097ffd0367e7895b485f080c1df46640.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

Grid Security: PKI Based Authentication Infrastructure Source: The Globus Project Argonne National Laboratory USC Information Sciences Institute http: //www. globus. org/ Updated/Localised: Rajkumar Buyya

Security n n As Grid Resources and Users are Distributed and Owned by different organizations, only authorized users should be allowed to access them. A simple authentication infrastructure is needed. Also, both users and owners should be protected from each other. The Users need be assured about security of their: n n n 2 Data Code Message

Example Secure Remote Startup 1. Exchange certificates, jobmanager authenticate, delegate 4. 2. Check gridmap file 3. Lookup service map services 3. cert 4. Run service program 2. cert (e. g. jobmanager) 1. key client GSC 3 key gatekeeper GSP
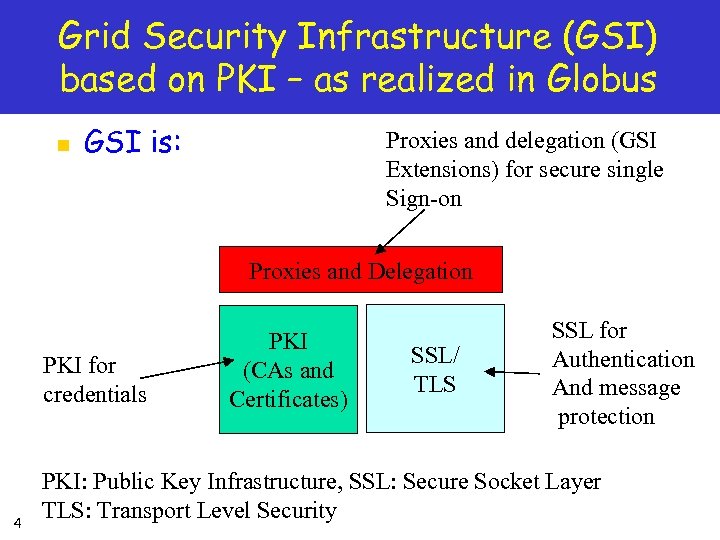
Grid Security Infrastructure (GSI) based on PKI – as realized in Globus n GSI is: Proxies and delegation (GSI Extensions) for secure single Sign-on Proxies and Delegation PKI for credentials 4 PKI (CAs and Certificates) SSL/ TLS SSL for Authentication And message protection PKI: Public Key Infrastructure, SSL: Secure Socket Layer TLS: Transport Level Security
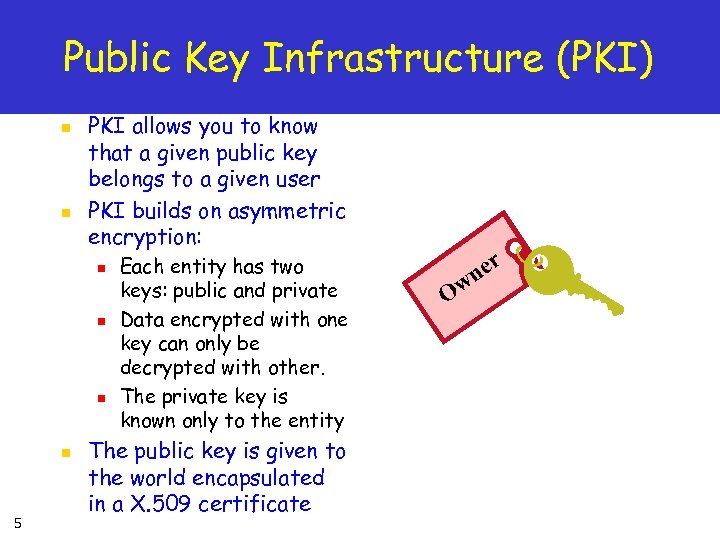
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) n n PKI allows you to know that a given public key belongs to a given user PKI builds on asymmetric encryption: n n 5 Each entity has two keys: public and private Data encrypted with one key can only be decrypted with other. The private key is known only to the entity The public key is given to the world encapsulated in a X. 509 certificate r O ne w

Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Overview n n n X. 509 Certificates Certificate Authorities (CAs) Certificate Policies n n Requesting a certificate n n 6 Namespaces Certificate Request Registration Authority r ne Ow

X. 509 n 7 A widely used standard for defining digital certificates. X. 509 is actually an ITU (International Telecommunication Union) Recommendation, which means that it has not yet been officially defined or approved for standardized usage. As a result, companies have implemented the standard in different ways. For example, both Netscape and Microsoft use X. 509 certificates to implement SSL in their Web servers and browsers. But an X. 509 Certificate generated by Netscape may not be readable by Microsoft products, and vice versa.

Certificates n n 8 A X. 509 certificate binds a public key to a name It includes a name and a public key (among other things) bundled together and signed by a trusted party (Issuer) Name Issuer Public Key Signature
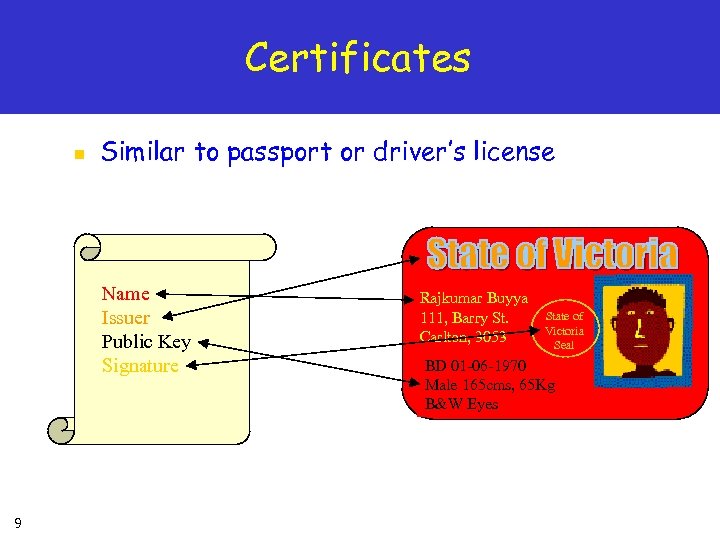
Certificates n Similar to passport or driver’s license Name Issuer Public Key Signature 9 Rajkumar Buyya 111, Barry St. Carlton, 3053 State of Victoria Seal BD 01 -06 -1970 Male 165 cms, 65 Kg B&W Eyes
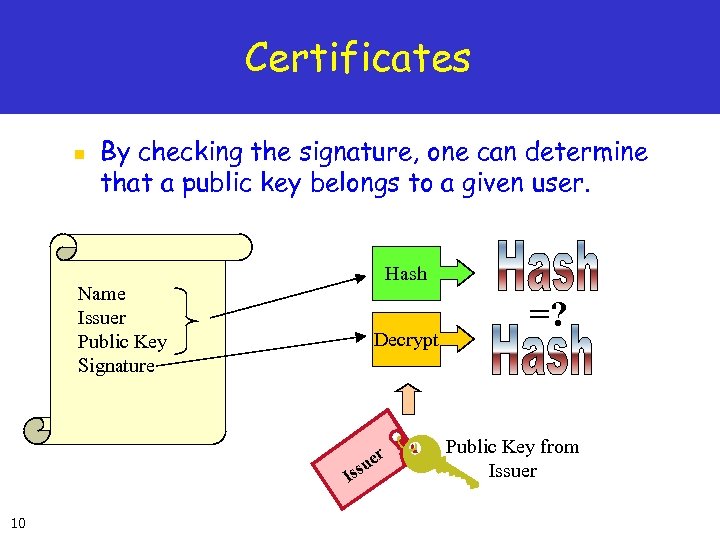
Certificates n By checking the signature, one can determine that a public key belongs to a given user. Hash Name Issuer Public Key Signature Decrypt er su s I 10 =? Public Key from Issuer

