d27fca3ad426829b3aa3631fcdfe9ff9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Hall C Opportunities at 12 Ge. V Dave Mack (TJNAF) for Steve Wood, Hall C Group Leader Workshop on Hadronic Physics in China and Opportunities with 12 Ge. V Jlab August 1, 2009 Lanzhou, China
Hall C Opportunities at 12 Ge. V Dave Mack (TJNAF) for Steve Wood, Hall C Group Leader Workshop on Hadronic Physics in China and Opportunities with 12 Ge. V Jlab August 1, 2009 Lanzhou, China
 Interactions of Electrons The well understood interactions of point-like electrons, and the high intensity and quality of modern electron beams, make them ideal for studying the charge and magnetization distributions in nuclear matter. Because of the different isospin coupling of the γ and Z 0, parity violating electron scattering provides an additional window on flavor. In precision measurements of Standard Model-suppressed observables, the large mass of the Z 0 even brings potential new physics at Te. V-scales within reach. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 2
Interactions of Electrons The well understood interactions of point-like electrons, and the high intensity and quality of modern electron beams, make them ideal for studying the charge and magnetization distributions in nuclear matter. Because of the different isospin coupling of the γ and Z 0, parity violating electron scattering provides an additional window on flavor. In precision measurements of Standard Model-suppressed observables, the large mass of the Z 0 even brings potential new physics at Te. V-scales within reach. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 2
 Where is Jlab? Jefferson Laboratory is a multi-Ge. V electron accelerator located in Newport News, Virginia, USA. Exploiting the intensity and precision frontiers, with state of the art spectrometers and targets, has made JLab an incredibly productive facility. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 3
Where is Jlab? Jefferson Laboratory is a multi-Ge. V electron accelerator located in Newport News, Virginia, USA. Exploiting the intensity and precision frontiers, with state of the art spectrometers and targets, has made JLab an incredibly productive facility. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 3
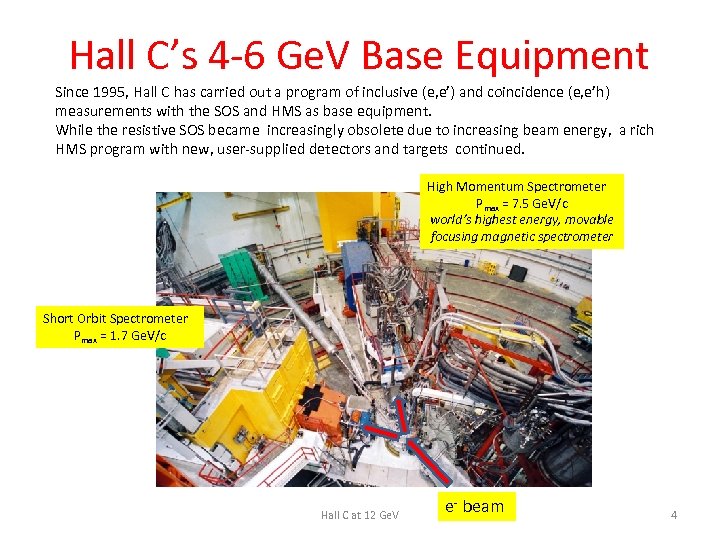 Hall C’s 4 -6 Ge. V Base Equipment Since 1995, Hall C has carried out a program of inclusive (e, e’) and coincidence (e, e’h) measurements with the SOS and HMS as base equipment. While the resistive SOS became increasingly obsolete due to increasing beam energy, a rich HMS program with new, user-supplied detectors and targets continued. High Momentum Spectrometer Pmax = 7. 5 Ge. V/c world’s highest energy, movable focusing magnetic spectrometer Short Orbit Spectrometer Pmax = 1. 7 Ge. V/c Hall C at 12 Ge. V e- beam 4
Hall C’s 4 -6 Ge. V Base Equipment Since 1995, Hall C has carried out a program of inclusive (e, e’) and coincidence (e, e’h) measurements with the SOS and HMS as base equipment. While the resistive SOS became increasingly obsolete due to increasing beam energy, a rich HMS program with new, user-supplied detectors and targets continued. High Momentum Spectrometer Pmax = 7. 5 Ge. V/c world’s highest energy, movable focusing magnetic spectrometer Short Orbit Spectrometer Pmax = 1. 7 Ge. V/c Hall C at 12 Ge. V e- beam 4
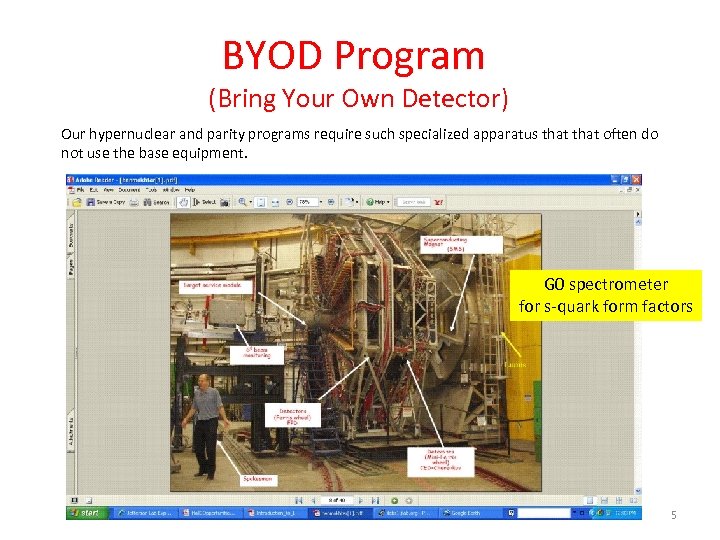 BYOD Program (Bring Your Own Detector) Our hypernuclear and parity programs require such specialized apparatus that often do not use the base equipment. G 0 spectrometer for s-quark form factors Hall C at 12 Ge. V 5
BYOD Program (Bring Your Own Detector) Our hypernuclear and parity programs require such specialized apparatus that often do not use the base equipment. G 0 spectrometer for s-quark form factors Hall C at 12 Ge. V 5
