4a4a5f2db406dcfd0144b3f637e864c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Harvesting SSL Certificate Data to Identify Web-Fraud Reporter : 鄭志欣 Advisor : Hsing-Kuo Pao 2010/10/04 1

Conference Mishari Al Mishari, Emiliano De Cristofaro, Karim El Defrawy, and Gene Tsudik. "Harvesting SSL Certificate Data to Identify Web-Fraud. " , Submitted to ICDCS’ 10, http: //arxiv. org/abs/0909. 3688 2

Outline Introduction X. 509 certificates Measurements and Analysis of SSL Certificates Certificate-Based Classifier Conclusion 3

Introduction Web-fraud is one of the most unpleasant features of today’s Internet. Phishing , Typosquatting Can we use the information in the SSL certificates to identify web-fraud activities such as phishing and typosquatting , without compromising user privacy? This paper presents a novel technique to detect webfraud domains that utilize HTTPS. 4
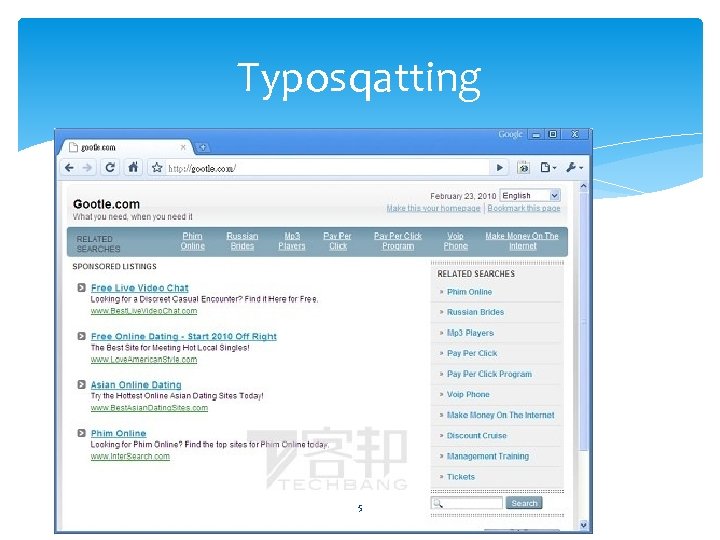
Typosqatting 5

Contributions The classifier achieves a detection accuracy over 80% and, in some cases, as high as 95%. Our classifier is orthogonal to prior mitigation techniques and can be integrated with other methods. Note that the classifier only relies on data in the SSL certificate and not any other private user information. 6
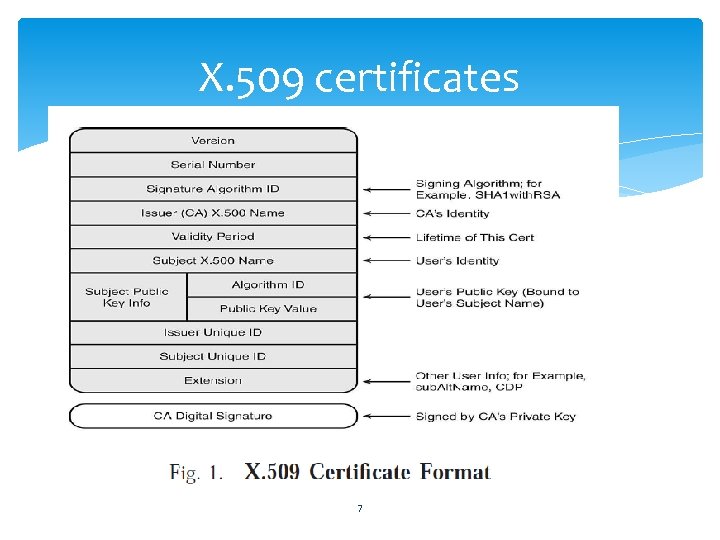
X. 509 certificates 7
