771b6a64ecc0612fd8fd0ca4c4953902.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 101

Happy Thursday!!! • Turn in vocab and pick up an agenda on the stand in the front • Did you know: The tombstone of Mel Blanc, the famous voice of cartoon characters Bugs Bunny, Sylvester the Cat, Tweety Bird and Porky Pig, reads: “That’s all folks. ”

Cold War Origins

Origins • The Cold War lasted from the end of WWII until the collapse of the Soviet Union (USSR) in 1991 • The US and Soviet Union represented very different fundamental values – The US represented democratic political institutions and a free market economic system • Capitalism- private citizens control all economic activity – The Soviet Union was a totalitarian government with a communist economic system • The state controlled all property and economic activity

What is a “cold war”? • A war fought using methods that are short of actual fighting – Arms race- US and USSR built large military forces and nuclear weapons to scare each other – Alliances- US and USSR created alliances to protect themselves and friends from attack – Proxy wars- at times war broke out between a nations friendly to US and a nation friendly to USSR- each side sent money, supplies, troops – Propaganda- each side created and spread information to influence world opinion

Make mine freedom

United Nations • 50 nations- INCLUDING U. S. • Charter resembled the League of Nations • Initial successes: – Created Israel and preserve peace in the Middle East – Guided former colonies to independence – Set up a benefit organization (UNICEF) • Failure- to control the use/build up of nuclear weapons


Eastern Europe • The Soviets faced a lot of death in WWII and for that they justified their claims to Eastern Europe – Felt they could stop future invasions from the west • Stalin installed communist gov’ts in Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania and Poland – Called satellite nations • Europe was now divided into 2 political regions • Winston Churchill of Britain made a speech creating the phrase “iron curtain” – Stood for the division of Europe
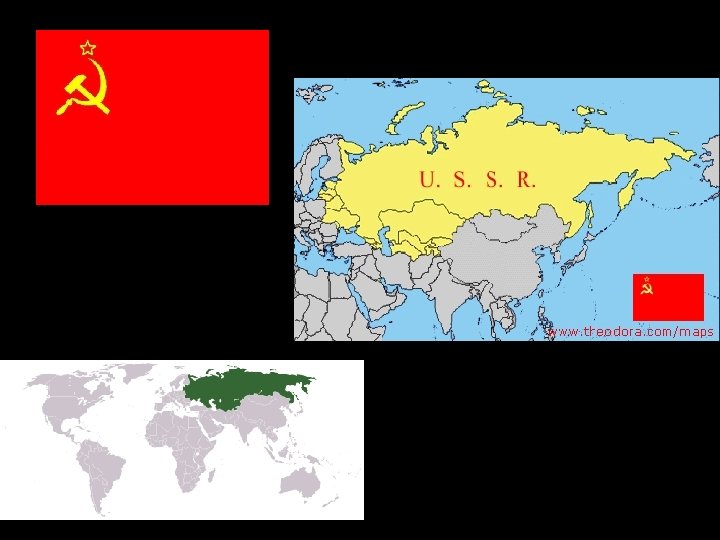

Germany Divided • West Germany- democratic and friendly with US • East Germany- communist and friendly with USSR • Berlin was divided as well – West-democratic and capitalist – East- communist and command economy
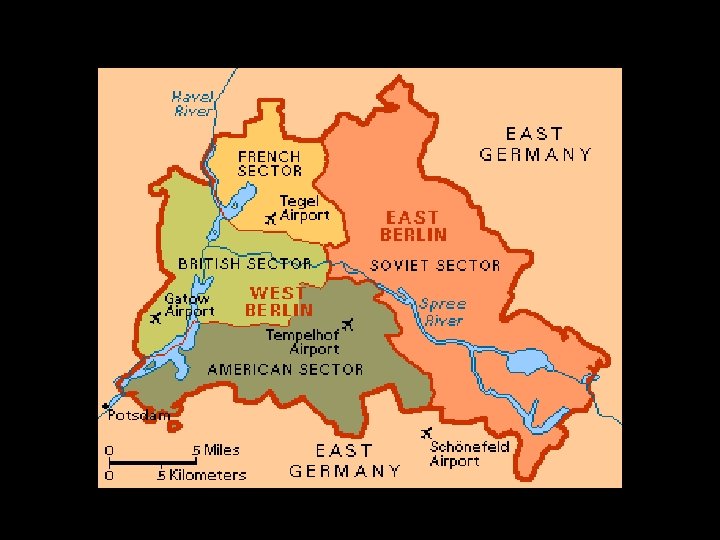

The Truman Doctrine • “Containment of communism” • Guiding principle of American foreign policy throughout the Cold War • Didn’t want to roll it back but wanted to keep it from spreading and to resist communist aggression into other countries • Truman asks Congress for $400 million in military aid for Greece and Turkey to fight communism • Created alliances- most famous being NATO

NATO • North Atlantic Treaty Organization • Formed as a defense alliance among the US and western European countries (12 nations in total) to prevent a Soviet invasion of Western Europe – “an attack on 1 is an attack on all” • Soviet allies in the eastern Europe formed the Warsaw Pact – for nearly 50 years both sides maintained large military forces facing each other in Europe

Marshall Plan • Western Europe was in chaos • June 1947, Sec of State George Marshall proposed the US provide aid to all European nations • Over the next 3 year, 16 countries receive about $13 billion in aid

