6208e28a7d1558de0114cd19cf462316.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 HAZARD COMMUNICATIONS OSHA 29 CFR 1910. 1200
HAZARD COMMUNICATIONS OSHA 29 CFR 1910. 1200
 • HISTORY u Late 1970’s-- “Right to Know” u Early 1980’s--City Ordinances/State Laws u Late 1980’s--Federal Law
• HISTORY u Late 1970’s-- “Right to Know” u Early 1980’s--City Ordinances/State Laws u Late 1980’s--Federal Law
 Goals of Standard u Requires development of information on hazardous materials u Requires a written program addressing employee exposures to hazardous materials
Goals of Standard u Requires development of information on hazardous materials u Requires a written program addressing employee exposures to hazardous materials
 Key Points: u Communication u Hazardous Materials vs. Hazardous Chemicals u Performance Standard
Key Points: u Communication u Hazardous Materials vs. Hazardous Chemicals u Performance Standard
 Purpose u OSHA CFR 29 1910. 1200 (a)(1)
Purpose u OSHA CFR 29 1910. 1200 (a)(1)
 Scope u OSHA CFR 29 1910. 1200 (b)(2)
Scope u OSHA CFR 29 1910. 1200 (b)(2)
 Costs and Benefits u Costs: – Requires time and effort to start – Must be maintained u Benefits – Safer work practices – Hazard reduction
Costs and Benefits u Costs: – Requires time and effort to start – Must be maintained u Benefits – Safer work practices – Hazard reduction
 How Important is HCS u Latest information on OSHA citations indicates Haz Com-- MOST commonly cited standard.
How Important is HCS u Latest information on OSHA citations indicates Haz Com-- MOST commonly cited standard.
 Requirements of the Standard MSDS Labeling Written Program Inventory Training
Requirements of the Standard MSDS Labeling Written Program Inventory Training
 HOW TO CONDUCT A WORKPLACE INVENTORY u Identify Materials By Department. u Note Operations Performed Dept. By Dept. u Look at Labeling. u Identify Material by Processes. u Look at materials use by other Contractors. u Look at materials on site and in storage. u Look in all areas.
HOW TO CONDUCT A WORKPLACE INVENTORY u Identify Materials By Department. u Note Operations Performed Dept. By Dept. u Look at Labeling. u Identify Material by Processes. u Look at materials use by other Contractors. u Look at materials on site and in storage. u Look in all areas.
 HAZARDOUS MATERIAL INVENTORY
HAZARDOUS MATERIAL INVENTORY
 Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) u Purpose u What Information they provide u Readily accessible/complete/retain u Someone responsible
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) u Purpose u What Information they provide u Readily accessible/complete/retain u Someone responsible
 Labeling u Purpose u What information is required u Accessible/Legible/in English u Types; Mfg. ’s, HMIS, NFPA u Someone responsible Zip Cleaner
Labeling u Purpose u What information is required u Accessible/Legible/in English u Types; Mfg. ’s, HMIS, NFPA u Someone responsible Zip Cleaner
 Manufacturers Label Mfg. ’s Name/Address n Product Name n Physical Warnings n Health Hazard Warnings Including Target Organs n Zip Cleaner XYZ Company PO Box 1 Anytown, OH Flammable, Avoid Prolong Breathing
Manufacturers Label Mfg. ’s Name/Address n Product Name n Physical Warnings n Health Hazard Warnings Including Target Organs n Zip Cleaner XYZ Company PO Box 1 Anytown, OH Flammable, Avoid Prolong Breathing
 In House Label Product Name n Physical Hazards n Health Hazard Warnings Including Target Organs n Zip Cleaner Flammable, Avoid prolonged breathing.
In House Label Product Name n Physical Hazards n Health Hazard Warnings Including Target Organs n Zip Cleaner Flammable, Avoid prolonged breathing.
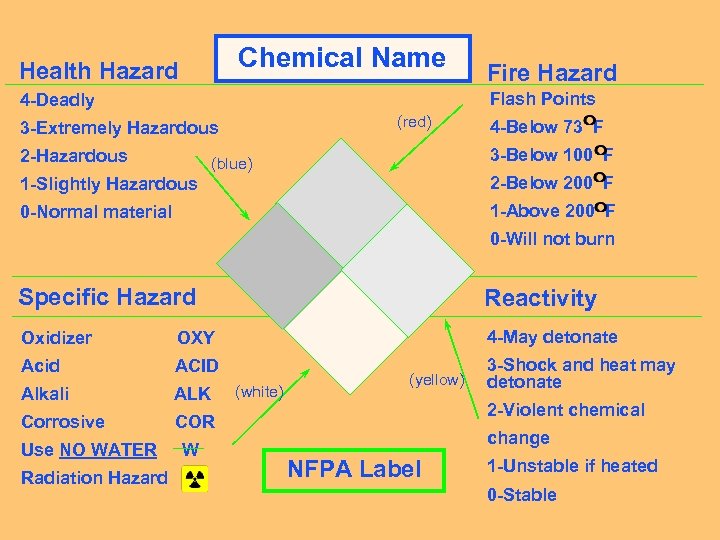 Chemical Name Health Hazard Fire Hazard Flash Points 4 -Deadly (red) 3 -Extremely Hazardous 2 -Hazardous 4 -Below 73 F 3 -Below 100 F (blue) 1 -Slightly Hazardous 2 -Below 200 F 0 -Normal material 1 -Above 200 F 0 -Will not burn Specific Hazard Reactivity Oxidizer OXY 4 -May detonate Acid ACID 3 -Shock and heat may detonate Alkali ALK Corrosive (white) (yellow) COR Use NO WATER Radiation Hazard W 2 -Violent chemical change NFPA Label 1 -Unstable if heated 0 -Stable
Chemical Name Health Hazard Fire Hazard Flash Points 4 -Deadly (red) 3 -Extremely Hazardous 2 -Hazardous 4 -Below 73 F 3 -Below 100 F (blue) 1 -Slightly Hazardous 2 -Below 200 F 0 -Normal material 1 -Above 200 F 0 -Will not burn Specific Hazard Reactivity Oxidizer OXY 4 -May detonate Acid ACID 3 -Shock and heat may detonate Alkali ALK Corrosive (white) (yellow) COR Use NO WATER Radiation Hazard W 2 -Violent chemical change NFPA Label 1 -Unstable if heated 0 -Stable
