 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 1 Pfizer in Russia Internationalization International Business Strategies, Prof. A. Yu. Panibratov Polina Zinchenko, Ekatarina Zaytseva, Ekatarina Selenkina, Arina Lekomtseva, Basil Tschumperlin 05. 10. 2012
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 1 Pfizer in Russia Internationalization International Business Strategies, Prof. A. Yu. Panibratov Polina Zinchenko, Ekatarina Zaytseva, Ekatarina Selenkina, Arina Lekomtseva, Basil Tschumperlin 05. 10. 2012
 Content ① History of Pfizer and global growth strategy ② Pharmaceutical industry in Russia ③ SWOT-analysis ④ Overview over Internationalization theory ⑤ Application of OLI-paradigm to Pfizer ⑥ Elements of Pfizer‘s internationalization strategy ⑦ Problems of Pfizer ⑧ Data analysis ⑨ Recommendations ⑩ Bibliography Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 05. 10. 2012 Slide 2
Content ① History of Pfizer and global growth strategy ② Pharmaceutical industry in Russia ③ SWOT-analysis ④ Overview over Internationalization theory ⑤ Application of OLI-paradigm to Pfizer ⑥ Elements of Pfizer‘s internationalization strategy ⑦ Problems of Pfizer ⑧ Data analysis ⑨ Recommendations ⑩ Bibliography Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 05. 10. 2012 Slide 2
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 3 History of Pfizer Global growth strategy
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 3 History of Pfizer Global growth strategy
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 4 Getting to know Pfizer Facts Found in 1849 in the USA First manufacturer of antibiotics Penicillin and Terramycin Hit drugs: antibiotics, Viagra, Diflucan, etc. Global growth strategy Extensive M&A in order to gain ‘Blockbusters’ Vast autonomy of overseas offices Go global to exploit R&D potential and/or increase profit from sales until licenses expire
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 4 Getting to know Pfizer Facts Found in 1849 in the USA First manufacturer of antibiotics Penicillin and Terramycin Hit drugs: antibiotics, Viagra, Diflucan, etc. Global growth strategy Extensive M&A in order to gain ‘Blockbusters’ Vast autonomy of overseas offices Go global to exploit R&D potential and/or increase profit from sales until licenses expire
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 5 Pharmaceutical industry in Russia
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 5 Pharmaceutical industry in Russia
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 6 Russian pharmaceutical industry High potential Weakly concentrated: 10 companies-leaders share 30% of sales CAGR 17% 6, 3% of European pharmaceutical market value
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 6 Russian pharmaceutical industry High potential Weakly concentrated: 10 companies-leaders share 30% of sales CAGR 17% 6, 3% of European pharmaceutical market value
 Porter’s 5 Forces Competitors: Sanofi-Aventis, Pharmstandart, Novartis (Pfizer – 20 th) Moderate rivalry Suppliers: Numerous suppliers Low switching costs High prices for new active ingredients imposed by suppliers Investments in production facilities of chemicals by large pharmaceutical manufacturers Moderate power Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 7
Porter’s 5 Forces Competitors: Sanofi-Aventis, Pharmstandart, Novartis (Pfizer – 20 th) Moderate rivalry Suppliers: Numerous suppliers Low switching costs High prices for new active ingredients imposed by suppliers Investments in production facilities of chemicals by large pharmaceutical manufacturers Moderate power Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 7