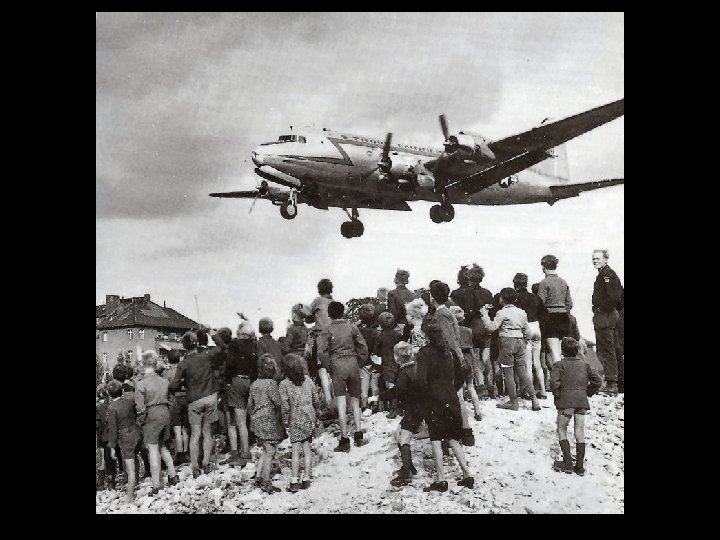
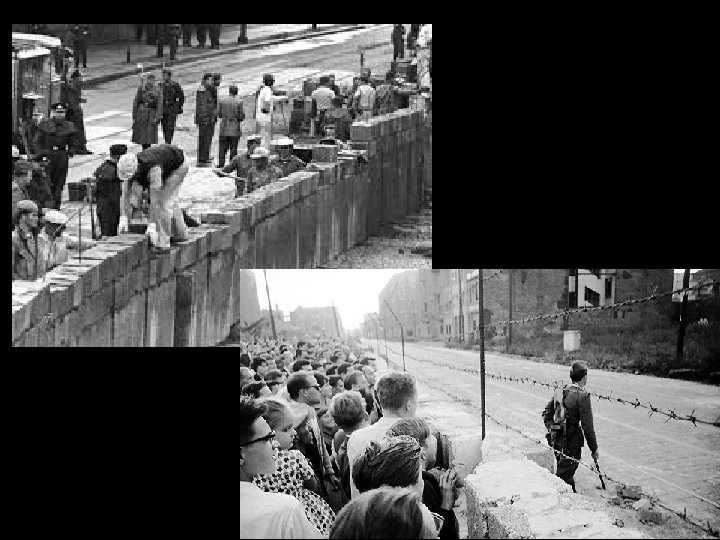
Berlin Airlift • Remember Berlin is split but is located right in the middle of USSR territory • 1948 - Stalin attempted to push the US, GB and FR out of Berlin by blocking rail and road traffic in and out. – Thought W. Berlin would suffer from lack of supplies and eventually get absorbed into USSR • US Air Force supplied West Berlin by air for a year forcing an end to the blockade • Later the USSR built a wall around West Berlin – prevent a US invasion of East Germany and to separate E and W Germany



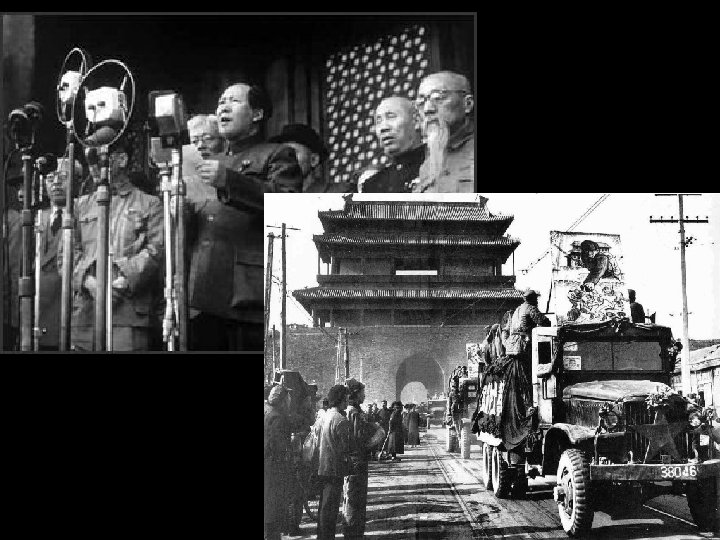
Communist Takeover in China • Revolution in 1949: Nationalists v. Communists – Communists win- Mao Zedong • increased American fears of communist domination of most of the world • The communist nations of China and the Soviet Union eventually became rivals for territory and diplomatic influence – Later President Nixon exploited this in 1970 s


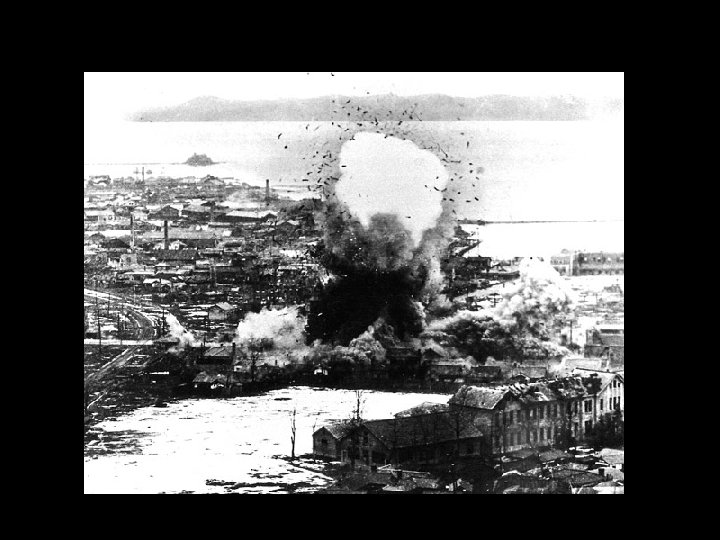
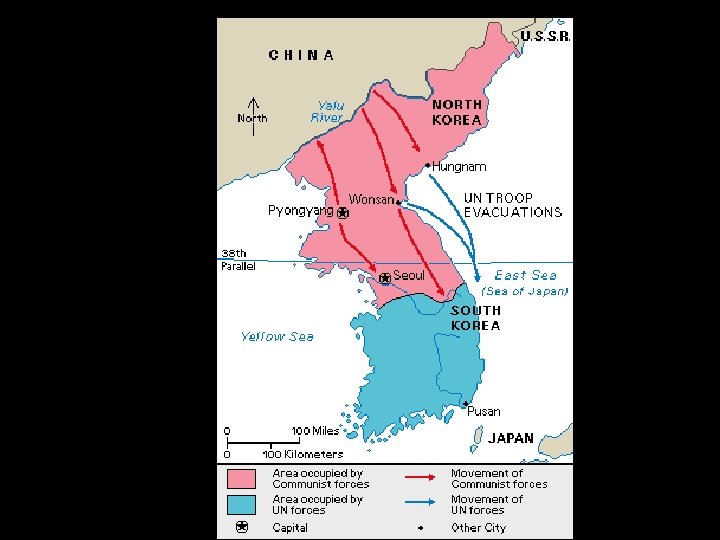
Korean War • At the end of WWII, Korea split into procommunist North and pro-democratic South along the 38 th parallel • North Korean forces attacked South Korea in 1950 – UN voted to help defend South Korea – US forces made up 90% of UN force • American involvement reflected the policy of containment of communism • Us led forces under Douglas Mac. Arthur counter-attacked North Korean forces • China Sent 300, 000 troops to help N. Korea

