1f56643d6652cc49d0ec4461b8cdef2b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 H. 323 Gatekeepers Lucent Technologies - elemedia 1
H. 323 Gatekeepers Lucent Technologies - elemedia 1
 Agenda • Introduction • Overview of Gatekeeper Functions • Why are Gatekeepers Useful? • Gatekeeper Concepts • Signalling Models • Gatekeeper Operations • Signalling Flows • Policy/Service Examples • Gatekeepers and H. 323 v 2 • Beyond H. 323 v 2 2
Agenda • Introduction • Overview of Gatekeeper Functions • Why are Gatekeepers Useful? • Gatekeeper Concepts • Signalling Models • Gatekeeper Operations • Signalling Flows • Policy/Service Examples • Gatekeepers and H. 323 v 2 • Beyond H. 323 v 2 2
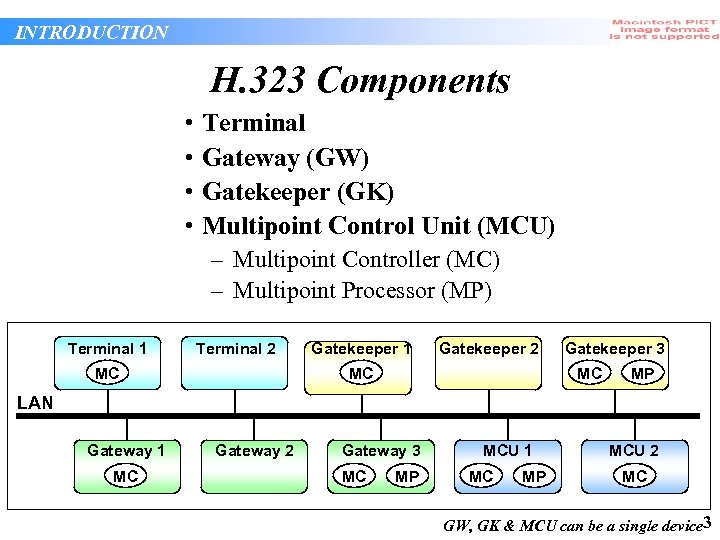 INTRODUCTION H. 323 Components • • Terminal Gateway (GW) Gatekeeper (GK) Multipoint Control Unit (MCU) – Multipoint Controller (MC) – Multipoint Processor (MP) Terminal 1 Terminal 2 MC Gatekeeper 1 Gatekeeper 2 MC Gatekeeper 3 MC MP LAN Gateway 1 MC Gateway 2 Gateway 3 MC MP MCU 1 MC MP MCU 2 MC GW, GK & MCU can be a single device 3
INTRODUCTION H. 323 Components • • Terminal Gateway (GW) Gatekeeper (GK) Multipoint Control Unit (MCU) – Multipoint Controller (MC) – Multipoint Processor (MP) Terminal 1 Terminal 2 MC Gatekeeper 1 Gatekeeper 2 MC Gatekeeper 3 MC MP LAN Gateway 1 MC Gateway 2 Gateway 3 MC MP MCU 1 MC MP MCU 2 MC GW, GK & MCU can be a single device 3
 INTRODUCTION Gatekeeper in H. 323 • Gatekeepers are optional • Mandatory functions if present: – Address translation (routing) to determine destination address of H. 323 endpoint for a call – Admission control to determine whether to allow endpoints to originate and terminate calls – Bandwidth control to, at a minimum, process bandwidth requests (can be a null function) – Zone management 4
INTRODUCTION Gatekeeper in H. 323 • Gatekeepers are optional • Mandatory functions if present: – Address translation (routing) to determine destination address of H. 323 endpoint for a call – Admission control to determine whether to allow endpoints to originate and terminate calls – Bandwidth control to, at a minimum, process bandwidth requests (can be a null function) – Zone management 4
 INTRODUCTION Gatekeeper in H. 323 (contd. ) • Gatekeeper optional functions: – Call control signalling to handle directly the Q. 931 signalling between the H. 323 endpoints – Call authorization using some policy (e. g. subscription status) – Bandwidth management to process bandwidth requests using some policy (e. g. based on current conditions) – Call management to process call requests using some policy (e. g. based on endpoint status) – Gatekeeper management information (MIB) – Bandwidth reservation for terminals not capable of performing it – Directory services 5
INTRODUCTION Gatekeeper in H. 323 (contd. ) • Gatekeeper optional functions: – Call control signalling to handle directly the Q. 931 signalling between the H. 323 endpoints – Call authorization using some policy (e. g. subscription status) – Bandwidth management to process bandwidth requests using some policy (e. g. based on current conditions) – Call management to process call requests using some policy (e. g. based on endpoint status) – Gatekeeper management information (MIB) – Bandwidth reservation for terminals not capable of performing it – Directory services 5
 INTRODUCTION Why are Gatekeepers Useful? • Centralized Management – Authentication, routing, call detail recording, etc. • Isolate Endpoints from Network Internals – Knowledge of naming structures, gateway routing algorithms, etc, stays in network • Interface to New and Existing Network Databases – LDAP directories, RADIUS servers, SCPs, etc. • Interfaces to Other H. 323 Networks – Calls between service providers 6
