f56fb82b105dca62a46e72845dfd356b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 GST STUDY CIRCLE MEETING INTER-STATE SUPPLIES UNDER GOODS AND SERVICES TAX IN INDIA © Economic Laws Practice 2015 August 20, 2015 /MR. ROHIT JAIN
GST STUDY CIRCLE MEETING INTER-STATE SUPPLIES UNDER GOODS AND SERVICES TAX IN INDIA © Economic Laws Practice 2015 August 20, 2015 /MR. ROHIT JAIN
 SCHEME & STRUCTURE OF INTER-STATE SUPPLIES © Economic Laws Practice 2015 2
SCHEME & STRUCTURE OF INTER-STATE SUPPLIES © Economic Laws Practice 2015 2
 Constitutional amendments proposed by 122 nd Bill Article 286 • Prohibits States from taxing sale or purchase of goods • Outside the State • In the course of the import of goods into or export of the goods outside, the territory of India Article 246 • Provides for Parliament and State Legislature to exclusively and mutually legislate on subjects in Lists I and II of the 7 th Schedule, respectively Entry 92 A - Union List • Taxes on the sale or purchase of goods other than newspapers, where such sale or purchase takes place in the course of inter. State trade or commerce. No power to States to levy tax on any inter-State transactio ns (goods and services) Entry 92 B – Union List • Taxes on the consignment of goods (whether the consignment is to the person making it or to any other person), where such consignment takes place in the course of inter-State trade or commerce. © Economic Laws Practice 2015 3
Constitutional amendments proposed by 122 nd Bill Article 286 • Prohibits States from taxing sale or purchase of goods • Outside the State • In the course of the import of goods into or export of the goods outside, the territory of India Article 246 • Provides for Parliament and State Legislature to exclusively and mutually legislate on subjects in Lists I and II of the 7 th Schedule, respectively Entry 92 A - Union List • Taxes on the sale or purchase of goods other than newspapers, where such sale or purchase takes place in the course of inter. State trade or commerce. No power to States to levy tax on any inter-State transactio ns (goods and services) Entry 92 B – Union List • Taxes on the consignment of goods (whether the consignment is to the person making it or to any other person), where such consignment takes place in the course of inter-State trade or commerce. © Economic Laws Practice 2015 3
 Key issues under current regime • • • Determining nature of supply • Intra-State versus Inter-State supply of goods under Central Sales Tax Act, 1956 to mean: • “Occasioning movement of goods from one State to another” – Both originating State and destination State demanding taxes Need absolute clarity on place of supply under GST to avoid multiplicity of payment and tax demands: • State A versus State B • Center versus State © Economic Laws Practice 2015 4
