44600d18407170cbef9c2411c1ef78ff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
Harmonisation Handbook Close Handbook Introduction to Harmonisation Benefits of Harmonisation Harmonised Principles NSHG Members Harmonisation Process Harmonisation Governance Roles and Responsibilities NSHG Harmonisation Case Studies Meetings and Workshops NSHG Terms of Reference Harmonisation Resources Harmonisation Team Details

What is Harmonisation? • it is a UK cross governmental programme • it aims to harmonise statistical inputs, processes and outputs across the Government Statistical Service • it aims to facilitate clearer and more robust comparison between data sources and to improve data quality Next Page Main Index

What is Harmonisation? Harmonisation is about making questions, definitions, variables and outputs across all official statistics comparable. Back Next Page Main Index
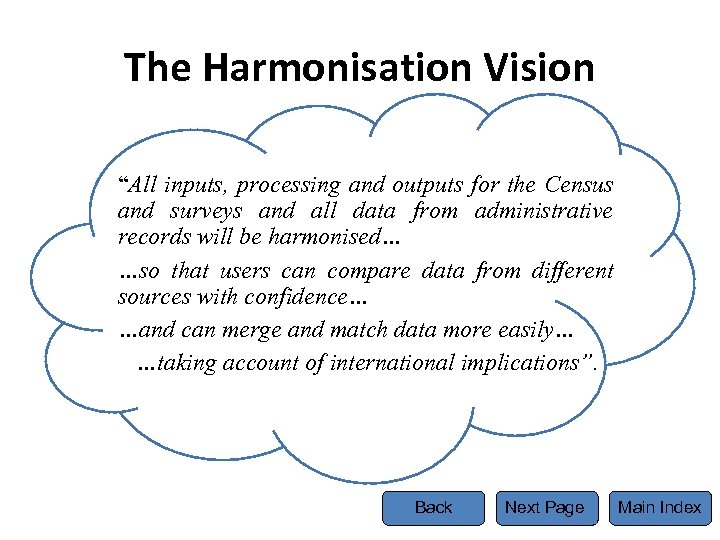
The Harmonisation Vision “All inputs, processing and outputs for the Census and surveys and all data from administrative records will be harmonised… …so that users can compare data from different sources with confidence… …and can merge and match data more easily… …taking account of international implications”. Back Next Page Main Index

Why Harmonise? The UK has a wide range of government surveys that provide sources of social and economic information. The Census is the largest and best known, but there are many others covering topics such as economic activity, income, expenditure, food, health, education, housing and transport. These surveys were designed at different times, to meet different needs, and have been commissioned by a range of departments. Consequently, the surveys were developed mostly in isolation from each other. This resulted in a lack of cohesion. Differences arose in concepts, definitions, design, fieldwork and processing practices, or “inputs”, and also in the way results are released, or “outputs”. Therefore data are often inconsistent and therefore not comparable. Much work has already been done with the harmonisation of Government social surveys and work is now taking place to look at harmonising business statistics and administrative data. Several initiatives have been identified across the GSS that harmonisation can facilitate as part of the delivery of these programmes. Back Next Page Main Index

Harmonised not Standardised Back Next Page Main Index
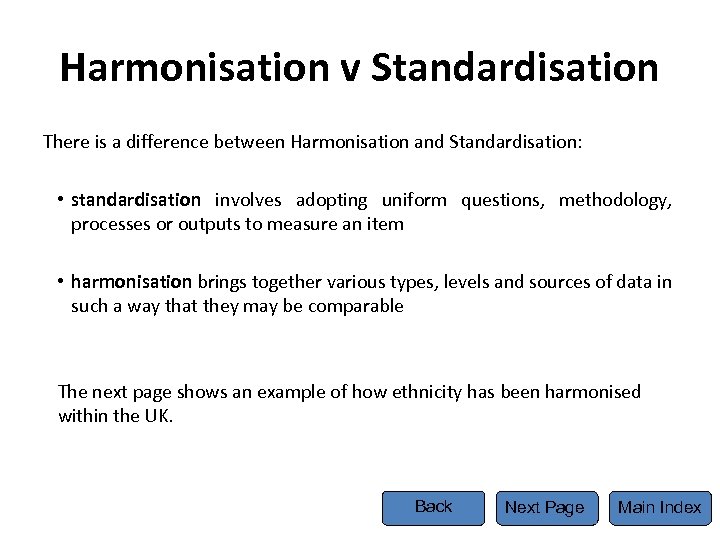
Harmonisation v Standardisation There is a difference between Harmonisation and Standardisation: • standardisation involves adopting uniform questions, methodology, processes or outputs to measure an item • harmonisation brings together various types, levels and sources of data in such a way that they may be comparable The next page shows an example of how ethnicity has been harmonised within the UK. Back Next Page Main Index

Ethnicity Response Categories on UK Censuses What is your ethnic group? England White 1. English/Welsh/Scottish/Northern Irish/British 2. Irish 3. Gypsy or Irish Traveller 4. Any other White background, please describe Scotland White 1. Scottish 2. Other British 3. Irish 4. Gypsy/Traveller 5. Polish 6. Any other White ethnic group, please describe Welsh and English forms differ in response order, the Northern Irish form has less options and the Scottish census enables reporting of Polish ethnicity. Standardisation would mandate use of the same question and not allow subtle, but necessary differences. Harmonisation allows this by providing output categories that allow for the aggregation of responses at UK level. The harmonised ethnicity principle recognises that differences are required at the national level, but enables comparable reporting at UK level: Northern Ireland White 1. White 2. Irish Traveller Wales White 1. Welsh/English/Scottish/Northern Irish/British 2. Irish 3. Gypsy or Irish Traveller 4. Any other White background, please describe UK Output White Irish Traveller Back Main Index