 Porter’s 5 Forces Consumers: 2 types: health care services providers and drug retailers Moderate buyer power Substitutes Traditional remedies Generics and biosimilars Low switching costs Strong power Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 8
Porter’s 5 Forces Consumers: 2 types: health care services providers and drug retailers Moderate buyer power Substitutes Traditional remedies Generics and biosimilars Low switching costs Strong power Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 8
 Porter’s 5 Forces New entrants Regulations and legal framework Drug safety regulations Significant seed capital Time constraints Difference of intellectual property laws Moderate power Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 9
Porter’s 5 Forces New entrants Regulations and legal framework Drug safety regulations Significant seed capital Time constraints Difference of intellectual property laws Moderate power Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 9
 Macroeconomic factors Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 10 Introduction of medical insurance Intensification of the control of ethical promotion of the medicines Restrictions in the field of advertising of the prescription drugs Governmental focus on financing treatment of socially significant diseases Intensification of the price regulation Government preferences in regard to local producers Project “Pharma 2020”
Macroeconomic factors Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 10 Introduction of medical insurance Intensification of the control of ethical promotion of the medicines Restrictions in the field of advertising of the prescription drugs Governmental focus on financing treatment of socially significant diseases Intensification of the price regulation Government preferences in regard to local producers Project “Pharma 2020”
 PEST-analysis Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 11 Political aspect: Governmental encouragement of diffusion of foreign experience Restrictions on interactions between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers Restrictions on prices of essential drugs Enhancement of antitrust and bribery regulation Fast track registration for generics and biosimilars Accession to WTO (improvement of intellectual property protection, technical regulations and general lawmaking) Introduction of GMP regulation Compulsory health insurance
PEST-analysis Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 11 Political aspect: Governmental encouragement of diffusion of foreign experience Restrictions on interactions between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers Restrictions on prices of essential drugs Enhancement of antitrust and bribery regulation Fast track registration for generics and biosimilars Accession to WTO (improvement of intellectual property protection, technical regulations and general lawmaking) Introduction of GMP regulation Compulsory health insurance
 PEST-analysis Economic aspect: Pharmaceutical market growth - 7, 8% (2009 -> 2010) Positive GDP forecasts Social aspect: Ageing of population Increasing number of illnesses Poor information awareness concerning treatments Technological aspect: Key-role of IT-technologies in production Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 12
