d69e54269ddc01f4bf7f3f43e0c5d5c0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

H-Cube – The next generation in Hydrogenation Asynt Ltd.
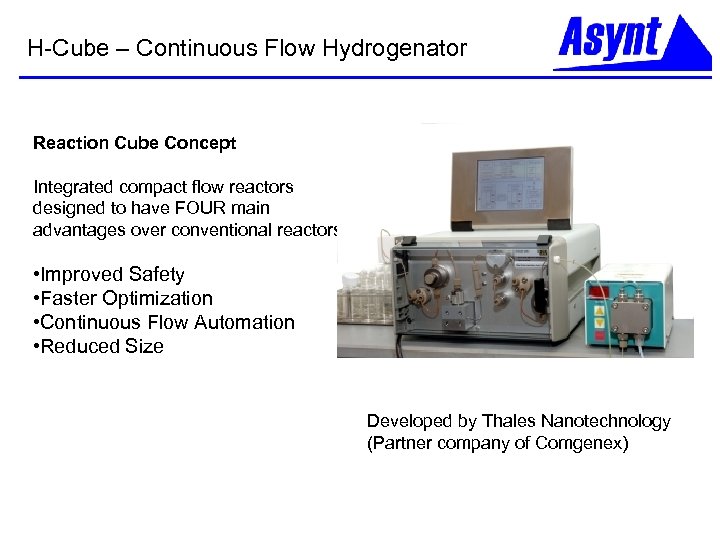
H-Cube – Continuous Flow Hydrogenator Reaction Cube Concept Integrated compact flow reactors designed to have FOUR main advantages over conventional reactors. • Improved Safety • Faster Optimization • Continuous Flow Automation • Reduced Size Developed by Thales Nanotechnology (Partner company of Comgenex)
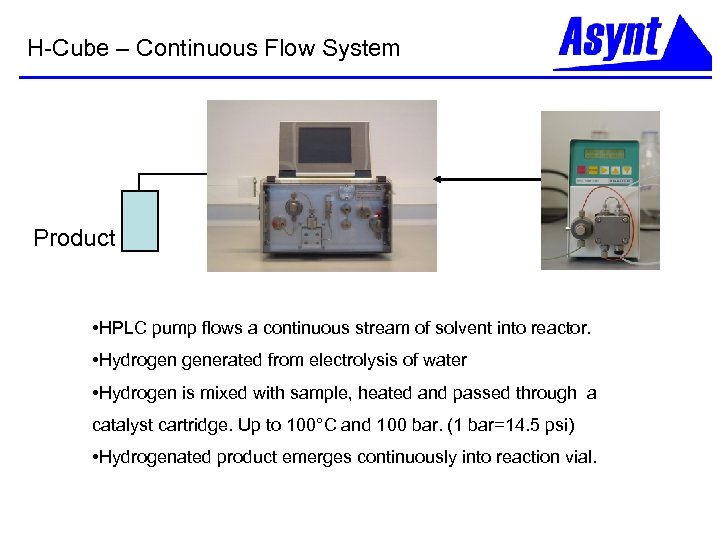
H-Cube – Continuous Flow System Product • HPLC pump flows a continuous stream of solvent into reactor. • Hydrogen generated from electrolysis of water • Hydrogen is mixed with sample, heated and passed through a catalyst cartridge. Up to 100°C and 100 bar. (1 bar=14. 5 psi) • Hydrogenated product emerges continuously into reaction vial.