Benefits of Harmonisation The use of harmonised principles can provide a range of benefits including: • cost savings and efficiencies by avoiding duplication and providing more outputs from less investment • comparability and coherence within time series and between separate datasets • help to support a wider reuse of survey structural information • help reduce respondent burden • increase options for data sharing and linkage of official statistics datasets • Improves data quality Next Page Main Index
Benefits of Harmonisation “There ha the GSS s been fantast ic progr r ess in ra recently and it isin 's publish ed UK S important tha g the profile o a coord tatistics f t inated and coh Authorit we keep this harmonisation and to eren y Bu mo acr m Increas ake more use t approach to siness Plan ch mentum going oss ed harm allenge s us to d. The onisatio of integrated reporting acro these o , e s n acros bjective s the va administrative s UK Official S velop s. “ tatistics rious da and big ta sour data s ces will help us ources. r’. ” t o braine to deliv no tion are a ‘n er f harmonisa s, ity u x ) nefits o D tistician “The be r Sta J e fo ple ill er (National Pop puty Director ennet Woolfo ity com his w e, John Pulling rd of Life E ulation iv l Source vents a act and ns. T pab pril 2015 A s (ONS) a y nt o March nd rta antit uesti al, C 2016 po im he qu ew q ssion lly t n fe rea duce test , Pro a re d ul s “I believe now e i l to p an elpf that we are ga mm ntia velo of H ining momentu of harmonisati ra te de ls m in raising th on that this will e profile a rog po to become increa look to use mo o p e singly importa re non-survey d on s th o do our g 5 nt as we ata. ” Jacqui Jones t ati r 01 r 2 nis offe eed inst o it Deputy Direct be rm or of Governm e n ga cto ent Corporatio Ha ause rk w ver a e” (ONS) Decemb ns and Classif ) O er 2015 he bec wo eli tiv S T t ications N “ s s, y (O ial to d nova a ec s e g c le sp In u rvi lo of able t and st Se hodo l en icien d Be igita Met Eff Davi r of D and Dr ecto logy Dir chno Te Back Next Page Main Index

Benefits of Harmonisation also helps to comply with the specific requirements of the: UK Statistics and Registration Service Act 2007 and the Code of Practice for Official Statistics. Link to complete versions: UK Statistics and Registration Service Act 2007 Code of Practice for Official Statistics Back Main Index

Benefits of Harmonisation also helps to comply with specific requirements of the: UK Statistics and Registration Service Act 2007, Section 13 Back Main Index
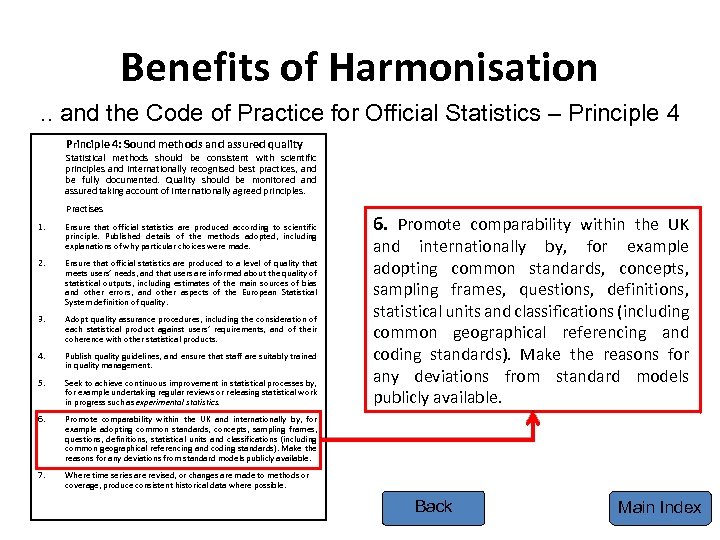
Benefits of Harmonisation. . and the Code of Practice for Official Statistics – Principle 4: Sound methods and assured quality Statistical methods should be consistent with scientific principles and internationally recognised best practices, and be fully documented. Quality should be monitored and assured taking account of internationally agreed principles. Practises 1. Ensure that official statistics are produced according to scientific principle. Published details of the methods adopted, including explanations of why particular choices were made. 2. Ensure that official statistics are produced to a level of quality that meets users’ needs, and that users are informed about the quality of statistical outputs, including estimates of the main sources of bias and other errors, and other aspects of the European Statistical System definition of quality. 3. Adopt quality assurance procedures, including the consideration of each statistical product against users’ requirements, and of their coherence with other statistical products. 4. Publish quality guidelines, and ensure that staff are suitably trained in quality management. 5. Seek to achieve continuous improvement in statistical processes by, for example undertaking regular reviews or releasing statistical work in progress such as experimental statistics. 6. Promote comparability within the UK and internationally by, for example adopting common standards, concepts, sampling frames, questions, definitions, statistical units and classifications (including common geographical referencing and coding standards). Make the reasons for any deviations from standard models publicly available. 7. 6. Promote comparability within the UK Where time series are revised, or changes are made to methods or coverage, produce consistent historical data where possible. and internationally by, for example adopting common standards, concepts, sampling frames, questions, definitions, statistical units and classifications (including common geographical referencing and coding standards). Make the reasons for any deviations from standard models publicly available. Back Main Index