Key issues under current regime • • • Determining nature of supply • Intra-State versus Inter-State supply of goods under Central Sales Tax Act, 1956 to mean: • “Occasioning movement of goods from one State to another” – Both originating State and destination State demanding taxes Need absolute clarity on place of supply under GST to avoid multiplicity of payment and tax demands: • State A versus State B • Center versus State © Economic Laws Practice 2015 4
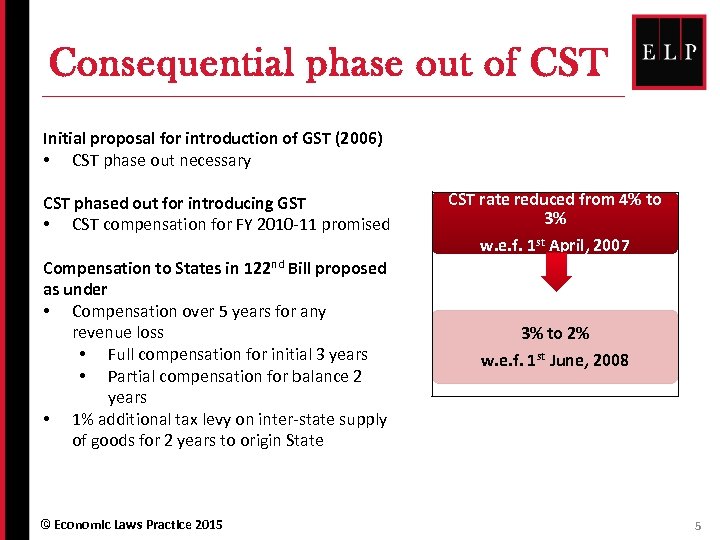 Consequential phase out of CST Initial proposal for introduction of GST (2006) • CST phase out necessary CST phased out for introducing GST • CST compensation for FY 2010 -11 promised CST rate reduced from 4% to 3% w. e. f. 1 st April, 2007 Compensation to States in 122 nd Bill proposed as under • Compensation over 5 years for any revenue loss • Full compensation for initial 3 years • Partial compensation for balance 2 years • 1% additional tax levy on inter-state supply of goods for 2 years to origin State 3% to 2% w. e. f. 1 st June, 2008 © Economic Laws Practice 2015 5
Consequential phase out of CST Initial proposal for introduction of GST (2006) • CST phase out necessary CST phased out for introducing GST • CST compensation for FY 2010 -11 promised CST rate reduced from 4% to 3% w. e. f. 1 st April, 2007 Compensation to States in 122 nd Bill proposed as under • Compensation over 5 years for any revenue loss • Full compensation for initial 3 years • Partial compensation for balance 2 years • 1% additional tax levy on inter-state supply of goods for 2 years to origin State 3% to 2% w. e. f. 1 st June, 2008 © Economic Laws Practice 2015 5
 Constitutional amendments proposed by 122 nd Bill Article 246 A • Parliament and State legislatures empowered to Article 269 A legislate on GST (CGST & SGST), respectively • Centre exclusively empowered to legislate on GST levied on inter-State movement of goods and/ or services (IGST) • Power to States to levy tax on services for the first time Article 246 A – “(1)… (2) Parliament has exclusive power to make laws with respect to goods and services tax where the supply of goods, or of services, or both takes place in the course of inter-State trade or commerce. ” Article 286 prohibits States from • Centre to levy GST on Inter-State supplies taxing both inter-State supplies and imports, of goods and • Import of goods or provision of services from outside services India will be treated as Inter-State supplies © Economic Laws Practice 2015 • ‘Place of supply’ of goods & services to be determined 6
Constitutional amendments proposed by 122 nd Bill Article 246 A • Parliament and State legislatures empowered to Article 269 A legislate on GST (CGST & SGST), respectively • Centre exclusively empowered to legislate on GST levied on inter-State movement of goods and/ or services (IGST) • Power to States to levy tax on services for the first time Article 246 A – “(1)… (2) Parliament has exclusive power to make laws with respect to goods and services tax where the supply of goods, or of services, or both takes place in the course of inter-State trade or commerce. ” Article 286 prohibits States from • Centre to levy GST on Inter-State supplies taxing both inter-State supplies and imports, of goods and • Import of goods or provision of services from outside services India will be treated as Inter-State supplies © Economic Laws Practice 2015 • ‘Place of supply’ of goods & services to be determined 6