INTRODUCTION Why are Gatekeepers Useful? • Centralized Management – Authentication, routing, call detail recording, etc. • Isolate Endpoints from Network Internals – Knowledge of naming structures, gateway routing algorithms, etc, stays in network • Interface to New and Existing Network Databases – LDAP directories, RADIUS servers, SCPs, etc. • Interfaces to Other H. 323 Networks – Calls between service providers 6
 INTRODUCTION Gatekeeper Standards • Standards specify the communications between H. 323 entities and Gatekeepers (RAS messages) • Standards specify the services a Gatekeeper must provide BUT • Standards DO NOT specify how the Gatekeeper should provide those services • Standards DO NOT fully specify how Gatekeepers locate other Gatekeepers 7
INTRODUCTION Gatekeeper Standards • Standards specify the communications between H. 323 entities and Gatekeepers (RAS messages) • Standards specify the services a Gatekeeper must provide BUT • Standards DO NOT specify how the Gatekeeper should provide those services • Standards DO NOT fully specify how Gatekeepers locate other Gatekeepers 7
 CONCEPTS AND FUNCTIONS H. 323 ZONE • Simply defined as the collection of H. 323 devices managed by a single gatekeeper • Boundaries of a zone can be based on administrative, naming structure, geographic, engineering (or other) criteria • Calls between endpoints in a zone handled by a single gatekeeper • Calls between endpoints in different zones might involve gatekeepers from both zones 8
CONCEPTS AND FUNCTIONS H. 323 ZONE • Simply defined as the collection of H. 323 devices managed by a single gatekeeper • Boundaries of a zone can be based on administrative, naming structure, geographic, engineering (or other) criteria • Calls between endpoints in a zone handled by a single gatekeeper • Calls between endpoints in different zones might involve gatekeepers from both zones 8
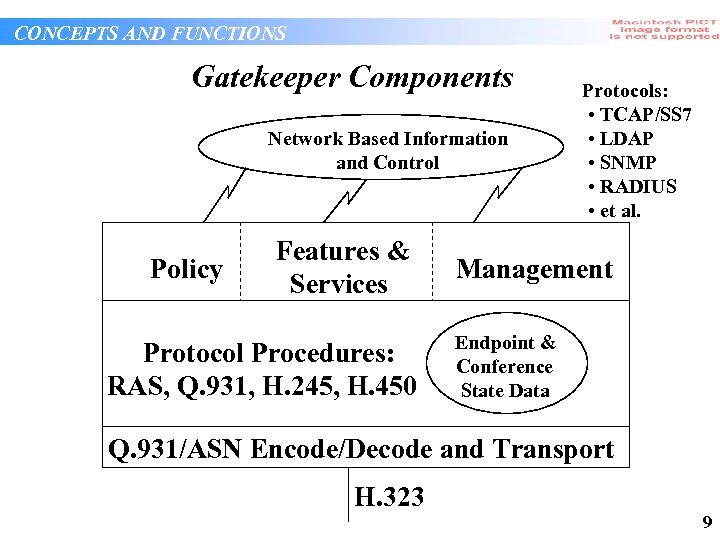 CONCEPTS AND FUNCTIONS Gatekeeper Components Network Based Information and Control Policy Features & Services Protocol Procedures: RAS, Q. 931, H. 245, H. 450 Protocols: • TCAP/SS 7 • LDAP • SNMP • RADIUS • et al. Management Endpoint & Conference State Data Q. 931/ASN Encode/Decode and Transport H. 323 9
CONCEPTS AND FUNCTIONS Gatekeeper Components Network Based Information and Control Policy Features & Services Protocol Procedures: RAS, Q. 931, H. 245, H. 450 Protocols: • TCAP/SS 7 • LDAP • SNMP • RADIUS • et al. Management Endpoint & Conference State Data Q. 931/ASN Encode/Decode and Transport H. 323 9
 SIGNALLING MODELS Signalling Models • The signalling model determines which protocol messages pass through the gatekeeper, and which pass directly between the two endpoints • The more messages that are routed between the gatekeeper, the more informational and control it has -- and more load and responsibility • The gatekeeper ultimately decides the signalling model • Media never passes through the gatekeeper function (although a proxy could be co-located on same host) 10
SIGNALLING MODELS Signalling Models • The signalling model determines which protocol messages pass through the gatekeeper, and which pass directly between the two endpoints • The more messages that are routed between the gatekeeper, the more informational and control it has -- and more load and responsibility • The gatekeeper ultimately decides the signalling model • Media never passes through the gatekeeper function (although a proxy could be co-located on same host) 10
 CONCEPTS AND FUNCTIONS Signalling Models Notes: • The following signalling model scenarios show calls between a PC terminal and a PSTN gateway, but generally apply to any call between two H. 323 endpoints 11
CONCEPTS AND FUNCTIONS Signalling Models Notes: • The following signalling model scenarios show calls between a PC terminal and a PSTN gateway, but generally apply to any call between two H. 323 endpoints 11