 Motivations for Hall C Upgrade • • Pion and nucleon elastic form factors at high momentum transfer Deep inelastic scattering at high Bjorken x Semi-inclusive scattering at high hadron momenta Polarized and unpolarized scattering on nuclei The HMS will remain important in the 12 Ge. V program, especially for electron detection. What is needed is a new spectrometer better suited for detecting charged hadrons at very high energies: • Higher momentum capability (11 Ge. V/c) • Smaller angle capability (5. 5 degrees) • Very good particle identification (e, π, k, p) • Accurate and reproducible angle and momentum settings The SHMS (Super High Momentum Spectrometer) meets these requirements. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 6
Motivations for Hall C Upgrade • • Pion and nucleon elastic form factors at high momentum transfer Deep inelastic scattering at high Bjorken x Semi-inclusive scattering at high hadron momenta Polarized and unpolarized scattering on nuclei The HMS will remain important in the 12 Ge. V program, especially for electron detection. What is needed is a new spectrometer better suited for detecting charged hadrons at very high energies: • Higher momentum capability (11 Ge. V/c) • Smaller angle capability (5. 5 degrees) • Very good particle identification (e, π, k, p) • Accurate and reproducible angle and momentum settings The SHMS (Super High Momentum Spectrometer) meets these requirements. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 6
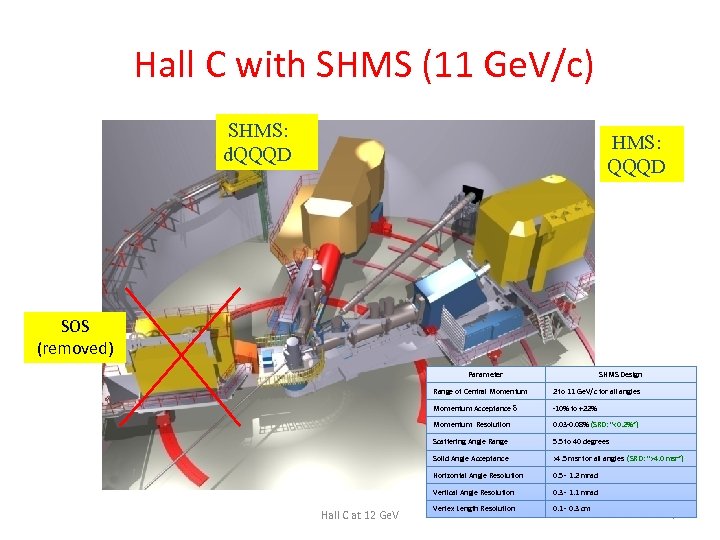 Hall C with SHMS (11 Ge. V/c) SHMS: d. QQQD HMS: QQQD SOS (removed) Parameter SHMS Design Range of Central Momentum Acceptance -10% to +22% Momentum Resolution 0. 03 -0. 08% (SRD: “<0. 2%”) Scattering Angle Range 5. 5 to 40 degrees Solid Angle Acceptance >4. 5 msr for all angles (SRD: “>4. 0 msr”) Horizontal Angle Resolution 0. 5 - 1. 2 mrad Vertical Angle Resolution Hall C at 12 Ge. V 2 to 11 Ge. V/c for all angles 0. 3 - 1. 1 mrad Vertex Length Resolution 0. 1 - 0. 3 cm 7
Hall C with SHMS (11 Ge. V/c) SHMS: d. QQQD HMS: QQQD SOS (removed) Parameter SHMS Design Range of Central Momentum Acceptance -10% to +22% Momentum Resolution 0. 03 -0. 08% (SRD: “<0. 2%”) Scattering Angle Range 5. 5 to 40 degrees Solid Angle Acceptance >4. 5 msr for all angles (SRD: “>4. 0 msr”) Horizontal Angle Resolution 0. 5 - 1. 2 mrad Vertical Angle Resolution Hall C at 12 Ge. V 2 to 11 Ge. V/c for all angles 0. 3 - 1. 1 mrad Vertex Length Resolution 0. 1 - 0. 3 cm 7
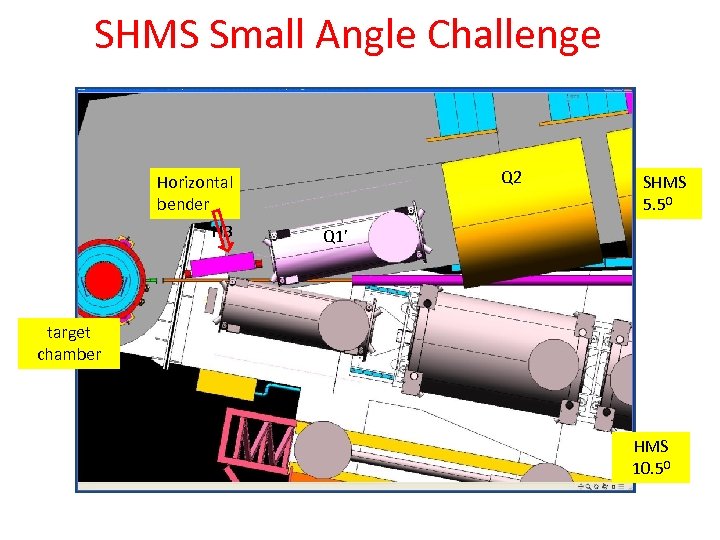 SHMS Small Angle Challenge Q 2 Horizontal bender HB SHMS 5. 50 Q 1’ target chamber HMS 10. 50
SHMS Small Angle Challenge Q 2 Horizontal bender HB SHMS 5. 50 Q 1’ target chamber HMS 10. 50
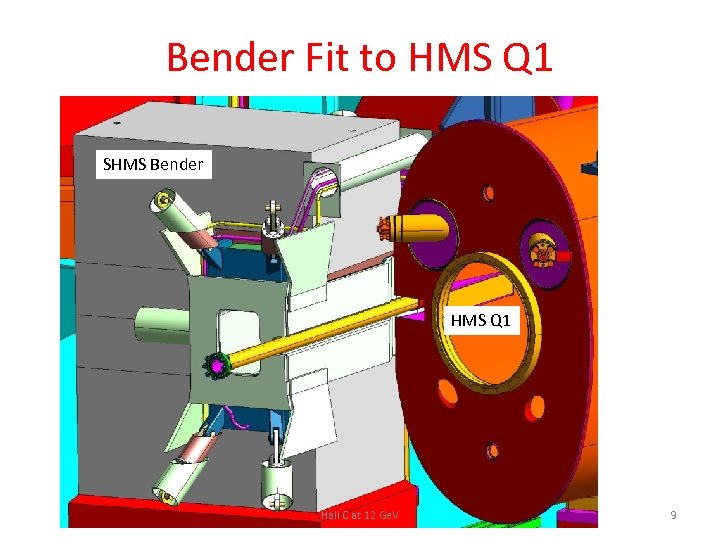 Bender Fit to HMS Q 1 SHMS Bender HMS Q 1 Hall C at 12 Ge. V 9
Bender Fit to HMS Q 1 SHMS Bender HMS Q 1 Hall C at 12 Ge. V 9
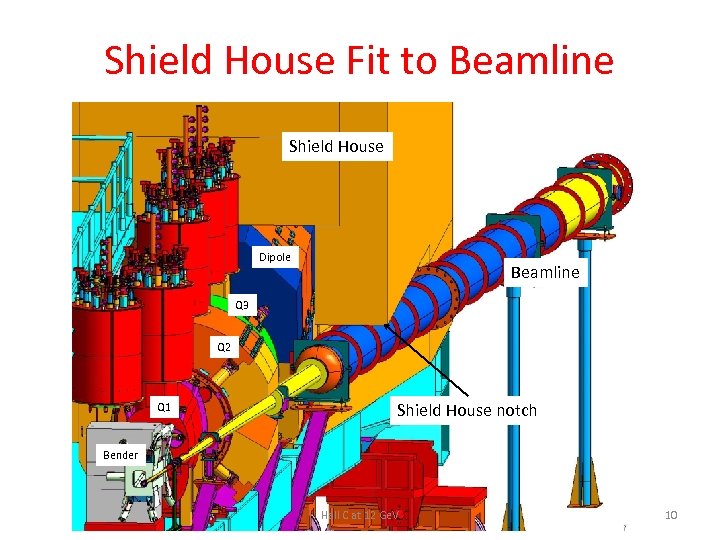 Shield House Fit to Beamline Shield House Dipole Beamline Q 3 Q 2 Q 1 Shield House notch Bender Hall C at 12 Ge. V 10
Shield House Fit to Beamline Shield House Dipole Beamline Q 3 Q 2 Q 1 Shield House notch Bender Hall C at 12 Ge. V 10
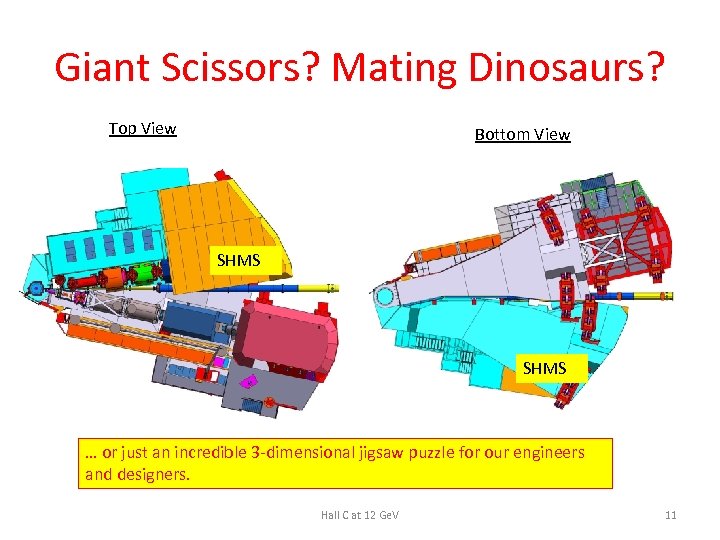 Giant Scissors? Mating Dinosaurs? Top View Bottom View SHMS … or just an incredible 3 -dimensional jigsaw puzzle for our engineers and designers. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 11
Giant Scissors? Mating Dinosaurs? Top View Bottom View SHMS … or just an incredible 3 -dimensional jigsaw puzzle for our engineers and designers. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 11
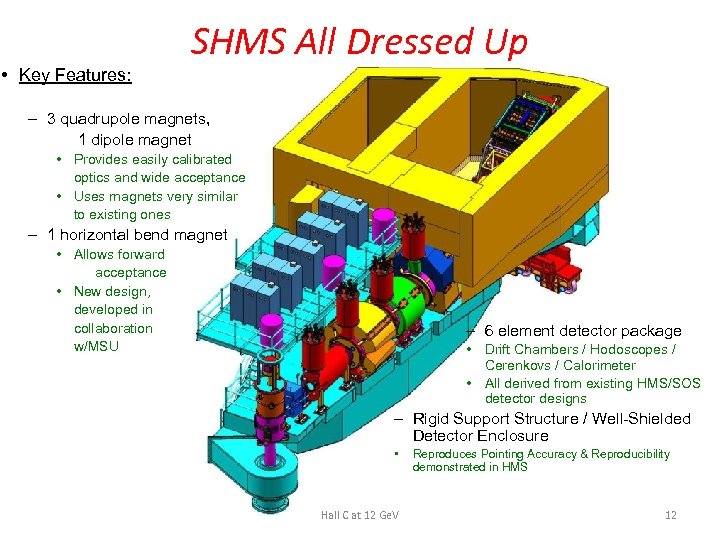 • Key Features: SHMS All Dressed Up – 3 quadrupole magnets, 1 dipole magnet • Provides easily calibrated optics and wide acceptance • Uses magnets very similar to existing ones – 1 horizontal bend magnet • Allows forward acceptance • New design, developed in collaboration w/MSU – 6 element detector package • Drift Chambers / Hodoscopes / Cerenkovs / Calorimeter • All derived from existing HMS/SOS detector designs – Rigid Support Structure / Well-Shielded Detector Enclosure • Hall C at 12 Ge. V Reproduces Pointing Accuracy & Reproducibility demonstrated in HMS 12