Result of Korean War • End in a stalemate at 38 th parallel – Success or failure? • 1953 - Armistice signed ending war – 38 th parallel line still divides North and South Korea – Containment of communism successful – US casualties= 54, 000 dead
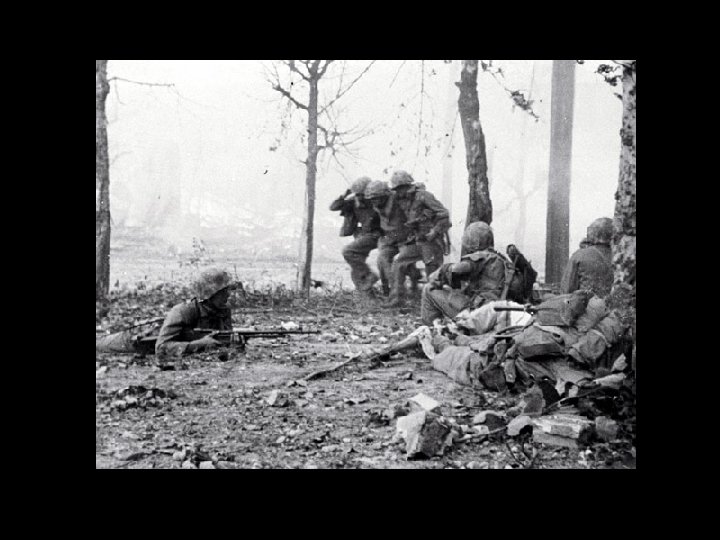



Happy Monday • Pick up an agenda • Start the SOL quiz on the back • Take out cold war packet, I will come around and check that you have completed the first 3

Cold War at home

Post WWII America • GI Bill- paid part of college tuition, a years worth of unemployment benefits, low interest loans – Helped families get new homes in suburbscookie cutter towns • Baby Boom- 40 s-60 s the birthrate in US soared- largest generation in the nation’s history

Levittown

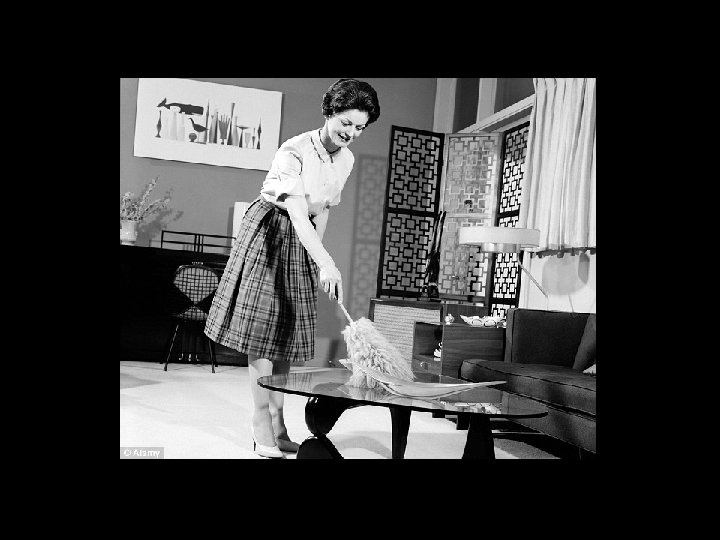
Changing Roles • Women were often reluctant to give up their independence after the war – Most left their jobs and went back home however – Women were homemakers and images were glorified by tv shows • African-American veterans demanded more civil rights – Truman attempted to expand civil rights but Congress shut it down – Jackie Robinson 1947 – Dixiecrats- led by Strom Thurmond to protest Truman’s efforts




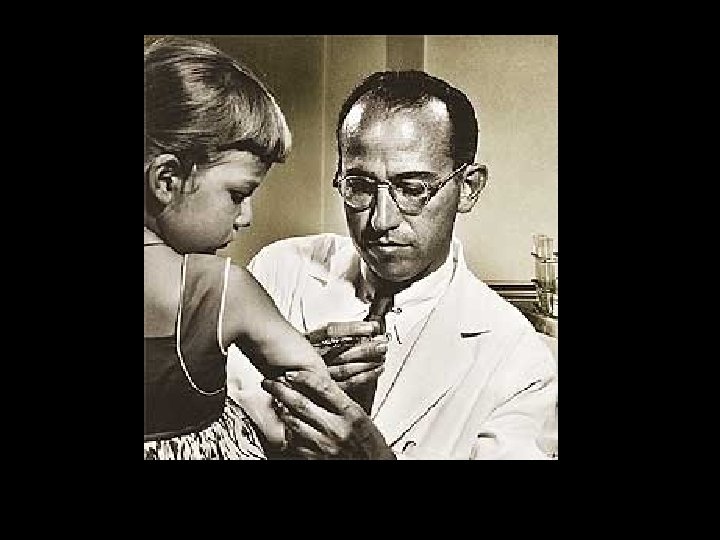
Medical advances • Dr. Jonas Salk- developed a vaccine for polio • Dr. Benjamin Spock- Common Sense Book of Baby and Child Care – Advised parents not to spank or scold children – Mothers need to be home

Interstate Highway system • After WWII Americans bought a lot of cars – Suburban living required cars • President Eisenhower authorized the building of a nationwide highway network – In turn encouraged more development – Long-haul trucking replacing need for railroads • Disneyland opened in 1955


