1a7f6a3742058b87cec7c926d23c35a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Hardware requirements for a Castor instance Castor deployment team Castor Readiness Review – June 2006
Hardware requirements for a Castor instance Castor deployment team Castor Readiness Review – June 2006
 Outline v Anatomy of Castor instances v Hardware characteristics Ø midrange servers Ø diskservers v Software characteristics Ø main Castor services Ø OS, filesystems v Achieving operational scalability Ø automated installation + configuration Ø monitoring, (some) automated recovery actions Ø remaining manual interventions… Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 2
Outline v Anatomy of Castor instances v Hardware characteristics Ø midrange servers Ø diskservers v Software characteristics Ø main Castor services Ø OS, filesystems v Achieving operational scalability Ø automated installation + configuration Ø monitoring, (some) automated recovery actions Ø remaining manual interventions… Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 2
 Hardware used for Castor v Anatomy of a Castor-2 instance Ø cluster of headnodes to run main services Ø lots of diskservers provide disk cache, grouped in pools Ø two database servers stager and dlf Oracle databases v Anatomy of a Castor-1 instance Ø single headnode to run stager Ø lots of diskservers provide disk cache, grouped in pools v Shared infrastructure both for Castor-1 and Castor-2 Ø nameserver cluster database server + 4 CPU servers Ø admin cluster 4 CPU servers Ø tape libraries robots, drives, servers, media Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 3
Hardware used for Castor v Anatomy of a Castor-2 instance Ø cluster of headnodes to run main services Ø lots of diskservers provide disk cache, grouped in pools Ø two database servers stager and dlf Oracle databases v Anatomy of a Castor-1 instance Ø single headnode to run stager Ø lots of diskservers provide disk cache, grouped in pools v Shared infrastructure both for Castor-1 and Castor-2 Ø nameserver cluster database server + 4 CPU servers Ø admin cluster 4 CPU servers Ø tape libraries robots, drives, servers, media Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 3
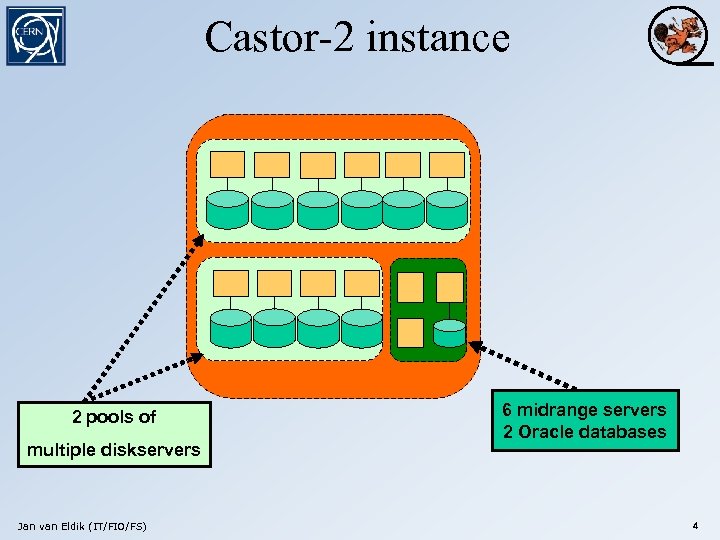 Castor-2 instance 2 pools of multiple diskservers Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 6 midrange servers 2 Oracle databases 4
Castor-2 instance 2 pools of multiple diskservers Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 6 midrange servers 2 Oracle databases 4
 Hardware used for Castor v Today Ø 6 Castor-2 instances • 4 LHC experiments, SC 4, ITDC • 180 diskservers, ~800 TB Ø 18 Castor-1 experiment stagers • Compass, NA 48, LEP, Harp, Ntof, public, lhcb, … • 110 older diskservers, ~200 TB • plus ~20 infrastructure stagers… v “Tomorrow” Ø more Castor-2 instances • castorpublic for “small” experiments • dedicated instances for experiments with CDR? What about LHC CDR? Ø bigger Castor-2 instances • LHC experiments: 1. 6 PB of diskcache on ~500 servers by Feb 2007 Ø fewer Castor-1 stagers… Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 5
