269155120a9b1f047a9fb37ef45fd10b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 HACCP
HACCP
 HACCP FOOD HYGIENE All conditions and measures necessary to ensure the safety and suitability of food at all stages of the food chain
HACCP FOOD HYGIENE All conditions and measures necessary to ensure the safety and suitability of food at all stages of the food chain
 HACCP FOOD SAFETY Assurance that food will not cause harm to the consumer when it is prepared and / or eaten according to its intended use.
HACCP FOOD SAFETY Assurance that food will not cause harm to the consumer when it is prepared and / or eaten according to its intended use.
 HACCP FOOD SAFETY ASSURANCE HACCP is a method of food safety assurance Ø Ø It identifies what we need to do to make food safe It makes sure that what is planned is correctly implemented
HACCP FOOD SAFETY ASSURANCE HACCP is a method of food safety assurance Ø Ø It identifies what we need to do to make food safe It makes sure that what is planned is correctly implemented
 HACCP QUALITY Types of Quality: Ø Ø Organoleptic quality (Senses) Functional quality (e. g. convenience, shelf-life or “keepability”) Ø Nutritional quality Ø Hygienic quality (safety)
HACCP QUALITY Types of Quality: Ø Ø Organoleptic quality (Senses) Functional quality (e. g. convenience, shelf-life or “keepability”) Ø Nutritional quality Ø Hygienic quality (safety)
 HACCP QUALITY CONTROL A system for maintaining standards in production or in a product, especially by inspecting samples of the product Webster’s Dictionary (1980)
HACCP QUALITY CONTROL A system for maintaining standards in production or in a product, especially by inspecting samples of the product Webster’s Dictionary (1980)
 HACCP QUALITY ASSURANCE All planned and systematic actions necessary to provide adequate confidence that a product or service will satisfy given requirements for quality (ISO/UNCTAD/GATT)
HACCP QUALITY ASSURANCE All planned and systematic actions necessary to provide adequate confidence that a product or service will satisfy given requirements for quality (ISO/UNCTAD/GATT)
 HACCP CONCEPT Ø Identification of potential food safety problems Ø Determination of how and where these can be prevented Ø Description of what to do and training of the personnel Ø Implementation and recording
HACCP CONCEPT Ø Identification of potential food safety problems Ø Determination of how and where these can be prevented Ø Description of what to do and training of the personnel Ø Implementation and recording
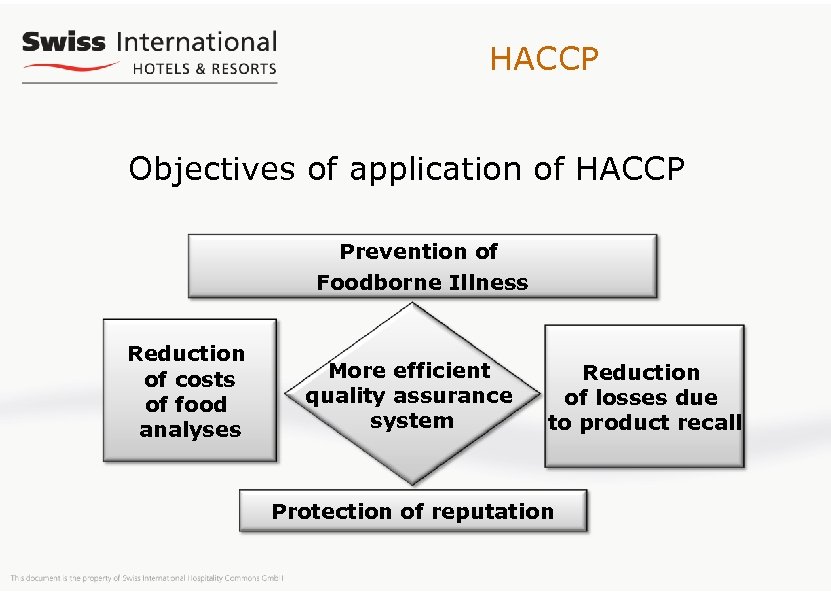 HACCP Objectives of application of HACCP Prevention of Foodborne Illness Reduction of costs of food analyses More efficient quality assurance system Reduction of losses due to product recall Protection of reputation
HACCP Objectives of application of HACCP Prevention of Foodborne Illness Reduction of costs of food analyses More efficient quality assurance system Reduction of losses due to product recall Protection of reputation
 HACCP SYSTEM Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points Danger, Risk Discovering, Researching Of Immense Importance Checking, Managing Steps, Events