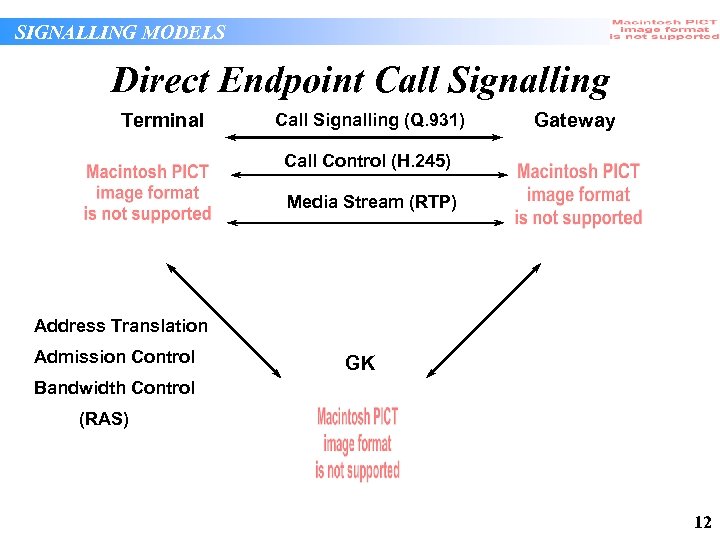 SIGNALLING MODELS Direct Endpoint Call Signalling Terminal Call Signalling (Q. 931) Gateway Call Control (H. 245) Media Stream (RTP) Address Translation Admission Control GK Bandwidth Control (RAS) 12
SIGNALLING MODELS Direct Endpoint Call Signalling Terminal Call Signalling (Q. 931) Gateway Call Control (H. 245) Media Stream (RTP) Address Translation Admission Control GK Bandwidth Control (RAS) 12
 SIGNALLING MODELS Direct Endpoint Call Signalling • Gatekeeper participates in call admission but has limited direct knowledge of connected calls • Due to limited involvement, single gatekeeper can process large number of calls • Limits service management functions: gatekeeper cannot determine call completion rates, for example • Limits centralized security: gatekeeper cannot validate Q. 931 message fields (e. g. caller’s ID) • Limits call detail recording function: gatekeeper depends on endpoint(s) for call duration information, for example 13
SIGNALLING MODELS Direct Endpoint Call Signalling • Gatekeeper participates in call admission but has limited direct knowledge of connected calls • Due to limited involvement, single gatekeeper can process large number of calls • Limits service management functions: gatekeeper cannot determine call completion rates, for example • Limits centralized security: gatekeeper cannot validate Q. 931 message fields (e. g. caller’s ID) • Limits call detail recording function: gatekeeper depends on endpoint(s) for call duration information, for example 13
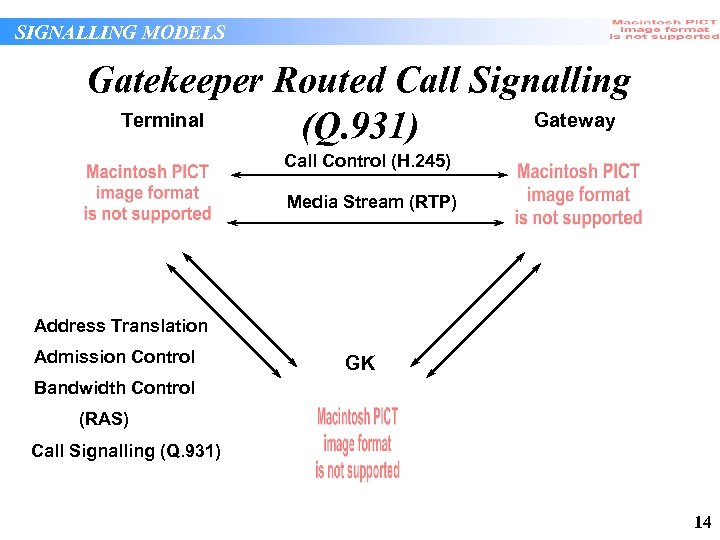 SIGNALLING MODELS Gatekeeper Routed Call Signalling Terminal Gateway (Q. 931) Call Control (H. 245) Media Stream (RTP) Address Translation Admission Control GK Bandwidth Control (RAS) Call Signalling (Q. 931) 14
SIGNALLING MODELS Gatekeeper Routed Call Signalling Terminal Gateway (Q. 931) Call Control (H. 245) Media Stream (RTP) Address Translation Admission Control GK Bandwidth Control (RAS) Call Signalling (Q. 931) 14
 SIGNALLING MODELS Gatekeeper Routed Call Signalling • Gatekeeper aware (Q. 931) of connection state of call but not media usage (no access to H. 245 signalling) • More load on gatekeeper as it must process Q. 931 messages and maintain Q. 931 signalling channel • Service management functions can include connection statistics but not media usage • Gatekeeper can validate Q. 931 message parameters such as calling party information • Call detail recording functions enhanced by direct knowledge of connection state 15
SIGNALLING MODELS Gatekeeper Routed Call Signalling • Gatekeeper aware (Q. 931) of connection state of call but not media usage (no access to H. 245 signalling) • More load on gatekeeper as it must process Q. 931 messages and maintain Q. 931 signalling channel • Service management functions can include connection statistics but not media usage • Gatekeeper can validate Q. 931 message parameters such as calling party information • Call detail recording functions enhanced by direct knowledge of connection state 15
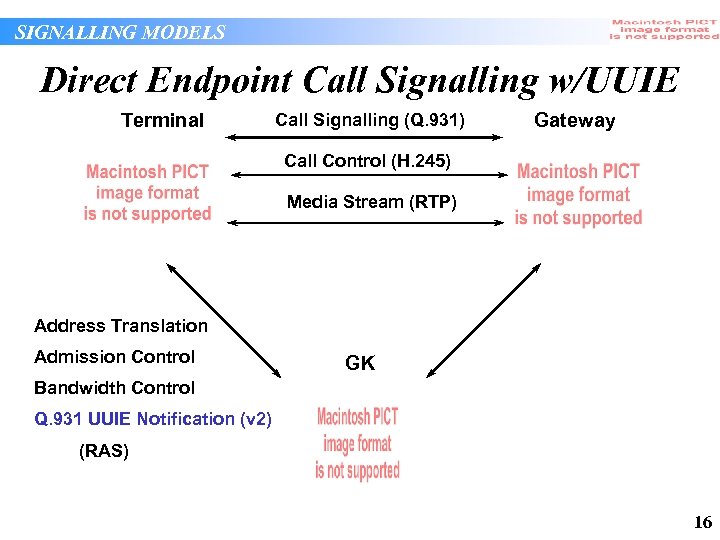 SIGNALLING MODELS Direct Endpoint Call Signalling w/UUIE Terminal Call Signalling (Q. 931) Gateway Call Control (H. 245) Media Stream (RTP) Address Translation Admission Control GK Bandwidth Control Q. 931 UUIE Notification (v 2) (RAS) 16
SIGNALLING MODELS Direct Endpoint Call Signalling w/UUIE Terminal Call Signalling (Q. 931) Gateway Call Control (H. 245) Media Stream (RTP) Address Translation Admission Control GK Bandwidth Control Q. 931 UUIE Notification (v 2) (RAS) 16
 SIGNALLING MODELS Direct Endpoint Call Signalling w/UUIE • Hybrid between direct call signalling and gatekeeper routed signalling • Q. 931 messages do not flow through the gatekeeper, but gatekeeper is notified of Q. 931 content in RAS messages. 17
SIGNALLING MODELS Direct Endpoint Call Signalling w/UUIE • Hybrid between direct call signalling and gatekeeper routed signalling • Q. 931 messages do not flow through the gatekeeper, but gatekeeper is notified of Q. 931 content in RAS messages. 17