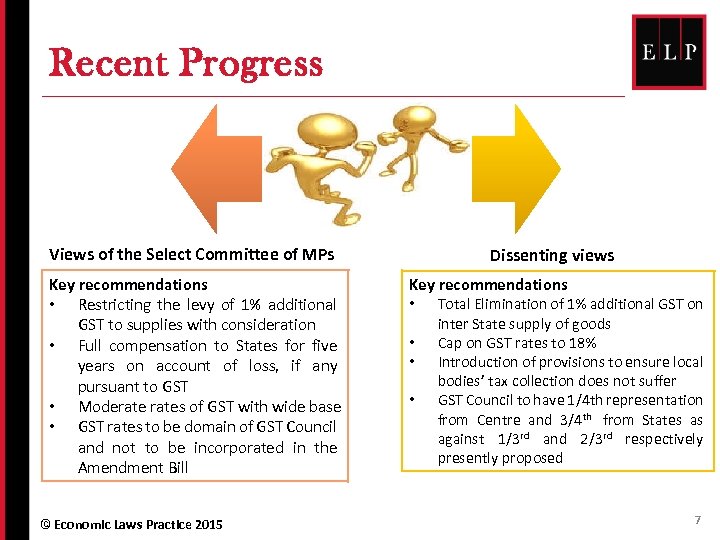 Recent Progress Views of the Select Committee of MPs Key recommendations • Restricting the levy of 1% additional GST to supplies with consideration • Full compensation to States for five years on account of loss, if any pursuant to GST • Moderates of GST with wide base • GST rates to be domain of GST Council and not to be incorporated in the Amendment Bill © Economic Laws Practice 2015 Dissenting views Key recommendations • Total Elimination of 1% additional GST on • • • inter State supply of goods Cap on GST rates to 18% Introduction of provisions to ensure local bodies’ tax collection does not suffer GST Council to have 1/4 th representation from Centre and 3/4 th from States as against 1/3 rd and 2/3 rd respectively presently proposed 7
Recent Progress Views of the Select Committee of MPs Key recommendations • Restricting the levy of 1% additional GST to supplies with consideration • Full compensation to States for five years on account of loss, if any pursuant to GST • Moderates of GST with wide base • GST rates to be domain of GST Council and not to be incorporated in the Amendment Bill © Economic Laws Practice 2015 Dissenting views Key recommendations • Total Elimination of 1% additional GST on • • • inter State supply of goods Cap on GST rates to 18% Introduction of provisions to ensure local bodies’ tax collection does not suffer GST Council to have 1/4 th representation from Centre and 3/4 th from States as against 1/3 rd and 2/3 rd respectively presently proposed 7
 Recent Progress “I’m game, are you? ” - FM • FM’s clarifies the Government’s stand on the Constitution Amendment Bill via Social Media – • GST rate to be decided by the GST Council • GST on Inter unit transfer – GST charged on supplies will be VATable and will not have any cascading effect • Share of local bodies in the revenue buoyancy should be a part of the proposed constitution amendment – not acceptable • Two years transient provision which provided for an additional tax of 1% added to allay the fears of manufacturing States • Electricity, tobacco products and alcohol for human consumption should be given the same treatment as petroleum in the Amendment bill – no such consensus with the States © Economic Laws Practice 2015 8
Recent Progress “I’m game, are you? ” - FM • FM’s clarifies the Government’s stand on the Constitution Amendment Bill via Social Media – • GST rate to be decided by the GST Council • GST on Inter unit transfer – GST charged on supplies will be VATable and will not have any cascading effect • Share of local bodies in the revenue buoyancy should be a part of the proposed constitution amendment – not acceptable • Two years transient provision which provided for an additional tax of 1% added to allay the fears of manufacturing States • Electricity, tobacco products and alcohol for human consumption should be given the same treatment as petroleum in the Amendment bill – no such consensus with the States © Economic Laws Practice 2015 8
