997f2b6d08bc9d75ae475adc567298c5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 82

Guidance on Creating Strong Partnerships between Operating Engineers and Urban Search & Rescue Teams IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Disclaimer This material was produced under grant number 46 C 6 -HT 33 from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U. S. Department of Labor. It does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the U. S. Department of Labor, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U. S. Government. IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 2 2

There is a guidance document on which this presentation is based “Building Alliances Between Operating Engineers and Emergency Responders to Save Lives During Disasters” Available through the National HAZMAT Program 304 -253 -8674 www. iuoeiettc. org IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 3 3

Learning Objectives At the end of this module, you should be able to: • Explain the term “Skilled Support Personnel” (SSP) and describe the importance of their contribution during disasters, giving examples • Explain the importance of the OSHA Disaster Site Worker course for SSP training • Explain the role, skills and training of Urban Search and Rescue (US&R) Teams • Explain why the partnership between IUOE Locals and State US&R teams is so important • Describe the difference between FEMA and State US&R teams • Explain how to initiate or join an alliance of US&R and IUOE Locals in your community • List several safety issues that emergency response personnel should know about working around heavy equipment IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Background on this module • The National HAZMAT Program was instrumental in developing OSHA’s Disaster Site Worker course and has been funded by OSHA to create this module. • This module provides practical guidance on building alliances between Operating Engineers and US&R teams. • The module also contains lessons learned from ongoing and successful alliances. • This module is based on a guidance document available for free by calling 304 -253 -8674 or send email to hazmat@iuoeiettc. org IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Operating Engineers First part of the alliance IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 6 6

The International Union of Operating Engineers A union with a long history of disaster response • 119 local unions nationwide representing 360, 000 members • Hoisting & Portable (H&P) – operate heavy equipment on construction sites • Stationary Engineers – operate building systems in offices, schools, hospitals, chemical plants and water treatment facilities IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

The International Union of Operating Engineers Responses to disasters • San Francisco and LA earthquakes • Oklahoma City • Ground Zero • The Pentagon • Space shuttle disaster • Hurricanes Katrina and Rita IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Ground Zero Response of the National HAZMAT Program • Arrived onsite within days of the towers collapse • Stayed until the end of the cleanup • Distributed 11, 000 respirators • Collected air samples on heavy equipment operators • Delivered official training to 1, 500 workers • Participated in site safety mtgs IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Hurricanes Katrina and Rita Responses of the National HAZMAT Team and IUOE Locals • Printed and distributed over 10, 000 copies of main safety booklet for responders • Provided training to federal responders in the Gulf • Moved thousands of tons of debris IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