Harmonised Principles The GSS Harmonised Principles are agreed documents containing sets of questions, concepts and outputs and provide a harmonised means of collecting information about a given topic. Harmonised Principles are divided into Primary and Secondary principles. Primary Harmonised Principles Harmonised concepts, questions and outputs on key topics, that should be used on all major government surveys, can be thought of as belonging to a primary harmonised principle. Primary harmonised principles include Demographic Information (age, sex, etc) and Ethnicity. Secondary Harmonised Principles Harmonised concepts, questions and outputs on specific topics, that are only used on Selected government Surveys, can be thought of as belonging to a secondary harmonised principle. Secondary harmonised principles include General Health, Benefits and Tax Credits, Consumer Durables, Income, Accommodation, Housing Costs and Benefits and Crime. Next Page Main Index

Primary Harmonised Principles Title Description Demographic information, household composition and relationships (69 Kb Pdf) Basic descriptive information about respondents, including age, sex and marital status. Also standard ways of categorising and describing households and families by their members and relationships. Ethnic group (504. 6 Kb Pdf) Standard ways of collecting information on how people describe their ethnic identity. Economic status and industry (83. 4 A number of principles used to classify respondents according to their industry, occupation and Kb Pdf) employment status. These are used to produce standard economic status and socio-economic classifications. General Health and Carers (37. 8 Kb Provides questions about general health for respondents. Also includes questions on basic caring Pdf) for other people. Long-lasting Health Conditions and Provides questions about long-term health conditions and illnesses for respondents. Also includes Illnesses: Impairments and questions on impairments and disabilities. Disability (136 Kb Pdf) Other primary harmonised principles (72. 6 Kb Pdf) Contains miscellaneous topics, including survey reference period, geography, educational attainment and tenure. Back Next Page Main Index

Secondary Harmonised Principles Title Description Benefits and tax credits (184 Kb Pdf) Benefits and tax credits received by respondents. Consumer durables (80. 1 Kb Pdf) Typical electrical or electronic goods, such as televisions, computers, telephones and washing machines. Income (52. 2 Kb Pdf) Guidance for collecting detailed income for substantive analysis, as well as guidance for collecting income as a classificatory variable. Selected job details (39. 5 Kb Pdf) More detailed than Primary Principles. Length of time since respondent last worked and the number of hours (paid and unpaid) worked. Accommodation and Household information (44. 9 Kb Pdf) Type of accommodation a household occupies, length of time they have been resident there, and availability of motor vehicles to the household. Housing costs and benefits (83. 1 Kb Pdf) Housing costs (rent and mortgages) and housing benefits. Crime and fear of crime (46. 1 Kb Pdf) Crime, fear of crime and problems in the area, as perceived by respondents. Social capital (59 Kb Pdf) This harmonised principle has been temporarily removed, pending review National Identity and Religion (59. 5 Kb Pdf) Standard questions for data collection on national identity and religion. Internet access (32. 3 Kb Pdf) Questions on internet access asked on the Opinions and Lifestyle Survey. Sexual Identity (37. 3 Kb Pdf) Provides a standard question and guidance, for both users of sexual identity statistics and those organisations collecting data on sexual identity. Other secondary harmonised principles (39. 7 Kb Pdf) Contains miscellaneous topics, including qualifications. Interim principle - Personal Well-being (72. 1 Kb Pdf) Provides standard questions and guidance, for users wishing to add personal well-being questions to surveys. Back Main Index

Harmonisation Process Introduction For data comparability and coherence it is essential for data providers to use GSS Harmonised Principles. The Harmonisation Team at the Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for maintaining the current list of GSS Harmonised Principles. Occasionally the need arises for a new principle, or the revision of an existing principle and in these instances there is an approved process to follow to ensure ratification and dissemination. The harmonisation process outlines the stages that need to be followed by the topic lead. Topic leads will need to contact the Harmonisation Team for the full document including the templates to be used at each stage of the process. To see the process model and an explanation of each stage, please go to the next page. Next Page Main Index
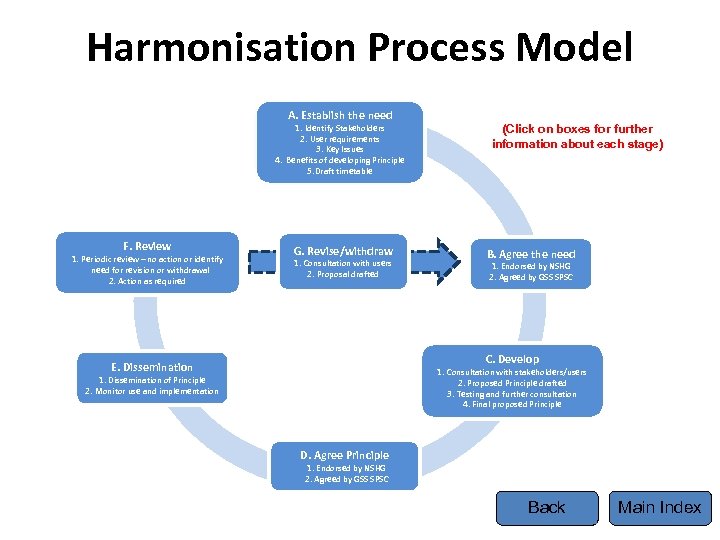
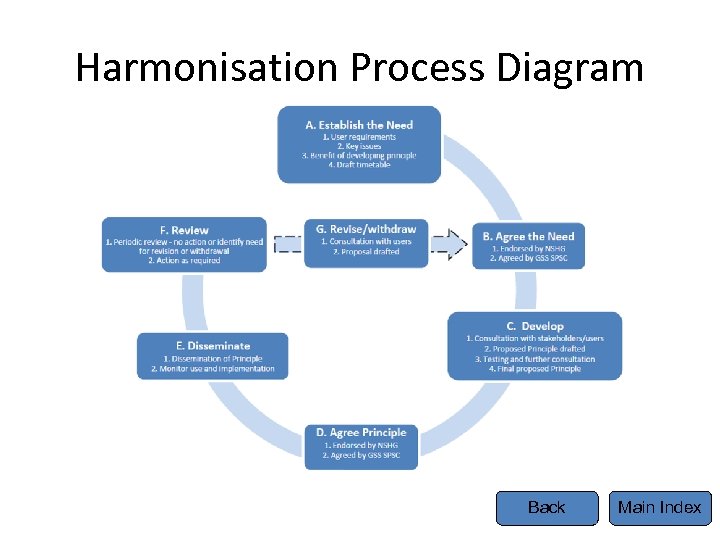
Harmonisation Process Model A. Establish the need 1. Identify Stakeholders 2. User requirements 3. Key Issues (Click on boxes for further information about each stage) 4. Benefits of developing Principle 5. Draft timetable F. Review 1. Periodic review – no action or identify need for revision or withdrawal 2. Action as required G. Revise/withdraw 1. Consultation with users 2. Proposal drafted B. Agree the need 1. Endorsed by NSHG 2. Agreed by GSS SPSC C. Develop E. Dissemination 1. Consultation with stakeholders/users 2. Proposed Principle drafted 3. Testing and further consultation 4. Final proposed Principle 1. Dissemination of Principle 2. Monitor use and implementation D. Agree Principle 1. Endorsed by NSHG 2. Agreed by GSS SPSC Back Main Index