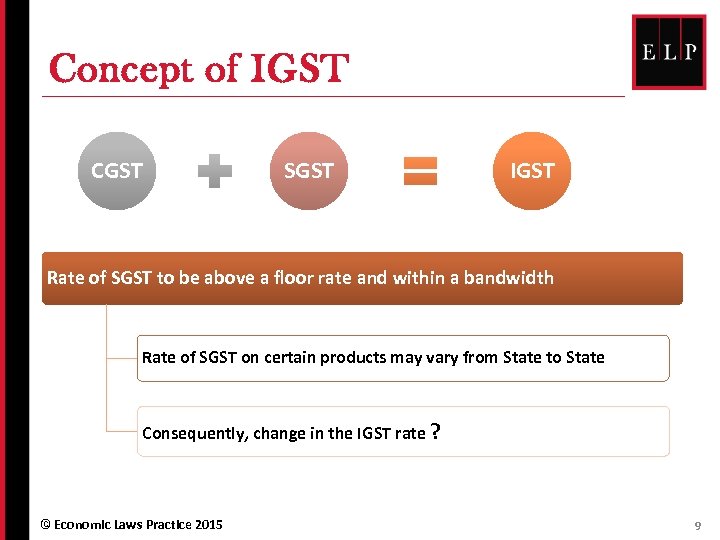 Concept of IGST CGST SGST IGST Rate of SGST to be above a floor rate and within a bandwidth Rate of SGST on certain products may vary from State to State Consequently, change in the IGST rate ? © Economic Laws Practice 2015 9
Concept of IGST CGST SGST IGST Rate of SGST to be above a floor rate and within a bandwidth Rate of SGST on certain products may vary from State to State Consequently, change in the IGST rate ? © Economic Laws Practice 2015 9
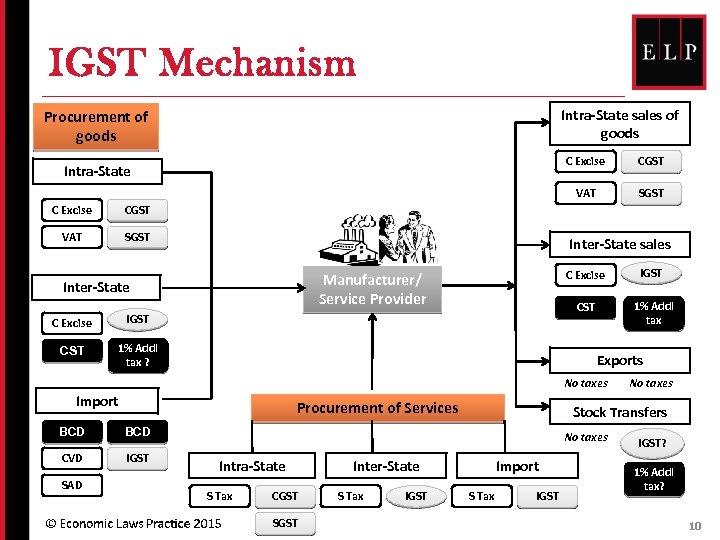 IGST Mechanism Intra-State sales of goods Procurement of goods C Excise SGST CGST VAT Intra-State Inter-State sales Inter-State C Excise 1% Addl tax ? IGST CST C Excise Manufacturer/ Service Provider 1% Addl tax Exports No taxes Import Procurement of Services BCD IGST Stock Transfers BCD CVD SAD No taxes Intra-State S Tax CGST SGST Inter-State S Tax IGST No taxes Import S Tax IGST? 1% Addl tax? 10
IGST Mechanism Intra-State sales of goods Procurement of goods C Excise SGST CGST VAT Intra-State Inter-State sales Inter-State C Excise 1% Addl tax ? IGST CST C Excise Manufacturer/ Service Provider 1% Addl tax Exports No taxes Import Procurement of Services BCD IGST Stock Transfers BCD CVD SAD No taxes Intra-State S Tax CGST SGST Inter-State S Tax IGST No taxes Import S Tax IGST? 1% Addl tax? 10
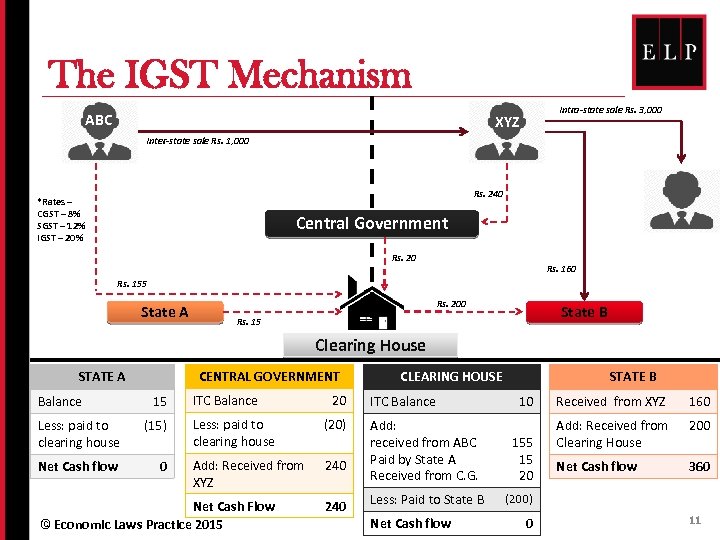 The IGST Mechanism ABC Intra-state sale Rs. 3, 000 XYZ Inter-state sale Rs. 1, 000 Rs. 240 *Rates – CGST – 8% SGST – 12% IGST – 20% Central Government Rs. 20 Rs. 160 Rs. 155 State A Rs. 200 State B Rs. 15 Clearing House STATE A Balance CENTRAL GOVERNMENT 15 Less: paid to clearing house (15) Net Cash flow 0 ITC Balance 20 Less: paid to clearing house (20) Add: Received from XYZ 240 Net Cash Flow © Economic Laws Practice 2015 240 CLEARING HOUSE ITC Balance Add: received from ABC Paid by State A Received from C. G. Less: Paid to State B Net Cash flow STATE B 10 155 15 20 Received from XYZ 160 Add: Received from Clearing House 200 Net Cash flow 360 (200) 0 11
The IGST Mechanism ABC Intra-state sale Rs. 3, 000 XYZ Inter-state sale Rs. 1, 000 Rs. 240 *Rates – CGST – 8% SGST – 12% IGST – 20% Central Government Rs. 20 Rs. 160 Rs. 155 State A Rs. 200 State B Rs. 15 Clearing House STATE A Balance CENTRAL GOVERNMENT 15 Less: paid to clearing house (15) Net Cash flow 0 ITC Balance 20 Less: paid to clearing house (20) Add: Received from XYZ 240 Net Cash Flow © Economic Laws Practice 2015 240 CLEARING HOUSE ITC Balance Add: received from ABC Paid by State A Received from C. G. Less: Paid to State B Net Cash flow STATE B 10 155 15 20 Received from XYZ 160 Add: Received from Clearing House 200 Net Cash flow 360 (200) 0 11