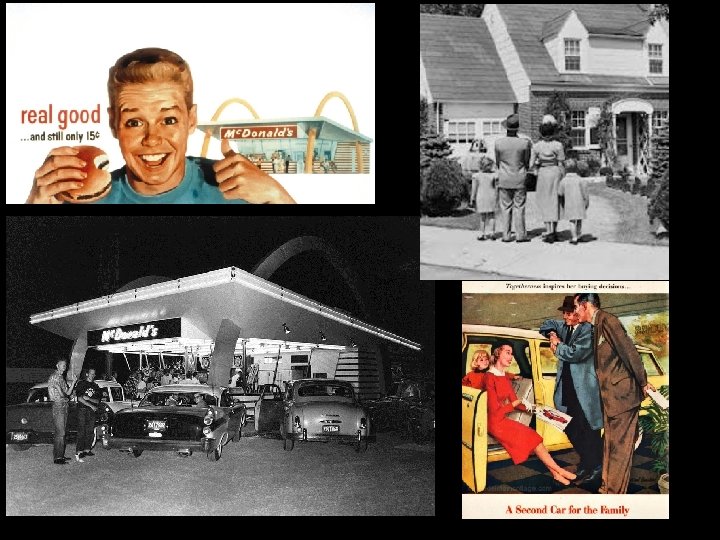
Consumerism and Leisure • People bought lots of stuff!! – Washing machines, dishwashers, microwaves, freezers, televisions, tape recorders, record players, grills, pools, toys etc. • Recreational activities– Fishing, bowling, boating, golf, baseball, basketball, football (on tv too!)

Social conformity • Fast food restaurants standardized what people ate • Corporations didn’t want individual thinkers – Personality tests to make sure you “fit in” • Idea was to not draw unwanted attention to yourself • Everyone following the “American Dream”


Subculture 1950 s • Beat movement- social and literary nonconformity of artists, poets and writers – Went against conformity • Rock ‘n’ roll- heavy rhythm, simple melodies and lyrics – Elvis, Chuck Berry, Little Richard – Condemned by adults- lead to teenage delinquency


Pop Culture • TV was HUGE! – People having TV in their house • 1948 -0. 4%, 1954 - 55. 7%, 1958 -83. 2% – FCC-Federal Communication Commission to regulate – Stereotypical portrayal of women and minorities


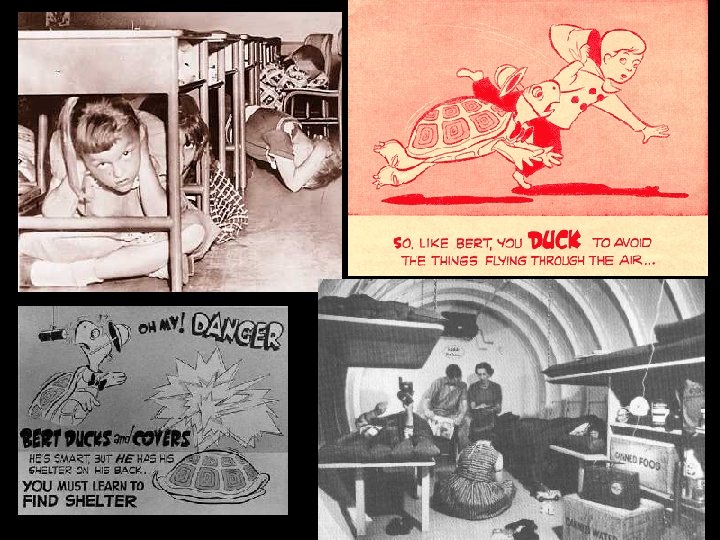
Threat of Nuclear War • The fear of communism and the threat of nuclear war affected American life throughout the Cold War – US developed the Hydrogen bomb- more powerful than atomic bomb – USSR developed one too!! – US encouraged math and science programs in schools in order to get ahead of the Soviets • During the 1950 s and 1960 s American schools regularly held drills to train children what to do in case of nuclear attacks – “duck and cover” • American citizens were urged by the gov’t to build bomb shelters in their basements

Fear and Paranoia • The Soviet domination of Eastern Europe and the Communist take over in China fueled a fear that communism would spread around the world and to the US – At the height of WWII, about 80, 000 Americans claimed membership in the Communist Party • People thought they had loyalty to USSR • Loyalty Review Board- set up to investigate gov’t employees and dismiss those found to be disloyal to the US – List of 91 “subversive” organizations was formedmembership in these groups were grounds for suspicion

HUAC • House Un-American Activities Committee • Investigated Communist influence in the movie industry – Believed the Communists were sneaking propaganda into films • “Hollywood Ten”- group of actors that refused to testify- sent to prison • Hollywood execs issued a blacklist- list of people condemned for having communist background – Actors, writers, producers and directors (about 500 in total)

How to spot a communist • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=KQVXH l. Mv. Oo. U

Spies in the US • Alger Hiss- accused of spying for the USSR – Document “found” that were said to have been written by Hiss – Convicted of perjury and sent to jail • Julius and Ethel Rosenberg- accused of spying for the USSR – When the USSR exploded their atomic bomb quickly, people thought that they were spying on the US – Rosenbergs were activist in the American Communist Party – Denied the charges and said they were being persecuted b/c they were Jewish – Found guilty of espionage and sentenced to death