PEST-analysis Economic aspect: Pharmaceutical market growth - 7, 8% (2009 -> 2010) Positive GDP forecasts Social aspect: Ageing of population Increasing number of illnesses Poor information awareness concerning treatments Technological aspect: Key-role of IT-technologies in production Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 12
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 13 SWOT-analysis
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 13 SWOT-analysis
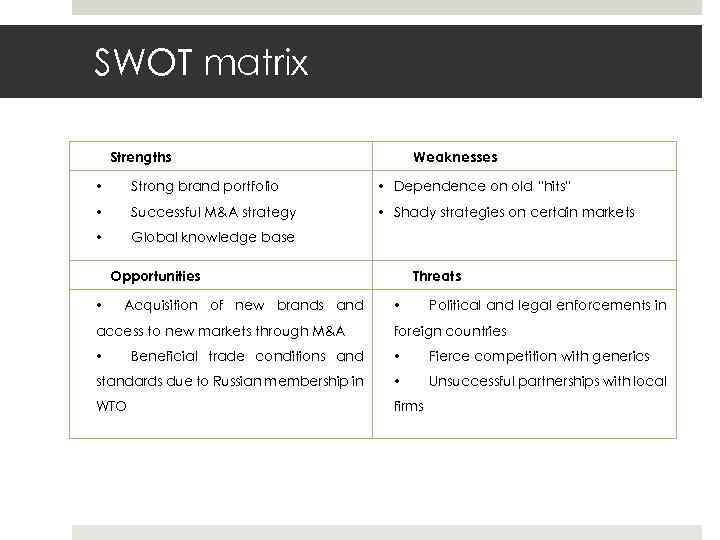 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 14 SWOT matrix Strengths Weaknesses • Strong brand portfolio • Dependence on old “hits” • Successful M&A strategy • Shady strategies on certain markets • Global knowledge base Opportunities • Acquisition of new brands and access to new markets through M&A Threats • Political and legal enforcements in foreign countries Beneficial trade conditions and • Fierce competition with generics standards due to Russian membership in • Unsuccessful partnerships with local WTO firms •
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 14 SWOT matrix Strengths Weaknesses • Strong brand portfolio • Dependence on old “hits” • Successful M&A strategy • Shady strategies on certain markets • Global knowledge base Opportunities • Acquisition of new brands and access to new markets through M&A Threats • Political and legal enforcements in foreign countries Beneficial trade conditions and • Fierce competition with generics standards due to Russian membership in • Unsuccessful partnerships with local WTO firms •
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 15 Overview over internationalization theory
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 15 Overview over internationalization theory
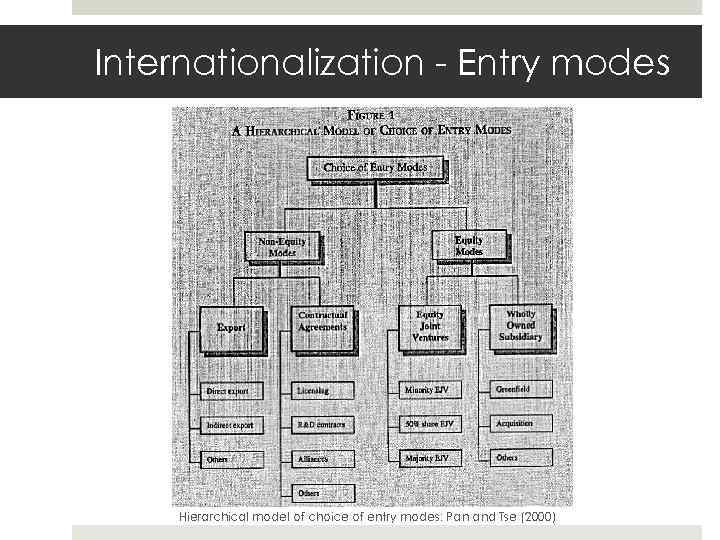 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 16 Internationalization - Entry modes Hierarchical model of choice of entry modes: Pan and Tse (2000)
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 16 Internationalization - Entry modes Hierarchical model of choice of entry modes: Pan and Tse (2000)
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 17 Application of OLI-paradigm to Pfizer
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 17 Application of OLI-paradigm to Pfizer
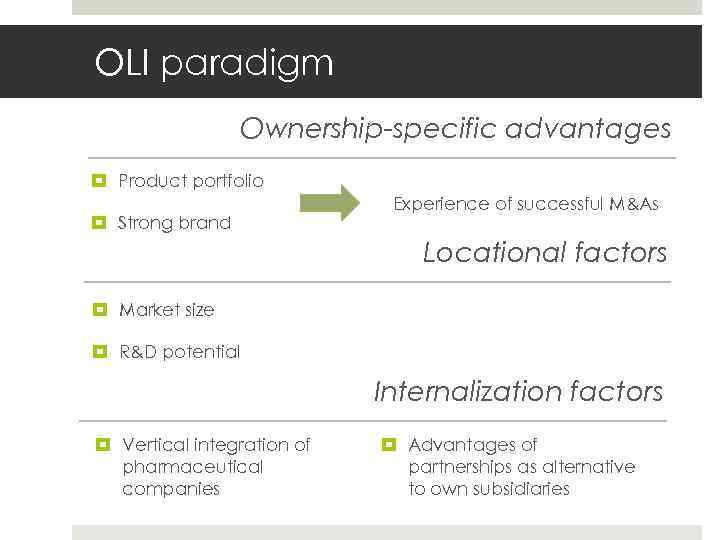 OLI paradigm Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 18 Ownership-specific advantages Product portfolio Strong brand Experience of successful M&As Locational factors Market size R&D potential Internalization factors Vertical integration of pharmaceutical companies Advantages of partnerships as alternative to own subsidiaries
OLI paradigm Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 18 Ownership-specific advantages Product portfolio Strong brand Experience of successful M&As Locational factors Market size R&D potential Internalization factors Vertical integration of pharmaceutical companies Advantages of partnerships as alternative to own subsidiaries
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 19 Internationalization: Russia
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 19 Internationalization: Russia
 Pfizer in Russia Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 20 Export Own channels Acquired north-western companies (Ferrosan, Pharmacia) Local office Promotional activities Partnerships R&D consortia Biocad and new pharmaceuticals against hemophilia Production through licensing Petrowaks Pharm to produce the pneumococcal vaccine
