keep the bacteria in a known space and with MRSA we want to minimise person-person contact …. in the making! – Two styles of temporary isolation facility for patients with C. Difficile and MRSA – Portable hand wash facility – New style infection reducing toilet/commode – Air door