HACCP SYSTEM Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points Danger, Risk Discovering, Researching Of Immense Importance Checking, Managing Steps, Events
 HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 1 Conduct a hazard analysis Ø What is a hazard? • Any biological, chemical or physical property which may cause a food to be unsafe for human consumption
HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 1 Conduct a hazard analysis Ø What is a hazard? • Any biological, chemical or physical property which may cause a food to be unsafe for human consumption
 HAZZARD VS RISK Ø Hazards are evaluated based on the importance of the danger, the seriousness of the danger as well as the frequency of occurrence Ø Risks are evaluated based on the probability that a hazard could occur
HAZZARD VS RISK Ø Hazards are evaluated based on the importance of the danger, the seriousness of the danger as well as the frequency of occurrence Ø Risks are evaluated based on the probability that a hazard could occur
 BACTERIA AND VIRUSES Ø Bacteria are germs producing toxins either in the food or inside the body Ø Viruses are microscopic pathogens that multiply in the living cells of their host Ø Your objective: reduce bacterial and viral contamination on PHF’s
BACTERIA AND VIRUSES Ø Bacteria are germs producing toxins either in the food or inside the body Ø Viruses are microscopic pathogens that multiply in the living cells of their host Ø Your objective: reduce bacterial and viral contamination on PHF’s
 CRITICAL FOOD Foods with Ø high protein contents Ø high carbohydrate contents Ø high fat content Ø Foods that grow over or in soil Ø Foods that come into contact with organic matters = POTENTIALLY HAZARDOUS FOODS (PHF’S)
CRITICAL FOOD Foods with Ø high protein contents Ø high carbohydrate contents Ø high fat content Ø Foods that grow over or in soil Ø Foods that come into contact with organic matters = POTENTIALLY HAZARDOUS FOODS (PHF’S)
 CRITICAL FOOD Common hazards in meat and meat products: Ø Salmonella Ø Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum Escherichia coli Listeria monocytogenes Parasites Ø Ø Ø
CRITICAL FOOD Common hazards in meat and meat products: Ø Salmonella Ø Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum Escherichia coli Listeria monocytogenes Parasites Ø Ø Ø
 CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in Milk Ø Ø Ø Salmonella Listeria monocytogenes Escheridia coli Staphillococcus aureus Clostridium botulinum Campylobacter jejuni
CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in Milk Ø Ø Ø Salmonella Listeria monocytogenes Escheridia coli Staphillococcus aureus Clostridium botulinum Campylobacter jejuni
 CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in poultry and poultry products Ø Salmonella Ø Campylobacter jejuni Ø Clostridium perfringens Ø Staphylococcus aureus Ø Listeria monocytogenes
CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in poultry and poultry products Ø Salmonella Ø Campylobacter jejuni Ø Clostridium perfringens Ø Staphylococcus aureus Ø Listeria monocytogenes
 CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in eggs and egg products Salmonella !
CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in eggs and egg products Salmonella !
 CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in Fish and Shellfish Bacteria Ø Clostridium botulinum Ø Vibrio vulnificus Ø Listeria monocytogenes Parasites Viruses u Hepatitis A virus u Norwalk virus
CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in Fish and Shellfish Bacteria Ø Clostridium botulinum Ø Vibrio vulnificus Ø Listeria monocytogenes Parasites Viruses u Hepatitis A virus u Norwalk virus
 CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in vegetables, fruits and nuts Bacteria Ø Salmonella Ø Listeria monocytogenes Ø E. coli Ø Clostridium botulinum Hepatitis A Parasites Moulds
CRITICAL FOOD Common Hazards in vegetables, fruits and nuts Bacteria Ø Salmonella Ø Listeria monocytogenes Ø E. coli Ø Clostridium botulinum Hepatitis A Parasites Moulds
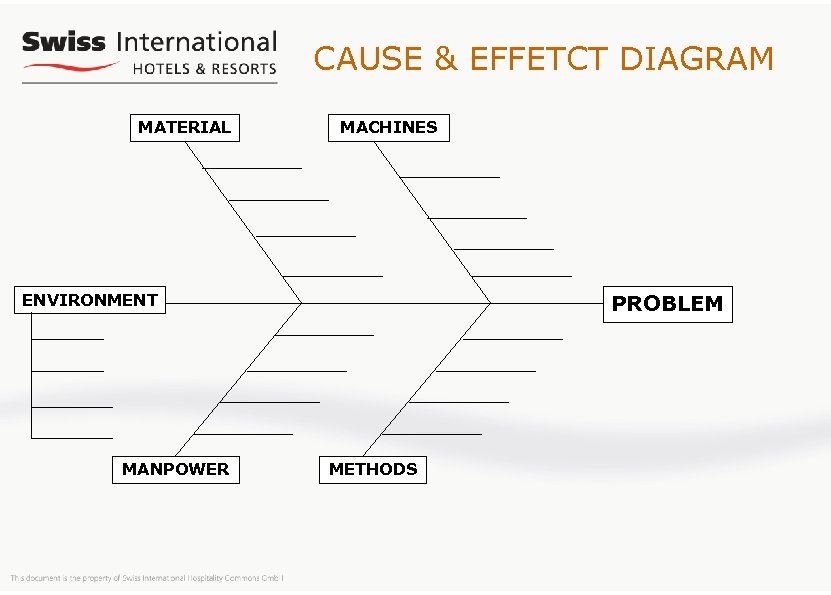 CAUSE & EFFETCT DIAGRAM MATERIAL MACHINES PROBLEM ENVIRONMENT MANPOWER METHODS
CAUSE & EFFETCT DIAGRAM MATERIAL MACHINES PROBLEM ENVIRONMENT MANPOWER METHODS
 HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 2 Ø Determine the critical control points
HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 2 Ø Determine the critical control points
 CRITICAL CONTROL POINTS Any operation/practice/procedure where a preventive or control measure can be applied which would Ø eliminate/remove a hazard Ø prevent a hazard Ø lessen the risk a hazard will happen Measurable or quantifiable, usually involves a PHF
CRITICAL CONTROL POINTS Any operation/practice/procedure where a preventive or control measure can be applied which would Ø eliminate/remove a hazard Ø prevent a hazard Ø lessen the risk a hazard will happen Measurable or quantifiable, usually involves a PHF
 HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 3 Ø Set the critical limits for each critical control point
HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 3 Ø Set the critical limits for each critical control point
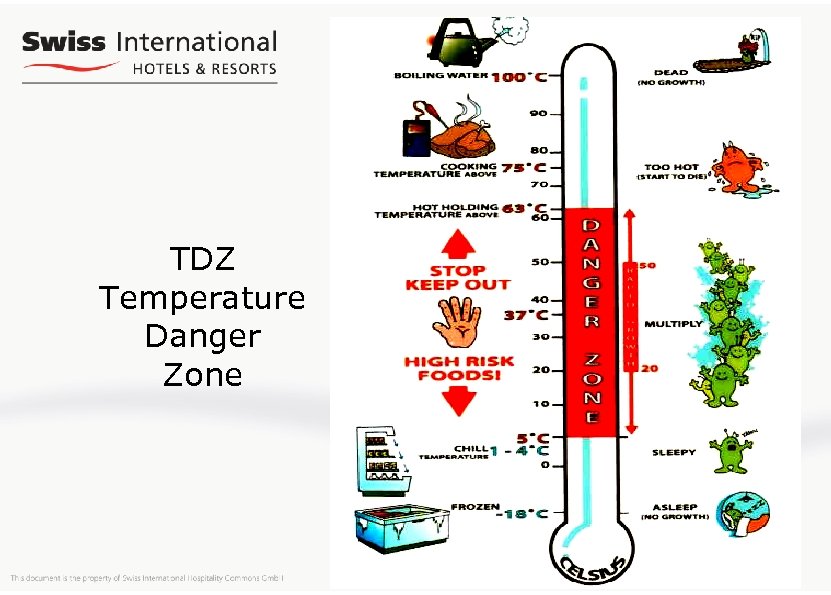 TDZ Temperature Danger Zone
TDZ Temperature Danger Zone