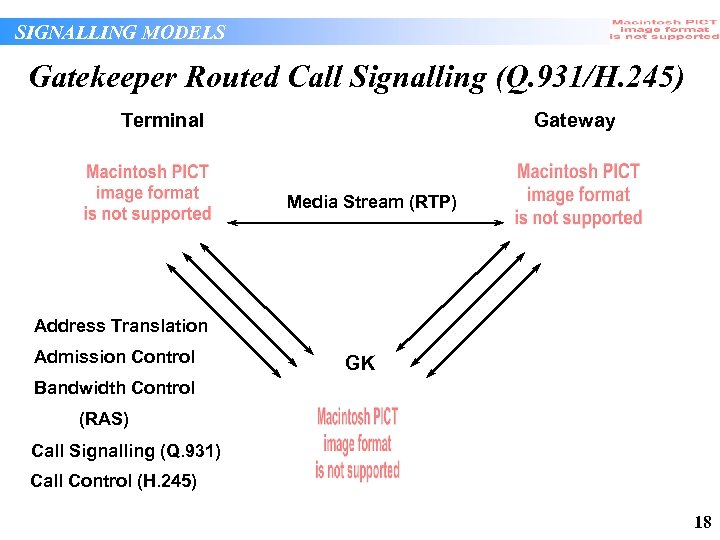 SIGNALLING MODELS Gatekeeper Routed Call Signalling (Q. 931/H. 245) Terminal Gateway Media Stream (RTP) Address Translation Admission Control GK Bandwidth Control (RAS) Call Signalling (Q. 931) Call Control (H. 245) 18
SIGNALLING MODELS Gatekeeper Routed Call Signalling (Q. 931/H. 245) Terminal Gateway Media Stream (RTP) Address Translation Admission Control GK Bandwidth Control (RAS) Call Signalling (Q. 931) Call Control (H. 245) 18
 SIGNALLING MODELS Gatekeeper Routed Call Signalling (Q. 931/H. 245) • Gatekeeper aware of connection state of call and media channels in use (can audit bandwidth usage) • Highest load on gatekeeper as it must process Q. 931 and H. 245 messages and maintain the corresponding signalling channels • Service management functions can include connection and media usage statistics • Call detail recording functions further enhanced by direct knowledge of media usage 19
SIGNALLING MODELS Gatekeeper Routed Call Signalling (Q. 931/H. 245) • Gatekeeper aware of connection state of call and media channels in use (can audit bandwidth usage) • Highest load on gatekeeper as it must process Q. 931 and H. 245 messages and maintain the corresponding signalling channels • Service management functions can include connection and media usage statistics • Call detail recording functions further enhanced by direct knowledge of media usage 19
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Gatekeeper Operations and Policy Notes: • List of parameters in messages is not inclusive • Parameter names displayed as follows: – Required parameters shown in bold – Optional parameters shown in italic – Version 2 parameters shown in blue (bold or italic) • LDAP/TCAP message content is paraphrased for illustration 20
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Gatekeeper Operations and Policy Notes: • List of parameters in messages is not inclusive • Parameter names displayed as follows: – Required parameters shown in bold – Optional parameters shown in italic – Version 2 parameters shown in blue (bold or italic) • LDAP/TCAP message content is paraphrased for illustration 20
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Endpoint/GK Discovery (1) Who is my GK? Endpoint (2) I can be your GK (1) GRQ GK (2) GCF/GRJ Gatekeeper. Request: request. Seq. Num ras. Address endpoint. Type gatekeeper. Identifier endpoint. Alias Gatekeeper. Confirm: request. Seq. Num gatekeeper. Identifier ras. Address alternate. Gatekeeper et al. 21
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Endpoint/GK Discovery (1) Who is my GK? Endpoint (2) I can be your GK (1) GRQ GK (2) GCF/GRJ Gatekeeper. Request: request. Seq. Num ras. Address endpoint. Type gatekeeper. Identifier endpoint. Alias Gatekeeper. Confirm: request. Seq. Num gatekeeper. Identifier ras. Address alternate. Gatekeeper et al. 21
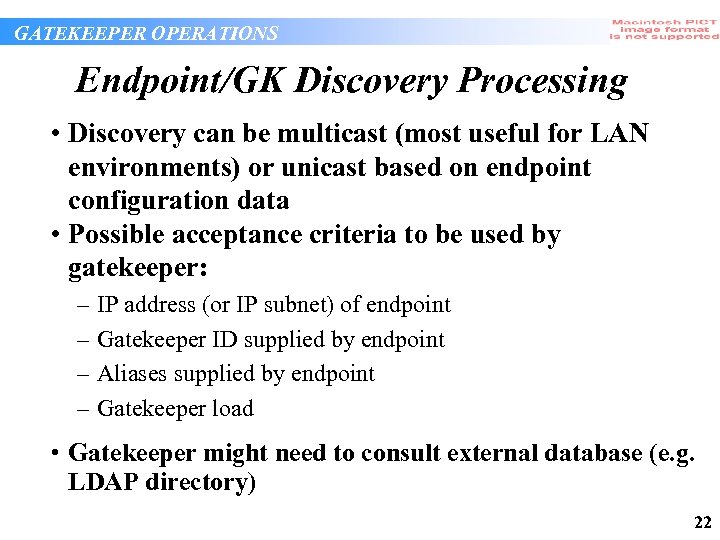 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Endpoint/GK Discovery Processing • Discovery can be multicast (most useful for LAN environments) or unicast based on endpoint configuration data • Possible acceptance criteria to be used by gatekeeper: – – IP address (or IP subnet) of endpoint Gatekeeper ID supplied by endpoint Aliases supplied by endpoint Gatekeeper load • Gatekeeper might need to consult external database (e. g. LDAP directory) 22
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Endpoint/GK Discovery Processing • Discovery can be multicast (most useful for LAN environments) or unicast based on endpoint configuration data • Possible acceptance criteria to be used by gatekeeper: – – IP address (or IP subnet) of endpoint Gatekeeper ID supplied by endpoint Aliases supplied by endpoint Gatekeeper load • Gatekeeper might need to consult external database (e. g. LDAP directory) 22