 Additional GST Article 279 A (18) provides for Additional GST @ 1% for 2 years • To be levied by Centre on Inter-State supply of goods • Will be remitted to States from where the supply originates – contra destination principle • Will be a cost as it is not a part of the credit chain – contra principle of complete fungibility of credit • Levy only on supply of goods meaning that – • - Differentiation between goods and services will continue to exist • - Duality issues (e. g. IPR, software) and issues with determining goods and service components (e. g. works contract, catering contract) will continue to exist Com com prom abo pen ise GST lishin sate meas for g CS Stat ure wa t rd T and es fo o mo r ve Ide pro ally, pos sho ed uld sch em not b eo e f G in ST • Will stock transfer also suffer this levy? © Economic Laws Practice 2015 12
Additional GST Article 279 A (18) provides for Additional GST @ 1% for 2 years • To be levied by Centre on Inter-State supply of goods • Will be remitted to States from where the supply originates – contra destination principle • Will be a cost as it is not a part of the credit chain – contra principle of complete fungibility of credit • Levy only on supply of goods meaning that – • - Differentiation between goods and services will continue to exist • - Duality issues (e. g. IPR, software) and issues with determining goods and service components (e. g. works contract, catering contract) will continue to exist Com com prom abo pen ise GST lishin sate meas for g CS Stat ure wa t rd T and es fo o mo r ve Ide pro ally, pos sho ed uld sch em not b eo e f G in ST • Will stock transfer also suffer this levy? © Economic Laws Practice 2015 12
 ISSUES & IMPLICATIONS © Economic Laws Practice 2015 13
ISSUES & IMPLICATIONS © Economic Laws Practice 2015 13
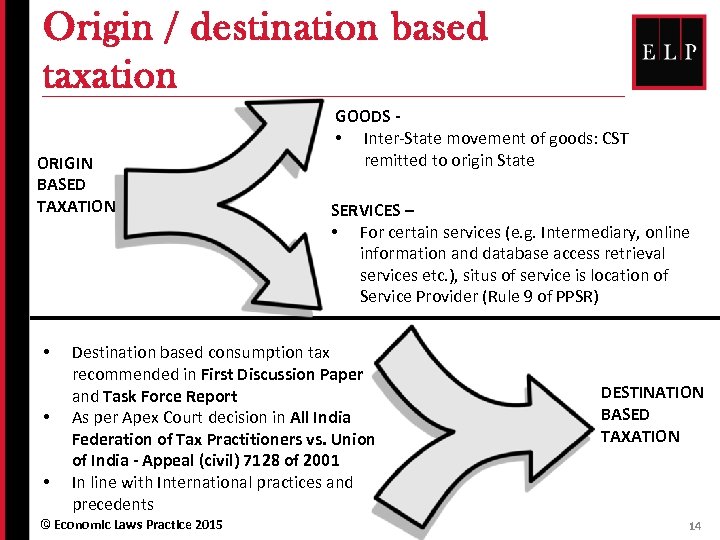 Origin / destination based taxation ORIGIN BASED TAXATION • • • GOODS • Inter-State movement of goods: CST remitted to origin State SERVICES – • For certain services (e. g. Intermediary, online information and database access retrieval services etc. ), situs of service is location of Service Provider (Rule 9 of PPSR) Destination based consumption tax recommended in First Discussion Paper and Task Force Report As per Apex Court decision in All India Federation of Tax Practitioners vs. Union of India - Appeal (civil) 7128 of 2001 In line with International practices and precedents © Economic Laws Practice 2015 DESTINATION BASED TAXATION 14
Origin / destination based taxation ORIGIN BASED TAXATION • • • GOODS • Inter-State movement of goods: CST remitted to origin State SERVICES – • For certain services (e. g. Intermediary, online information and database access retrieval services etc. ), situs of service is location of Service Provider (Rule 9 of PPSR) Destination based consumption tax recommended in First Discussion Paper and Task Force Report As per Apex Court decision in All India Federation of Tax Practitioners vs. Union of India - Appeal (civil) 7128 of 2001 In line with International practices and precedents © Economic Laws Practice 2015 DESTINATION BASED TAXATION 14