Pfizer in Russia Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 20 Export Own channels Acquired north-western companies (Ferrosan, Pharmacia) Local office Promotional activities Partnerships R&D consortia Biocad and new pharmaceuticals against hemophilia Production through licensing Petrowaks Pharm to produce the pneumococcal vaccine
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 21 Problems of Pfizer
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 21 Problems of Pfizer
 Problems of Pfizer Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 22 Bribery and illegal payment issues 2012: US regulators fined Pfizer in height of $60 mio. Goal: boost sales and obtain regulatory approvals Russia: «Hospital programs» : price reduction in exchange for future sales Fine reduced as a result of good cooperation
Problems of Pfizer Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 22 Bribery and illegal payment issues 2012: US regulators fined Pfizer in height of $60 mio. Goal: boost sales and obtain regulatory approvals Russia: «Hospital programs» : price reduction in exchange for future sales Fine reduced as a result of good cooperation
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 23 Data analysis
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 23 Data analysis
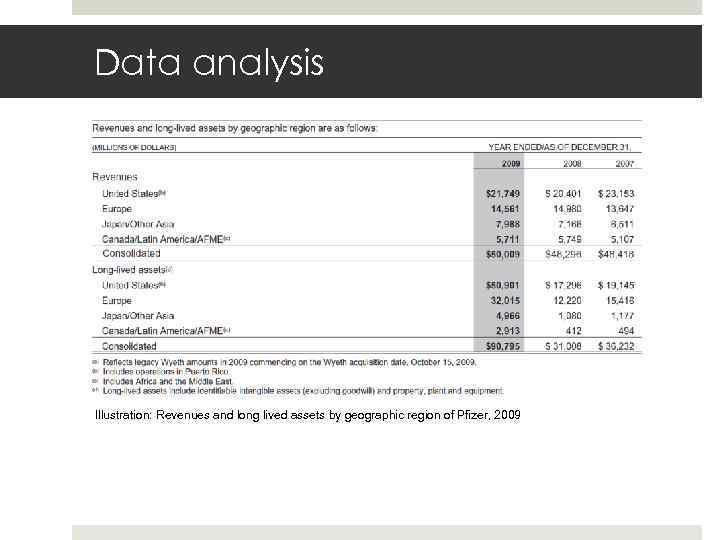 Data analysis Illustration: Revenues and long lived assets by geographic region of Pfizer, 2009 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 24
Data analysis Illustration: Revenues and long lived assets by geographic region of Pfizer, 2009 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 24
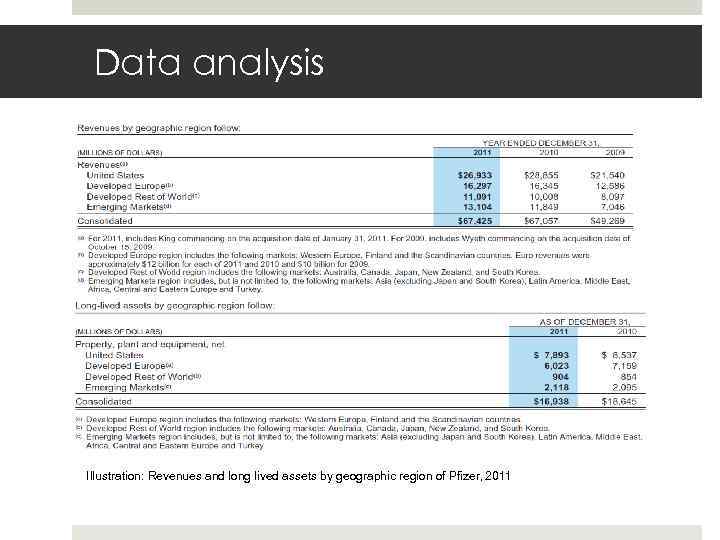 Data analysis Illustration: Revenues and long lived assets by geographic region of Pfizer, 2011 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 25
Data analysis Illustration: Revenues and long lived assets by geographic region of Pfizer, 2011 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 25
 Data analysis Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 26 2007 - 2009: Focus on emerging markets and away from domestic market USA 2009: Acquisition of Wyeth 2009 – 2011: Stagnation in developed Europe and USA (crisis) High revenue growth in emerging markets 2010 – 2011: little investments made in rest of the world Pfizer still exports a lot of medication rather than producing them locally (e. g. Russia)
Data analysis Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 26 2007 - 2009: Focus on emerging markets and away from domestic market USA 2009: Acquisition of Wyeth 2009 – 2011: Stagnation in developed Europe and USA (crisis) High revenue growth in emerging markets 2010 – 2011: little investments made in rest of the world Pfizer still exports a lot of medication rather than producing them locally (e. g. Russia)
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 27 Recommendations
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 27 Recommendations
 Recommendations Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 28 1. M&A with local producers to acquire new licenses or R&D facilities 2. Entering pharmaceutical cluster in St. Petersburg in order to benefit from its two cores: § Manufacturing of drugs § R&D potential 3. FDI § While entering cluster or separately