• Key Features: SHMS All Dressed Up – 3 quadrupole magnets, 1 dipole magnet • Provides easily calibrated optics and wide acceptance • Uses magnets very similar to existing ones – 1 horizontal bend magnet • Allows forward acceptance • New design, developed in collaboration w/MSU – 6 element detector package • Drift Chambers / Hodoscopes / Cerenkovs / Calorimeter • All derived from existing HMS/SOS detector designs – Rigid Support Structure / Well-Shielded Detector Enclosure • Hall C at 12 Ge. V Reproduces Pointing Accuracy & Reproducibility demonstrated in HMS 12
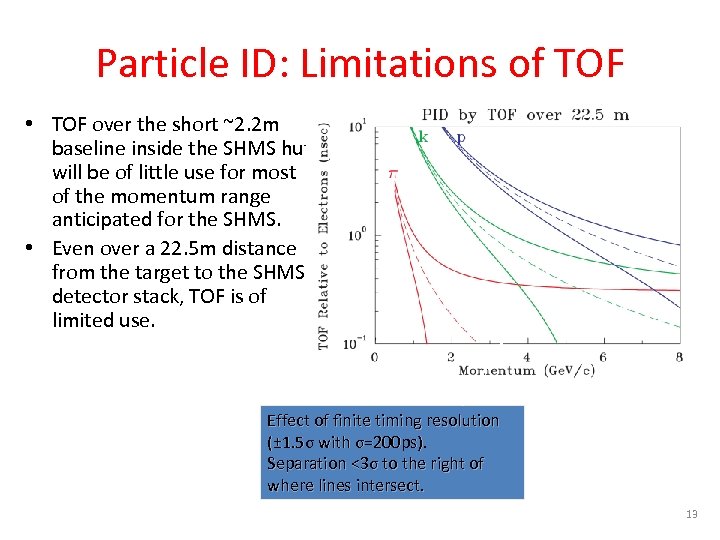 Particle ID: Limitations of TOF • TOF over the short ~2. 2 m baseline inside the SHMS hut will be of little use for most of the momentum range anticipated for the SHMS. • Even over a 22. 5 m distance from the target to the SHMS detector stack, TOF is of limited use. Effect of finite timing resolution (± 1. 5σ with σ=200 ps). Separation <3σ to the right of where lines intersect. 13
Particle ID: Limitations of TOF • TOF over the short ~2. 2 m baseline inside the SHMS hut will be of little use for most of the momentum range anticipated for the SHMS. • Even over a 22. 5 m distance from the target to the SHMS detector stack, TOF is of limited use. Effect of finite timing resolution (± 1. 5σ with σ=200 ps). Separation <3σ to the right of where lines intersect. 13
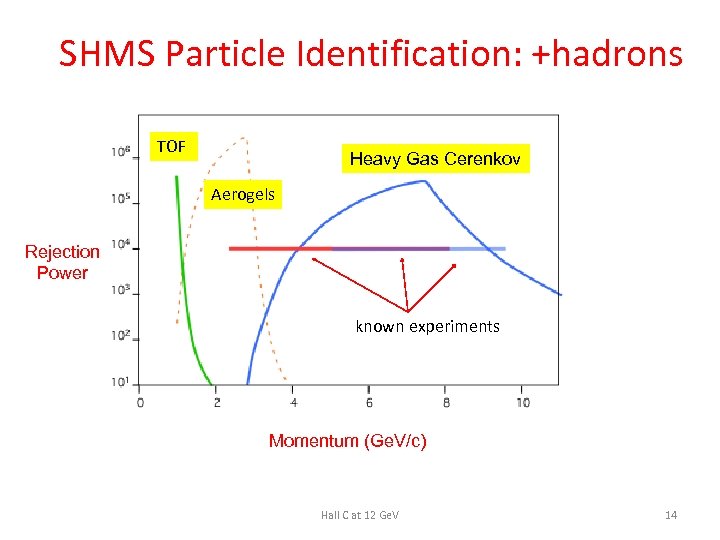 SHMS Particle Identification: +hadrons TOF Heavy Gas Cerenkov Aerogels Rejection Power known experiments Momentum (Ge. V/c) Hall C at 12 Ge. V 14
SHMS Particle Identification: +hadrons TOF Heavy Gas Cerenkov Aerogels Rejection Power known experiments Momentum (Ge. V/c) Hall C at 12 Ge. V 14
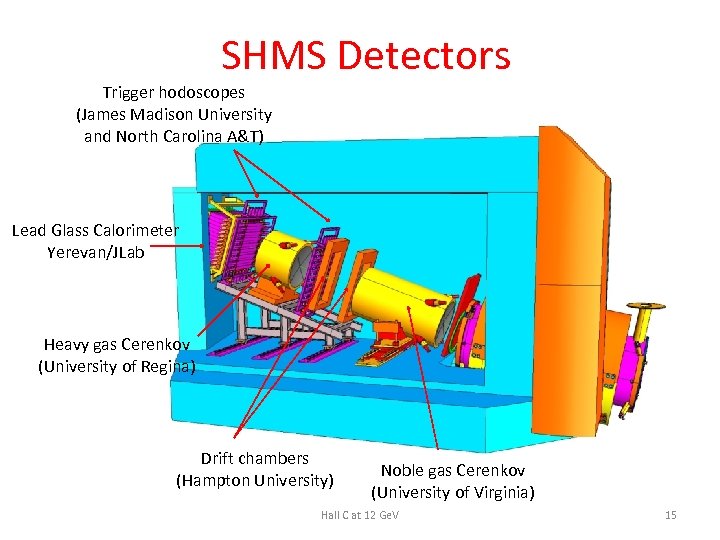 SHMS Detectors Trigger hodoscopes (James Madison University and North Carolina A&T) Lead Glass Calorimeter Yerevan/JLab Heavy gas Cerenkov (University of Regina) Drift chambers (Hampton University) Noble gas Cerenkov (University of Virginia) Hall C at 12 Ge. V 15
SHMS Detectors Trigger hodoscopes (James Madison University and North Carolina A&T) Lead Glass Calorimeter Yerevan/JLab Heavy gas Cerenkov (University of Regina) Drift chambers (Hampton University) Noble gas Cerenkov (University of Virginia) Hall C at 12 Ge. V 15
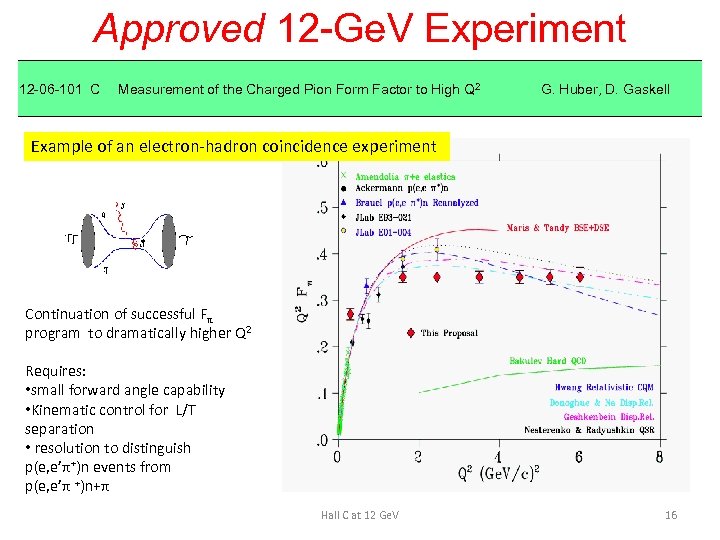 Approved 12 -Ge. V Experiment 12 -06 -101 C Measurement of the Charged Pion Form Factor to High Q 2 G. Huber, D. Gaskell Example of an electron-hadron coincidence experiment Continuation of successful Fπ program to dramatically higher Q 2 Requires: • small forward angle capability • Kinematic control for L/T separation • resolution to distinguish p(e, e’π+)n events from p(e, e’π +)n+π Hall C at 12 Ge. V 16
Approved 12 -Ge. V Experiment 12 -06 -101 C Measurement of the Charged Pion Form Factor to High Q 2 G. Huber, D. Gaskell Example of an electron-hadron coincidence experiment Continuation of successful Fπ program to dramatically higher Q 2 Requires: • small forward angle capability • Kinematic control for L/T separation • resolution to distinguish p(e, e’π+)n events from p(e, e’π +)n+π Hall C at 12 Ge. V 16
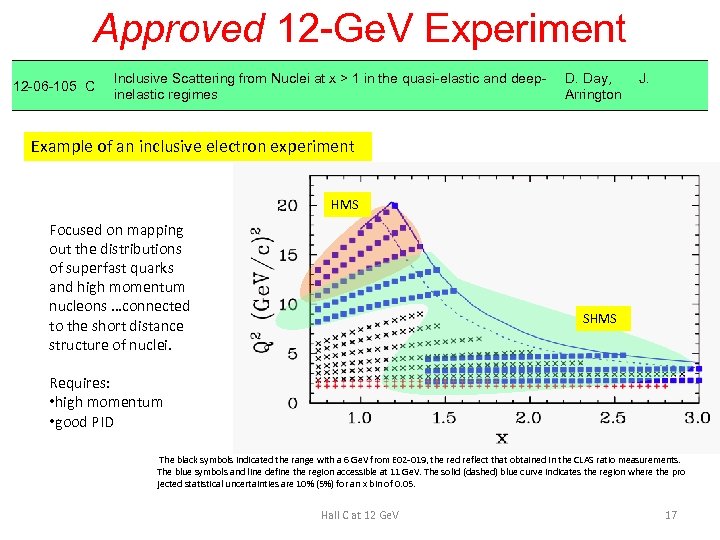 Approved 12 -Ge. V Experiment 12 -06 -105 C Inclusive Scattering from Nuclei at x > 1 in the quasi-elastic and deepinelastic regimes D. Day, Arrington J. Example of an inclusive electron experiment HMS Focused on mapping out the distributions of superfast quarks and high momentum nucleons …connected to the short distance structure of nuclei. SHMS Requires: • high momentum • good PID The black symbols indicated the range with a 6 Ge. V from E 02 -019, the red reflect that obtained in the CLAS ratio measurements. The blue symbols and line define the region accessible at 11 Ge. V. The solid (dashed) blue curve indicates the region where the pro jected statistical uncertainties are 10% (5%) for an x bin of 0. 05. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 17