Hardware used for Castor v Today Ø 6 Castor-2 instances • 4 LHC experiments, SC 4, ITDC • 180 diskservers, ~800 TB Ø 18 Castor-1 experiment stagers • Compass, NA 48, LEP, Harp, Ntof, public, lhcb, … • 110 older diskservers, ~200 TB • plus ~20 infrastructure stagers… v “Tomorrow” Ø more Castor-2 instances • castorpublic for “small” experiments • dedicated instances for experiments with CDR? What about LHC CDR? Ø bigger Castor-2 instances • LHC experiments: 1. 6 PB of diskcache on ~500 servers by Feb 2007 Ø fewer Castor-1 stagers… Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 5
![Scaling Castor-2 instances May 2006 space [TB] servers Sep 2006 space [TB] Feb 2007 Scaling Castor-2 instances May 2006 space [TB] servers Sep 2006 space [TB] Feb 2007](https://present5.com/presentation/1a7f6a3742058b87cec7c926d23c35a6/image-6.jpg) Scaling Castor-2 instances May 2006 space [TB] servers Sep 2006 space [TB] Feb 2007 servers space [TB] servers Alice 78 20 231 ~60 500 Atlas 123 25 176 ~45 370 CMS 138 27 176 ~45 370 LHCb 121 26 188 ~45 370 460 98 771 ~180 1610 ~480 SC 4 187 40 ITDC 169 42 170 ~40 ~200 ~100 ~2000 ~600 total LHC public total 816 180 940 220 Experiment capacity should grow to 1. 6 PB by Feb 2007, by adding ~300 servers Assuming no SC instance needed, and a catch-all castorpublic instance we will need to operate 600 diskservers Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 6
Scaling Castor-2 instances May 2006 space [TB] servers Sep 2006 space [TB] Feb 2007 servers space [TB] servers Alice 78 20 231 ~60 500 Atlas 123 25 176 ~45 370 CMS 138 27 176 ~45 370 LHCb 121 26 188 ~45 370 460 98 771 ~180 1610 ~480 SC 4 187 40 ITDC 169 42 170 ~40 ~200 ~100 ~2000 ~600 total LHC public total 816 180 940 220 Experiment capacity should grow to 1. 6 PB by Feb 2007, by adding ~300 servers Assuming no SC instance needed, and a catch-all castorpublic instance we will need to operate 600 diskservers Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 6
 Head nodes cluster Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 7
Head nodes cluster Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 7
 head nodes v Oracle databases Ø stagerdb, dlfdb Ø currently, on production instances, we use 2 “standard” diskservers (dual CPUs, H/W RAID-1, RHEL 3) Ø future? see Eric’s presentations… v Castor-2 services Ø LSF scheduler, rtcpclientd, stager, request handler, dlfserver, rmmaster, expertd Ø could be run on a single PC, but… Ø currently, on production instances: split them over 6 “midrange servers” Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 8
head nodes v Oracle databases Ø stagerdb, dlfdb Ø currently, on production instances, we use 2 “standard” diskservers (dual CPUs, H/W RAID-1, RHEL 3) Ø future? see Eric’s presentations… v Castor-2 services Ø LSF scheduler, rtcpclientd, stager, request handler, dlfserver, rmmaster, expertd Ø could be run on a single PC, but… Ø currently, on production instances: split them over 6 “midrange servers” Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 8
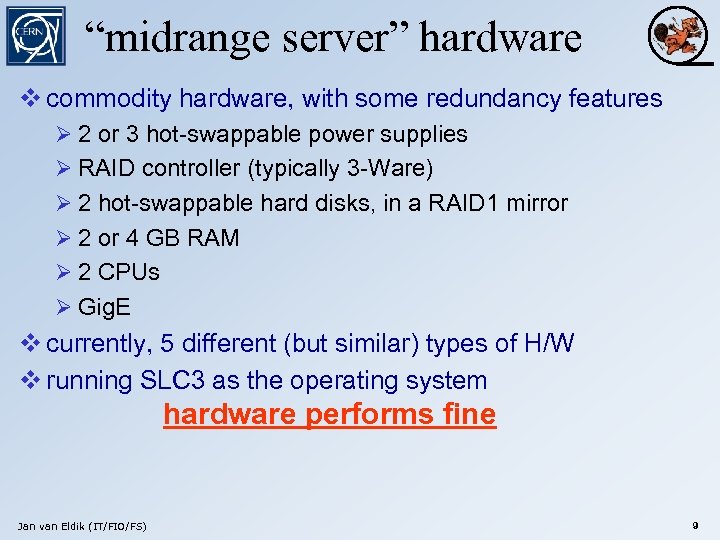 “midrange server” hardware v commodity hardware, with some redundancy features Ø 2 or 3 hot-swappable power supplies Ø RAID controller (typically 3 -Ware) Ø 2 hot-swappable hard disks, in a RAID 1 mirror Ø 2 or 4 GB RAM Ø 2 CPUs Ø Gig. E v currently, 5 different (but similar) types of H/W v running SLC 3 as the operating system hardware performs fine Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 9