Recommendations Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 28 1. M&A with local producers to acquire new licenses or R&D facilities 2. Entering pharmaceutical cluster in St. Petersburg in order to benefit from its two cores: § Manufacturing of drugs § R&D potential 3. FDI § While entering cluster or separately
 Bibliography Barkema, H. & Vermeulen, F. (1998). International expansion through start-up or acquisition: a learning perspective. Academy of Management Journal, 41, 7 -26. Batlett, J. , Goshal, S. & Birkinshaw, J. (2004). Transnational Management: text, cases and readings in cross-border management. Mc Graw Hill Irwin: Boston. Cheng, Y. -M. (2006). Determinants of FDI Mode Choice: Acquisition, Brownfield, and Greenfield Entry in Foreign Markets. Canadian Journal of Administrative Science, 23, 200 -220. Dunning J. H. (2001) ‘The Eclectic (OLI) Paradigm of International Production: Past, Present and Future’, Int. J. of the Economics of Business, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 173± 190 [EBSCO] Dunning J. H. , Sarianna M. L. (2008) ‘Institutions and the OLI paradigm of the multinational enterprise’, Asia Pacific Journal of Management [EBSCO] Fosfuri, A. (2006): The Licensing Dilemma: Understanding the Determinants of the Rate of Licensing. In: Strategic Management Journal, 27, pp. 1141– 1158. Gardiner H. (2004, 14. May). Pfizer to Pay $430 Million Over Promoting Drug to Doctors. New York Times. Gassmann O. , Zadtwitz M. (2008). Market versus technology drive in R&D internationalization: four different patterns of managing research and development. Retrieved from: Institute of Finance and Management (2012). Managing Accounts Payable, 12(9), p 15. Jack, A. (2012, ) Pfizer fined for decade of bribery. Financial Times. Kuiper H. (2011). Pfizer motivation to go abroad: pull and push factors. Melin L. (1992) ‘Internationalization as a strategy process’, Strategic Management Journal, pp. 103 -104 [JSTOR] Pfizer Financial Report (2011). Pan, Y. & Tse, D. (2000). The hierarchical model of market entry modes. Journal of international business studies, 31, p. 535 -554. Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 29 Pfizer Inc: Exploring our history. Russia’s pharmaceutical market (2010). Strategy of pharmaceutical industry development in the Russian Federation up to 2020 (2009). Retrieved from: Smirnov S. (2012). Pharmaceutical industry practice regulatory harmonization: Challenges and opportunities for 2012 Xia, J. (2011). Mutual dependence, partner substitutability, and repeated Partnership: The survival of cross-border alliances. Strategic Management Journal, 32, p. 229 -253. Zekiri, J. & Angelova, B. (2011). Factors that influence entry mode choice in foreign markets. European Journal of social sciences, 22, p. 572 -584. Pfizer и «Биокад» планируют начать в России производство лекарства для лечения гемофилии (2012). РБК. На: Pfizer и партнеры подводят первые итоги реализации инвестиционной стратегии в России (2012). Российская фармацевтика. Pfizer сократил дорогу к дистрибьюторам (2008). Коммерсантъ. Кутузов Р. (2007). Хождение по мукам. Forbes. Заболеваемость населения России в 2010 году (2010). Минздрав России. Получено на: Завод Pfizer в России – вполне возможно (s. a. ). Odamis. ru. Получено на: Система обязательного медицинского страхования в Российской Федерации (2012). On: Современное состояние и перспективы развития российской фармацевтической промышленности (2012). ВЭБ «Финансовая газета» . Центр «Химрар» купил у Pfizer эксклюзивную молекулу препарата для лечения диабета (2012). Агенство экономической информации «Прайм» .
