Radiobiology School_lecture_Olga_2014.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 52
 -H 2 AX and REPAIR OF RADIATION-INDUCED DNA DOUBLE STRAND BREAKS Associate Professor Olga Martin Division of Radiation Oncology & Molecular Radiation Biology Laboratory Peter Mac. Callum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, Australia Olga. martin@petermac. org XII международная молодежная научная школа им. А. С. Саенко «Проблемы фундаментальной и прикладной радиобиологии» 27/05/2014
-H 2 AX and REPAIR OF RADIATION-INDUCED DNA DOUBLE STRAND BREAKS Associate Professor Olga Martin Division of Radiation Oncology & Molecular Radiation Biology Laboratory Peter Mac. Callum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, Australia Olga. martin@petermac. org XII международная молодежная научная школа им. А. С. Саенко «Проблемы фундаментальной и прикладной радиобиологии» 27/05/2014
 Peter Mac. Callum Cancer Centre, Melbourne • Comprehensive cancer centre which incorporates research labs (25 project groups, ~400 staff and students) • Clinical part involves the major modes on cancer treatment, surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy • The biggest radiotherapy centre in Australia treating 6000 new patients per year.
Peter Mac. Callum Cancer Centre, Melbourne • Comprehensive cancer centre which incorporates research labs (25 project groups, ~400 staff and students) • Clinical part involves the major modes on cancer treatment, surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy • The biggest radiotherapy centre in Australia treating 6000 new patients per year.
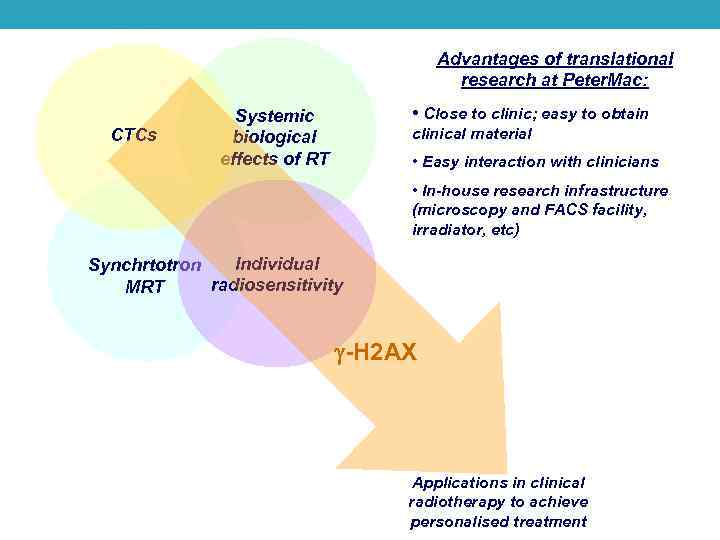 Advantages of translational research at Peter. Mac: CTCs • Close to clinic; easy to obtain Systemic biological effects of RT clinical material • Easy interaction with clinicians • In-house research infrastructure (microscopy and FACS facility, irradiator, etc) Individual Synchrtotron radiosensitivity MRT -H 2 AX Applications in clinical radiotherapy to achieve personalised treatment
Advantages of translational research at Peter. Mac: CTCs • Close to clinic; easy to obtain Systemic biological effects of RT clinical material • Easy interaction with clinicians • In-house research infrastructure (microscopy and FACS facility, irradiator, etc) Individual Synchrtotron radiosensitivity MRT -H 2 AX Applications in clinical radiotherapy to achieve personalised treatment
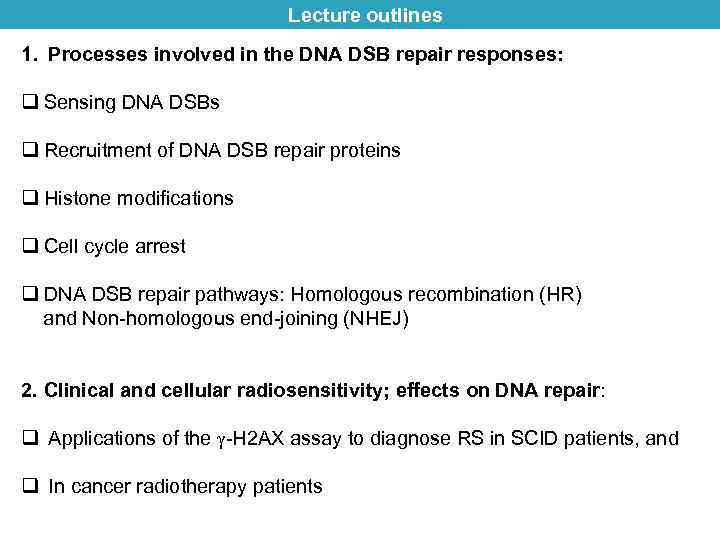 Lecture outlines 1. Processes involved in the DNA DSB repair responses: q Sensing DNA DSBs q Recruitment of DNA DSB repair proteins q Histone modifications q Cell cycle arrest q DNA DSB repair pathways: Homologous recombination (HR) and Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) 2. Clinical and cellular radiosensitivity; effects on DNA repair: q Applications of the -H 2 AX assay to diagnose RS in SCID patients, and q In cancer radiotherapy patients
