f82a94a80b31194d8f2e516c21754471.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Hal. World Re-Development Creating a Single-Entry Portal: Overview Employee Central. Migrating Hal. World to a personalized portal environment – Employee Central – supported by three major components: • Portal • Content Management System -- CMS • Taxonomy Learning Objectives: To learn all the basics, including governance, about Halliburton’s Portal, Content Management System (CMS), and Taxonomy and what these components provide for Halliburton’s Employee Central. 1
Hal. World Re-Development Creating a Single-Entry Portal: Overview Employee Central. Migrating Hal. World to a personalized portal environment – Employee Central – supported by three major components: • Portal • Content Management System -- CMS • Taxonomy Learning Objectives: To learn all the basics, including governance, about Halliburton’s Portal, Content Management System (CMS), and Taxonomy and what these components provide for Halliburton’s Employee Central. 1
 Portal Employee Central. 2
Portal Employee Central. 2
 Industry leaders and analysts recognize the value in employee portals to improve their businesses “GE’s new online travel center has saved GE $200 million this year in improved efficiencies and reduced travel. Altogether, according to GE executives, online process improvements will shave off about $1. 6 billion in costs for this year and up to $10 billion in coming years. ” – e-Week article on GE’s “digitization” effort Cisco’s corporate intranet gets 28 million page views per month and has processed over $200 million in internal purchasing transactions. Employee productivity has increased 5%. – Various articles on Cisco’s intranet efforts “In 2001, IBM’s intranet surpassed all channels – internal or external – as the most credible, preferred and useful source of information about the company. ” – IBM Global Employee Survey “For enterprises that adopt a strategic view, 80 percent of successful ebusiness transformations will include an explicit portal program through 2006 (0. 8 probability). ” – Gartner Group portal paper Halliburton, like GE, IBM, and Cisco, will derive great value from its employee portal 3
Industry leaders and analysts recognize the value in employee portals to improve their businesses “GE’s new online travel center has saved GE $200 million this year in improved efficiencies and reduced travel. Altogether, according to GE executives, online process improvements will shave off about $1. 6 billion in costs for this year and up to $10 billion in coming years. ” – e-Week article on GE’s “digitization” effort Cisco’s corporate intranet gets 28 million page views per month and has processed over $200 million in internal purchasing transactions. Employee productivity has increased 5%. – Various articles on Cisco’s intranet efforts “In 2001, IBM’s intranet surpassed all channels – internal or external – as the most credible, preferred and useful source of information about the company. ” – IBM Global Employee Survey “For enterprises that adopt a strategic view, 80 percent of successful ebusiness transformations will include an explicit portal program through 2006 (0. 8 probability). ” – Gartner Group portal paper Halliburton, like GE, IBM, and Cisco, will derive great value from its employee portal 3
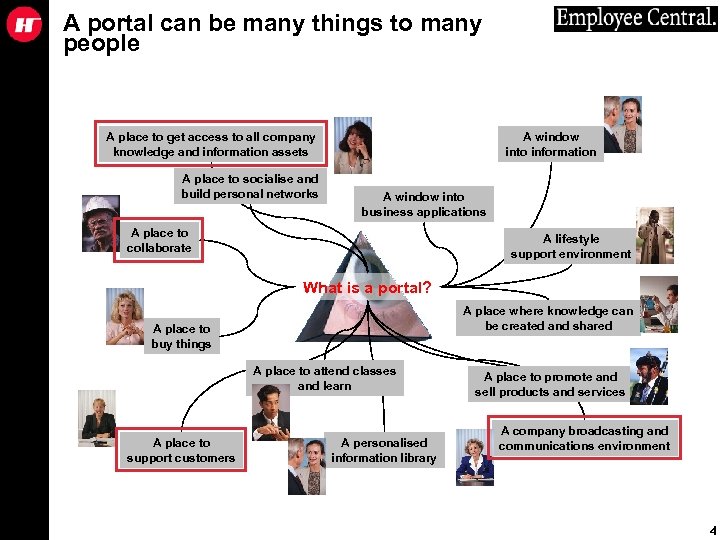 A portal can be many things to many people A place to get access to all company knowledge and information assets A place to socialise and build personal networks A window into information A window into business applications A place to collaborate A lifestyle support environment What is a portal? A place where knowledge can be created and shared A place to buy things A place to attend classes and learn A place to support customers A personalised information library A place to promote and sell products and services A company broadcasting and communications environment 4
A portal can be many things to many people A place to get access to all company knowledge and information assets A place to socialise and build personal networks A window into information A window into business applications A place to collaborate A lifestyle support environment What is a portal? A place where knowledge can be created and shared A place to buy things A place to attend classes and learn A place to support customers A personalised information library A place to promote and sell products and services A company broadcasting and communications environment 4
 Employee Central Defined Employee Central has three key attributes 1) It integrates applications, functions, content, and users. 2) It provides access to information employees need anywhere, anytime. 3) It is personalized to the role, location, and organization of its user, which helps strengthen and automate workflows. 5
Employee Central Defined Employee Central has three key attributes 1) It integrates applications, functions, content, and users. 2) It provides access to information employees need anywhere, anytime. 3) It is personalized to the role, location, and organization of its user, which helps strengthen and automate workflows. 5