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Endpoint/GK Registration (1) Here are my aliases and IP address (2) OK (1) RRQ Endpoint GK (2) RCF/RRJ Registration. Request: request. Seq. Num call. Signal. Address Registration. Confirm: request. Seq. Num terminal. Alias time. To. Live endpoint. Identifier will. Respond. To. IRR keep. Alive will. Supply. UUIEs et al. alternate. Gatekeeper time. To. Live pre. Granted. ARQ et al. 23
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Endpoint/GK Registration (1) Here are my aliases and IP address (2) OK (1) RRQ Endpoint GK (2) RCF/RRJ Registration. Request: request. Seq. Num call. Signal. Address Registration. Confirm: request. Seq. Num terminal. Alias time. To. Live endpoint. Identifier will. Respond. To. IRR keep. Alive will. Supply. UUIEs et al. alternate. Gatekeeper time. To. Live pre. Granted. ARQ et al. 23
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Endpoint/GK Registration Processing • Gatekeeper might authenticate endpoint – H 323 v 1 must use ad hoc/proprietary methods such as supplied aliases, IP address, etc. – H. 323 v 2 can use encrypted password or certificates • Gatekeeper might authorize endpoint – Validate list of supplied aliases • Associate aliases with the IP address for later location • Gatekeeper assigns and returns Endpoint ID to be used in subsequent messages 24
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Endpoint/GK Registration Processing • Gatekeeper might authenticate endpoint – H 323 v 1 must use ad hoc/proprietary methods such as supplied aliases, IP address, etc. – H. 323 v 2 can use encrypted password or certificates • Gatekeeper might authorize endpoint – Validate list of supplied aliases • Associate aliases with the IP address for later location • Gatekeeper assigns and returns Endpoint ID to be used in subsequent messages 24
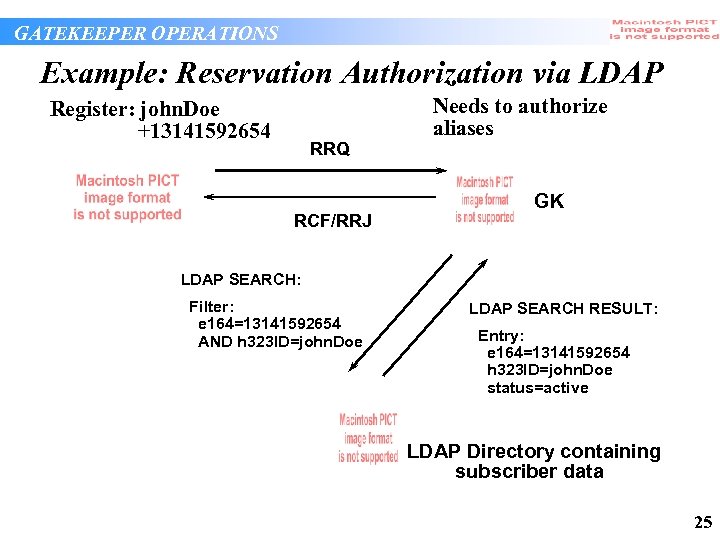 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Example: Reservation Authorization via LDAP Register: john. Doe +13141592654 RRQ RCF/RRJ Needs to authorize aliases GK LDAP SEARCH: Filter: e 164=13141592654 AND h 323 ID=john. Doe LDAP SEARCH RESULT: Entry: e 164=13141592654 h 323 ID=john. Doe status=active LDAP Directory containing subscriber data 25
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Example: Reservation Authorization via LDAP Register: john. Doe +13141592654 RRQ RCF/RRJ Needs to authorize aliases GK LDAP SEARCH: Filter: e 164=13141592654 AND h 323 ID=john. Doe LDAP SEARCH RESULT: Entry: e 164=13141592654 h 323 ID=john. Doe status=active LDAP Directory containing subscriber data 25
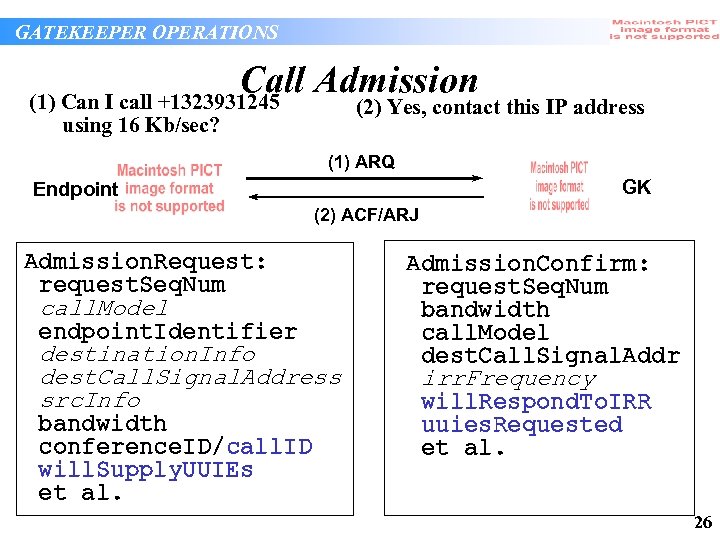 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Call Admission (1) Can I call +1323931245 (2) Yes, contact this IP address using 16 Kb/sec? (1) ARQ GK Endpoint (2) ACF/ARJ Admission. Request: request. Seq. Num call. Model endpoint. Identifier destination. Info dest. Call. Signal. Address src. Info bandwidth conference. ID/call. ID will. Supply. UUIEs et al. Admission. Confirm: request. Seq. Num bandwidth call. Model dest. Call. Signal. Addr irr. Frequency will. Respond. To. IRR uuies. Requested et al. 26
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Call Admission (1) Can I call +1323931245 (2) Yes, contact this IP address using 16 Kb/sec? (1) ARQ GK Endpoint (2) ACF/ARJ Admission. Request: request. Seq. Num call. Model endpoint. Identifier destination. Info dest. Call. Signal. Address src. Info bandwidth conference. ID/call. ID will. Supply. UUIEs et al. Admission. Confirm: request. Seq. Num bandwidth call. Model dest. Call. Signal. Addr irr. Frequency will. Respond. To. IRR uuies. Requested et al. 26