Certificate Authorities (CAs) n n n 11 A small set of trusted entities known as Certificate Authorities (CAs) are established to sign certificates A Certificate Authority is an entity that exists only to sign user certificates The CA signs it’s own certificate which is distributed in a trusted manner Name: CA Issuer: CA CA’s Public Key CA’s Signature

Certificate Authorities (CAs) n The public key from the CA certificate can then be used to verify other certificates Name Issuer Public Key Signature Name: CA Issuer: CA CA’s Public Key CA’s Signature 12 Hash Decrypt =?
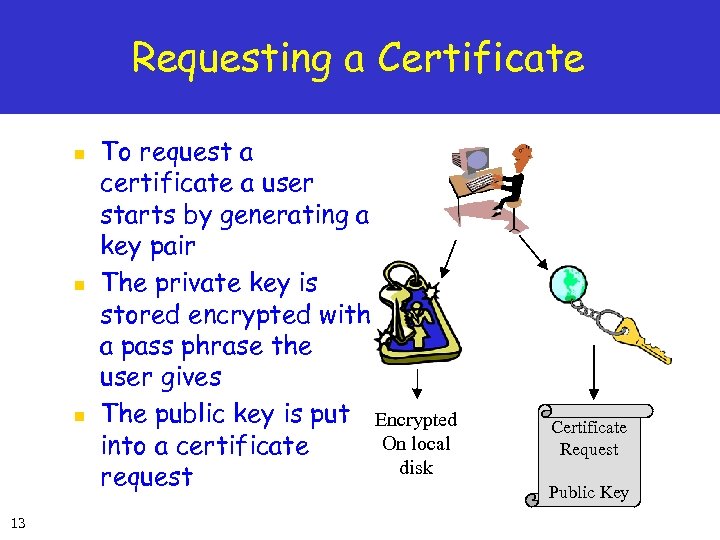
Requesting a Certificate n n n 13 To request a certificate a user starts by generating a key pair The private key is stored encrypted with a pass phrase the user gives The public key is put Encrypted On local into a certificate disk request Certificate Request Public Key

Certificate Issuance n n The user then takes the certificate to the CA The CA usually includes a Registration Authority (RA) which verifies the request: n n n 14 The name is unique with respect to the CA It is the real name of the user Etc. Certificate Request ID Public Key
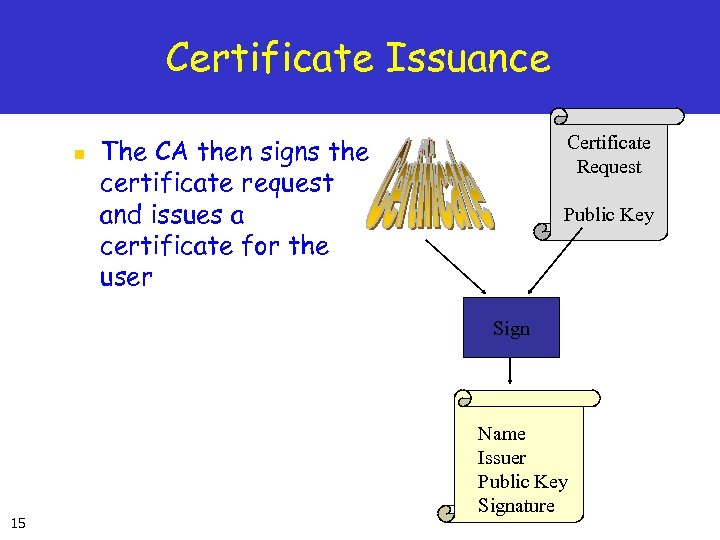
Certificate Issuance n Certificate Request The CA then signs the certificate request and issues a certificate for the user Public Key Sign 15 Name Issuer Public Key Signature
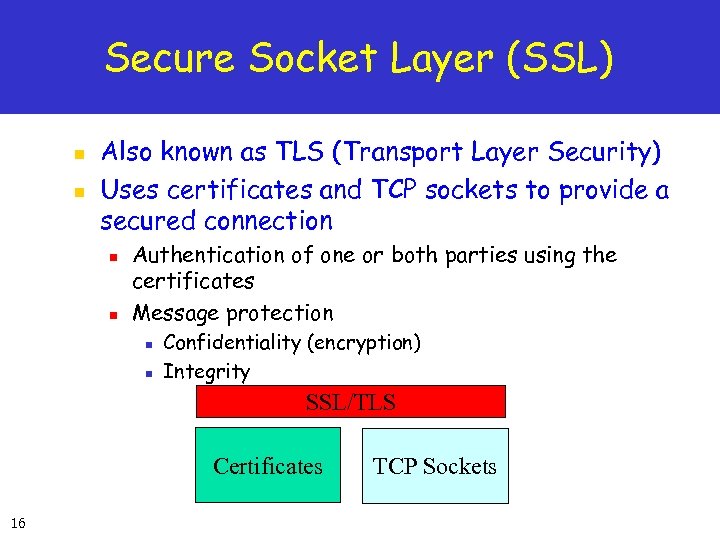
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) n n Also known as TLS (Transport Layer Security) Uses certificates and TCP sockets to provide a secured connection n n Authentication of one or both parties using the certificates Message protection n n Confidentiality (encryption) Integrity SSL/TLS Certificates 16 TCP Sockets