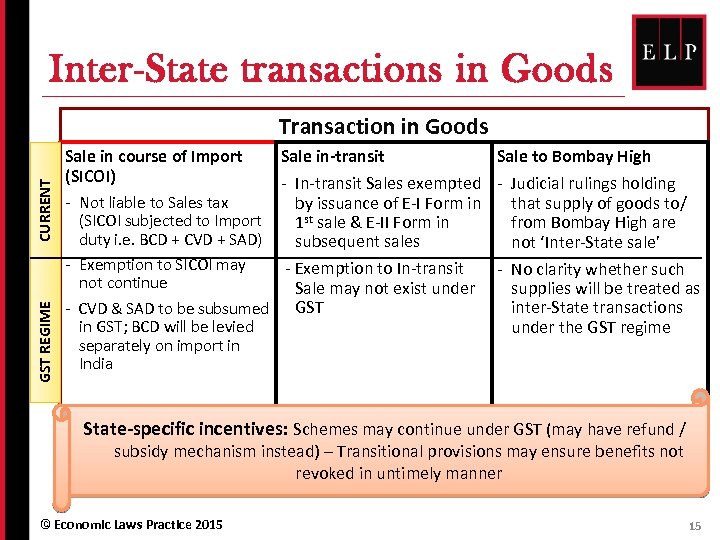 Inter-State transactions in Goods GST REGIME CURRENT Transaction in Goods Sale in course of Import (SICOI) Sale in-transit Sale to Bombay High - In-transit Sales exempted - Judicial rulings holding - Not liable to Sales tax by issuance of E-I Form in that supply of goods to/ (SICOI subjected to Import 1 st sale & E-II Form in from Bombay High are duty i. e. BCD + CVD + SAD) subsequent sales not ‘Inter-State sale’ - Exemption to SICOI may - Exemption to In-transit - No clarity whether such not continue Sale may not exist under supplies will be treated as inter-State transactions - CVD & SAD to be subsumed GST in GST; BCD will be levied under the GST regime separately on import in India State-specific incentives: Schemes may continue under GST (may have refund / subsidy mechanism instead) – Transitional provisions may ensure benefits not revoked in untimely manner © Economic Laws Practice 2015 15
Inter-State transactions in Goods GST REGIME CURRENT Transaction in Goods Sale in course of Import (SICOI) Sale in-transit Sale to Bombay High - In-transit Sales exempted - Judicial rulings holding - Not liable to Sales tax by issuance of E-I Form in that supply of goods to/ (SICOI subjected to Import 1 st sale & E-II Form in from Bombay High are duty i. e. BCD + CVD + SAD) subsequent sales not ‘Inter-State sale’ - Exemption to SICOI may - Exemption to In-transit - No clarity whether such not continue Sale may not exist under supplies will be treated as inter-State transactions - CVD & SAD to be subsumed GST in GST; BCD will be levied under the GST regime separately on import in India State-specific incentives: Schemes may continue under GST (may have refund / subsidy mechanism instead) – Transitional provisions may ensure benefits not revoked in untimely manner © Economic Laws Practice 2015 15
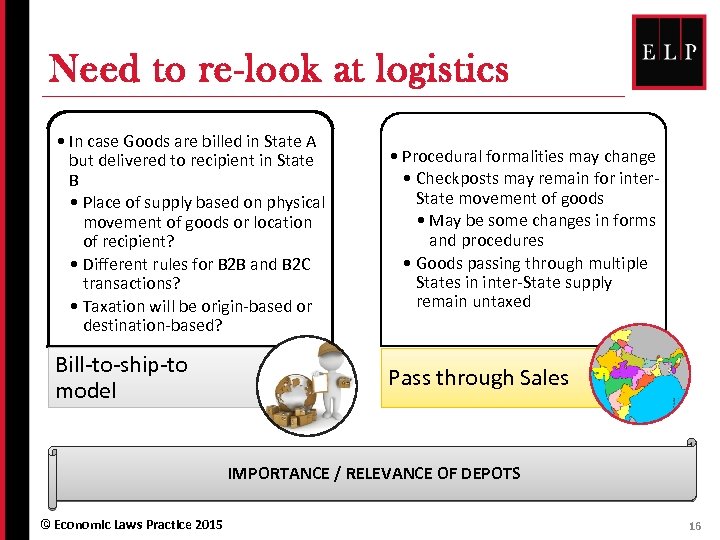 Need to re-look at logistics • In case Goods are billed in State A but delivered to recipient in State B • Place of supply based on physical movement of goods or location of recipient? • Different rules for B 2 B and B 2 C transactions? • Taxation will be origin-based or destination-based? • Procedural formalities may change • Checkposts may remain for inter. State movement of goods • May be some changes in forms and procedures • Goods passing through multiple States in inter-State supply remain untaxed Bill-to-ship-to model Pass through Sales IMPORTANCE / RELEVANCE OF DEPOTS © Economic Laws Practice 2015 16
Need to re-look at logistics • In case Goods are billed in State A but delivered to recipient in State B • Place of supply based on physical movement of goods or location of recipient? • Different rules for B 2 B and B 2 C transactions? • Taxation will be origin-based or destination-based? • Procedural formalities may change • Checkposts may remain for inter. State movement of goods • May be some changes in forms and procedures • Goods passing through multiple States in inter-State supply remain untaxed Bill-to-ship-to model Pass through Sales IMPORTANCE / RELEVANCE OF DEPOTS © Economic Laws Practice 2015 16