The Sago Mine Disaster Stationary Engineers developed models of air flow inside the mine after the disaster as part of the investigation IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Capabilities of the National HAZMAT Program • Based in Beckley, WV • Provided safety and health training to over 285, 000 workers over last 17 years • Trained largest number of workers in OSHA Disaster Site Worker course in Region III IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Capabilities of the National HAZMAT Program (2) • Can be activated by FEMA under National Response Plan to conduct training • Offers training for free – HAZWOPER – OSHA 10 - and OSHA 30 -Hour – OSHA Disaster Site Worker 7600 and 5600 IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program
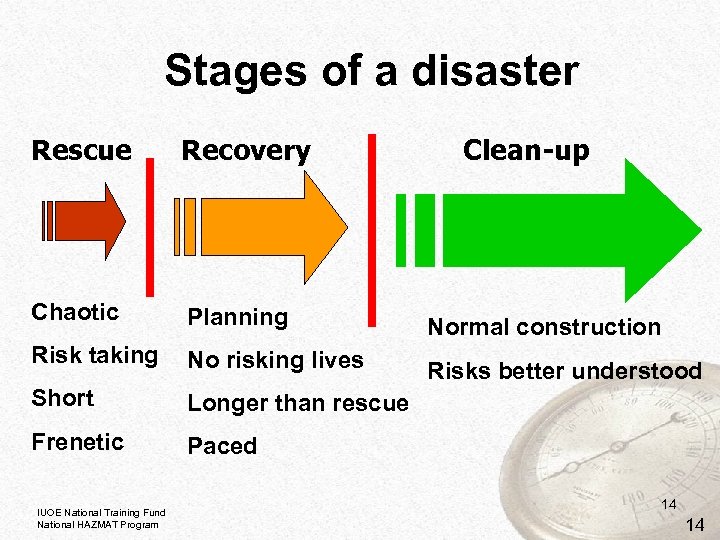
Stages of a disaster Rescue Recovery Chaotic Planning Normal construction Risk taking No risking lives Risks better understood Short Longer than rescue Frenetic Paced IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program Clean-up 14 14
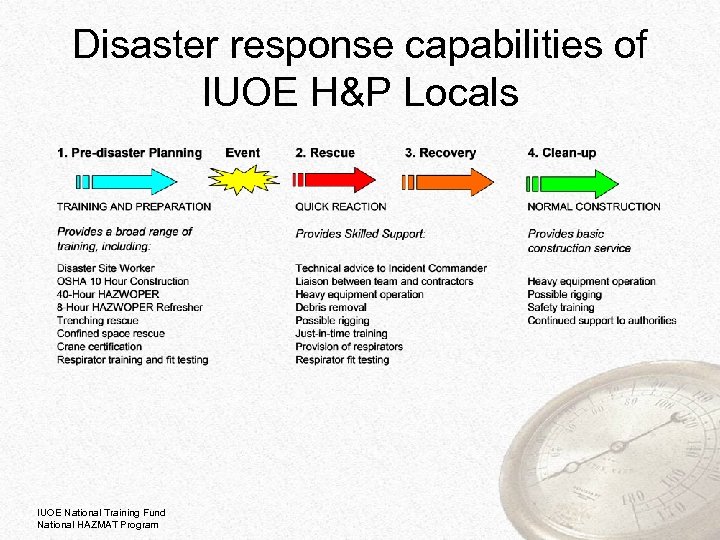
Disaster response capabilities of IUOE H&P Locals IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program
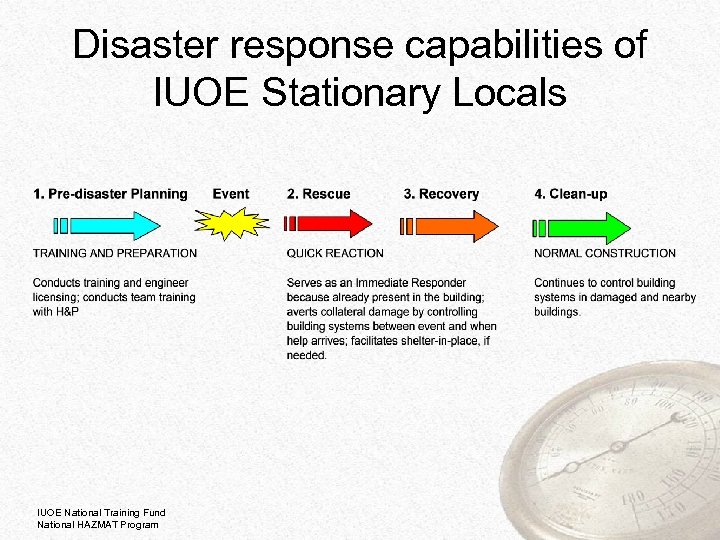
Disaster response capabilities of IUOE Stationary Locals IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Who are Skilled Support Personnel? • Under OSHA’s HAZWOPER Standard, 29 CFR 1910. 120(q)(4): “personnel, not necessarily an employer's own employees, who are skilled in the operation of certain equipment, such as mechanized earth moving or digging equipment or crane and hoisting equipment, and who are needed temporarily to perform immediate emergency support work that cannot reasonably be performed in a timely fashion by an employer's own employees, and who will be or may be exposed to the hazards at an emergency response scene. ” IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

