8ef7b5327279467a1b1d9b823b90873a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

HACCP Principle 4 – Establish CCP Monitoring Procedures 1

HACCP Principle 4 • Establish CCP monitoring requirements. Establish procedures for using the results of monitoring to adjust the process and maintain control. 2
Definition of Monitoring The act of conducting a planned sequence of observations or measurements of control parameters to assess whether a CCP is under control. 3

purpose of monitoring § Track the operation of the process and enable the identification of trends toward a critical limit that may trigger process adjustments § Identify when there is a loss of control (a deviation at a CCP) § Provide written documentation of the process control system 4
Types of Monitoring • Observations • Measurements • Continuous and. Discontinuous 5
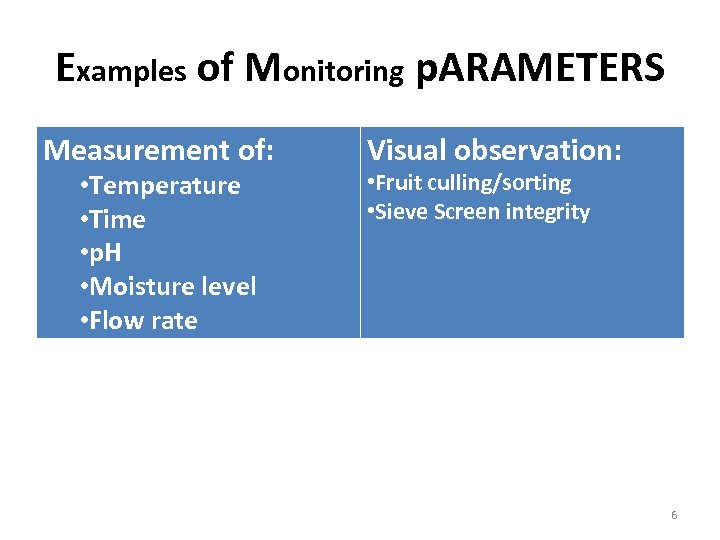
Examples of Monitoring p. ARAMETERS Measurement of: • Temperature • Time • p. H • Moisture level • Flow rate Visual observation: • Fruit culling/sorting • Sieve Screen integrity 6
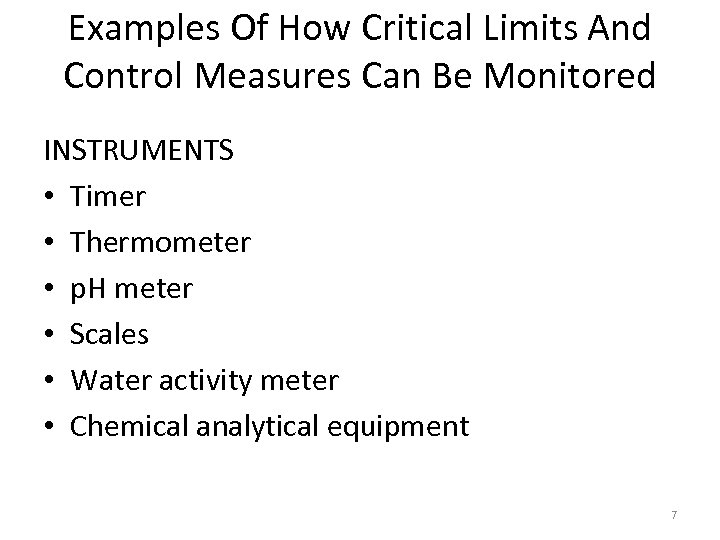
Examples Of How Critical Limits And Control Measures Can Be Monitored INSTRUMENTS • Timer • Thermometer • p. H meter • Scales • Water activity meter • Chemical analytical equipment 7