Bibliography Barkema, H. & Vermeulen, F. (1998). International expansion through start-up or acquisition: a learning perspective. Academy of Management Journal, 41, 7 -26. Batlett, J. , Goshal, S. & Birkinshaw, J. (2004). Transnational Management: text, cases and readings in cross-border management. Mc Graw Hill Irwin: Boston. Cheng, Y. -M. (2006). Determinants of FDI Mode Choice: Acquisition, Brownfield, and Greenfield Entry in Foreign Markets. Canadian Journal of Administrative Science, 23, 200 -220. Dunning J. H. (2001) ‘The Eclectic (OLI) Paradigm of International Production: Past, Present and Future’, Int. J. of the Economics of Business, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 173± 190 [EBSCO] Dunning J. H. , Sarianna M. L. (2008) ‘Institutions and the OLI paradigm of the multinational enterprise’, Asia Pacific Journal of Management [EBSCO] Fosfuri, A. (2006): The Licensing Dilemma: Understanding the Determinants of the Rate of Licensing. In: Strategic Management Journal, 27, pp. 1141– 1158. Gardiner H. (2004, 14. May). Pfizer to Pay $430 Million Over Promoting Drug to Doctors. New York Times. Gassmann O. , Zadtwitz M. (2008). Market versus technology drive in R&D internationalization: four different patterns of managing research and development. Retrieved from: Institute of Finance and Management (2012). Managing Accounts Payable, 12(9), p 15. Jack, A. (2012, ) Pfizer fined for decade of bribery. Financial Times. Kuiper H. (2011). Pfizer motivation to go abroad: pull and push factors. Melin L. (1992) ‘Internationalization as a strategy process’, Strategic Management Journal, pp. 103 -104 [JSTOR] Pfizer Financial Report (2011). Pan, Y. & Tse, D. (2000). The hierarchical model of market entry modes. Journal of international business studies, 31, p. 535 -554. Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 29 Pfizer Inc: Exploring our history. Russia’s pharmaceutical market (2010). Strategy of pharmaceutical industry development in the Russian Federation up to 2020 (2009). Retrieved from: Smirnov S. (2012). Pharmaceutical industry practice regulatory harmonization: Challenges and opportunities for 2012 Xia, J. (2011). Mutual dependence, partner substitutability, and repeated Partnership: The survival of cross-border alliances. Strategic Management Journal, 32, p. 229 -253. Zekiri, J. & Angelova, B. (2011). Factors that influence entry mode choice in foreign markets. European Journal of social sciences, 22, p. 572 -584. Pfizer и «Биокад» планируют начать в России производство лекарства для лечения гемофилии (2012). РБК. На: Pfizer и партнеры подводят первые итоги реализации инвестиционной стратегии в России (2012). Российская фармацевтика. Pfizer сократил дорогу к дистрибьюторам (2008). Коммерсантъ. Кутузов Р. (2007). Хождение по мукам. Forbes. Заболеваемость населения России в 2010 году (2010). Минздрав России. Получено на: Завод Pfizer в России – вполне возможно (s. a. ). Odamis. ru. Получено на: Система обязательного медицинского страхования в Российской Федерации (2012). On: Современное состояние и перспективы развития российской фармацевтической промышленности (2012). ВЭБ «Финансовая газета» . Центр «Химрар» купил у Pfizer эксклюзивную молекулу препарата для лечения диабета (2012). Агенство экономической информации «Прайм» .
 Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 30 Thank you for your attention. Polina Zinchenko, Ekatarina Zaytseva, Ekatarina Selenkina, Arina Lekomtseva, Basil Tschumperlin
Gruppe 22 E 17. Mai 2010 Slide 30 Thank you for your attention. Polina Zinchenko, Ekatarina Zaytseva, Ekatarina Selenkina, Arina Lekomtseva, Basil Tschumperlin