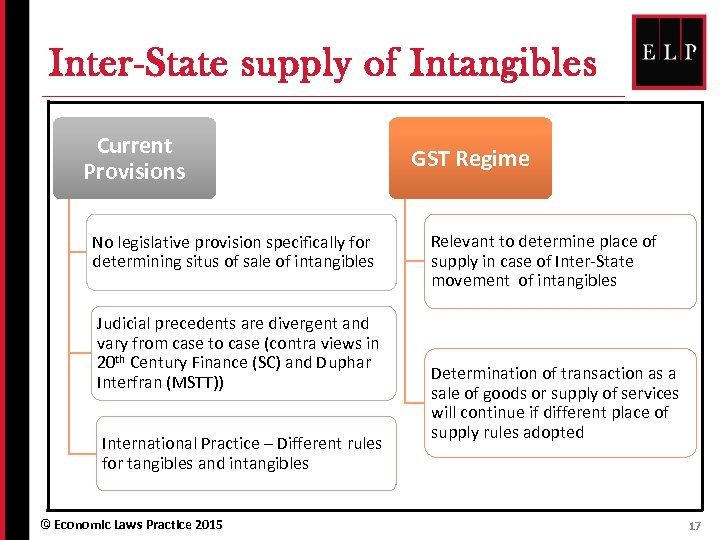 Inter-State supply of Intangibles Current Provisions No legislative provision specifically for determining situs of sale of intangibles Judicial precedents are divergent and vary from case to case (contra views in 20 th Century Finance (SC) and Duphar Interfran (MSTT)) International Practice – Different rules for tangibles and intangibles © Economic Laws Practice 2015 GST Regime Relevant to determine place of supply in case of Inter-State movement of intangibles Determination of transaction as a sale of goods or supply of services will continue if different place of supply rules adopted 17
Inter-State supply of Intangibles Current Provisions No legislative provision specifically for determining situs of sale of intangibles Judicial precedents are divergent and vary from case to case (contra views in 20 th Century Finance (SC) and Duphar Interfran (MSTT)) International Practice – Different rules for tangibles and intangibles © Economic Laws Practice 2015 GST Regime Relevant to determine place of supply in case of Inter-State movement of intangibles Determination of transaction as a sale of goods or supply of services will continue if different place of supply rules adopted 17
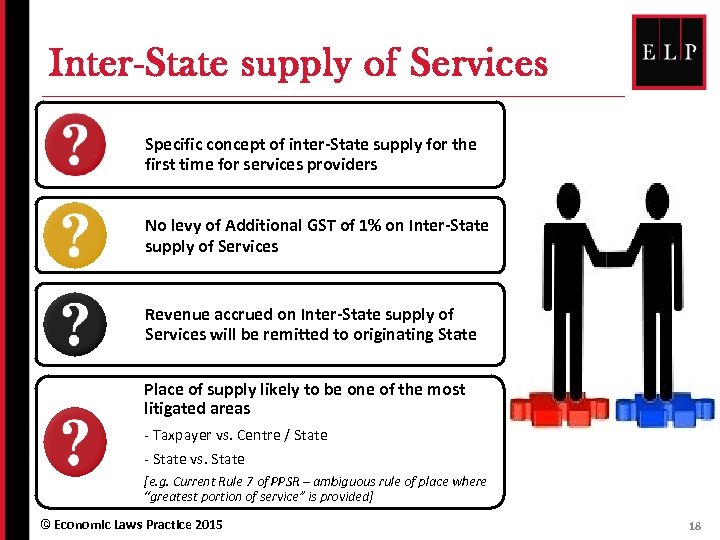 Inter-State supply of Services Specific concept of inter-State supply for the first time for services providers No levy of Additional GST of 1% on Inter-State supply of Services Revenue accrued on Inter-State supply of Services will be remitted to originating State Place of supply likely to be one of the most litigated areas - Taxpayer vs. Centre / State - State vs. State [e. g. Current Rule 7 of PPSR – ambiguous rule of place where “greatest portion of service” is provided] © Economic Laws Practice 2015 18
Inter-State supply of Services Specific concept of inter-State supply for the first time for services providers No levy of Additional GST of 1% on Inter-State supply of Services Revenue accrued on Inter-State supply of Services will be remitted to originating State Place of supply likely to be one of the most litigated areas - Taxpayer vs. Centre / State - State vs. State [e. g. Current Rule 7 of PPSR – ambiguous rule of place where “greatest portion of service” is provided] © Economic Laws Practice 2015 18
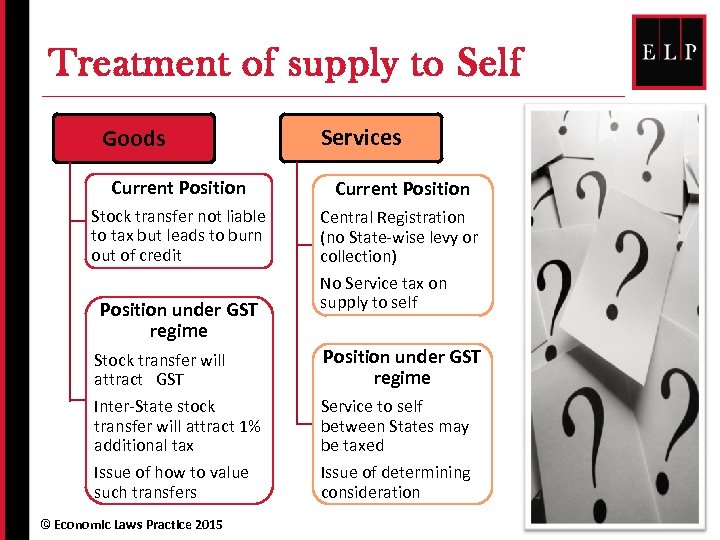 Treatment of supply to Self Goods Services Current Position Stock transfer not liable to tax but leads to burn out of credit Central Registration (no State-wise levy or collection) No Service tax on supply to self Position under GST regime Stock transfer will attract GST Inter-State stock transfer will attract 1% additional tax Issue of how to value such transfers © Economic Laws Practice 2015 Position under GST regime Service to self between States may be taxed Issue of determining consideration 19