Harmonisation Process Stage A. Establish the Need This stage requires identifying stakeholders, user requirements, any key issues, the benefits of developing the principle and a draft timetable. The Topic Lead must complete the template ‘Request for NSHG to Agree the Need for Harmonisation’ at Annex A, which requires information on: Identifying Stakeholders • identify producers, users and other interested parties who will be able to help with the development of the proposed Harmonised Principle (or revision to an existing one) • this should include the devolved administrations where applicable. User requirements • who has requested the principle and what is the need • when is the principle required • provide evidence that the principle is required Key issues • if implemented, how regularly would maintenance be required, and what is the likelihood for change • describe any potential issues relating to implementation and how these can be mitigated Benefit of developing the principle For both data providers and users: • illustrate the value added by the principle • describe the impact of not implementing the principle Draft Timetable Complete the draft timetable, including milestone dates against tasks to be undertaken. Back Main Index

Harmonisation Process Stage B. Agree the Need This stage requires the National Statistics Harmonisation Group (NSHG) and GSS Statistical Policy and Standards Committee (SPSC) to agree the need for the principle to be developed. Endorsement by NSHG • once completed, the template ‘Request for NSHG to Agree the Need for Harmonisation’ at Annex A, should be submitted to the NSHG via the secretariat • this will be presented at the next NSHG meeting or circulated for comment via correspondence depending on requirements • the NSHG will endorse, reject, or request further information about the proposal • if the proposal is rejected the reasons for this must be stated by the NSHG Approval by GSS SPSC • once endorsed by the NSHG the proposal will be submitted to the GSS SPSC for their approval, again using the template ‘Request for NSHG to Agree the Need for Harmonisation’ (Annex A) • this will be submitted at the next GSS SPSC meeting or by correspondence • the GSS SPSC will either approve the proposal to continue to develop the principle, request further information about the proposal or reject the proposal • if the proposal is rejected the reasons for this must be stated by the GSS SPSC Inform Ho. Ps • the Harmonisation Team will inform Ho. Ps when a proposal is being considered Back Main Index

Harmonisation Process Stage C. Develop This stage details the steps required when developing or revising the principle. The Topic Lead must complete the template ‘Request for NSHG Endorsement for Harmonised Principle’ at Annex B, which requires information on: Stakeholder/User Considerations • contact key stakeholders (this must include representatives from the UK nations) • assign milestone dates to the consultation plan and undertake the steps outlined • provide stakeholders with the consultation document, which includes information such as explaining why the principle/revision is required, and its benefits • provide a summary of feedback received from stakeholders, highlighting areas of concern from and how these will be addressed Proposed Principle Drafted • after considering stakeholder feedback, provide a draft proposed principle Testing and Further Consultation • any question testing undertaken detailing issues raised and what was done to mitigate these • details of any further consultation as a result of the question testing • if Data Collection Methodology (DCM) resource is required for question testing, please contact the Harmonisation Team Final Proposal Produced The Topic Lead should produce the final proposal, detailing information such as: • the development process • stakeholder/User consultation • questions and issues raised and planned resolutions • results of testing and feedback from stakeholders and UK nations for the proposed questions, definitions and outputs. • timetable for finalising the principle, including key milestone, risks, dependencies and contingencies Back Main Index