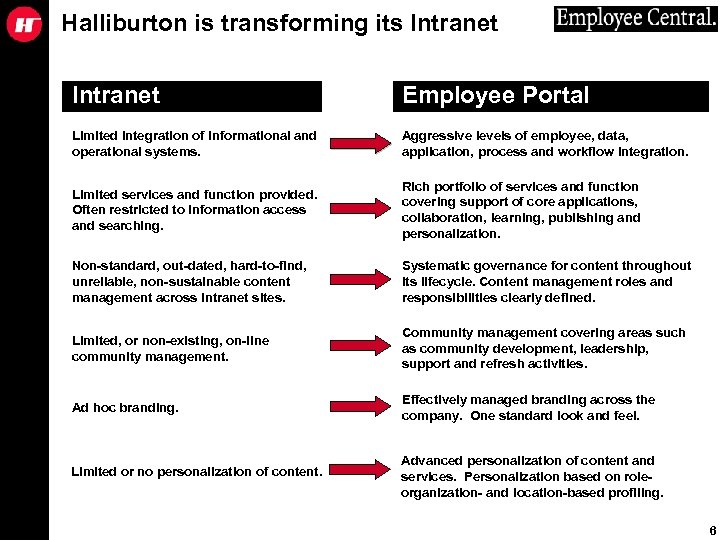 Halliburton is transforming its Intranet Employee Portal Limited integration of informational and operational systems. Aggressive levels of employee, data, application, process and workflow integration. Limited services and function provided. Often restricted to information access and searching. Rich portfolio of services and function covering support of core applications, collaboration, learning, publishing and personalization. Non-standard, out-dated, hard-to-find, unreliable, non-sustainable content management across Intranet sites. Systematic governance for content throughout its lifecycle. Content management roles and responsibilities clearly defined. Limited, or non-existing, on-line community management. Community management covering areas such as community development, leadership, support and refresh activities. Ad hoc branding. Effectively managed branding across the company. One standard look and feel. Limited or no personalization of content. Advanced personalization of content and services. Personalization based on role- organization- and location-based profiling. 6
Halliburton is transforming its Intranet Employee Portal Limited integration of informational and operational systems. Aggressive levels of employee, data, application, process and workflow integration. Limited services and function provided. Often restricted to information access and searching. Rich portfolio of services and function covering support of core applications, collaboration, learning, publishing and personalization. Non-standard, out-dated, hard-to-find, unreliable, non-sustainable content management across Intranet sites. Systematic governance for content throughout its lifecycle. Content management roles and responsibilities clearly defined. Limited, or non-existing, on-line community management. Community management covering areas such as community development, leadership, support and refresh activities. Ad hoc branding. Effectively managed branding across the company. One standard look and feel. Limited or no personalization of content. Advanced personalization of content and services. Personalization based on role- organization- and location-based profiling. 6
 Halliburton Intranet Discovery… what employees said “It is a vast source of information, if you know where to find it. ” “…too Houston-centric…” “It’s a garden full of weeds. ” “I don’t rely on Hal. World. ” “I don’t think to use Hal. World first. ” “No one owns Hal. World. ” “ There’s no solid process for managing content. ” “We need balanced governance, control with flexibility” Source: AGENCY. COM 7
Halliburton Intranet Discovery… what employees said “It is a vast source of information, if you know where to find it. ” “…too Houston-centric…” “It’s a garden full of weeds. ” “I don’t rely on Hal. World. ” “I don’t think to use Hal. World first. ” “No one owns Hal. World. ” “ There’s no solid process for managing content. ” “We need balanced governance, control with flexibility” Source: AGENCY. COM 7
 Employee Central Vision Effectively use online technology to improve workforce productivity… • • …that integrates: employee to business processes, …leading to better: employee to supplier and employee to customer relations. 8
Employee Central Vision Effectively use online technology to improve workforce productivity… • • …that integrates: employee to business processes, …leading to better: employee to supplier and employee to customer relations. 8
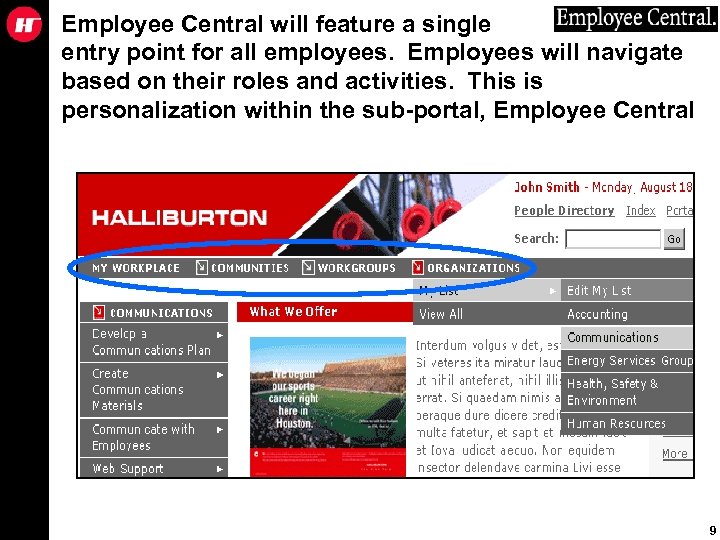 Employee Central will feature a single entry point for all employees. Employees will navigate based on their roles and activities. This is personalization within the sub-portal, Employee Central 9
Employee Central will feature a single entry point for all employees. Employees will navigate based on their roles and activities. This is personalization within the sub-portal, Employee Central 9
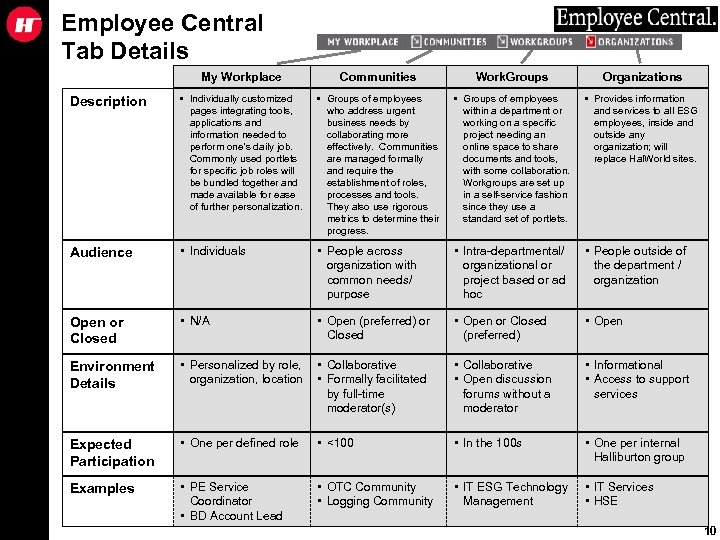 Employee Central Tab Details My Workplace Communities Work. Groups Organizations Description • Individually customized pages integrating tools, applications and information needed to perform one’s daily job. Commonly used portlets for specific job roles will be bundled together and made available for ease of further personalization. • Groups of employees who address urgent business needs by collaborating more effectively. Communities are managed formally and require the establishment of roles, processes and tools. They also use rigorous metrics to determine their progress. • Groups of employees within a department or working on a specific project needing an online space to share documents and tools, with some collaboration. Workgroups are set up in a self-service fashion since they use a standard set of portlets. • Provides information and services to all ESG employees, inside and outside any organization; will replace Hal. World sites. Audience • Individuals • People across organization with common needs/ purpose • Intra-departmental/ organizational or project based or ad hoc • People outside of the department / organization Open or Closed • N/A • Open (preferred) or Closed • Open or Closed (preferred) • Open Environment Details • Personalized by role, organization, location • Collaborative • Formally facilitated by full-time moderator(s) • Collaborative • Open discussion forums without a moderator • Informational • Access to support services Expected Participation • One per defined role • <100 • In the 100 s • One per internal Halliburton group Examples • PE Service Coordinator • BD Account Lead • OTC Community • Logging Community • IT ESG Technology Management • IT Services • HSE 10