Measurements and Analysis of SSL Certificates A. HTTPS Usage and Certificate Harvest Legitimate Phishing and Typosquatting B. Certificate Analysis of Certificate Boolean Features Analysis of Certificate Non-Boolean Features 8
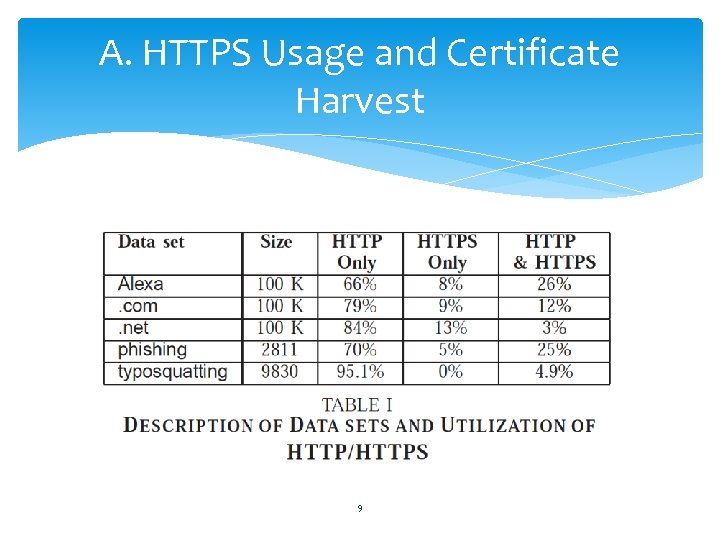
A. HTTPS Usage and Certificate Harvest 9

A. HTTPS Usage and Certificate Harvest Legitimate and Popular Domain Data Sets. Alexa: 100, 000 most popular domains according to Alexa. . com: 100, 000 random samples of. com domain zone file, collected from Veri. Sign. . net: 100, 000 random samples of. net domain zone file, collected from Veri. Sign. We find that 34% of Alexa domains use HTTPS; 21% in . com and 16% in. net. (Commercial) 10

A. HTTPS Usage and Certificate Harvest Phishing Data Set We collected 2, 811 domains considered to be hosting phishing scams from the Phish. Tank web site. 30% of these phishing web sites employ HTTPS. Typosquatting Data Set we first identified the typo domains in our. com and. net data sets by using Google’s typo correction service. We discovered that 9, 830 out of 38, 617 are parked domains. 11
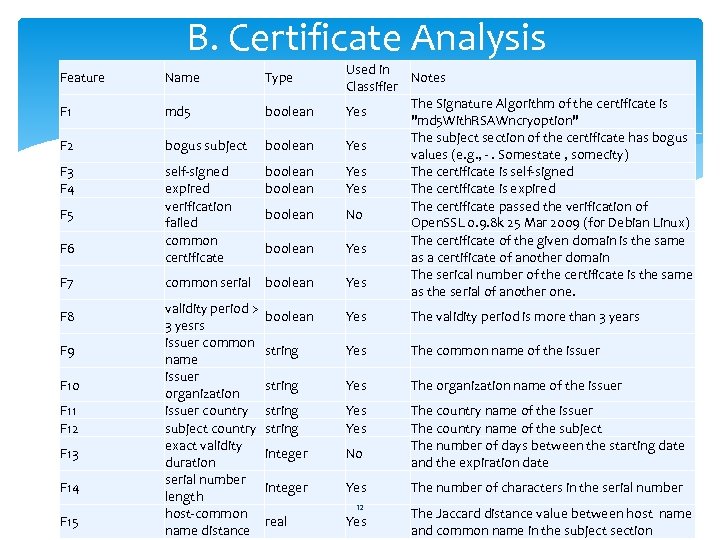
B. Certificate Analysis Feature Name Type F 1 md 5 boolean F 2 bogus subject boolean F 3 F 4 self-signed expired verification failed common certificate boolean F 5 F 6 F 7 F 8 F 9 F 10 F 11 F 12 F 13 F 14 F 15 boolean common serial boolean validity period > boolean 3 yesrs issuer common string