Harmonisation Process Stage D. Agree Principle At this stage endorsement, agreement and ratification of the new principle will be sought. Throughout this stage, and nce the principle documentation has been received, the Harmonisation Team will take the proposal through each approval stage, requesting further information from the Topic Lead as required. Endorsed by NSHG • the Topic Lead should submit the completed template ‘Request for NSHG Endorsement for Harmonised Principle’ at Annex B to the NSHG via the Harmonisation Team • this will be through an NSHG meeting or via correspondence depending on time constraints • if successful at NSHG the proposal will be passed to the GSS SPSC for agreement • if unsuccessful, the NSHG will provide feedback via the Harmonisation Team for comments/revisions, as required, for the topic lead to address Agreed by GSS SPSC • once endorsed by the NSHG, formal agreement will be required from the GSS SPSC for a new Harmonised Principle. • the Harmonisation Team will submit the proposed Harmonised Principle, using the completed template at Annex B, to the GSS SPSC at their next meeting or via correspondence, as directed by the GSS SPSC • the GSS SPSC will either ratify or return the principle, requesting further information to support the principle • the GSS SPSC will notify the NSHG secretariat of its decision, who, in turn, will notify the respective Topic Lead • once ratified, the Harmonisation Team will assist the Topic Lead with preparing the new or revised Harmonised Principle for publication on the GSS website Agreement of Revised Principles Stage D, should also be used when agreeing revisions to any existing Harmonised Principle. In such cases the template ‘Request for NSHG Endorsement for Revised Harmonised Principle’ at Annex C should be used. Back Main Index

Harmonisation Process Stage E. Disseminate This stage details the steps required in the dissemination and promotion of the new or revised Harmonised Principle. The Topic Lead and the Harmonisation Team must complete the template ‘Dissemination of New or Revised Harmonised Principle’ at Annex D, which addresses: Dissemination of the Principle • the Topic Lead should complete a Dissemination Plan, outlining the dissemination methods and target audience and attach it to the Template at Annex D • the Topic Lead and the Harmonisation Team will disseminate the new/revised Harmonised Principle as detailed at Annex D Monitor use and implementation • ensure that outputs which use the harmonised question(s) (as identified in Stage C) are aware of the new or revised principle and have plans for its implementation • complete the summary report of implementation and use, identifying which stakeholders use the new principle, when it was adopted, or is planned to be adopted • if problems are encountered during implementation record these and inform the Harmonisation Team Back Main Index

Harmonisation Process Stage F. Review This stage outlines how principles should be reviewed to ensure they are s till required and fit for purpose. Periodic Review Once a Harmonised Principle has been ratified, a desk review of the principle should be undertaken once a year by the Topic Lead. This may lead to a full review if required and will ensure the principle remains current and reflects user/producer needs. The review period can be more frequent if the Topic Lead deems necessary (i. e. if the subject matter is likely to evolve quickly or is subject to statutory changes). The topic lead is responsible for: • conducting a ‘desk review’ of the principle to gauge if a revision is required and for what reason, or if the principle is no longer required • liaison with Topic Group to discuss findings and evidence that a revision/withdrawal is required • if review identifies a revision is not required, the Harmonisation Team should be informed that no further action is required other than adding the ‘next review due’ date to the Harmonised Principle and republishing it. • if the need for a revision or withdrawal is identified, the steps at Stage G. Revise/withdraw, should be followed Inform Ho. Ps Although Ho. Ps agreement is not required for ratification, the Harmonisation Team will inform Ho. Ps when a proposal is being reviewed. Back Main Index

Harmonisation Process Stage G. Revise/Withdraw This stage provides guidance for addressing principles that have been identified as needing revision or no longer required and should be withdrawn. The steps below should be followed: Consultation with Users The Topic Lead should ensure all users of the principle are consulted and views considered. The consultation should cover the following areas: • what the required changes are • reason for the changes • benefits of making the change • an overview of any testing required • a deadline for comments Proposal Drafted for Endorsement by the NSHG/GSS SPSC Following completion of the consultation a draft proposal of the proposed changes or withdrawal request must be prepared using Stage A as a guide. This is then submitted as detailed at Stage B. Agree the Need, via the Harmonisation Team, using the template ‘Request for NSHG to Agree the Need for Revision to Existing Harmonised Principle’ at Annex E. From this point on, the remaining stages in the process are followed. Withdrawal of Harmonised Principles Request for the withdrawal of an existing Harmonised Principle should use the template ‘Request to Withdraw Harmonised Principle’ at Annex F. Back Main Index

Roles and Responsibilities The National Statistics Harmonisation Group (NSHG) is a cross government group comprising mainly (but not exclusively) government departments that produce statistics. The NSHG meets every four months to discuss harmonised principles and issues relating to harmonisation across the GSS. NSHG Topic Groups have been formed to take forward proposed harmonisation work, with each topic group being responsible for a number of topic related Harmonised Principles. The membership of these groups will include expert members from relevant government departments across the GSS including the devolved administrations. The groups are led by a Topic Lead, who is responsible for guiding the work through the recognised Harmonisation Process and managing the flow of the work. The Roles and Responsibilities of NSHG members, Topic Leads and the Harmonisation Team are outlined over the next few pages. A complete list of the current Topic Groups and Leads and the Harmonised Principles for which they are responsible for are also listed. Next Page Main Index

Roles and Responsibilities The roles and responsibilities for NSHG members and the current list of NSHG Topic Groups and Leads, can be found by clicking on the titles below: • • NSHG Members NSHG Topic Leads List of Topic Groups and Leads Harmonisation Team Back Main Index