What training is required for Skilled Support Personnel? • Under OSHA’s HAZWOPER Standard only a site briefing of no specific length is needed • That has proven unsatisfactory • Training at Ground Zero: 3 hours long, 3 months after the destruction • This was reason for Disaster Site Worker course and designation of SSP as “first responders” under HSPD-8 IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program
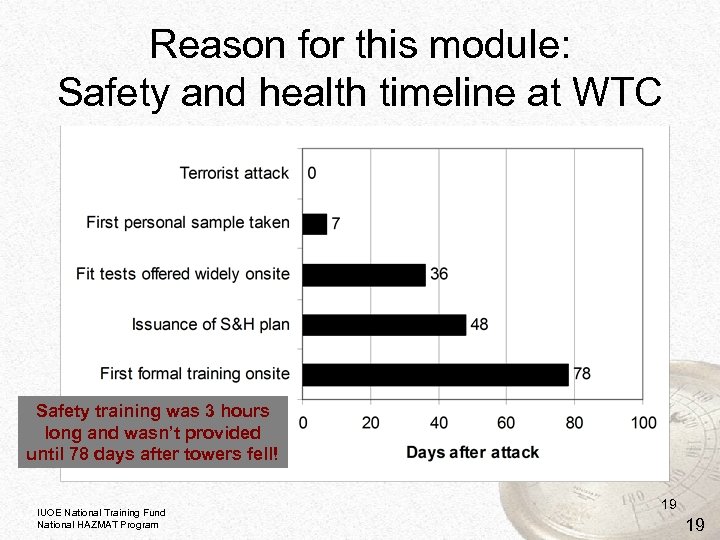
Reason for this module: Safety and health timeline at WTC Safety training was 3 hours long and wasn’t provided until 78 days after towers fell! IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 19 19

Reason for this module: The need for better communication (TOPOFF 2 example) • May 12, 2003, largest national drill, involved mock radioactive “dirty” bomb in Seattle • Crane operator came to site but did nothing and hadn’t been pre-qualified IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Reason for this module: (TOPOFF 2 example) • Operating Engineers within several hours drive were trained on radiation safety and to operate equipment in Level B PPE • Incident Commander did not know about them and they were never called! IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Reason for this module: Over 60 percent of the Skilled Support Personnel who were at Ground Zero are still having health problems. Herbert, R. et al. (2006, Dec. ). Environ Health Perspectives. IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 22 22

Urban Search & Rescue Second part of the Alliance Connecticut Task Force One search specialists using equipment. IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 23 23

National Urban Search and Rescue Response System • Framework for integrating local services into disaster response task forces • 28 national US&R task forces in U. S. • Any can be activated and deployed by FEMA under National Incident Management System • Team must have personnel and equipment ready to go within 6 hours of activation • Each task force has 70 specialists, divided into two 35 -member teams for rotation and relief IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

National Incident Management System (NIMS) Came out of HSPD-5, Management of Domestic Incidents • Directed Dept. of Homeland Security to create the National Response Plan IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

NIMS Key Concepts and Principles 1. Flexibility 2. Standardization through Incident Command System IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

NIMS 14 Essential Features (FEMA, ICS Basic Information) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Common terminology Modular organization Management by objectives Reliance on an Incident Action Plan Chain of Command Unity of Command Unified command Manageable span of control IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

NIMS 14 Essential Features (continued) 8. Predesignated incident locations and facilities 9. Resource management 10. Information and intelligence management 11. Integrated communications 12. Transfer of command 13. Accountability 14. Deployment IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program
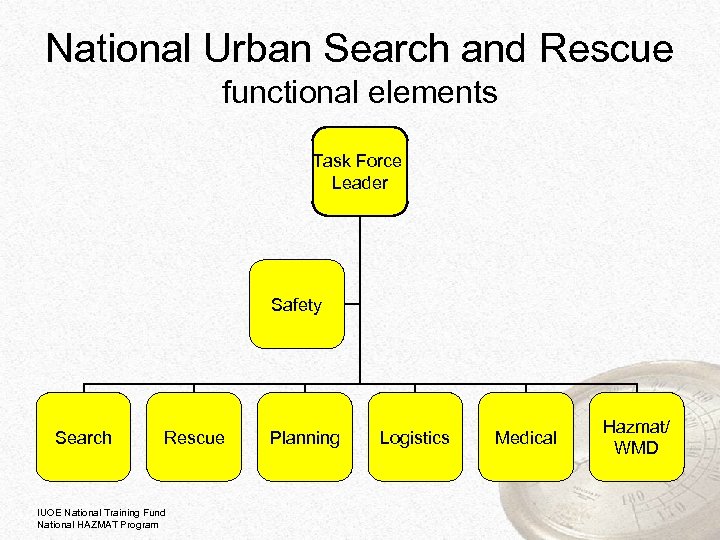
National Urban Search and Rescue functional elements Task Force Leader Safety Search Rescue IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program Planning Logistics Medical Hazmat/ WMD