“midrange server” hardware v commodity hardware, with some redundancy features Ø 2 or 3 hot-swappable power supplies Ø RAID controller (typically 3 -Ware) Ø 2 hot-swappable hard disks, in a RAID 1 mirror Ø 2 or 4 GB RAM Ø 2 CPUs Ø Gig. E v currently, 5 different (but similar) types of H/W v running SLC 3 as the operating system hardware performs fine Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 9
 Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 10
Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 10
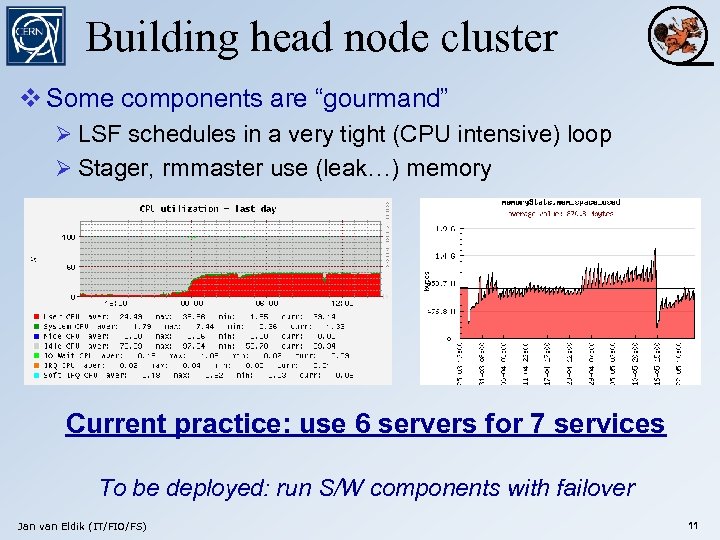 Building head node cluster v Some components are “gourmand” Ø LSF schedules in a very tight (CPU intensive) loop Ø Stager, rmmaster use (leak…) memory Current practice: use 6 servers for 7 services To be deployed: run S/W components with failover Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 11
Building head node cluster v Some components are “gourmand” Ø LSF schedules in a very tight (CPU intensive) loop Ø Stager, rmmaster use (leak…) memory Current practice: use 6 servers for 7 services To be deployed: run S/W components with failover Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 11
 diskservers Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 12
diskservers Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 12
 general remarks v Provide cache between analysis jobs and tapes v But experiments also want to store ‘durable’ data v Grouped in diskpools for distinct activities (example: CDR, experiment data sets, user files) v Different protocols for data access Ø rfio Ø root Ø gridftp v Lots of them… Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 13
general remarks v Provide cache between analysis jobs and tapes v But experiments also want to store ‘durable’ data v Grouped in diskpools for distinct activities (example: CDR, experiment data sets, user files) v Different protocols for data access Ø rfio Ø root Ø gridftp v Lots of them… Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 13
 diskserver hardware v commodity hardware, with redundancy features v 2 or 3 hot-swappable power supplies v 2, 3 or 4 RAID controllers (typically 3 -Ware, now also Areca) v 12 -- 24 hot-swappable SATA/IDE hard disks v disksizes vary 100 – 400 GB v 1, 2 or 4 GB RAM v 1 or 2 CPUs v Gig. E network interface v “midrange server plus diskspace” Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 14
diskserver hardware v commodity hardware, with redundancy features v 2 or 3 hot-swappable power supplies v 2, 3 or 4 RAID controllers (typically 3 -Ware, now also Areca) v 12 -- 24 hot-swappable SATA/IDE hard disks v disksizes vary 100 – 400 GB v 1, 2 or 4 GB RAM v 1 or 2 CPUs v Gig. E network interface v “midrange server plus diskspace” Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 14
 Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 15
Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 15