Lecture outlines 1. Processes involved in the DNA DSB repair responses: q Sensing DNA DSBs q Recruitment of DNA DSB repair proteins q Histone modifications q Cell cycle arrest q DNA DSB repair pathways: Homologous recombination (HR) and Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) 2. Clinical and cellular radiosensitivity; effects on DNA repair: q Applications of the -H 2 AX assay to diagnose RS in SCID patients, and q In cancer radiotherapy patients
 1. Processes involved in the DNA DSB repair responses
1. Processes involved in the DNA DSB repair responses
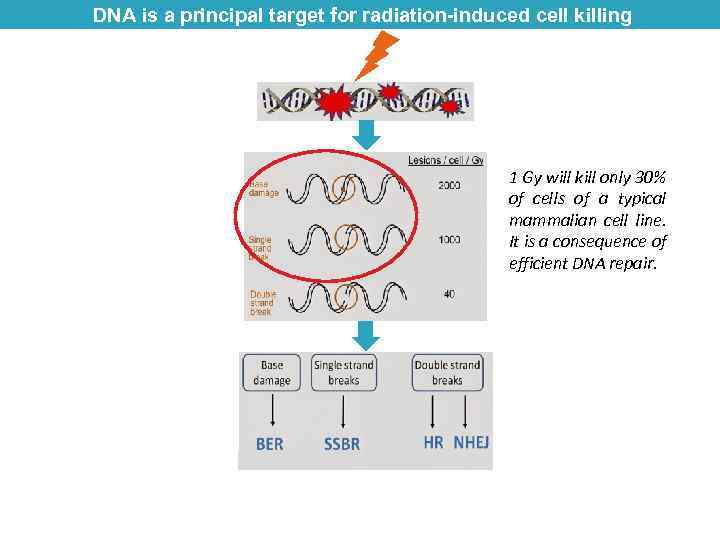 DNA is a principal target for radiation-induced cell killing 1 Gy will kill only 30% of cells of a typical mammalian cell line. It is a consequence of efficient DNA repair.
DNA is a principal target for radiation-induced cell killing 1 Gy will kill only 30% of cells of a typical mammalian cell line. It is a consequence of efficient DNA repair.
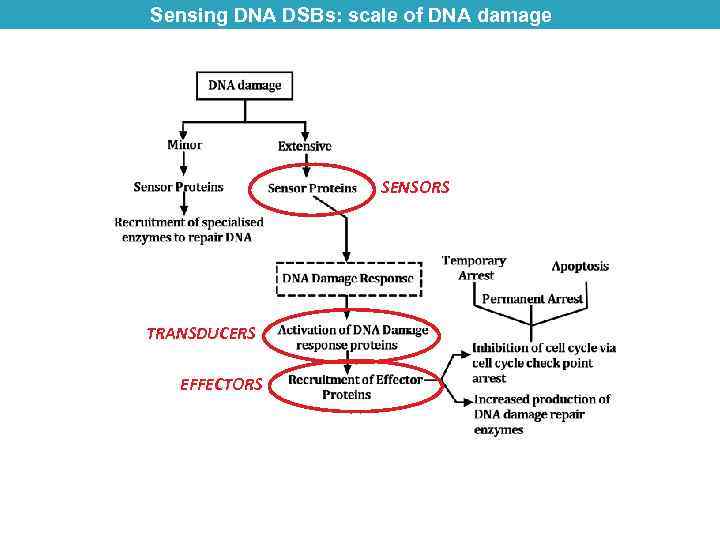 Sensing DNA DSBs: scale of DNA damage SENSORS TRANSDUCERS EFFECTORS
Sensing DNA DSBs: scale of DNA damage SENSORS TRANSDUCERS EFFECTORS
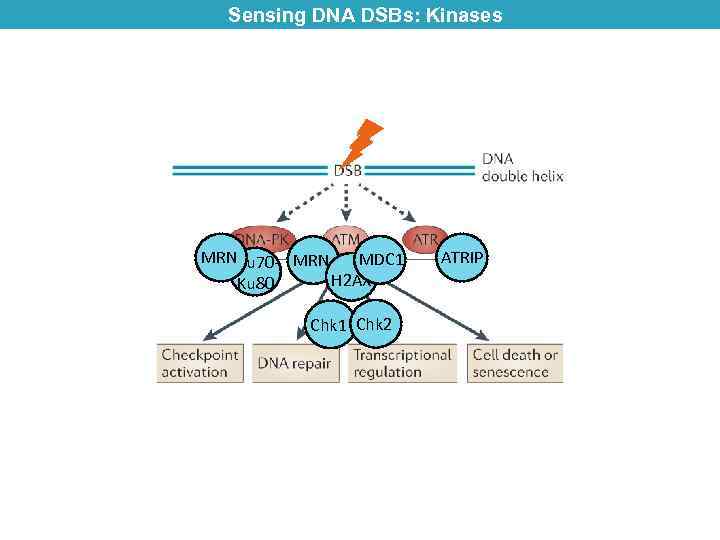 Sensing DNA DSBs: Kinases MRNKu 70 - MRN MDC 1 H 2 AX Ku 80 Chk 1 Chk 2 ATRIP
Sensing DNA DSBs: Kinases MRNKu 70 - MRN MDC 1 H 2 AX Ku 80 Chk 1 Chk 2 ATRIP
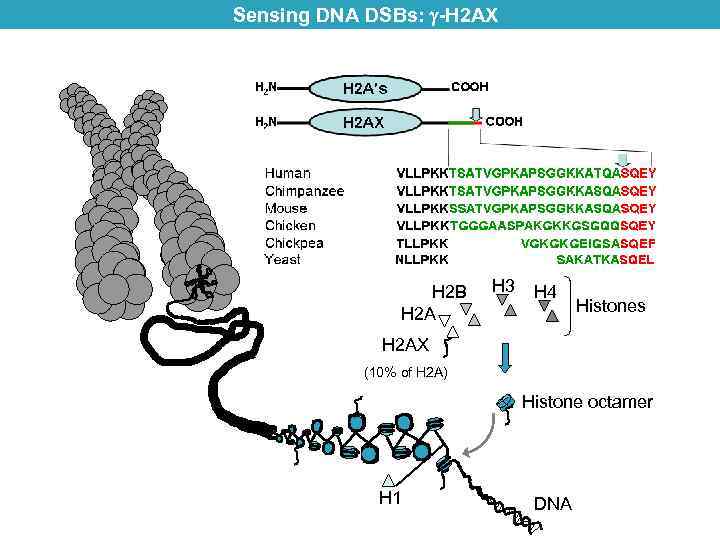 Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX H 2 B H 2 A H 3 H 4 Histones H 2 AX (10% of H 2 A) Histone octamer H 1 DNA
Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX H 2 B H 2 A H 3 H 4 Histones H 2 AX (10% of H 2 A) Histone octamer H 1 DNA
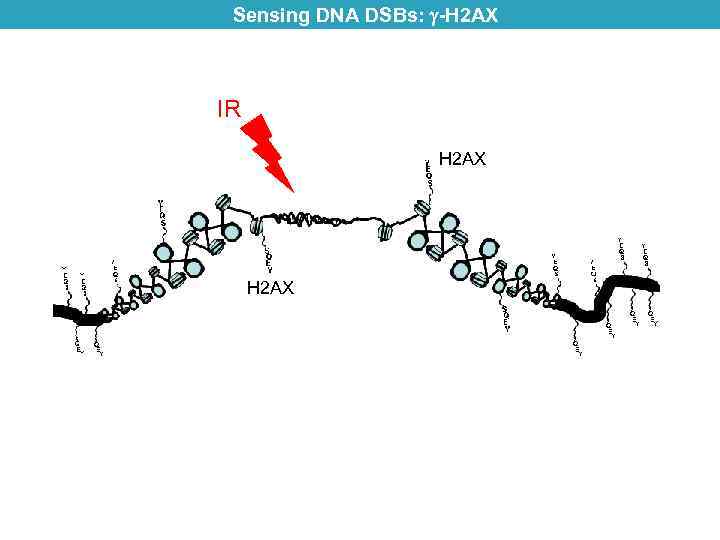 Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX IR H 2 AX
Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX IR H 2 AX
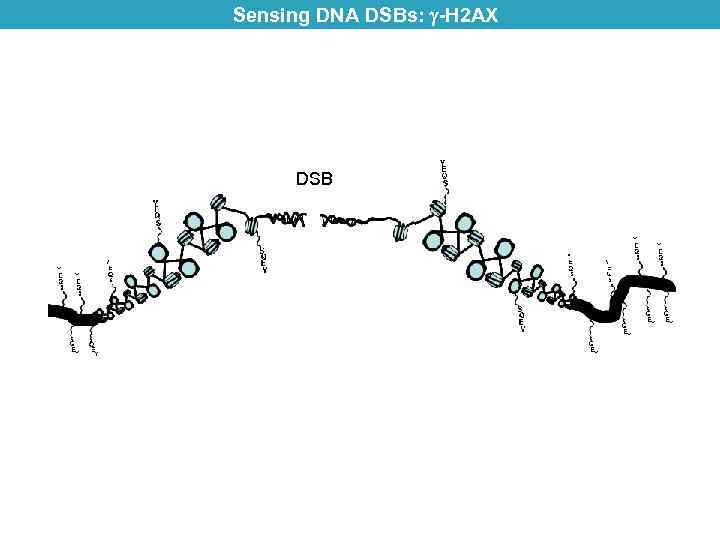 Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX DSB H 2 AX
Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX DSB H 2 AX
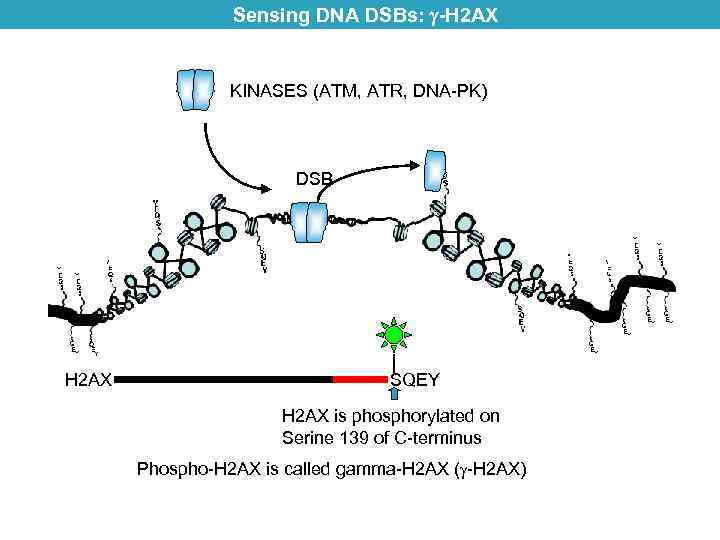 Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX KINASES (ATM, ATR, DNA-PK) DSB H 2 AX SQEY H 2 AX is phosphorylated on Serine 139 of C-terminus Phospho-H 2 AX is called gamma-H 2 AX ( -H 2 AX)
Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX KINASES (ATM, ATR, DNA-PK) DSB H 2 AX SQEY H 2 AX is phosphorylated on Serine 139 of C-terminus Phospho-H 2 AX is called gamma-H 2 AX ( -H 2 AX)
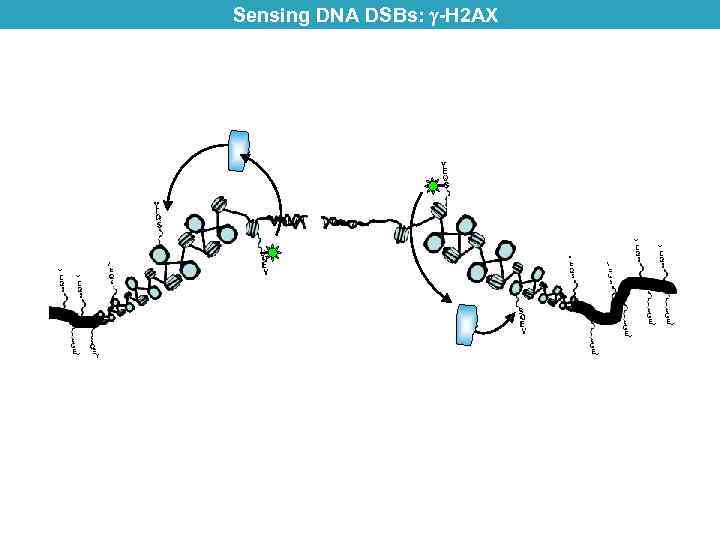 Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX
Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX
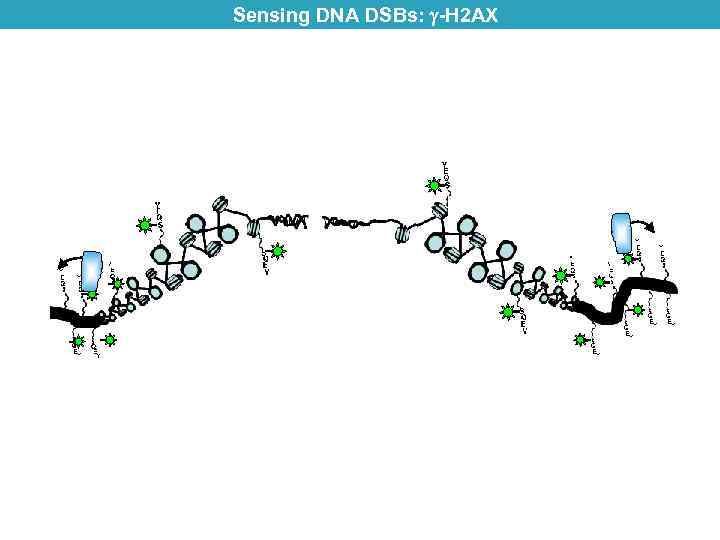 Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX
Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX
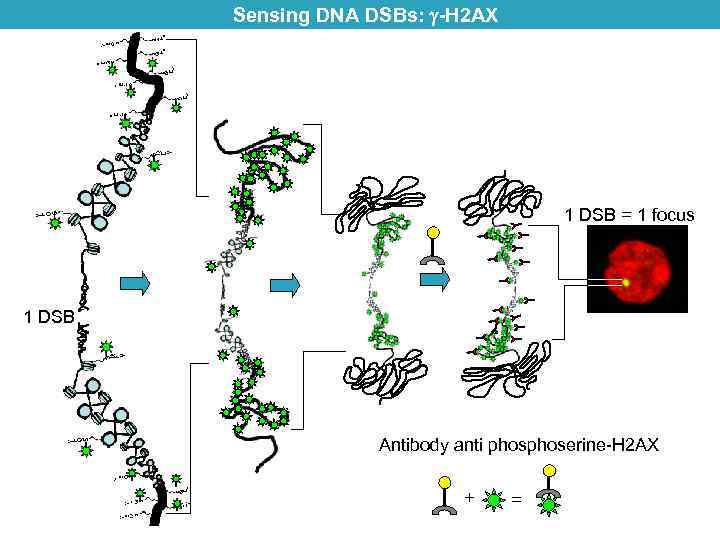 Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX 1 DSB = 1 focus 1 DSB Antibody anti phoserine-H 2 AX + =
Sensing DNA DSBs: -H 2 AX 1 DSB = 1 focus 1 DSB Antibody anti phoserine-H 2 AX + =
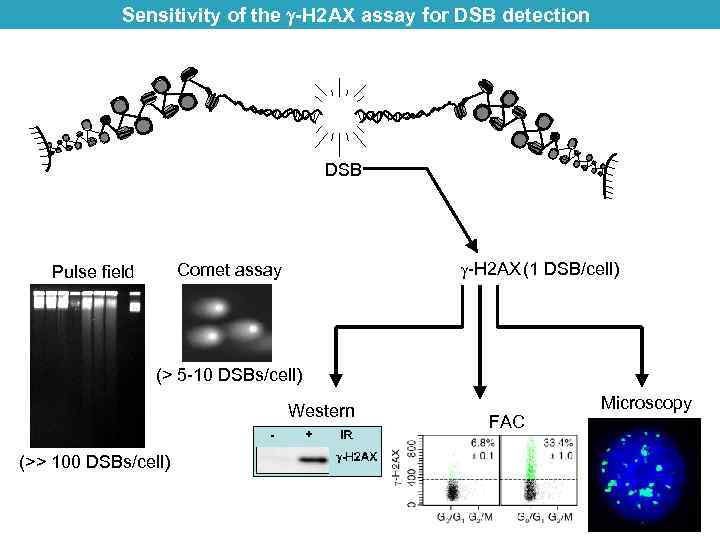 Sensitivity of the -H 2 AX assay for DSB detection DSB -H 2 AX (1 DSB/cell) Comet assay Pulse field (> 5 -10 DSBs/cell) Western (>> 100 DSBs/cell) FAC S Microscopy
Sensitivity of the -H 2 AX assay for DSB detection DSB -H 2 AX (1 DSB/cell) Comet assay Pulse field (> 5 -10 DSBs/cell) Western (>> 100 DSBs/cell) FAC S Microscopy