name issuer string organization issuer country string subject country string exact validity integer duration serial number integer length host-common real name distance Used in Notes Classifier The Signature Algorithm of the certificate is Yes "md 5 With. RSAWncryoption" The subject section of the certificate has bogus Yes values (e. g. , -. Somestate , somecity) Yes The certificate is self-signed Yes The certificate is expired The certificate passed the verification of No Open. SSL 0. 9. 8 k 25 Mar 2009 (for Debian Linux) The certificate of the given domain is the same Yes as a certificate of another domain The serical number of the certificate is the same Yes as the serial of another one. Yes The validity period is more than 3 years Yes The common name of the issuer Yes The organization name of the issuer Yes The country name of the issuer The country name of the subject The number of days between the starting date and the expiration date No Yes 12 Yes The number of characters in the serial number The Jaccard distance value between host name and common name in the subject section
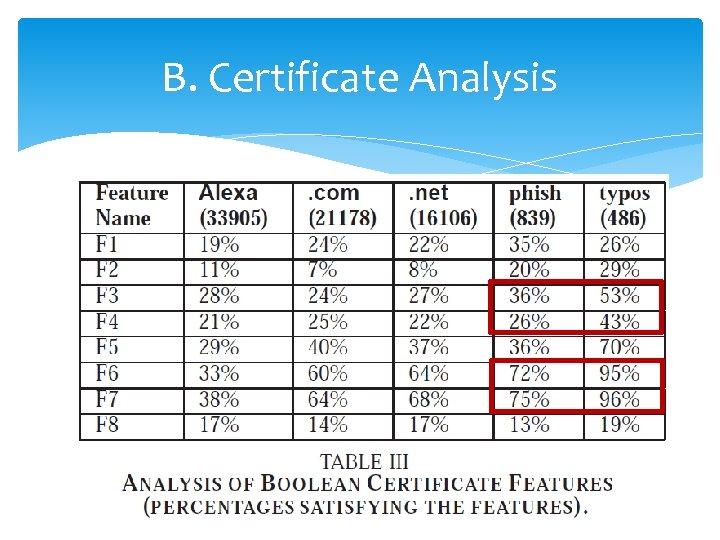
B. Certificate Analysis of Certificate Boolean Features 13
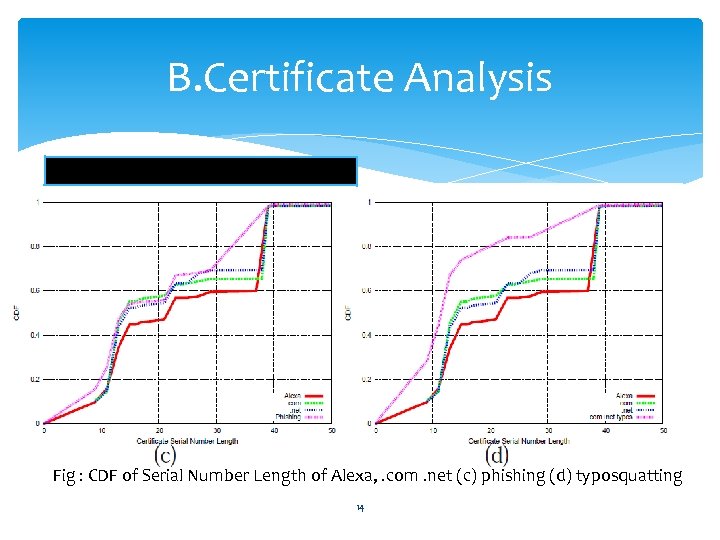
B. Certificate Analysis F 14 : Serial Number Length Fig : CDF of Serial Number Length of Alexa, . com. net (c) phishing (d) typosquatting 14