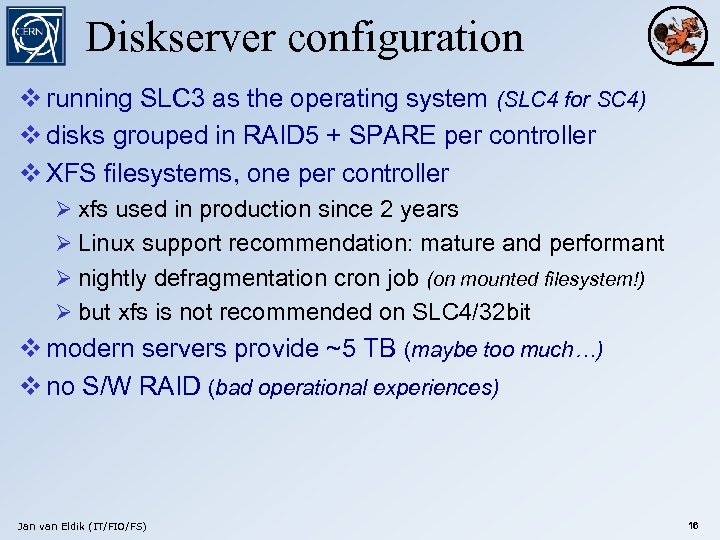 Diskserver configuration v running SLC 3 as the operating system (SLC 4 for SC 4) v disks grouped in RAID 5 + SPARE per controller v XFS filesystems, one per controller Ø xfs used in production since 2 years Ø Linux support recommendation: mature and performant Ø nightly defragmentation cron job (on mounted filesystem!) Ø but xfs is not recommended on SLC 4/32 bit v modern servers provide ~5 TB (maybe too much…) v no S/W RAID (bad operational experiences) Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 16
Diskserver configuration v running SLC 3 as the operating system (SLC 4 for SC 4) v disks grouped in RAID 5 + SPARE per controller v XFS filesystems, one per controller Ø xfs used in production since 2 years Ø Linux support recommendation: mature and performant Ø nightly defragmentation cron job (on mounted filesystem!) Ø but xfs is not recommended on SLC 4/32 bit v modern servers provide ~5 TB (maybe too much…) v no S/W RAID (bad operational experiences) Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 16
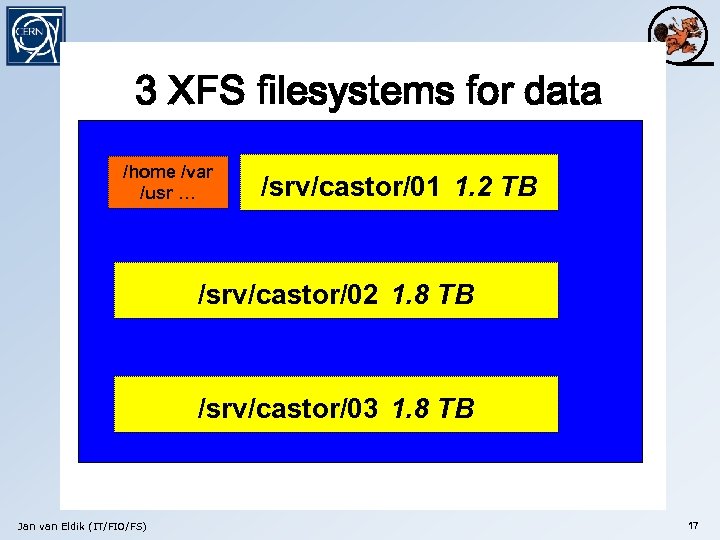 3 RAID controllers, 24 disks 3 XFS filesystems for data Hardware RAID configuration RAID-1 /home /var 80 GB /usr … 80 GB 300 /srv/castor/01 1. 2 300 GB RAID-5 GB 300 GB TB 1. 2 TB 300 GB S 300 GB 300 /srv/castor/02 1. 8300 GB RAID-5 GB 300 GB TB 1. 8 TB 300 GB 300 GB /srv/castor/03 TBTB RAID-5 1. 8 300 GB 300 GB Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) S 300 GB S 17
3 RAID controllers, 24 disks 3 XFS filesystems for data Hardware RAID configuration RAID-1 /home /var 80 GB /usr … 80 GB 300 /srv/castor/01 1. 2 300 GB RAID-5 GB 300 GB TB 1. 2 TB 300 GB S 300 GB 300 /srv/castor/02 1. 8300 GB RAID-5 GB 300 GB TB 1. 8 TB 300 GB 300 GB /srv/castor/03 TBTB RAID-5 1. 8 300 GB 300 GB Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) S 300 GB S 17
 Diskserver hardware • Strong points – Commodity (affordable!) H/W we already run 100’s of these servers – RAID does its job: individual disk failures (and the replacements) do not impact services • Difficulties – we run many generations, with large variations • 2, 3 or 4 RAID controllers, of different vendors, with 6, 8, 12 disks each • disksizes between 100 and 400 GB • filesystems between 400 GB and 2 TB (Linux limit) – complex systems, requiring experienced experts • RAID controller failures, 3 Ware erratic behaviour, internal connectivity problems, backplane failure, power failures Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 18
Diskserver hardware • Strong points – Commodity (affordable!) H/W we already run 100’s of these servers – RAID does its job: individual disk failures (and the replacements) do not impact services • Difficulties – we run many generations, with large variations • 2, 3 or 4 RAID controllers, of different vendors, with 6, 8, 12 disks each • disksizes between 100 and 400 GB • filesystems between 400 GB and 2 TB (Linux limit) – complex systems, requiring experienced experts • RAID controller failures, 3 Ware erratic behaviour, internal connectivity problems, backplane failure, power failures Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 18
 Managing 600 diskservers… Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 19
Managing 600 diskservers… Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 19