Task Force Operations: As one unit or divided into separate units • Search • Rescue • Advance life support (crush syndrome and confined space medicine) • Structural assessment • Hazmat assessments • Heavy equipment operations IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 30 30
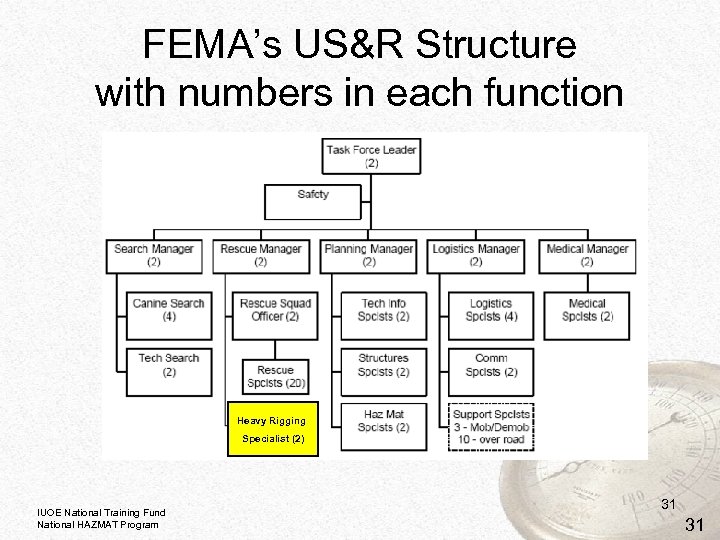
FEMA’s US&R Structure with numbers in each function Heavy Rigging Specialist (2) IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 31 31
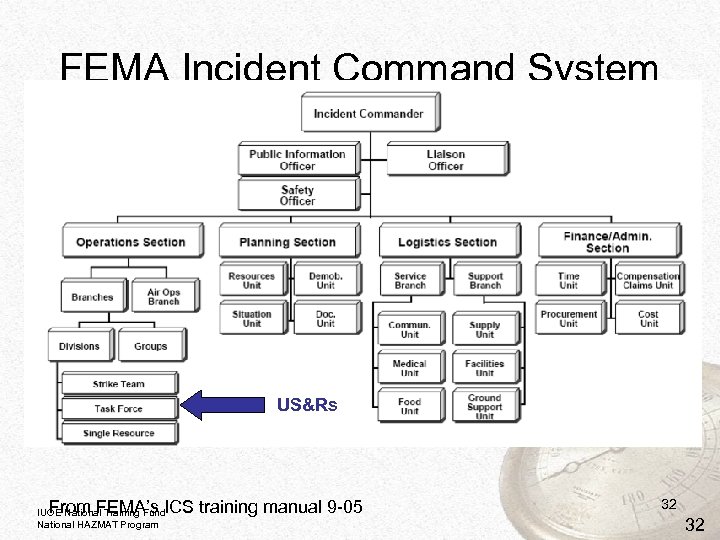
FEMA Incident Command System US&Rs From FEMA’s ICS training manual 9 -05 IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 32 32
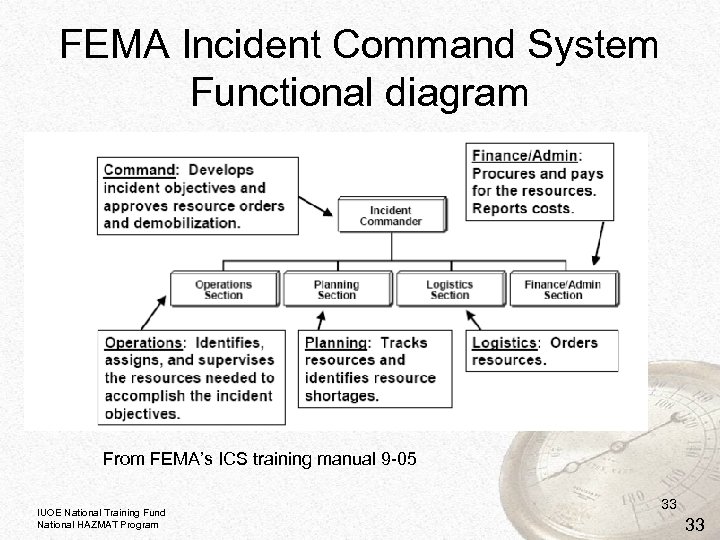
FEMA Incident Command System Functional diagram From FEMA’s ICS training manual 9 -05 IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 33 33
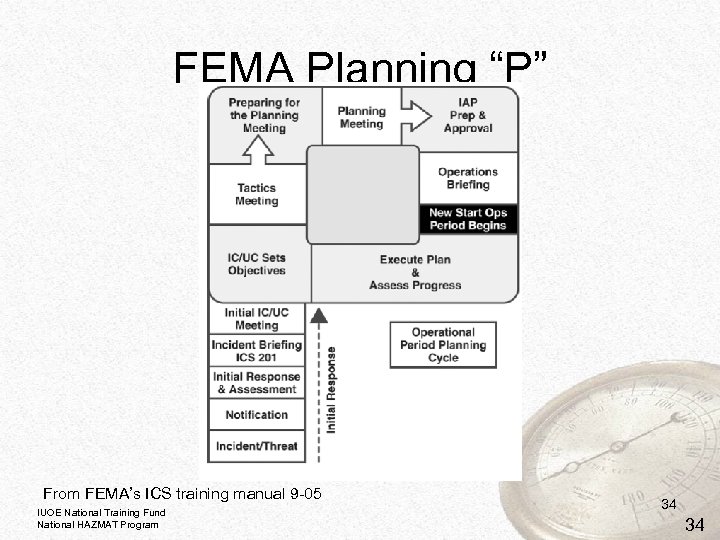
FEMA Planning “P” From FEMA’s ICS training manual 9 -05 IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 34 34