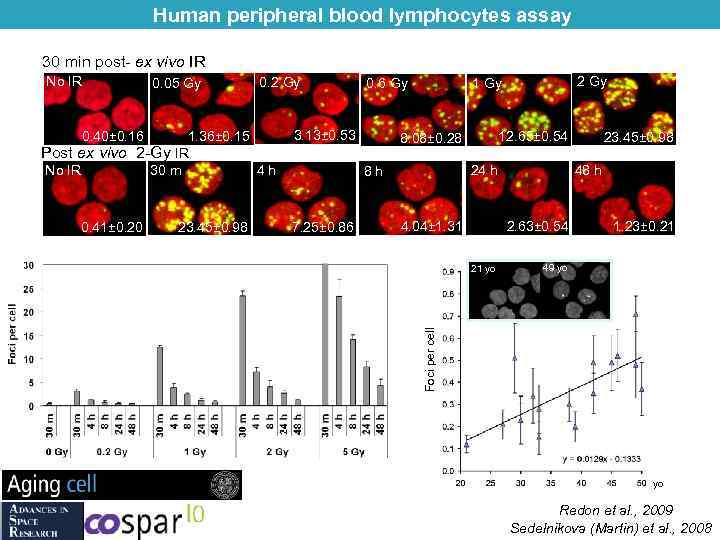 Human peripheral blood lymphocytes assay 30 min post- ex vivo IR 0. 05 Gy 0. 40± 0. 16 0. 2 Gy 1. 36± 0. 15 Post ex vivo 2 -Gy IR No IR 30 m 4 h 0. 41± 0. 20 23. 45± 0. 98 0. 6 Gy 3. 13± 0. 53 12. 65± 0. 54 8. 08± 0. 28 24 h 8 h 7. 25± 0. 86 2 Gy 1 Gy 4. 04± 1. 31 48 h 2. 63± 0. 54 21 yo 23. 45± 0. 98 1. 23± 0. 21 49 yo Foci per cell No IR yo Redon et al. , 2009 Sedelnikova (Martin) et al. , 2008
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes assay 30 min post- ex vivo IR 0. 05 Gy 0. 40± 0. 16 0. 2 Gy 1. 36± 0. 15 Post ex vivo 2 -Gy IR No IR 30 m 4 h 0. 41± 0. 20 23. 45± 0. 98 0. 6 Gy 3. 13± 0. 53 12. 65± 0. 54 8. 08± 0. 28 24 h 8 h 7. 25± 0. 86 2 Gy 1 Gy 4. 04± 1. 31 48 h 2. 63± 0. 54 21 yo 23. 45± 0. 98 1. 23± 0. 21 49 yo Foci per cell No IR yo Redon et al. , 2009 Sedelnikova (Martin) et al. , 2008
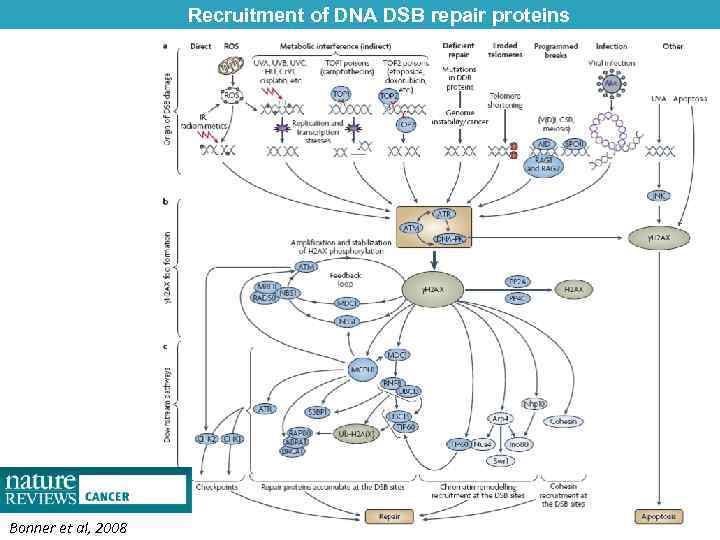 Recruitment of DNA DSB repair proteins Bonner et al, 2008
Recruitment of DNA DSB repair proteins Bonner et al, 2008
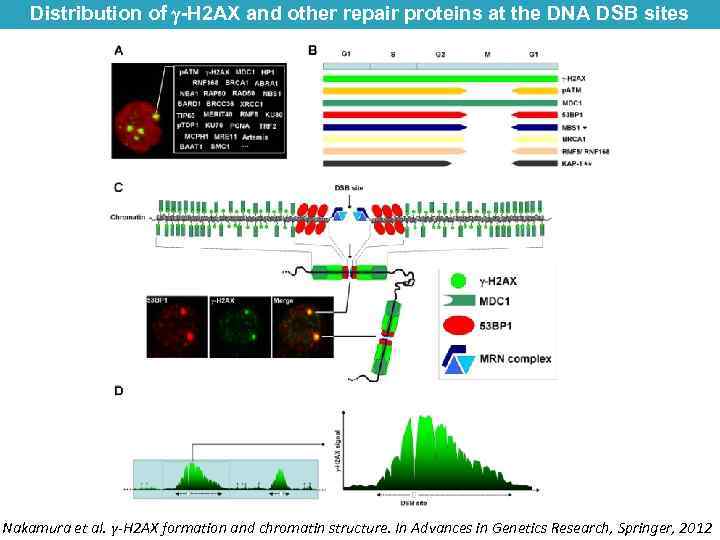 Distribution of -H 2 AX and other repair proteins at the DNA DSB sites Nakamura et al. γ-H 2 AX formation and chromatin structure. In Advances in Genetics Research, Springer, 2012
Distribution of -H 2 AX and other repair proteins at the DNA DSB sites Nakamura et al. γ-H 2 AX formation and chromatin structure. In Advances in Genetics Research, Springer, 2012
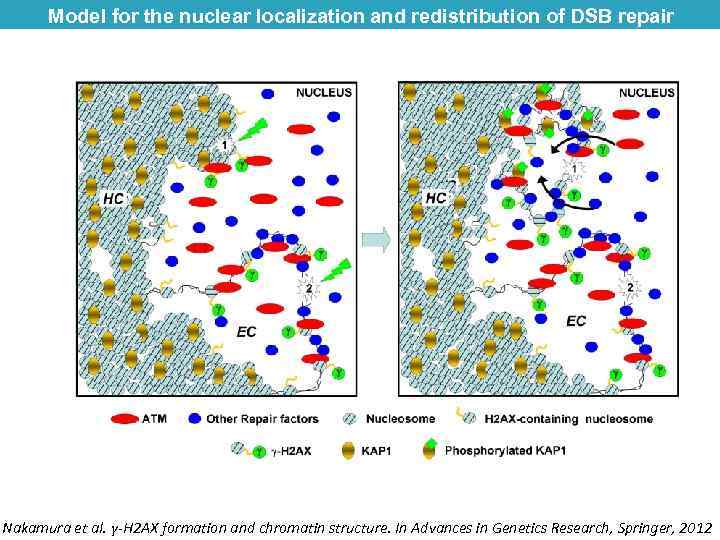 Model for the nuclear localization and redistribution of DSB repair proteins Nakamura et al. γ-H 2 AX formation and chromatin structure. In Advances in Genetics Research, Springer, 2012
Model for the nuclear localization and redistribution of DSB repair proteins Nakamura et al. γ-H 2 AX formation and chromatin structure. In Advances in Genetics Research, Springer, 2012
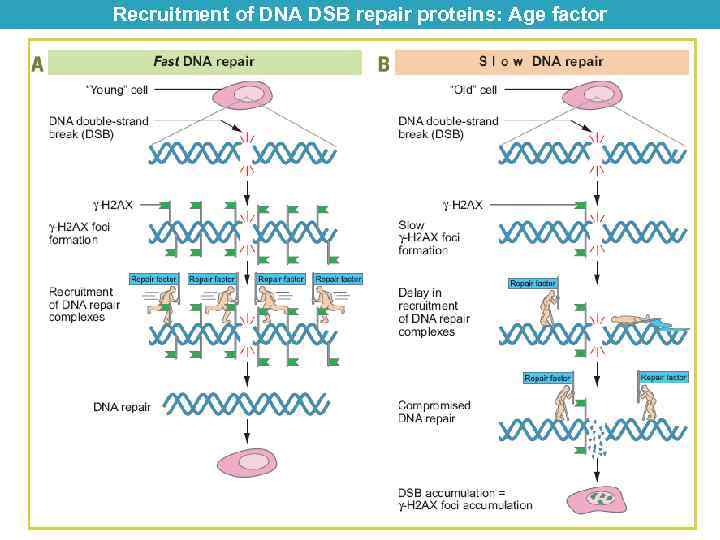 Recruitment of DNA DSB repair proteins: Age factor
Recruitment of DNA DSB repair proteins: Age factor
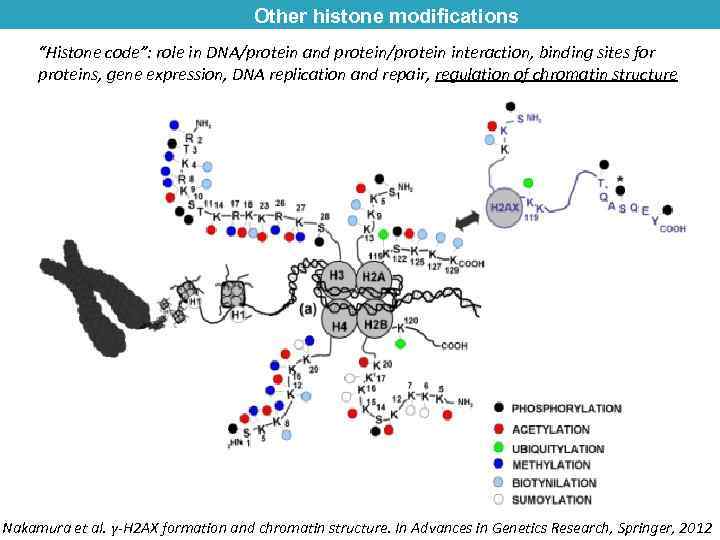 Other histone modifications “Histone code”: role in DNA/protein and protein/protein interaction, binding sites for proteins, gene expression, DNA replication and repair, regulation of chromatin structure Nakamura et al. γ-H 2 AX formation and chromatin structure. In Advances in Genetics Research, Springer, 2012
Other histone modifications “Histone code”: role in DNA/protein and protein/protein interaction, binding sites for proteins, gene expression, DNA replication and repair, regulation of chromatin structure Nakamura et al. γ-H 2 AX formation and chromatin structure. In Advances in Genetics Research, Springer, 2012
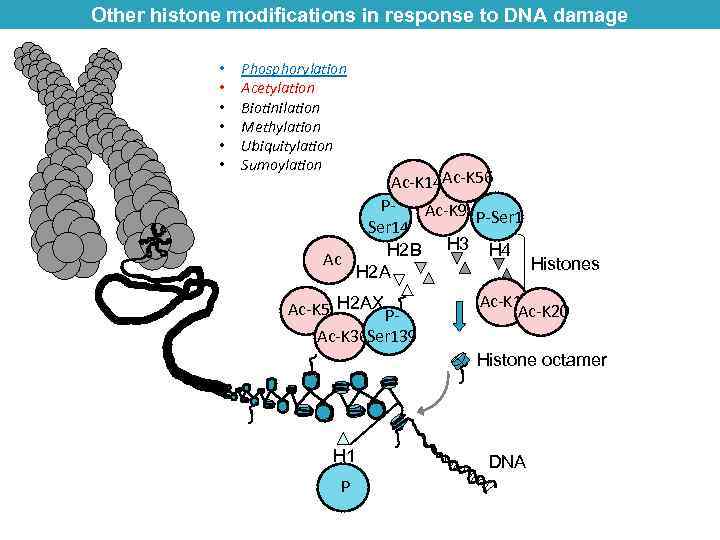 Other histone modifications in response to DNA damage • • • Phosphorylation Acetylation Biotinilation Methylation Ubiquitylation Sumoylation Ac-K 14 Ac-K 56 PAc-K 9 P-Ser 14 H 2 B H 3 H 4 Ac Histones H 2 A Ac-K 5 H 2 AX PAc-K 36 Ser 139 Ac-K 16 Ac-K 20 Histone octamer H 1 P DNA
Other histone modifications in response to DNA damage • • • Phosphorylation Acetylation Biotinilation Methylation Ubiquitylation Sumoylation Ac-K 14 Ac-K 56 PAc-K 9 P-Ser 14 H 2 B H 3 H 4 Ac Histones H 2 A Ac-K 5 H 2 AX PAc-K 36 Ser 139 Ac-K 16 Ac-K 20 Histone octamer H 1 P DNA