 need for automation v going to many Castor instances means increasing need for automation: Ø installation + upgrades Ø configuration Ø monitoring Ø recovery actions… v cannot afford handwork! error prone, not reproducible, too expensive v we operate the instances in the same way as the other FIO production clusters Ø Quattor Ø Lemon Ø Sys. Admins Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) software installation and configuration performance and exception monitoring H/W failures, OS-level problems 20
need for automation v going to many Castor instances means increasing need for automation: Ø installation + upgrades Ø configuration Ø monitoring Ø recovery actions… v cannot afford handwork! error prone, not reproducible, too expensive v we operate the instances in the same way as the other FIO production clusters Ø Quattor Ø Lemon Ø Sys. Admins Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) software installation and configuration performance and exception monitoring H/W failures, OS-level problems 20
 Quattorizing Castor v describe Castor instances in CDB templates Ø Ø describe headnodes, diskpools software packages, filesystems, configuration information consistent descriptions between OSes and architectures not always trivial… v install software only through RPMs Ø work closely with software responsibles Ø many improvements in many packages • Castor, LSF, oracle instant client, rootd, STK-SSI, lcg-mon-gridftp, yaim • benefits other sites and projects (hopefully) v configure software only with Quattor NCM components Ø re-use/enhance existing components lsfclient, sysctl, access_control, rgmaclient, yaim, sindes Ø write new components castorconf, stageconf, rmmaster/rmnode, localgridmap Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 21
Quattorizing Castor v describe Castor instances in CDB templates Ø Ø describe headnodes, diskpools software packages, filesystems, configuration information consistent descriptions between OSes and architectures not always trivial… v install software only through RPMs Ø work closely with software responsibles Ø many improvements in many packages • Castor, LSF, oracle instant client, rootd, STK-SSI, lcg-mon-gridftp, yaim • benefits other sites and projects (hopefully) v configure software only with Quattor NCM components Ø re-use/enhance existing components lsfclient, sysctl, access_control, rgmaclient, yaim, sindes Ø write new components castorconf, stageconf, rmmaster/rmnode, localgridmap Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 21
 Quattorizing Castor (2) v in quite a good shape… v adding diskservers to diskpools (and registering them to central Castor services) is now a straightforward procedure, and scales with the number of diskservers v still lots of odds and ends to be improved Ø management of grid-mapfiles Ø mighunter, expert system configured by hand (once per instance) Ø srm. cern. ch and castorgrid. cern. ch provide very similar functionality, but software packaging and configuration is very different v need to port to SLC 4, and to x 86_64 Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 22