Mutual Authentication n n n 17 A and B are two parties: Both need to trust each others’ CA. A B (A establishes connection to B and gives his certificate (name, pub. Key) to B). B makes sure that it can trust CA of A. B generates random message A and asks it encrypt it. A encrypts it and send to B B decrypts using A’s public key. If the msg. is same as what B has sent, then A is who it is claiming to be.

Globus Security: Review n GSI extends existing standard protocols & APIs n n n Based on standards: SSL/TLS, X. 509, GSS-API Extensions for single sign-on and delegation The Globus Toolkit provides: n Generic Security Services API (GSS-API) on GSI protocols n n 18 The GSS-API is the IETF standard for adding authentication, delegation, message integrity, and message confidentiality to applications. Various tools for credential management, login/logout, etc.

Obtaining a Certificate n The program grid-cert-request is used to create a public/private key pair and unsigned certificate in ~/. globus/: n n usercert_request. pem: Unsigned certificate file userkey. pem: Encrypted private key file n n n Must be readable only by the owner Mail usercert_request. pem to ca@ausgrid. org Receive a Globus-signed certificate Place in ~/. globus/usercert. pem n Other organizations use different approaches n 19 NCSA, NPACI, NASA, etc. have their own CA

My Certificate (certified by CA) Certificate: Data: Version: 3 (0 x 2) Serial Number: 26 (0 x 1 a) Signature Algorithm: md 5 With. RSAEncryption Issuer: O=Australian Grid Forum, OU=Aus. Grid Testbed, CN=ausgrid. org Validity Not Before: Feb 8 03: 40: 20 2004 GMT Not After : Feb 7 03: 40: 20 2005 GMT Subject: O=Australian Grid Forum, OU=Aus. Grid Testbed, OU=cs. mu. oz. au, CN=Rajkumar Buyya Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsa. Encryption RSA Public Key: (1024 bit) Modulus (1024 bit): 00: bb: c 7: 92: a 8: 14: 75: 81: 2 c: 38: b 6: 45: e 9: db: 12: a 3: 6 b: e 2: 66: 41: 62: 44: ef: 1 a: 56: 5 c: 42: 71: ec: 8 b: 04: 1 e: 01: 53: 43: 84: 1 a: cb: 8 e: a 9: d 1: 99: 67: 1 f: ef: . . 07: 5 f: 92: 04: 6 e: ca: 29: 77: ec: 9 d: f 3: 36: c 2: 49: 40: 8 f: 51: 8 e: 63: 4 e: 82: 2 b: c 7: c 9: 0 c: bc: 55: ce: 01: d 1: 8 a: f 4: dc: 19: c 4: 01: 37: f 9: 9 f Exponent: 65537 (0 x 10001) X 509 v 3 extensions: Netscape Cert Type: SSL Client, SSL Server, S/MIME, Object Signing Signature Algorithm: md 5 With. RSAEncryption b 2: f 0: a 2: 79: bc: 2 d: 0 f: 02: 15: f 2: 4 d: 8 a: e 8: 5 f: 7 c: 79: 1 e: 43: 09: d 9: 6 e: 59: 7 b: 7 c: 71: 87: 8 c: 4 a: 10: 9 c: 0 e: 74: ea: 26: 48: 8 c: . . 4 e: fb: d 7: f 9: 81: eb: d 8: 74: 59: 17: fa: c 9: 64: 8 d: 88: 0 e: 98: 1 e: 20 Validity Start/End