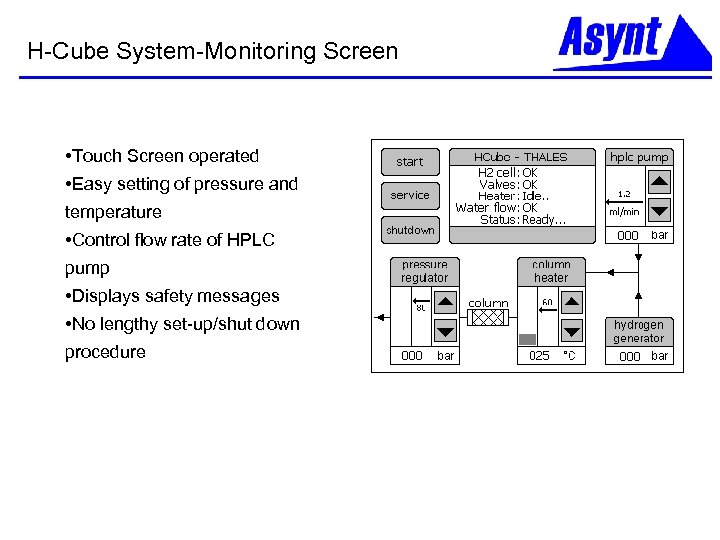
H-Cube System-Monitoring Screen • Touch Screen operated • Easy setting of pressure and temperature • Control flow rate of HPLC pump • Displays safety messages • No lengthy set-up/shut down procedure
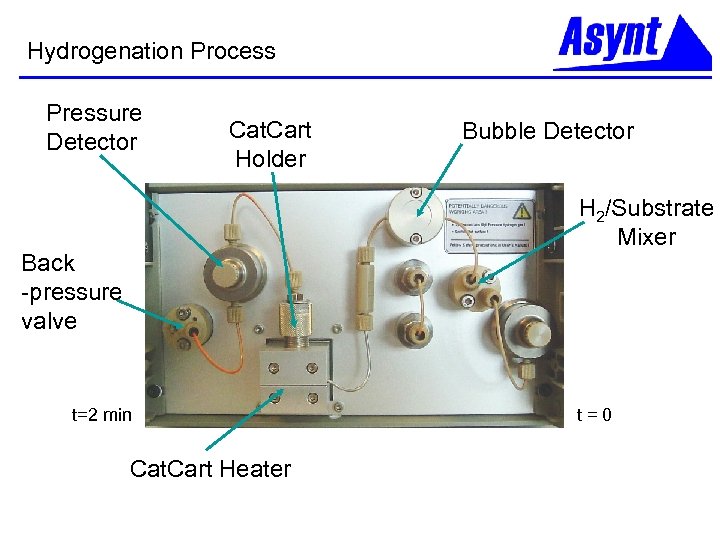
Hydrogenation Process Pressure Detector Cat. Cart Holder Bubble Detector H 2/Substrate Mixer Back -pressure valve t=2 min Cat. Cart Heater t=0
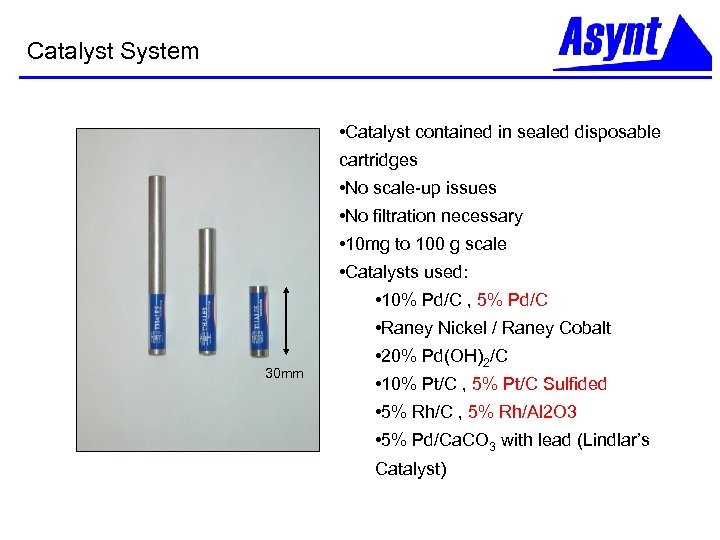
Catalyst System • Catalyst contained in sealed disposable cartridges • No scale-up issues • No filtration necessary • 10 mg to 100 g scale • Catalysts used: • 10% Pd/C , 5% Pd/C • Raney Nickel / Raney Cobalt 30 mm • 20% Pd(OH)2/C • 10% Pt/C , 5% Pt/C Sulfided • 5% Rh/C , 5% Rh/Al 2 O 3 • 5% Pd/Ca. CO 3 with lead (Lindlar’s Catalyst)
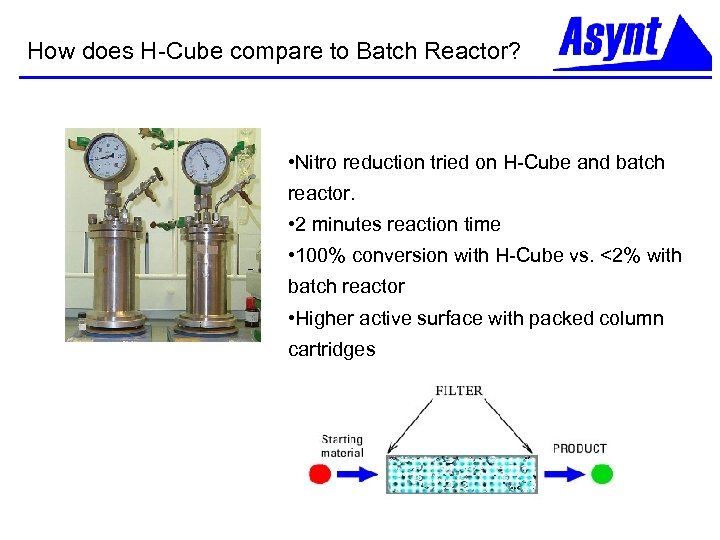
How does H-Cube compare to Batch Reactor? • Nitro reduction tried on H-Cube and batch reactor. • 2 minutes reaction time • 100% conversion with H-Cube vs. <2% with batch reactor • Higher active surface with packed column cartridges

Reaction Examples • Reductions – – – – – Nitro group Nitrile group Imine Heterocycle C=C bond Alkyne Dehalogenation Desulphurization Oxime • Deprotection – N-benzyl – O-benzyl – c. Bz • Deuteration