NSHG Members - Roles and Responsibilities Members include government departmental and other organisation representatives, harmonisation champions and topic leads. Your general responsibilities as a member of the (NSHG) are to: • attend and contribute to the four monthly NSHG meetings and the Annual NSHG Workshop • promote Harmonisation and act as a Harmonisation Champion within your department and business areas • respond to papers and documents circulated for comment, taking into account the responses from your department/business area (as a Harmonisation Champion) • respond to proposed new and revised Harmonised Principles, taking into account the views of your department/business area • provide feedback from your department when necessary regarding Harmonisation • provide input to the Harmonisation Strategy and Implementation plan • promote ‘Harmonisation by default’ (Harmonised Principles should be used in the first instance unless sufficient reason to do otherwise is provided) • promote the various Harmonisation Tools to your department/business area • raise ‘horizon scanning’ or other issues that may affect the work of Harmonisation • identify upcoming conferences/high level meetings that may be targeted for promotion of harmonisation • before leaving the NSHG, it is your responsibility to find a replacement member from your department/business area Back Main Index

NSHG Topic Leads - Roles and Responsibilities National Statistics Harmonisation Group (NSHG) Topic Groups are formed to take forward proposed harmonisation work. Each topic group may be responsible for a number of Harmonised Principles. The membership of these groups will include expert members from relevant government departments and devolved administrations, across the GSS. Each Group has a Topic Lead whose general responsibilities will include: • Managing the development of proposed Harmonised Principles and maintaining the current Harmonised Principles via regular review and ‘horizon scanning’ to ensure content remains relevant and current. • Providing updates for the GSS NSHG meetings on the progress of work, including which surveys the harmonised questions are used on and all topic group members. • Acting as subject matter expert by providing responses to topic related queries received by the Harmonisation Team. • Helping promote the benefits of using harmonised principles and encouraging user/producer buy-in to ‘harmonisation’. Back Main Index
Topic Group Contact Details Benefits & Tax Credits Consumer Durables Joy Preece(ONS) Joy. Preece@ons. gov. uk 01633 455372 Migration, Country of Birth & Citizenship Penni Mc. Clure(ONS) penni. mcclure@ons. gov. uk 01329 444636 Crime & Anti-social Behaviour Fiona Aitchison (ONS) fiona. aitchison@ons. gov. uk 01329 444694 Thomas Sims (DWP) thomas. sims@dwp. gsi. gov. uk 020 7449 7342 Demographic Information Economic Activity Educational Attainment Emily Knipe (ONS) emily. knipe@ons. gov. uk 01329 447890 Roger Smith (ONS) roger. smith@ons. gov. uk 01633 455277 Nazma Nessa (BIS) nazma. nessa@bis. gov. uk 0114 207 5104 Ethnicity, Identity, Language & Religion Gender Identity Health, Disability & Carers Housing & Tenure Income Michelle Monkman (ONS) Michelle. monkman@ons. gov. uk 01329 444986 Steven Webster (HSCIC) steven. webster 1@hscic. gov. uk 0113 866 5603 Scott Edgar(DCLG) Scott. Edgar@communities. gsi. go v. uk 0303 444 2904 Matthew Minifie (ONS) matthew. minifie@ons. gov. uk 01633 455658 Pensions Personal Well-being Social Capital Bonang (Bonnie) Lewis(ONS) bonang. lewis@ons. gov. uk 01633 451780 Matthew Steel (ONS) matthew. steel@ons. gov. uk 01633 455860 Katrina Morrison (ONS) katrina. morrison@ons. gov. uk 01633 451745 Back To Be Confirmed Harmonised Principles Main Index
Topic Group Contact Details Topic Lead Email Telephone Benefits and Tax Credits Thomas Sims (DWP) thomas. sims@dwp. gsi. gov. uk 020 7449 7342 Consumer Durables Joy Preece (ONS) Joy. preece@ons. gov. uk 01633 455372 Crime and Anti-Social Behaviour Fiona Aitchison (ONS) fiona. aitchison@ons. gov. uk 01329 444694 Demographic Information Emily Knipe (ONS) emily. knipe@ons. gov. uk 01329 447890 Economic Activity Roger Smith roger. smith@ons. gov. uk 01633 455277 Education Attainment Nazma Nessa (BIS) nazma. nessa@bis. gov. uk 0114 207 5104 Ethnicity, Identity, Language, Religion To be confirmed Gender Identity Michelle Monkman (ONS) michelle. monkman@ons. gov. uk 01329 444986 Health, Disability and Carers Steven Webster (HSCIC) steven. webster 1@hscic. gov. uk 0113 866 5603 Housing and Tenure Scott Edgar Scott. Edgar@communities. gsi. gov. uk 0303 444 2904 Income Matthew Minifie (ONS) matthew. minifie@ons. gov. uk 01633 455658 Migration, Country of Birth and Citizenship Penni Mc. Clure penni. mcclure@ons. gov. uk 01329 444636 Pensions Bonang Lewis (ONS) bonang. lewis@ons. gov. uk 01633 451780 Personal Well-being Matthew Steel (ONS) matthew. steel@ons. gov. uk 01633 455860 Social Capital Katrina Morrison (ONS) Katrina. morrison@ons. gov. uk 01633 451745

Topic Groups’ Harmonised Principles Benefits & Tax Credits Consumer Durables Migration, Country of Birth & Citizenship Under development Crime & Anti-social Behaviour Benefits & Tax Credits Consumer Durables Internet Access Demographic Information Economic Activity Educational Attainment Demographic Information Economic Status & Industry Educational Attainment Qualifications Ethnicity, Identity, Language & Religion Ethnic Group National Identity & Religion Sexual Identity Gender Identity Health, Disability & Carers Housing & Tenure Income Under development General Health & Carers Long-lasting Health Conditions & Illnesses Accommodation & Household Information Housing Costs & Benefits Tenure Income Pensions Personal Well-being Social Capital Under development Personal Well-being Social Capital (removed pending review) Back Crime & Fear of Crime Main Index