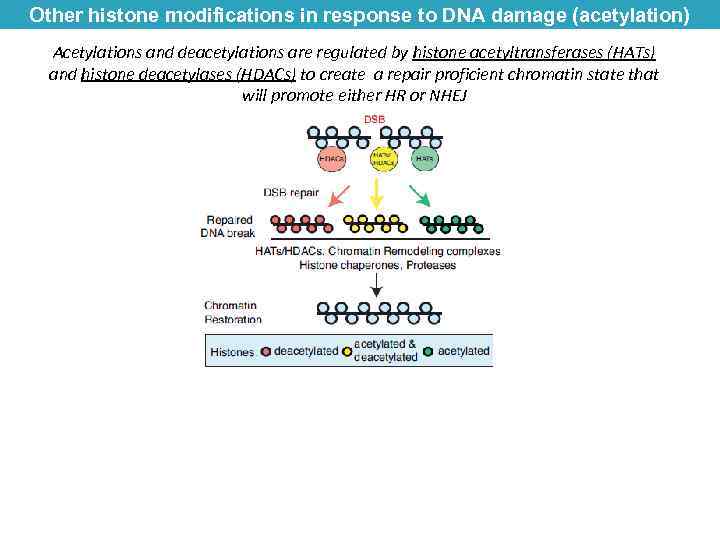 Other histone modifications in response to DNA damage (acetylation) Acetylations and deacetylations are regulated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) to create a repair proficient chromatin state that will promote either HR or NHEJ
Other histone modifications in response to DNA damage (acetylation) Acetylations and deacetylations are regulated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) to create a repair proficient chromatin state that will promote either HR or NHEJ
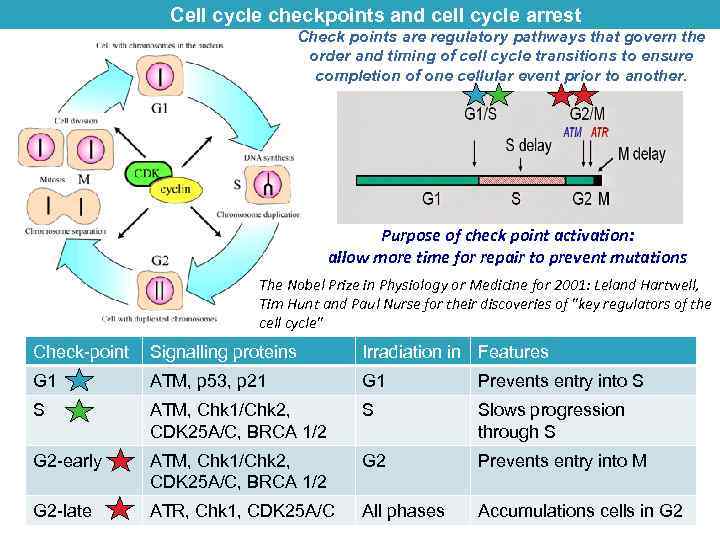 Cell cycle checkpoints and cell cycle arrest Check points are regulatory pathways that govern the order and timing of cell cycle transitions to ensure completion of one cellular event prior to another. Purpose of check point activation: allow more time for repair to prevent mutations The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2001: Leland Hartwell, Tim Hunt and Paul Nurse for their discoveries of "key regulators of the cell cycle" Check-point Signalling proteins Irradiation in Features G 1 ATM, p 53, p 21 G 1 Prevents entry into S S ATM, Chk 1/Chk 2, CDK 25 A/C, BRCA 1/2 S Slows progression through S G 2 -early ATM, Chk 1/Chk 2, CDK 25 A/C, BRCA 1/2 G 2 Prevents entry into M G 2 -late ATR, Chk 1, CDK 25 A/C All phases Accumulations cells in G 2
Cell cycle checkpoints and cell cycle arrest Check points are regulatory pathways that govern the order and timing of cell cycle transitions to ensure completion of one cellular event prior to another. Purpose of check point activation: allow more time for repair to prevent mutations The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2001: Leland Hartwell, Tim Hunt and Paul Nurse for their discoveries of "key regulators of the cell cycle" Check-point Signalling proteins Irradiation in Features G 1 ATM, p 53, p 21 G 1 Prevents entry into S S ATM, Chk 1/Chk 2, CDK 25 A/C, BRCA 1/2 S Slows progression through S G 2 -early ATM, Chk 1/Chk 2, CDK 25 A/C, BRCA 1/2 G 2 Prevents entry into M G 2 -late ATR, Chk 1, CDK 25 A/C All phases Accumulations cells in G 2
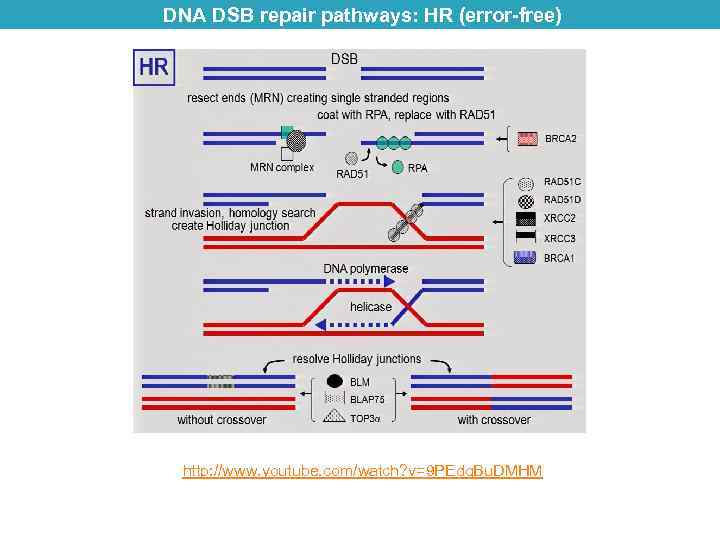 DNA DSB repair pathways: HR (error-free) http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=9 PEdq. Bu. DMHM
DNA DSB repair pathways: HR (error-free) http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=9 PEdq. Bu. DMHM
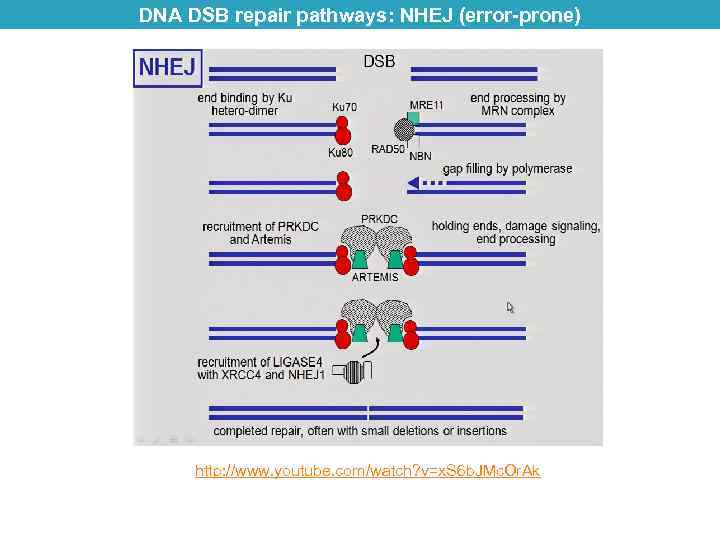 DNA DSB repair pathways: NHEJ (error-prone) http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=x. S 6 b. JMc. Or. Ak
DNA DSB repair pathways: NHEJ (error-prone) http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=x. S 6 b. JMc. Or. Ak
 2. Clinical and cellular radiosensitivity; effects on DNA repair
2. Clinical and cellular radiosensitivity; effects on DNA repair
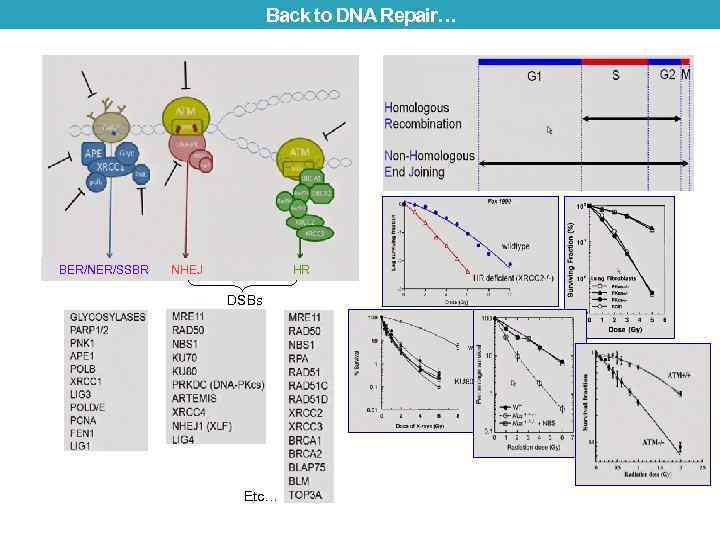 Back to DNA Repair… BER/NER/SSBR NHEJ HR DSBs Etc…
Back to DNA Repair… BER/NER/SSBR NHEJ HR DSBs Etc…
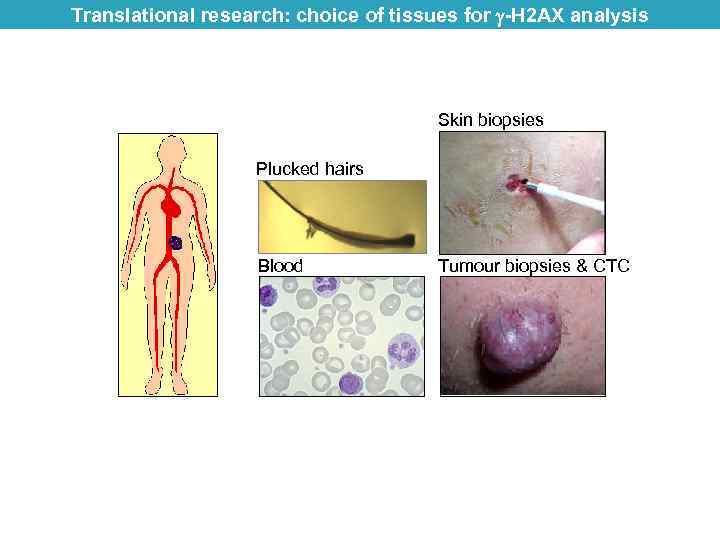 Translational research: choice of tissues for -H 2 AX analysis Skin biopsies Plucked hairs Blood Tumour biopsies & CTC