Employee Central Tab Details My Workplace Communities Work. Groups Organizations Description • Individually customized pages integrating tools, applications and information needed to perform one’s daily job. Commonly used portlets for specific job roles will be bundled together and made available for ease of further personalization. • Groups of employees who address urgent business needs by collaborating more effectively. Communities are managed formally and require the establishment of roles, processes and tools. They also use rigorous metrics to determine their progress. • Groups of employees within a department or working on a specific project needing an online space to share documents and tools, with some collaboration. Workgroups are set up in a self-service fashion since they use a standard set of portlets. • Provides information and services to all ESG employees, inside and outside any organization; will replace Hal. World sites. Audience • Individuals • People across organization with common needs/ purpose • Intra-departmental/ organizational or project based or ad hoc • People outside of the department / organization Open or Closed • N/A • Open (preferred) or Closed • Open or Closed (preferred) • Open Environment Details • Personalized by role, organization, location • Collaborative • Formally facilitated by full-time moderator(s) • Collaborative • Open discussion forums without a moderator • Informational • Access to support services Expected Participation • One per defined role • <100 • In the 100 s • One per internal Halliburton group Examples • PE Service Coordinator • BD Account Lead • OTC Community • Logging Community • IT ESG Technology Management • IT Services • HSE 10
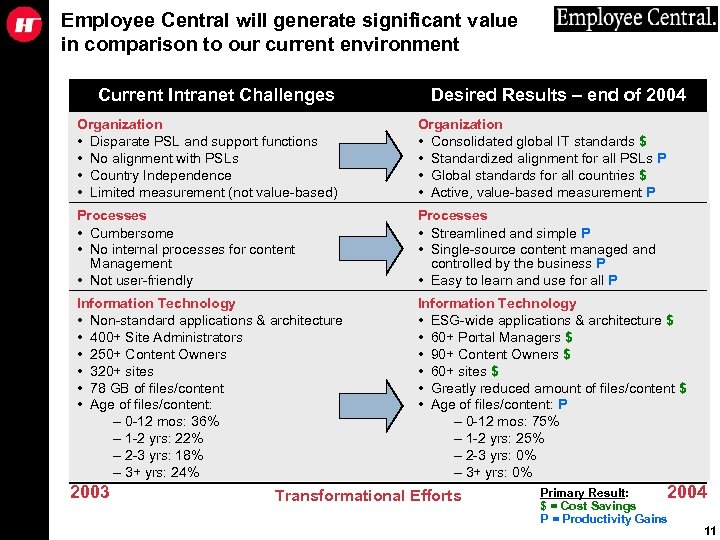 Employee Central will generate significant value in comparison to our current environment Current Intranet Challenges Desired Results – end of 2004 Organization • Disparate PSL and support functions • No alignment with PSLs • Country Independence • Limited measurement (not value-based) Organization • Consolidated global IT standards $ • Standardized alignment for all PSLs P • Global standards for all countries $ • Active, value-based measurement P Processes • Cumbersome • No internal processes for content Management • Not user-friendly Processes • Streamlined and simple P • Single-source content managed and controlled by the business P • Easy to learn and use for all P Information Technology • Non-standard applications & architecture • 400+ Site Administrators • 250+ Content Owners • 320+ sites • 78 GB of files/content • Age of files/content: – 0 -12 mos: 36% – 1 -2 yrs: 22% – 2 -3 yrs: 18% – 3+ yrs: 24% Information Technology • ESG-wide applications & architecture $ • 60+ Portal Managers $ • 90+ Content Owners $ • 60+ sites $ • Greatly reduced amount of files/content $ • Age of files/content: P – 0 -12 mos: 75% – 1 -2 yrs: 25% – 2 -3 yrs: 0% – 3+ yrs: 0% 2003 Transformational Efforts Primary Result: 2004 $ = Cost Savings P = Productivity Gains 11
Employee Central will generate significant value in comparison to our current environment Current Intranet Challenges Desired Results – end of 2004 Organization • Disparate PSL and support functions • No alignment with PSLs • Country Independence • Limited measurement (not value-based) Organization • Consolidated global IT standards $ • Standardized alignment for all PSLs P • Global standards for all countries $ • Active, value-based measurement P Processes • Cumbersome • No internal processes for content Management • Not user-friendly Processes • Streamlined and simple P • Single-source content managed and controlled by the business P • Easy to learn and use for all P Information Technology • Non-standard applications & architecture • 400+ Site Administrators • 250+ Content Owners • 320+ sites • 78 GB of files/content • Age of files/content: – 0 -12 mos: 36% – 1 -2 yrs: 22% – 2 -3 yrs: 18% – 3+ yrs: 24% Information Technology • ESG-wide applications & architecture $ • 60+ Portal Managers $ • 90+ Content Owners $ • 60+ sites $ • Greatly reduced amount of files/content $ • Age of files/content: P – 0 -12 mos: 75% – 1 -2 yrs: 25% – 2 -3 yrs: 0% – 3+ yrs: 0% 2003 Transformational Efforts Primary Result: 2004 $ = Cost Savings P = Productivity Gains 11
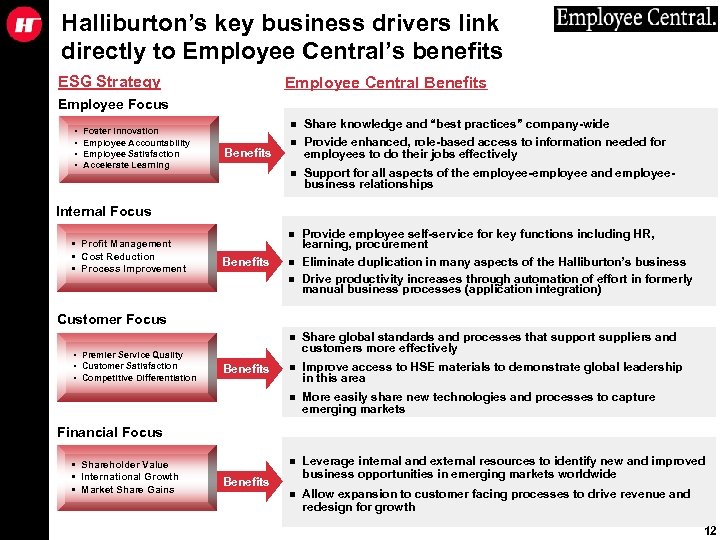 Halliburton’s key business drivers link directly to Employee Central’s benefits ESG Strategy Employee Central Benefits Employee Focus • • Foster Innovation Employee Accountability Employee Satisfaction Accelerate Learning n n Provide enhanced, role-based access to information needed for employees to do their jobs effectively n Support for all aspects of the employee-employee and employeebusiness relationships n Benefits Share knowledge and “best practices” company-wide Provide employee self-service for key functions including HR, learning, procurement Eliminate duplication in many aspects of the Halliburton’s business Drive productivity increases through automation of effort in formerly manual business processes (application integration) Internal Focus • Profit Management • Cost Reduction • Process Improvement Benefits n n Customer Focus n Improve access to HSE materials to demonstrate global leadership in this area More easily share new technologies and processes to capture emerging markets n Benefits n n • Premier Service Quality • Customer Satisfaction • Competitive Differentiation Share global standards and processes that support suppliers and customers more effectively Leverage internal and external resources to identify new and improved business opportunities in emerging markets worldwide n Allow expansion to customer facing processes to drive revenue and redesign for growth Financial Focus • Shareholder Value • International Growth • Market Share Gains Benefits 12