Approved 12 -Ge. V Experiment 12 -06 -105 C Inclusive Scattering from Nuclei at x > 1 in the quasi-elastic and deepinelastic regimes D. Day, Arrington J. Example of an inclusive electron experiment HMS Focused on mapping out the distributions of superfast quarks and high momentum nucleons …connected to the short distance structure of nuclei. SHMS Requires: • high momentum • good PID The black symbols indicated the range with a 6 Ge. V from E 02 -019, the red reflect that obtained in the CLAS ratio measurements. The blue symbols and line define the region accessible at 11 Ge. V. The solid (dashed) blue curve indicates the region where the pro jected statistical uncertainties are 10% (5%) for an x bin of 0. 05. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 17
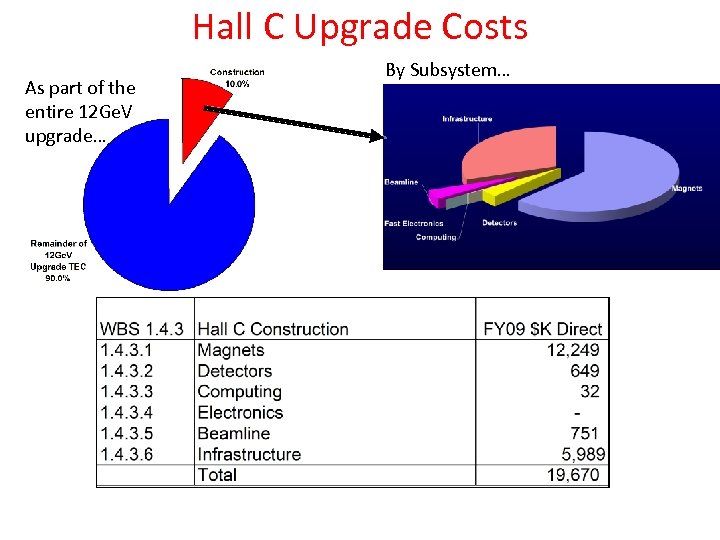 Hall C Upgrade Costs As part of the entire 12 Ge. V upgrade… By Subsystem…
Hall C Upgrade Costs As part of the entire 12 Ge. V upgrade… By Subsystem…
 Proposing Experiments at 12 Ge. V Hall C Jlab is an open laboratory. By this I mean that, if you have a great idea for one of our end-stations, you can propose it to our Program Advisory Committee (PAC) of mostly outside experts. Your proposal will be judged on the merit of the physics as well as the technical feasibility. An internal cospokesperson may be helpful but is not required. A tremendous amount of information can be gain from our website at http: //www. jlab. org/ and looking under topics such as “Nuclear Physics”, “Experiment Research”, and “ 12 Ge. V Upgrade”. Proposals now mostly fall into two categories: standard 12 Ge. V equipment, or major new detectors. Proponents are expected to help build or commission new apparatus. Of course, funding, manpower (both collaboration and Jlab), and multiendstation scheduling issues will eventually be looked at carefully. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 19
Proposing Experiments at 12 Ge. V Hall C Jlab is an open laboratory. By this I mean that, if you have a great idea for one of our end-stations, you can propose it to our Program Advisory Committee (PAC) of mostly outside experts. Your proposal will be judged on the merit of the physics as well as the technical feasibility. An internal cospokesperson may be helpful but is not required. A tremendous amount of information can be gain from our website at http: //www. jlab. org/ and looking under topics such as “Nuclear Physics”, “Experiment Research”, and “ 12 Ge. V Upgrade”. Proposals now mostly fall into two categories: standard 12 Ge. V equipment, or major new detectors. Proponents are expected to help build or commission new apparatus. Of course, funding, manpower (both collaboration and Jlab), and multiendstation scheduling issues will eventually be looked at carefully. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 19
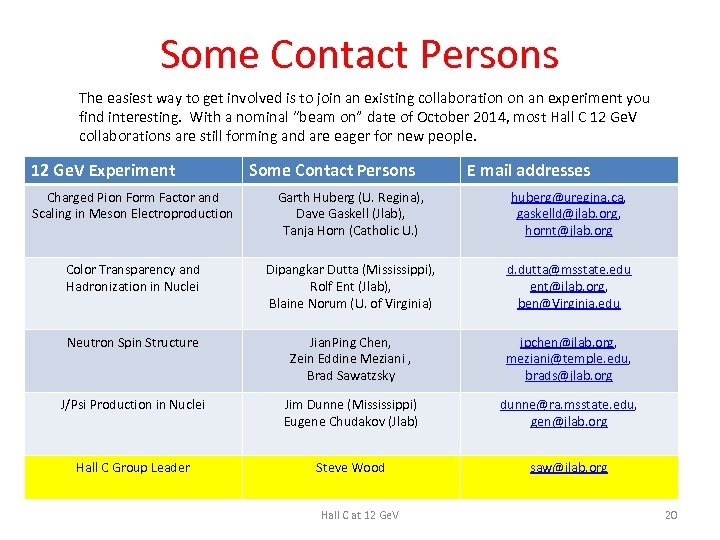 Some Contact Persons The easiest way to get involved is to join an existing collaboration on an experiment you find interesting. With a nominal “beam on” date of October 2014, most Hall C 12 Ge. V collaborations are still forming and are eager for new people. 12 Ge. V Experiment Some Contact Persons E mail addresses Charged Pion Form Factor and Scaling in Meson Electroproduction Garth Huberg (U. Regina), Dave Gaskell (Jlab), Tanja Horn (Catholic U. ) huberg@uregina. ca, gaskelld@jlab. org, hornt@jlab. org Color Transparency and Hadronization in Nuclei Dipangkar Dutta (Mississippi), Rolf Ent (Jlab), Blaine Norum (U. of Virginia) d. dutta@msstate. edu ent@jlab. org, ben@Virginia. edu Neutron Spin Structure Jian. Ping Chen, Zein Eddine Meziani , Brad Sawatzsky jpchen@jlab. org, meziani@temple. edu, brads@jlab. org J/Psi Production in Nuclei Jim Dunne (Mississippi) Eugene Chudakov (Jlab) dunne@ra. msstate. edu, gen@jlab. org Hall C Group Leader Steve Wood saw@jlab. org Hall C at 12 Ge. V 20