Translational research: choice of tissues for -H 2 AX analysis Skin biopsies Plucked hairs Blood Tumour biopsies & CTC
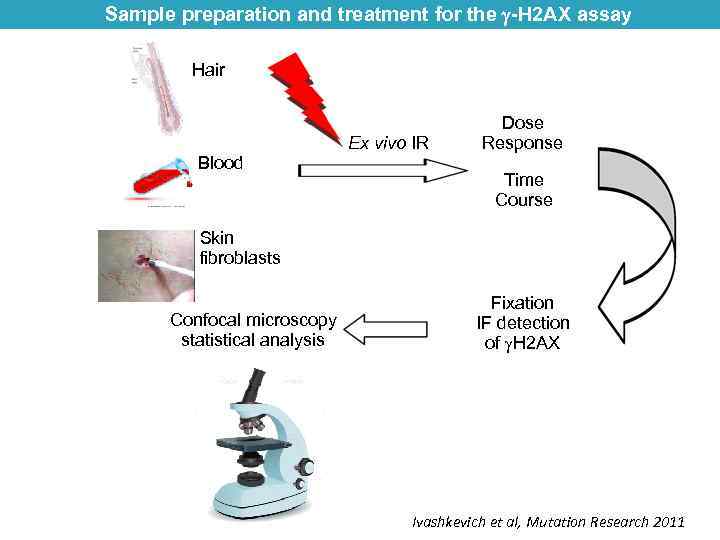 Sample preparation and treatment for the -H 2 AX assay Hair Ex vivo IR Blood Dose Response Time Course Skin fibroblasts Confocal microscopy statistical analysis Fixation IF detection of H 2 AX Ivashkevich et al, Mutation Research 2011
Sample preparation and treatment for the -H 2 AX assay Hair Ex vivo IR Blood Dose Response Time Course Skin fibroblasts Confocal microscopy statistical analysis Fixation IF detection of H 2 AX Ivashkevich et al, Mutation Research 2011
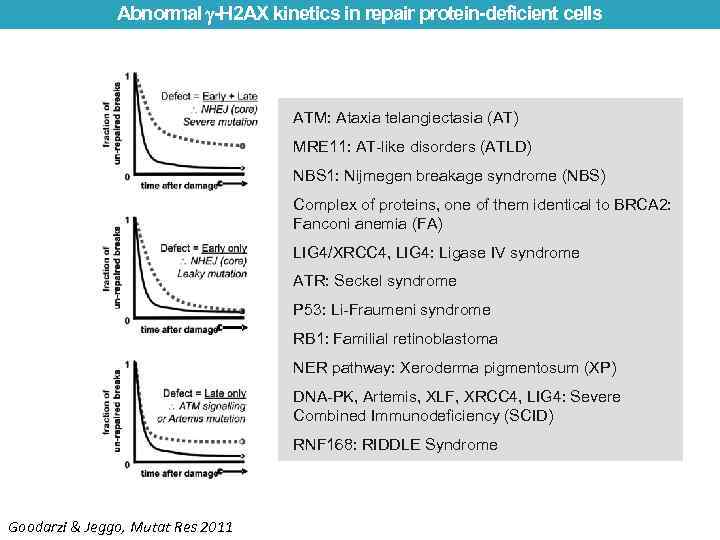 Abnormal -H 2 AX kinetics in repair protein-deficient cells ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia (AT) MRE 11: AT-like disorders (ATLD) NBS 1: Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS) Complex of proteins, one of them identical to BRCA 2: Fanconi anemia (FA) LIG 4/XRCC 4, LIG 4: Ligase IV syndrome ATR: Seckel syndrome P 53: Li-Fraumeni syndrome RB 1: Familial retinoblastoma NER pathway: Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) DNA-PK, Artemis, XLF, XRCC 4, LIG 4: Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) RNF 168: RIDDLE Syndrome Goodarzi & Jeggo, Mutat Res 2011
Abnormal -H 2 AX kinetics in repair protein-deficient cells ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia (AT) MRE 11: AT-like disorders (ATLD) NBS 1: Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS) Complex of proteins, one of them identical to BRCA 2: Fanconi anemia (FA) LIG 4/XRCC 4, LIG 4: Ligase IV syndrome ATR: Seckel syndrome P 53: Li-Fraumeni syndrome RB 1: Familial retinoblastoma NER pathway: Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) DNA-PK, Artemis, XLF, XRCC 4, LIG 4: Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) RNF 168: RIDDLE Syndrome Goodarzi & Jeggo, Mutat Res 2011
 Severe combined immunodefficiency (SCID) & radiosensitivity “Boy in the bubble” – David Vetter (1970 s – 80 s) 1 in 100, 000 births (1 in 65, 000 reported in Austraia) The most common treatment for SCID is bone marrow transplantation (BMT)
Severe combined immunodefficiency (SCID) & radiosensitivity “Boy in the bubble” – David Vetter (1970 s – 80 s) 1 in 100, 000 births (1 in 65, 000 reported in Austraia) The most common treatment for SCID is bone marrow transplantation (BMT)
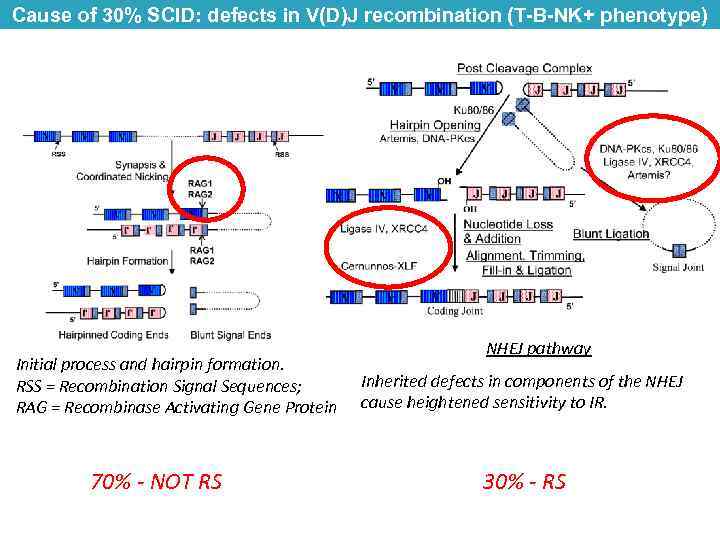 Cause of 30% SCID: defects in V(D)J recombination (T-B-NK+ phenotype) Initial process and hairpin formation. RSS = Recombination Signal Sequences; RAG = Recombinase Activating Gene Protein 70% - NOT RS NHEJ pathway Inherited defects in components of the NHEJ cause heightened sensitivity to IR. 30% - RS
Cause of 30% SCID: defects in V(D)J recombination (T-B-NK+ phenotype) Initial process and hairpin formation. RSS = Recombination Signal Sequences; RAG = Recombinase Activating Gene Protein 70% - NOT RS NHEJ pathway Inherited defects in components of the NHEJ cause heightened sensitivity to IR. 30% - RS
 Treatment of SCID: BMT (Special guide for RS disorders)
Treatment of SCID: BMT (Special guide for RS disorders)