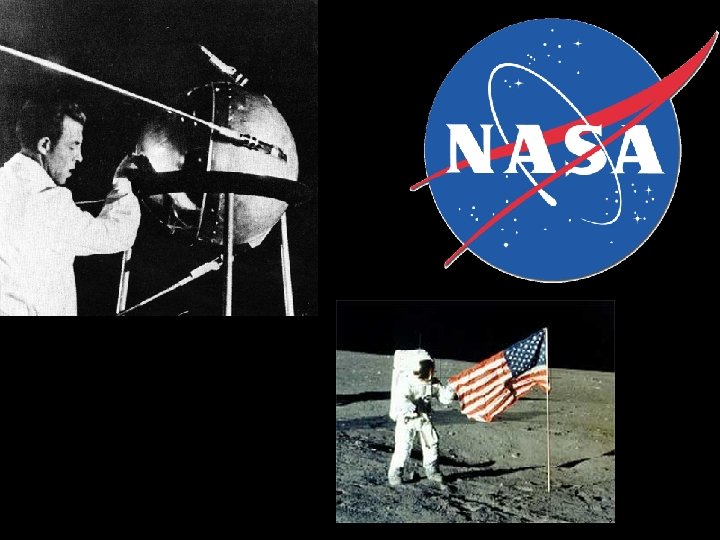
Space Race • 1957 - the USSR launched Sputnik 1 - satellite – People thought it was used to either spy on the US or launch missiles at the US • April 12, 1961 - Soviet cosmonauts went into space – Kennedy saw this as a challenge and set out to send a man to the moon • July 20, 1969 - Neil Armstrong took his first steps on the moon – Universities expanded their science programs

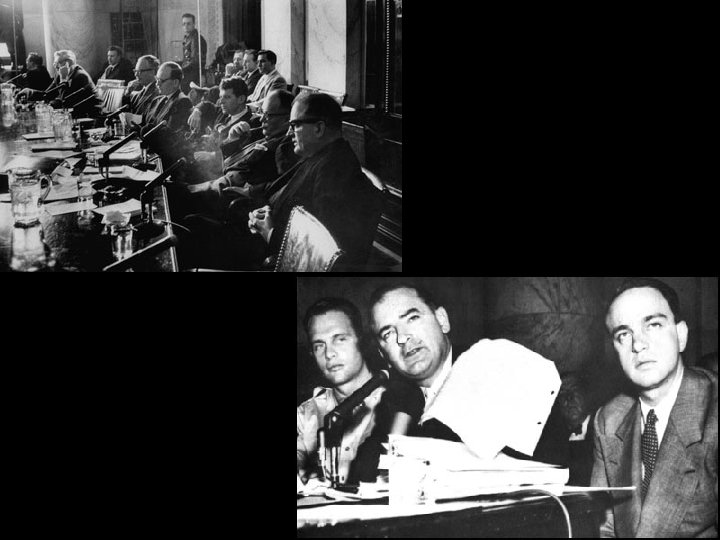
Mc. Carthyism • Republican from Wisconsin • Took advantage of people’s concerns about communism • Recklessly accused many American gov’t officials and citizens of being communist – Based these accusations on flimsy or no evidence • Led to the term Mc. Carthyism- making of false accusations based on rumor or guilt by association • 1954, Mc. Carthy made accusations against the Us Army which resulted in a nationally televised Senate investigation – Mc. Carthy bullied the witnesses and alienated the audience


The Cold War in Virginia • The heavy military expenditures throughout the Cold War benefited Virginia’s economy proportionately more than any other state • Hampton Roads was home to several large naval and air bases • Northern Virginia- home to the Pentagon and numerous private companies that contracted with the military

Election of 1960 • John F. Kennedy (D) vs. Richard Nixon (R) – TV played a huge role in election • First televised debate- favored Kennedy • Kennedy’s inaugural address- rally the US – US would “pay any price, bear any burden, meet an hardship, support any friend, oppose any foe, in order to assure the survival and the success of liberty” – “ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country”

Happy Wednesday!! • Take out your cold war packet so I can check them • Pick up an agenda on the stand in the front and do the SOL quiz on the back • Did you know: Pat Sajak, Host of Wheel of Fortune is a Vietnam Veteran

Cold War Cuba and Vietnam

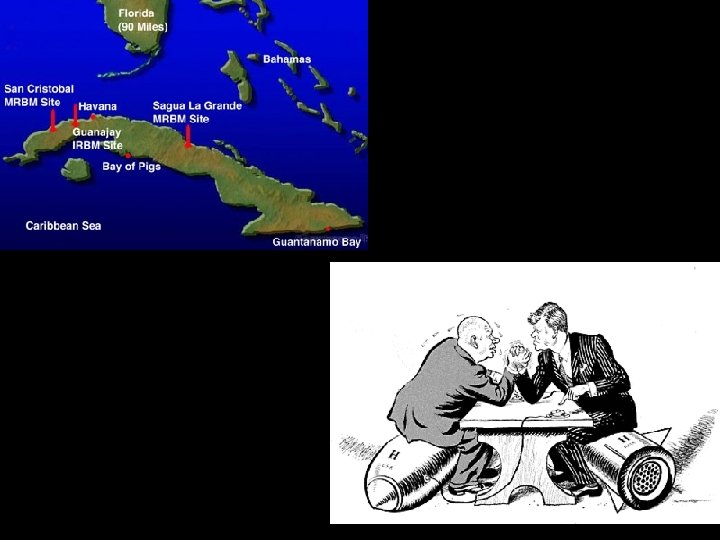
Castro and Cuba • Fidel Castro led a communist revolution that took over Cuba in 1959 – Relied on support and aid from USSR – Many Cubans fled to Florida • Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961)- failed attempt to overthrow Castro by Cuban exiles that had been trained by CIA – Kennedy accepted blame for the failure-humiliating defeat for the US

13 Days of Terror • In 1962, the USSR stationed missiles in Cuba - Cuban Missile Crises – Nikita Khrushchev (USSR) gave Castro missiles – US spy planes (U 2) photographed these missiles • President Kennedy ordered the Soviets to remove their missiles – 13 days, US and USSR on brink of nuclear war • Naval confrontation resulted in the USSR backing down – “We are eyeball to eyeball, and the other fellow just blinked. ”- Dean Rusk (Sec. of State) • Resolution- USSR removed missiles in exchange for US pledge not to invade Cuba