Capabilities of FEMA US&R teams • Search and rescue operations in damaged or collapsed structures • Operations in weapons-of-massdestruction environment • Emergency medical care for entrapped victims, task force personnel and search canines • Assessment/shut-off of utilities to houses and other buildings • Hazardous materials evaluations • Structural and hazard evaluations of buildings • Stabilization of damaged structures, including shoring and cribbing operations • Quick deployment with the team of 62, 000 pound equipment caches IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Task Force Capabilities Management • • Task Force Leader Safety Officer Planning Manager Search Manager Rescue Manager Logistics Manager Connecticut Task Force One Medical Manager Functions — provides overall management and coordination of task force operations. IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Command Staff Responsibility • The overall management of the Task Force including Command, Planning, Logistics, Safety and Training. • Carrying out the missions of the program, as well as the development and completion of all team objectives. IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Safety Officer Responsibility Monitoring and assessing the safety aspects of the Task Force during training or at an incident. IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 38 38

Task Force Capabilities Search Component • Canine Search Specialists • Technical Search Specialists Biloxi, MI 9 -3 -2005 Indiana Task Force 1 search for victims of Hurricane Katrina IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 39 39

Search Component Technical Search • Trained to use broad range of equipment for detecting victims by noise, thermal and visual observation • Trained on equipment for detecting hazards to the team IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program Indiana Task Force 1 checks for hazardous gases in Biloxi, MI after Katrina 40 40

Technical Search Component Equipment of NJ-TF 1 – Advanced Optical Search Equipment • • • Snake Eye Camera Borescope/Fiberscope Videoscope Search. Cam 2000 Generation III Night Vision Thermal Imaging – Advanced Seismic/Acoustic Search Equipment • Delsar Acoustical Listening Device IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 41 41

Rescue Component consists of…. • Rescue Managers • Rescue Squad Officers • Rescue Specialists • Heavy Rigging Specialists • Law Enforcement Specialists IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 42 42

Rescue Technicians Responsibilities • Performing victim rescues at incidents requiring specialized technical skills in areas such as rope use, structural collapse, confined space and trench • Breaching, breaking and shoring of collapsed structures IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 43 43