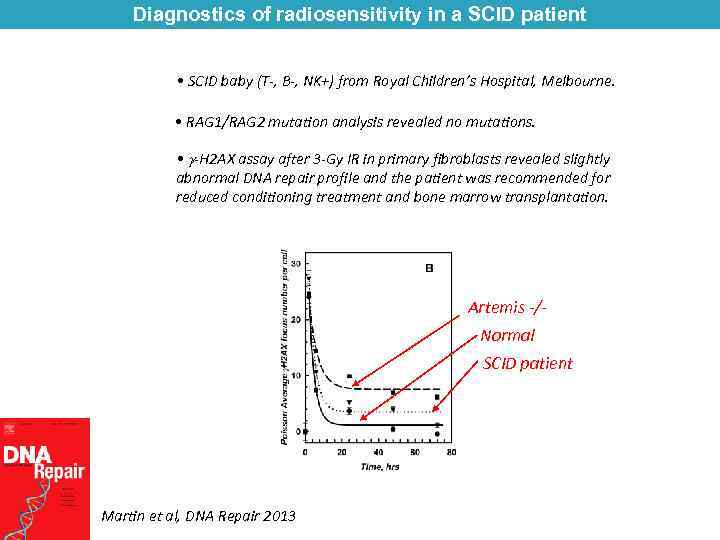 Diagnostics of radiosensitivity in a SCID patient • SCID baby (T-, B-, NK+) from Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne. • RAG 1/RAG 2 mutation analysis revealed no mutations. • -H 2 AX assay after 3 -Gy IR in primary fibroblasts revealed slightly abnormal DNA repair profile and the patient was recommended for reduced conditioning treatment and bone marrow transplantation. Artemis -/Normal SCID patient Martin et al, DNA Repair 2013
Diagnostics of radiosensitivity in a SCID patient • SCID baby (T-, B-, NK+) from Royal Children’s Hospital, Melbourne. • RAG 1/RAG 2 mutation analysis revealed no mutations. • -H 2 AX assay after 3 -Gy IR in primary fibroblasts revealed slightly abnormal DNA repair profile and the patient was recommended for reduced conditioning treatment and bone marrow transplantation. Artemis -/Normal SCID patient Martin et al, DNA Repair 2013
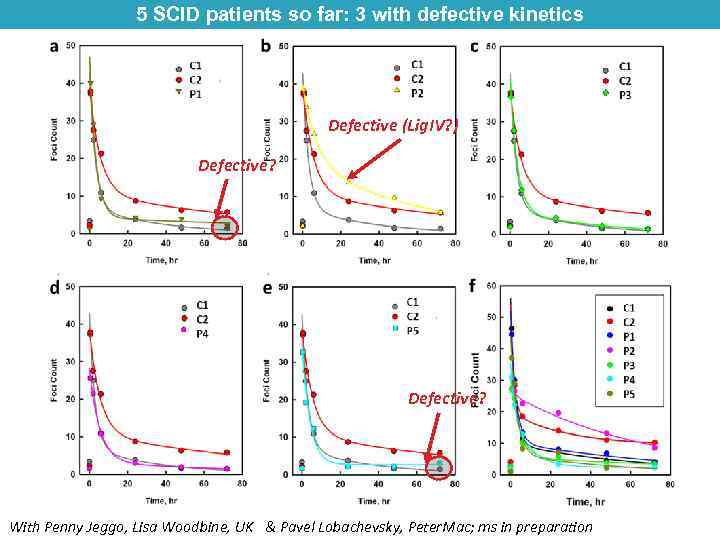 5 SCID patients so far: 3 with defective kinetics Defective (Lig. IV? ) Defective? With Penny Jeggo, Lisa Woodbine, UK & Pavel Lobachevsky, Peter. Mac; ms in preparation
5 SCID patients so far: 3 with defective kinetics Defective (Lig. IV? ) Defective? With Penny Jeggo, Lisa Woodbine, UK & Pavel Lobachevsky, Peter. Mac; ms in preparation
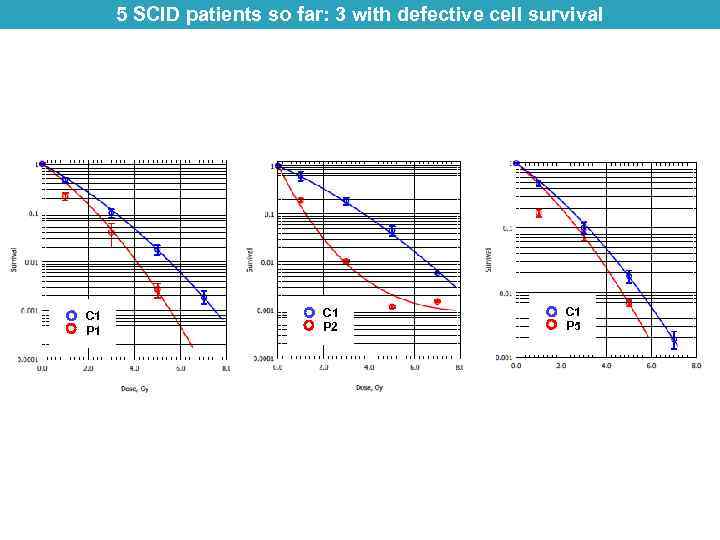 5 SCID patients so far: 3 with defective cell survival C 1 P 1 C 1 P 2 C 1 P 5
5 SCID patients so far: 3 with defective cell survival C 1 P 1 C 1 P 2 C 1 P 5
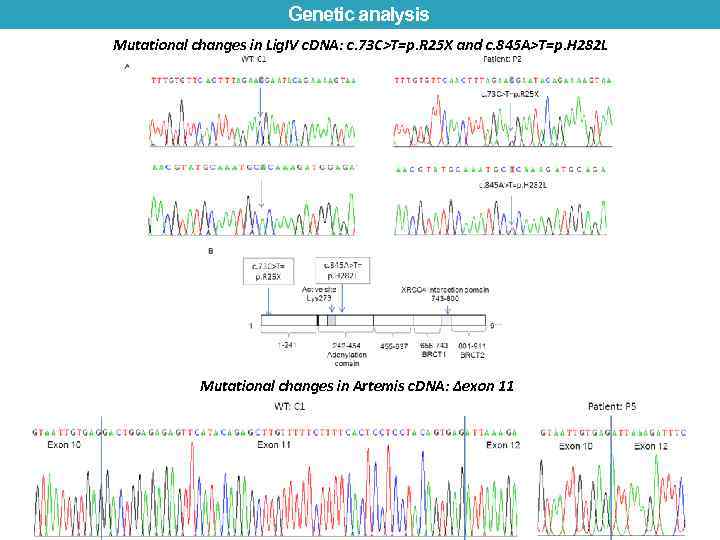 Genetic analysis Mutational changes in Lig. IV c. DNA: c. 73 C>T=p. R 25 X and c. 845 A>T=p. H 282 L Mutational changes in Artemis c. DNA: ∆exon 11
Genetic analysis Mutational changes in Lig. IV c. DNA: c. 73 C>T=p. R 25 X and c. 845 A>T=p. H 282 L Mutational changes in Artemis c. DNA: ∆exon 11
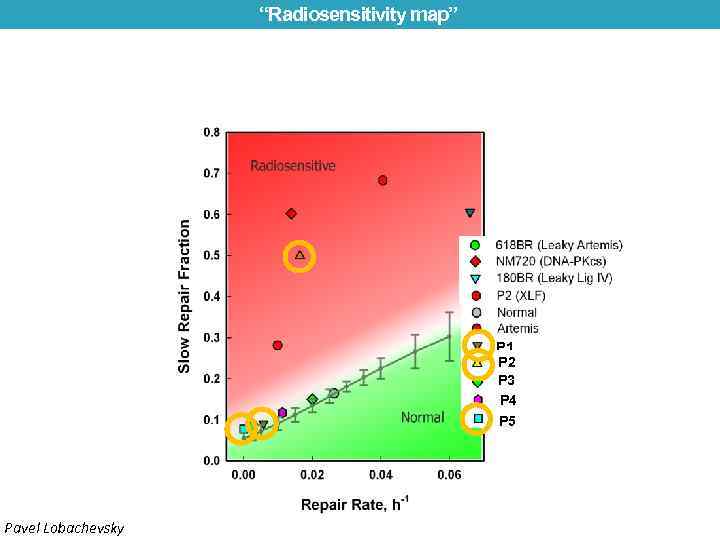 “Radiosensitivity map” P 1 P 2 P 3 P 4 P 5 Pavel Lobachevsky
“Radiosensitivity map” P 1 P 2 P 3 P 4 P 5 Pavel Lobachevsky
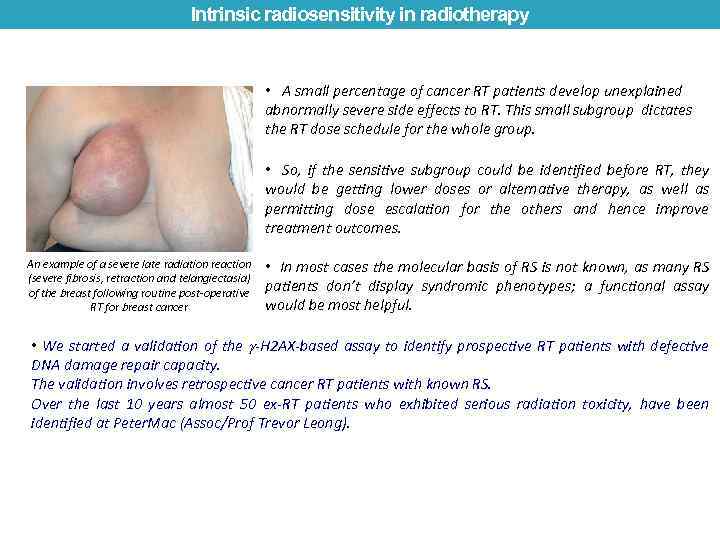 Intrinsic radiosensitivity in radiotherapy • A small percentage of cancer RT patients develop unexplained abnormally severe side effects to RT. This small subgroup dictates the RT dose schedule for the whole group. • So, if the sensitive subgroup could be identified before RT, they would be getting lower doses or alternative therapy, as well as permitting dose escalation for the others and hence improve treatment outcomes. An example of a severe late radiation reaction (severe fibrosis, retraction and telangiectasia) of the breast following routine post-operative RT for breast cancer • In most cases the molecular basis of RS is not known, as many RS patients don’t display syndromic phenotypes; a functional assay would be most helpful. • We started a validation of the -H 2 AX-based assay to identify prospective RT patients with defective DNA damage repair capacity. The validation involves retrospective cancer RT patients with known RS. Over the last 10 years almost 50 ex-RT patients who exhibited serious radiation toxicity, have been identified at Peter. Mac (Assoc/Prof Trevor Leong).