Halliburton’s key business drivers link directly to Employee Central’s benefits ESG Strategy Employee Central Benefits Employee Focus • • Foster Innovation Employee Accountability Employee Satisfaction Accelerate Learning n n Provide enhanced, role-based access to information needed for employees to do their jobs effectively n Support for all aspects of the employee-employee and employeebusiness relationships n Benefits Share knowledge and “best practices” company-wide Provide employee self-service for key functions including HR, learning, procurement Eliminate duplication in many aspects of the Halliburton’s business Drive productivity increases through automation of effort in formerly manual business processes (application integration) Internal Focus • Profit Management • Cost Reduction • Process Improvement Benefits n n Customer Focus n Improve access to HSE materials to demonstrate global leadership in this area More easily share new technologies and processes to capture emerging markets n Benefits n n • Premier Service Quality • Customer Satisfaction • Competitive Differentiation Share global standards and processes that support suppliers and customers more effectively Leverage internal and external resources to identify new and improved business opportunities in emerging markets worldwide n Allow expansion to customer facing processes to drive revenue and redesign for growth Financial Focus • Shareholder Value • International Growth • Market Share Gains Benefits 12
 Content Management System (CMS) Employee Central. What is Content Management? Content Management is a broad term referring to applications and processes to manage Web content, document content and e-commerce-focused content. Managing content includes the steps to design, create, implement, modify, archive, review, approve and deploy. 13
Content Management System (CMS) Employee Central. What is Content Management? Content Management is a broad term referring to applications and processes to manage Web content, document content and e-commerce-focused content. Managing content includes the steps to design, create, implement, modify, archive, review, approve and deploy. 13
 Overview • After extensive evaluations, Halliburton chose Interwoven as the application for the enterprise-wide Content Management System -- CMS • Interwoven leverages our enterprise-wide taxonomy • Interwoven compliments our Plumtree Portal • Interwoven’s key components: – Team. Site “Web. Desk” (application user interface) – Metatagger (web-based tagging interface) – Workflow notification (e-mails) • Sample actions (roles): – Review Documents – Tag Documents – Approve Documents 14
Overview • After extensive evaluations, Halliburton chose Interwoven as the application for the enterprise-wide Content Management System -- CMS • Interwoven leverages our enterprise-wide taxonomy • Interwoven compliments our Plumtree Portal • Interwoven’s key components: – Team. Site “Web. Desk” (application user interface) – Metatagger (web-based tagging interface) – Workflow notification (e-mails) • Sample actions (roles): – Review Documents – Tag Documents – Approve Documents 14
 What are the benefits of CMS? • Enterprise-wide Benefits: – Lower costs by standardizing our content management processes – Single source for internal and external content – Increased content quality • Other Benefits for CMS Users: – Complete content management process flow – One content source (to maintain) for multiple venues – Taxonomy integration to enhance search capabilities, improving content access and reuse – Processes improved, with streamlined content to portal delivery – Features such as Email Notification – to renew, update, and remove content – Preview Capability, Greater Report Generating, and Versioning/Rollback 15
What are the benefits of CMS? • Enterprise-wide Benefits: – Lower costs by standardizing our content management processes – Single source for internal and external content – Increased content quality • Other Benefits for CMS Users: – Complete content management process flow – One content source (to maintain) for multiple venues – Taxonomy integration to enhance search capabilities, improving content access and reuse – Processes improved, with streamlined content to portal delivery – Features such as Email Notification – to renew, update, and remove content – Preview Capability, Greater Report Generating, and Versioning/Rollback 15
 Future Benefits • Additional content creation sources • Live content editing for additional Content Owners/Authors • Continuing reduction in costs associated with duplicative content 16
Future Benefits • Additional content creation sources • Live content editing for additional Content Owners/Authors • Continuing reduction in costs associated with duplicative content 16