 HACCP FATTOM Factors Affecting Bacterial or Viral Growth FATTOM: Ø Ø Ø Food Acidity Time Temperature Oxygen Moisture
HACCP FATTOM Factors Affecting Bacterial or Viral Growth FATTOM: Ø Ø Ø Food Acidity Time Temperature Oxygen Moisture
 HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 4 Establish Monitoring Procedures Measurable Ø Frequent Ø Accurate Ø Recorded Ø Verifiable Ø
HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 4 Establish Monitoring Procedures Measurable Ø Frequent Ø Accurate Ø Recorded Ø Verifiable Ø
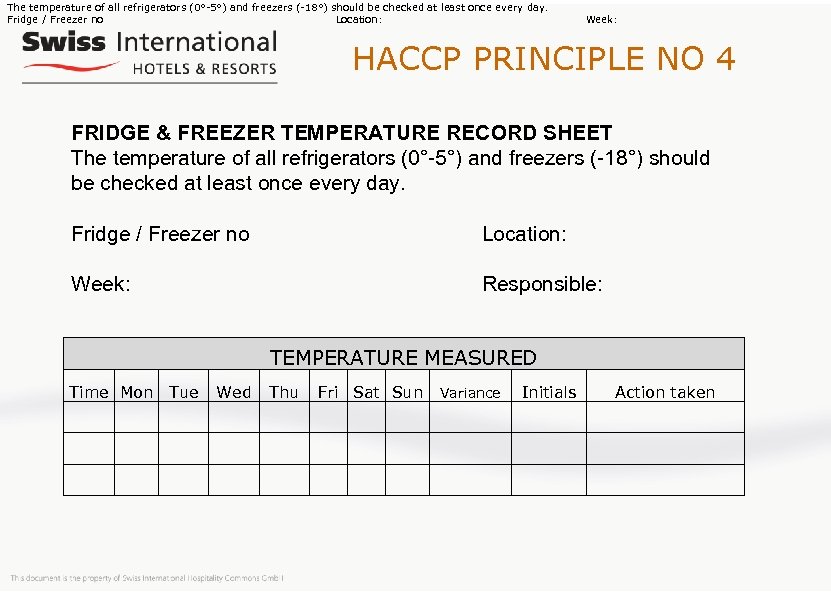 The temperature of all refrigerators (0°-5°) and freezers (-18°) should be checked at least once every day. Fridge / Freezer no Location: Week: HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 4 FRIDGE & FREEZER TEMPERATURE RECORD SHEET The temperature of all refrigerators (0°-5°) and freezers (-18°) should be checked at least once every day. Fridge / Freezer no Location: Week: Responsible: TEMPERATURE MEASURED Time Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Sun Initials Variance Action taken
The temperature of all refrigerators (0°-5°) and freezers (-18°) should be checked at least once every day. Fridge / Freezer no Location: Week: HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 4 FRIDGE & FREEZER TEMPERATURE RECORD SHEET The temperature of all refrigerators (0°-5°) and freezers (-18°) should be checked at least once every day. Fridge / Freezer no Location: Week: Responsible: TEMPERATURE MEASURED Time Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Sun Initials Variance Action taken
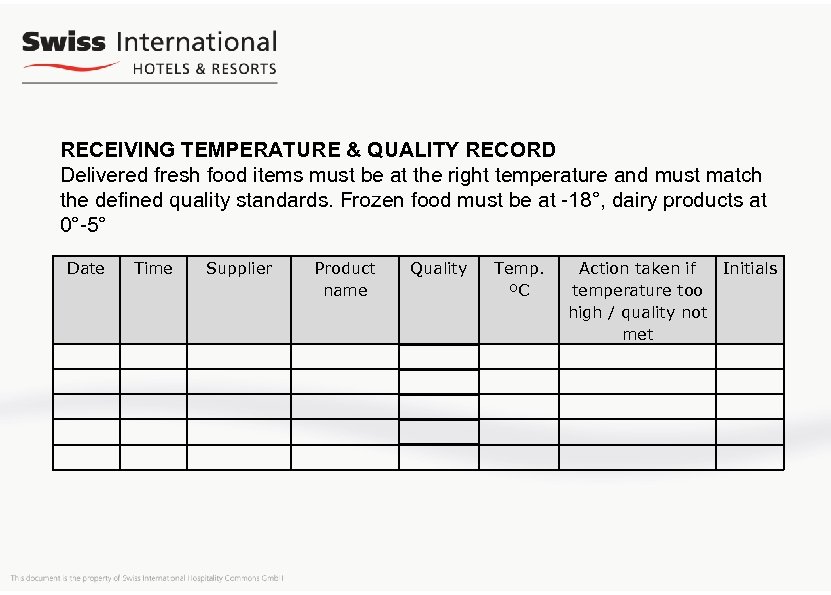 RECEIVING TEMPERATURE & QUALITY RECORD Delivered fresh food items must be at the right temperature and must match the defined quality standards. Frozen food must be at -18°, dairy products at 0°-5° Date Time Supplier Product name Quality Temp. ºC Action taken if Initials temperature too high / quality not met
RECEIVING TEMPERATURE & QUALITY RECORD Delivered fresh food items must be at the right temperature and must match the defined quality standards. Frozen food must be at -18°, dairy products at 0°-5° Date Time Supplier Product name Quality Temp. ºC Action taken if Initials temperature too high / quality not met