Harmonisation Team Roles and Responsibilities The Harmonisation Team is based at the Office for National Statistics (ONS) and is responsible for the management and promotion of Harmonised Principles across the GSS. The Harmonisation Team coordinates the cross government programme of work looking into harmonising inputs and outputs for use in National Statistics and is the Secretariat for the National Statistics Harmonisation Group (NSHG). Its main responsibilities are to: • • • • • produce the Harmonisation Strategy and Implementation Plan create, implement and monitor the Communication Plan monitor the workplan against the NSHG Terms of Reference (To. R) and report to the NSHG disseminate Harmonised Principles once ratified create ‘Harmonisation Tools’ to promote harmonisation review National Statistics assessments and provide a report to the UK Statistics Authority Monitoring and Assessment Team (M&A Team) present the Harmonisation Roadshow across the GSS to raise awareness of Harmonisation act as secretariat for the National Statistics Harmonisation Steering Group organise , attend and contribute to the NSHG meetings and the Annual NSHG Workshop produce reports for the GSS Statistical Policy and Standards Committee (SPSC) maintain NSHG membership list and identify gaps in stakeholders produce harmonisation case studies to promote harmonisation co-ordinate queries via the harmonisation inbox and the harmonisation helpline provide NSHG Topic Leads with guidance and support for their role liaise with the UK Data Service and the Variable and Question Bank Team maintain the Harmonisation web pages on the GSS website maintain Harmonisation Community on Stats. User. Net Back Main Index
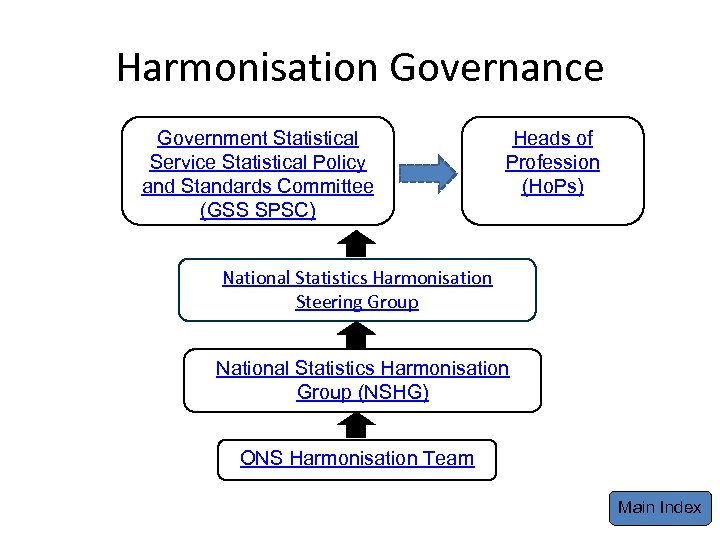
Harmonisation Governance Government Statistical Service Statistical Policy and Standards Committee (GSS SPSC) Heads of Profession (Ho. Ps) National Statistics Harmonisation Steering Group National Statistics Harmonisation Group (NSHG) ONS Harmonisation Team Main Index

Harmonisation Governance ONS Harmonisation Team The Harmonisation Team is the secretariat for the National Statistics Harmonisation Group (NSHG) providing all administrative support as well as guidance around the harmonisation process to members. The Team is also working on 3 projects; facilitating revision to existing harmonised social principles, facilitating developing of new harmonised principles for business statistics (in the short to medium term) and for administrative data (longer term). The Team has identified several business and administrative data initiatives occurring across the Government Statistical Service (GSS) that harmonisation can facilitate and is working with colleagues to develop harmonised principles as part of the delivery of these programmes. More information on the latest developments can be found on the GSS Harmonisation pages on the GSS website. If you have any further questions or suggestions, please email: harmonisation@ons. gsi. gov. uk. Back Main Index

Harmonisation Resources (Links opens the page in a web browser) • Harmonisation Web pages The Harmonisation pages are located on the GSS website and contain links to the Harmonisation principles and other information on harmonisation. • Variable and Question Bank An online resource where users can research survey variables and questions. • Stats. User. Net A site hosted by the RSS designed to stimulate engagement between users and producers of official statistics, where information and views can be shared. • Newsletter Produced after each NSHG meeting, to promote harmonisation to the GSS and wider community. • GSS Blogs Access to the GSS Blogs, where GSS members can register and engage with other members. Includes the Good Practice Blog, GSS Data Blog and the GSS Harmonisation Blog. • Harmonisation Diagrams and Posters Diagrams and posters that can be used to promote harmonisation. Main Index

Harmonisation Diagrams & Posters Back Main Index
Harmonisation Process Diagram Back Main Index

Harmonised principles may take many forms, and still be comparable Tel https: //gss. civilservice. gov. uk/statistics/ methodology-2/harmonisation/ email: harmonisation@ons. gov. uk Back Main Index

Harmonised not standardised https: //gss. civilservice. gov. uk/statistics/ methodology-2/harmonisation/ or email: harmonisation@ons. gsi. gov. uk Back Main Index

Harmonisation https: //gss. civilservice. gov. uk/statistics/ methodology-2/harmonisation/ or email: harmonisation@ons. gsi. gov. uk Back Main Index

Harmonisation https: //gss. civilservice. gov. uk/statistics/ methodology-2/harmonisation/ or email: harmonisation@ons. gsi. gov. uk Back Main Index

Harmonisation Tel https: //gss. civilservice. gov. uk/statistics/ methodology-2/harmonisation/ or email: harmonisation@ons. gsi. gov. uk Back Main Index