 Challenges • This is a new application • There is a learning curve • Effort will be needed to prepare/update existing content • A new approach to classifying – an Enterprise-wide Taxonomy 17
Challenges • This is a new application • There is a learning curve • Effort will be needed to prepare/update existing content • A new approach to classifying – an Enterprise-wide Taxonomy 17
 Taxonomy Employee Central. 18
Taxonomy Employee Central. 18
 Taxonomy What is taxonomy? • Taxonomy is the science or technique of classification or categorization. The method is to create a series of hierarchical groups to make them easier to identify, study, or locate. • A taxonomy has the following elements: – List of standard terms – Hierarchical relationships – Cross references Why are taxonomies important? • Taxonomies are important because they provide a framework for users to efficiently and effectively search through large volumes or information in order to find what they need. Taxonomies increase efficiency by assisting users to find the categories of information. Taxonomies also improve effectiveness by displaying relevant information based upon the context of the query. • In addition, taxonomies are important because they can help focus users on additional categories of information that may provide additional context to an issue on Employee Central. 19
Taxonomy What is taxonomy? • Taxonomy is the science or technique of classification or categorization. The method is to create a series of hierarchical groups to make them easier to identify, study, or locate. • A taxonomy has the following elements: – List of standard terms – Hierarchical relationships – Cross references Why are taxonomies important? • Taxonomies are important because they provide a framework for users to efficiently and effectively search through large volumes or information in order to find what they need. Taxonomies increase efficiency by assisting users to find the categories of information. Taxonomies also improve effectiveness by displaying relevant information based upon the context of the query. • In addition, taxonomies are important because they can help focus users on additional categories of information that may provide additional context to an issue on Employee Central. 19
 Taxonomy (categories) (w/definitions) • Content Type*: These are classifications of information that help filter the type of content. For example, sales and marketing material is typically not to the same technical level as a procedure or policy would be. • Security*: Identifying access to content – restricted, confidential, internal use, public access. • Location*: These are “places on earth” that are generally well known to everyone. Although we may think of NWA's as a place, they are really just a collection of Locations. • Organization*: A collection of people organized in PSL & sub PSL groupings. Our customers do not generally care about our organization. • E & P Lifecycle: This is reflective of a normal working timeline since it represents the serial sequence of events in the life of a well. Many documents relate to several of the lifecycle categories. • Business Process: This relates the document to the HMS system. Many documents relate to several Business Process categories but the majority of the documents are under categories called “Develop Solutions” and "Execute and maintain Business. ” • HSE: Categories of Health Safety & Environment. Note that the HSE facet actually contains HSE categories of information. • Product Groups: These are high-level Services or high-level (large category) Products that a customer understands. Sub Categories of Product Groups are smaller groupings of services or Products. For example, “Drill Bits” is a product group and “PDC bits” is a subcategory of Drill Bits. • Tools & Components: These are the downhole tools that are used to perform services or make up products. Note that a 6" bit is a tool. • Oil, Gas, Chemicals & Lubricants: These are the chemicals, additives, etc that make up the chemical services we offer. • Challenges: This is the root problem that a customer faces. Anything that is a service in our price book is not challenge. Challenges are generally reservoir- and environment-related. • Other Materials & Equipment: These are basic materials like cement & salt; as well as items that are purchased from others like pumps, trucks and cables. Most of the surface equipment falls in this category. * = (likely) Required Fields 20
Taxonomy (categories) (w/definitions) • Content Type*: These are classifications of information that help filter the type of content. For example, sales and marketing material is typically not to the same technical level as a procedure or policy would be. • Security*: Identifying access to content – restricted, confidential, internal use, public access. • Location*: These are “places on earth” that are generally well known to everyone. Although we may think of NWA's as a place, they are really just a collection of Locations. • Organization*: A collection of people organized in PSL & sub PSL groupings. Our customers do not generally care about our organization. • E & P Lifecycle: This is reflective of a normal working timeline since it represents the serial sequence of events in the life of a well. Many documents relate to several of the lifecycle categories. • Business Process: This relates the document to the HMS system. Many documents