Vietnam • American involvement in Vietnam reflected the policy of containment – US provided France with economic and military support to keep control of Vietnam • Ho Chi Minh= communist leader of North Vietnam who wanted to unite all of Vietnam under communist rule • DOMINO THEORY- Eisenhower believed that if one country in SE Asia fell to communism, other would follow- like dominoes • Dien Bien Phu (1954)- N. Vietnamese forces defeated French- Vietnam divided- North-Communist, Southanticommunist
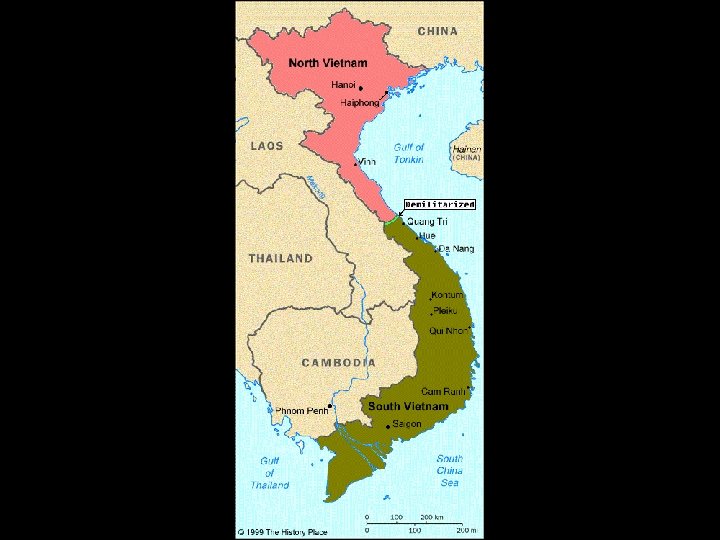

US Involvement in Vietnam • When France left Vietnam, the US continued to provide economic and military support to S. Vietnam to resist the spread of communism • Vietcong (procommunist S. Vietnamese fighters) – Ho Chi Minh Trail- supply route through Laos and Cambodia along which the Vietcong received weapons and supplies from N. Vietnam • Kennedy sent US military advisers to train S. Vietnamese army – Assassinated in Dallas, TX by Lee Harvey Oswald in Nov. 1963 • Shakes the nation’s confidence and begins a period of internal strife and divisiveness especially over Vietnam

American military build-up • Lyndon B. Johnson (LBJ) agreed with JFK that a communist takeover in S. Vietnam would be a disaster • Tonkin Gulf Resolution (1964): granted LBJ broad military power in Vietnam to escalate the conflict (but no official war declaration) – Led to increased military buildup of operations • the scale of conflict grew larger over the course of the 1960 s • American military forces repeatedly defeated the N. Vietnamese forces in the field, but couldn’t force an end on favorable terms

Escalation • Pleiku (1965): Vietcongs attack US air base. US steps up bombing raids and use land troops for the first time • Operation Rolling Thunder (1965): full scale bombing attacks- obvious escalation of war • Tet Offensive (1968): Jan. 30 - the Vietcong launched an attack on over 100 towns and cities in S. Vietnam and 12 US air bases – Lasted for about a month – American public increasingly turned against the war


American strategy • In March of 1965, Johnson began dispatching tens of thousands of US soldiers to fight in Vietnam – The draft was implemented to increase troops • Vietcong used hit-and run -tactics – Lived amongst civilians so it was hard for the US to know who was on their side and who wasn’t – Also built elaborate tunnels so they can withstand air raids • American strategy was the wear down the enemy by continuing harassment • Another strategy was to keep the Vietcong from winning support from S. Vietnam’s rural population – Green Berets (US Army Special Forces) sent in to win the people over • US dropped napalm (a gasoline-based bomb) and Agent Orange (a leaf –killing toxic chemical) to expose the tunnels and hideouts
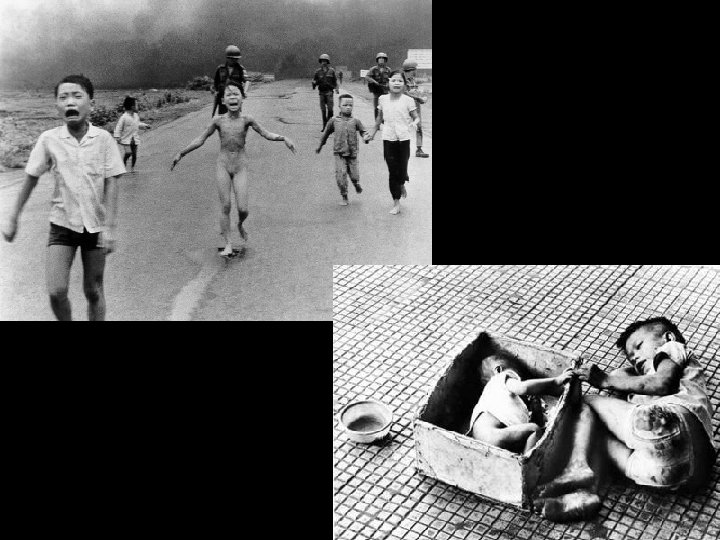


Reactions to President Johnson • LBJ’s popularity plummeted after the Tet offensive • In public opinion polls taken at the end of Feb 1968 showed nearly 60% of Americans disapproved of his handling of the war • LBJ decides not to run in election of 1968

Discontent at home • Vietnam became America’s first “living room war” – Combat footage appeared nightly on the news • Thousands of men attempted to find ways around the draft – Medical exemptions, college deferment – Many African-Americans fought in the war b/c it was harder for them to dodge the draft • Those who opposed the war but couldn’t dodge the draft often resorted to alcohol and drug use while in Vietnam
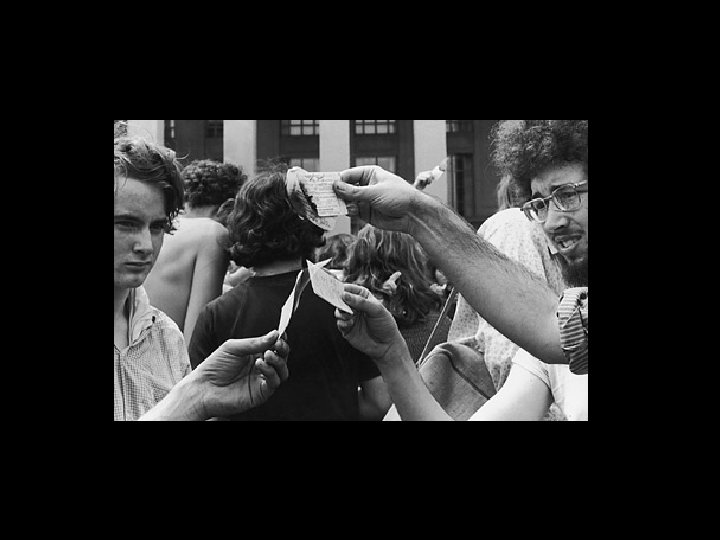