Some Contact Persons The easiest way to get involved is to join an existing collaboration on an experiment you find interesting. With a nominal “beam on” date of October 2014, most Hall C 12 Ge. V collaborations are still forming and are eager for new people. 12 Ge. V Experiment Some Contact Persons E mail addresses Charged Pion Form Factor and Scaling in Meson Electroproduction Garth Huberg (U. Regina), Dave Gaskell (Jlab), Tanja Horn (Catholic U. ) huberg@uregina. ca, gaskelld@jlab. org, hornt@jlab. org Color Transparency and Hadronization in Nuclei Dipangkar Dutta (Mississippi), Rolf Ent (Jlab), Blaine Norum (U. of Virginia) d. dutta@msstate. edu ent@jlab. org, ben@Virginia. edu Neutron Spin Structure Jian. Ping Chen, Zein Eddine Meziani , Brad Sawatzsky jpchen@jlab. org, meziani@temple. edu, brads@jlab. org J/Psi Production in Nuclei Jim Dunne (Mississippi) Eugene Chudakov (Jlab) dunne@ra. msstate. edu, gen@jlab. org Hall C Group Leader Steve Wood saw@jlab. org Hall C at 12 Ge. V 20
 Summary I’ve tried to introduce some of the standard apparatus for Hall C at 12 Ge. V. More detailed information on the SHMS can be obtained at http: //www. jlab. org/Hall-C/upgrade/index. html Hall C at 12 Ge. V 21
Summary I’ve tried to introduce some of the standard apparatus for Hall C at 12 Ge. V. More detailed information on the SHMS can be obtained at http: //www. jlab. org/Hall-C/upgrade/index. html Hall C at 12 Ge. V 21
 Acknowledgements Hall C colleagues Howard Fenker and Paul Brindza whose slides formed the basis of my talk. The organizers of this workshop for their invitation and the countless headaches they must have undergone. The workshop support staff for making it all work. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 22
Acknowledgements Hall C colleagues Howard Fenker and Paul Brindza whose slides formed the basis of my talk. The organizers of this workshop for their invitation and the countless headaches they must have undergone. The workshop support staff for making it all work. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 22
 Extras Hall C at 12 Ge. V 23
Extras Hall C at 12 Ge. V 23
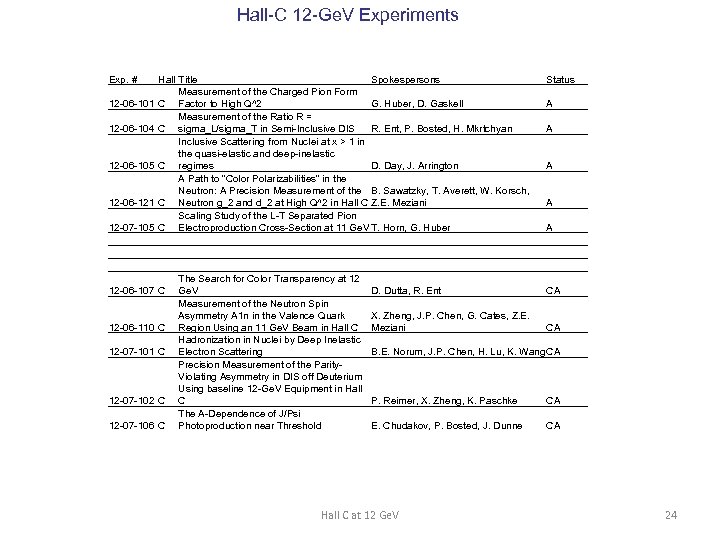 Hall-C 12 -Ge. V Experiments Exp. # 12 -06 -101 12 -06 -104 12 -06 -105 12 -06 -121 12 -07 -105 Hall Title Spokespersons Measurement of the Charged Pion Form C Factor to High Q^2 G. Huber, D. Gaskell Measurement of the Ratio R = C sigma_L/sigma_T in Semi-Inclusive DIS R. Ent, P. Bosted, H. Mkrtchyan Inclusive Scattering from Nuclei at x > 1 in the quasi-elastic and deep-inelastic C regimes D. Day, J. Arrington A Path to “Color Polarizabilities” in the Neutron: A Precision Measurement of the B. Sawatzky, T. Averett, W. Korsch, C Neutron g_2 and d_2 at High Q^2 in Hall C Z. E. Meziani Scaling Study of the L-T Separated Pion C Electroproduction Cross-Section at 11 Ge. V T. Horn, G. Huber 12 -06 -107 C 12 -06 -110 C 12 -07 -101 C 12 -07 -102 C 12 -07 -106 C The Search for Color Transparency at 12 Ge. V Measurement of the Neutron Spin Asymmetry A 1 n in the Valence Quark Region Using an 11 Ge. V Beam in Hall C Hadronization in Nuclei by Deep Inelastic Electron Scattering Precision Measurement of the Parity. Violating Asymmetry in DIS off Deuterium Using baseline 12 -Ge. V Equipment in Hall C The A-Dependence of J/Psi Photoproduction near Threshold Status A A A D. Dutta, R. Ent CA X. Zheng, J. P. Chen, G. Cates, Z. E. Meziani CA B. E. Norum, J. P. Chen, H. Lu, K. Wang. CA P. Reimer, X. Zheng, K. Paschke CA E. Chudakov, P. Bosted, J. Dunne CA Hall C at 12 Ge. V 24