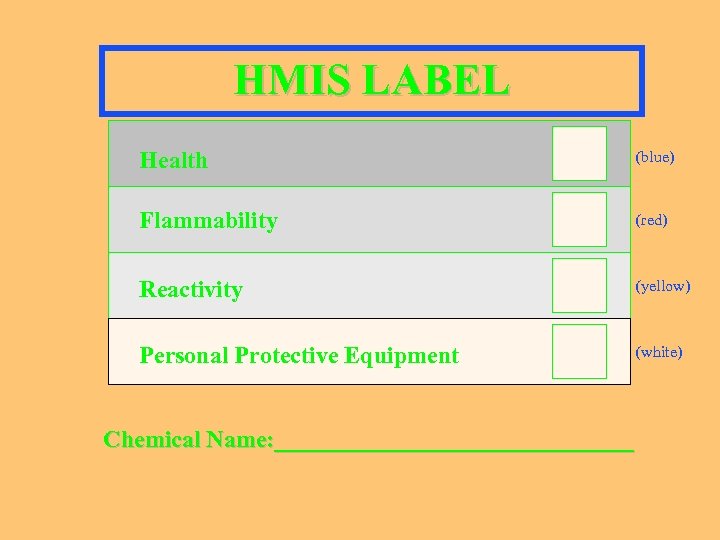 HMIS LABEL Health (blue) Flammability (red) Reactivity (yellow) Personal Protective Equipment (white) Chemical Name: _______________
HMIS LABEL Health (blue) Flammability (red) Reactivity (yellow) Personal Protective Equipment (white) Chemical Name: _______________
 Employee Training u General Training u Specific Training
Employee Training u General Training u Specific Training
 General Training u Hazard Communication Standard u Employer’s Written Program u Location/Availability Of Written Program & MSDS u How to read labels & MSDS’s
General Training u Hazard Communication Standard u Employer’s Written Program u Location/Availability Of Written Program & MSDS u How to read labels & MSDS’s
 Specific Training u Characteristics - How to detect u Health & Safety Hazards u Work practices or SOPs u Emergency action plans u Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) u Non-routine tasks u Industrial Hygiene monitoring results
Specific Training u Characteristics - How to detect u Health & Safety Hazards u Work practices or SOPs u Emergency action plans u Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) u Non-routine tasks u Industrial Hygiene monitoring results
 Written Program u Must be developed, implemented & maintained u A blueprint for how the requirements will be met m z. Com u Readily accessible Ha am Progr
Written Program u Must be developed, implemented & maintained u A blueprint for how the requirements will be met m z. Com u Readily accessible Ha am Progr
 Written Program u Develop, implement, and maintain at each workplace, a written program that describes: – Labels and other forms of warning – MSDSs – Employee Training and Information – and includes:
Written Program u Develop, implement, and maintain at each workplace, a written program that describes: – Labels and other forms of warning – MSDSs – Employee Training and Information – and includes:
 Miscellaneous u. Chemical Inventory u Non-Routine Tasks u Piping Systems u Contractors/ Multi-Employer Worksites
Miscellaneous u. Chemical Inventory u Non-Routine Tasks u Piping Systems u Contractors/ Multi-Employer Worksites
 Multi-Employer Workplaces u Use hazardous materials in such a way other employers are exposed – Methods to provide access to MSDS and Written Program – Methods to inform of precautionary measures and labeling system u Intent is met when information on haz. materials at the worksite is available to all
Multi-Employer Workplaces u Use hazardous materials in such a way other employers are exposed – Methods to provide access to MSDS and Written Program – Methods to inform of precautionary measures and labeling system u Intent is met when information on haz. materials at the worksite is available to all
 Other Exemptions u By Size? No u By Type of Substance? Does not apply to substances covered by other laws: i. e. -tobacco, wood/wood products, articles u By Extent of Use? Does not apply if substance is used in manner, duration, & frequency as a consumer product
Other Exemptions u By Size? No u By Type of Substance? Does not apply to substances covered by other laws: i. e. -tobacco, wood/wood products, articles u By Extent of Use? Does not apply if substance is used in manner, duration, & frequency as a consumer product
 Summary u What is Hazcom? u Why was the Hazcom Standard implemented? u What are the 4 major elements of our written Hazcom program? u Why is a workplace inventory important? u What is the purpose of an MSDS?
Summary u What is Hazcom? u Why was the Hazcom Standard implemented? u What are the 4 major elements of our written Hazcom program? u Why is a workplace inventory important? u What is the purpose of an MSDS?
 Summary (continued) u Where do we keep MSDSs & Written Program? u Who is responsible for maintaining MSDS in your area? u What labeling system do we use? u Why do we need MSDS and labeling? u Why do we train on Hazcom? u What’s the difference between General and Specific training?
Summary (continued) u Where do we keep MSDSs & Written Program? u Who is responsible for maintaining MSDS in your area? u What labeling system do we use? u Why do we need MSDS and labeling? u Why do we train on Hazcom? u What’s the difference between General and Specific training?