Monitoring Procedures • • • Identify who (job position) What is to be monitored How it is to be monitored When, how often (frequency) Where it is monitored Documents that CLs are met 8
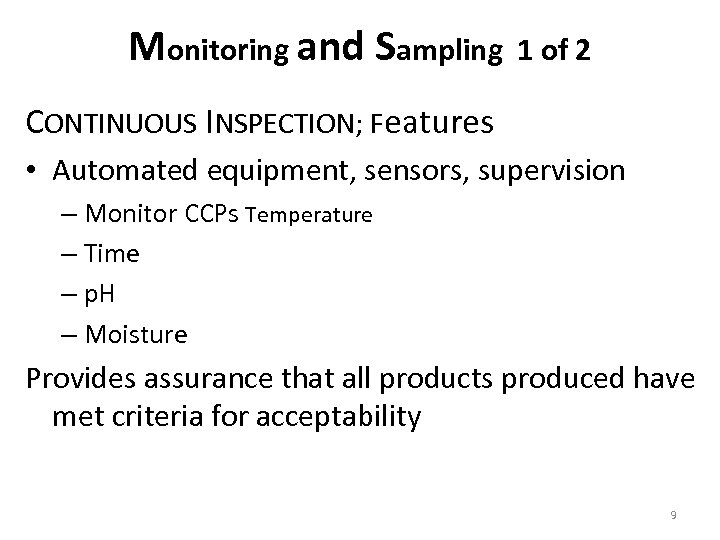
Monitoring and Sampling 1 of 2 CONTINUOUS INSPECTION; Features • Automated equipment, sensors, supervision – Monitor CCPs Temperature – Time – p. H – Moisture Provides assurance that all products produced have met criteria for acceptability 9
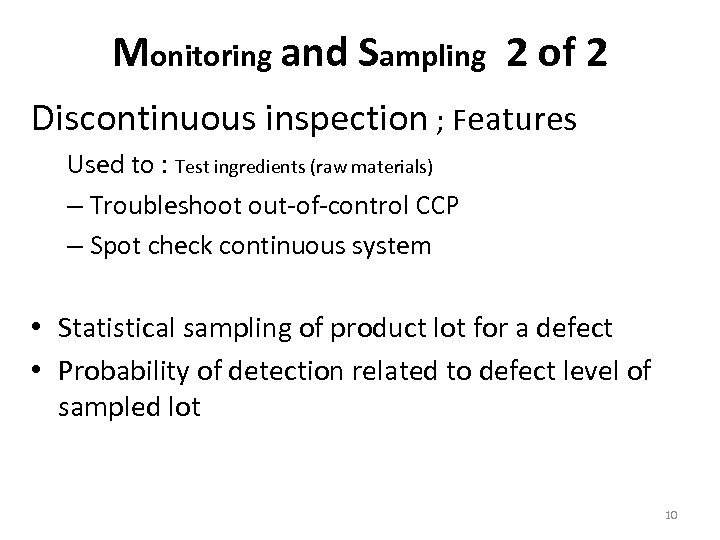
Monitoring and Sampling 2 of 2 Discontinuous inspection ; Features Used to : Test ingredients (raw materials) – Troubleshoot out-of-control CCP – Spot check continuous system • Statistical sampling of product lot for a defect • Probability of detection related to defect level of sampled lot 10

Staff Responsible For Monitoring The staff shall have clearly defined responsibilities. The staff responsible for specific monitoring activities should be designated in the HACCP plan (title, not name). Must be adequately trained to perform the monitoring procedures and to prepare the monitoring records. Follows clearly delineated procedures. Is responsible for documentation of monitoring activities, and signs or initials the monitoring records. 11

Monitoring Records MUST INCLUDE: • Actual monitoring information • Date and time the activity took place • Signature or initials of person conducting the monitoring procedure. 12
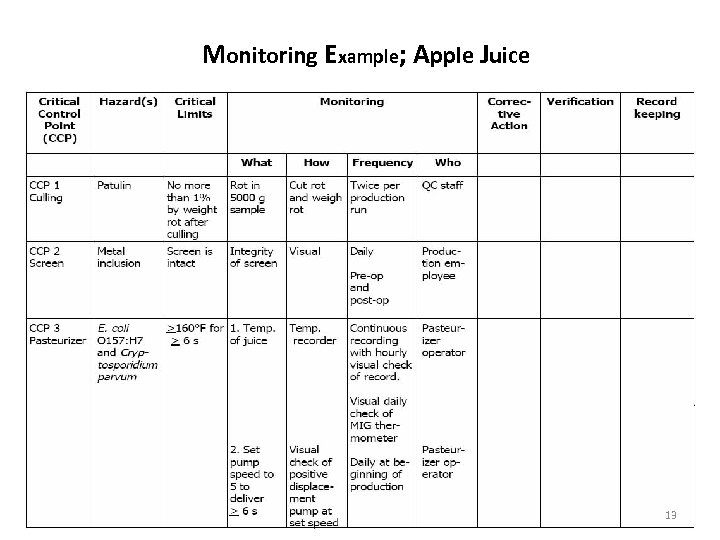
Monitoring Example; Apple Juice 13

Patulin • Patulin is a mycotoxin produced by a variety of molds, in particular, Aspergillus and Penicillium and Byssochlamys. Most commonly found in rotting apples, in general the amount of patulin in apple products is viewed as a measure of the quality of the apples used in production. • The World Health Organization recommends a maximum concentration of 50 µg/L in apple juice. [3] In the European Union, the limit is set to 50 micrograms per kilogram (µg/kg) in both apple juice and cider, and to half of that concentration, 25 µg/kg, in solid apple products and 10 µg/kg in products for infants and young children 14

Summary • Each CCP should have defined the best monitoring procedure available under the given circumstances • the frequency of monitoring • the decision criteria for acceptable and unacceptable control at CCPs 15
8ef7b5327279467a1b1d9b823b90873a.ppt