relate to several Business Process categories but the majority of the documents are under categories called “Develop Solutions” and "Execute and maintain Business. ” • HSE: Categories of Health Safety & Environment. Note that the HSE facet actually contains HSE categories of information. • Product Groups: These are high-level Services or high-level (large category) Products that a customer understands. Sub Categories of Product Groups are smaller groupings of services or Products. For example, “Drill Bits” is a product group and “PDC bits” is a subcategory of Drill Bits. • Tools & Components: These are the downhole tools that are used to perform services or make up products. Note that a 6" bit is a tool. • Oil, Gas, Chemicals & Lubricants: These are the chemicals, additives, etc that make up the chemical services we offer. • Challenges: This is the root problem that a customer faces. Anything that is a service in our price book is not challenge. Challenges are generally reservoir- and environment-related. • Other Materials & Equipment: These are basic materials like cement & salt; as well as items that are purchased from others like pumps, trucks and cables. Most of the surface equipment falls in this category. * = (likely) Required Fields 20
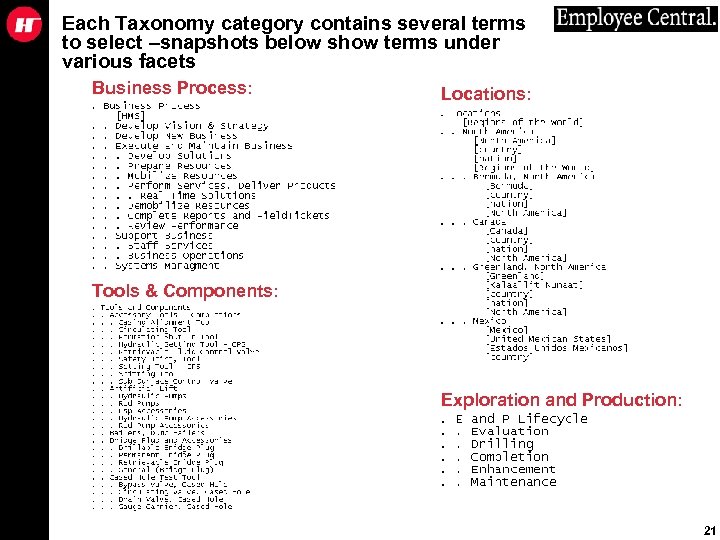 Each Taxonomy category contains several terms to select –snapshots below show terms under various facets Business Process: Locations: Tools & Components: Exploration and Production: 21
Each Taxonomy category contains several terms to select –snapshots below show terms under various facets Business Process: Locations: Tools & Components: Exploration and Production: 21
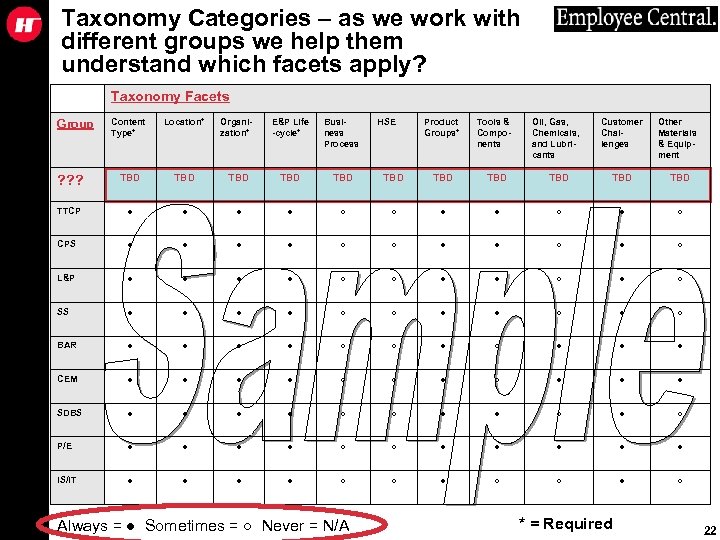 Taxonomy Categories – as we work with different groups we help them understand which facets apply? Taxonomy Facets Content Type* Location* Organization* E&P Life -cycle* Business Process Product Groups* Tools & Components Oil, Gas, Chemicals, and Lubricants Customer Challenges Other Materials & Equipment ? ? ? TBD TBD TBD TTCP ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ CPS ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ L&P ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ SS ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ BAR ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ● CEM ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ● SDBS ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ P/E ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ● IS/IT ● ● ○ ○ ● ○ Group Always = ● Sometimes = ○ Never = N/A HSE * = Required 22
Taxonomy Categories – as we work with different groups we help them understand which facets apply? Taxonomy Facets Content Type* Location* Organization* E&P Life -cycle* Business Process Product Groups* Tools & Components Oil, Gas, Chemicals, and Lubricants Customer Challenges Other Materials & Equipment ? ? ? TBD TBD TBD TTCP ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ CPS ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ L&P ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ SS ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ BAR ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ● CEM ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ● SDBS ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ○ P/E ● ● ○ ○ ● ● ● IS/IT ● ● ○ ○ ● ○ Group Always = ● Sometimes = ○ Never = N/A HSE * = Required 22
 Summary Employee Central. What are the plans/next steps? What about governance? How can you prepare? 23
Summary Employee Central. What are the plans/next steps? What about governance? How can you prepare? 23
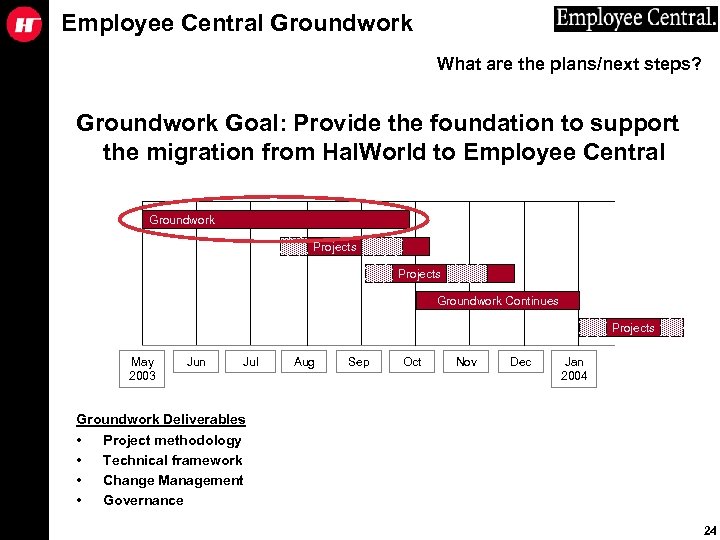 Employee Central Groundwork What are the plans/next steps? Groundwork Goal: Provide the foundation to support the migration from Hal. World to Employee Central Groundwork Projects Groundwork Continues Projects May 2003 Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan 2004 Groundwork Deliverables • Project methodology • Technical framework • Change Management • Governance 24
Employee Central Groundwork What are the plans/next steps? Groundwork Goal: Provide the foundation to support the migration from Hal. World to Employee Central Groundwork Projects Groundwork Continues Projects May 2003 Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan 2004 Groundwork Deliverables • Project methodology • Technical framework • Change Management • Governance 24
 Migration Strategy (Plans) What are the plans/next steps? • Migrate Hal. World by 2004 – Iterative project approach (several at a time) – Group similar sites – Leverage existing best practices • Use self-service model • Some key metrics – – Site migration statistics Amount of content in Hal. World vs. CMS Streamlined support Employee surveys 25
Migration Strategy (Plans) What are the plans/next steps? • Migrate Hal. World by 2004 – Iterative project approach (several at a time) – Group similar sites – Leverage existing best practices • Use self-service model • Some key metrics – – Site migration statistics Amount of content in Hal. World vs. CMS Streamlined support Employee surveys 25