Intrinsic radiosensitivity in radiotherapy • A small percentage of cancer RT patients develop unexplained abnormally severe side effects to RT. This small subgroup dictates the RT dose schedule for the whole group. • So, if the sensitive subgroup could be identified before RT, they would be getting lower doses or alternative therapy, as well as permitting dose escalation for the others and hence improve treatment outcomes. An example of a severe late radiation reaction (severe fibrosis, retraction and telangiectasia) of the breast following routine post-operative RT for breast cancer • In most cases the molecular basis of RS is not known, as many RS patients don’t display syndromic phenotypes; a functional assay would be most helpful. • We started a validation of the -H 2 AX-based assay to identify prospective RT patients with defective DNA damage repair capacity. The validation involves retrospective cancer RT patients with known RS. Over the last 10 years almost 50 ex-RT patients who exhibited serious radiation toxicity, have been identified at Peter. Mac (Assoc/Prof Trevor Leong).
 -H 2 AX assay in patients’ lymphocytes for radiosensitivity screening Int J Cancer. 2011 Dec 15; 129(12): 2928 -34. Prolonged expression of the -H 2 AX DNA repair biomarker correlates with excess acute and chronic toxicity from radiotherapy treatment. Bourton EC, Plowman PN, Smith D, Arlett CF, Parris CN. Brunel Institute of Cancer Genetics and Pharmacogenomics, Division of Biosciences, Brunel University, Uxbridge, Middlesex, United Kingdom. In 12 cancer patients that experienced severe atypical NTT following RT, there was a failure to repair DNA DSBs as measured by -H 2 AX induction and persistence. We conclude that a flow cytometric assay based on -H 2 AX induction in PBL of RT patients may represent a robust, rapid and reliable biomarker to predict NTT during RT. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Jan; 87(1): 46 -56. Lack of a correlation between -H 2 AX foci kinetics in lymphocytes and the severity of acute normal tissue reactions during IMRT treatment for head and neck cancer. Werbrouck J, Duprez F, De Neve W, Thierens H. Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Ghent University, Gent, Belgium. No correlation was found between the -H 2 AX foci kinetics pattern and the risk for acute normal tissue complications among the three patient subgroups. Scoring of -H 2 AX foci cannot be applied to predict for the development of acute normal tissue complications. Br J Cancer. 2010 May 11; 102(10): 1511 -8. H 2 AX phosphorylation screen of cells from radiosensitive cancer patients reveals a novel DNA double-strand break repair cellular phenotype. Vasireddy RS, Sprung CN, Cempaka NL, Chao M, Mc. Kay MJ. Division of Research, Peter Mac. Callum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, Victoria 3002, Australia. We identified a RS cancer patient cell line with a novel IR-induced DNA DSB repair defect (DNA ligase IV). -H 2 AX focus measurement has limited scope as a pre-RT predictive assay in lymphoblast cell lines from RT patients; however, the assay can successfully identify DNA DSB repair-defective patient cell lines, thus potentially facilitating the discovery of novel constitutional contributions to clinical RS.
-H 2 AX assay in patients’ lymphocytes for radiosensitivity screening Int J Cancer. 2011 Dec 15; 129(12): 2928 -34. Prolonged expression of the -H 2 AX DNA repair biomarker correlates with excess acute and chronic toxicity from radiotherapy treatment. Bourton EC, Plowman PN, Smith D, Arlett CF, Parris CN. Brunel Institute of Cancer Genetics and Pharmacogenomics, Division of Biosciences, Brunel University, Uxbridge, Middlesex, United Kingdom. In 12 cancer patients that experienced severe atypical NTT following RT, there was a failure to repair DNA DSBs as measured by -H 2 AX induction and persistence. We conclude that a flow cytometric assay based on -H 2 AX induction in PBL of RT patients may represent a robust, rapid and reliable biomarker to predict NTT during RT. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Jan; 87(1): 46 -56. Lack of a correlation between -H 2 AX foci kinetics in lymphocytes and the severity of acute normal tissue reactions during IMRT treatment for head and neck cancer. Werbrouck J, Duprez F, De Neve W, Thierens H. Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Ghent University, Gent, Belgium. No correlation was found between the -H 2 AX foci kinetics pattern and the risk for acute normal tissue complications among the three patient subgroups. Scoring of -H 2 AX foci cannot be applied to predict for the development of acute normal tissue complications. Br J Cancer. 2010 May 11; 102(10): 1511 -8. H 2 AX phosphorylation screen of cells from radiosensitive cancer patients reveals a novel DNA double-strand break repair cellular phenotype. Vasireddy RS, Sprung CN, Cempaka NL, Chao M, Mc. Kay MJ. Division of Research, Peter Mac. Callum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, Victoria 3002, Australia. We identified a RS cancer patient cell line with a novel IR-induced DNA DSB repair defect (DNA ligase IV). -H 2 AX focus measurement has limited scope as a pre-RT predictive assay in lymphoblast cell lines from RT patients; however, the assay can successfully identify DNA DSB repair-defective patient cell lines, thus potentially facilitating the discovery of novel constitutional contributions to clinical RS.
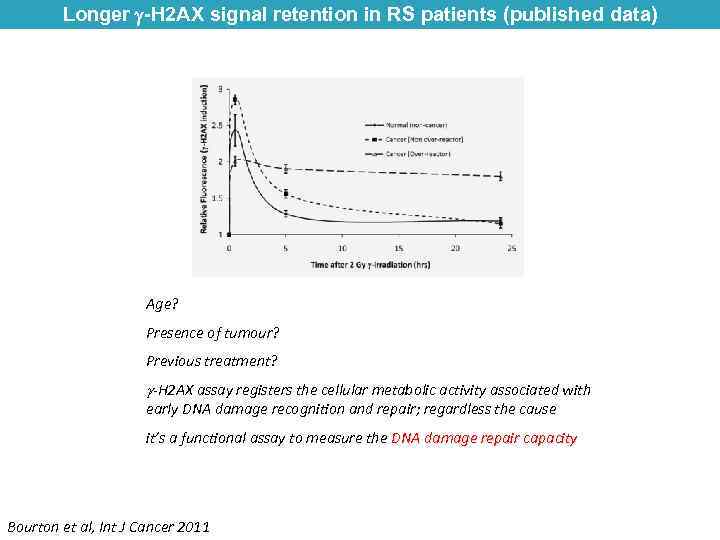 Longer -H 2 AX signal retention in RS patients (published data) Age? Presence of tumour? Previous treatment? -H 2 AX assay registers the cellular metabolic activity associated with early DNA damage recognition and repair; regardless the cause it’s a functional assay to measure the DNA damage repair capacity Bourton et al, Int J Cancer 2011