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Call Admission Processing • Gatekeeper might authenticate endpoint to ensure it is registered and check if it is authorized to make call • Gatekeeper must determine call model – Endpoint can ask for preference but gatekeeper will decide • Gatekeeper might check for bandwidth • If direct signalling, gatekeeper supplies destination endpoint address (discussed later) • If gatekeeper routed signalling, it supplies its own address and can defer routing 27
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Call Admission Processing • Gatekeeper might authenticate endpoint to ensure it is registered and check if it is authorized to make call • Gatekeeper must determine call model – Endpoint can ask for preference but gatekeeper will decide • Gatekeeper might check for bandwidth • If direct signalling, gatekeeper supplies destination endpoint address (discussed later) • If gatekeeper routed signalling, it supplies its own address and can defer routing 27
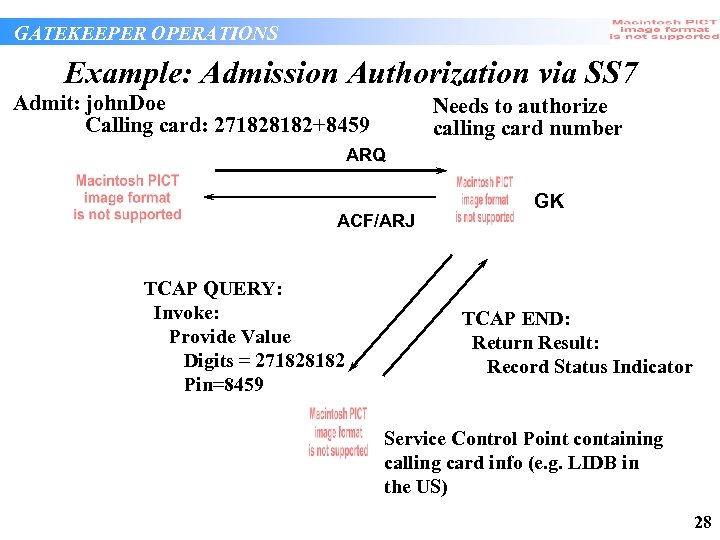 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Example: Admission Authorization via SS 7 Admit: john. Doe Calling card: 271828182+8459 Needs to authorize calling card number ARQ ACF/ARJ TCAP QUERY: Invoke: Provide Value Digits = 271828182 Pin=8459 GK TCAP END: Return Result: Record Status Indicator Service Control Point containing calling card info (e. g. LIDB in the US) 28
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Example: Admission Authorization via SS 7 Admit: john. Doe Calling card: 271828182+8459 Needs to authorize calling card number ARQ ACF/ARJ TCAP QUERY: Invoke: Provide Value Digits = 271828182 Pin=8459 GK TCAP END: Return Result: Record Status Indicator Service Control Point containing calling card info (e. g. LIDB in the US) 28
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS (1) Connect me to +108061998 Endpoint Q. 931 Setup (2) Determine gateway (2) Start PSTN origination SETUP GK SETUP message IEs: Bearer capability IE GW User-to-user IE: Display IE h 245 Address Calling party number IE source. Info Called party number IE destination. Addr conference. ID call. Identifier fast. Start fast. Cap et al. 29
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS (1) Connect me to +108061998 Endpoint Q. 931 Setup (2) Determine gateway (2) Start PSTN origination SETUP GK SETUP message IEs: Bearer capability IE GW User-to-user IE: Display IE h 245 Address Calling party number IE source. Info Called party number IE destination. Addr conference. ID call. Identifier fast. Start fast. Cap et al. 29
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Setup Processing • Gatekeeper associates Setup with previous admission using Conference ID • Destination determined using Calling Party Number or destination alias(es) • External databases might be consulted to determine destination endpoint: – Map full destination alias to a terminal – Map leading digits of E. 164 number to gateway(s) • Setup message is forwarded to destination 30
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Setup Processing • Gatekeeper associates Setup with previous admission using Conference ID • Destination determined using Calling Party Number or destination alias(es) • External databases might be consulted to determine destination endpoint: – Map full destination alias to a terminal – Map leading digits of E. 164 number to gateway(s) • Setup message is forwarded to destination 30
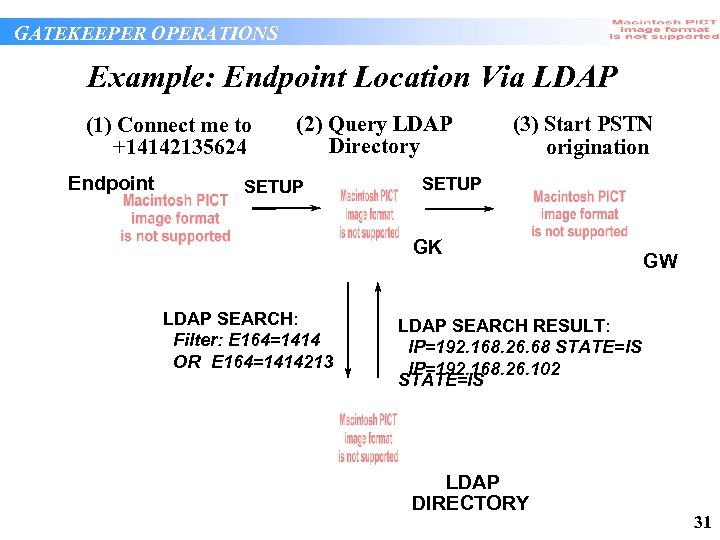 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Example: Endpoint Location Via LDAP (1) Connect me to +14142135624 Endpoint (2) Query LDAP Directory SETUP (3) Start PSTN origination SETUP GK LDAP SEARCH: Filter: E 164=1414 OR E 164=1414213 GW LDAP SEARCH RESULT: IP=192. 168. 26. 68 STATE=IS IP=192. 168. 26. 102 STATE=IS LDAP DIRECTORY 31