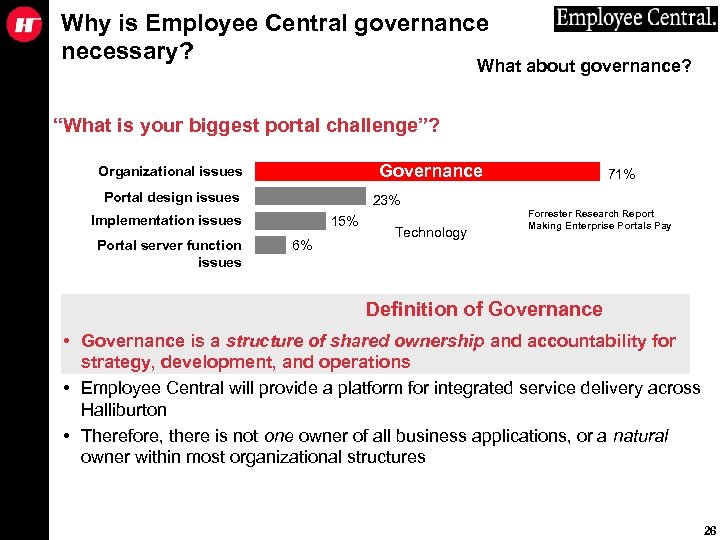 Why is Employee Central governance necessary? What about governance? “What is your biggest portal challenge”? Governance Organizational issues Portal design issues 23% Implementation issues Portal server function issues 15% 6% Technology 71% Forrester Research Report Making Enterprise Portals Pay Definition of Governance • Governance is a structure of shared ownership and accountability for strategy, development, and operations • Employee Central will provide a platform for integrated service delivery across Halliburton • Therefore, there is not one owner of all business applications, or a natural owner within most organizational structures 26
Why is Employee Central governance necessary? What about governance? “What is your biggest portal challenge”? Governance Organizational issues Portal design issues 23% Implementation issues Portal server function issues 15% 6% Technology 71% Forrester Research Report Making Enterprise Portals Pay Definition of Governance • Governance is a structure of shared ownership and accountability for strategy, development, and operations • Employee Central will provide a platform for integrated service delivery across Halliburton • Therefore, there is not one owner of all business applications, or a natural owner within most organizational structures 26
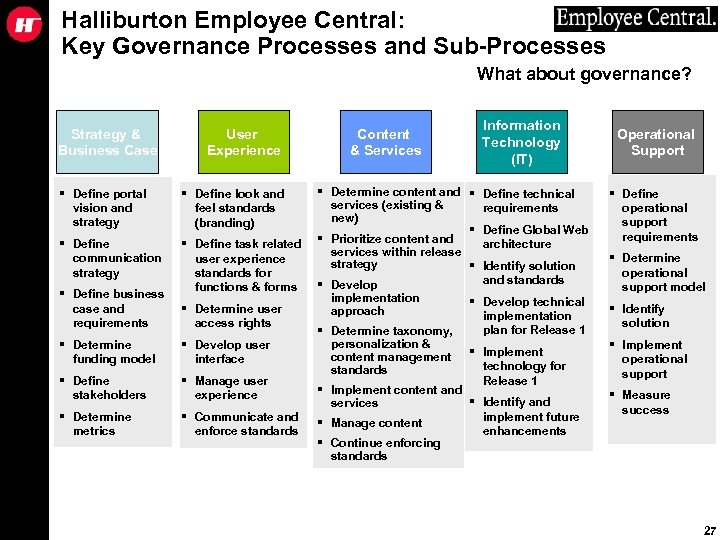 Halliburton Employee Central: Key Governance Processes and Sub-Processes What about governance? Strategy & Business Case § Define portal vision and strategy § Define communication strategy § Define business case and requirements § Determine funding model § Define stakeholders § Determine metrics User Experience Content & Services Information Technology (IT) § Determine content and § Define technical services (existing & requirements new) § Define Global Web § Prioritize content and architecture § Define task related services within release user experience strategy § Identify solution standards for and standards § Develop functions & forms implementation § Develop technical § Determine user approach implementation access rights plan for Release 1 § Determine taxonomy, personalization & § Develop user content management § Implement interface technology for standards Release 1 § Manage user § Implement content and experience § Identify and services implement future § Communicate and § Manage content enhancements enforce standards § Continue enforcing standards § Define look and feel standards (branding) Operational Support § Define operational support requirements § Determine operational support model § Identify solution § Implement operational support § Measure success 27
Halliburton Employee Central: Key Governance Processes and Sub-Processes What about governance? Strategy & Business Case § Define portal vision and strategy § Define communication strategy § Define business case and requirements § Determine funding model § Define stakeholders § Determine metrics User Experience Content & Services Information Technology (IT) § Determine content and § Define technical services (existing & requirements new) § Define Global Web § Prioritize content and architecture § Define task related services within release user experience strategy § Identify solution standards for and standards § Develop functions & forms implementation § Develop technical § Determine user approach implementation access rights plan for Release 1 § Determine taxonomy, personalization & § Develop user content management § Implement interface technology for standards Release 1 § Manage user § Implement content and experience § Identify and services implement future § Communicate and § Manage content enhancements enforce standards § Continue enforcing standards § Define look and feel standards (branding) Operational Support § Define operational support requirements § Determine operational support model § Identify solution § Implement operational support § Measure success 27
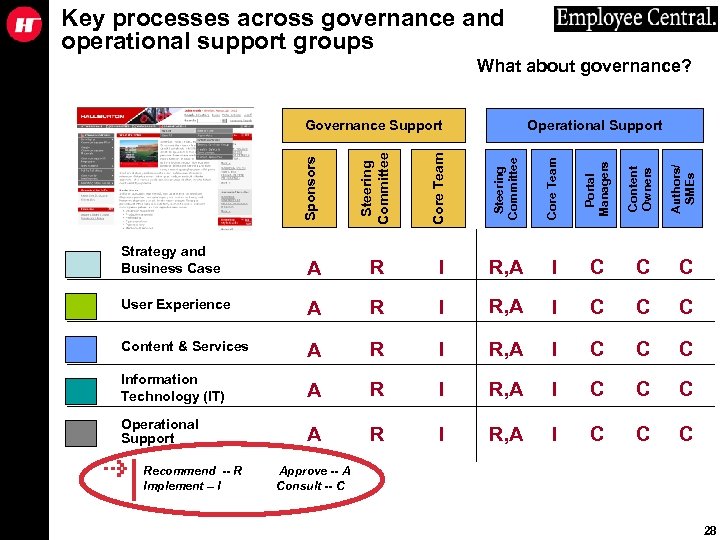 Key processes across governance and operational support groups What about governance? Steering Committee Core Team Portal Managers Content Owners Authors/ SMEs Strategy and Business Case A R I R, A I C C C User Experience A R I R, A I C Content & Services A R I R, A I C C C Information Technology (IT) A R I R, A I C C C Operational Support A R I R, A I C C C Sponsors Core Team Operational Support Steering Committee Governance Support Recommend -- R Implement – I Approve -- A Consult -- C 28
Key processes across governance and operational support groups What about governance? Steering Committee Core Team Portal Managers Content Owners Authors/ SMEs Strategy and Business Case A R I R, A I C C C User Experience A R I R, A I C Content & Services A R I R, A I C C C Information Technology (IT) A R I R, A I C C C Operational Support A R I R, A I C C C Sponsors Core Team Operational Support Steering Committee Governance Support Recommend -- R Implement – I Approve -- A Consult -- C 28
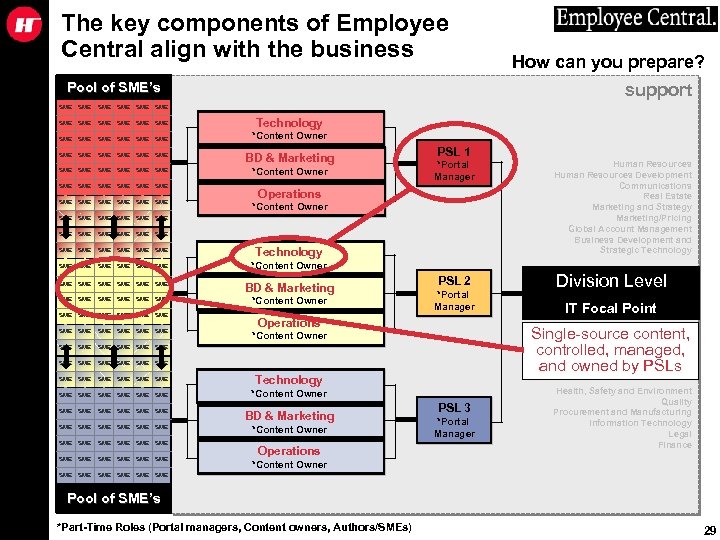 The key components of Employee Central align with the business Pool of SME’s How can you prepare? support SME SME SME Technology *Content Owner SME SME SME BD & Marketing SME SME SME *Content Owner SME SME SME SME SME SME SME SME Technology SME SME SME *Content Owner SME SME SME PSL 1 *Portal Manager Operations *Content Owner BD & Marketing *Content Owner SME SME SME SME SME SME SME SME SME Technology SME SME SME *Content Owner SME SME SME PSL 2 *Portal Manager SME SME SME SME SME SME Operations *Content Owner SME Operations Division Level IT Focal Point Single-source content, controlled, managed, and owned by PSLs *Content Owner BD & Marketing Human Resources Development Communications Real Estate Marketing and Strategy Marketing/Pricing Global Account Management Business Development and Strategic Technology PSL 3 *Portal Manager Health, Safety and Environment Quality Procurement and Manufacturing Information Technology Legal Finance *Content Owner Pool of SME’s *Part-Time Roles (Portal managers, Content owners, Authors/SMEs) 29