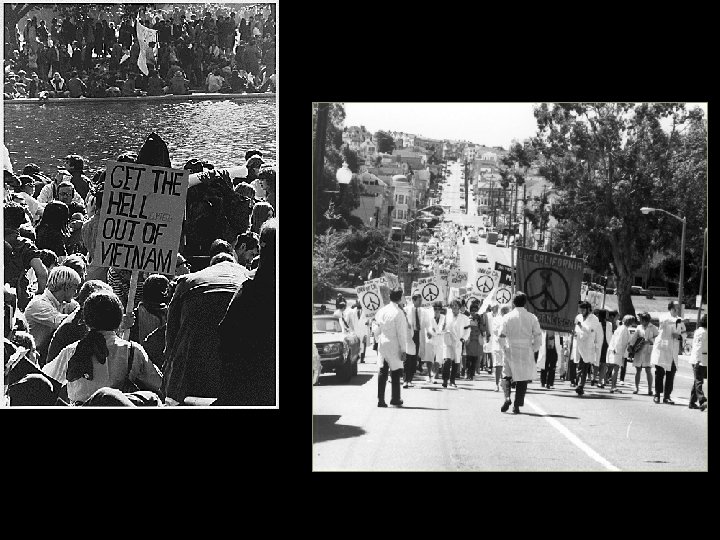
Country divided • Those who opposed the war were known as doves, those who supported US involvement were called hawks • Free Speech Movement (FSM) and Students for a Democratic Society (SDS) spread to college campuses – Protests were held on a number of college campuses as well as in cities like Washington DC • Encouraged people to burn their draft cards



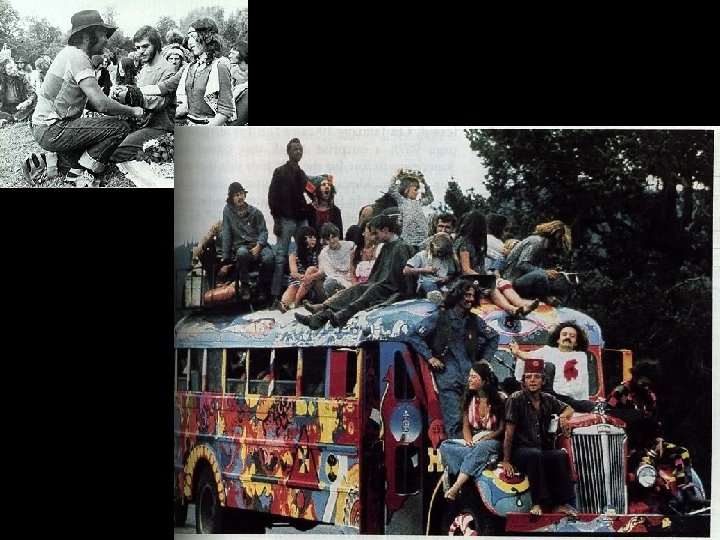
Counterculture • A movement made up mostly of white middle-class college youths who had grown disillusioned with the war in Vietnam and injustices in America – Hippie era, AKA “Age of Aquarius” • Made a lasting impression in art and music – Andy Warhol- criticized the “cookie cutter” lifestyle – Woodstock • Conservative Response- “revolutionary terrorism” was a threat on campuses and cities – Helped propel Nixon into office
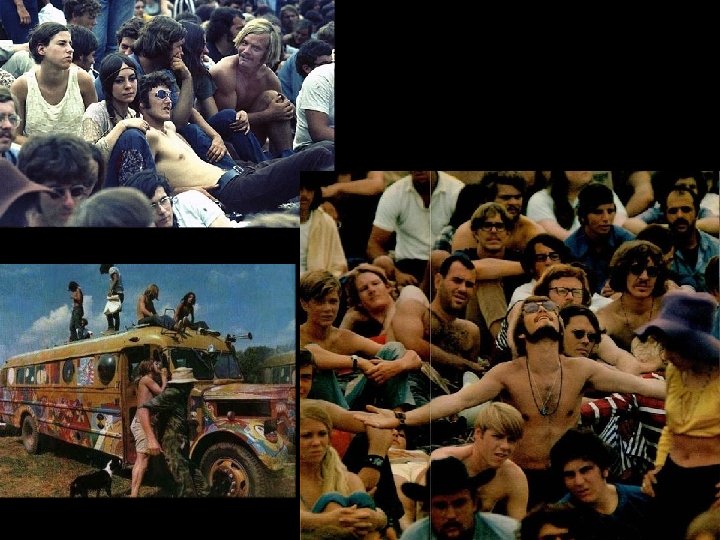



Nixon and Vietnamization • Nixon wins the election of 1968 – Campaigned on a promise to restore law and order – Also promised to end the war • Summer 1969, Nixon announces the first US troop withdrawals – War continued against N. Vietnam – “Vietnamization”- gradual withdrawal of US troops in order for S. Vietnamese to take over more active combat roles

Mishandling of the war • My Lai massacre (1969): Americans found out that a US platoon killed innocent civilians in My Lai – People were outraged!