Planning Component consists of…. • Planning Managers • Technical Information Specialists • Structural Specialists IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Planning Component • Planning Managers assist in creation of Incident Action Plan • Technical Information Specialists document incident and provide accountability • Structure Specialists are licensed engineers who specialize in building collapse and triage IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 45 45

Planning Component is responsible for…. • Establishing work goals • Developing operational plans for work periods • Coordinating communication efforts • Assessing structural components & stability • Accountability of team members IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 46 46

Logistics Component consists of…. • Logistics Managers • Communications Specialists • Logistics / Support Specialists IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 47 47

Logistics Component is responsible for…. Issuing, maintaining, and repairing all of the equipment assigned to the taskforce cache. IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Medical Component consists of…. • Medical Managers • Medical Specialists called DMAT (Disaster Medical Assistance Team) IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 49 49

Medical Component Responsibility • Specializing in extended pre-hospital emergency care • Treatment of disaster victims • Health and welfare of Task Force members and canine search and rescue dogs IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 50 50

Hazardous Materials Component consists of…. • Haz-Mat Managers • Haz-Mat Technicians IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 51 51

Hazardous Materials Component is responsible for…. • Conducting air monitoring • Assessing hazardous conditions • Developing, implementing and overseeing decontamination • Operating in a variety of hazardous atmospheres in support of team operations IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Law Enforcement consists of…. • Personnel from municipal police departments • Often State Police • Connecticut State Police in this photo IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 53 53

Law Enforcement Component is responsible for…. • Collecting, processing and maintaining the integrity of physical evidence that may be related to the cause of the disaster • Meeting any legal requirements of the court for that jurisdiction • Acting as a liaison between the Task Force Leader and the other law enforcement agencies IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

State US&R Teams • Most, but not all, states have their own US&R team that can be activated irrespective of FEMA’s action • State team’s often differ from FEMA teams, based on hazards of the area • Examples: swift water rescue, NJ-TF 1 pictured IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Success Story #1 Local 825 and New Jersey Task Force One • In 2003, Local 825 arranged heavy equipment for NJ-TF 1 • Two weeks later, Tropicana parking lot collapsed. They were ready! • NJ-TF 1 started in 1997 and has 220+ members IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program
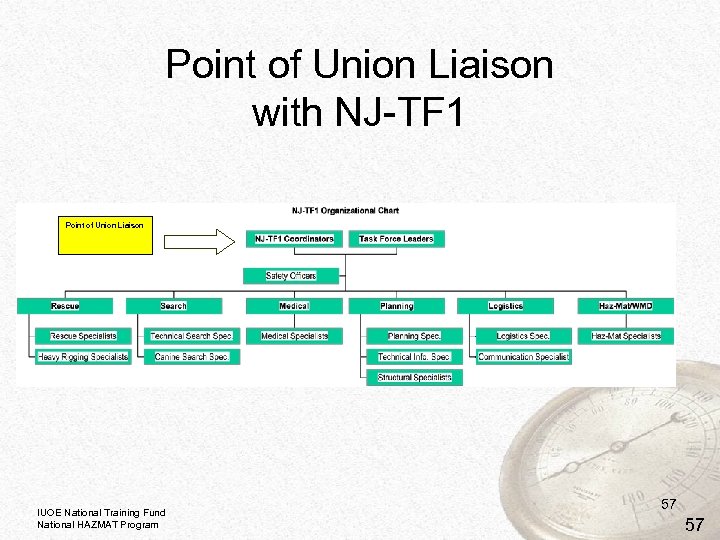
Point of Union Liaison with NJ-TF 1 Point of Union Liaison IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 57 57

Both Local 825 and NJ-TF 1 served with distinction at WTC IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 58 58