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Example: Endpoint Location Via LDAP (1) Connect me to +14142135624 Endpoint (2) Query LDAP Directory SETUP (3) Start PSTN origination SETUP GK LDAP SEARCH: Filter: E 164=1414 OR E 164=1414213 GW LDAP SEARCH RESULT: IP=192. 168. 26. 68 STATE=IS IP=192. 168. 26. 102 STATE=IS LDAP DIRECTORY 31
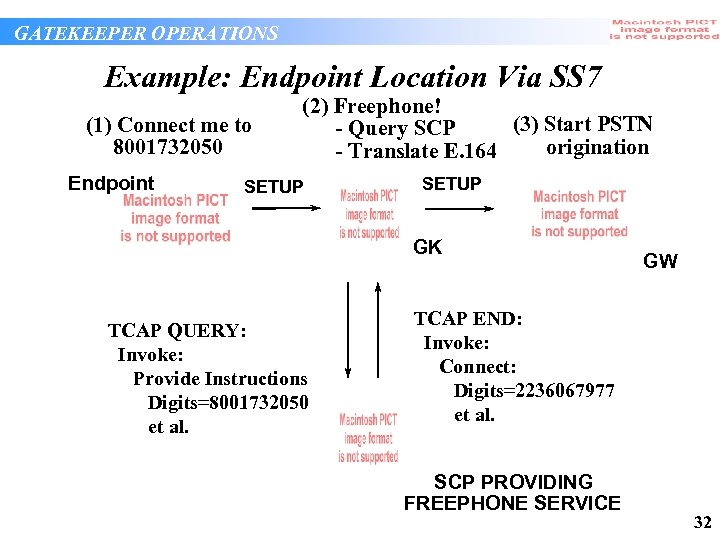 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Example: Endpoint Location Via SS 7 (1) Connect me to 8001732050 Endpoint (2) Freephone! (3) Start PSTN - Query SCP origination - Translate E. 164 SETUP GK TCAP QUERY: Invoke: Provide Instructions Digits=8001732050 et al. GW TCAP END: Invoke: Connect: Digits=2236067977 et al. SCP PROVIDING FREEPHONE SERVICE 32
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Example: Endpoint Location Via SS 7 (1) Connect me to 8001732050 Endpoint (2) Freephone! (3) Start PSTN - Query SCP origination - Translate E. 164 SETUP GK TCAP QUERY: Invoke: Provide Instructions Digits=8001732050 et al. GW TCAP END: Invoke: Connect: Digits=2236067977 et al. SCP PROVIDING FREEPHONE SERVICE 32
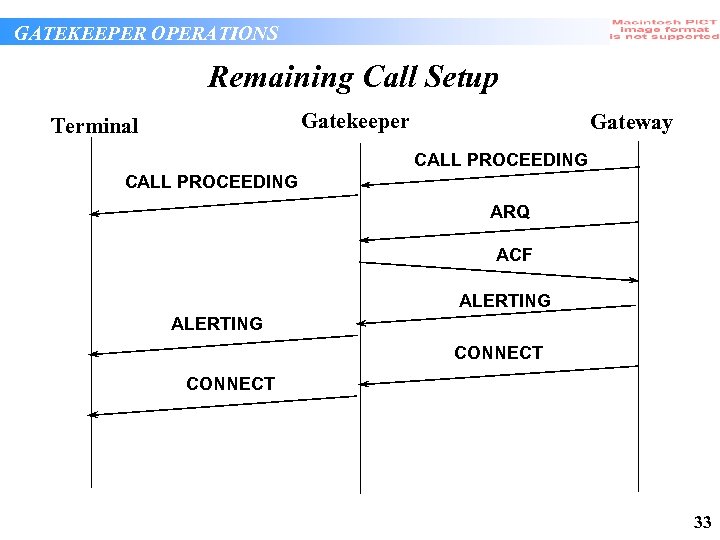 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Remaining Call Setup Gatekeeper Terminal Gateway CALL PROCEEDING ARQ ACF ALERTING CONNECT 33
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Remaining Call Setup Gatekeeper Terminal Gateway CALL PROCEEDING ARQ ACF ALERTING CONNECT 33
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Remaining Call Setup Processing • Gatekeeper processes terminating admissions request doing potential authorization and bandwidth checks • Gatekeeper primarily a “pipe” for Q. 931 messages but might authorize some fields (e. g. Display) • Gatekeeper substitutes its own address in “h 245 address” fields if it wishes to route H. 245 34
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Remaining Call Setup Processing • Gatekeeper processes terminating admissions request doing potential authorization and bandwidth checks • Gatekeeper primarily a “pipe” for Q. 931 messages but might authorize some fields (e. g. Display) • Gatekeeper substitutes its own address in “h 245 address” fields if it wishes to route H. 245 34
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Stable Call Processing • Gatekeeper verifies calls are “alive” using one of the following techniques: – Wait for periodic IRRs (as requested in the ACF) – Periodically send an IRQ, expecting an IRR – Periodically send a Q. 931 Status Enquiry, expecting a Status • Gatekeeper might receive bandwidth changes requests (BRQ) and must allow (BCF) or deny (BRJ) the request 35
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Stable Call Processing • Gatekeeper verifies calls are “alive” using one of the following techniques: – Wait for periodic IRRs (as requested in the ACF) – Periodically send an IRQ, expecting an IRR – Periodically send a Q. 931 Status Enquiry, expecting a Status • Gatekeeper might receive bandwidth changes requests (BRQ) and must allow (BCF) or deny (BRJ) the request 35
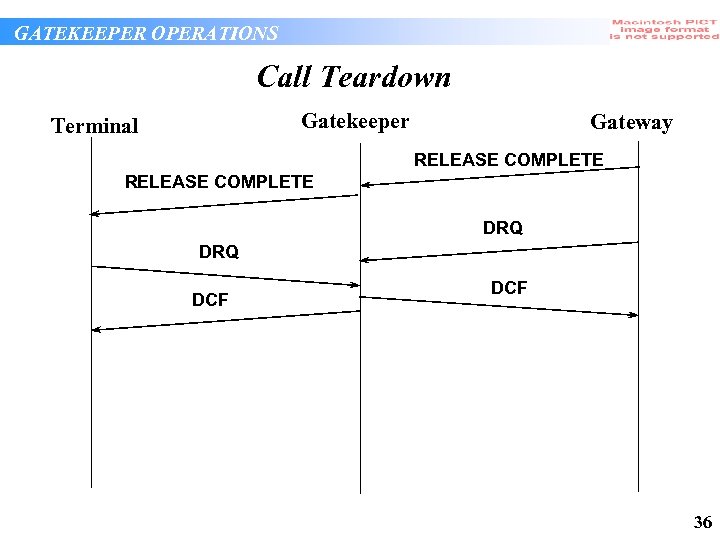 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Call Teardown Gatekeeper Terminal Gateway RELEASE COMPLETE DRQ DCF 36
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Call Teardown Gatekeeper Terminal Gateway RELEASE COMPLETE DRQ DCF 36
 GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Call Teardown Processing • Gatekeeper processes Release Complete, noting the time and forwards it to the other endpoint • Gatekeeper processes DRQ from both endpoints and releases any allocated bandwidth • Gatekeeper might create call detail record for the call, recording endpoint information and Connect and Release times for example 37
GATEKEEPER OPERATIONS Call Teardown Processing • Gatekeeper processes Release Complete, noting the time and forwards it to the other endpoint • Gatekeeper processes DRQ from both endpoints and releases any allocated bandwidth • Gatekeeper might create call detail record for the call, recording endpoint information and Connect and Release times for example 37