Hall-C 12 -Ge. V Experiments Exp. # 12 -06 -101 12 -06 -104 12 -06 -105 12 -06 -121 12 -07 -105 Hall Title Spokespersons Measurement of the Charged Pion Form C Factor to High Q^2 G. Huber, D. Gaskell Measurement of the Ratio R = C sigma_L/sigma_T in Semi-Inclusive DIS R. Ent, P. Bosted, H. Mkrtchyan Inclusive Scattering from Nuclei at x > 1 in the quasi-elastic and deep-inelastic C regimes D. Day, J. Arrington A Path to “Color Polarizabilities” in the Neutron: A Precision Measurement of the B. Sawatzky, T. Averett, W. Korsch, C Neutron g_2 and d_2 at High Q^2 in Hall C Z. E. Meziani Scaling Study of the L-T Separated Pion C Electroproduction Cross-Section at 11 Ge. V T. Horn, G. Huber 12 -06 -107 C 12 -06 -110 C 12 -07 -101 C 12 -07 -102 C 12 -07 -106 C The Search for Color Transparency at 12 Ge. V Measurement of the Neutron Spin Asymmetry A 1 n in the Valence Quark Region Using an 11 Ge. V Beam in Hall C Hadronization in Nuclei by Deep Inelastic Electron Scattering Precision Measurement of the Parity. Violating Asymmetry in DIS off Deuterium Using baseline 12 -Ge. V Equipment in Hall C The A-Dependence of J/Psi Photoproduction near Threshold Status A A A D. Dutta, R. Ent CA X. Zheng, J. P. Chen, G. Cates, Z. E. Meziani CA B. E. Norum, J. P. Chen, H. Lu, K. Wang. CA P. Reimer, X. Zheng, K. Paschke CA E. Chudakov, P. Bosted, J. Dunne CA Hall C at 12 Ge. V 24
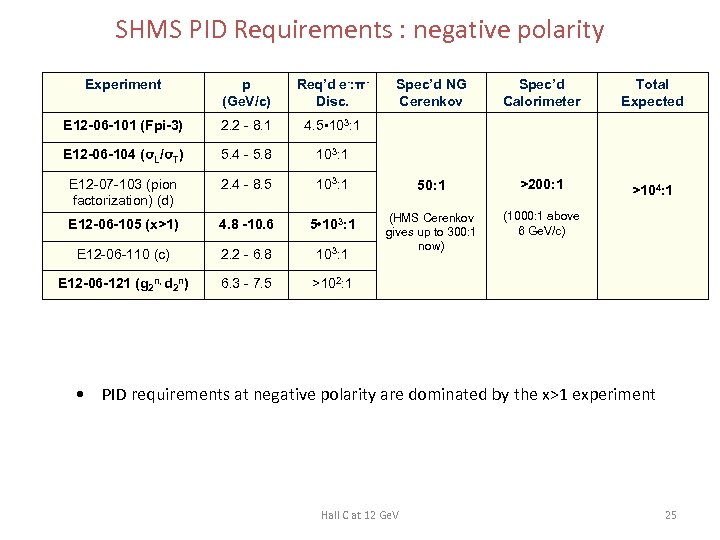 SHMS PID Requirements : negative polarity Experiment p (Ge. V/c) Req’d e-: πDisc. Spec’d NG Cerenkov Spec’d Calorimeter Total Expected E 12 -06 -101 (Fpi-3) 2. 2 - 8. 1 4. 5 • 103: 1 E 12 -06 -104 (σL/σT) 5. 4 - 5. 8 103: 1 E 12 -07 -103 (pion factorization) (d) 2. 4 - 8. 5 103: 1 50: 1 >200: 1 >104: 1 E 12 -06 -105 (x>1) 4. 8 -10. 6 5 • 103: 1 (1000: 1 above 6 Ge. V/c) E 12 -06 -110 (c) 2. 2 - 6. 8 103: 1 (HMS Cerenkov gives up to 300: 1 now) E 12 -06 -121 (g 2 n, d 2 n) 6. 3 - 7. 5 >102: 1 • PID requirements at negative polarity are dominated by the x>1 experiment Hall C at 12 Ge. V 25
SHMS PID Requirements : negative polarity Experiment p (Ge. V/c) Req’d e-: πDisc. Spec’d NG Cerenkov Spec’d Calorimeter Total Expected E 12 -06 -101 (Fpi-3) 2. 2 - 8. 1 4. 5 • 103: 1 E 12 -06 -104 (σL/σT) 5. 4 - 5. 8 103: 1 E 12 -07 -103 (pion factorization) (d) 2. 4 - 8. 5 103: 1 50: 1 >200: 1 >104: 1 E 12 -06 -105 (x>1) 4. 8 -10. 6 5 • 103: 1 (1000: 1 above 6 Ge. V/c) E 12 -06 -110 (c) 2. 2 - 6. 8 103: 1 (HMS Cerenkov gives up to 300: 1 now) E 12 -06 -121 (g 2 n, d 2 n) 6. 3 - 7. 5 >102: 1 • PID requirements at negative polarity are dominated by the x>1 experiment Hall C at 12 Ge. V 25
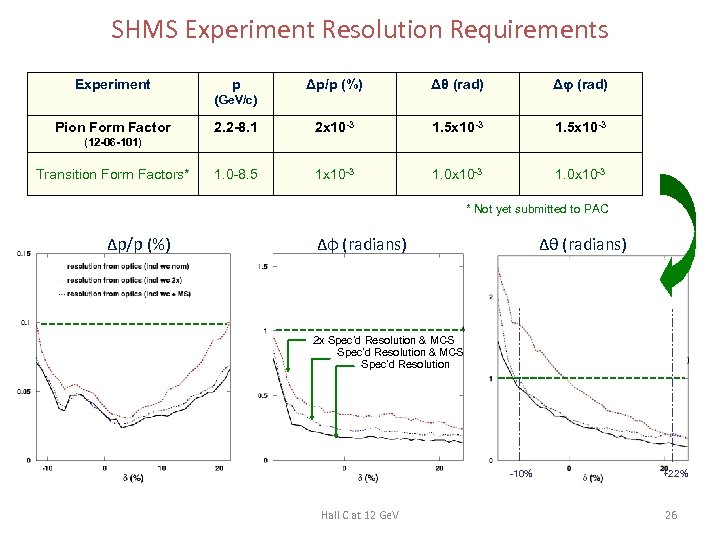 SHMS Experiment Resolution Requirements Experiment p Δp/p (%) Δθ (rad) Δφ (rad) 2. 2 -8. 1 2 x 10 -3 1. 5 x 10 -3 1. 0 -8. 5 1 x 10 -3 1. 0 x 10 -3 (Ge. V/c) Pion Form Factor (12 -06 -101) Transition Form Factors* * Not yet submitted to PAC Δp/p (%) Δφ (radians) Δθ (radians) 2 x Spec’d Resolution & MCS Spec’d Resolution -10% Hall C at 12 Ge. V +22% 26
SHMS Experiment Resolution Requirements Experiment p Δp/p (%) Δθ (rad) Δφ (rad) 2. 2 -8. 1 2 x 10 -3 1. 5 x 10 -3 1. 0 -8. 5 1 x 10 -3 1. 0 x 10 -3 (Ge. V/c) Pion Form Factor (12 -06 -101) Transition Form Factors* * Not yet submitted to PAC Δp/p (%) Δφ (radians) Δθ (radians) 2 x Spec’d Resolution & MCS Spec’d Resolution -10% Hall C at 12 Ge. V +22% 26
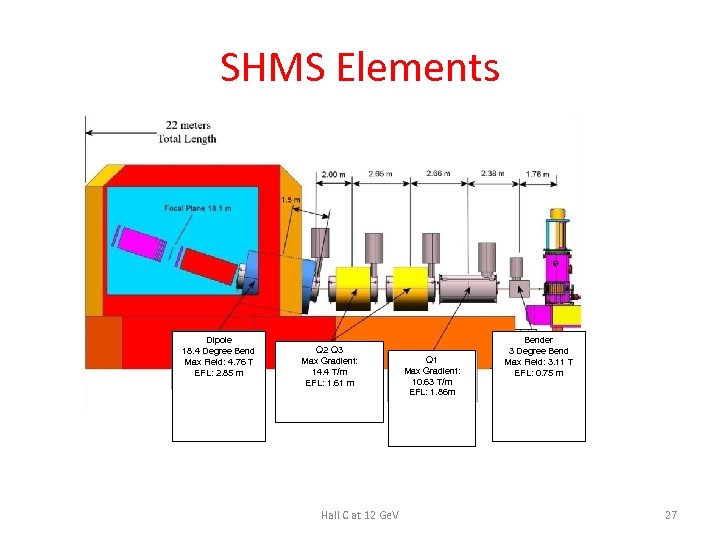 SHMS Elements Dipole 18. 4 Degree Bend Max Field: 4. 76 T EFL: 2. 85 m Q 2 Q 3 Max Gradient: 14. 4 T/m EFL: 1. 61 m Hall C at 12 Ge. V Q 1 Max Gradient: 10. 63 T/m EFL: 1. 86 m Bender 3 Degree Bend Max Field: 3. 11 T EFL: 0. 75 m 27
SHMS Elements Dipole 18. 4 Degree Bend Max Field: 4. 76 T EFL: 2. 85 m Q 2 Q 3 Max Gradient: 14. 4 T/m EFL: 1. 61 m Hall C at 12 Ge. V Q 1 Max Gradient: 10. 63 T/m EFL: 1. 86 m Bender 3 Degree Bend Max Field: 3. 11 T EFL: 0. 75 m 27