Certificate and Key Data Sample usercert. pem: (public key) -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----MIICAz. CCAWyg. Aw. IBAg. IBCDANBgkqhki. G 9 w 0 BAQQFADBHMQsw. CQY <snip> u 5 t. X 5 R 1 m 7 Lr. Be. I 3 d. FMvi. Judlihlo. Xf. J 2 Bdu. Ig 7 XOKk 5 g 3 Jmgau. K 4 -----END CERTIFICATE----- Sample userkey. pem (private key): -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----Proc-Type: 4, ENCRYPTED DEK-Info: DES-EDE 3 -CBC, 1 E 924694 DBA 7 D 9 D 1 +W 4 FEPdn/o. Ynt. AJPw 2 tfmr. GZ 82 FH 611 o 1 gtvj. SKH 79 wd. Fxz. Khnz 474 Ijo 5 Bl <snip> et 5 Qn. J 6 h. AO 4 Bhya 1 Xk. Wy. KHTPs/2 t. Ifl. Kn 0 BNIIIYM+s= -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY----21

Certificate Information n To get cert information run grid-cert-info % grid-cert-info –subject /O=Australian Grid Forum/OU=Aus. Grid Testbed/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya n Options for printing cert information n [raj@belle. globus]$ grid-proxy-info -all -subject -issuer n n n n 22 -startdate -enddate -help subject : /O=Australian Grid Forum/OU=Aus. Grid Testbed/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya/CN=proxy issuer : /O=Australian Grid Forum/OU=Aus. Grid Testbed/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya identity : /O=Australian Grid Forum/OU=Aus. Grid Testbed/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya type : full legacy globus proxy strength : 512 bits path : /tmp/x 509 up_u 501 timeleft : 0: 59: 25

“Logging on” to the Grid n To run programs, authenticate to Globus: % grid-proxy-init Enter PEM pass phrase: ****** n n Creates a temporary, local, short-lived proxy credential for use by our computations Options for grid-proxy-init: -hours <lifetime of credential> -bits <length of key> -help 23

grid-proxy-init Details n n n grid-proxy-init creates the local proxy file. User enters pass phrase, which is used to decrypt private key. Private key is used to sign a proxy certificate with its own, new public/private key pair. n n 24 User’s private key not exposed after proxy has been signed Proxy placed in /tmp, read-only by user NOTE: No network traffic! grid-proxy-info displays proxy details

Grid Sign-On With grid-proxy-init User certificate file Pass Phrase 25 Private Key (Encrypted) User Proxy certificate file

Destroying Your Proxy (logout) n To destroy your local proxy that was created by grid-proxy-init: % grid-proxy-destroy n This does NOT destroy any proxies that were delegated from this proxy. n n 26 You cannot revoke a remote proxy Usually create proxies with short lifetimes