Reaction Conditions • 0. 05 M – 0. 2 M Solution in organic solvent, acetic acid or NH 3/Me. OH • Choose Cat. Cart (Catalyst and size) • Set flow rate between 1 ml/min and 3 ml/min • Set Pressure 1 bar – 100 bar • Set Temperature 25 -100 C • Set Mode • Controlled mode • Full H 2 mode • No H 2 mode (introduce a different gas) • How much throughput? • If RMM = 200 • Worst case 1 ml/min, 0. 05 M, 3 mmol/hour (600 mg) • Best Case 3 ml/min, 0. 2 M, 36 mmol/hour (7. 2 g)
![Catalyst Recycling H-Cube conditions: 0. 1 M, [50: 50] Et. OAc: Et. OH, ~1 Catalyst Recycling H-Cube conditions: 0. 1 M, [50: 50] Et. OAc: Et. OH, ~1](https://present5.com/presentation/d69e54269ddc01f4bf7f3f43e0c5d5c0/image-10.jpg)
Catalyst Recycling H-Cube conditions: 0. 1 M, [50: 50] Et. OAc: Et. OH, ~1 bar, 30 o. C, 1 m. L/min; Total material processed = 30 x 10 fractions = 30 mmol = 4. 85 g with 140 mg Pd/C
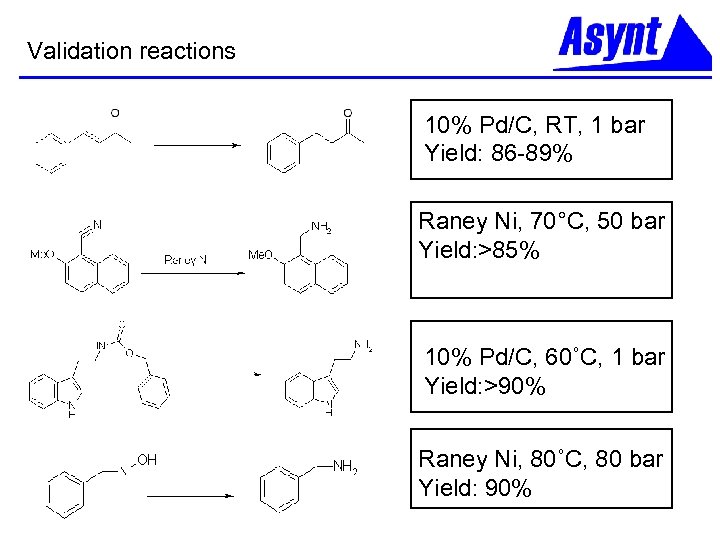
Validation reactions 10% Pd/C, RT, 1 bar Yield: 86 -89% Raney Ni, 70°C, 50 bar Yield: >85% 10% Pd/C, 60˚C, 1 bar Yield: >90% Raney Ni, 80˚C, 80 bar Yield: 90%
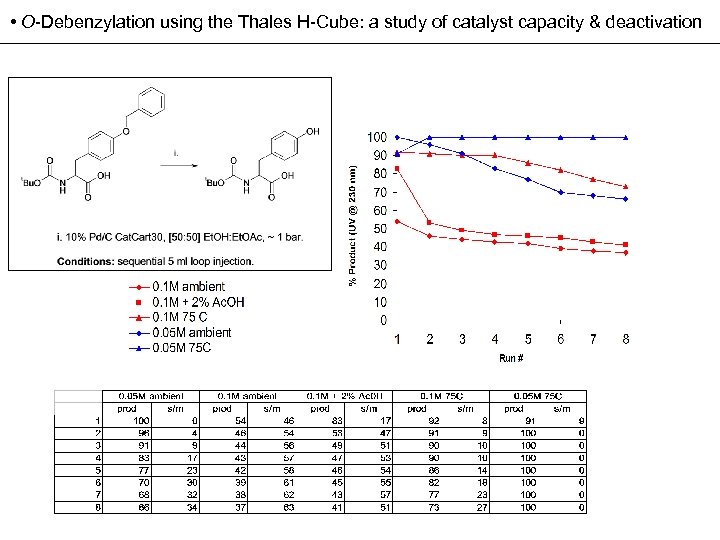
• O-Debenzylation using the Thales H-Cube: a study of catalyst capacity & deactivation