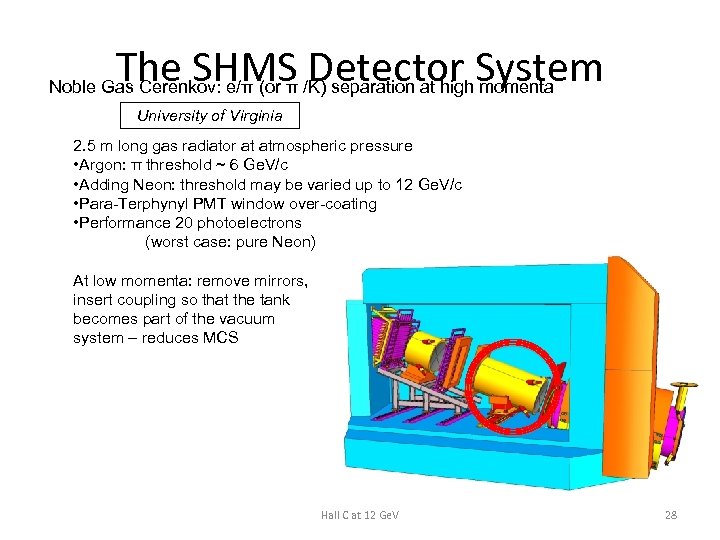 The SHMS Detector System Noble Gas Cerenkov: e/π (or π /K) separation at high momenta University of Virginia 2. 5 m long gas radiator at atmospheric pressure • Argon: π threshold ~ 6 Ge. V/c • Adding Neon: threshold may be varied up to 12 Ge. V/c • Para-Terphynyl PMT window over-coating • Performance 20 photoelectrons (worst case: pure Neon) At low momenta: remove mirrors, insert coupling so that the tank becomes part of the vacuum system – reduces MCS Hall C at 12 Ge. V 28
The SHMS Detector System Noble Gas Cerenkov: e/π (or π /K) separation at high momenta University of Virginia 2. 5 m long gas radiator at atmospheric pressure • Argon: π threshold ~ 6 Ge. V/c • Adding Neon: threshold may be varied up to 12 Ge. V/c • Para-Terphynyl PMT window over-coating • Performance 20 photoelectrons (worst case: pure Neon) At low momenta: remove mirrors, insert coupling so that the tank becomes part of the vacuum system – reduces MCS Hall C at 12 Ge. V 28
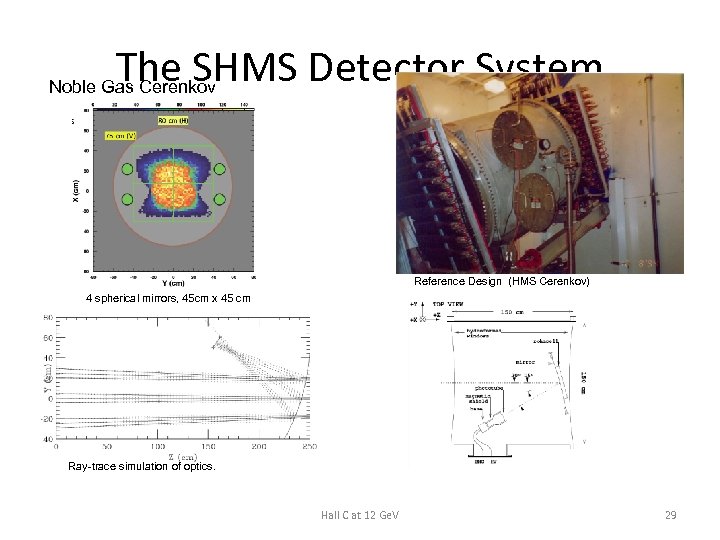 The SHMS Detector System Noble Gas Cerenkov Reference Design (HMS Cerenkov) 4 spherical mirrors, 45 cm x 45 cm Ray-trace simulation of optics. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 29
The SHMS Detector System Noble Gas Cerenkov Reference Design (HMS Cerenkov) 4 spherical mirrors, 45 cm x 45 cm Ray-trace simulation of optics. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 29
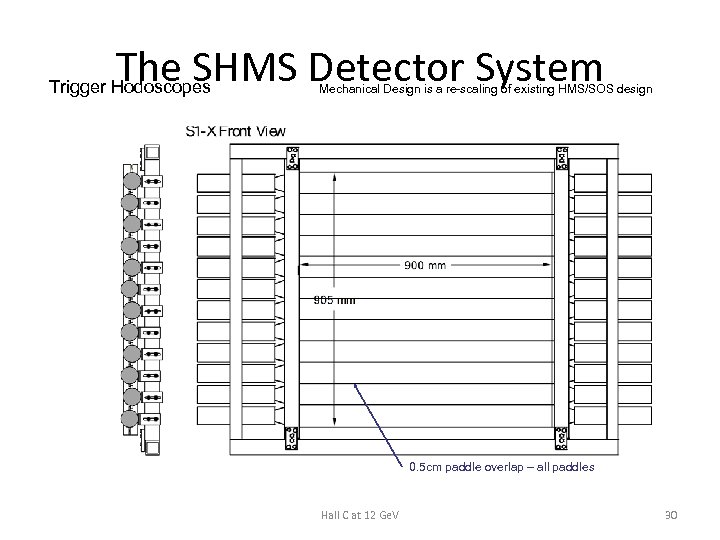 The SHMS Detector System Trigger Hodoscopes Mechanical Design is a re-scaling of existing HMS/SOS design 0. 5 cm paddle overlap – all paddles Hall C at 12 Ge. V 30
The SHMS Detector System Trigger Hodoscopes Mechanical Design is a re-scaling of existing HMS/SOS design 0. 5 cm paddle overlap – all paddles Hall C at 12 Ge. V 30
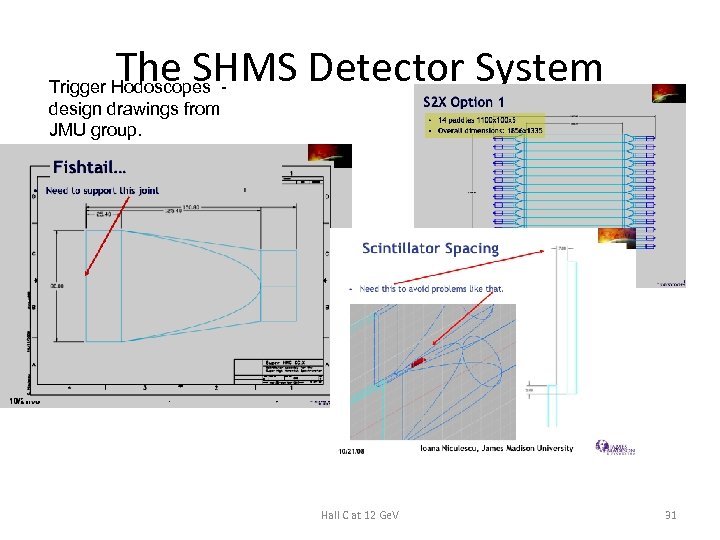 The SHMS Detector System Trigger Hodoscopes design drawings from JMU group. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 31
The SHMS Detector System Trigger Hodoscopes design drawings from JMU group. Hall C at 12 Ge. V 31
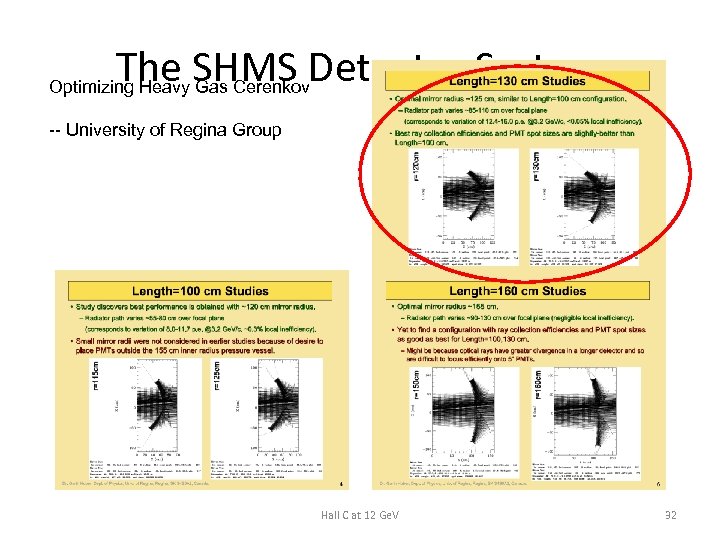 The SHMS Detector System Optimizing Heavy Gas Cerenkov -- University of Regina Group Hall C at 12 Ge. V 32
The SHMS Detector System Optimizing Heavy Gas Cerenkov -- University of Regina Group Hall C at 12 Ge. V 32
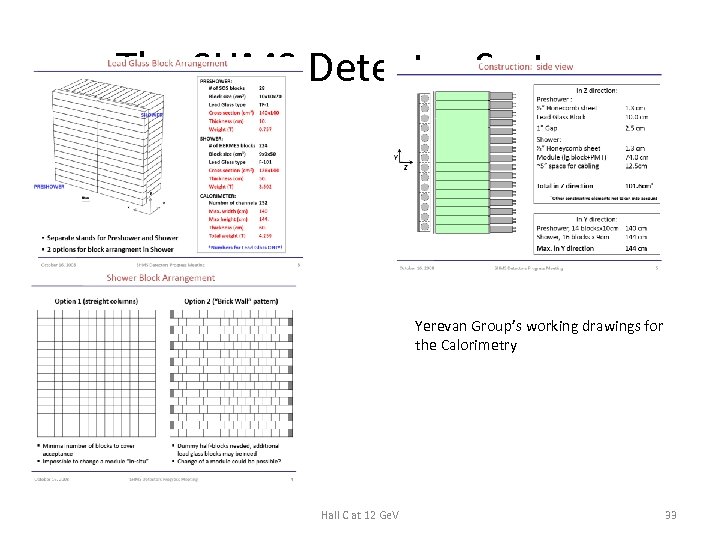 The SHMS Detector System Yerevan Group’s working drawings for the Calorimetry Hall C at 12 Ge. V 33
The SHMS Detector System Yerevan Group’s working drawings for the Calorimetry Hall C at 12 Ge. V 33
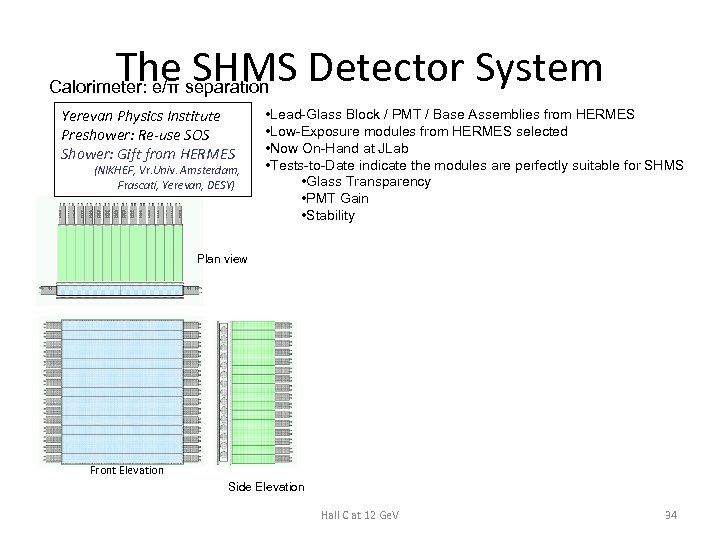 The SHMS Detector System Calorimeter: e/π separation Yerevan Physics Institute Preshower: Re-use SOS Shower: Gift from HERMES (NIKHEF, Vr. Univ. Amsterdam, Frascati, Yerevan, DESY) • Lead-Glass Block / PMT / Base Assemblies from HERMES • Low-Exposure modules from HERMES selected • Now On-Hand at JLab • Tests-to-Date indicate the modules are perfectly suitable for SHMS • Glass Transparency • PMT Gain • Stability Plan view Front Elevation Side Elevation Hall C at 12 Ge. V 34
The SHMS Detector System Calorimeter: e/π separation Yerevan Physics Institute Preshower: Re-use SOS Shower: Gift from HERMES (NIKHEF, Vr. Univ. Amsterdam, Frascati, Yerevan, DESY) • Lead-Glass Block / PMT / Base Assemblies from HERMES • Low-Exposure modules from HERMES selected • Now On-Hand at JLab • Tests-to-Date indicate the modules are perfectly suitable for SHMS • Glass Transparency • PMT Gain • Stability Plan view Front Elevation Side Elevation Hall C at 12 Ge. V 34
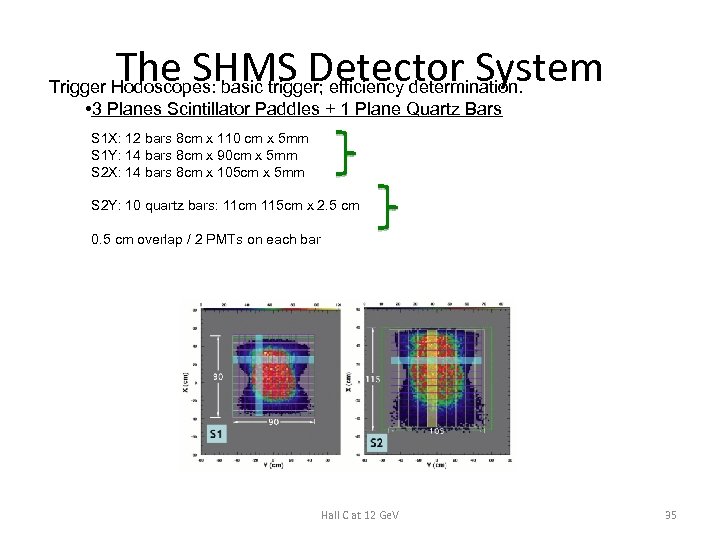 The SHMS Detector System Trigger Hodoscopes: basic trigger; efficiency determination. • 3 Planes Scintillator Paddles + 1 Plane Quartz Bars S 1 X: 12 bars 8 cm x 110 cm x 5 mm S 1 Y: 14 bars 8 cm x 90 cm x 5 mm S 2 X: 14 bars 8 cm x 105 cm x 5 mm S 2 Y: 10 quartz bars: 11 cm 115 cm x 2. 5 cm 0. 5 cm overlap / 2 PMTs on each bar Hall C at 12 Ge. V 35