Lessons Learned from the Partnership of Local 825 and NJ-TF 1 • Members of task force must meet with the contractors and discuss available equipment • Arrangements must be made to get SSP and equipment to the site • Credentials for the Task Force must be established beforehand – In NJ, Operators are designated “Support Specialists” – Must have HAZWOPER, OSHA 10 -hour and OSHA Disaster Site Worker (OSHA Program Card) – Crane operators must be NJ certified (CCO) IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Lessons Learned (2) • Unions should have Business Agents trained in OSHA Disaster Site Worker • Team must jointly develop checklist of equipment needed, prior to event • Task Force must be strict on training – everyone must be current to get on site IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Success Story #2 Local 324 and Michigan Urban Search & Rescue • Local 324 in Livonia, Michigan has been working with MUSAR since 1999 • MUSAR was formed in 1990 to: – Expand opportunity to include the remainder of the state. Only 50 (approximately) of 1147 fire departments in Michigan have personnel that are trained for technical rescue – Improve coverage – most teams are in the south (90% of rescues from collapsed buildings occur within first 2 hours) – Develop and deliver training for task force management personnel IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program
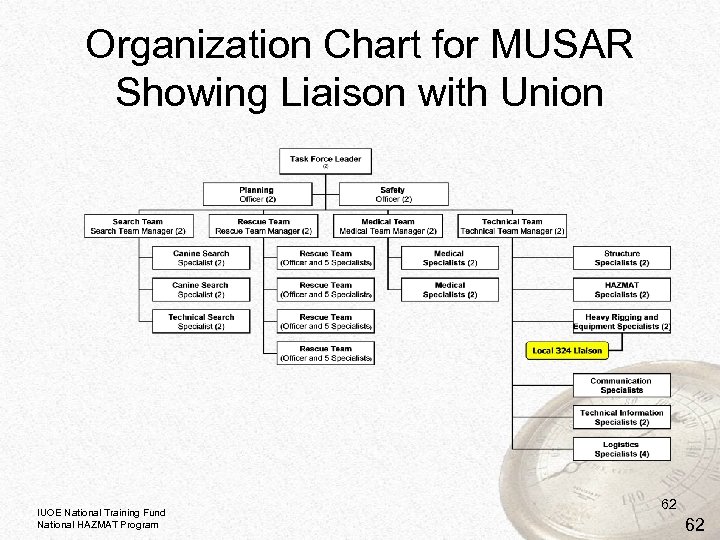
Organization Chart for MUSAR Showing Liaison with Union IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 62 62

Major Success: Development of the MUSAR Homeland Security Training Facility View of construction of the confined space facility IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 63 63

Dedication Day Sept. 7, 2005 IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 64 64

Success Story #3 Local 478 and Connecticut Task Force One • Local 478: 4, 000 members and advanced training capabilities, including crane simulator • CT-TF 1 is working towards MOU between State and Local 478 CT-TF 1 responding to a propane gas explosion in Colchester, CT, September 9, 2004. IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

CT-TF 1 Base of Operation • 269 Maxim Rd. (Brainard Field) Hartford, CT • Share facilities with – CT State Police – CT- Disaster Medical Assistance Team – CT- Office of Emergency Management – Coast Guard Auxiliary – Civil Air Patrol IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 66 66

Training Needs of Members of the Alliance IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 67 67

Training for Operating Engineers NIMS Training • Intro to Incident Command System IS-100 • Basic Incident Command System IS-200 • Intro to National Incident Management System (IS-700) • Intro to National Response Plan (IS-800) These are available for free online at: http: //training. fema. gov/emiweb/ IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Training for Operating Engineers OSHA Disaster Site Worker Course • 16 -hour course that the National HAZMAT Program helped create • Offered by National HAZMAT Program • Requires donning and doffing respirators • Covers ICS for construction workers • Covers Critical Incident Stress Management • #7600 for workers, #5600 for instructors IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

OSHA Disaster Site Worker Course Program versus Course Card For Program Card, must have: • OSHA 10 -hour Construction (or 30 -hour) • 16 -hour Disaster Site Worker (7600) • Current on HAZWOPER Course Card, must have: • OSHA 10 -hour Construction (or 30 -hour) • 16 -hour Disaster Site Worker (7600) IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Heavy Equipment and Rigging Specialist • NFPA 1670, Standard on Operations and Training for Technical Search and Rescue Incidents describes training for riggers • IUOE members are serving in this capacity on some State US&R teams • Rigging specialist reports directly to Rescue Team Leader IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