Proxy Information n To get proxy information run grid-proxy-info % grid-proxy-info -subject /O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya n Options for printing proxy information n Options for scripting proxy queries -subject -type -strength -exists -hours <lifetime of credential> -exists -bits <length of key> n 27 -issuer -timeleft -help Returns 0 status for true, 1 for false:

Important Files n /etc/grid-security n n /etc/grid-security/certificates n n 28 hostcert. pem: certificate used by the server in mutual authentication hostkey. pem: private key corresponding to the server’s certificate (read-only by root) grid-mapfile: maps grid subject names to local user accounts (really part of gatekeeper) CA certificates: certs that are trusted when validating certs, and thus needn’t be verified ca-signing-policy. conf: defines the subject names that can be signed by each CA

Important Files n $HOME/. globus n n n usercert. pem: User’s certificate (subject name, public key, CA signature) userkey. pem: User’s private key (encrypted using the user’s pass phrase) /tmp n Proxy file(s): Temporary file(s) containing unencrypted proxy private key and certificate (readable only by user’s account) n 29 Same approach Kerberos uses for protecting tickets

Secure Services n n On most Unix machines, inetd listens for incoming service connections and passes connections to daemons for processing. On Grid servers, the gatekeeper securely performs the same function for many services n n 30 It handles mutual authentication using files in /etc/grid-security It maps to local users via the gridmap file

Sample Gridmap File n n Gridmap file maintained by Globus administrator Entry maps Grid-id into local user name(s) # Distinguished name # "/O=Australian Grid Forum/OU=Aus. Grid Testbed/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya" Local username bellegrid "/O=Australian Grid Forum/OU=Aus. Grid Testbed/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Srikumar Venugopal" bellegrid "/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Jia Yu" jiayu "/C=JP/O=AIST GTRC/CN=Peerapon Vateekul/Email=griddemo@mike-33 -98. cpe. ku. ac. th" mikegrid 31
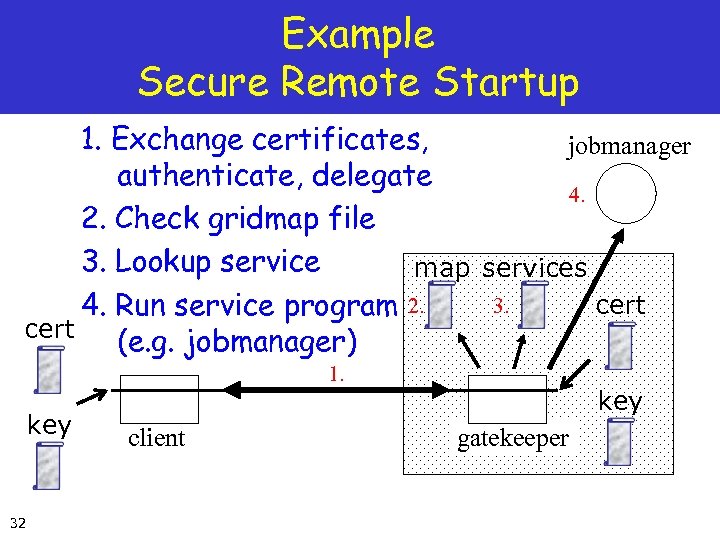
Example Secure Remote Startup 1. Exchange certificates, jobmanager authenticate, delegate 4. 2. Check gridmap file 3. Lookup service map services 3. cert 4. Run service program 2. cert (e. g. jobmanager) 1. key 32 client key gatekeeper

Simple job submission n globus-job-run provides a simple RSH compatible interface n n n Authentication Test n 33 % grid-proxy-init Enter PEM pass phrase: ***** % globus-job-run host program [args] % globusrun –a –r hostname

Delegation n Delegation = remote creation of a (second level) proxy credential n n n Allows remote process to authenticate on behalf of the user n 34 New key pair generated remotely on server Proxy cert and public key sent to client Clients signs proxy cert and returns it Server (usually) puts proxy in /tmp Remote process “impersonates” the user