Quattorizing Castor (2) v in quite a good shape… v adding diskservers to diskpools (and registering them to central Castor services) is now a straightforward procedure, and scales with the number of diskservers v still lots of odds and ends to be improved Ø management of grid-mapfiles Ø mighunter, expert system configured by hand (once per instance) Ø srm. cern. ch and castorgrid. cern. ch provide very similar functionality, but software packaging and configuration is very different v need to port to SLC 4, and to x 86_64 Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 22
 Lemonizing Castor v Exception metrics Ø Castor-specific daemons, error messages in logfiles Ø Associated operator alarms and instructions Ø Automatic recovery actions if really, really necessary… Ø Automatic disabling of diskservers with alarms v Performance metrics Ø standard Lemon plots per host/diskpool/instance Ø LSF activity plots Ø lots of Castor-specific metrics Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 23
Lemonizing Castor v Exception metrics Ø Castor-specific daemons, error messages in logfiles Ø Associated operator alarms and instructions Ø Automatic recovery actions if really, really necessary… Ø Automatic disabling of diskservers with alarms v Performance metrics Ø standard Lemon plots per host/diskpool/instance Ø LSF activity plots Ø lots of Castor-specific metrics Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 23
 Intrusive H/W interventions v Sys. Admins coordinate intervention between vendor and Castor service managers Ø Sys. Admin analyses Lemon alarm, decides to call in vendor Ø Sys. Admin asks Castor. Ops for downtime Ø Castor. Ops drain server (stop new requests, make sure all data is safe, wait until active requests finish) Ø Vendor fixes the node Ø Sys. Admin informs Castor. Ops, who put node back in production v many intrusive hardware interventions Ø May 2006: 15 intrusive interventions, 45 simple ones v This procedure is too heavy for the number of intrusive interventions Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 24
Intrusive H/W interventions v Sys. Admins coordinate intervention between vendor and Castor service managers Ø Sys. Admin analyses Lemon alarm, decides to call in vendor Ø Sys. Admin asks Castor. Ops for downtime Ø Castor. Ops drain server (stop new requests, make sure all data is safe, wait until active requests finish) Ø Vendor fixes the node Ø Sys. Admin informs Castor. Ops, who put node back in production v many intrusive hardware interventions Ø May 2006: 15 intrusive interventions, 45 simple ones v This procedure is too heavy for the number of intrusive interventions Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 24
 Conclusion v Castor instances use different types of hardware Ø midrange servers for head nodes Ø diskservers for database servers Ø diskservers for diskpools v midrange servers are behaving fine, diskservers are more problematic v automated fabric management and procedures are in place to install, configure, monitor, maintain the servers but always need to be improved! Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 25
Conclusion v Castor instances use different types of hardware Ø midrange servers for head nodes Ø diskservers for database servers Ø diskservers for diskpools v midrange servers are behaving fine, diskservers are more problematic v automated fabric management and procedures are in place to install, configure, monitor, maintain the servers but always need to be improved! Jan van Eldik (IT/FIO/FS) 25