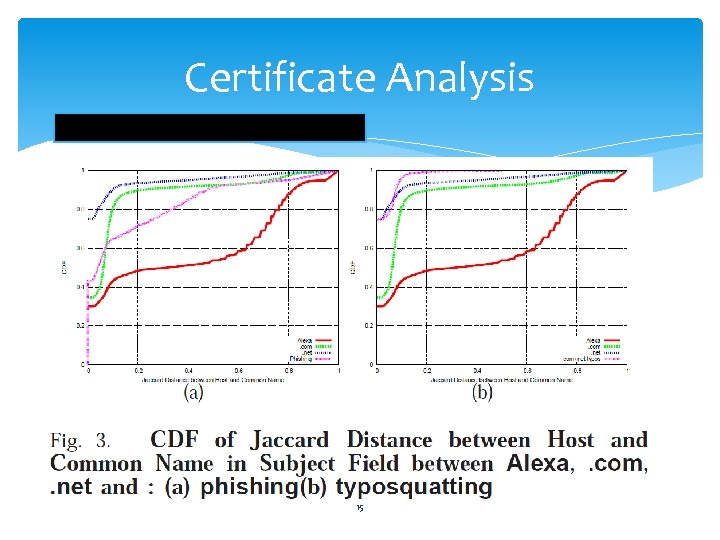
Certificate Analysis F 15 : Jaccard Distance 15
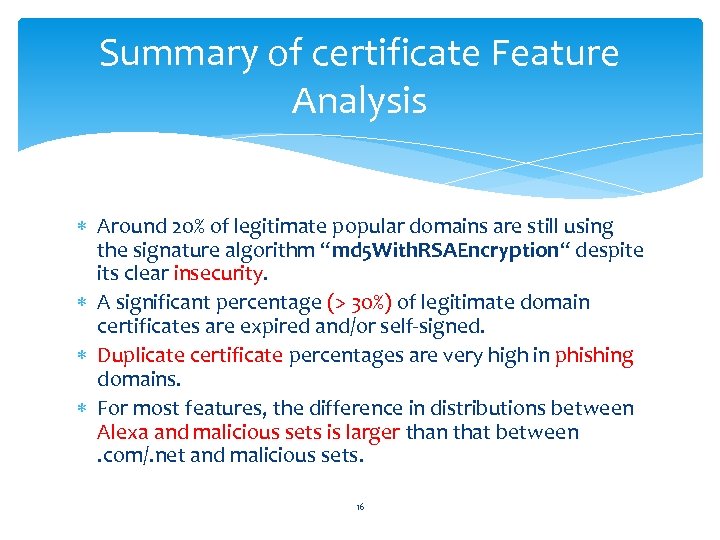
Summary of certificate Feature Analysis Around 20% of legitimate popular domains are still using the signature algorithm “md 5 With. RSAEncryption“ despite its clear insecurity. A significant percentage (> 30%) of legitimate domain certificates are expired and/or self-signed. Duplicate certificate percentages are very high in phishing domains. For most features, the difference in distributions between Alexa and malicious sets is larger than that between . com/. net and malicious sets. 16

Certificate-Based Classifier A. Phishing Classifier B. Typosquatting Classifier 17
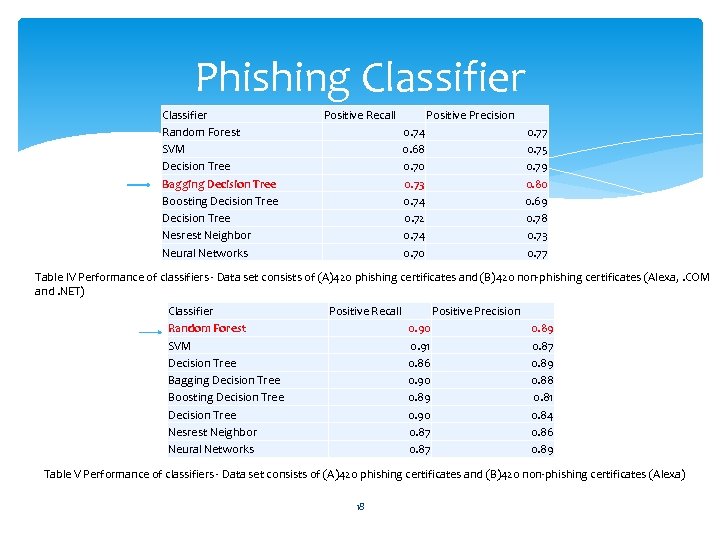
Phishing Classifier Random Forest SVM Decision Tree Bagging Decision Tree Boosting Decision Tree Nesrest Neighbor Neural Networks Positive Recall Positive Precision 0. 74 0. 68 0. 70 0. 73 0. 74 0. 72 0. 74 0. 70 0. 77 0. 75 0. 79 0. 80 0. 69 0. 78 0. 73 0. 77 Table IV Performance of classifiers - Data set consists of (A)420 phishing certificates and (B)420 non-phishing certificates (Alexa, . COM and. NET) Classifier Random Forest SVM Decision Tree Bagging Decision Tree Boosting Decision Tree Nesrest Neighbor Neural Networks Positive Recall Positive Precision 0. 90 0. 91 0. 86 0. 90 0. 89 0. 90 0. 87 0. 89 0. 88 0. 81 0. 84 0. 86 0. 89 Table V Performance of classifiers - Data set consists of (A)420 phishing certificates and (B)420 non-phishing certificates (Alexa) 18