Limited Proxy n During delegation, the client can elect to delegate only a “limited proxy”, rather than a “full” proxy n n Each service decides whether it will allow authentication with a limited proxy n n 35 GRAM (job submission) client does this Job manager service requires a full proxy Grid. FTP server allows either full or limited proxy to be used

Restricted Proxies n A generalization of the simple limited proxies n n n Desirable to have fine-grained restrictions Reduces exposure from compromised proxies Embed restriction policy in proxy cert n n Policy is evaluated by resource upon proxy use Reduces rights available to the proxy to a subset of those held by the user n n 36 A proxy no longer grants full impersonation rights Extensible to support any policy language

Exercise Sign-On & Remote Process Creation n Use grid-cert-info to examine your cert: % grid-cert-info -all n Use grid-proxy-init to create a proxy certificate: % grid-proxy-init Enter PEM pass phrase: . . +++++. . . +++++ n Use grid-proxy-info to query proxy: % grid-proxy-info -subject n Use globus-job-run to start remote programs: % globus-job-run jupiter. isi. edu /usr/bin/ls -l /tmp 37

Generic Security Service API n The GSS-API is the IETF draft standard for adding authentication, delegation, message integrity, and message confidentiality to apps n n GSS-API separates security from communication, which allows security to be easily added to existing communication code. n n 38 n For secure communication between two parties over a reliable channel (e. g. TCP) Filters on each end of the communications link GSS-API Extensions defined in GGF draft Globus Toolkit components all use GSS-API

gss_inquire_cred() n Extract information (e. g. the subject name) from a credential gss_inquire_cred_by_oid() Extract information associated with a OID (owner ID) from a credential (e. g. information in certificate extensions) Will be in future version > GT 2. 0 39

Authorization n n GSI handles authentication, but authorization is a separate issue Authorization issues: n n Management of authorization on a multi-organization grid is still an interesting problem. The grid-mapfile doesn’t scale well, and works only at the resource level, not the collective level. Large communities that share resources exacerbates authorization issues, which has led us to CAS (Community Authorization Service)… Why not use Grid Bank Services ? n 40 All those GSPs providing services through the Grid Marketplace can allow any consumer to access their services as long as Grid. Bank guarantees the payment,

Access Scalability Problem Resource access authorization file (grid-mapfile) “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. uwa. edu. au/CN=Alexander Barmouta” alex “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya” rajkumar Clients “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. uwa. edu. au/CN=Chris Mc. Donald” chris X 509 v 3 Digital Certificate ………… Subject: “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. uwa. edu. au/CN=Alexander Barmouta” ………… X 509 v 3 Digital Certificate ………… Subject: “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya” ………… 41 X 509 v 3 Digital Certificate ………… Subject: “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. uwa. edu. au/CN=Chris Mc. Donald” ………… Resources

Grid. Bank’s Solution to Access Scalability Problem: Modified gatekeeper Grid. Bank Accounts “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. uwa. edu. au/CN=Alexander Barmouta” “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. mu. oz. au/CN=Rajkumar Buyya” Request to access resource “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. uwa. edu. au/CN=Chris Mc. Donald” Passing client’s Certificate Subject Execute job Template (local) accounts gbaccount 1 gbaccount 2 gbaccount 3 Resource access authorization file (grid-mapfile) “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. uwa. edu. au/CN=Grid. Bank” gridbank “/O=Grid/O=Globus/OU=cs. uwa. edu. au/CN=Alexander Barmouta” gbaccount 1 42

Security Summary n Programs for credential management n n n 43 grid-cert-info, grid-proxy-init, grid-proxydestroy, grid-proxy-info GSS-API: The Globus Toolkit Grid Security Infrastructure (GSI) uses this API, which allows programs to easily add security globus_gss_assist: This is a simple wrapper around GSS-API, making it easier to use
097ffd0367e7895b485f080c1df46640.ppt