The key components of Employee Central align with the business Pool of SME’s How can you prepare? support SME SME SME Technology *Content Owner SME SME SME BD & Marketing SME SME SME *Content Owner SME SME SME SME SME SME SME SME Technology SME SME SME *Content Owner SME SME SME PSL 1 *Portal Manager Operations *Content Owner BD & Marketing *Content Owner SME SME SME SME SME SME SME SME SME Technology SME SME SME *Content Owner SME SME SME PSL 2 *Portal Manager SME SME SME SME SME SME Operations *Content Owner SME Operations Division Level IT Focal Point Single-source content, controlled, managed, and owned by PSLs *Content Owner BD & Marketing Human Resources Development Communications Real Estate Marketing and Strategy Marketing/Pricing Global Account Management Business Development and Strategic Technology PSL 3 *Portal Manager Health, Safety and Environment Quality Procurement and Manufacturing Information Technology Legal Finance *Content Owner Pool of SME’s *Part-Time Roles (Portal managers, Content owners, Authors/SMEs) 29
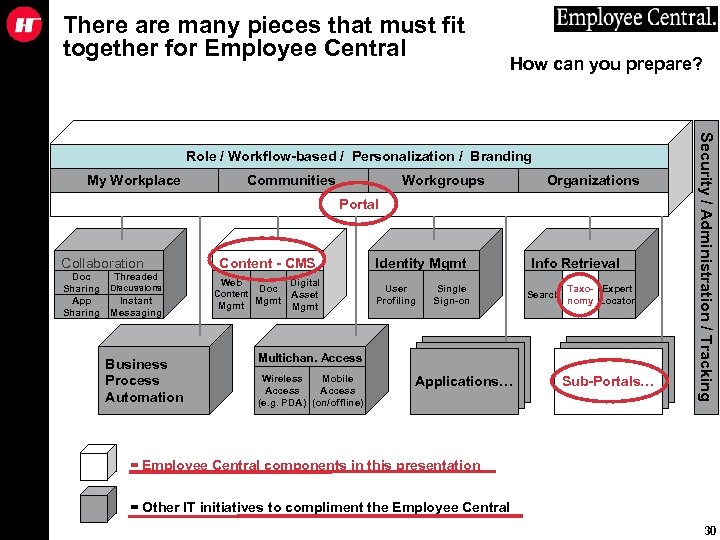 There are many pieces that must fit together for Employee Central How can you prepare? My Workplace Communities Workgroups Organizations Portal Collaboration Doc Threaded Sharing Discussions App Instant Sharing Messaging Business Process Automation Content - CMS Web Content Mgmt Digital Doc Asset Mgmt Identity Mgmt User Profiling Single Sign-on Info Retrieval Search Taxo- Expert nomy Locator Multichan. Access Wireless Mobile Access (e. g. PDA) (on/offline) Applications… Sub-Portals… Security / Administration / Tracking Role / Workflow-based / Personalization / Branding = Employee Central components in this presentation = Other IT initiatives to compliment the Employee Central 30
There are many pieces that must fit together for Employee Central How can you prepare? My Workplace Communities Workgroups Organizations Portal Collaboration Doc Threaded Sharing Discussions App Instant Sharing Messaging Business Process Automation Content - CMS Web Content Mgmt Digital Doc Asset Mgmt Identity Mgmt User Profiling Single Sign-on Info Retrieval Search Taxo- Expert nomy Locator Multichan. Access Wireless Mobile Access (e. g. PDA) (on/offline) Applications… Sub-Portals… Security / Administration / Tracking Role / Workflow-based / Personalization / Branding = Employee Central components in this presentation = Other IT initiatives to compliment the Employee Central 30
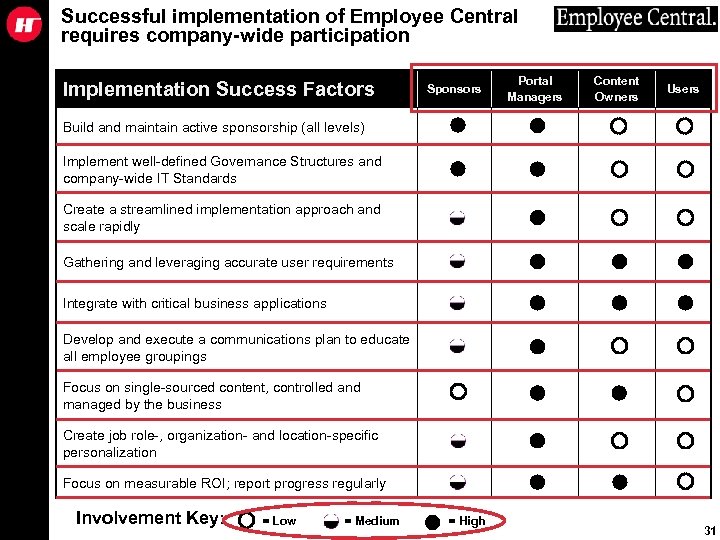 Successful implementation of Employee Central requires company-wide participation Implementation Success Factors Sponsors Portal Managers Content Owners Users Build and maintain active sponsorship (all levels) Implement well-defined Governance Structures and company-wide IT Standards Create a streamlined implementation approach and scale rapidly Gathering and leveraging accurate user requirements Integrate with critical business applications Develop and execute a communications plan to educate all employee groupings Focus on single-sourced content, controlled and managed by the business Create job role-, organization- and location-specific personalization Focus on measurable ROI; report progress regularly Involvement Key: = Low = Medium = High 31
Successful implementation of Employee Central requires company-wide participation Implementation Success Factors Sponsors Portal Managers Content Owners Users Build and maintain active sponsorship (all levels) Implement well-defined Governance Structures and company-wide IT Standards Create a streamlined implementation approach and scale rapidly Gathering and leveraging accurate user requirements Integrate with critical business applications Develop and execute a communications plan to educate all employee groupings Focus on single-sourced content, controlled and managed by the business Create job role-, organization- and location-specific personalization Focus on measurable ROI; report progress regularly Involvement Key: = Low = Medium = High 31
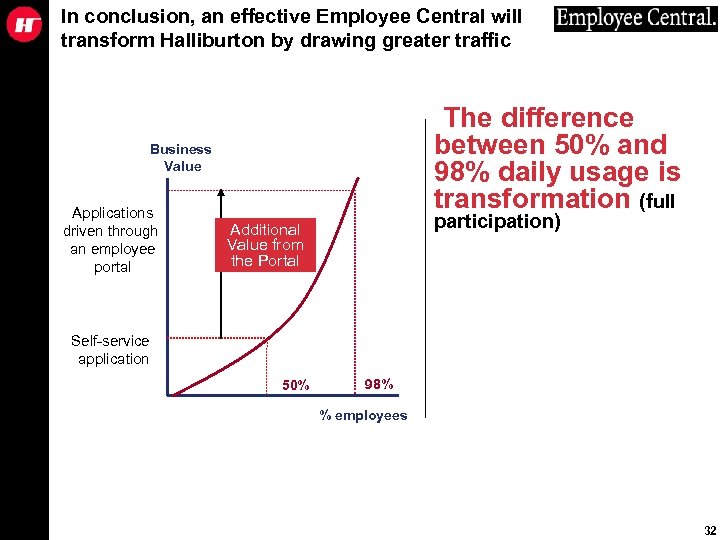 In conclusion, an effective Employee Central will transform Halliburton by drawing greater traffic The difference between 50% and 98% daily usage is transformation (full Business Value Applications driven through an employee portal participation) Additional Value from the Portal Self-service application 50% 98% % employees 32
In conclusion, an effective Employee Central will transform Halliburton by drawing greater traffic The difference between 50% and 98% daily usage is transformation (full Business Value Applications driven through an employee portal participation) Additional Value from the Portal Self-service application 50% 98% % employees 32
 Thank You Overview Employee Central. community pages only More Training: Portal Training and Policies Site 33
Thank You Overview Employee Central. community pages only More Training: Portal Training and Policies Site 33