Considerable training is needed to be a US&R team member! CT-TF 1 practicing rope rescues IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 72 72

Safety Issues for Team Considerations IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 73 73
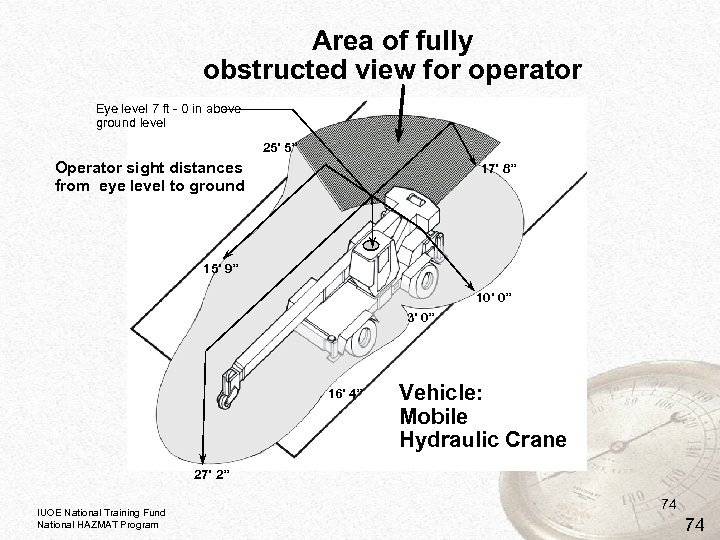
Area of fully obstructed view for operator Eye level 7 ft - 0 in above ground level 25’ 5” Operator sight distances from eye level to ground 17’ 8” 15’ 9” 10’ 0” 3’ 0” 16’ 4” Vehicle: Mobile Hydraulic Crane 27’ 2” IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 74 74

Uncontrolled materials in buckets pose serious risks IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 75 75

So does uncontrolled debris in trucks IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 76 76

PPE Concerns for US&Rs at structural collapses (RAND, 2006) • Fires or high temperature requires structural firefighting ensemble (NFPA 1971, 2000 a) • Additional biological protection is needed • Additional respiratory protection is needed IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program New Jersey Task Force One at Ground Zero

20 Questions Illustrating Difficulty of Ordering a Crane (Taken from FEMA) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Who are you and what are you doing? How quickly do you want a machine? What do you intend for this machine to do? Pick and swing? Pick and carry? Lift small objects at large distances? Will multiple machines be needed? (Second machine to set up primary machine. ) What are the capabilities of the onsite crew? (Are they qualified to assist with set up? ) If this machine is for a single task, what is the load weight and what is the load radius? If this is for multiple tasks, what are several combinations of load and distance? IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

20 Questions Illustrating Difficulty of Ordering a Crane (2) 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Will this task require pick and carry capability? What are the limits of room available for operation of the machine? Overhead clearance, tail swing clearance, underground obstructions? Is there a place to assemble boom (if lattice) and crane (counterweights)? Including room for assisting crane? Are there limitations on delivery of crane or parts? Posted bridges, low clearances, underground utilities? What areas of operation are anticipated? Over rear, Over side, Over front, On rubber? Are two crane (simultaneous) picks anticipated? Will work be performed on a continuous (24 hr) basis? Is auxiliary lighting available? IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

20 Questions Illustrating Difficulty of Ordering a Crane (3) 15. Will radio communication be required to control load? Are dedicated radios available? 16. How much boom is required? Are special boom features (offset, open-throat) needed? 17. What size hook block is needed? Are shackles to fit hook available? 18. Will jib be needed? Jib length? Offset? Load? 19. Are additional rigging components needed? Load cell, lift beams, slings, shackles? 20. Who is the contact person and who is the person directing the rigging operations? IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program

to unite the USAR world so we can all work together. We're looking for what is best for the common good. That's what we're all about. ” Jim Riley, SUSAR Alliance Chairman and National HAZMAT Program Steering Committee member IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 81 81

Questions? National HAZMAT Program 1293 Airport Road, Beaver, WV 25813 304. 253. 8674 www. iuoeiettc. org IUOE National Training Fund National HAZMAT Program 82 82
997f2b6d08bc9d75ae475adc567298c5.ppt