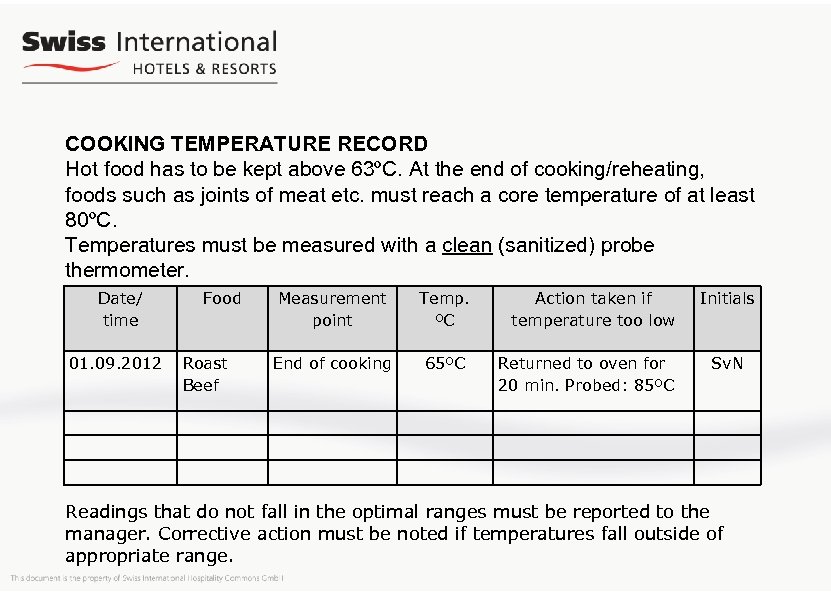 COOKING TEMPERATURE RECORD Hot food has to be kept above 63ºC. At the end of cooking/reheating, foods such as joints of meat etc. must reach a core temperature of at least 80ºC. Temperatures must be measured with a clean (sanitized) probe thermometer. Date/ time 01. 09. 2012 Food Roast Beef Measurement point Temp. ºC End of cooking 65ºC Action taken if temperature too low Returned to oven for 20 min. Probed: 85ºC Initials Sv. N Readings that do not fall in the optimal ranges must be reported to the manager. Corrective action must be noted if temperatures fall outside of appropriate range.
COOKING TEMPERATURE RECORD Hot food has to be kept above 63ºC. At the end of cooking/reheating, foods such as joints of meat etc. must reach a core temperature of at least 80ºC. Temperatures must be measured with a clean (sanitized) probe thermometer. Date/ time 01. 09. 2012 Food Roast Beef Measurement point Temp. ºC End of cooking 65ºC Action taken if temperature too low Returned to oven for 20 min. Probed: 85ºC Initials Sv. N Readings that do not fall in the optimal ranges must be reported to the manager. Corrective action must be noted if temperatures fall outside of appropriate range.
 HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 5 Take Corrective Actions Ø what should you do if… Ø specific Ø planned Ø verifiable Ø recorded
HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 5 Take Corrective Actions Ø what should you do if… Ø specific Ø planned Ø verifiable Ø recorded
 HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 6 Verification Ø Those activities other than monitoring that determine: ØThe validity of the plan ØThat the system is operating according to the plan
HACCP PRINCIPLE NO 6 Verification Ø Those activities other than monitoring that determine: ØThe validity of the plan ØThat the system is operating according to the plan
 Q&A
Q&A