Longer -H 2 AX signal retention in RS patients (published data) Age? Presence of tumour? Previous treatment? -H 2 AX assay registers the cellular metabolic activity associated with early DNA damage recognition and repair; regardless the cause it’s a functional assay to measure the DNA damage repair capacity Bourton et al, Int J Cancer 2011
 Radiotherapy: Clinical case study Intrinsic radiosensitivity after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in a patient with acoustic neuroma 78 -year old female with a strong clinical suspicion of radiosensitivity after stereotactic 12 Gyradiosurgery for a right sided acoustic neuroma in 2009 (Royal Adelaide Hospital). 8 months later the size of the tumour reduced, and the patient complained of new right sided facial numbness and tingling. 19 months after treatment showed further shrinkage of the tumour and the development of central necrosis. She was still experiencing tingling of the right side of the face and had developed subjective right facial weakness and reduced taste on the right side of the tongue. Adams, Martin, Roos, et al, 2012
Radiotherapy: Clinical case study Intrinsic radiosensitivity after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in a patient with acoustic neuroma 78 -year old female with a strong clinical suspicion of radiosensitivity after stereotactic 12 Gyradiosurgery for a right sided acoustic neuroma in 2009 (Royal Adelaide Hospital). 8 months later the size of the tumour reduced, and the patient complained of new right sided facial numbness and tingling. 19 months after treatment showed further shrinkage of the tumour and the development of central necrosis. She was still experiencing tingling of the right side of the face and had developed subjective right facial weakness and reduced taste on the right side of the tongue. Adams, Martin, Roos, et al, 2012
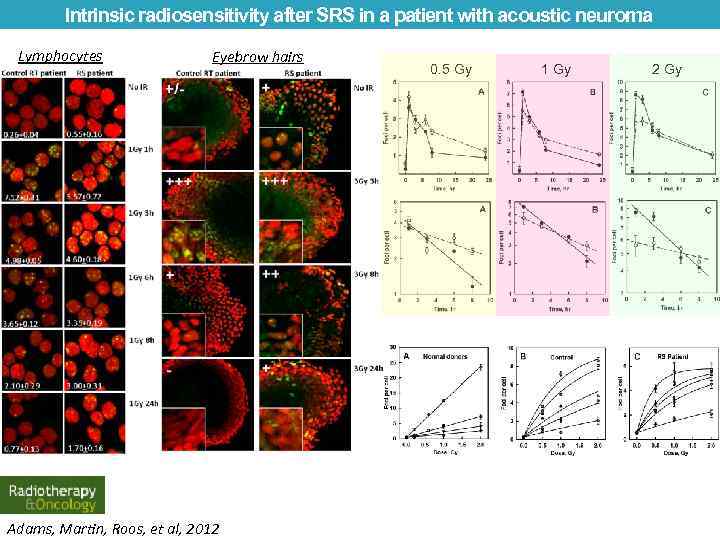 Intrinsic radiosensitivity after SRS in a patient with acoustic neuroma Lymphocytes Eyebrow hairs Adams, Martin, Roos, et al, 2012 0. 5 Gy 1 Gy 2 Gy
Intrinsic radiosensitivity after SRS in a patient with acoustic neuroma Lymphocytes Eyebrow hairs Adams, Martin, Roos, et al, 2012 0. 5 Gy 1 Gy 2 Gy
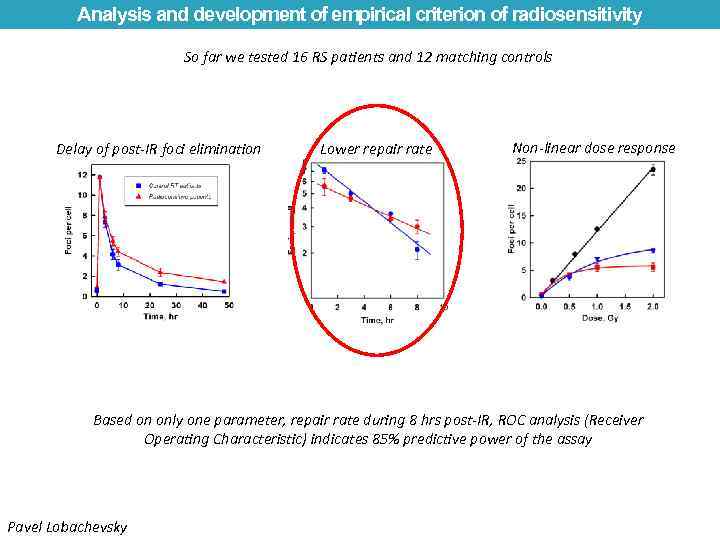 Analysis and development of empirical criterion of radiosensitivity So far we tested 16 RS patients and 12 matching controls Delay of post-IR foci elimination Lower repair rate Non-linear dose response Based on only one parameter, repair rate during 8 hrs post-IR, ROC analysis (Receiver Operating Characteristic) indicates 85% predictive power of the assay Pavel Lobachevsky
Analysis and development of empirical criterion of radiosensitivity So far we tested 16 RS patients and 12 matching controls Delay of post-IR foci elimination Lower repair rate Non-linear dose response Based on only one parameter, repair rate during 8 hrs post-IR, ROC analysis (Receiver Operating Characteristic) indicates 85% predictive power of the assay Pavel Lobachevsky
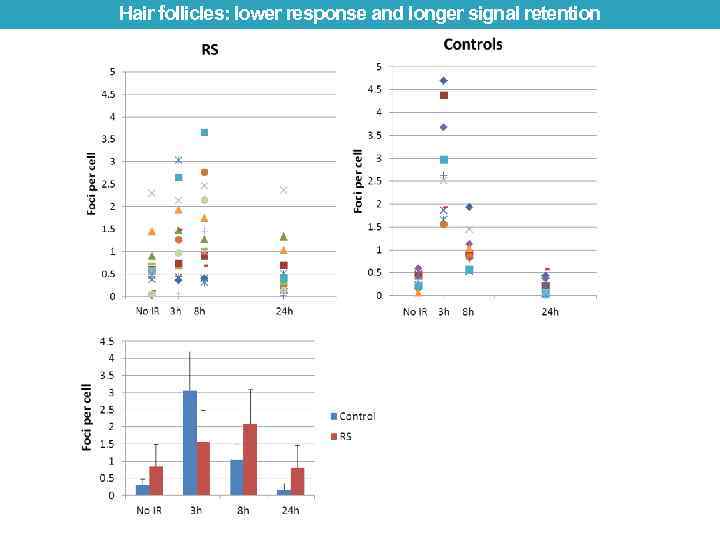 Hair follicles: lower response and longer signal retention
Hair follicles: lower response and longer signal retention
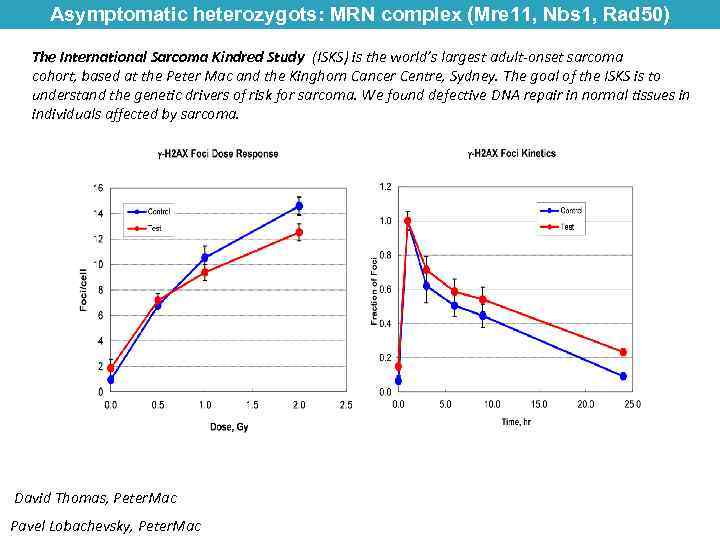 Asymptomatic heterozygots: MRN complex (Mre 11, Nbs 1, Rad 50) The International Sarcoma Kindred Study (ISKS) is the world’s largest adult-onset sarcoma cohort, based at the Peter Mac and the Kinghorn Cancer Centre, Sydney. The goal of the ISKS is to understand the genetic drivers of risk for sarcoma. We found defective DNA repair in normal tissues in individuals affected by sarcoma. David Thomas, Peter. Mac Pavel Lobachevsky, Peter. Mac
Asymptomatic heterozygots: MRN complex (Mre 11, Nbs 1, Rad 50) The International Sarcoma Kindred Study (ISKS) is the world’s largest adult-onset sarcoma cohort, based at the Peter Mac and the Kinghorn Cancer Centre, Sydney. The goal of the ISKS is to understand the genetic drivers of risk for sarcoma. We found defective DNA repair in normal tissues in individuals affected by sarcoma. David Thomas, Peter. Mac Pavel Lobachevsky, Peter. Mac
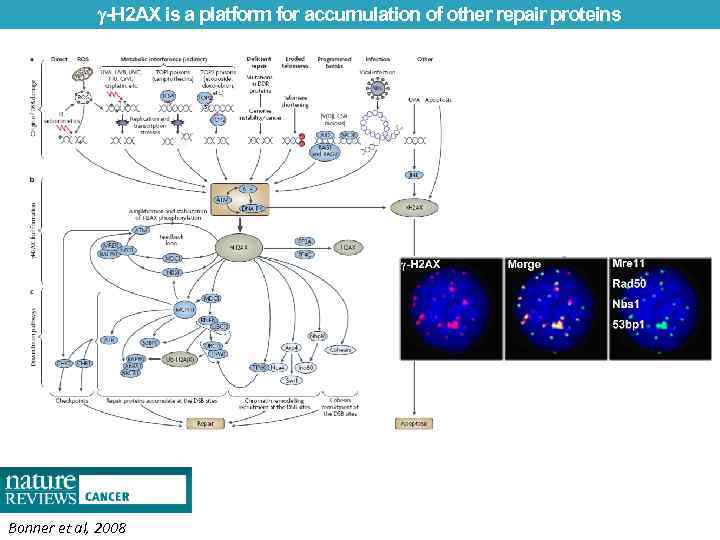 -H 2 AX is a platform for accumulation of other repair proteins Bonner et al, 2008
-H 2 AX is a platform for accumulation of other repair proteins Bonner et al, 2008
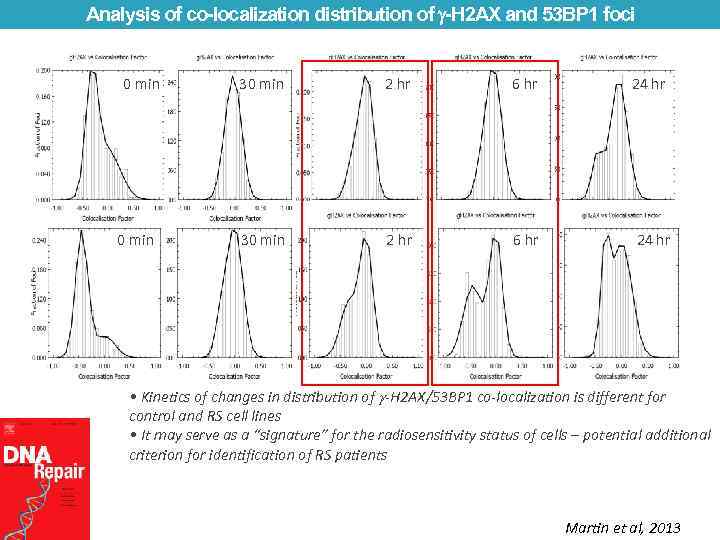 Analysis of co-localization distribution of -H 2 AX and 53 BP 1 foci 0 min 30 min 2 hr 6 hr 24 hr • Kinetics of changes in distribution of -H 2 AX/53 BP 1 co-localization is different for control and RS cell lines • It may serve as a “signature” for the radiosensitivity status of cells – potential additional criterion for identification of RS patients Martin et al, 2013
Analysis of co-localization distribution of -H 2 AX and 53 BP 1 foci 0 min 30 min 2 hr 6 hr 24 hr • Kinetics of changes in distribution of -H 2 AX/53 BP 1 co-localization is different for control and RS cell lines • It may serve as a “signature” for the radiosensitivity status of cells – potential additional criterion for identification of RS patients Martin et al, 2013
 -H 2 AX repair kinetics - visual presentation Analysis and selection of predictive criteria Refinement – accumulation of data Addition of a new dimension – analysis of repair foci co-localization
-H 2 AX repair kinetics - visual presentation Analysis and selection of predictive criteria Refinement – accumulation of data Addition of a new dimension – analysis of repair foci co-localization
 СПАСИБО! Basic Clinical Radiobiology, Eds Michael Joiner and Albert van der Kogel, Hodder Arnold an Hachette UK Company, 2009 DNA Repair, Mutagenesis, and Other Responses to DNA Damage, Eds Errol Friedberg et al, Cold Spring harbor Laboratory Press, 2014
СПАСИБО! Basic Clinical Radiobiology, Eds Michael Joiner and Albert van der Kogel, Hodder Arnold an Hachette UK Company, 2009 DNA Repair, Mutagenesis, and Other Responses to DNA Damage, Eds Errol Friedberg et al, Cold Spring harbor Laboratory Press, 2014