Automated High-throughput Hydrogenation • H-Cube integrated into CAVRO work station • Automated injection and collection • Timed injections, link to UV detector possible
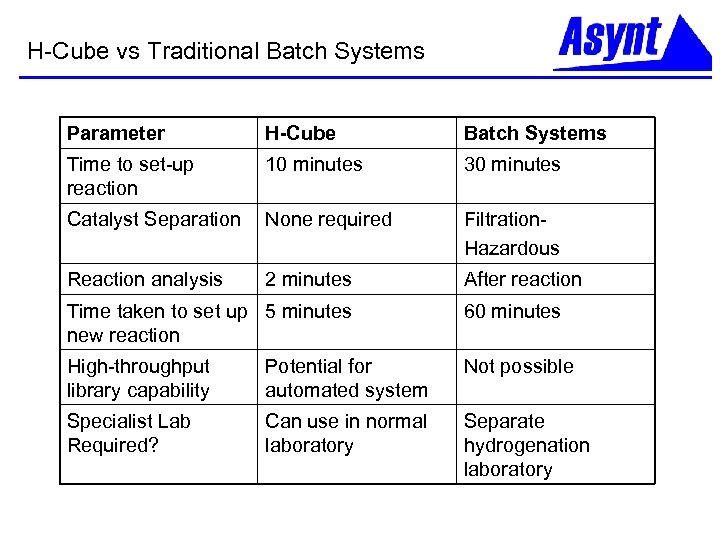
H-Cube vs Traditional Batch Systems Parameter H-Cube Batch Systems Time to set-up reaction 10 minutes 30 minutes Catalyst Separation None required Filtration. Hazardous Reaction analysis 2 minutes After reaction Time taken to set up 5 minutes new reaction 60 minutes High-throughput library capability Potential for automated system Not possible Specialist Lab Required? Can use in normal laboratory Separate hydrogenation laboratory

Advantages of H-Cube Safer… • No hydrogen cylinders necessary • Uses deionised water • No filtration of catalyst necessary • Only µmolar quantities react at any one time Smaller… • H-Cube footprint is less than 0. 3 m 3 • Easy storage • Scaleable reactions from mg to 100 g Faster… • Monitor reaction progress after 2 minutes! • 30 reaction conditions can be validated in less than a half day. • Simple to use, minimal training required

Acknowledgements Richard Jones, Thales Nanotechnology Mark Ladlow, GSK Cambridge
d69e54269ddc01f4bf7f3f43e0c5d5c0.ppt