Treatment of supply to Self Goods Services Current Position Stock transfer not liable to tax but leads to burn out of credit Central Registration (no State-wise levy or collection) No Service tax on supply to self Position under GST regime Stock transfer will attract GST Inter-State stock transfer will attract 1% additional tax Issue of how to value such transfers © Economic Laws Practice 2015 Position under GST regime Service to self between States may be taxed Issue of determining consideration 19
 International Precedents • EU countries, like UK, offer the option of VAT grouping • Single registration for various companies in a group • Intra-group supplies not taxed • One representative company pays VAT and files returns on behalf of the group • May be ideally suited to a unitary GST/ VAT, like in the UK • Less suitable for GST within a federal structure, as in India © Economic Laws Practice 2015 20
International Precedents • EU countries, like UK, offer the option of VAT grouping • Single registration for various companies in a group • Intra-group supplies not taxed • One representative company pays VAT and files returns on behalf of the group • May be ideally suited to a unitary GST/ VAT, like in the UK • Less suitable for GST within a federal structure, as in India © Economic Laws Practice 2015 20
 Q&A © Economic Laws Practice 2015
Q&A © Economic Laws Practice 2015
 © Economic Laws Practice 2015 MUMBAI 109, A Wing Dalamal Towers Nariman Point Mumbai 400 021 T: +91 22 6636 7000 F: +91 22 6636 7172 E: mumbai@elp-in. com DELHI 405 -406 World Trade Centre Barakhamba Lane New Delhi 110 001 T: +91 11 4152 8400 F: +91 11 4152 8404 E: delhi@elp-in. com BENGALURU 6 th Floor Rockline Centre 54, Richmond Road Bangalore 560 025 T: +91 80 4168 5530/1 E: bengaluru@elp-in. com AHMEDABAD 801, Abhijeet III Mithakali Six Roads Ellisbridge Ahmedabad 380 006 T: +91 79 6605 4480/8 F: +91 79 6605 4482 E: ahmedabad@elp-in. com PUNE Suyog Fusion 7 th Floor, No. 1 97 Dhole Patil Road Pune 411 001 T: +91 20 4146 7400 F: +91 20 4146 7402 E: pune@elp-in. com CHENNAI No. 6, 4 th Lane Nungambakkam High Road Chennai 600 034 T: +91 44 4210 4863 E: chennai@elp-in. com
© Economic Laws Practice 2015 MUMBAI 109, A Wing Dalamal Towers Nariman Point Mumbai 400 021 T: +91 22 6636 7000 F: +91 22 6636 7172 E: mumbai@elp-in. com DELHI 405 -406 World Trade Centre Barakhamba Lane New Delhi 110 001 T: +91 11 4152 8400 F: +91 11 4152 8404 E: delhi@elp-in. com BENGALURU 6 th Floor Rockline Centre 54, Richmond Road Bangalore 560 025 T: +91 80 4168 5530/1 E: bengaluru@elp-in. com AHMEDABAD 801, Abhijeet III Mithakali Six Roads Ellisbridge Ahmedabad 380 006 T: +91 79 6605 4480/8 F: +91 79 6605 4482 E: ahmedabad@elp-in. com PUNE Suyog Fusion 7 th Floor, No. 1 97 Dhole Patil Road Pune 411 001 T: +91 20 4146 7400 F: +91 20 4146 7402 E: pune@elp-in. com CHENNAI No. 6, 4 th Lane Nungambakkam High Road Chennai 600 034 T: +91 44 4210 4863 E: chennai@elp-in. com