Harmonisation Tel https: //gss. civilservice. gov. uk/statistics/ methodology-2/harmonisation/ or email: harmonisation@ons. gsi. gov. uk Back Main Index
LIFE’S A BEACH… Tel …WHEN YOU HARMONISE https: //gss. civilservice. gov. uk/statistics/ methodology-2/harmonisation/ or email: harmonisation@ons. gsi. gov. uk Back Main Index

Harmonisation Tel https: //gss. civilservice. gov. uk/statistics/ methodology-2/harmonisation/ or email: harmonisation@ons. gsi. gov. uk Back Main Index

Harmonisation Case Studies The Harmonisation Team have developed some case studies to support the use of harmonisation: 1. Meeting the European Systems of Accounting (ESA) 2010 Regulation - Purchases of computer software 2. Citizenship - Producing a single UK output Main Index
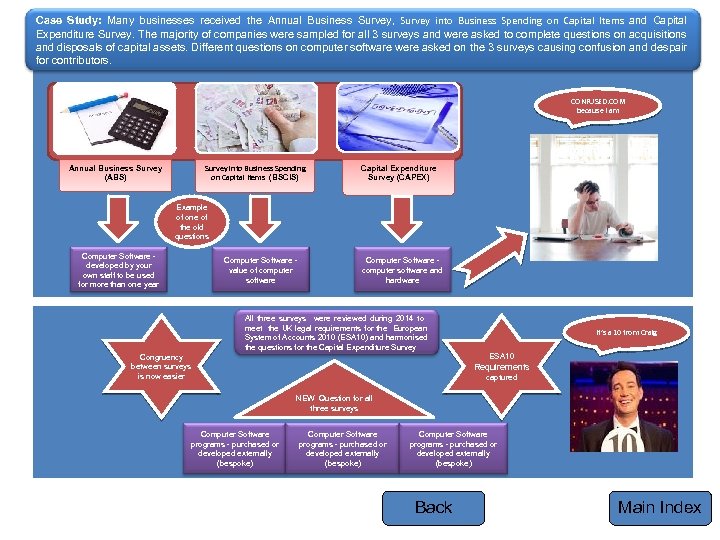
Case Study: Many businesses received the Annual Business Survey, Survey into Business Spending on Capital Items and Capital Expenditure Survey. The majority of companies were sampled for all 3 surveys and were asked to complete questions on acquisitions and disposals of capital assets. Different questions on computer software were asked on the 3 surveys causing confusion and despair for contributors. CONFUSED. COM because I am Survey into Business Spending on Capital Items (BSCIS) Annual Business Survey (ABS) Capital Expenditure Survey (CAPEX) Example of one of the old questions Computer Software - developed by your own staff to be used for more than one year Computer Software - value of computer software Computer Software - computer software and hardware All three surveys were reviewed during 2014 to meet the UK legal requirements for the European System of Accounts 2010 (ESA 10) and harmonised the questions for the Capital Expenditure Survey It’s a 10 from Craig ESA 10 Congruency between surveys is now easier Requirements captured NEW Question for all three surveys Computer Software programs - purchased or developed externally (bespoke) Back Main Index
Citizenship – Producing a single UK Output Case Study: It is a legal requirement to supply UK-level Citizenship Census data To Eurostat, as it is key dimension when considering stock and flow of migrants. However, the countries of the UK do not collect consistent information to determine citizenship. England primarily used passport held, and country of birth if necessary. Scotland primarily used country of birth, supported by national identify, year of UK arrival, and relationships data. Wales use passport held, and country of birth if necessary. Northern Ireland use passport held, with stated National Identity used to distinguish UK and Irish citizenship for those holding both passports. Considerations: Can be a UK citizen, but still have English, Scottish, Welsh or Northern Irish nationality. Therefore cannot interchange citizenship and nationality. England Wales Census research shows National Identity is a poor citizenship proxy for non UK-born population alone. Solutions: ONS research Identified, via the Opinions Survey, that the concept of ‘citizenship’ is misunderstood, and that passport information is more likely to be accurate. National Records Scotland created an algorithm to predict citizenship using Country of Birth, National Identity, Year of UK arrival and relationship data, which was then compared to England Wales rehearsal data. Comparison found the algorithm a good proxy for citizenship so it was adopted. Outcome: Although not collected, the UK was able to supply a measure of citizenship to Eurostat using proxy variables that were demonstrated to be valid, reliable, and accurate, despite using different source information. Back Main Index

Harmonisation Team Contact Details Ria Sanderson Chair of NSHG Charlie Wroth-Smith Head of Classification and Harmonisation Unit 01329 444672 Becki Aquilina Social Harmonisation 01329 444017 Mark Herniman Social Harmonisation 01329 444018 Joe Ellison Social Harmonisation 01329 444519 Suzanne Ellis Administrative and Business 01633 456040 Steve Cooley Administrative Sources 01329 444180 Ian Sidney Business Harmonisation 01633 455542 Email: harmonisation@ons. gov. uk Main Index

NSHG Meetings and Workshops The next NSHG meeting will take place on: Wednesday 9 th November 2016 at 1 Drummond Gate, London, SW 1 V 2 QQ from 11: 00 - 13: 30 pm The next Annual NSHG Workshop will take place on: Wednesday 9 th November 2016 at 1 Drummond Gate, London, SW 1 V 2 QQ from 14: 00 - 17: 00 pm Meeting agendas, papers and minutes are available on the GSS Website. Main Index
44600d18407170cbef9c2411c1ef78ff.ppt