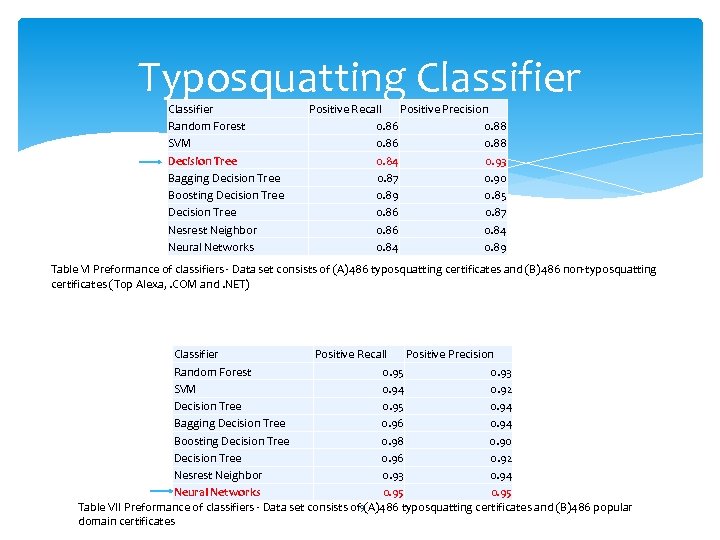
Typosquatting Classifier Random Forest SVM Decision Tree Bagging Decision Tree Boosting Decision Tree Nesrest Neighbor Neural Networks Positive Recall Positive Precision 0. 86 0. 88 0. 84 0. 93 0. 87 0. 90 0. 89 0. 85 0. 86 0. 87 0. 86 0. 84 0. 89 Table VI Preformance of classifiers - Data set consists of (A)486 typosquatting certificates and (B)486 non-typosquatting certificates (Top Alexa, . COM and. NET) Classifier Positive Recall Positive Precision Random Forest 0. 95 0. 93 SVM 0. 94 0. 92 Decision Tree 0. 95 0. 94 Bagging Decision Tree 0. 96 0. 94 Boosting Decision Tree 0. 98 0. 90 Decision Tree 0. 96 0. 92 Nesrest Neighbor 0. 93 0. 94 Neural Networks 0. 95 19 Table VII Preformance of classifiers - Data set consists of (A)486 typosquatting certificates and (B)486 popular domain certificates

Conclusion We design and build a machine-learning-based classifier that identifies fraudulent domains using HTTPS based solely on their SSL certificates, thus also preserving user privacy. We believe that our results may serve as a motivating factor to increase the use of HTTPS on the Web. Use of HTTPS can help identifying web-fraud domains. 20
4a4a5f2db406dcfd0144b3f637e864c2.ppt