 H. 323 v 2 and Gatekeepers H. 323 v 2 Features Related to Gatekeeper • Authentication Framework – – Tokens (password or certificate based) for RAS TLS (certificate based) for Q. 931 Negotiated H. 245 security H. 323 defines the framework - need profiles to nail down specific choices of algorithms • Mechanism to specify alternative gatekeepers to endpoints • Registration “keep alive” similar to conference IRR “keep alive” 38
H. 323 v 2 and Gatekeepers H. 323 v 2 Features Related to Gatekeeper • Authentication Framework – – Tokens (password or certificate based) for RAS TLS (certificate based) for Q. 931 Negotiated H. 245 security H. 323 defines the framework - need profiles to nail down specific choices of algorithms • Mechanism to specify alternative gatekeepers to endpoints • Registration “keep alive” similar to conference IRR “keep alive” 38
 H. 323 v 2 and Gatekeepers H. 323 v 2 Features Related to Gatekeeper • RAS Transport Improvements – IRR ACK/NAK – Request In Progress (RIP) to ask for more time • Signalling changes – Excuse endpoints from Admission Requests – Fast call setup / tunneled H. 245 – Gatekeeper can request Q. 931 information be forwarded to it on direct routed calls • H. 450 Services – Call transfer and call forwarding 39
H. 323 v 2 and Gatekeepers H. 323 v 2 Features Related to Gatekeeper • RAS Transport Improvements – IRR ACK/NAK – Request In Progress (RIP) to ask for more time • Signalling changes – Excuse endpoints from Admission Requests – Fast call setup / tunneled H. 245 – Gatekeeper can request Q. 931 information be forwarded to it on direct routed calls • H. 450 Services – Call transfer and call forwarding 39
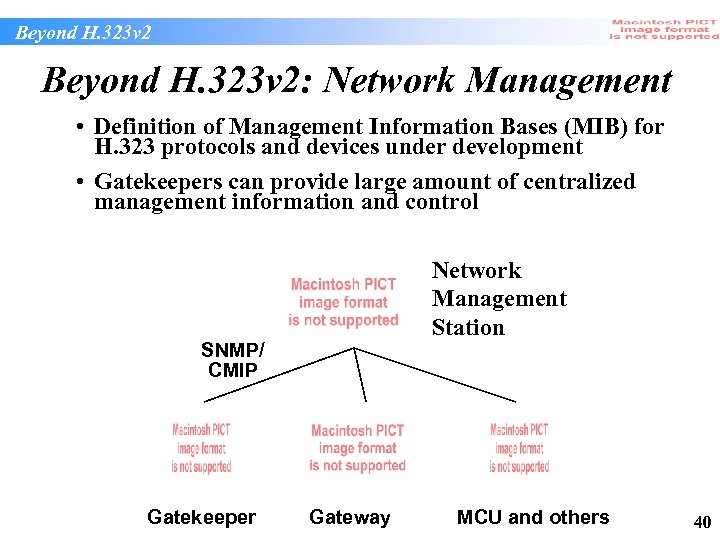 Beyond H. 323 v 2: Network Management • Definition of Management Information Bases (MIB) for H. 323 protocols and devices under development • Gatekeepers can provide large amount of centralized management information and control Network Management Station SNMP/ CMIP Gatekeeper Gateway MCU and others 40
Beyond H. 323 v 2: Network Management • Definition of Management Information Bases (MIB) for H. 323 protocols and devices under development • Gatekeepers can provide large amount of centralized management information and control Network Management Station SNMP/ CMIP Gatekeeper Gateway MCU and others 40
 Beyond H. 323 v 2: Inter-gatekeeper Communication • Current H. 323 standards do not provide an interzone model that scales well for large networks • Inter-gatekeeper protocols being discussed to enable gatekeepers to efficiently locate one another to route calls to non-local address • Hierarchical arrangements with “clearinghouse” gatekeepers have been proposed 41
Beyond H. 323 v 2: Inter-gatekeeper Communication • Current H. 323 standards do not provide an interzone model that scales well for large networks • Inter-gatekeeper protocols being discussed to enable gatekeepers to efficiently locate one another to route calls to non-local address • Hierarchical arrangements with “clearinghouse” gatekeepers have been proposed 41
 Internet Multimedia Communications Software. . . integratingvoice, fax, data and video integrating voice, fax, data and video For information on elemedia’s H. 323 Gateway Toolkits and H. 323 Gatekeeper Toolkits, please contact us at: +1 732 -949 -2184 888 -elemedia (1 -888 -353 -6334) (U. S. and Canada) Email: elemedia@lucent. com http: //www. elemedia. com 42
Internet Multimedia Communications Software. . . integratingvoice, fax, data and video integrating voice, fax, data and video For information on elemedia’s H. 323 Gateway Toolkits and H. 323 Gatekeeper Toolkits, please contact us at: +1 732 -949 -2184 888 -elemedia (1 -888 -353 -6334) (U. S. and Canada) Email: elemedia@lucent. com http: //www. elemedia. com 42