Cambodia • By 1970 it seemed like the war was winding down • April 30, 1970, Nixon announced that US troops had invaded Cambodia to clear out Vietcong supply centers – Had notified Congress – Congress passed the War Powers Act: the president must report to Congress within 24 hours after committing troops to a foreign conflict, or enlarging American combat units in foreign nations • College students burst into protest – Closed down some 1, 200 campuses


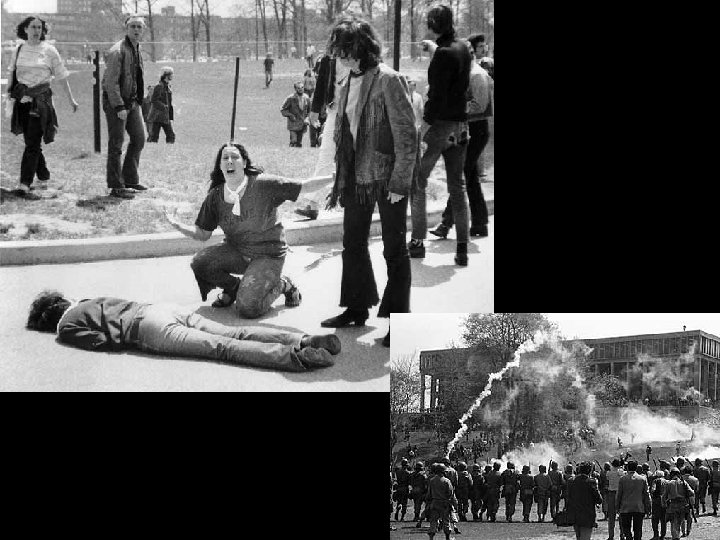
Kent State • Kent State University in Ohio • Massive student protest led to the burning of the ROTC building • The local mayor called in the National Guard • May 4, 1970, the Guards fired into a crowd of protesters – Wounded 9 and killed 4 (2 weren't even involved)


Result of Vietnamization • Ultimately Vietnamization failed when South Vietnamese troops proved unable to resist invasions by the Soviet- supplied North Vietnamese Army • In 1975, both North and South Vietnam were merged under communist control

Legacy of War • Demonstrated power of the American public • Casualties- 58, 000 killed, 303, 000 wounded – 15% with PTSD • Unlike WWII veterans who returned to a grateful and supportive nation, Vietnam vets returned to often face indifference or outright hostility from some who opposed the war


Happy Friday! • Turn in your Vietnam song wordle • Pick up an agenda and start on the SOL quiz

Cold War Ends

Let’s hop in our De. Lorean and flash forward to the 1980 s!

Internal Problems for USSR • Increasing soviet military expenses to compete with the US – USSR had trouble keeping up with the U. S. , didn’t have enough money • Economic inefficiency that led to stagnation and recession

New Policies • Mikhail Gorbachev- general secretary of the Communist Party in the USSR • “Glasnost” (openness)- allowed for open criticism of the government and took steps towards freedom of the press • “perestroika” (economic restructuring)-less government control of the economy – Allowed for some private enterprise – Took steps for establishing a democratic gov’t in USSR • Significance- revealed the communist system was failing – Rising nationalism in Soviet republics resulted • 14 non-Russian republics declared independence in 1991

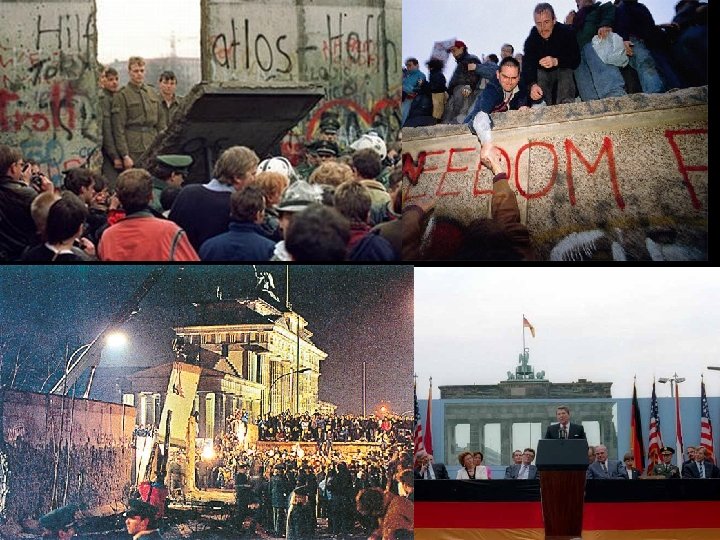
External Pressures from Reagan • President Ronald Reagan’s policies increased pressure on the USSR that contributed to its collapse – Increased military spending that USSR couldn’t match • Example: SDI (aka “Star Wars”)- missile defense shield – Challenged moral legitimacy of the USSR • Example: Speech at Berlin Wall- Mr. Gorbechev, tear down this wall” – Berlin Wall torn down in Nov. 1989

Cold War Legacy in US • During the Cold War era, millions of Americans served in the military to defend freedom in wars and conflicts that weren’t always popular • As a result the US and American ideals of democracy and freedom ultimately prevailed in the Cold War struggle with the Soviet Union’s communist system


The “Reagan Revolution” • Election of 1980 - Ronald Reagan (R) v. Jimmy Carter (D) • “Reagan Revolution”- term used to describe the shift to a more conservative path during President Reagan’s time in office – Redefining of federalism= more power to the states, less power to the national government

Reagan and the Supreme Court • Made appointments of conservative federal judges and supreme court justices who exercised “judicial restraint” – Sandra Day O’Connor- first woman to be appointed to the Supreme Court

Reagan’s influence • Extends beyond his time in office – 1988 - Reagan’s VP, George H. W. Bush was elected president – 1994 - Republican candidates dominated congressional elections – 2000 - election of George W. Bush

Reaganomics • Definition- President Reagan’s economic policies that included – Budget cuts- reduction in number and scope of government

Flash forward to the 1980’s! • March 1985, Mikhail Gorbachev became general secretary of the Communist Party in the Soviet Union – Advocated a policy known as “glasnost” (“openness”)allowed open criticism of the soviet gov’t and took steps towards freedom of press – In 1987 - outlined “perestrokia”- reconstructing Soviet society • Less gov’t control of economy, some private enterprise, and steps towards democracy

President Ronald Reagan • Reagan challenged moral legitimacy of the Soviet Union – “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!” • Referring to the Berlin Wall in Germany • Reagan increased the US military and economic pressures on the Soviet Union • The Cold War officially ends in 1990
771b6a64ecc0612fd8fd0ca4c4953902.ppt