The SHMS Detector System Trigger Hodoscopes: basic trigger; efficiency determination. • 3 Planes Scintillator Paddles + 1 Plane Quartz Bars S 1 X: 12 bars 8 cm x 110 cm x 5 mm S 1 Y: 14 bars 8 cm x 90 cm x 5 mm S 2 X: 14 bars 8 cm x 105 cm x 5 mm S 2 Y: 10 quartz bars: 11 cm 115 cm x 2. 5 cm 0. 5 cm overlap / 2 PMTs on each bar Hall C at 12 Ge. V 35
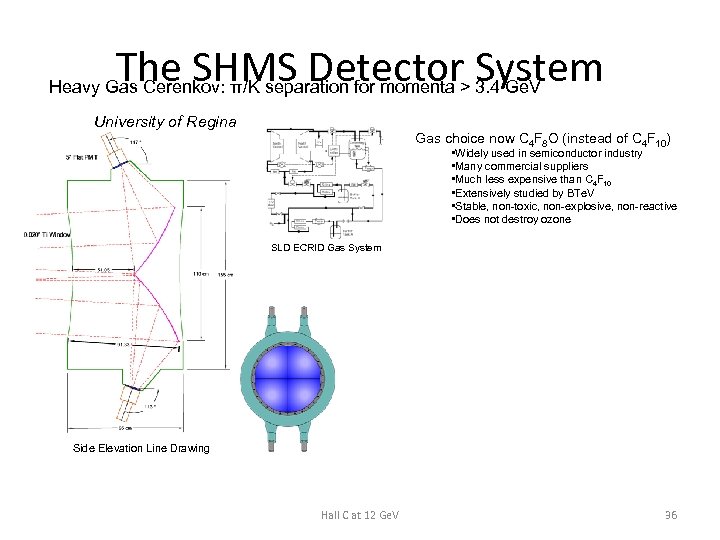 The SHMS Detector System Heavy Gas Cerenkov: π/K separation for momenta > 3. 4 Ge. V University of Regina Gas choice now C 4 F 8 O (instead of C 4 F 10) • Widely used in semiconductor industry • Many commercial suppliers • Much less expensive than C 4 F 10 • Extensively studied by BTe. V • Stable, non-toxic, non-explosive, non-reactive • Does not destroy ozone SLD ECRID Gas System Side Elevation Line Drawing Hall C at 12 Ge. V 36
The SHMS Detector System Heavy Gas Cerenkov: π/K separation for momenta > 3. 4 Ge. V University of Regina Gas choice now C 4 F 8 O (instead of C 4 F 10) • Widely used in semiconductor industry • Many commercial suppliers • Much less expensive than C 4 F 10 • Extensively studied by BTe. V • Stable, non-toxic, non-explosive, non-reactive • Does not destroy ozone SLD ECRID Gas System Side Elevation Line Drawing Hall C at 12 Ge. V 36
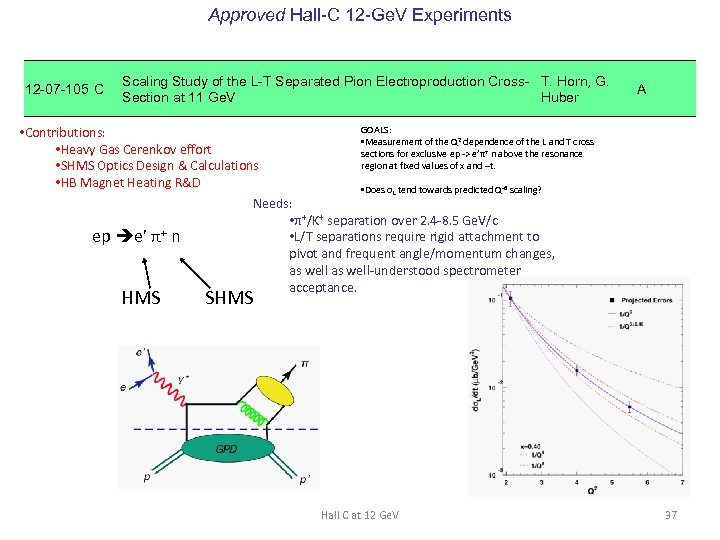 Approved Hall-C 12 -Ge. V Experiments 12 -07 -105 C Scaling Study of the L-T Separated Pion Electroproduction Cross- T. Horn, G. Section at 11 Ge. V Huber A GOALS: • Contributions: • Measurement of the Q 2 dependence of the L and T cross • Heavy Gas Cerenkov effort sections for exclusive ep -> e’π+ n above the resonance region at fixed values of x and –t. • SHMS Optics Design & Calculations • HB Magnet Heating R&D • Does σL tend towards predicted Q-6 scaling? Needs: • π+/K+ separation over 2. 4 -8. 5 Ge. V/c • L/T separations require rigid attachment to ep e’ π+ n pivot and frequent angle/momentum changes, as well-understood spectrometer acceptance. HMS SHMS Hall C at 12 Ge. V 37
Approved Hall-C 12 -Ge. V Experiments 12 -07 -105 C Scaling Study of the L-T Separated Pion Electroproduction Cross- T. Horn, G. Section at 11 Ge. V Huber A GOALS: • Contributions: • Measurement of the Q 2 dependence of the L and T cross • Heavy Gas Cerenkov effort sections for exclusive ep -> e’π+ n above the resonance region at fixed values of x and –t. • SHMS Optics Design & Calculations • HB Magnet Heating R&D • Does σL tend towards predicted Q-6 scaling? Needs: • π+/K+ separation over 2. 4 -8. 5 Ge. V/c • L/T separations require rigid attachment to ep e’ π+ n pivot and frequent angle/momentum changes, as well-understood spectrometer acceptance. HMS SHMS Hall C at 12 Ge. V 37
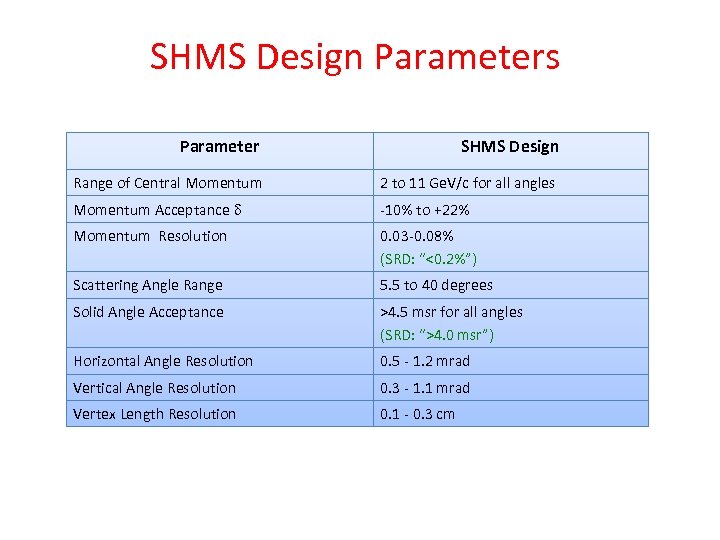 SHMS Design Parameters Parameter SHMS Design Range of Central Momentum 2 to 11 Ge. V/c for all angles Momentum Acceptance -10% to +22% Momentum Resolution 0. 03 -0. 08% (SRD: “<0. 2%”) Scattering Angle Range 5. 5 to 40 degrees Solid Angle Acceptance >4. 5 msr for all angles (SRD: “>4. 0 msr”) Horizontal Angle Resolution 0. 5 - 1. 2 mrad Vertical Angle Resolution 0. 3 - 1. 1 mrad Vertex Length Resolution 0. 1 - 0. 3 cm
SHMS Design Parameters Parameter SHMS Design Range of Central Momentum 2 to 11 Ge. V/c for all angles Momentum Acceptance -10% to +22% Momentum Resolution 0. 03 -0. 08% (SRD: “<0. 2%”) Scattering Angle Range 5. 5 to 40 degrees Solid Angle Acceptance >4. 5 msr for all angles (SRD: “>4. 0 msr”) Horizontal Angle Resolution 0. 5 - 1. 2 mrad Vertical Angle Resolution 0. 3 - 1. 1 mrad Vertex Length Resolution 0. 1 - 0. 3 cm
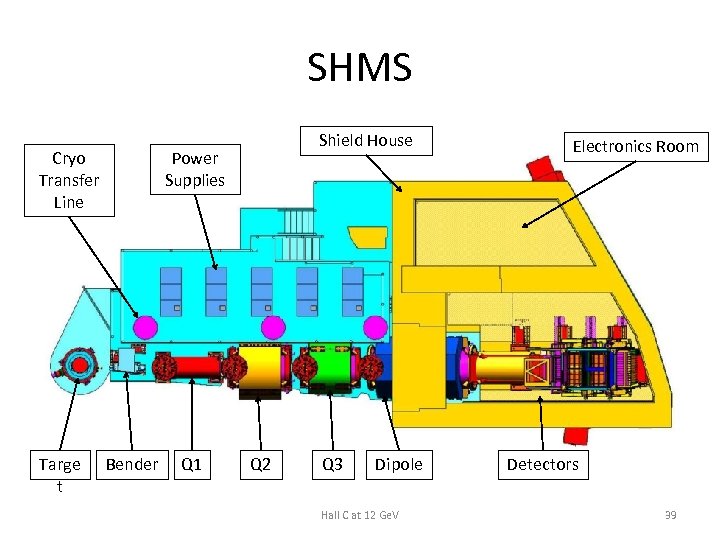 SHMS Cryo Transfer Line Targe t Shield House Power Supplies Bender Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 Dipole Hall C at 12 Ge. V Electronics Room Detectors 39
SHMS Cryo Transfer Line Targe t Shield House Power Supplies Bender Q 1 Q 2 Q 3 Dipole Hall C at 12 Ge. V Electronics Room Detectors 39


